Residue of Chlormequat and Regulatory Effects on the Specialized Metabolites of Astragali Radix
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Residue of Chlormequat in Astragali Radix
2.2. Metabolite Changes of Astragali Radix
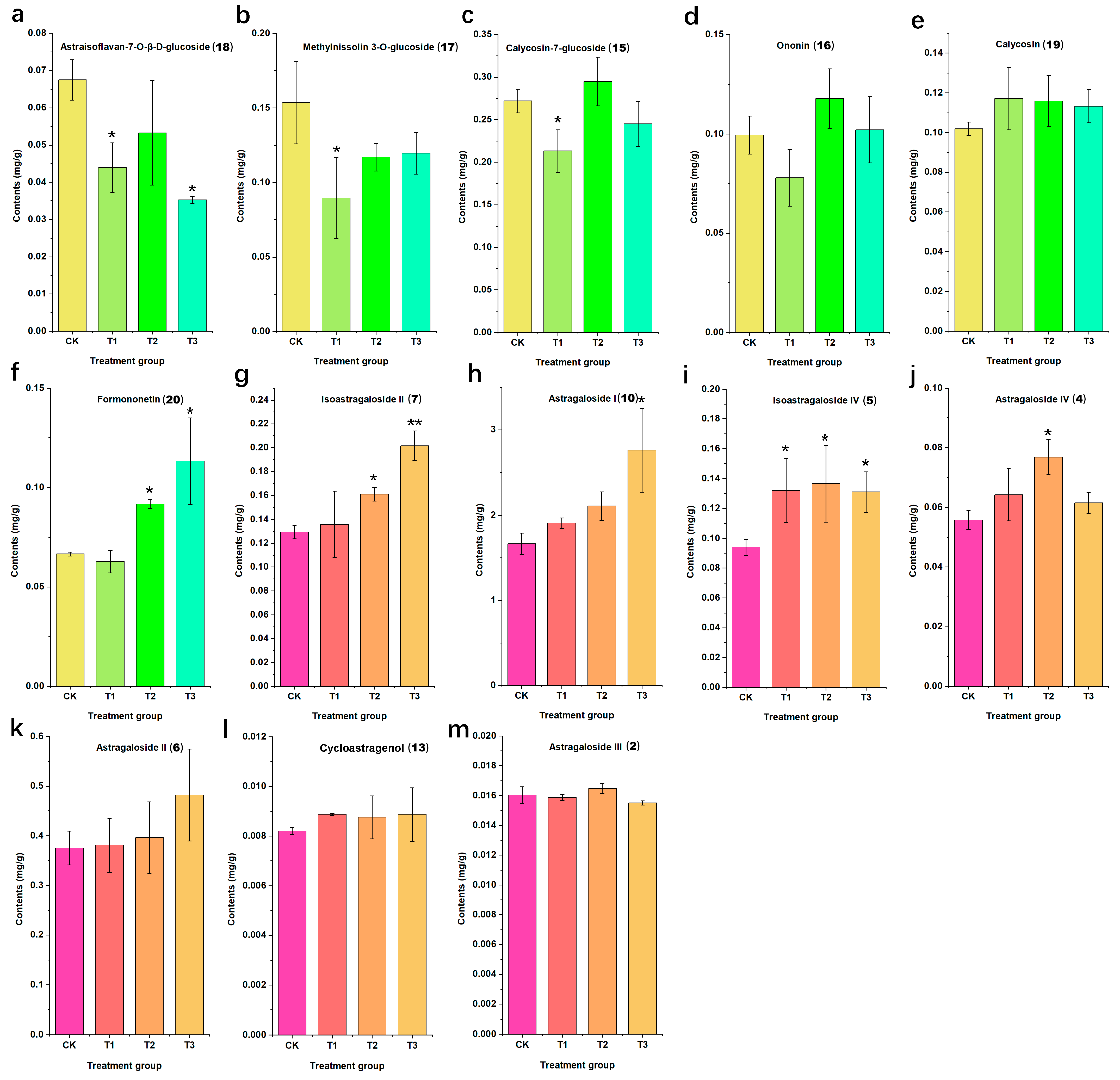
2.3. Quantitative Analysis of Thirteen Active Compounds in Astragali Radix
2.3.1. Optimization of UFLC-MS/MS Condition
2.3.2. Method Validation
2.3.3. Sample Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Plant Materials and Chlormequat Treatment
3.3. Instruments
3.4. Standard and Sample Solution Preparation
3.5. Metabolic Profiling Analysis of Astragali Radix
3.6. Quantitative Analysis of Thirteen Main Components in Astragali Radix
3.6.1. UFLC-QTRAP-MS/MS Conditions
3.6.2. Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China; Chemical Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Gao, C.; Chen, W.; Vong, C.T.; Yao, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, S. Astragali Radix (Huangqi): A promising edible immunomodulatory herbal medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 258, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Q. Astragalus, an ancient medicinal root in traditional Chinese medicine, a gift from silk road. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2019, 3, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, A.G.; Duan, R.; Wang, H.Y.; Kong, X.P.; Dong, T.T.; Tsim, K.W.; Chan, K. Evaluation of the pharmaceutical properties and value of Astragali Radix. Medicines 2018, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahrajabian, M.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Q. A review of Astragalus species as foodstuffs, dietary supplements, a traditional Chinese medicine and a part of modern pharmaceutical science. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 13371–13382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Gao, F.; Hou, L.; Wan, C. Anti-inflammatory and immunostimulatory activities of astragalosides. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2017, 45, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Lou, Y.; Kong, M.; Luo, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J. A systematic review of phytochemistry, pharmacology and pharmacokinetics on astragali radix: Implications for astragali radix as a personalized medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auyeung, K.K.; Han, Q.B.; Ko, J.K. Astragalus membranaceus: A review of its protection against inflammation and gastrointestinal cancers. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Carneiro, J.N.P.; Rocha, J.E.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Morais Braga, M.F.B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Semwal, P.; Painuli, S.; Moujir, L.M.; de Zarate Machado, V. Astragalus species: Insights on its chemical composition toward pharmacological applications. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 2445–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yan, Z. Identification of geographical origins of Astragalus membranaceus in China using electrochemical fingerprinting. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2023, 18, 100183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, Y.; Jin, H.Y.; Ma, S.C. Research progress in plant growth regulators and their application, content determination in planting traditional Chinese medicine. Chin. Pharm. J. 2016, 51, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.; Guo, B.; Huang, W. Detection of agent “zhuanggenling” and investigation of utilization of plant growth retardants in traditional Chinese medicine cultivation. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2015, 40, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ratnakumar, P.; Khan, M.I.R.; Minhas, P.S.; Per, T.S.; Rane, J. Can plant bioregulators minimize the crop productivity losses caused by drought, heat stress and salinity. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2016, 89, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Katel, S.; Yadav, S.P.S.; Sharma, B. Impacts of plant growth regulators in strawberry plant: A review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Mou, Y.; Yang, M.; Yu, J.; Tang, D.; Guo, F.; Gu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Ma, X. Application and safety evaluation of plant growth regulators in traditional Chinese medicine. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2020, 45, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.; Guo, Y.; Yao, H.; Chen, S.; Zhou, T. Impacts of cycocel and gibberellin on the biomass and flavonoid production in Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bullet. 2008, 24, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Liu, G.N.; Zhang, B. Impacts of “zhuanggenling” and chlormequat chloride (“aizhuangsu”) on yield and polysaccharide content of Polygonatum odoratum. Anim. Husb. Feed Sci. 2016, 37, 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Mou, Y.; Cui, S.; Gu, Z.; Yu, J.; Ma, X. Multi-residue analysis of plant growth regulators and pesticides in traditional Chinese medicines by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 2447–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 2763-2021; National Food Safety Standard-Maximum Residue Limits for Pesticides in Food. National Health and Family Planning Commission: Beijing, China; Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Hou, X.; Hu, H.; Xiagedeer, B.; Wang, P.; Kang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, Q.; Hao, W. Effects of chlorocholine chloride on pubertal development and reproductive functions in male rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 319, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Hou, X.; Kang, C.; Xiagedeer, B.; Hu, H.; Meng, Q.; Jiang, J.; Hao, W. Effects of prenatal chlorocholine chloride exposure on pubertal development and reproduction of male offspring in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 351, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiagedeer, B.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Hao, W. Chlormequat chloride retards rat embryo growth in vitro. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 34, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiagedeer, B.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, H.; Kang, C.; Xiao, Q.; Hao, W. Maternal chlormequat chloride exposure disrupts embryonic growth and produces postnatal adverse effects. Toxicology 2020, 442, 152534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.W.; Cao, J.; Li, P.; Yu, Q.T.; Wen, X.D.; Wang, Y.X.; Li, C.Y.; Bao, K.D.; Ge, X.X.; Cheng, X.L. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of Radix Astragali products by fast high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection coupled with time-of-flight mass spectrometry through dynamic adjustment of fragmentor voltage. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1203, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Chen, H.; Shi, Z.; Feng, Y.; Rui, W. Rapid and reliable method for analysis of raw and honey-processed astragalus by UPLC/ESI-Q-TOF-MS using HSS T3 columns. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 8045–8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, Z.; Michela, P.; Antonio, P.; Annamaria, P. Biological active ingredients of traditional Chinese herb Astragalus membranaceus on treatment of diabetes: A systematic review. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klejdus, B.; Vitamvásová-Štěrbová, D.; Kubáň, V. Identification of isoflavone conjugates in red clover (Trifolium pratense) by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry after two-dimensional solid-phase extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 450, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.f.; Shaker, S.; Kuang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ye, M.; Qiao, X. Phytochemistry and cardiovascular protective effects of Huang-Qi (Astragali Radix). Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 1999–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.W.; Yu, Q.T.; Li, P.; Li, S.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Sheng, L.H.; Yi, L. Quality evaluation of Radix Astragali through a simultaneous determination of six major active isoflavonoids and four main saponins by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array and evaporative light scattering detectors. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1134, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Qu, L.; Dong, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, E.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. A review of recent research progress on the Astragalus Genus. Molecules 2014, 19, 18850–18880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Puri, S. Plant growth regulator mediated consequences of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2018, 9, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Qian, X.Y.; Sun, J.J.; Ren, M.J.; Tang, Y.C.; Zhang, X.Q.; Shao, G.Q.; Hu, Y.F. Advances in research on effects of plant growth regulators on the quality of radix and rhizome medicinal materials. Chin. J. New Drugs 2022, 31, 752–761. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, Y.; Yan, M.; Fu, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Gu, C.; Efferth, T. Determination and quantification of astragalosides in Radix Astragali and its medicinal products using LC–MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, X.; Sun, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhu, N.; Yang, J.; Ma, G.; Xu, X. Quantitative Evaluation of twelve major components of Sulfur-Fumigated Astragali Radix with different durations by UPLC-MS. Molecules 2018, 23, 2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Gao, L.; Du, G.; Qin, X. Astragaloside IV derived from Astragalus membranaceus: A research review on the pharmacological effects. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 87, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Qi, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, D.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, G.; Liu, P. Astragalus saponins and its main constituents ameliorate ductular reaction and liver fibrosis in a mouse model of DDC-induced cholestatic liver disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 965914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Liu, Z.L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, Z.M.; Liu, C.H. A combination of astragaloside I, levistilide A and calycosin exerts anti-liver fibrosis effects in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Shi, Y.; Dai, Y.; Han, S.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Wei, B.; Liu, Y. Protective effect of Astragalus membranaceus and its bioactive compounds against the intestinal inflammation in Drosophila. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1019594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Zheng, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S. Review of the botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi). Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.; Lu, J. Anti-inflammatory effects of ononin on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 83, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.G. Clinical efficacy and therapeutic mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine for neuroprotection and neurogenesis in stroke treatment. Digit. Chin. Med. 2018, 1, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Ahmed, M.; Surapaneni, K.M.; Veeraraghavan, V.P.; Arulselvan, P. Neuroprotective effects of ononin against the aluminium chloride-induced Alzheimer’s disease in rats. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4232–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Gu, Y.; Lv, L.; Chen, C.; Feng, F.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Hong, Z.; Chai, Y. Screening of immune cell activators from Astragali Radix using a comprehensive two-dimensional NK-92MI cell membrane chromatography/C18 column/time-of-flight mass spectrometry system. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 12, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH). Q2 (R1): Text on Validation of Analytical Procedures; SANCO. Guidance Document Onanalytical Quality Control and Validation Procedures for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed; ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
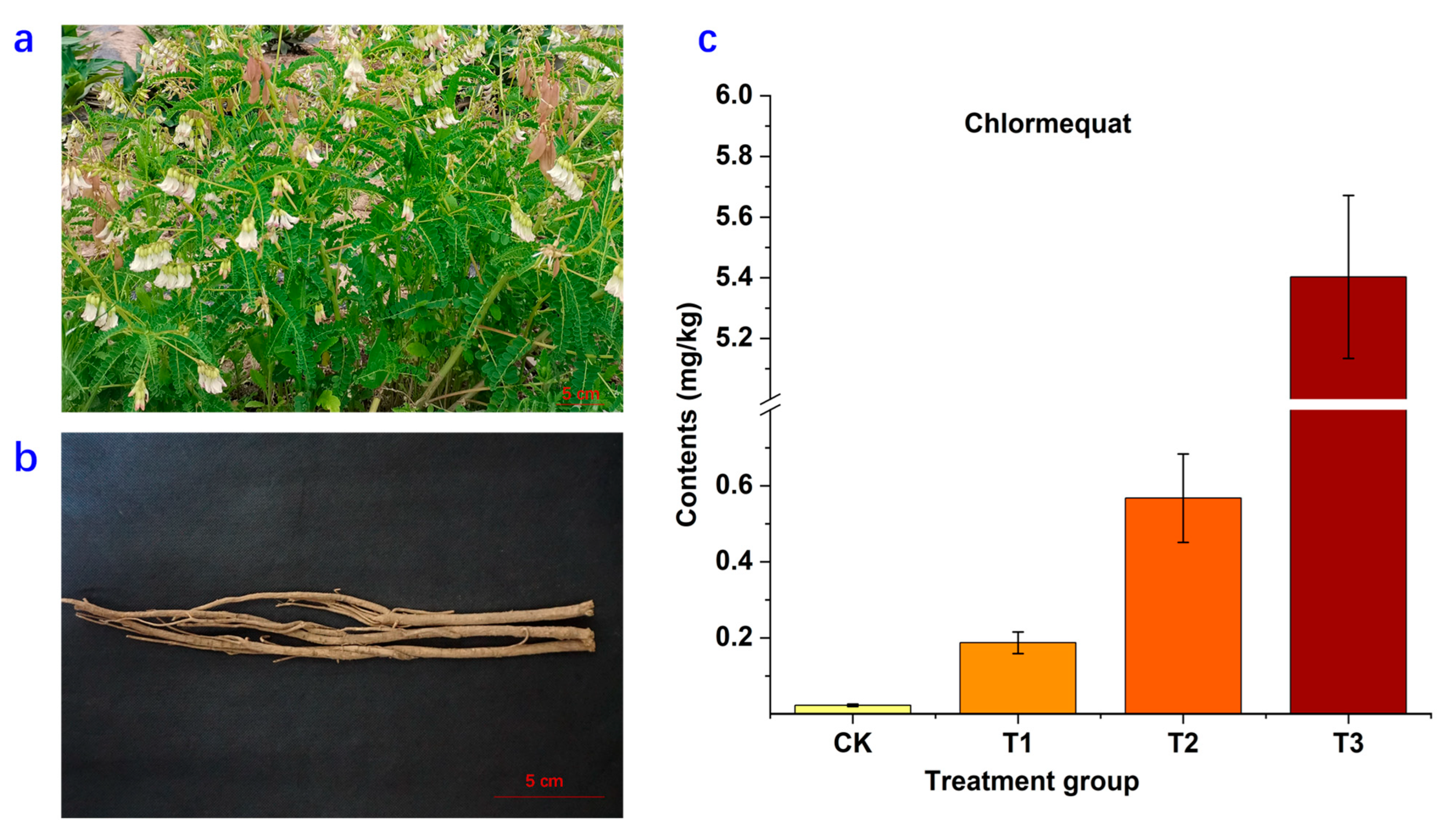
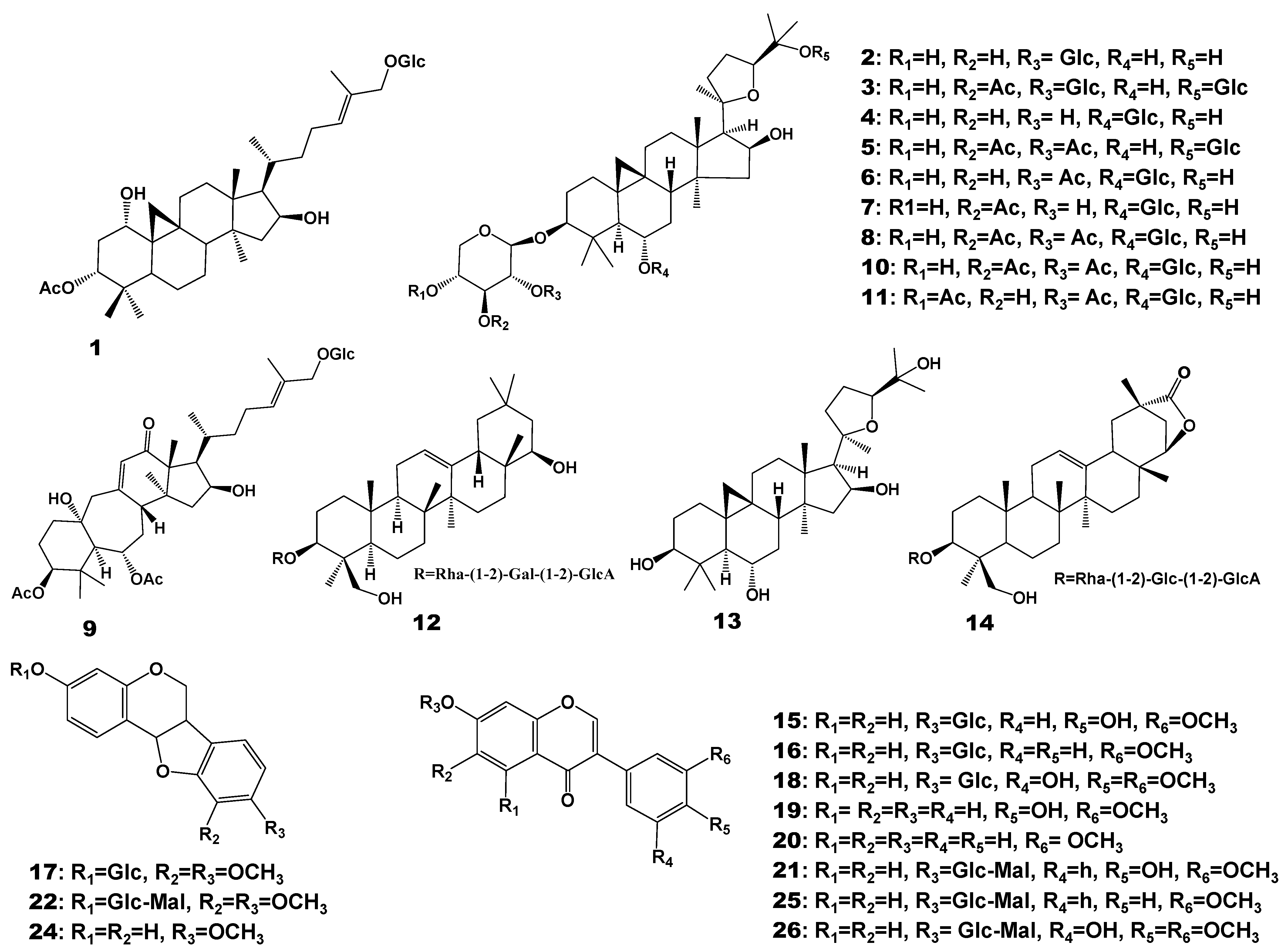
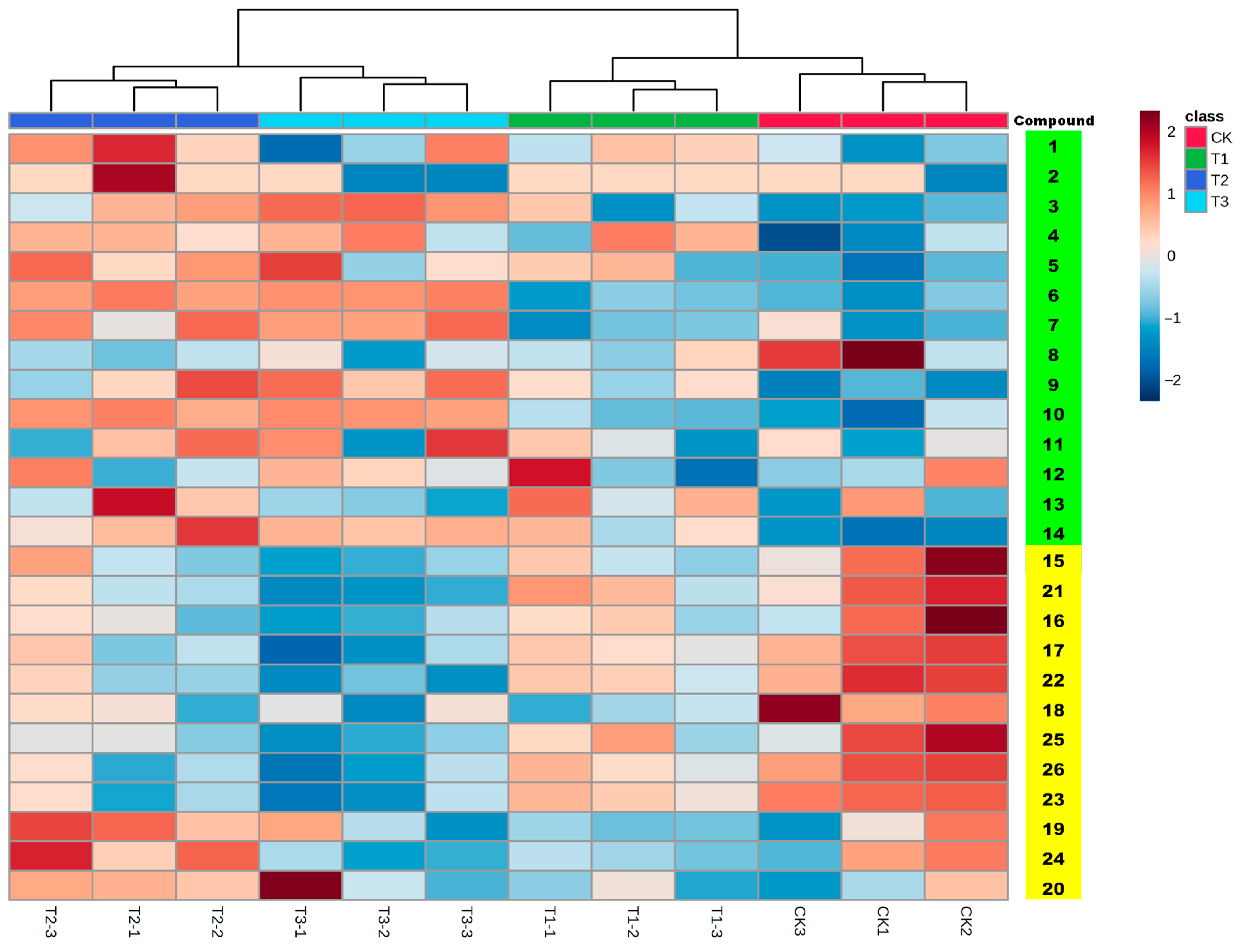
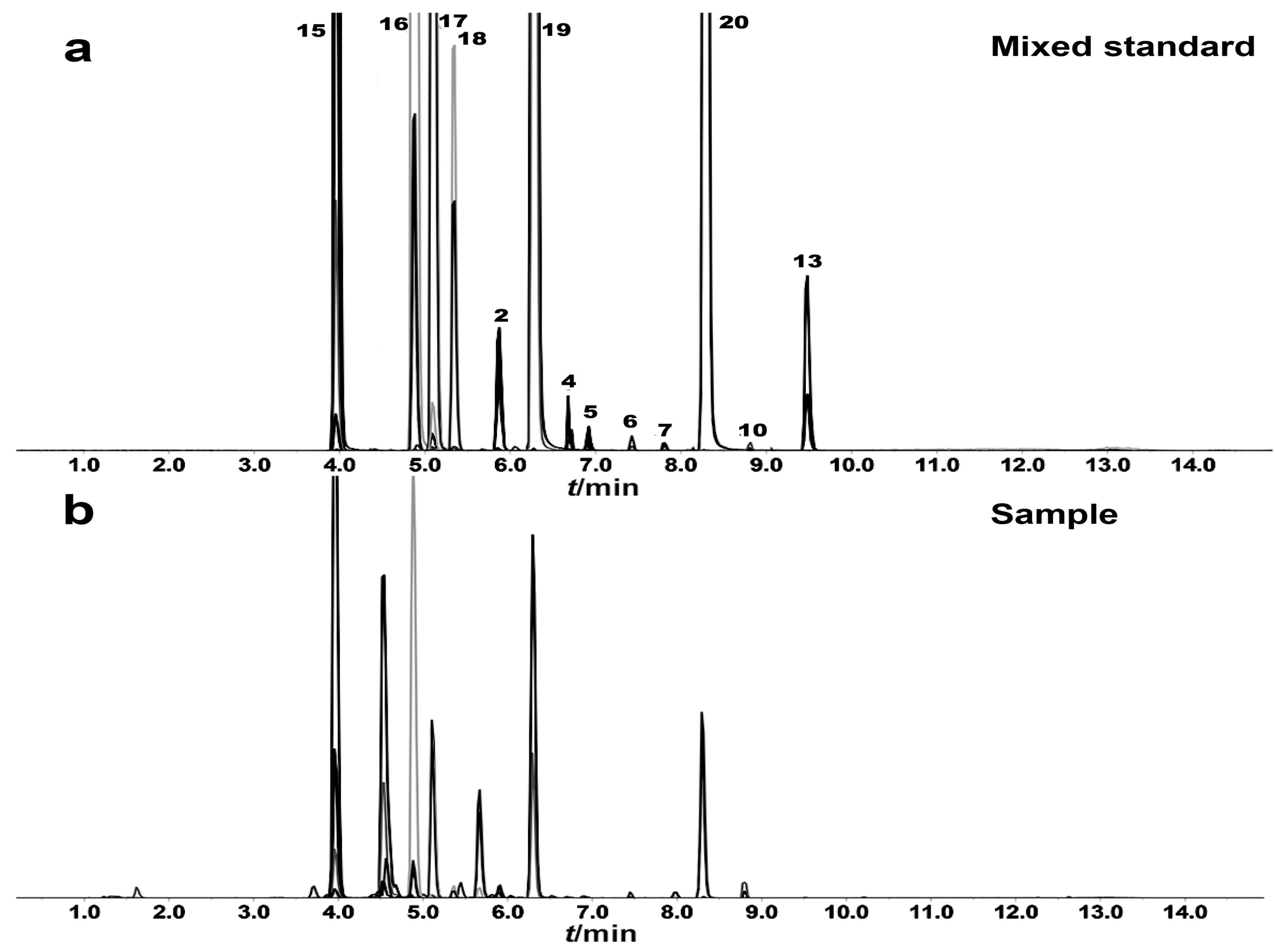
| Compound No. | Rt | m/z | Formula | Fragment | Identification | Classification | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.71 | 679.5082 | C38H63O10 | 661.4999; 359.2351; 340.2571; 114.0903 | 3β-acetoxy-9β, 19-cyclolanost-24E-ene-1α, 16β-diol-27-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | Saponins | |
| 2 | 10.37 | 785.4671 | C41H69O14 | 455.3521; 437.3397; 419.3304; 285.0744; 270.0528 | Astragaloside III | Up | |
| 3 | 10.95 | 947.517 | C47H79O19 | 774.3220; 473.3628; 437.3397 | Astragaloside V | Up | |
| 4 | 11.44 | 785.4645 | C41H69O14 | 455.3477; 437.3397; 419.3304; 143.1061 | Astragaloside IV | ||
| 5 | 11.75 | 785.4687 | C41H69O14 | 455.3628; 437.3397; 419.3304 | Isoastragaloside IV | ||
| 6 | 12.5 | 827.4783 | C43H71O15 | 809.4662; 455.3628; 419.3304; 175.0590 | Astragaloside II | Up | |
| 7 | 12.99 | 827.4793 | C43H71O15 | 809.4662; 455.3628; 437.3397; 419.3304; 143.1061 | Isoastragaloside II | Up | |
| 8 | 13.38 | 827.478 | C43H71O15 | 629.4077; 611.3973; 437.3397; 419.3304; 143.1061 | Cyclocephaloside II | ||
| 9 | 13.88 | 751.4265 | C40H63O13 | 733.4155; 715.4075; 419.3304; 261.0570; 157.0492 | Huangqiyenin G | Up | |
| 10 | 14.32 | 869.4891 | C45H73O16 | 851.4815; 689.4276; 671.4146; 455.3628; 437.3397; 419.3304; 217.0688; 157.0492; 143.1061 | Astragaloside I | Up | |
| 11 | 14.71 | 869.4876 | C45H73O16 | 851.4815; 689.4276; 671.4146; 455.3628; 437.3397; 419.3304; 376.2594; 217.0688; 157.0492 | Isoastragaloside I | ||
| 12 | 14.74 | 943.5263 | C48H79O18 | 617.4073; 599.3953; 441.3712; 423.3624 | Soyasaponin I | ||
| 13 | 14.97 | 491.374 | C30H51O5 | 491.3740; 473.3628; 455.3628 | Cycloastragenol | ||
| 14 | 15.39 | 955.4885 | C48H75O19 | 937.4789; 775.4269; 455.3628; 243.0472; 157.0492; 143.1061 | Astroolesaponin D | Up | |
| 15 | 5.43 | 447.1276 | C22H23O10 | 447.1286; 285.0744; 270.0494 | Calycosin-7-glucoside | Flavonoids | |
| 16 | 7.99 | 431.1326 | C22H23O9 | 431.1317; 269.0785 | Ononin | ||
| 17 | 8.45 | 463.1571 | C23H27O10 | 301.1059; 167.0686 | Methylnissolin-3-O-glucoside | Down | |
| 18 | 9.04 | 465.1754 | C23H29O10 | 429.1541; 302.1151; 167.0686 | Astraisoflavan-7-O-β-d-glucoside | Down | |
| 19 | 10.33 | 285.0752 | C16H13O5 | 270.052; 253.0495; 225.0543; 197.0592; 137.0234 | Calycosin | ||
| 20 | 13.3 | 269.0801 | C16H13O4 | 253.0495; 237.0525; 226.0623; 213.0898; 197.0592 | Formononetin | ||
| 21 | 7.46 | 533.1271 | C25H25O13 | 285.0744 | Calycosin-7-glucoside-6″-malonate | Down | |
| 22 | 8.97 | 549.1232 | C25H25O14 | 301.1059; 270.0528 | Methylnissolin-3-O-glucoside-6″-malonate | Down | |
| 23 | 10.1 | 301.1059 | C17H17O5 | 204.0861; 167.0686 | Isomer of medicarpin | Down | |
| 24 | 12.77 | 301.1059 | C16H13O6 | 285.0744; 167.0686; 152.0485; 134.0388 | Medicarpin | ||
| 25 | 9.6 | 517.1331 | C25H25O12 | 269.0785 | Formononetin-7-O-β-d-glucoside-6″-malonate | ||
| 26 | 9.81 | 549.1595 | C25H25O14 | 371.0977; 301.1059; 167.0686 | Astrapterocarpanglucoside-6″--malonate | Down |
| Compounds | Treatment Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | T1 | T2 | T3 | |
| Astragaloside I (10) | 1664.77 ± 128.69 | 1907.67 ± 61.20 | 2106.41 ± 166.72 | 2760.05 ± 490.77 |
| Astragaloside II (6) | 375.33 ± 34.27 | 380.84 ± 54.53 | 396.20 ± 71.63 | 482.21 ± 92.36 |
| Astragaloside III (2) | 16.04 ± 0.56 | 15.87 ± 0.20 | 16.47 ± 0.33 | 15.50 ± 0.15 |
| Astragaloside IV (4) | 55.83 ± 3.13 | 64.22 ± 8.67 | 76.80 ± 5.90 | 61.51 ± 3.41 |
| Isoastragaloside II (7) | 129.58 ± 5.79 | 135.84 ± 27.74 | 160.97 ± 5.60 | 201.66 ± 12.30 |
| Isoastragaloside IV (5) | 94.00 ± 5.42 | 131.95 ± 21.39 | 136.62 ± 25.60 | 131.04 ± 13.51 |
| Cycloastragenol (13) | 8.19 ± 0.14 | 8.87 ± 0.05 | 8.75 ± 0.87 | 8.87 ± 1.08 |
| Methylnissolin 3-O-glucoside (17) | 153.62 ± 27.63 | 89.58 ± 27.11 | 116.98 ± 9.37 | 119.55 ± 13.98 |
| Astraisoflavan-7-O-β-d-glucoside (18) | 67.48 ± 5.38 | 43.89 ± 6.69 | 53.25 ± 14.05 | 35.24 ± 0.89 |
| Formononetin (20) | 66.57 ± 0.97 | 62.70 ± 5.64 | 91.68 ± 2.16 | 113.22 ± 21.71 |
| Ononin (16) | 99.41 ± 9.64 | 77.88 ± 14.29 | 117.79 ± 14.91 | 102.07 ± 16.68 |
| Calycosin (19) | 101.95 ± 3.41 | 117.17 ± 15.73 | 115.85 ± 12.88 | 113.24 ± 8.31 |
| Calycosin-7-glucoside (15) | 271.93 ± 14.00 | 213.12 ± 24.96 | 294.81 ± 28.58 | 245.15 ± 26.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, H.; Xie, L.; Zang, Y.; Han, J.; Yu, J.; Luo, Z.; Ma, X. Residue of Chlormequat and Regulatory Effects on the Specialized Metabolites of Astragali Radix. Molecules 2023, 28, 6754. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196754
Qin H, Xie L, Zang Y, Han J, Yu J, Luo Z, Ma X. Residue of Chlormequat and Regulatory Effects on the Specialized Metabolites of Astragali Radix. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6754. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196754
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Honghan, Lei Xie, Yimei Zang, Jia Han, Jing Yu, Zuliang Luo, and Xiaojun Ma. 2023. "Residue of Chlormequat and Regulatory Effects on the Specialized Metabolites of Astragali Radix" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6754. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196754
APA StyleQin, H., Xie, L., Zang, Y., Han, J., Yu, J., Luo, Z., & Ma, X. (2023). Residue of Chlormequat and Regulatory Effects on the Specialized Metabolites of Astragali Radix. Molecules, 28(19), 6754. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196754






