The Different Mechanisms of Lipid Accumulation in Hepatocytes Induced by Oleic Acid/Palmitic Acid and High-Fat Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Establishment of a Cell Model of Lipid Accumulation Induced by OA/PA
2.2. De Novo Synthesis Was Inhibited in OA/PA-Induced Lipid-Accumulation Cell Models
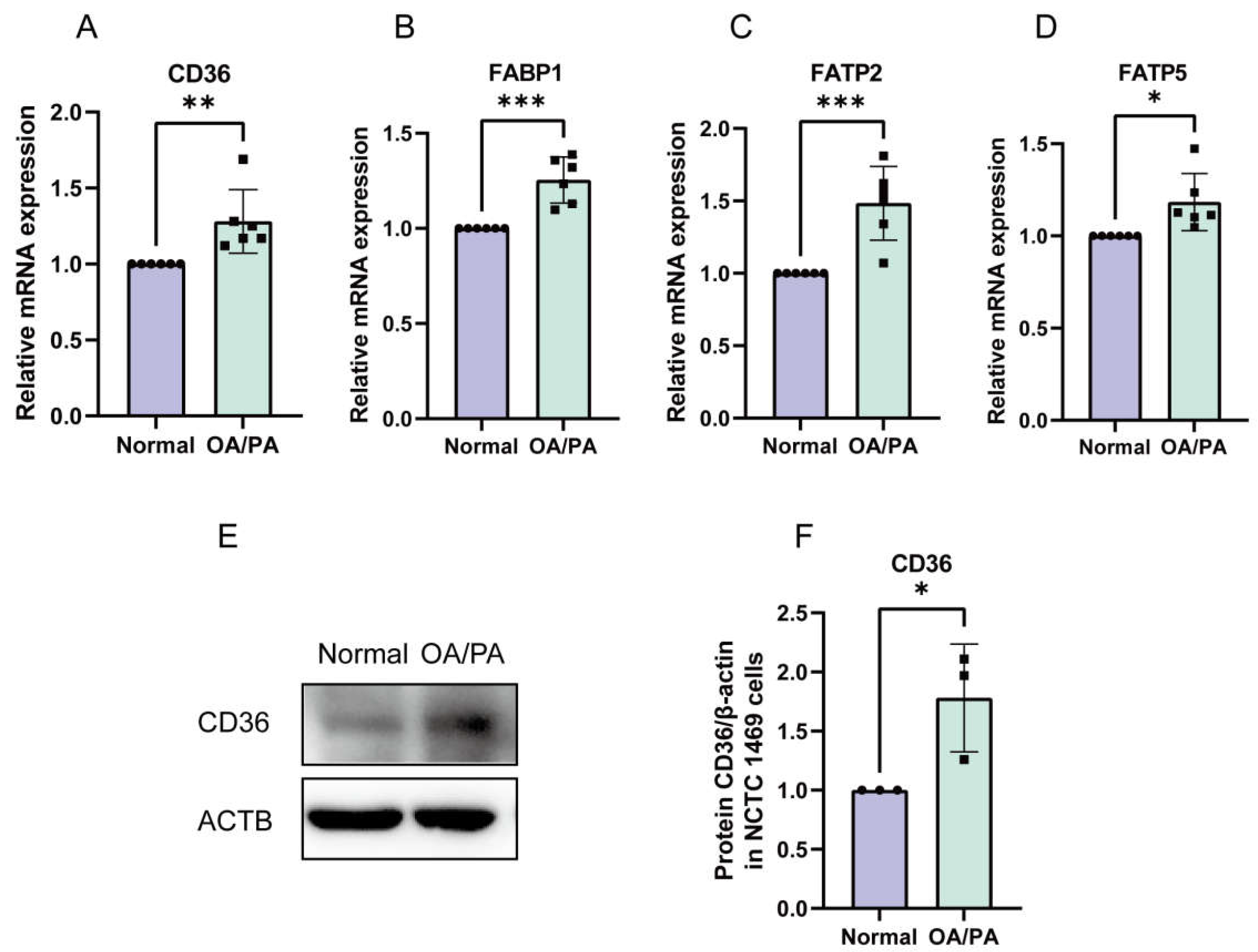
2.3. Enhanced Absorption of FFAs in OA/PA-Induced Lipid-Accumulation Cell Models
2.4. Establishment of an HFD-Induced NAFLD Model
2.5. De Novo Synthesis in HFD-Induced NAFLD Model was Enhanced
2.6. Enhanced Absorption of FFAs in NAFLD Models Induced by HFD
2.7. Serum FASN Levels Were Reduced in NAFLD Mice
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cells and Cell Culture
3.2. Establishment of NAFLD Mouse Models
3.3. Cell Staining
3.4. Evaluation of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in Mice
3.5. LDL-C Measurements
3.6. Glucose Metabolism Evaluation in Mice
3.7. Mouse FASN Elisa Assay
3.8. FASN Activity Assay
3.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
3.10. Western Blot Analysis
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease as a Nexus of Metabolic and Hepatic Diseases. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, L.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Bo, L.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Chen, C. Study on structure characterization of pectin from the steamed ginseng and the inhibition activity of lipid accumulation in oleic acid-induced HepG2 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, B.; Song, Q.; Du, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Song, H.; Shao, C. Protective Effect of Isoorientin on Oleic Acid-Induced Oxidative Damage and Steatosis in Rat Liver Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 818159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Guo, T.; Deng, R.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y. Apigenin Ameliorates Insulin Resistance and Lipid Accumulation by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and SREBP-1c/SREBP-2 Pathway in Palmitate-Induced HepG2 Cells and High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2021, 377, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhu, L.; Lai, S.; Ding, Q.; Xu, T.; Guo, R.; Dou, X.; Chai, H.; Yu, Z.; Li, S. Cimifugin Ameliorates Lipotoxicity-Induced Hepatocyte Damage and Steatosis through TLR4/p38 MAPK- and SIRT1-Involved Pathways. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 4557532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhai, T.; You, J.; Chen, Y. Silibinin ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in mice with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating CFLAR-JNK pathway. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, J.; Kim, S.; Yoon, H.G.; You, Y.; Kim, O.K.; Choi, K.C.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, J.; Park, J.; Jun, W. Water Extract of Curcuma longa L. Ameliorates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, S.; Peng, J.; Liang, X.; Yang, Q.; Bai, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Dong, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Amelioration of hepatic steatosis by dietary essential amino acid-induced ubiquitination. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 1528–1542.e1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, S.; Dragan, M.; Kwon, H.; de Oliveira, V.; Rao, S.; Bhatt, V.; Kalemba, K.M.; Shah, A.; Rustgi, V.K.; Wang, H.; et al. Targeting hepatic kisspeptin receptor ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a mouse model. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e145889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevzorova, Y.A.; Boyer-Diaz, Z.; Cubero, F.J.; Gracia-Sancho, J. Animal models for liver disease-A practical approach for translational research. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.W.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Sun, H.H.; Li, Y.F.; Lai, X.Y.; Zhao, N.; Wang, X.; Xie, C.; et al. CD36 facilitates fatty acid uptake by dynamic palmitoylation-regulated endocytosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.; Yucel, N.; Kim, B.; Arany, Z. Local Mitochondrial ATP Production Regulates Endothelial Fatty Acid Uptake and Transport. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 309–319.e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Q.; An, J.; Liu, P.; Song, Y.; Zhai, X.; Yang, R.; Niu, J.; Yang, C.; Li, B. Repurposing a tricyclic antidepressant in tumor and metabolism disease treatment through fatty acid uptake inhibition. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20221316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attane, C.; Muller, C. Drilling for Oil: Tumor-Surrounding Adipocytes Fueling Cancer. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Fatty acid-binding proteins: Role in metabolic diseases and potential as drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smathers, R.L.; Petersen, D.R. The human fatty acid-binding protein family: Evolutionary divergences and functions. Hum. Genom. 2011, 5, 170–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, A.; Aoyama, T.; Kamijo, K.; Uchida, Y.; Kondo, N.; Orii, T.; Hashimoto, T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding rat very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 30360–30365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, M.; Peng, R.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. FATP2-targeted therapies-A role beyond fatty liver disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.M.; Stahl, A. SLC27 fatty acid transport proteins. Mol. Aspects Med. 2013, 34, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuda, O.; Pietka, T.A.; Demianova, Z.; Kudova, E.; Cvacka, J.; Kopecky, J.; Abumrad, N.A. Sulfo-N-succinimidyl oleate (SSO) inhibits fatty acid uptake and signaling for intracellular calcium via binding CD36 lysine 164: SSO also inhibits oxidized low density lipoprotein uptake by macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 15547–15555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.G.; Tran, J.L.; Erion, D.M.; Vera, N.B.; Febbraio, M.; Weiss, E.J. Hepatocyte-Specific Disruption of CD36 Attenuates Fatty Liver and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in HFD-Fed Mice. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Y.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Y.; Liu, H.; Tan, W. CD36 as a Molecular Target of Functional DNA Aptamer NAFLD01 Selected against NAFLD Cells. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3951–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ge, Z.; Wang, H.; Feng, W.; Sun, X.; Chu, X.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Bi, Y. Prolactin improves hepatic steatosis via CD36 pathway. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, K.; Zhao, J.; Le, S.; Jiang, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, P.; Xiao, X.; et al. B-cell lymphoma 6 alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice through suppression of fatty acid transporter CD36. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Alimujiang, M.; Hu, L.; Liu, F.; Bao, Y.; Yin, J. Berberine alleviates lipid metabolism disorders via inhibition of mitochondrial complex I in gut and liver. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1693–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Aa, J.; Wang, G.; Xie, Y. Curcumin regulates endogenous and exogenous metabolism via Nrf2-FXR-LXR pathway in NAFLD mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Chen, W.; Yan, C.; Yang, R.; Chen, Q.; Xu, H.; Huang, Y. Gypenosides improve the intestinal microbiota of non-alcoholic fatty liver in mice and alleviate its progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, K.L.; Smith, C.I.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Jessurun, J.; Boldt, M.D.; Parks, E.J. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Wei, Y.; Yu, H.; Ma, X.; Yan, S.; Zhao, L.; Ding, L.; Cheng, J.; Feng, H. Erythritol Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Activating Nrf2 Antioxidant Capacity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 13080–13092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Sang, T.; Peng, H.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, S.; Eling, T.; Wang, X. Overexpression of NAG-1/GDF15 prevents hepatic steatosis through inhibiting oxidative stress-mediated dsDNA release and AIM2 inflammasome activation. Redox Biol. 2022, 52, 102322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Li, X. Apple polyphenol extract alleviates lipid accumulation in free-fatty-acid-exposed HepG2 cells via activating autophagy mediated by SIRT1/AMPK signaling. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 1416–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hu, M.; Ye, C.; Liao, L.; Ding, C.; Sun, L.; Liang, J.; Chen, Y. Isosilybin regulates lipogenesis and fatty acid oxidation via the AMPK/SREBP-1c/PPARalpha pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 368, 110250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Su, S.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, Q.; Zeng, X.; Fu, F.; Lu, Y.; et al. Oleic acid improves hepatic lipotoxicity injury by alleviating autophagy dysfunction. Exp. Cell Res. 2023, 429, 113655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatta, M.A.; El-Derany, M.O.; Gibriel, A.A.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. Rhamnetin ameliorates non-alcoholic steatosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2023, 478, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Sinclair, A.J.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Barr, D.P.; Molero-Navajas, J.C.; Konstantopoulos, N. Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5n-3) down-regulates the expression of genes involved in fat synthesis in liver cells. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2011, 85, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, M.A.; Samuel, V.T. The Sweet Path to Metabolic Demise: Fructose and Lipid Synthesis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geidl-Flueck, B.; Hochuli, M.; Nemeth, A.; Eberl, A.; Derron, N.; Kofeler, H.C.; Tappy, L.; Berneis, K.; Spinas, G.A.; Gerber, P.A. Fructose- and sucrose- but not glucose-sweetened beverages promote hepatic de novo lipogenesis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Softic, S.; Stanhope, K.L.; Boucher, J.; Divanovic, S.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Johnson, R.J.; Kahn, C.R. Fructose and hepatic insulin resistance. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Chander Sharma, B.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.; Green, C.R.; Roberts, L.S.; Lee, Y.M.; McCarville, J.L.; Sanchez-Gurmaches, J.; Meurs, N.; Gengatharan, J.M.; Hover, J.D.; Phillips, S.A.; et al. Enzyme promiscuity drives branched-chain fatty acid synthesis in adipose tissues. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Q.; Wang, H.; Tong, L.; Fang, Q.; Xiang, M.; Han, L.; Jin, L.; Yang, J.; Qian, Z.; Ning, G.; et al. Betulinic acid improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through YY1/FAS signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 13033–13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; He, W.; Huang, Y.; Xiang, H.; Guo, J.; Che, Y.; Cheng, X.; Hu, F.; Hu, M.; Ma, T.; et al. Fatty Acid Synthase-Suppressor Screening Identifies Sorting Nexin 8 as a Therapeutic Target for NAFLD. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2508–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Mohseni, R.; Lucas, K.J.; Gutierrez, J.A.; Perry, R.G.; Trotter, J.F.; Rahimi, R.S.; Harrison, S.A.; Ajmera, V.; Wayne, J.D.; et al. TVB-2640 (FASN Inhibitor) for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: FASCINATE-1, a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2a Trial. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Gene Symbol | NCBI Reference Sequence | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMGCR | NM_008255.2 | CTTGTGGAATGCCTTGTGATTG | AGCCGAAGCAGCACATGAT |
| SREBP-1C | NM_011480.4 | GTGAGCCTGACAAGCAATCA | GGTGCCTACAGAGCAAGAG |
| SREBP-2 | NM_033218.1 | GCGTTCTGGAGACCATGGA | ACAAAGTTGCTCTGAAAACAAATCA |
| ACC1 | NM_133360.3 | GAGGTACCGAAGTGGCATCC | GTGACCTGAGCGTGGGAGAA |
| FASN | NM_007988.3 | GGTGTGGTGGGTTTGGTGAATTGT | TCACGAGGTCATGCTTTAGCACCT |
| SCD1 | NM_009127.4 | TTCTTCTCTCACGTGGGTTG | CGGGCTTGTAGTACCTCCTC |
| CD36 | NM_007643.4 | ATGGGCTGTGATCGGAACTG | TTTGCCACGTCATCTGGGTTT |
| FABP1 | NM_017399.5 | AGTCGTCAAGCTGGAAGGTGACAA | GACAATGTCGCCCAATGTCATGGT |
| FATP2 | NM_011978.2 | ACACACCGCAGAAACCAAATGACC | TGCCTTCAGTGGATGCGTAGAACT |
| FATP5 | NM_009512.2 | TGTAACGTCCCTGAGCAACCAGAA | ATTCCCAGATCCGAATGGGACCAA |
| β-actin | NM_007393.5 | GATCTGGCACCACACCTTCT | GGGGTGTTGAAGGTCTCAAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Bai, X.; Du, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Dong, K.; Chen, Z.; Yang, J. The Different Mechanisms of Lipid Accumulation in Hepatocytes Induced by Oleic Acid/Palmitic Acid and High-Fat Diet. Molecules 2023, 28, 6714. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186714
Zhang M, Bai X, Du Q, Xu J, Wang D, Chen L, Dong K, Chen Z, Yang J. The Different Mechanisms of Lipid Accumulation in Hepatocytes Induced by Oleic Acid/Palmitic Acid and High-Fat Diet. Molecules. 2023; 28(18):6714. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186714
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Miao, Xue Bai, Qian Du, Jiaojiao Xu, Danqing Wang, Lei Chen, Keting Dong, Ziyue Chen, and Jianhong Yang. 2023. "The Different Mechanisms of Lipid Accumulation in Hepatocytes Induced by Oleic Acid/Palmitic Acid and High-Fat Diet" Molecules 28, no. 18: 6714. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186714
APA StyleZhang, M., Bai, X., Du, Q., Xu, J., Wang, D., Chen, L., Dong, K., Chen, Z., & Yang, J. (2023). The Different Mechanisms of Lipid Accumulation in Hepatocytes Induced by Oleic Acid/Palmitic Acid and High-Fat Diet. Molecules, 28(18), 6714. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186714






