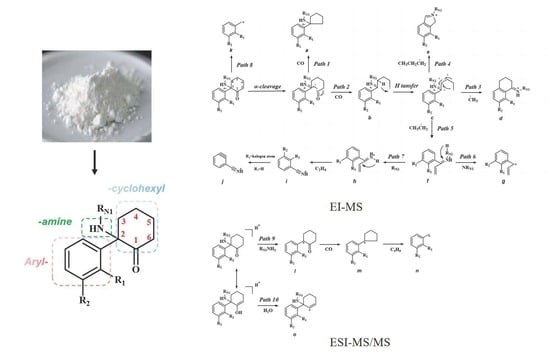
Study on the Mass Spectrometry Fragmentation Patterns for Rapid Screening and Structure Identification of Ketamine Analogues in Illicit Powders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
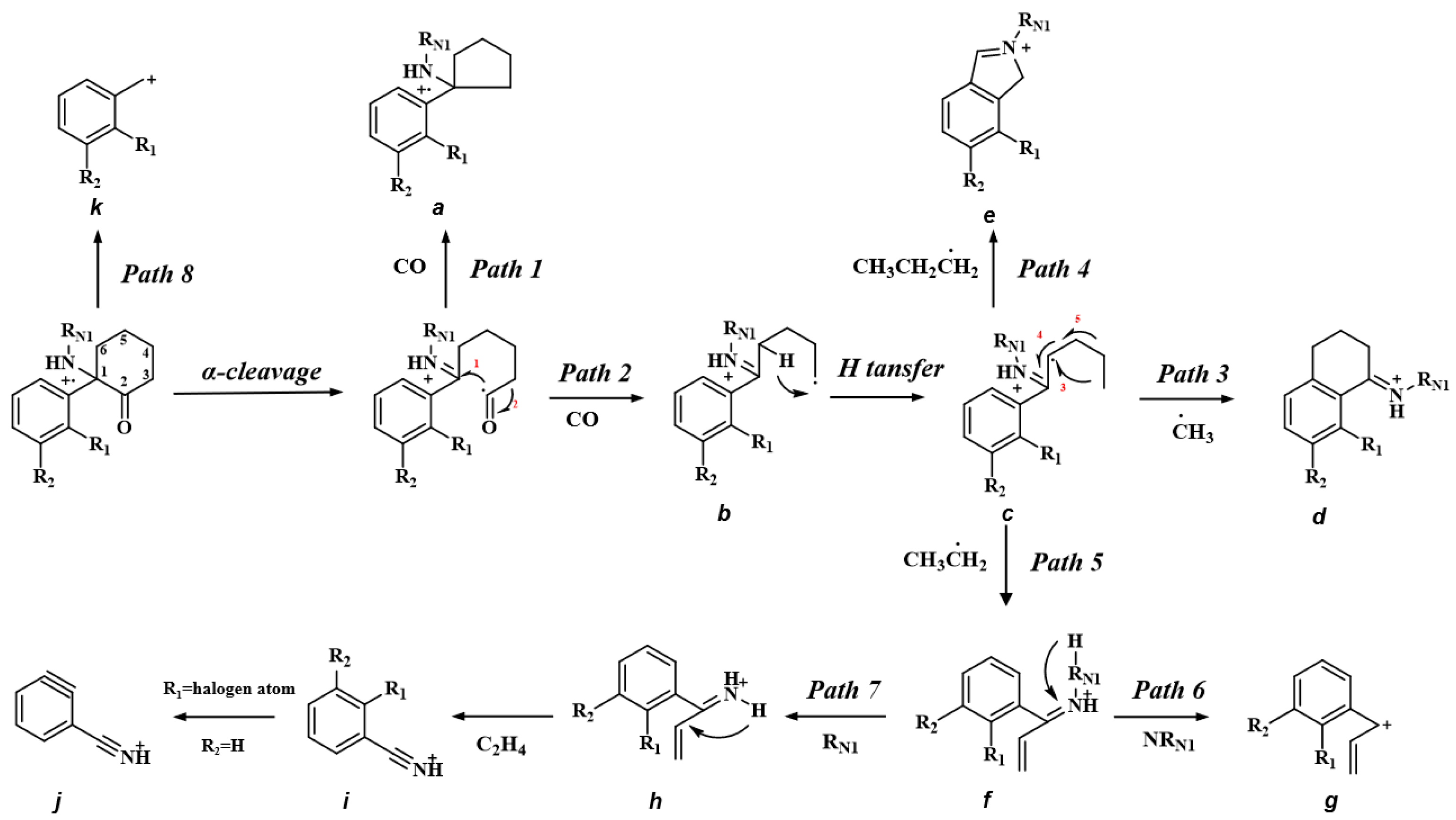
2.1. Overview of the Common Structure, EI-MS and ESI-MS/MS Fragmentation Patterns of Ketamine Analogues
2.2. Mass Spectra Results of Ketamine Analogues Reference Substances
2.3. Structure Elucidation of Ketamine Analogues Reference Substances
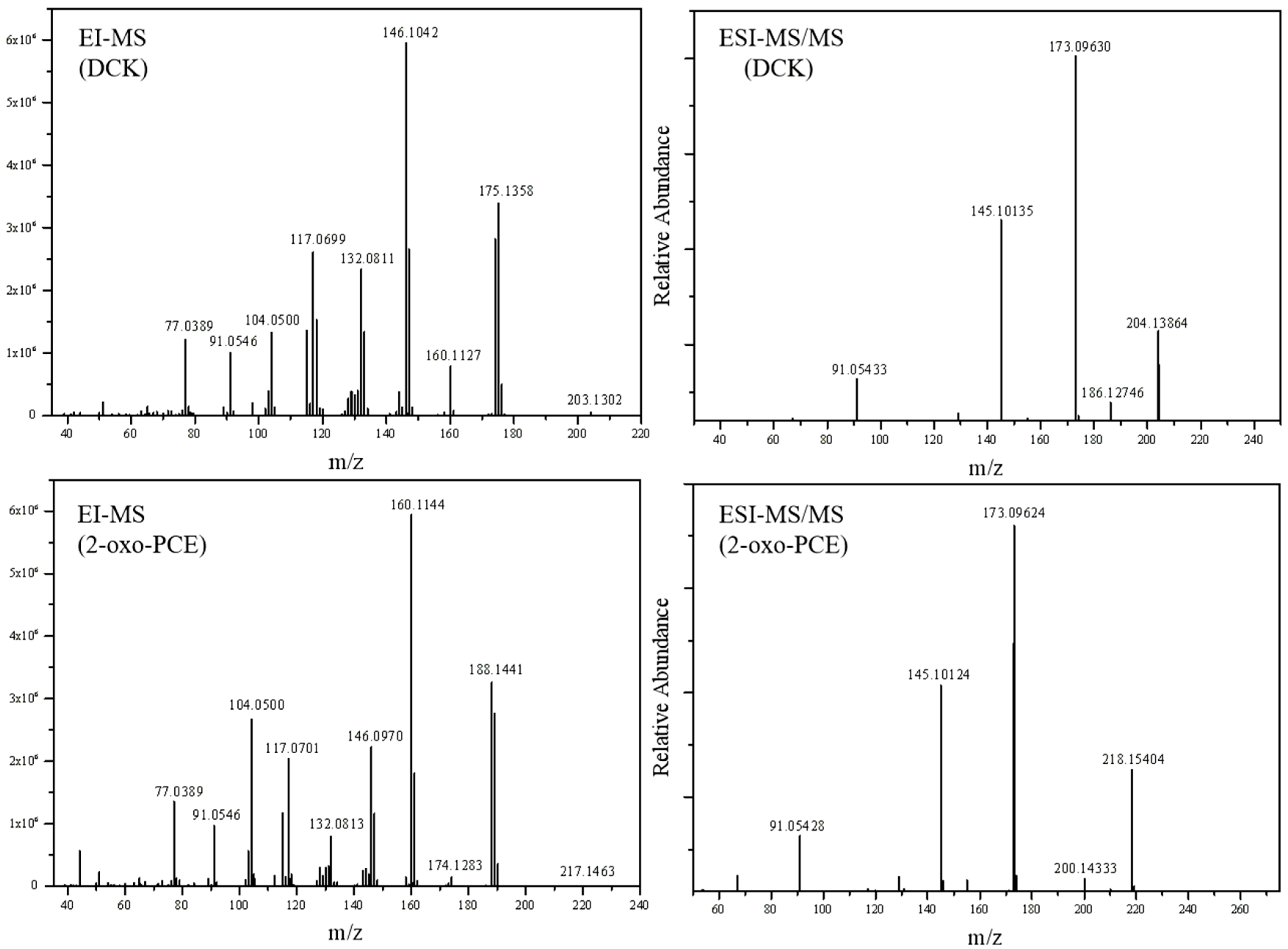
2.3.1. 2-phenyl-2-(methylamino)cyclohexanone (DCK) and 2-(Ethylamino)-2-phenylcyclohexan-1-one (2-oxo-PCE)
2.3.2. 2-(3-methoxyphenyl)-2-(ethylamino)cyclohexanone (MXE)
2.3.3. 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexanone (Ketamine), 2-(2-Fluorophenyl)-2-(methylamino) cyclohexan-1-one (F-Ketamine), 2-(2-Bromophenyl)-2-(methylamino) cyclohexan-1-one (Br-Ketamine) and 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-2-(ethylamino) cyclohexanone (NENK)
2.3.4. 2-(Ethylamino)-2-(m-tolyl)cyclohexan-1-one (DMXE)
2.4. Analysis of Mass Spectrometry Fragmentation Patterns of Ketamine Analogues
3. Qualitative Analysis of Suspicious Powder
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Instrument
4.2.1. GC-Q-TOF/MS Analysis
4.2.2. LC-Q-Orbitrap/MS Analysis
4.3. Sample Preparation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Liu, C.M.; Hua, Z.D.; Song, C.H.; Jia, W. Identification and analytical characterization of N-propyl norbutylone, N-butyl norbutylone, N-benzyl norheptedrone, and N-pyrrolidinyl-3,4-DMA. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 15, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.X.; Ren, X.X.; Dong, L.P.; Jiang, H.; Wang, R.H. Research progress of ketamine analogues. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 42, 735–747. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.M.; Hua, Z.D.; Jia, W.; Liu, P.P.; Xu, Y. Characterization of 17 unknown ketamine manufacturing by-product impurities by UHPLC-QTOF-MS. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vari, M.R.; Ricci, G.; Cavallo, M.; Pichini, S.; Sirignano, A.; Graziano, S. Ketamine: From prescription anaesthetic to a new psychoactive substance. Curr. Pharm. Design 2022, 28, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matey, J.M.; Montalva, G.; Ruiz, G.G.; Zapata, F.; Fernandez, A.L.; Martinez, M.A. Prevalence study of drugs and new psychoactive substances in hair of ketamine consumers using a methanolic direct extraction prior to high-resolution mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 329, 111080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.H.Y.; Li, T.C.; Lai, C.K.; Chong, Y.K.; Ching, C.K.; Mak, T.W.L. Emergence of new psychoactive substance 2-fluorodeschloroketamine: Toxicology and urinary analysis in a cluster of patients exposed to ketamine and multiple analogues. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 312, 110327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, R.; Dare, B.L.; Bouedec, D.L.; Kernalleguen, A.; Ferron, P.J.; Morel, I.; Gicquel, T. Arylcyclohexylamine Derivatives: Pharmacokinetic, Pharmacodynamic, Clinical and Forensic Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, E.L.; Hudson, S.C.; Dargan, P.I.; Parkin, M.C.; Wood, D.M.; Kicman, A.T. Characterizing metabolites and potential metabolic pathways for the novel psychoactive substance methoxetamine. Drug Test. Anal. 2014, 6, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestria, S.; Odoardi, S.; Biosa, G.; Valentini, V.; Masi, G.D.; Cittadini, F.; Rossi, S.S. Method development for the identification of methoxpropamine, 2-fluoro-deschloroketamine and deschloroketamine and their main metabolites in blood and hair and forensic application. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 323, 110817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Fang, W.J. Handbook of New Psychoactive Substances for Judicial Practice; Ma, Y., Wang, Y.M., Eds.; Law Press: Beijing, China, 2019; Chapter 8; p. 351. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; He, H.Y.; Liu, C.M.; Hua, Z.D. Study on vibrational spectral characteristics of fentanyl-class substances. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2021, 41, 2829–2834. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Hua, Z.D.; Cheng, F.B.; Liu, Y. Research progress on separation and analysis technology for isomers of new psychoactive substances. Chin. J. Anal. Lab. 2022, 41, 466–474. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.M.; Hua, Z.D.; Jia, W.; Li, T. Identification of AD-18, 5F-MDA-19, and pentyl MDA-19 in seized materials after the class-wide ban of synthetic cannabinoids in China. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.L.; Zong, X.S.; Liu, J.W.; Ke, X.; Huang, Z.P.; Xu, Y. Development of a fragmentation pattern of synthetic cannabinoids based on electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in positive ion mode to screen synthetic cannabinoids in illicit products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 193, 113723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Wu, H.J.; Xiang, P.; Shen, B.H.; Zhao, J.B.; Deng, H.X.; Qiang, H.S.; Song, F.Y.; Shi, Y. Investigation of fragmentation pathways of fentanyl analogues and novel synthetic opioids by electron ionization high-resolution mass spectrometry and electrospray ionization high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectr. 2020, 31, 277–291. [Google Scholar]
- Frison, G.; Zamengo, L.; Zancanaro, F.; Tisato, F.; Traldi, P. Characterization of the designer drug deschloroketamine(2-methylamino-2-phenylcyclohexanone) by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry, liquid chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry, multistage mass spectrometry, and nuclear magnetic resonance. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 30, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larabi, I.A.; Zerizer, F.; Ameline, A.; Etting, I.; Joseph, D.; Kintz, P.; Alvarez, J.C. Metabolic profiling of deschloro-N-ethyl-ketamine and identification of new target metabolites in urine and hair using human liver microsomes and high-resolution accurate mass spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1108–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, Y.T.; Tsai, Y.S.; Su, W.L.; Huang, D.Y.; Wu, H.H.; Tseng, S.H.; Wang, H.H.; Chiu, C.Y.; Wang, C.F.; Liu, C.Y.; et al. New ketamine analogue: 2-fluorodeschloro-N-ethyl-ketamine and its suggested metabolites. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 341, 111501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| No. | Compound Structures | Formula | Accurate m/z ([M+]) | Theoretical m/z ([M+]) | Accurate m/z ([M + H]+) | Theoretical m/z ([M + H]+) | RSD (ppm) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DCK: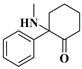 | C13H17NO | 203.1302 | 203.1310 | 204.13843 | 204.13829 | −3.94/0.69 |
| 2 | 2-oxo-PCE: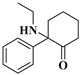 | C14H19NO | 217.1463 | 217.14666 | 218.15404 | 218.15394 | −1.65/0.46 |
| 3 | MXE: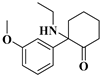 | C15H21NO2 | 247.1567 | 247.15723 | 248.16451 | 248.16451 | −2.14/0 |
| 4 | Ketamine: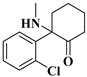 | C13H16ClNO | 237.0913 | 237.09204 | 238.09952 | 238.09932 | −3.12/0.84 |
| 5 | F-Ketamine: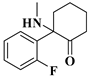 | C13H16FNO | 221.1205 | 221.12159 | 222.12936 | 222.12887 | −4.93/2.20 |
| 6 | Br-Ketamine: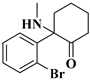 | C13H16BrNO | 281.0423 | 281.04153 | 282.04880 | 282.04880 | 2.73/0 |
| 7 | NENK: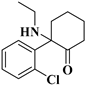 | C14H18ClNO | 251.1072 | 251.10769 | 252.11505 | 252.11497 | −1.95/0.32 |
| 8 | DMXE: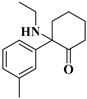 | C15H21NO | 231.1617 | 231.16231 | 232.16963 | 232.16959 | −2.64/0.17 |
| Comp. | Molecular Ion (m/z) | Fragmentation Ions (m/z) |
| EI-MS | ||
| 1 | 203.1302 | 175.1358 (Path 1, 2), 160.1127 (Path 3), 146.1042 (Path 5), 132.0811 (Path 4, 7), 117.0699 (Path 6), 104.0500 (Path 7), 91.0546 (Path 8), 77.0389 (Path 8) |
| 2 | 217.1463 | 189.1518 (Path 1, 2), 174.1283 (Path 3), 160.1144 (Path 5), 146.0970 (Path 4), 132.0813 (Path 7), 117.0701 (Path 6), 104.0500 (Path 7), 91.0546 (Path 8), 77.0389 (Path 8) |
| 3 | 247.1567 | 219.1619 (Path 1, 2), 204.1387 (Path 3), 190.1301 (Path 5), 176.1085 (Path 4), 162.0915 (Path 7), 147.0805 (Path 6), 134.0603 (Path 7), 121.0650 (Path 8),91.0539 (Path 8), 77.0388 (Path 8) |
| 4 | 237.0913 | 209.0965 (Path 1, 2), 194.0732 (Path 3), 180.0591 (Path 5), 166.0418 (Path 7), 145.0885 (Path 1) 138.0105 (Path 7), 125.0151 (Path 8), 115.0542 (Path 6), 102.0341 (Path 7), 75.0229 (Path 8) |
| 5 | 221.1205 | 193.1265 (Path 1, 2), 178.1034 (Path 3), 164.0942 (Path 5), 150.0718 (Path 4, 7), 135.0606 (Path 6), 122.0406 (Path 7), 115.0547 (Path 6), 109.0542 (Path 8), 102.0345 (Path 7), 75.0232 (Path 8) |
| 6 | 281.0423 | 253.0480 (Path 1, 2), 238.0219 (Path 3), 224.0092 (Path 5), 209.9915 (Path 4, 7), 194.9801 (Path 6), 181.9616 (Path 7), 168.9652 (Path 8), 145.0900 (Path 1), 115.0553 (Path 6), 102.0470 (Path 7), 75.0229 (Path 8) |
| 7 | 251.1072 | 223.1125 (Path 1, 2), 208.0890 (Path 3), 194.0758 (Path 5), 180.0579 (Path 4), 166.0423 (Path 7), 151.0312 (Path 6), 138.0108 (Path 7), 125.0156 (Path 8), 115.0545, 102.0342 (Path 8), 75.0232 (Path 8) |
| 8 | 231.1617 | 203.1669 (Path 1, 2), 188.1438 (Path 3), 174.1284 (Path 5), 160.1124 (Path 4), 146.0967 (Path 7), 131.0855 (Path 6), 118.0654 (Path 7), 105.0701 (Path 8), 91.0544 (Path 8), 77.0387 (Path 8) |
| Comp. | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Fragmentation Ions (m/z) |
| ESI-MS/MS | ||
| 1 | 204.13843 | 186.12746 (Path 10), 173.09630 (Path 9), 145.10135 (Path 9), 91.05433 (Path 9) |
| 2 | 218.15404 | 200.14333 (Path 10), 173.09624 (Path 9), 145.10124 (Path 9), 91.05428 (Path 9) |
| 3 | 248.16451 | 230.15408 (Path 10), 203.10672 (Path 9), 175.11182 (Path 9), 121.06484 (Path 9) |
| 4 | 238.09952 | 220.08894 (Path 10), 207.05742 (Path 9), 179.06247 (Path 9), 125.01547 (Path 9), 163.03113 |
| 5 | 222.12936 | 204.11887 (Path 10), 191.08719 (Path 9), 163.09216 (Path 9), 109.04510 (Path 9) |
| 6 | 282.04880 | 264.03821 (Path 10), 251.00664 (Path 9), 223.01180 (Path 9), 168.96486 (Path 9), 172.08832 |
| 7 | 252.11505 | 234.10452 (Path 10), 207.05725 (Path 9), 179.06230 (Path 9), 125.01538 (Path 9), 163.03096 |
| 8 | 232.16963 | 214.15903 (Path 10), 187.11192 (Path 9), 159.11699 (Path 9), 105.07034 (Path 9) |
| EI-QTOF/MS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Chemical Formula | Exact Mass | Accurate Mass | Error (ppm) |
| 1 | C14H19NO+ | 217.1461 | 217.1461 | 0.0 |
| C13H19N+ | 189.1512 | 189.1515 | 1.6 | |
| C12H16N+ | 174.1277 | 174.1282 | 2.9 | |
| C11H14N+ | 160.1121 | 160.1125 | 2.5 | |
| C10H12N+ | 146.0964 | 146.0967 | 2.1 | |
| C9H10N+ | 132.0808 | 132.0814 | 4.5 | |
| C10H11+ | 131.0855 | 131.0849 | −4.6 | |
| C8H9+ | 105.0699 | 105.0702 | 2.9 | |
| C7H7+ | 91.0542 | 91.0546 | 4.4 | |
| C6H5+ | 77.0386 | 77.0389 | 3.9 | |
| ESI-Q-Orbitrap MS/MS | ||||
| 1 | C14H20NO+ | 218.15394 | 218.15405 | 0.5 |
| C14H18N+ | 200.14338 | 200.14354 | 0.8 | |
| C13H15O+ | 187.11174 | 187.11191 | 0.9 | |
| C12H15+ | 159.11683 | 159.11697 | 0.9 | |
| C8H9+ | 105.06988 | 105.06996 | 4.7 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Ke, X.; Xu, Y. Study on the Mass Spectrometry Fragmentation Patterns for Rapid Screening and Structure Identification of Ketamine Analogues in Illicit Powders. Molecules 2023, 28, 6510. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186510
Fan Y, Gao J, Chen X, Wu H, Ke X, Xu Y. Study on the Mass Spectrometry Fragmentation Patterns for Rapid Screening and Structure Identification of Ketamine Analogues in Illicit Powders. Molecules. 2023; 28(18):6510. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186510
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yilei, Jianhong Gao, Xianxin Chen, Hao Wu, Xing Ke, and Yu Xu. 2023. "Study on the Mass Spectrometry Fragmentation Patterns for Rapid Screening and Structure Identification of Ketamine Analogues in Illicit Powders" Molecules 28, no. 18: 6510. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186510
APA StyleFan, Y., Gao, J., Chen, X., Wu, H., Ke, X., & Xu, Y. (2023). Study on the Mass Spectrometry Fragmentation Patterns for Rapid Screening and Structure Identification of Ketamine Analogues in Illicit Powders. Molecules, 28(18), 6510. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186510