Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Porous Brass by Chemical Dealloying for Efficient Emulsion Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
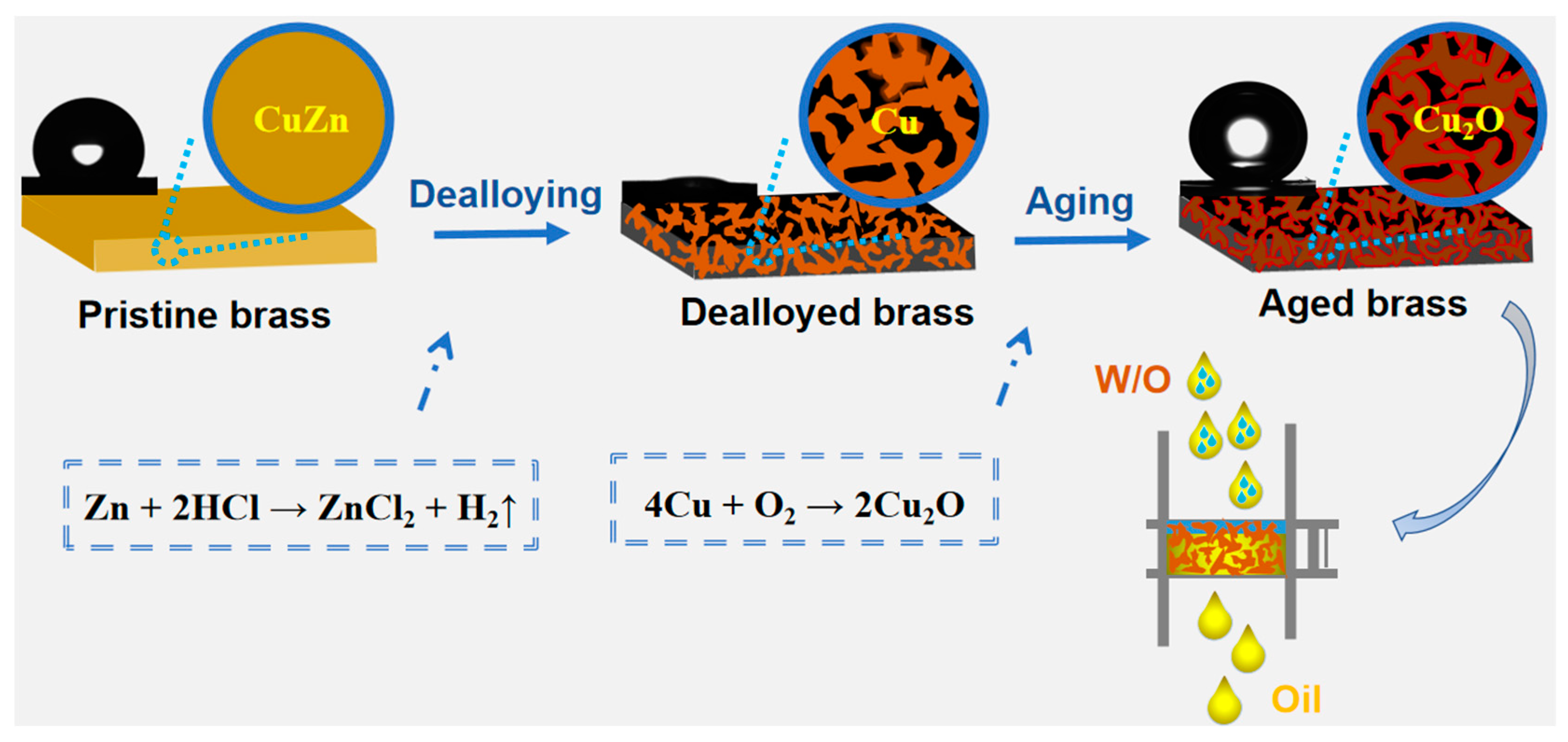
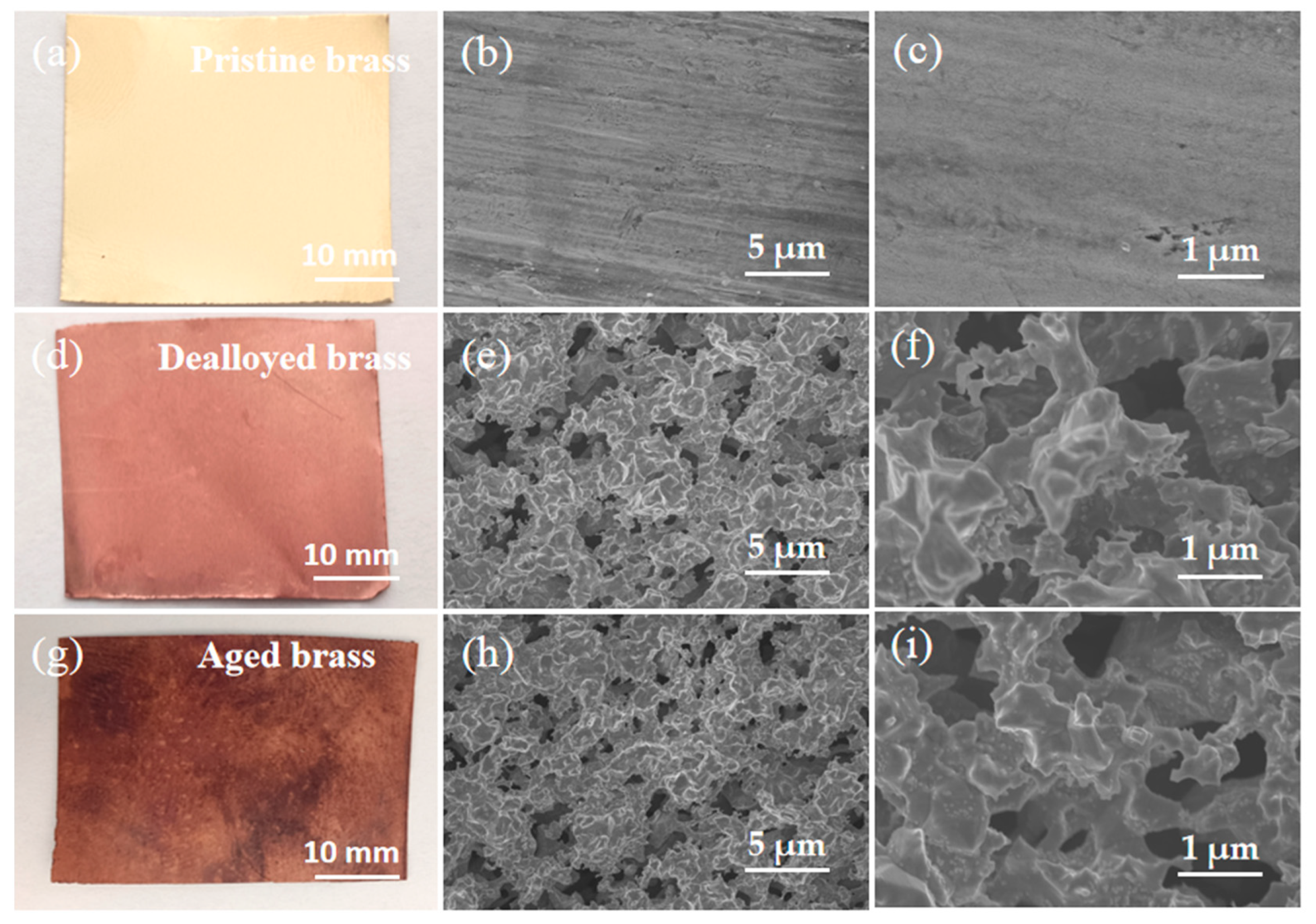
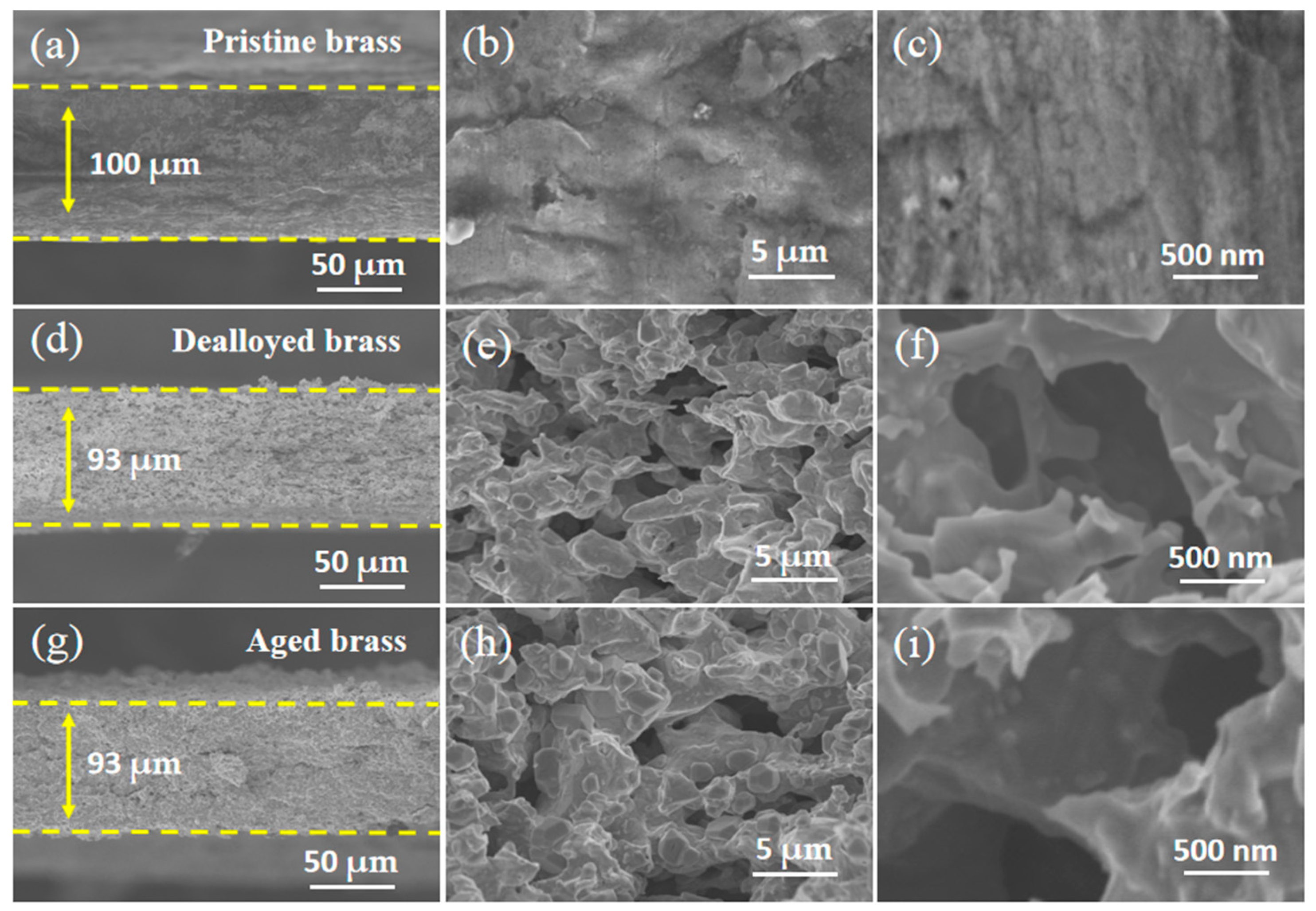
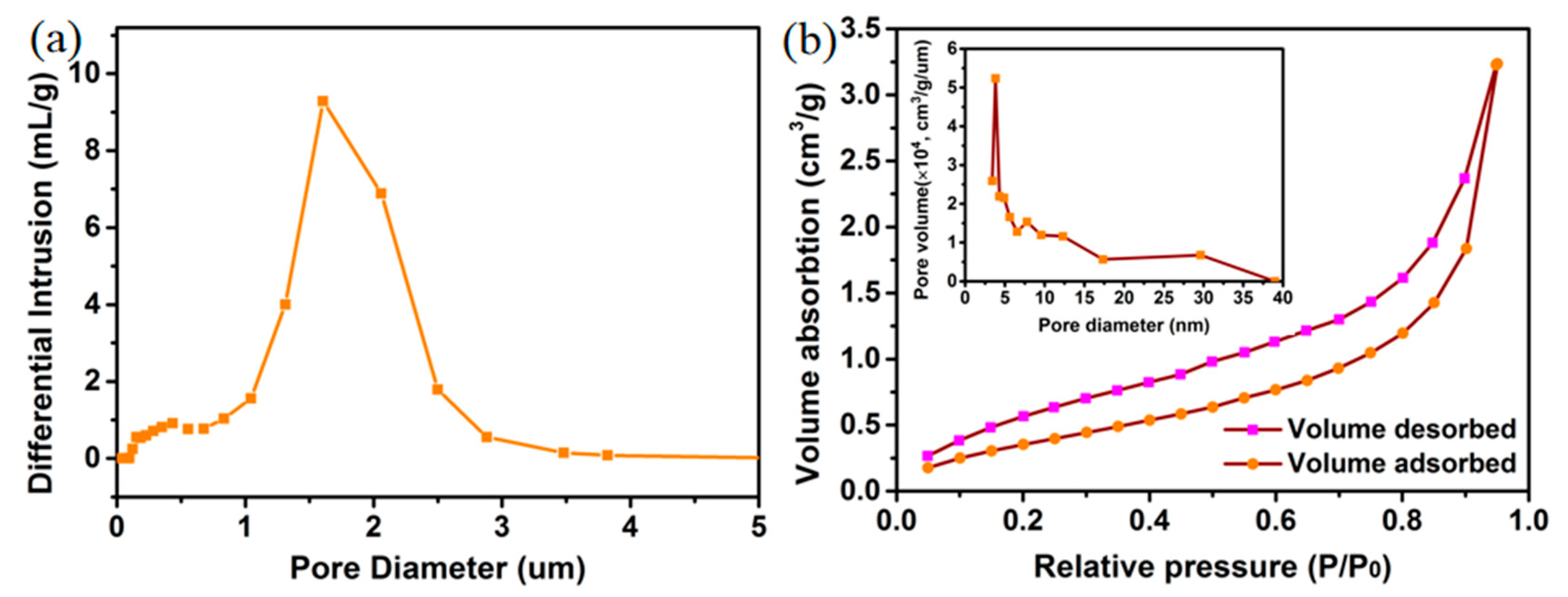
2.1. Construction of Bicontinuous Porous Structure by Dealloying
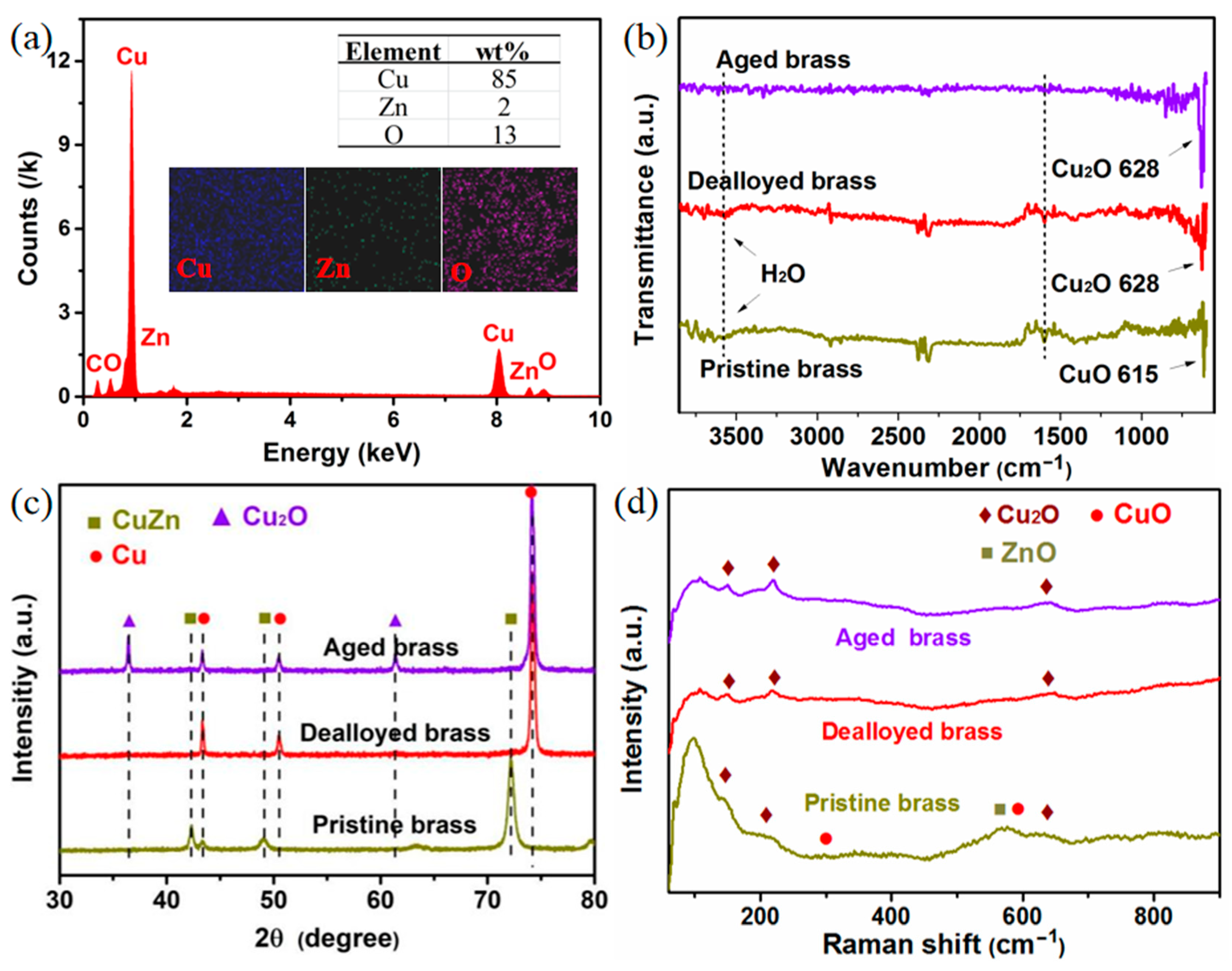
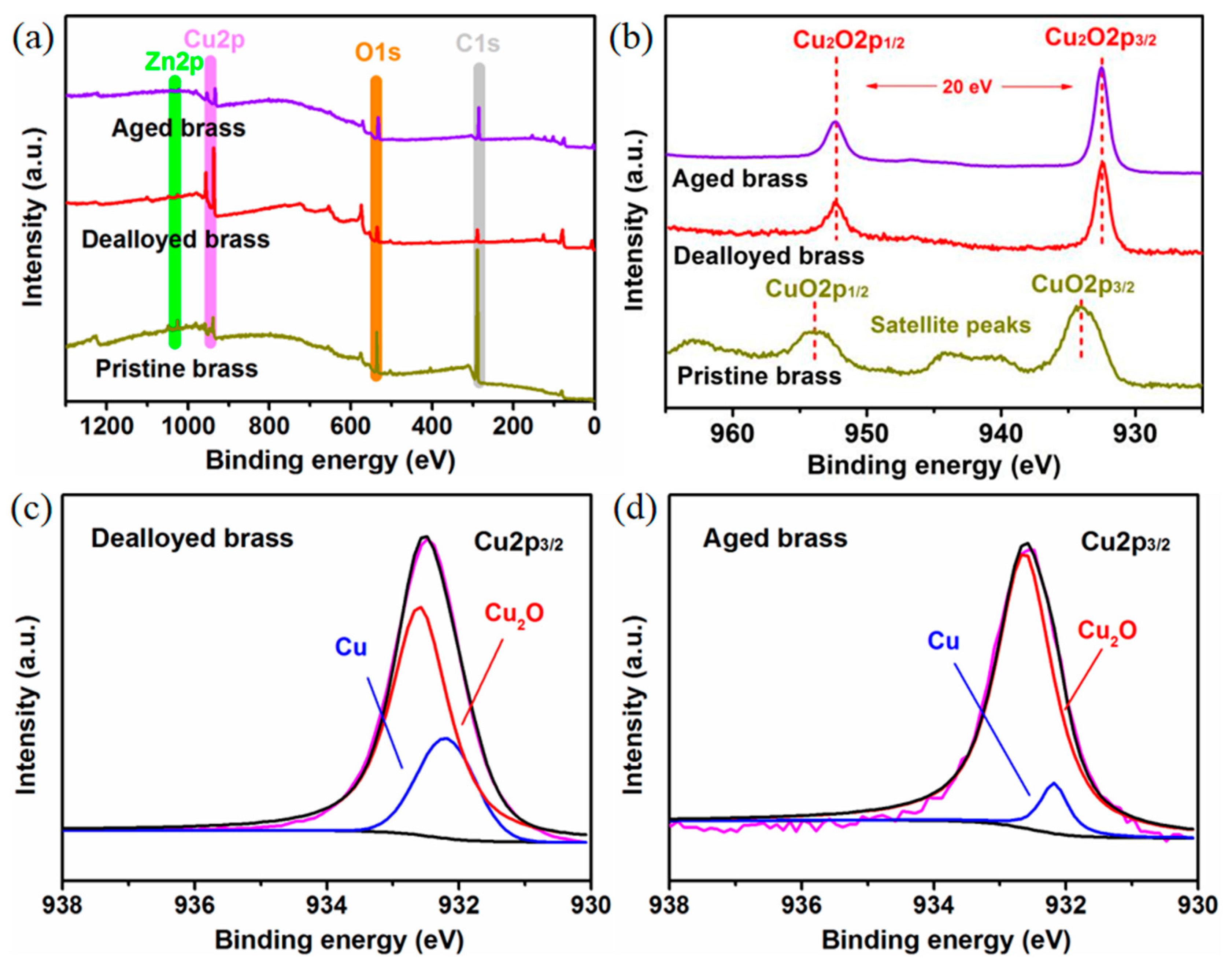
2.2. Effect of Aging on Chemical Composition
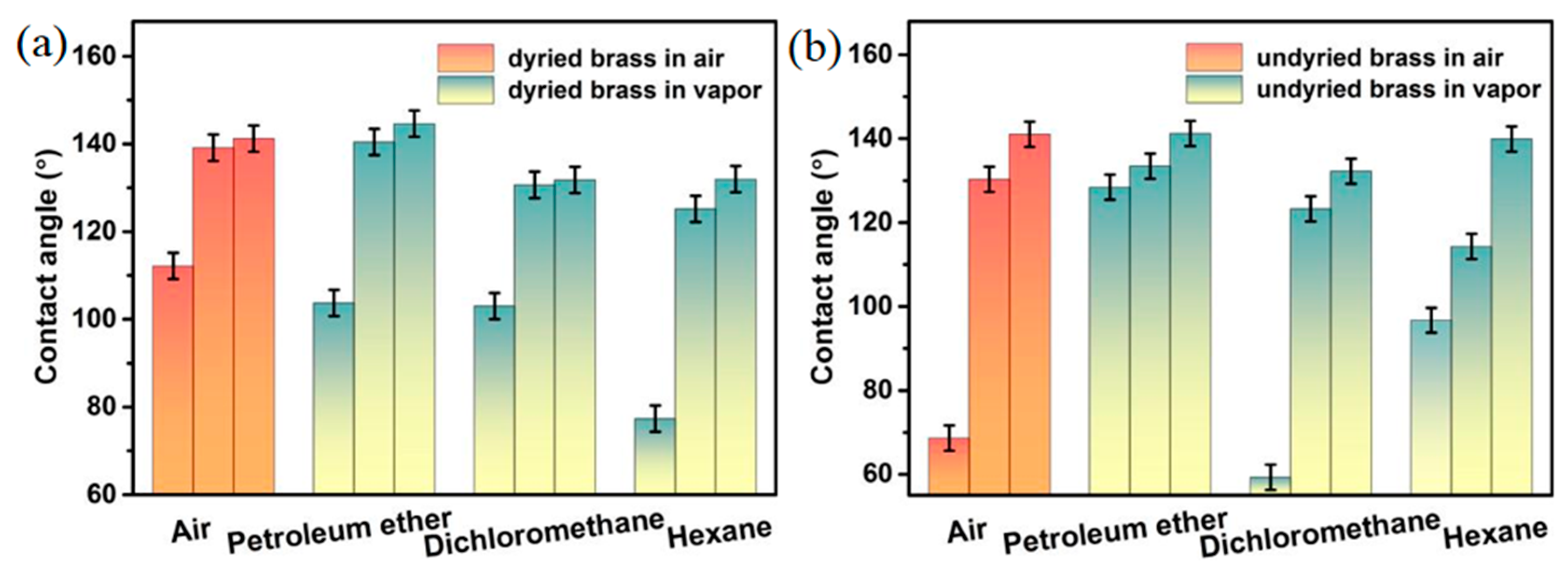
2.3. Effect of Aging Time on Wettability Transition
2.4. Mechanism of Wetting Transition
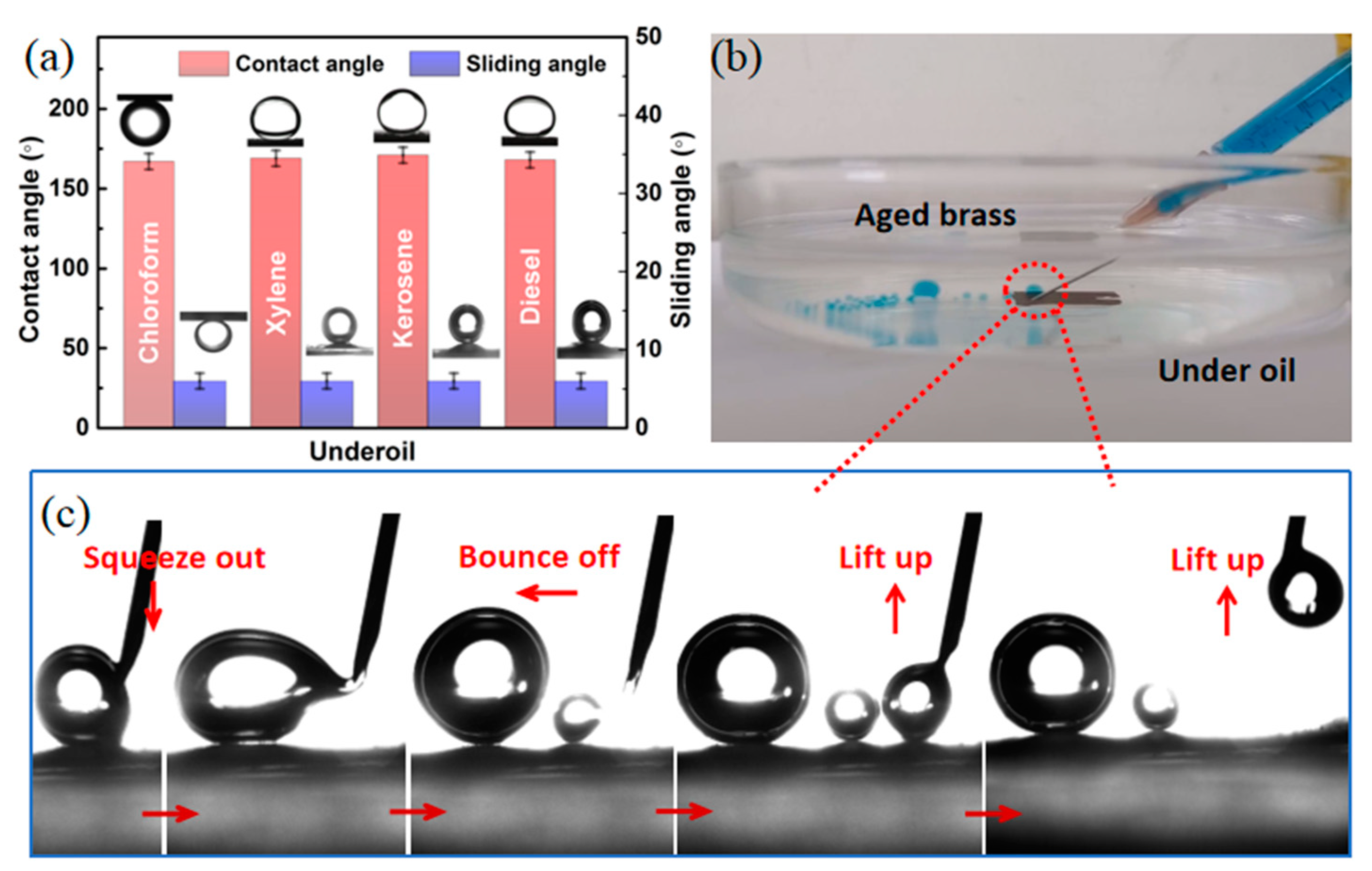
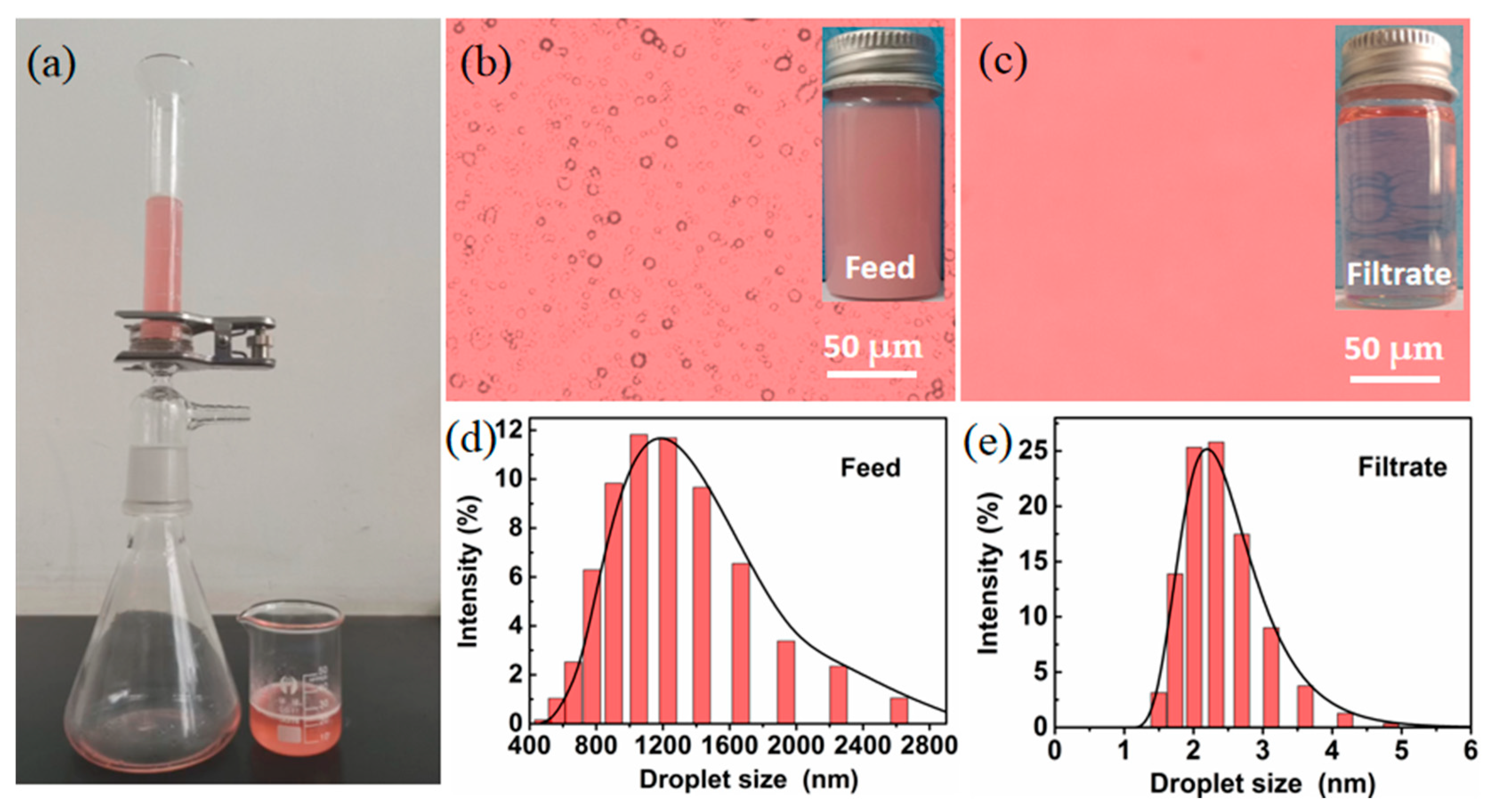
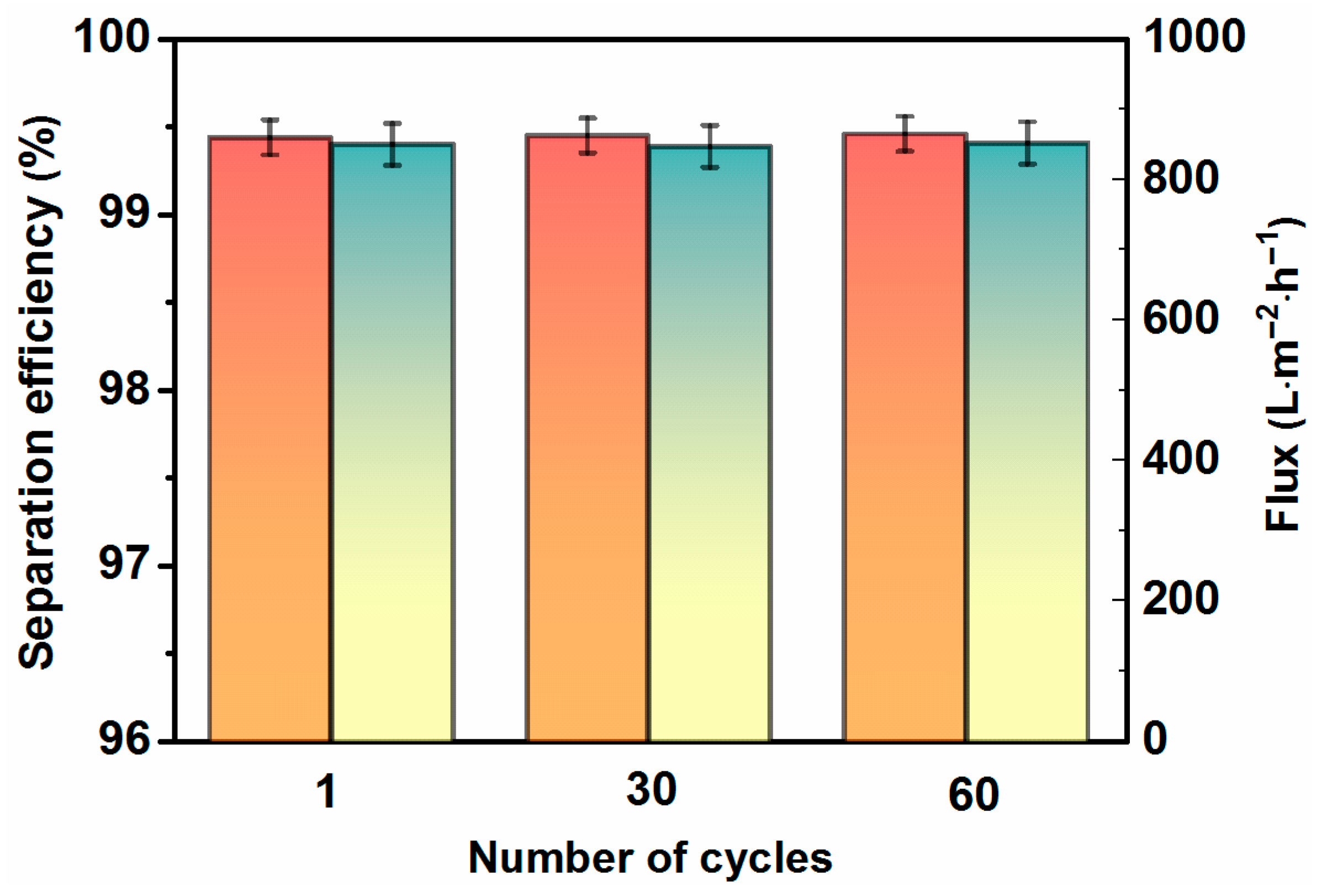
2.5. Water-in-Oil Emulsion Separation with High Efficiency
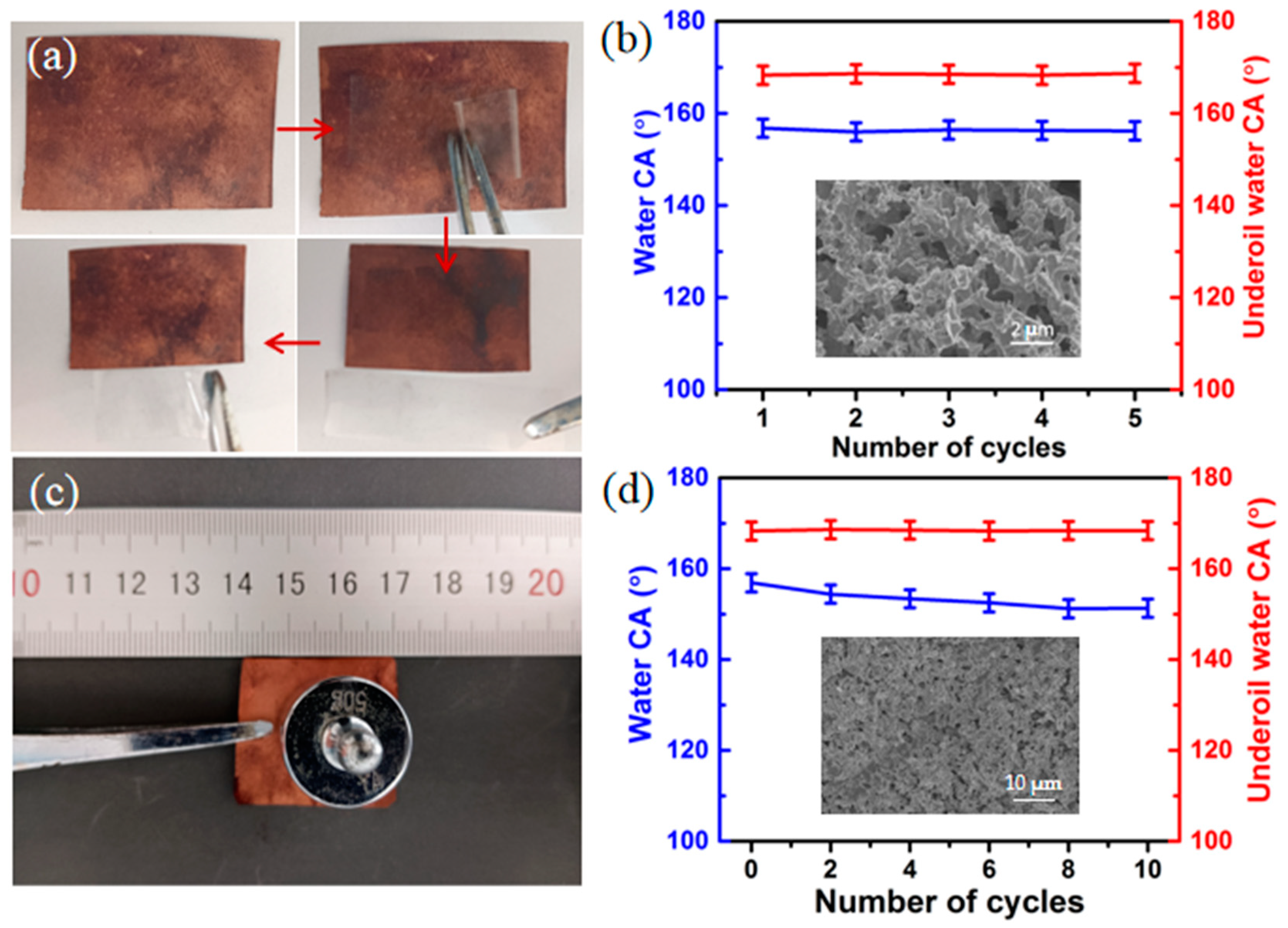
2.6. Mechanical, Thermal, and Chemical Stability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Superhydrophobic Porous Brass Fabricated by Dealloying and Aging
3.3. Aging in Ambient Air and Organic Vapors
3.4. Preparation and Separation of Water-in-Oil Emulsions
3.5. Instruments and Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Ke, Z.; Du, C.Z.; Zheng, L.; Wang, C.; Yuan, Z. Review: Porous metal filters and membranes for oil-water separation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Choi, W.S. 2D and 3D bulk materials for environmental remediation: Air filtration and oil/water separation. Materials 2020, 13, 5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Weng, Z.; Yu, H. Nanosecond laser-induced underwater superoleophobic and underoil superhydrophobic mesh for oil/water separation. Langmuir 2018, 34, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Deng, W.; Su, Y. Recent advances in preparation of metallic superhydrophobic surface by chemical etching and its applications. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 61, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, L.; He, T.; Fan, Y.; He, Y. A microgel-structured cellulose nanofibril coating with robust antifouling performance for highly efficient oil/water and immiscible organic solvent separation. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 647, 128875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Lin, H.; Chai, G.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Lu, H. Micro-arc oxidation enhances the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of oil-water separating mesh. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 18370–18384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.; Al Abdulgader, H.; Alsaeed, D.; Drmosh, Q.A.; Baroud, T.N.; Saleh, T.A. Hydrophobic tungsten oxide-based mesh modified with hexadecanoic branches for efficient oil/water separation. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 102931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.J.; Xu, Z.K. Wettability switchable membranes for separating both oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 624, 118976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.Y.; Chen, K.X.; Wang, J.H.; Mo, D.C.; Lyu, S.S. Hierarchical nanoparticle-induced superhydrophilic and under-water superoleophobic Cu foam with ultrahigh water permeability for effective oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 10566–10574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, N.; Azizian, S.; Mohazzab, B.F.; Jaleh, B. One-step fabrication of brass filter with reversible wettability by nanosecond fiber laser ablation for highly efficient oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 118139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Fan, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, Q.; Bo, Y.; Qian, L. Preparation and application of superhydrophobic copper mesh by chemical etching and in-situ growth. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 737550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Huang, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Xing, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Development of superhydrophilic Al foil with micropore arrays via mask electrochemical machining and chemical immersion for efficient oil/water separation. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Song, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zheng, H.; Huang, S.; Liu, X. Atmospheric pressure plasma functionalized polymer mesh: An environmentally friendly and efficient tool for oil/water separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6828–6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Aday, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. On demand oil/water separation enabled by microporous ultra-thin aluminum foil with asymmetric wettability. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 648, 129334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Gil, L.; Ramirez, J.; Fernandez-Morales, P. Ultra-hydrophobic aluminum foam development for potential application in continuous water-oil separation processes. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 26, 101362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wei, C.; Tao, Y.; Xi, B.; Xiong, S.; Qian, Y. Dealloying: An effective method for scalable fabrication of 0D, 1D, 2D, 3D materials and its application in energy storage. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Dworzak, A.; Crespo, D.; Renner, F.U.; Dosche, C.; Oezaslan, M. Nanoporous copper ribbons prepared by chemical dealloying of a melt-spun ZnCu alloy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 126, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; He, G.; Ding, Y. Dealloyed nanoporous materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Electrochem. Energy R. 2020, 3, 541–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajitha, M.; Abraham, B.; Nelliyil, R.B.; Yoosaf, K. Chemically etched nanoporous copper and galvanically displaced silver nanoflowers for SERS sensing. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 10038–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lei, D.; He, Y.B.; Yuan, Y.; Yun, Q.; Ni, B.; Lu, J. Compact 3D copper with uniform porous structure derived by electrochemical dealloying as dendrite-free lithium metal anode current collector. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, F.; Wang, D.; He, D. Preparation of 3D nanoporous copper-supported cuprous oxide for high-performance lithium ion battery anodes. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Chen, F.; Wang, H.; Shen, Q.; Lavernia, E.J.; Zhang, L. Influence of porosity on mechanical behavior of porous Cu fabricated via de-alloying of Cu-Fe alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 2019, 25, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, H.; Bücker, K.; Yang, F.; Nürnberger, P.; Hampp, N.A. Highly dynamic alloying and dealloying in the model system gold-silicon (AuSi). J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 5462–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Y.; Lewis, J.A.; Shetty, P.P.; Tippens, J.; Yeh, D.; Marchese, T.S.; McDowell, M.T. Porous metals from chemical dealloying for solid-state battery anodes. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 2461–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, H.; Xu, Q.; Wei, L.; Min, Y. Etching and heating treatment combined approach for superhydrophobic surface on brass substrates and the consequent corrosion resistance. Corros. Sci. 2016, 102, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Constructing superhydrophobic surface on copper substrate with dealloying-forming and solution-immersion method. Materials 2022, 15, 4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.L.; Tran, N.; Song, T.; Liang, D.; Qian, M. Robust bulk micro-nano hierarchical copper structures possessing exceptional bactericidal efficacy. Biomaterials 2022, 280, 121271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Kong, L.; Hodgson, P.D.; Dumée, L.F. Impact of the de-alloying kinetics and alloy microstructure on the final morphology of de-alloyed meso-porous metal films. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 856–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, C.C.; Zhang, Y.P.; Cui, C.X.; Chen, D.L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M.J. Controllable water penetration through a smart brass mesh modified by mercaptobenzoic acid and naphthalenethiol. Coatings 2022, 12, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Guo, Z. Fabrication of a durable brass mesh capable of rapid transformation between two modes of liquid transportation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 621, 156880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Si, Y.; Fu, Q.; Hong, F.; Yu, J.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Ding, B. Superwetting hierarchical porous silica nanofibrous membranes for oil/water microemulsion separation. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 12445–12449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shen, J.; Guo, S. Optimized microporous structure of ePTFE membranes by controlling the particle size of PTFE fine powders for achieving high oil-water separation performances. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 629, 119294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Kang, Z.; Li, W.; Su, F. Simultaneously spray-assisted assembling reversible superwetting coatings for oil-water separation. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 32, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Singha, N.R. MOF and derived materials as aerogels: Structure, property, and performance relations. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 446, 214125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Sun, Y.; Dai, H.; Ni, P.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Direct growth of pod-like Cu2O nanowire arrays on copper foam: Highly sensitive and efficient nonenzymatic glucose and H2O2 biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 231, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamam, A.; Dehchar, C.; Maiza, M.; Chikouche, I.; Merabti, H. Facile synthesis and electrochemical study of CuO thin films for hydrogen peroxide reduction in alkaline medium. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 3534–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babouri, L.; Belmokre, K.; Kabir, A.; Abdelouas, A.; Khettabi, R.; El Mendili, Y. Microstructure and crystallographic properties of Cu77Zn21 alloy under the effect of heat treatment. Mater. High Temp. 2019, 36, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, H.; Aghdam, H.D.; Malekfar, R.; Bellah, S.M. Effects of energy and hydrogen peroxide concentration on structural and optical properties of CuO nanosheets prepared by pulsed laser ablation. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y. Insights into the wettability transition of nanosecond laser ablated surface under ambient air exposure. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2019, 533, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantauzzi, M.; Elsener, B.; Cocco, F.; Passiu, C.; Rossi, A. Model protective films on Cu-Zn alloys simulating the inner surfaces of historical brass wind instruments by EIS and XPS. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhong, K.; Dang, Y.; Li, J.; Ruan, M.; Fang, Z. Chemical dealloying pore structure control of porous copper current collector for dendrite-free lithium anode. J. Porous Mat. 2021, 28, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zou, J.J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. Cu2O film via hydrothermal redox approach: Morphology and photocatalytic performance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 16335–16343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, C.H.; Zahiri, B.; Sow, P.K.; Mérida, W. On-demand oil-water separation via low-voltage wettability switching of core-shell structures on copper substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 444, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahiri, B.; Sow, P.K.; Kung, C.H.; Mérida, W. Active control over the wettability from superhydrophobic to superhydrophilic by electrochemically altering the oxidation state in a low voltage range. Adv. Mater. Interface 2017, 4, 1700121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C. Advanced analysis of copper X-ray photoelectron spectra. Surf. Interface Anal. 2017, 49, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmal, A.K.; Dutta, S.; Pal, T. A ternary Cu2O-Cu-CuO nanocomposite: A catalyst with intriguing activity. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 3139–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Wu, L.; Liu, P.; Guan, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W. Design and fabrication of superhydrophobic layered double hydroxide and oxides composite coating on brass mesh with excellent anticorrosion, delay icing and oil-water separation ability. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2023, 20, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Kang, Z. A facile approach for the fabrication of 3D flower-like Cu2S nanostructures on brass mesh with temperature-induced wetting transition for efficient oil-water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, P.; Hou, K.; Zhou, C.; Li, G.; Wen, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, S. Superhydrophobic Cu2S@Cu2O film on copper surface fabricated by a facile chemical bath deposition method and its application in oil-water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakerley, D.; Lamaison, S.; Ozanam, F.; Menguy, N.; Mercier, D.; Marcus, P.; Mougel, V. Bio-inspired hydrophobicity promotes CO2 reduction on a Cu surface. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, D.V.; Dunn, A.; Wasley, T.J.; Kay, R.W.; Stringer, J.; Smith, P.J.; Shephard, J.D. Nanosecond laser textured superhydrophobic metallic surfaces and their chemical sensing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzig, A.M.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G.; Englezos, P. Patterned superhydrophobic metallic surfaces. Langmuir 2009, 25, 4821–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Yin, K.; Yu, Z.; Wang, T.; Liu, X. Laser-heat surface treatment of superwetting copper foam for efficient oil-water separation. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wen, C.; Lian, J. Reversible wettability transition between superhydrophilicity and superhydrophobicity through alternate heating-reheating cycle on laser-ablated brass surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 492, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Zhong, M.; Fan, P.; Gong, D.; Zhang, H. Wettability conversion of ultrafast laser structured copper surface. J. Laser Appl. 2015, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.W.; Holtsch, A.; Lößlein, S.; Pauly, C.; Spengler, C.; Grandthyll, S.; Müller, F. In-depth investigation of copper surface chemistry modification by ultrashort pulsed direct laser interference patterning. Langmuir 2020, 36, 13415–13425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorsand, S.; Raeissi, K.; Ashrafizadeh, F.; Arenas, M.A. Super-hydrophobic nickel–cobalt alloy coating with micro-nano flower-like structure. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Cheng, J. Fabrication of robust surfaces with special wettability on porous copper substrates for various oil/water separations. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Tao, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Yue, R.; Cui, Z. 3D superhydrophobic sponge with a novel compression strategy for effective water-in-oil emulsion separation and its separation mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, L.; Li, H.; Xue, J.; Yu, S.; Xue, Q. Multifunctional superwetting positively charged foams for continuous oil/water emulsion separation and removal of hazardous pollutants from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 289, 120683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, W. Electrospun PVDF-SiO2 nanofibrous membranes with enhanced surface roughness for oil-water coalescence separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 269, 118726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Saxena, P.; Puri, Y.M. The manufacturing and applications of the porous metal membranes: A critical review. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2021, 33, 339–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Bilal, M.; Khan, A.; Ali, F.; Khan, H.; Khan, H.A.; Iqbal, H.M. Understanding the hierarchical assemblies and oil/water separation applications of metal-organic frameworks. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hou, L.; Guo, F.; Liu, J.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, Y. Pine-branch-like TiO2 nanofibrous membrane for high efficiency strong corrosive emulsion separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16134–16138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Shi, X.; Xue, F.; Bai, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L. SiO2 nanoparticle-containing superhydrophobic materials with enhanced durability via facile and scalable spray method. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 626, 127014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Sheng, Y.J.; Tsao, H.K. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic copper mesh for oil/water separation and theoretical principle for separation design. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 2018, 87, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liang, Z.J.; Yue, T.M.; Guo, Z.N.; Liu, J.W.; Chen, X.L. Fabrication of a superhydrophobic mesh via magnetically aided electrode electric discharge machining. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 612, 125963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Ye, Q.; Han, Y.; He, G.; Chen, C. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Porous Brass by Chemical Dealloying for Efficient Emulsion Separation. Molecules 2023, 28, 6509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186509
Zhou Y, Ye Q, Han Y, He G, Chen C. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Porous Brass by Chemical Dealloying for Efficient Emulsion Separation. Molecules. 2023; 28(18):6509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186509
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yanbiao, Qingqing Ye, Yongjun Han, Guoxu He, and Changdong Chen. 2023. "Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Porous Brass by Chemical Dealloying for Efficient Emulsion Separation" Molecules 28, no. 18: 6509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186509
APA StyleZhou, Y., Ye, Q., Han, Y., He, G., & Chen, C. (2023). Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Porous Brass by Chemical Dealloying for Efficient Emulsion Separation. Molecules, 28(18), 6509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186509







