Abstract
The rapid progress in the field of fluorescent probes and fluorescent sensing material extended this research area toward more complex molecular logic gates capable of carrying out a variety of sensing functions simultaneously. These molecules are able to calculate a composite result in which the analysis is not performed by a man but by the molecular device itself. Since the first report by de Silva of AND molecular logic gate, all possible logic gates have been achieved at the molecular level, and currently, utilization of more complicated molecular logic circuits is a major task in this field. Comparison between two digits is the simplest logic operation, which could be realized with the simplest logic circuit. That is why the right understanding of the applied principles during the implementation of molecular digital comparators could play a critical role in obtaining logic circuits that are more complicated. Herein, all possible ways for the construction of comparators on the molecular level were discussed, and recent achievements connected with these devices were presented.
1. Introduction
The great attention paid in the last thirty years to the design and fabrication of variety machinery and devices at the molecular level has led to significant progress, as a result of which this field has been expanded from intramolecular motion and molecular switches [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] to nanoscale motion in artificial muscles [8,9,10], nano cars [11,12,13], molecular cranes [14], molecular cursor caliper [15], molecular timers [16,17], molecular computing [18,19,20,21] and molecular cryptography [22,23].
One of the most important developments in the last time was made in semiconductor-based computer science and technology. Currently, computers perform binary arithmetic and logical operations using semiconductor logic gates as elementary units building digital circuits. The logic operations are based on the Boolean algebra in which the FALSE (NO) and TRUE (YES) are encoded in binary code as “0” and “1”, respectively. Usually, the semiconductor logic gates operate via two inputs and one output, which states they possess one of the two binary conditions “0” or “1” encoded using a low (0) or high (1) voltage. This process is achievable on the molecule level in many ways, but the most common ones are based on the optical switching properties of molecule chemosensors [24,25], using low and high analyte concentrations as inputs, resulting in an “off” or “on” state of the optical output. The idea for the molecular-logic-gates-based computation, initially started by Aviram’s pioneering work as an alternative minimization of the semiconductor logic gates, actually is a major factor for fast computation in conventional computers (miniaturizing electronic components to a very small size results in an electron travel on very short distances in a very short time) [26]. However, the new era of molecular Boolean logic operations began five years later after the work by de Silva, who illustrated that the ability of fluorescent probes to deal with binary “1” and “0” inputs allows the fabrication of logic gates using fluorescence as an output [27]. The proposed AND logic gate represented a PET (Photoinduced Electron Transfer) based molecular chemosensor containing two different selective receptor fragments—tertiary amine for H+ (input 1) and benzo crown ether moiety for Na+ (input 2). In order to obtain a strong fluorescence signaling output from the anthracene fluorophore, the PET quenching processes needed to be suppressed from both receptors. In the presence of protons, the PET from the alkylamine receptor was interrupted, but fluorescence emission was not observed because of the PET quenching effect from the crown ether. The presence of sodium cations inhibits a PET process from the crown ether but not from the amino receptor, and the system again does not fluoresce. Simultaneous use of both H+ and Na+ interrupts both PET processes to the anthracene fluorophore, resulting in strong fluorescence. In binary, the resulting behavior satisfied AND logic gates (Figure 1).
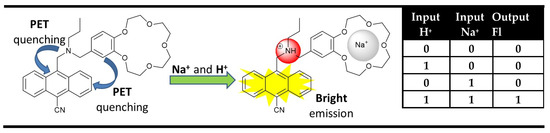
Figure 1.
The first AND logic gate was reported by A.P. de Silva in 1993, and the corresponding truth table [27].
Since the first report by de Silva et al. [27], the field of molecular logic gates has advanced considerably. All possible logic gates were achieved at the molecular level, and a series of synthetic molecules and biomolecules have been utilized in the molecular computation, including proteins, enzymes, DNA, and RNA [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. In addition, examples of more complicated logic circuits performing arithmetic functions [37,38], simple games such as Tic-Tac-Toe [39,40], and molecular scale anticancer terminator automaton [41,42] were reported. The illustrated logic gates have found practical applications in object coding [43], sensing systems [44,45,46,47], data storage [48,49], and drug delivery and drug activation systems [50,51,52,53]. All these molecules are able to calculate a composite result autonomously and often were determined as labs on the molecularly level. Furthermore, molecular computation could be applied to intelligent medical diagnostics where abnormal results are detected and interpreted using Boolean logic algebra during a medical examination. Such molecular devices can save time for doctors and are crucial when health services are in extreme conditions, for example, in epidemics or bioterrorism [54]. Therefore, despite the significant results achieved in this field, the construction of complex logic circuits with practical applications is still a great challenge. Due to the different nature of the used chemical inputs and optical outputs, the consecutive integration of molecular logic gates in molecular circuits is seriously restricted. Generally, the consecutive integration of fluorescent probes in logic circuits is achieved using multichromophoric systems and FRET communication between the separated gates [55]. The parallel integration of molecular logic gates is usually achieved by monitoring the different changes in the absorption and fluorescence spectra at different wavelengths at the same time. Currently, the reported molecular logic circuits use more “virtual” than physical integration of individual logic gates. The signaling output at various channels and thresholds (fluorescence and/or absorption at different wavelengths) are typically analyzed, and then a suitable set of logic gates is proposed to generate an apparent logical circuit that is only limited by the researcher’s creativity. This virtually gives more flexibility for the creation of logic circuits; therefore, some molecules are able to perform the action of more than one logic circuit [38,56].
Comparison between two digits is the simplest logic operation, which could be realized with the simplest logic circuit. The right understanding of the applied principles during the implementation of molecular digital comparators could play a critical role in obtaining logic circuits that are more complicated. However, review papers in the literature are very rare. Generally, the reported reviews were focused on the design and fabrication of molecular logic circuits such as devices for addition and subtraction, key lock pads, multiplexers, demultiplexers, encoders, decoders, “write-read-erase-read” function [16,19,20,24,25,57,58,59,60,61]. Even the monograph by de Silva [28], which is an essential inspiration in this field, is a detailed look at digital comparators, and they were only briefly reported. Therefore, in this tutorial review, all possible ways for the construction of comparators on the molecular level are discussed, and the recent achievements connected with these devices are presented. First, the XNOR and XOR molecular logic gates are introduced to the reader as the simplest logic device for comparison called the identity comparator. Then, more complicated molecular logic circuits operating as magnitude comparators are presented using two or three parallel acting gates in positive or negative logic. We believe that the presented information will be in help for researchers who wanted to be familiar with the molecular logic gates and molecular logic circuits.
2. Identity Molecular Digital Comparators (XNOR and XOR Molecular Logic Gates)
In general, there exist two basic types of digital comparators: identity comparators and magnitude comparators [62]. The simplest logic device able to make a comparison between two binary digits is an XNOR logic gate whose output is “1” (TRUE) only when both inputs are equal. The truth table and the electronic representation of an XNOR logic gate are presented in Figure 2. As can be seen from Figure 2, the XNOR can say that both inputs are equal, but if they are not equal, it cannot say which one is greater or less than other. This type of comparators that indicate only whether two inputs are equal or not equal were named Identity comparators. The digital comparators that signify which input is larger or smaller, if they are not equal, were called magnitude digital comparators and they will be presented later.
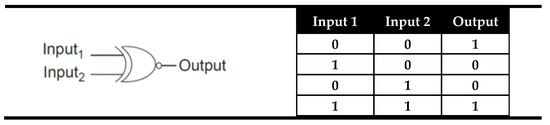
Figure 2.
The truth table and electronic representation of the XNOR logic gate.
The easiest way to obtain XNOR gates on the molecular level is based on the fluorescent probes that bind two fluorescent quenching analytes, which are able to interact with each other and so together to annihilate their individual effects. Compound 1 (Figure 3) was presented as an example of such a system [63]. It was designed as a pyrene appended probe using thiacalix[4]arene of 1,3-alternate conformation as a highly selective receptor towards Fe3+ and amide NH for selective interaction with F− anions. In the absence of both analytes, the probe showed a strong fluorescence emission at 386 nm. The presence of Fe3+ ions induced fluorescence quenching due to the paramagnetic nature of Fe3+ and reverse PET from pyrene units to the nitrogen atom. In addition, toward fluoride ions, compound 1 gave another fluorescence quenching response that was attributed to the hydrogen bonding of the amide moiety, leading to the formation of a static excimer. The addition of fluoride ions to a solution of 1-Fe3+ complex recovers the probe 1 fluorescence emission. The fluorescence revival process upon the addition of F− ions indicates that Fe3+ has more affinity for F− ions than with the amide NH receptor of probe 1. The observed fluorescence changes coded in binary as output upon the actions of two chemical inputs are correlated very well with the XNOR logic gate (Figure 3).
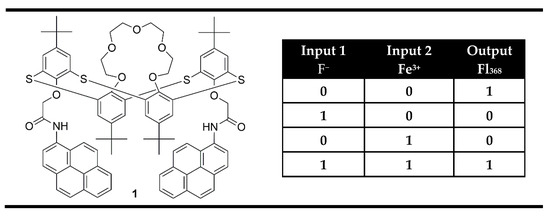
Figure 3.
XNOR molecular logic gate based on fluorescent properties of probe 1 and corresponding truth table [63].
Another useful concept for the rational designing of XNOR molecular logic gates was proposed by de Silva and McClenaghan using receptor1-chromophore-receptor2 ICT (Internal Charge Transfer) chemosensing architecture [64]. The main peculiarity of this model was laid on the opposite response of both analyte-bounded receptors. The binding process in the first receptor should result in a blue spectral shift, while in the second receptor, the shift is in the direction of longer wavelengths. This was very well illustrated with the ICT probe 2 for the detection of biologically important cations—Ca2+ and H+ (Figure 4).
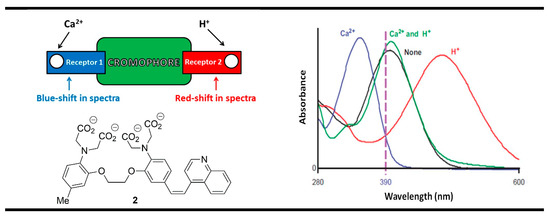
Figure 4.
XNOR molecular logic gate based on fluorescent properties of probe 2. Adapted from J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 3965–3966 [64] with permission from the American Chemical Society.
In the excited state of compound 2, a dipole arises due to an internal charge transfer (ICT) process from the electron-rich tertiary aniline receptor to the electron-accepting quinoline moiety in the molecule of the probe. The binding of the Ca2+ ion by the aniline moiety strongly reduced its electron density, thus destabilizing the ICT state of the compound and producing a blue shift in the absorption spectrum (Figure 4). At the same time, the protonation of the quinoline nitrogen receptor in the system resulted in a red shift owing to the increased electron-accepting ability of the protonated quinoline that increased the ICT efficiency of the system. The monitoring absorbance at 390 nm decreased in each case after the addition of Ca2+ and protons as chemical inputs because the absorption band moved away from the monitoring wavelength. The simultaneous action of both ionic inputs virtually cancels each other due to the opposite influences, and the absorption spectrum of compound 2 practically was returned to its initial state. Therefore, in binary, we have an XNOR logic gate, where a “high” output is registered only when both inputs are equal.
The ingenious strategy of acid-base neutralization as a means of achieving the required cancellation of inputs in “off-on-off” pH-sensing fluorescence probes is an excellent platform for the implementation of an XNOR logic gate on the molecular level (Figure 5).
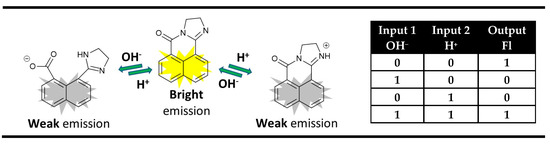
Figure 5.
XNOR molecular logic gate based on fluorescent properties of the dihydroimidazo 1,8-naphthalimide derivatives and corresponding truth table [65,66,67].
A typical example of that is the dihydroimidazo 1,8-naphthalimide derivatives that showed strong fluorescence at neutral pH. The addition of acid or base quenched the fluorescence signal due to the protonation or decyclization of the dihydroimidazo unit [65,66,67]. It was found that this process is reversible, and the neutralization of the acid and base regenerates the strong fluorescence of the probes. Hence, the monitoring of fluorescence emission in these derivatives as an output using acid and base as chemical inputs results in an XNOR logic gate at the molecular level (Figure 5).
XOR is the other logic gate that could be used as an identity comparator. This gate is logically connected with the XNOR logic gate using negative logic. The negative logic is the logic in the “land of liars” where the TRUE is presented as FALSE and FALSE as TRUE. In other words, negative logic is convention for the “high” output signals as logic state “0” and “low” signals as logic state “1”. The convention between normal and negative logic is called logic inversion and is sometimes invoked in semiconductor technology. In digital logic, the NOT gate is used as an inverter that implements logical negation owing to the opposite output state compared to the input. The truth table and the electronic representation of the XNOR logic gate are presented in Figure 2. As can be seen from Figure 6, in the XOR gate, the signal output is coded as “0” only when both inputs are equal and is coded as “1” if the inputs are different. This behavior is exactly the opposite of the XNOR gate, and here “0” is a sign of the input equality instead of “1” (Figure 6).
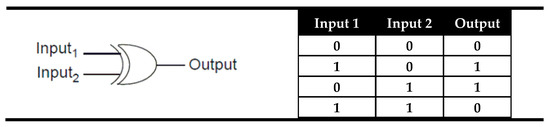
Figure 6.
The truth table and electronic representation of the XOR logic gate.
Among all logic gates, the XOR logic gate is the most difficult to implement at the molecular level. The first example of an XOR logic gate at the molecular scale was demonstrated by Balzani, Stoddart et al. [68] using the pseudorotaxane 3 (Figure 7), which was obtained after self-assembly of the electron-accepting 2,7-dibenzyldiazapyrenium dication (Input 1) with the crown ether containing two 2,3-dioxynaphthalene units (Input 2). Separately, both pseudorotaxane components exhibited bright fluorescence. Due to the electron donor/acceptor interaction in compound 3, a low energy charge transfer excited state is formed, and the strong former fluorescence of the inputs disappears. The monitoring of fluorescence as output and the individual pseudorotaxane moieties as inputs during the formation of pseudorotaxane 3 satisfies an XOR logic gate (Figure 7). However, it should be pointed out that the observed logic gate is not based on a molecule but on a volume of solution in the lack or presence of the chemical inputs.

Figure 7.
XOR molecular logic gate based on the formation of pseudorotaxane 3 and corresponding truth table [68].
Now, the most popular approach for the fabrication of XOR logic gates at the molecular level is based on the negative logic of XNOR gates operating via absorption outputs [64,69,70,71,72,73]. The observed XNOR gates in the absorption mode could easily be transformed in an XOR logic gate by logical inversion of the output by monitoring transmittance instead of absorption as output. The absorbance and transmittance are inversely related. Thus, if a “high” transmittance output was demonstrated, a “low” output via an absorbance would be obtained. Usually, the logical inversion by monitoring of the transmittance or negative logic was used in order to obtain XOR, which is required for the construction of a half-adder, a logical device for the addition of two binary digits. In fact, the above-mentioned XNOR molecular gate 2 [64] was reported by de Silva as transmittance of the XOR achieved gate in this context.
One of the rarest examples of XOR molecular logic gates using positive logic of the chemosensing probes was reported by Akkaya [74] with the BODIPY system 4 for the recognition of Zn2+ and Hg2+ (Figure 8). Probe 4 is an ICT-based sensing architecture configured on the receptor1-chromophore-receptor2 format. For a difference of the above-mentioned model proposed by de Silva and McClenaghan for the construction of the XNOR gate (Figure 4), here the analyte-bounded receptors showed a very similar blue-shifting response, which plays a key role in obtaining the desired XOR gate. Due to the strong ICT nature of compound 4, it showed an absorption spectrum with a maximum of 679 nm. When Zn2+ ions were added, the blue shifting to 674 nm was observed. A similar shift to 673 nm takes place after the addition of Hg2+. The resulting small individual effects of the electron-accepting analytes were explained with partially blocked ICT process after binding with the electron-rich amino-containing receptor fragments. However, when both ions were added the ICT state in system 4 was strongly destabilized due to the accumulated influence of the cations and the absorption of the new formed metal-bound complex was shifted further toward the shorter wavelengths at 630 nm. That is why the recoding of absorbance at 663 nm, where only the presence of each analyte alone showed a high absorption output, gives an XOR gate in binary.

Figure 8.
XOR molecular logic gate based on fluorescent properties of probe 4. Adapted from J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8029–8036 [74] with permission from the American Chemical Society.
An interesting example of an XOR molecular logic gate using positive logic was presented by Mardanya et al. probe 5 [75]. The pyridyl-imidazole-based chromophoric system in compound 5 showed good chemosensing properties toward ions of Zn2+ and F−. Similarly to XOR gate 4, the recognition of any one of the analytes resulted in the appearance of the absorption bands at the same place—around 404 nm. Thus, the monitoring of absorption spectra at 404 nm of compound 5 in binary allows the implementation of an XOR logic gate at the molecular level (Figure 9).
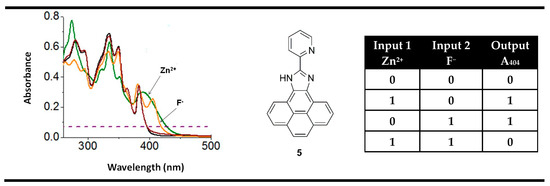
Figure 9.
XOR molecular logic gate based on fluorescent properties of probe 5 and corresponding truth table. Adapted from Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2015, 206, 701–713 [75] with permission from Elsevier.
3. Magnitude Molecular Digital Comparators
The magnitude digital comparators are logical devices that perform full comparison between two binary digits. A rational analysis of such a device reveals that it should be constructed on an architecture comprising two inputs and three parallel outputs. One of the outputs should have the value TRUE or binary “1” only when the inputs are equal and will be a sign of the inputs’ equality (“=”). Other output should be TRUE (binary “1”) only when the first input alone has a high value (coded as “1”), which will be a sign that the first input is greater (“>”) than the second. Additionally, the third output should show TRUE (binary “1”) as a signaling behavior only when the value of the second input is “1” in order to point out that the first input is less than (“<”) the second one. The parallel performance of these three outputs in a logic circuit satisfied all requirements for comparison of two binary digits hence it fulfills the action of the magnitude digital comparators. In the magnitude digital comparator the above discussed XOR gate is the used output for equality while two INHIBIT logic gates give the outputs “greater than” and “less than”. In fact, the magnitude digital comparator is identity comparator that is parallel extended with two INHIBIT logic gates. The INHIBIT gates output is high or “1”, only at a high value of the first or the second input. This logic gate was called INHIBIT because one of the inputs does nothing else than cancel the action of another. There are two possible INHIBIT gates: INHIBIT (Input 1) and INHIBIT (Input 2). In the INHIBIT (Input 2), which serves as the output “greater than” in the magnitude comparator, the second input disables the gates output. In contrast in INHIBIT (Input 1) the first input is the disabler which allows its function as the “less than” output in magnitude comparator. The truth table and electronic representation of magnitude digital comparators are presented on Figure 10.
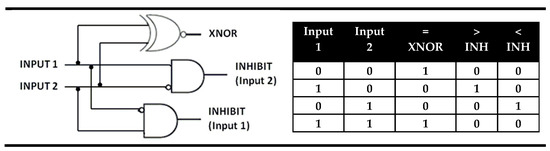
Figure 10.
Truth table and electronic representation of magnitude digital comparator.
In contrast to their semiconductor cousins, molecular logic devices are more flexible and can perform the work of several logic gates at the same time by monitoring the different changes in the absorption and fluorescence spectra at different wavelengths [28,76,77,78]. Furthermore, this flexibility results in a parallel action of several gates, allowing the construction of parallel logic circuits on a single molecule. This feature of the parallel measurements at different wavelengths is the base for the fabrication of digital magnitude comparators at the molecular level using optical outputs. For instance, Rurack et al. reported a multi-readout molecular gate capable of comparing K+ and F− as binary inputs using BODIPY dye 6 (Figure 11) with alkali metal ion and anion binding sites [79].
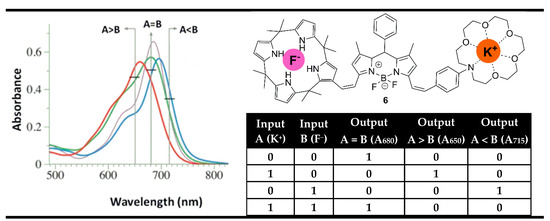
Figure 11.
Molecular magnitude digital comparator based on absorption properties of probe 6 and corresponding truth table. Adapted from Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 11056–11058 [79] with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry.
The binding of a positively charged K+ ion at the crown unit leads to hypsochromic (blue-shifted) absorption due to the weakened ICT process as a result of reduced electron-donor strength of the bonded aniline nitrogen atom. On the other hand, the binding of a negatively charged F− anion at the calix[4]pyrrole in compound 6 leads to a bathochromic (red) shift. The presence of K+ and F− reduced their opposite individual effects and returned the absorption spectrum of 6 near the former state. Hence, the recording of the absorption spectrum of probe 6 at shorter wavelengths (650 nm) showed high binary output only in the presence of K+ as an input alone, which is well correlated with the INHIBIT logic gate. In addition, the monitoring at a long wavelength (715 nm) gives another IHIBIT gate in which only F− is able to generate high absorption output. Meanwhile, the desired molecular comparator XNOR logic gate was achievable by monitoring the initial maximal absorption at 680 nm. As can be seen from Figure 11, the resulting parallel-acting logic gates completely cover the truth table of the digital magnitude comparator. The absorption output at 650 nm “greater than” is set to “1” (TRUE) when the value of input K+ is higher than F−. If the K+ input is less than F− then the output at 715 nm named “less than” is set to “1”. Finally, if the comparison between the both inputs gives equality the output “equal” at 680 nm is set to “1”.
In molecular logic architectures, the parallel action of three or more rationally selected logic gates is a real challenge. Fortunately, the magnitude digital comparator could be obtained using two gates instead of three. This is possible due to the specific connection between the three outputs, which always have a high value on one of them and a low value on the two others —after all, a comparison of two digits could give only one of the outputs “equal”, “greater than”, or “less than” at the same time. This connection allows the achievement of magnitude comparison only using two gates because if the output of two of the gates is low, then the third one necessarily must be high, and its measurement is not required. The one explained here was the most exploited logic in the design of magnitude comparators at the molecular level, and the majority of the reported systems operate on the parallel action of XNOR and one INHIBIT gate [37,62,78,80].
For instance, the reported by Tian et al. probe 7 for selective recognition of Zn2+ cations and OH− anions (detection of Zn2+ in alkaline media) could serve as a magnitude digital comparator in this manner [62]. In the absence of Zn2+ and OH− ions, compound 7 showed an absorption band centered at 442 nm and fluorescent emission at 615 nm. The addition of OH− deprotonated the phenolic electron-donating fragment in probe 7 and increased its electron-donating ability. Thus, the ICT efficiency increased, and the absorption band of 7 was red-shifted to 484 nm, which was accompanied by a strong fluorescence quenching. The complexation of Zn2+ with compound 7 bound its amino substituent, thus destabilizing the exited ICT process, which resulted in blue shifting to 415 nm and additional fluorescence quenching. The presence of Zn2+ and OH− simultaneously returned the absorption spectrum of probe 7 to the starting site and turned on the fluorescence emission at 615 nm. That is why the monitoring of the fluorescence at 615 nm in Boolean logic resulted in an XNOR gate. At the same time, based on the changes at 525 nm, where a high output was observed only in the presence of OH−, an INIHIBIT gate was constructed. The authors have used these two logic gates to construct a magnitude comparator at a molecular level. If both inputs are equal, then the fluorescence output at 615 nm is TRUE (“1”). If the OH− input is greater than Zn2+, then the absorbance output at 525 nm is TRUE (“1”). When both outputs are FALSE (“0”), then the input OH− is less than input Zn2+ (Figure 12).
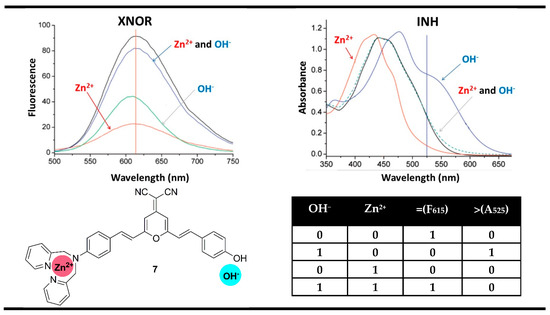
Figure 12.
Molecular magnitude digital comparator based on absorption properties of probe 7 and corresponding truth table. Adapted from J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 7047–7053 [62] with permission from the American Chemical Society.
The simplest approach to obtain magnitude comparators at a molecular level is based on the annihilating nature of the acids and bases as inputs in the “off-on-off” pH chemosensing probes possessing two easily distinguished “off” states. In this model, the “off-on-off” signaling is used to construct a molecular XNOR gate starting from “on” state that could be recovered after the canceled actions of the two inputs in their simultaneous work. The distinction of both “off” states is required for the implementation of the wanted additional INHIBIT gate. A typical example is the PET-based dihydroimidazo 1,8-naphthalimide derivative 8 [81]. This molecule exhibits bright green fluorescence emission at 520 nm in neutral pH, where it is in a monoprotonated form due to the protonation of the tertiary amino PET receptor. In the presence of OH− as an input, due to the possible PET quenching process in neutral form, compound 8 shows low fluorescence output at 520 nm. After the addition of acid to probe 8, fluorescence quenching accompanied by bathochromic (red) shifting of the absorption spectrum from 510 nm to 567 nm is observed, which is due to protonation and increasing electron accepting ability of imido-imino substituent that enhanced the ICT nature of excited compound 8. This results in an XNOR logic gate at the molecular level using the fluorescence changes at 520 nm that could be used as equal output during comparison. Additionally, it was found that the addition of acid that provokes a high output at 567 nm generates an IHIBIT logic gate at a molecular level that could be canceled in the presence of OH−. This indicates that the H+ input is high than OH− output. Thus, the “off-on-off” fluorescence output of compound 8 possessing different absorption spectra of the both “off” states could be applied as digital magnitude comparator (Figure 13). Moreover, compound 8 is water-soluble and low toxic, so it could be a very helpful tool in clinical diagnostics because it compares pH levels to the normal physiological pH.

Figure 13.
Molecular magnitude digital comparator based on fluorescent and absorption properties of probe 8 and corresponding truth table [81].
A magnitude digital comparator could be implemented at a molecular level using parallel performing INIHIBIT gates instead of one XOR and one INHIBIT gate. A rare example of that is 1,8-naphthalimide 9, which is a dual-channel pH-responsive probe [82]. The yellow-green emitting compound 9 showed only weak fluorescence due to the PET quenching from the piperazine amines. When adding acid as an input, the PET was blocked, and a bright emission at 508 nm was observed as a fluorescence output. The presence of OH− as a chemical input resulted in a non-emissive red-colored state with maximal absorption at 504 nm due to the enhanced ICT in deprotonated 4-hydrazino-1,8-naphthalimide chromophore. Based on these changes and the disabling action between the acid and hydroxide as outputs, parallel INHIBIT (input 1) and INHIBIT (input 2) gates could be constructed. Furthermore, the parallel performance of INHIBIT (input 1) and INHIBIT (input 2) in compound 9 allows digital comparison at a molecular level. When the H+ input is greater than OH− one, the fluorescence output is high. If the H+ input is less than OH− one, the absorption output is high. The low signaling values of both outputs indicate the equality of both inputs (Figure 14).
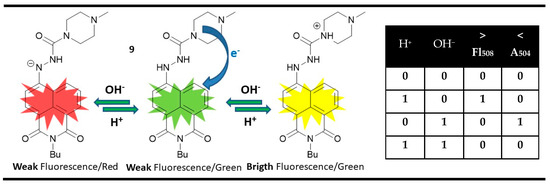
Figure 14.
Molecular magnitude digital comparator based on fluorescent and absorption properties of probe 9 and corresponding truth table [82].
The use of negative logic could be helpful during the construction of a molecular magnitude comparator. For instance, compound 10 performs a comparison of two digital inputs, H+ and OH−, using XNOR and IMPLICATION gates [83]. The IMPLICATION logic gate is related to the INHIBIT gate by logic inversion (negation). Contrary to INHIBIT logic gates, whose output is high only at a high value of the one input alone, the IMPLICATION gate shows a low output signal in this case and high at the other three combinations. Thus, the IMPLICATION logic gate could replace the INHIBIT gate during comparison. At pH 11, compound 10 is in its fluorescent dianion form, which was quenched in the presence of acid and base as outputs. The addition of acid formed a non-fluorescent form due to a possible ESIPT process, while the addition of base quenched the emission due to the deprotonation of the amide fragment in probe 10. Furthermore, for a difference of the OH− effect, the H+ shifted the absorption of compound 10 from 416 nm to 368 nm. The annihilating nature of the used acid/base inputs and the monitoring of the absorption and fluorescent changes gives parallel-acting XNOR and IMPLICATION logic gates, whose activity allows comparison at the molecular level. If both inputs are equal (H+ = OH−), then both outputs are high. If the input H+ is greater than OH− one, both outputs are low. If the input H+ is less than OH− one, then the fluorescence output is low, but the absorption output is high (Figure 15).

Figure 15.
Molecular magnitude digital comparator based on fluorescent and absorption properties of probe 10 and corresponding truth table [83].
Probe 11 is an interesting example of a molecular magnitude comparator, which works only in the fluorescent mode [84]. As a mono anion, compound 11 showed a strong yellow-green fluorescence at 511 nm. After the addition of acid as an input, due to the formation of a neutral molecule with reduced ICT efficiency, the fluorescence was blue-shifted to 482 nm. On the other hand, the addition of OH− resulted in a non-emissive dianion due to the presence of a PET quenching process from the formed phenolate anion. The presence of both acid and base cancels each other out, and the system returns to the starting yellow-green fluorescent form. The parallel monitoring of the fluorescence intensities at 511 nm and 482 nm results in obtaining XNOR and INHIBIT logic gates, respectively, whose performance is the above-mentioned classical requirement for the construction of a magnitude digital comparator at a molecular level, where the XNOR gate is “equal” output, while INHIBIT is “greater than”. Furthermore, the use of a paramagnetic quencher such as Cu2+ ion as a third chemical input disables both fluorescence outputs. Hence, based on probe 11, a magnitude digital comparator with disabled capability at a molecular level could be achieved (Figure 16). The enable/disable capability could play an important role in blocking the unnecessary and setting up the required gates during the configuration of multicomponent systems, which now is a serious drawback at the molecular level.

Figure 16.
Molecular magnitude digital comparator based on fluorescent and absorption properties of probe 11 and corresponding truth table [84].
4. Conclusions
In this tutorial review, all possible ways for the construction of digital comparators at the molecular level are discussed, and the recent achievements connected with these devices are presented. Comparison between two digits is the simplest arithmetic operation, and it could be realized with the simplest logic circuit. We hope the presented information will help young scientists to understand this field better and join it. The progress of molecular logic gates in the last thirty years is already impressive, but there are still plenty of outlets for the creative and innovative development of new concepts and applications for molecular computing of fluorescence probes. Improved recycling reset capabilities, reconfigurability, and integration of molecular logic gates on solid support will undoubtedly be an important theme. The higher-order logic circuits that could perform a comprehensive analysis of more than three targets are difficult to design at the molecular level. That is why such circuits need to be better designed and conceived. In addition, further intensive work on the functional integration of multichromophoric systems and interconnected cascades in supramolecular assemblies of multiple logic devices will be a great challenge.
Further extension of the principles of logic to applications in biomolecular recognition or theranostics will be the ultimate goal. While there has been success in the direction of logic operations, computational algorithms, sensing, and communication, some of the more unsolved fundamental challenges refer to concepts of intracellular applications. This is an area that ‘‘silicon-based computing cannot reach’’ and an important direction that needs to be studied more deeply in the future. Some fluorescent probes are related to the pathophysiological conditions in specific diseases; thus, a strategy could be designed of molecular logic based on this relationship that could complete the intelligent analysis of multi-targets, giving a unique YES or NO output. For many diseases, it is difficult to obtain an accurate diagnosis using a single or limited number of fluorescence probes, and it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive analysis of different permutations and combinations of multiple targets. Fortunately, the molecular logic gates enable the highly sensitive detection of multiple types of targets and the production of multiple signaling outputs. This development of molecular and computer science makes it a promising tool for clinical use. Although complex molecular logic gates are still not readily available in the clinic, and they serve only as proof of concept, healthcare professionals could greatly benefit from their existence.
As a whole, this exciting research area offers a great future working field that is limited only by the researcher’s imagination and inspiration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.B.B. and N.I.G.; writing—original draft preparation, N.I.G. and V.V.B.; writing—review and editing, V.B.B.; supervision, V.B.B.; design, V.B.B. and N.I.G.; funding acquisition, V.B.B. and N.I.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is funded by the European Union-NextGenerationEU, through the National Recovery and Resilience Plan of the Republic of Bulgaria, project № BG-RRP-2.004-0002, “BiOrgaMCT”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Callan, J.F.; de Silva, A.P.; Magri, D.C. Luminescent sensors and switches in the early 21st century. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 8551–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeur, B.; Leray, I. Design principles of fluorescent molecular sensors for cation recognition. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2000, 205, 3–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottas, G.S.; Clarke, L.I.; Horinek, D.; Michl, J. Artificial molecular rotors. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1281–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, E.R.; Leigh, D.A.; Zerbetto, F. Synthetic molecular motors and mechanical machines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 72–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzani, V.; Credi, A.; Raymo, F.M.; Stoddart, J.F. Artificial molecular machines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3348–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Yang, S. Recent progresses on diarylethene based photochromic switches. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Rao, S.-J.; Xie, T.; Li, X.; Xu, T.-Y.; Li, D.-W.; Qu, D.-H.; Long, Y.-T.; Tian, H. Muscle-like artificial molecular actuators for nanoparticles. Chem 2018, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, C.J.; Stoddart, J.F. Rotaxane-based molecular muscles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2186–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juluri, B.K.; Kumar, A.S.; Liu, Y.; Ye, T.; Yang, Y.-W.; Flood, A.H.; Fang, L.; Stoddart, J.; Weiss, P.; Huang, T.J. A mechanical actuator driven electrochemically by artificial molecular muscles. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, L.; Leung, F.K.-C.; Kajitani, T.; Stuart, M.C.A.; Fukushima, T.; van Rijn, P.; Feringa, B.L. Photoactuating artificial muscles of motor amphiphiles as an extracellular matrix mimetic scaffold for mesenchymal stem cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3543–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, Y.; Morin, J.-F.; Sasaki, T.; Guerrero, J.M.; Tour, J.M. Recent progress on nanovehicles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaezi, M.; Pishkenari, H.N.; Nem, A. Mechanism of the motion of nanovehicles on hexagonal boron-nitride: A molecular dynamics study. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 207, 111317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammerer, C.; Erbland, G.; Gisbert, Y.; Nishino, T.; Yasuhara, K.; Rapenne, G. Biomimetic and technomimetic single molecular machines. Chem. Lett. 2019, 48, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Petek, A.; Hori, Y.; Georgiev, A.; Hirashima, S.; Matsushima, Y.; Miura, T.; Antonov, L. Acylhydrazone subunits as a proton cargo delivery system in 7-hydroxyquinoline. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 11559–11566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Guo, C.; He, Q.; Chi, X.; Lynch, V.M.; Zhang, Z.; Su, J.; Tian, H.; Sessler, J.L. Molecular cursor caliper: A fluorescent sensor for dicarboxylate dianions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14798–14806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbas-Cakmak, S.; Kolemen, S.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; James, T.D.; Yoon, J.; Akkaya, E.U. Molecular logic gates: The past, present and future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2228–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavcheva, S.; Mendoza, J.; Stanimirov, S.; Petkov, I.; Basílio, N.; Pina, F.; Petrov, V. On the multistate of 2′-hydroxyflavylium-flavanone system. Illustrating the concept of a timer with reset at the molecular level. Dyes Pigm. 2018, 158, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buryak, A.; Zaubitzer, F.; Pozdnoukhov, A.; Severin, K. Indicator displacement assays as molecular timers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 11260–11261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Lin, H.; Crory, H.; de Silva, A.P. Supra-molecular agents running tasks intelligently (SMARTI): Recent developments in molecular logic-based computation. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2020, 5, 1325–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréasson, J.; Pischel, U. Light-stimulated molecular and supramolecular systems for information processing and beyond. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 429, 213695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojinov, V.; Georgiev, N. Molecular sensors and molecular logic gates. J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2011, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, T.; Selvakumar, K.; Motiei, L.; Margulies, D. Message in a molecule. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Duan, H.; Zhuang, H.; Cao, J.; Wei, Z.; Lin, Y. Using T-Hg-T and C-Ag-T: A four-input dual-core molecular logic gate and its new application in cryptography. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 5363–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, P.; Ga, L.; Ai, J. Advances in applications of molecular logic gates. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 30189–30204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, D.C. Logical sensing with fluorescent molecular logic gates based on photoinduced electron transfer. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 426, 213598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviram, A. Molecules for memory, logic, and amplification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 5687–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, P.; Gunaratne, N.; McCoy, C. A molecular photoionic AND gate based on fluorescent signalling. Nature 1993, 364, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, A.P. Molecular Logic-Based Computation; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhao, D.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Fan, L. Recent advances in molecular logic gate chemosensors based on luminescent metal organic frameworks. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 14967–14977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budyka, M.F. Design principles and action of molecular logic gates. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2014, 63, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréasson, J.; Pischel, U. Molecules with a sense of logic: A progress report. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1053–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Wang, F.; Fan, C.; Zuo, X.; Li, Q. Biosensors based on DNA logic gates. View 2020, 2, 20200038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pu, F.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Artificial enzyme-based logic operations to mimic an intracellular enzyme-participated redox balance system. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 9156–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, E. Boolean logic gates realized with enzyme-catalyzed reactions—Unusual look at usual chemical reactions. ChemPhysChem 2019, 20, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morihiro, K.; Ankenbruck, N.; Lukasak, B.; Deiters, A. Small molecule release and activation through DNA computing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13909–13915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, E.; Dong, S. Propelling DNA computing with materials’ power: Recent advancements in innovative DNA logic computing systems and smart bio-applications. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Unimolecular half-adders and half-subtractors based on acid-base reaction. Front. Chem. China 2009, 4, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xia, W.; Yang, C. Fluorescent 1:2 demultiplexer and half-subtractor based on the hydrolysis of N-salicylidene-3-aminopyridine. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2014, 117, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.; Li, Y.; Sutovic, M.; Lederman, H.; Pendri, K.; Lu, W.; Andrews, B.; Stefanovic, D.; Stojanovic, M. Medium scale integration of molecular logic gates in an automaton. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2598–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Chen, C.; Qiang, X.; Shi, X. Massively parallel DNA computing based on domino DNA strand displacement logic gates. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 2504–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozlem, S.; Akkaya, E. Thinking outside the silicon box: Molecular AND logic as an additional layer of selectivity in singlet oxygen generation forphotodynamic therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, I.S.; Gunaydin, G.; Ayan, S.; Akkaya, E.U. Molecular demultiplexer as a terminator automaton. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Naren, G.; Kelly, J.; Moody, T.; de Silva, A.P. Building pH sensors into paperbased small-molecular logic systems for very simple detection of edges of objects. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3763–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Q.; Mu, L.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, J.-L.; Zeng, L.; Chen, Z.-M.; Yang, C.; Wei, G.; Redshaw, C. A three-dimensional (time, wavelength and intensity) functioning fluorescent probe for the selective recognition/discrimination of Cu2+, Hg2+, Fe3+ and F− ions. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 3674–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglin, S.; Hollister, T.; Delohery, T.; Hackett, N.; McMahill, M.; Sphicas, E.; Domingo, D.; Yahalom, J. A novel response of cancer cells to radiation involves autophagy and formation of acidic vesicles. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Kelley, S.; Glass, T. A multi-component sensor system for detection of amphiphilic compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 130, 12741–12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, T.; Huo, F.; Yin, C. Pinpoint diagnostic kit for heat stroke by monitoring lysosomal pH. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11869–11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Du, J.; Hou, J.; Shi, P.; Wang, K.; Zhang, S.; Han, T.; Li, Z. Rewritable optical data storage based on mechanochromic fluorescence materials with aggregationinduced emission. Dyes Pigm. 2019, 160, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafferty, B.; Ten, A.; Fink, M.; Morey, S.; Preston, D.; Mrksich, M.; Whitesides, G. Storage of information using small organic molecules. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruskowitz, E.; Comerford, M.; Badeau, B.; DeFores, C. Logical stimuli-triggered delivery of small molecules from hydrogel biomaterials. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.; Mateus, P.; Matos, B.; Acuña, A.; García-Río, L.; Arteaga, J.; Pischel, U.; Basílio, N. Binding of flavylium ions to sulfonatocalix[4]arene and implication in the photorelease of biologically relevant guests in water. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 10852–10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, P.T.; Peneva, P.N.; Georgieva, S.I.; Tchekalarova, J.; Vitkova, V.; Antonova, K.; Georgiev, A. Synthesis, characterization and anticonvulsant activity of new azobenzene-containing VV-hemorphin-5 bio photoswitch. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, N.I.; Bakov, V.V.; Anichina, K.K.; Bojinov, V.B. Fluorescent probes as a tool in diagnostic and drug delivery systems. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, B.; Ling, J.; de Silva, A.P. What has supramolecular chemistry done for us? Supramol. Chem. 2016, 28, 2010203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guliyev, R.; Ozturk, S.; Kostereli, Z.; Akkaya, E.U. From virtual to physical: Integration of chemical logic gates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 9826–9831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, A.I.; Georgiev, N.I.; Bojinov, V.B. A smart chemosensor: Discriminative multidetection and various logic operations in aqueous solution at biological pH. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2019, 223, 117304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ga, L.; Ai, J. Ratiometric fluorescence sensing with logical operation: Theory, design and applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 213, 114456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréasson, J.; Pischel, U. Molecules for security measures: From keypad locks to advanced communication protocols. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2266–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzani, V.; Credi, A.; Venturi, M. Molecular logic circuits. ChemPhysChem 2003, 4, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, A.P.; Uchiyama, S. Molecular logic gates and luminescent sensors based on photoinduced electron transfer. Top. Curr. Chem. 2011, 300, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréasson, J.; Pischel, U. Smart molecules at work—Mimicking advanced logic operations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, W.; Huang, X.; Xie, Y.; Tian, H. Intramolecular charge-transfer process based on dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran derivative: An integrated operation of half-subtractor and comparator. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 7047–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, R.; Bhalla, V. ‘On–Off’ reversible switch for Fe3+ and F− mimicking XNOR logic function. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 5559–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, A.P.; McClenaghan, N.D. Proof-of-principle of molecular-scale arithmetic. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 3965–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.I.; Dimov, S.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Alamry, K.A.; Obaid, A.Y.; Bojinov, V.B. Synthesis, selective pH-sensing activity and logic behavior of highly water-soluble1,8-naphthalimide and dihydroimidazonaphthalimide derivatives. J. Lumin. 2014, 149, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhang, S. A pair of regio-isomeric compounds acting as molecular logic gates with different functions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2009, 207, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S. Effects of anionic surfactant SDS on the photophysical properties of two fluorescent molecular sensors. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2008, 200, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Credi, A.; Balzani, V.; Langford, S.; Stoddart, J. Logic operations at the molecular level. An XOR gate based on a molecular machine. J. Am. Chem.Soc. 1997, 119, 2679–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, A.; Deniz, E.; Akkaya, E.U. Effective PET and ICT switching of boradiazaindacene emission: A unimolecular, emission-mode, molecular half-subtractor with reconfigurable logic gates. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 5187–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margulies, D.; Melman, G.; Shanzer, A. A molecular full-adder and full-subtractor, an additional step toward a moleculator. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 4865–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, S.J.; Yann, T. Molecular logic: A half-subtractor based on tetraphenylporphyrin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 11198–11199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhang, S. Molecular logic operations based on surfactant nanoaggregates. ChemPhysChem 2008, 9, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Qian, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S. Multiple molecular logic functions and molecular calculations facilitated by surfactant’s versatility. Chem. Commun. 2008, 35, 4141–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdemir, O.A.; Guliyev, R.; Buyukcakir, O.; Selcuk, S.; Kolemen, G.; Gulseren, S.; Nalbantoglu, T.; Boyaci, H.; Akkaya, E.U. Selective manipulation of ICT and PET processes in styryl-Bodipy derivatives: Applications in molecular logic and fluorescence sensing of metal ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8029–8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardanya, S.; Karmakar, S.; Das, S.; Baitalik, S. Anion and cation triggered modulation of optical properties of a pyridyl-imidazole receptor rigidly linked to pyrene and construction of INHIBIT, OR and XOR molecular logic gates: Acombined experimental and DFT/TD-DFT investigation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.I.; Sakr, A.R.; Bojinov, V.B. Design and synthesis of a novel PET and ICT based 1,8-naphthalimide FRET bichromophore as a four-input Disabled–Enabled-OR logic gate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.I.; Lyulev, M.P.; Bojinov, V.B. Sensor activity and logic behaviour of PET based dihydroimidazonaphthalimide diester. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2012, 97, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Li, C.-J. A multifunctional arithmetical processor model integrated inside a single molecule. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 14231–14235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotor, R.; Costero, A.M.; Gil, S.; Parra, M.; Gaviña, P.; Rurack, K. Boolean operations mediated by an ion-pair receptor of a multi-readout molecular logic gate. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 11056–11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.I.; Lyulev, M.P.; Alamry, K.A.; El-Daly, S.A.; Taib, L.A.; Bojinov, V.B. Synthesis, sensor activity, and logic behavior of a highly water-soluble 9,10-dihydro-7H-imidazo[1,2-b]benz[d,e]isoqionolin-7-one dicarboxylic acid. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2015, 297, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.I.; Yaneva, I.S.; Surleva, A.R.; Asiri, A.M.; Bojinov, V.B. Synthesis, sensor activity and logic behavior of a highly water-solublenaphthalimide derivative. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 184, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.I.; Dimitrova, M.D.; Krasteva, P.V.; Bojinov, V.B. A novel water-soluble 1,8-naphthalimide as a fluorescent pH-probe and a molecular logic circuit. J. Lumin. 2017, 187, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.I.; Georgiev, N.I.; Bojinov, V.B. Sensor activity and logic behavior of dihydroxyphenyl hydrazone derivative as a chemosensor for Cu2+ determination in alkaline aqueous solutions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2015, 311, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.I.; Dimitrova, M.D.; Todorova, Y.D.; Bojinov, V.B. Synthesis, chemosensing properties and logic behaviour of a novel ratiometric 1,8-naphthalimide probe based on ICT and PET. Dyes Pigm. 2016, 131, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).