Abstract
Amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide deposition, hyperphosphorylated tau proteins, reactive astrocytes, high levels of metal ions, and upregulated monoamine oxidases are considered to be the primary pathological markers of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Among them, Aβ peptide deposition or Aβ plaques, is regarded as the initial factor in the pathogenesis of AD and a critical pathological hallmark in AD. This review highlights recently Aβ-specific fluorescent probes for two-photon imaging of Aβ plaques in vivo. It includes the synthesis and detection mechanism of probes, as well as their application to two-photon imaging of Aβ plaques in vivo.
1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the most common form of dementia that affects more than 35 million people worldwide [1], is characterized by extracellular amyloid plaques in the brain [2,3]. The major components of these plaques are aggregated forms of the amyloid-β peptide (Aβ), derived from the proteolytic cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β-secretase followed by γ-secretase [4]. Aβ contains two predominant isoforms: Aβ 40 and Aβ 42. Aβ 40 accounts for more than 90% of total Aβ, while Aβ 42 is more aggregation-prone than Aβ 40 and is the main composition in the plaques [5]. It is widely accepted that Aβ aggregation from monomers to oligomers, protofibrils, and eventually fibrils plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of AD [6,7]; therefore, Aβ plaques have been considered as main biomarkers for AD diagnosis [8,9]. The accurate detection and imaging of Aβ plaques can provide important information for early treatment of AD since Aβ plaques appear as early as ~10 years before the clinical symptoms of AD and go throughout the whole disease process [10,11]. Currently, the available approaches for detection of Aβ plaques in the brain through neuroimaging include positron emission tomography (PET) [12,13,14,15], single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) [16,17,18], magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [19,20,21], and optical imaging [22,23,24,25,26].
Recently, fluorescent detection and imaging of Aβ plaques has become a burgeoning technology since it provides high sensitivity, fast data analysis, real-time detection, and high-resolution imaging [27,28,29,30,31,32,33], which are necessary characteristics to achieve the early detection of AD. Fluorescent probe, in particular, near-infrared (NIR) fluorescent probe is favorable for Aβ plaque imaging in vivo due to its deep tissue penetration, low autofluorescence, and minimal photodamage. Up to now, numerous NIR fluorescent probes have been developed to detect and/or visualize Aβ plaques in vitro and in vivo [34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] and many are cited in some excellent reviews [43,44,45,46,47,48]. This review focuses on recent progress in NIR fluorescent probes for two-photon brain imaging of Aβ plaques based on organic small molecules. Probes based on complex and nanoparticles are not involved in the review. Two-photon microscopy (TPM) has emerged as an important tool for imaging of biological tissues due to the following merits. (1) Avoids light scattering which is a serious issue with one-photon confocal microscopy, (2) two-photon excitation only occurs on the focal point; therefore, it can provide a high-resolution imaging, and (3) excitation at NIR wavelengths allows for deeper penetration and minimal photodamage and photobleaching to tissues. These promising features have motivated the search for two-photon fluorescent probes for the detection and imaging of biological analytes in vivo [49,50,51,52,53].
2. Design of Aβ Plaque-Specific Fluorescent Probes
To better understand specific biomarkers that reliably correlate with AD, researchers have made great efforts in fluorescence imaging of Aβ plaques. Currently, the general structure of a classical NIR fluorescent probe for imaging Aβ species is a highly environment-sensitive fluorophore with D-π-A or D-π-A-π-D structure (D: electron-donor group; A: electron-acceptor group). The type of structure can significantly affect the optical and biological properties of probes, such as emission wavelength, two-photon absorption cross-sections, quantum yield, and blood−brain barrier permeability [54,55,56]. To date, a great deal of NIR fluorescent probes have been developed for the detection and imaging of Aβ plaques and other biomarkers of AD, including dicyanomethylene acceptor derivatives [57,58,59], difluoroboronate incorporated curcumin scaffold [60,61,62], and BODIPY derivatives [63,64,65]. Many reviews [66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73] have successively reported them.
This review focuses on the recent development of two-photon fluorescent probes and their application to TPM imaging of Aβ plaques in vivo. A successful candidate should have some merits of specific response to Aβ plaques, excellent two-photon cross-sections (δTPA or ϕδTPA), NIR fluorescence, and large fluorescence signal-to-background ratios (SBR). To meet the last requirement, fluorescent probes should be designed to have no fluorescence before the interaction with Aβ plaques; upon the interaction with Aβ plaques, a strong NIR fluorescence could be detected (Figure 1).
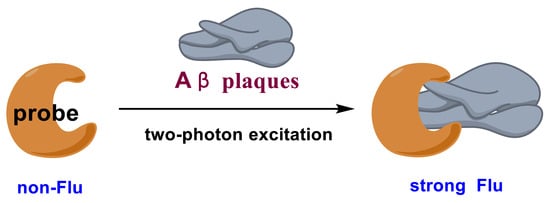
Figure 1.
Design strategy of fluorescent probes for Aβ plaques.
3. Fluorescent Detection and Imaging of Aβ Plaques
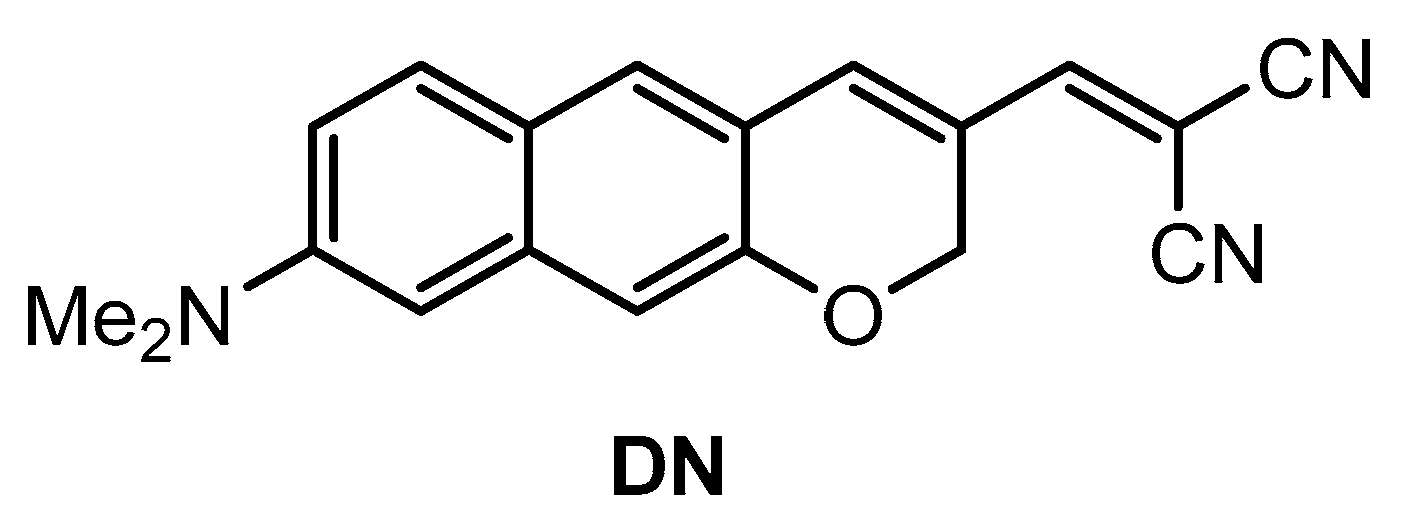
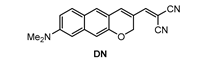
Kim and co-workers [74] developed a π-extended acedan derivative for Aβ plaques detection and two-photon imaging. Acedan, 6-acetyl-2-(dimethylamino)naphthalene, and its derivatives are environmentally sensitive fluorophores and have nonsymmetric D-π-A structures with large two-photon absorption properties, which benefit bioimaging applications [75,76,77]. Probe DN (Figure 2) was synthesized from a common intermidiate, 6-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthaldehyde. By employing a Baylis−Hillman reaction, introduction of the enone moiety enclosed in the new ring was performed.
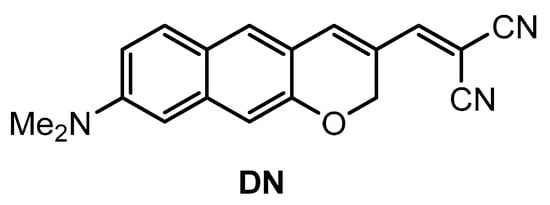
Figure 2.
Structure of probe DN.
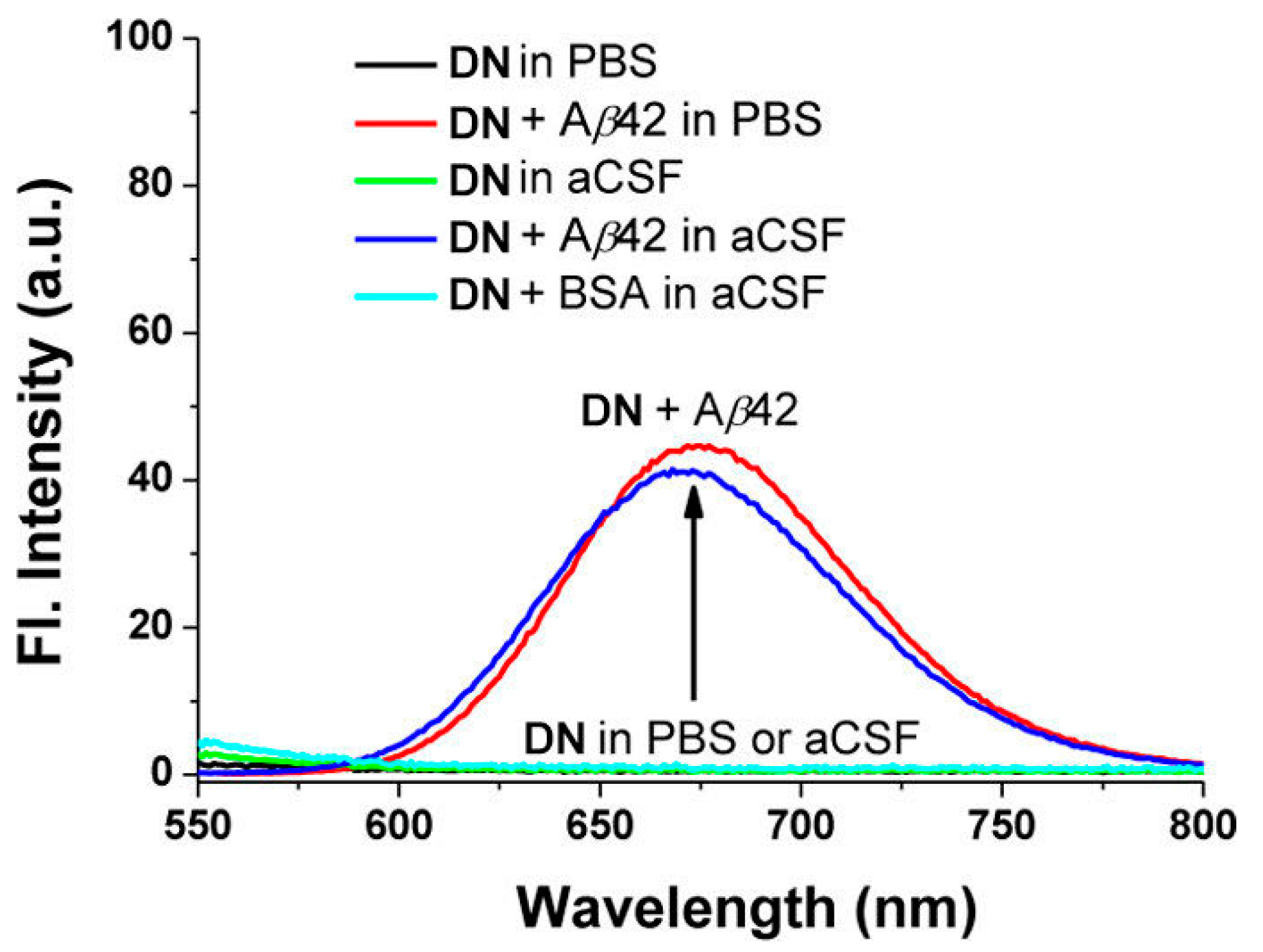
Probe DN exhibited the maximum absorption and fluorescence at 512 nm (λabs) and 679 nm (λem), respectively. In organic solution, a small fluorescence quantum yield (5% in EtOH, 9% in CH3CN, 14% in CH2Cl2) was obtained. The fluorescence was almost quenched when DN was in PBS solution (pH 7.4) or in artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF). Upon addition of Aβ42 aggregates into the solution of DN in PBS or aCSF, a large fluorescence enhancement (41- to 60-fold) was obtained (Figure 3). A control experiment demonstrated that bovine serum albumin (BSA) showed negligible interference. The dissociation constant of DN with Aβ42 aggregates was determined to be Kd = 44.6 ± 4.2 nM. The lipophilicity of DN was calculated to be log p = 3.5, which is close to the optimal value range considered for the blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeation (2.0–3.5) [78].
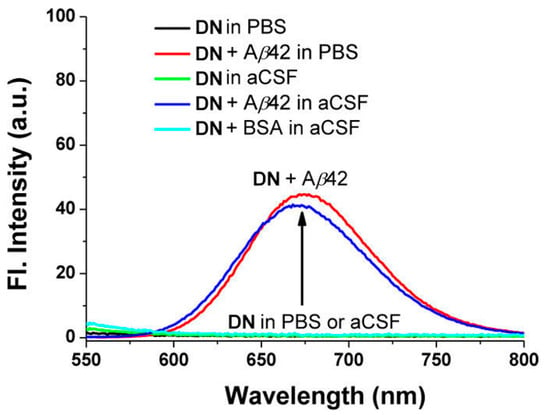
Figure 3.
Fluorescence changes of probe DN (10 μM) in the presence or absence of Aβ42 aggregates (20 μM) and BSA (20 μg mL−1) in PBS buffer (10 mM, pH 7.4, containing 1% DMSO) or in artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF, containing 1% DMSO), measured at 25 °C after mixing for 1 h under excitation at 500 nm. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [74]. Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society.
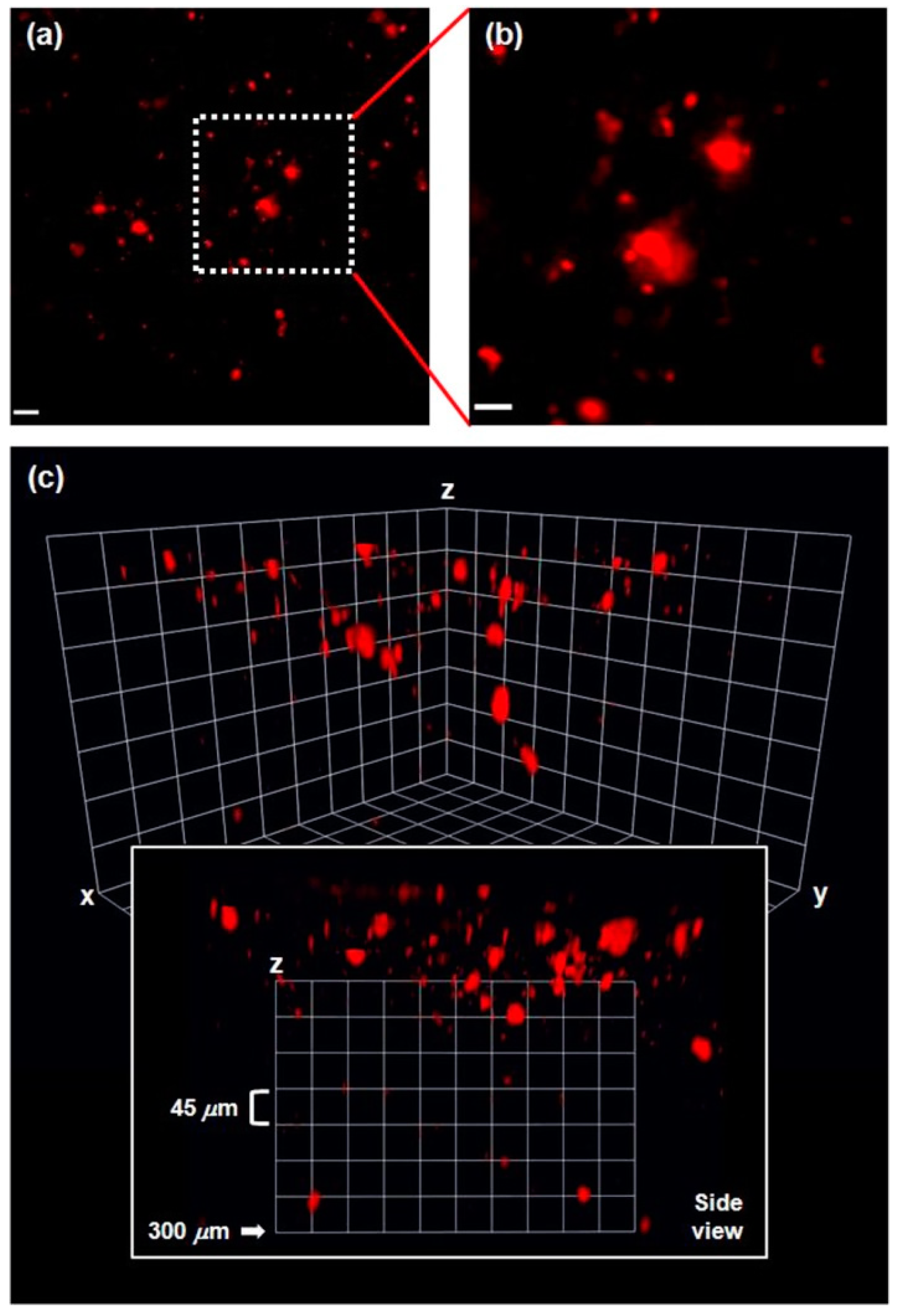
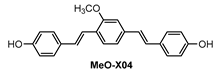
In vivo two-photon microscopy (TPM) imaging of Aβ plaques with probe DN was carried out in a live AD mouse model. DN was intraperitoneally injected into the 5XFAD mouse (10 mg kg−1, one time injection), and fluorescence imaging of the brain was conducted under two-photon excitation at 1000 nm. Clear and bright red fluorescence images of Aβ plaques were obtained (Figure 4), which also confirmed that DN readily penetrated BBB. In addition, the 3D images obtained down to 300 μm depth showed that Aβ plaques were spreading out to the cortex region [79] (Figure 4c side view). Furthermore, co-staining experiments showed well-merged fluorescence images by using MeO-X04, a known Aβ plaque-staining fluorescent probe [80], confirming that DN efficiently images Aβ plaques.
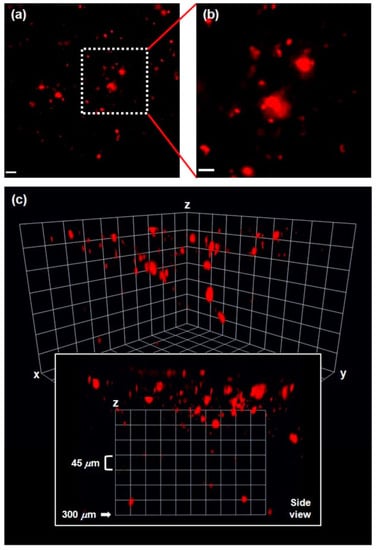
Figure 4.
(a) In vivo TPM images of Aβ plaques in the frontal cortex of a 5XFAD mouse after ip injection of DN (10 mg kg−1), 20× magnified at the depth of 50 μm (scale bar: 20 μm). (b) Magnified images (60×) of the square area in (a) (scale bar: 10 μm). (c) 3D images: the images were acquired with 20× magnification along the z-direction at the depth of up to 300 μm from the surface of the cortex, under excitation at 1000 nm with approximately 50 mW laser power at the focal point. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [74]. Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society.
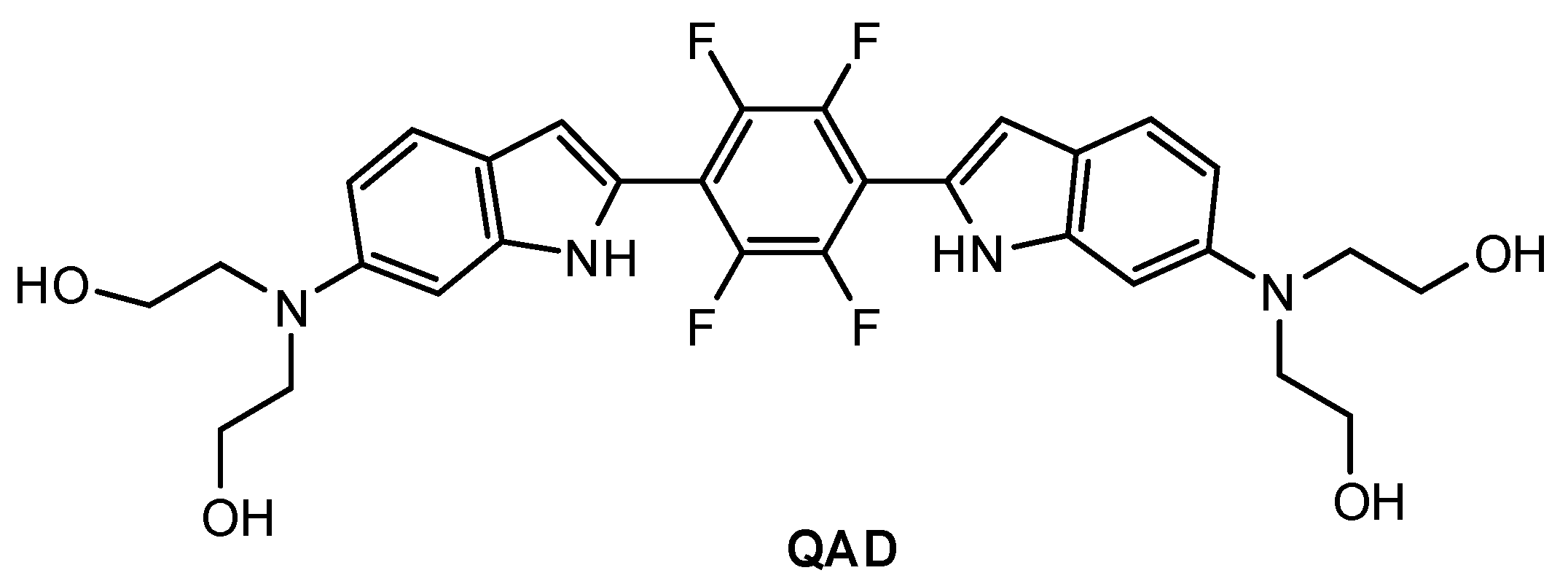
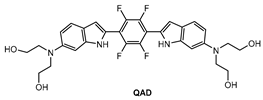
Mook-Jung and co-workers [81] designed a quadrupolar fluorescent probe for detection and imaging of Aβ42 plaques. Quadrupoles with D–π-A–π-D structure have been regarded as a promising motif for large δTPA values [82]. Probe QAD (Figure 5) was synthesized by coupling reaction of 4-dialkylamino-2-nitrobenzaldehyde and bisphosphonate-substituted tetra-fluorobenzene first, followed by reduction-induced cyclization. QAD exhibited almost no fluorescence in PBS buffer (pH 7.4) in the absence of Aβ42 aggregates. Upon addition of Aβ42 aggregates into the solution of QAD in PBS (pH 7.4), the fluorescence of QAD at 546 nm increased dramatically. The dissociation constant (Kd) of probe QAD with Aβ42 aggregates was found to be 16.2 nM. A control experiment demonstrated that BSA and human serum albumin (HSA) showed negligible interference. The lipophilicity value (log P) of QAD was calculated to be 3.42 by partitioning between n-octanol and PBS buffer. A large two-photon action cross section (δTPA = 420 GM) was obtained at 750 nm.
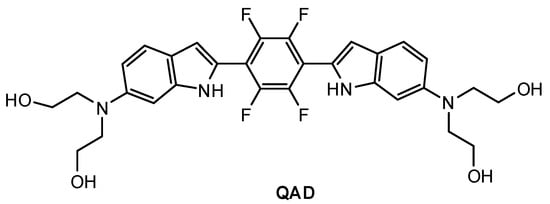
Figure 5.
Structure of probe QAD.
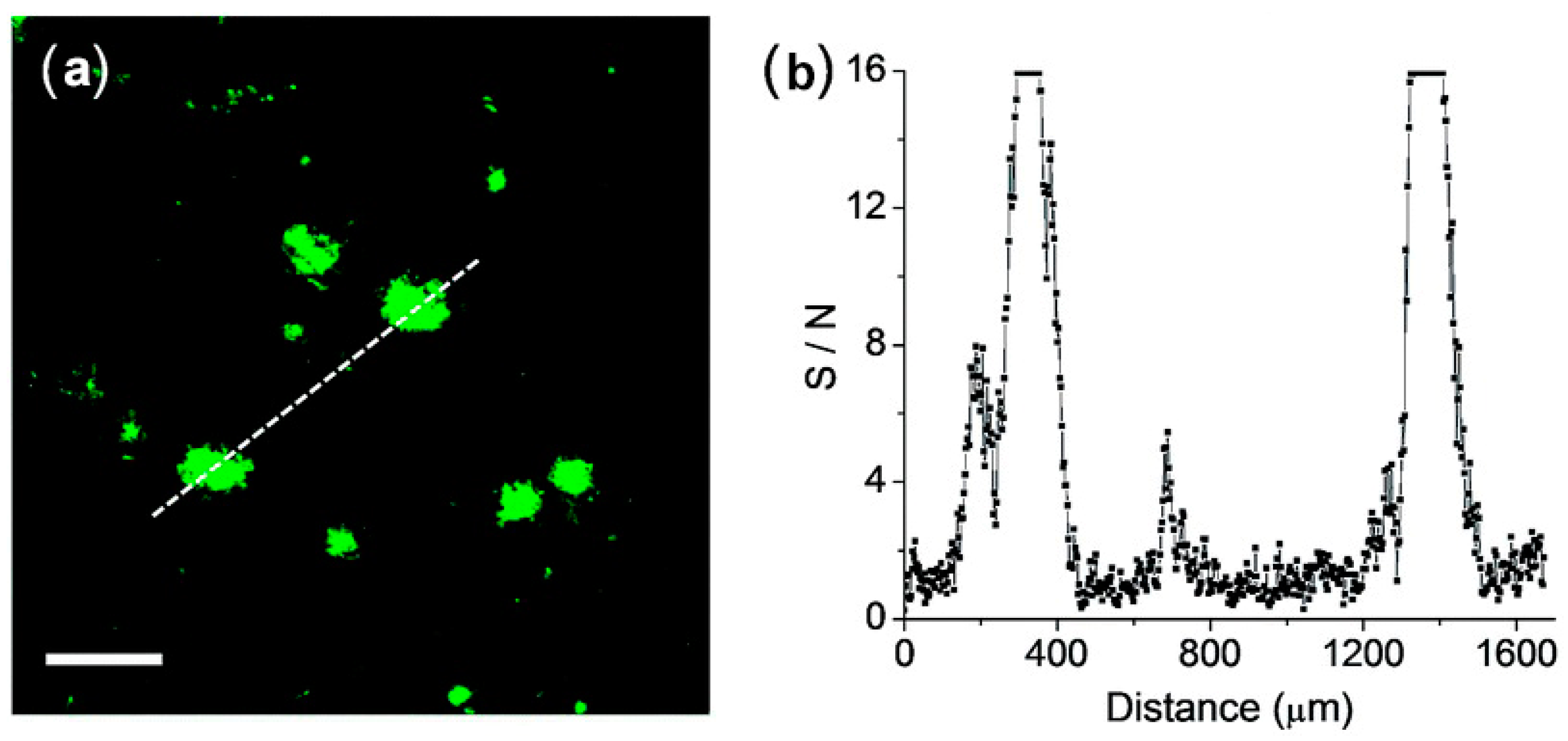
The feasibility of QAD for the detection of Aβ plaques in brain tissues was confirmed by TPM images in cortical slices which were taken from a transgenic 5XFAD mouse, an AD model mouse forming Aβ plaques in the brain [83]. Bright spots in TPM imaging were observed in the QAD-labeled slice with good S/N ratio (Figure 6).
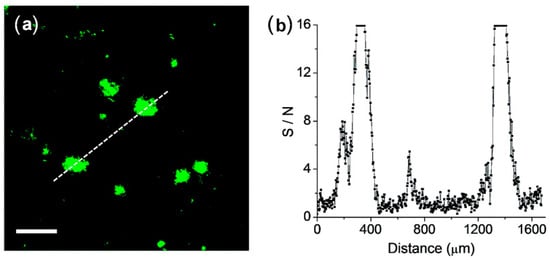
Figure 6.
(a) TPM images of a cortical slice of brain from transgenic 5XFAD mice stained with 20 mM of probe QAD for 90 min and (b) Signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio values measured by TPEF intensity of bright cluster and background regions along the white dotted lines in (a). The two-photon fluorescence intensities were collected at 450–520 nm upon excitation at 750 nm with fs pulse. Scale bars: 48 mm. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [81]. Copyright 2016 Royal Society Chemistry.
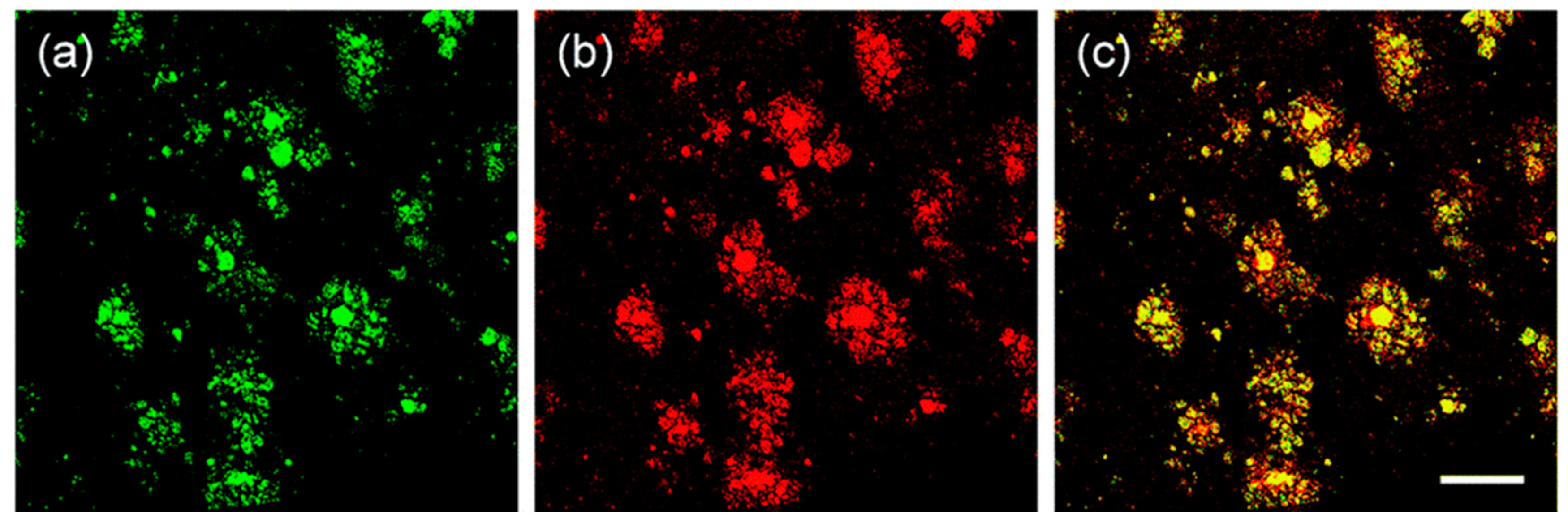
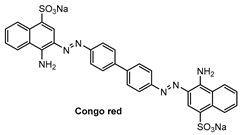
Specific location of QAD in Aβ plaques was confirmed by a co-localization experiment between QAD and Congo red, a known fluorescent marker for histology of Aβ plaques [84]. The bright fluorescence regions of QAD merged well with signals from Congo red with a Pearson’s co-localization coefficient of 0.85 (Figure 7).
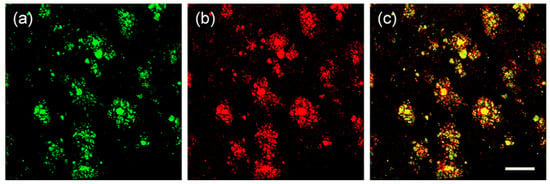
Figure 7.
TPM images of cortical slices of brain from transgenic 5XFAD mice co-labeled with (a) probe QAD and (b) Congo red for 90 min, and (c) merged image by 20× magnification. Scale bars: 72 µm. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [81]. Copyright 2016 Royal Society Chemistry.
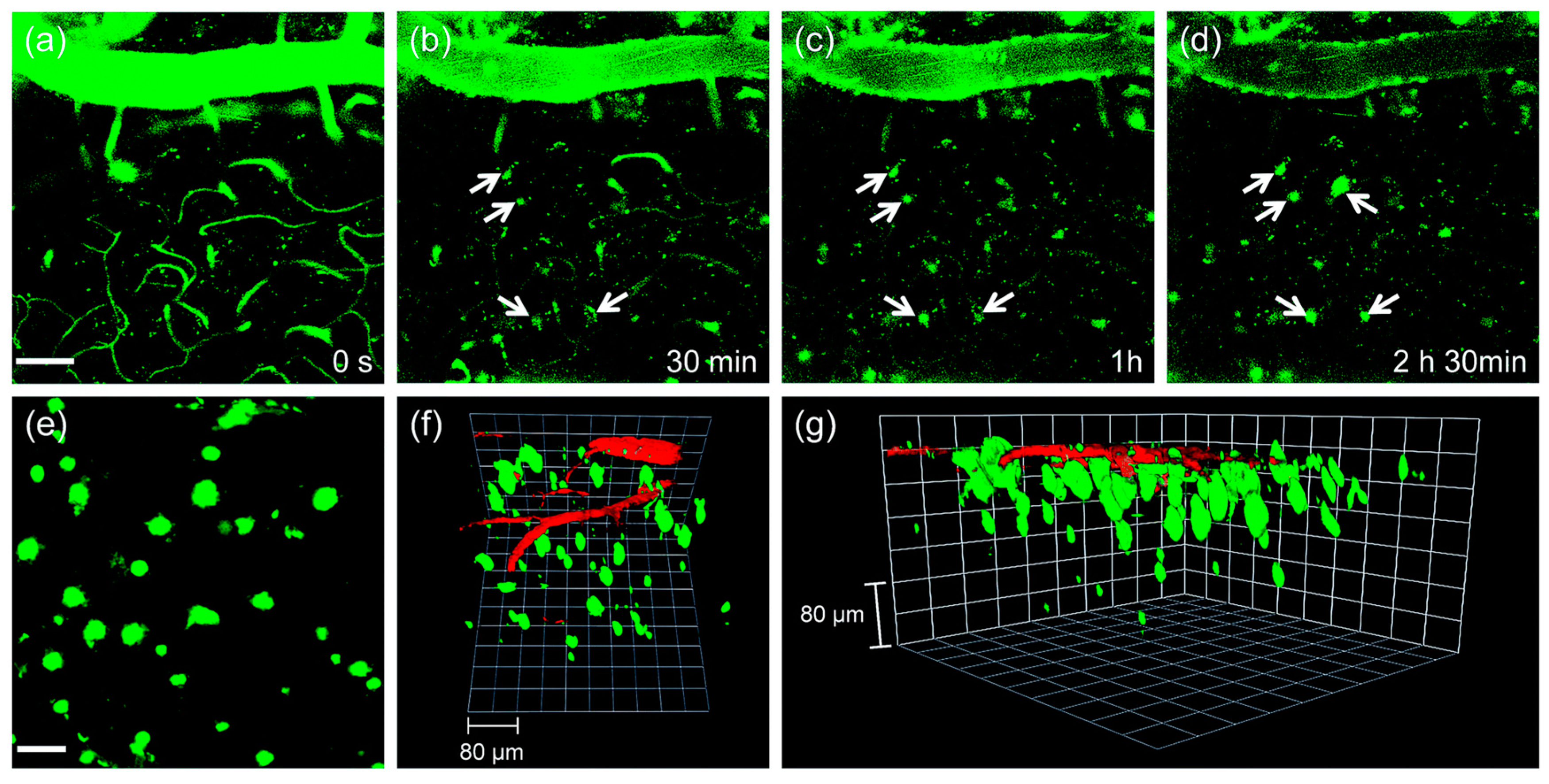
The utility of probe QAD in vivo imaging was evaluated in transgenic 5XFAD mice. As shown in Figure 8, the initial images showed bright fluorescence through the blood vessels in the cortex region (Figure 8a) upon excitation with 780 nm; the bright fluorescence at the vessels decreased with a concomitant increase at the plaques (white arrows in Figure 8b–d) until it reached a peak. Kinetic studies revealed that the circulating half-life (t1/2) at the vessels was 35.7 min. Both time constants for BBB penetration and for plaque binding were t0 = 23.4 min and Δτ = 46.9 min, respectively. The 3D images were constructed from approximately 270 sections in which a known blood marker, dextran 40 kDa-Texas red, was injected. Aβ plaques with different sizes at the specific positions were clearly visualized along with blood vessels (Figure 8f,g). In addition, cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), other deposited Aβ aggregates surrounding the wall of blood vessels of the central nervous system [85], were also directly observed.
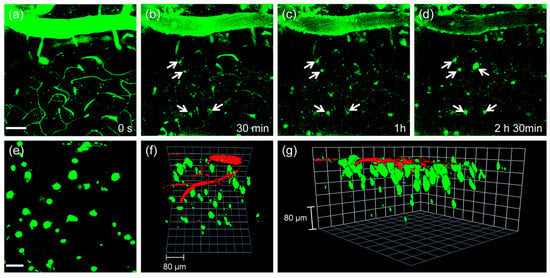
Figure 8.
In vivo TPM imaging of the frontal cortex of transgenic 5XFAD mice at (a) 0, (b) 30, (c) 60 and (d) 150 min after i.v. injection of probe QAD (10 mg kg−1). (e) 230 sections of images along the z-direction at the depth of ~300 µm from the surface of the cortex were accumulated to visualize Aβ plaque distribution. (f,g) 3D-reconstructed two-photon image of the frontal cortex of transgenic 5XFAD mice after i.v. injection of probe QAD (10 mg kg−1) and dextran 40 kDa-Texas red. Approximately 270 sections of images were acquired along the z-direction at a depth of ~300 µm from the surface of the cortex. Scale bars: (a) 50 and (e) 30 µm. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [81]. Copyright 2016 Royal Society Chemistry.
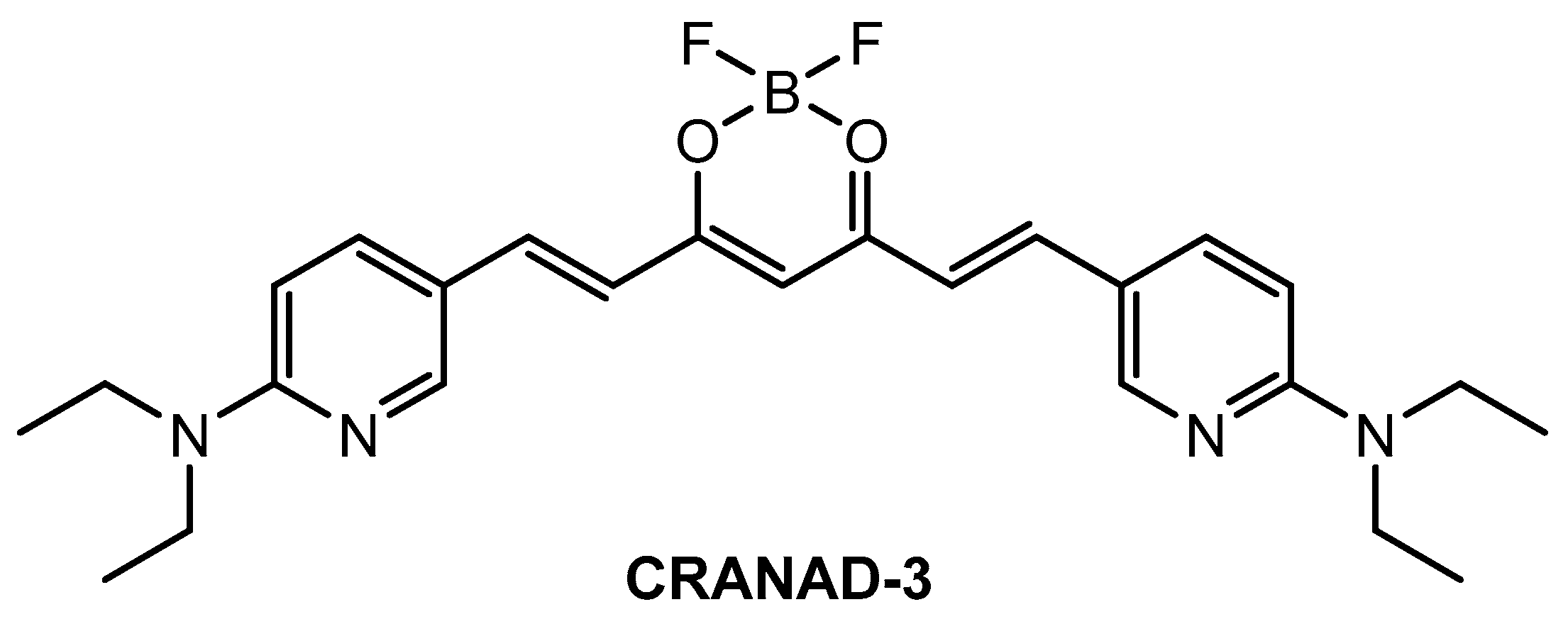
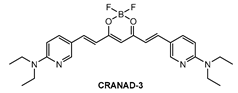
Ip and co-workers [86] employed a known fluorophore CRANAD-3 (Figure 9) as probe for in vivo deep two-photon imaging of Aβ in an AD transgenic mice model. CRANAD-3 was reported early to be able to image insoluble Aβ aggregates and soluble Aβ monomers and dimers in vitro [87]. The two-photon fluorescence properties of CRANAD-3 in living brain tissue were characterized in the brain of live APP/PS1 mice with the injections of CRANAD-3. It was found that the fluorescence excitation wavelength of CRANAD-3 is about 900 nm, much longer than that of MeO-X04 (720–750 nm), and the emission peak is about 630 nm, which suggested that CRANAD-3 is a potentially appropriate probe for two-photon deep brain imaging.
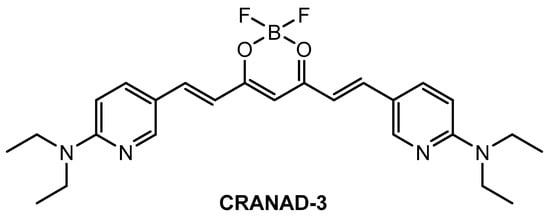
Figure 9.
Structure of probe CRANAD-3.
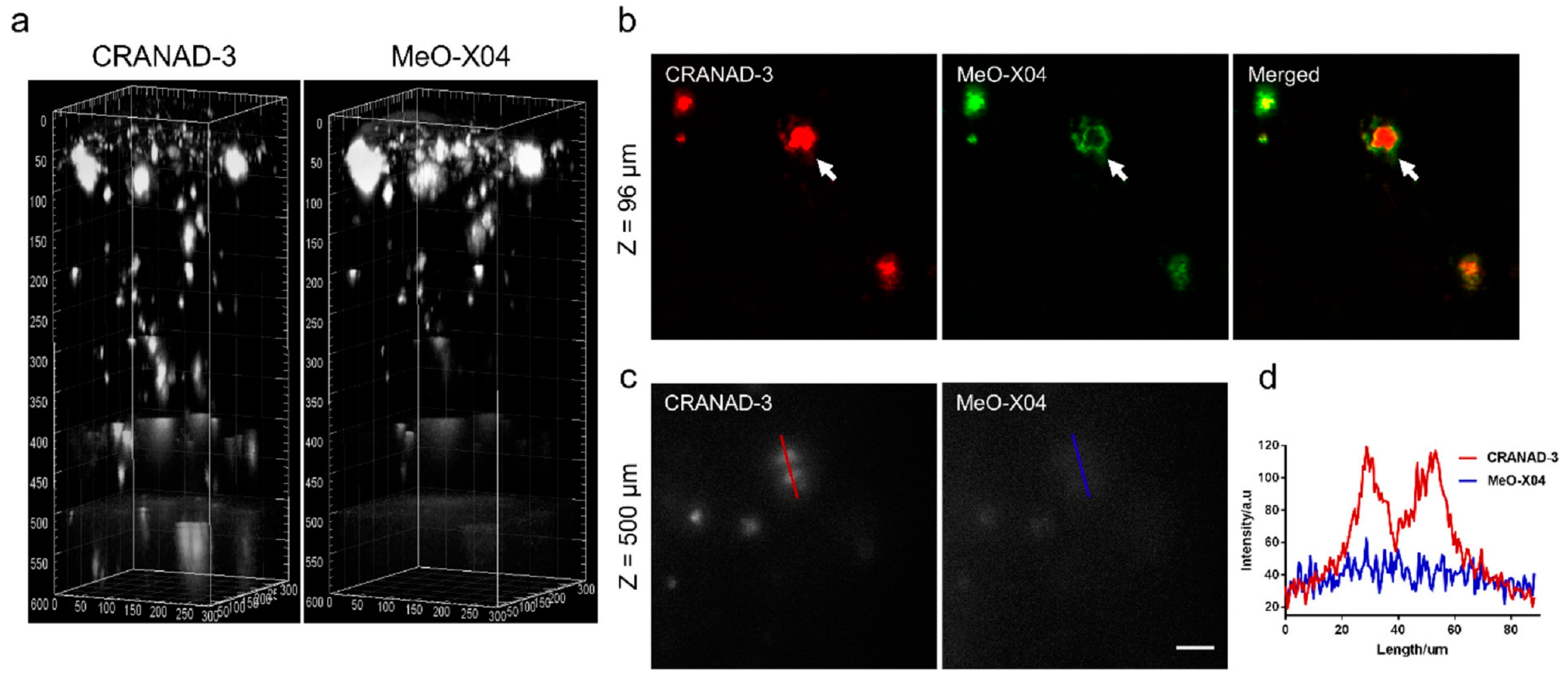
In vivo imaging of Aβ plaques with CRANAD-3 was evaluated in APP/PS1 mice by comparing with MeO-X04. CRANAD-3 and MeO-X04 were co-injected into the mice with dosages and delivery routes following individual protocols. Both CRANDA-3- and MeO-X04-labeled Aβ plaques of the cortex were imaged with excitation wavelengths of 900 and 760 nm, respectively. The well-co-localized images (Figure 10b) confirmed that CRANDA-3 could specifically image Aβ plaques. Furthermore, CRANDA-3 showed better labeling efficiency than MeO-X04. The image contrast of CRANDA-3 surpassed MeO-X04 significantly at deep cortical layers especially in the depth beyond 500 μm (Figure 10c), and a large SBR (4.1) was obtained (Figure 10d). In addition, the authors also indicated that the maximum depth where Aβ plaques could be detected is 900 µm (SBR~1.0) with CRANAD-3.
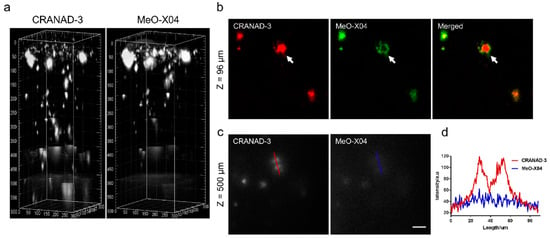
Figure 10.
Imaging depth comparison of CRANAD-3 and MeO-X04. (a) Deep brain imaging of amyloid plaques in a 17-month-old APP/PS1 mouse coinjected with CRANAD-3 (4 mg/kg) and MeO-X04 (5 mg/kg). The z-step in the stack is 2 μm. The 3D image was reconstructed based on the z-stack TPEF images using the commercial Imaris software. (b) TPEF images at upper layer (96 μm depth) in (a), showing differences in plaque labeling of CRANAD-3 and MeO-X04, a dense-core plaque is indicted by the white arrow. (c) TPEF images at deeper region (500 μm depth) and (d) quantitative comparison of SBR of amyloid plaques in (c). Scale bar: 40 μm. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [86]. Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society.
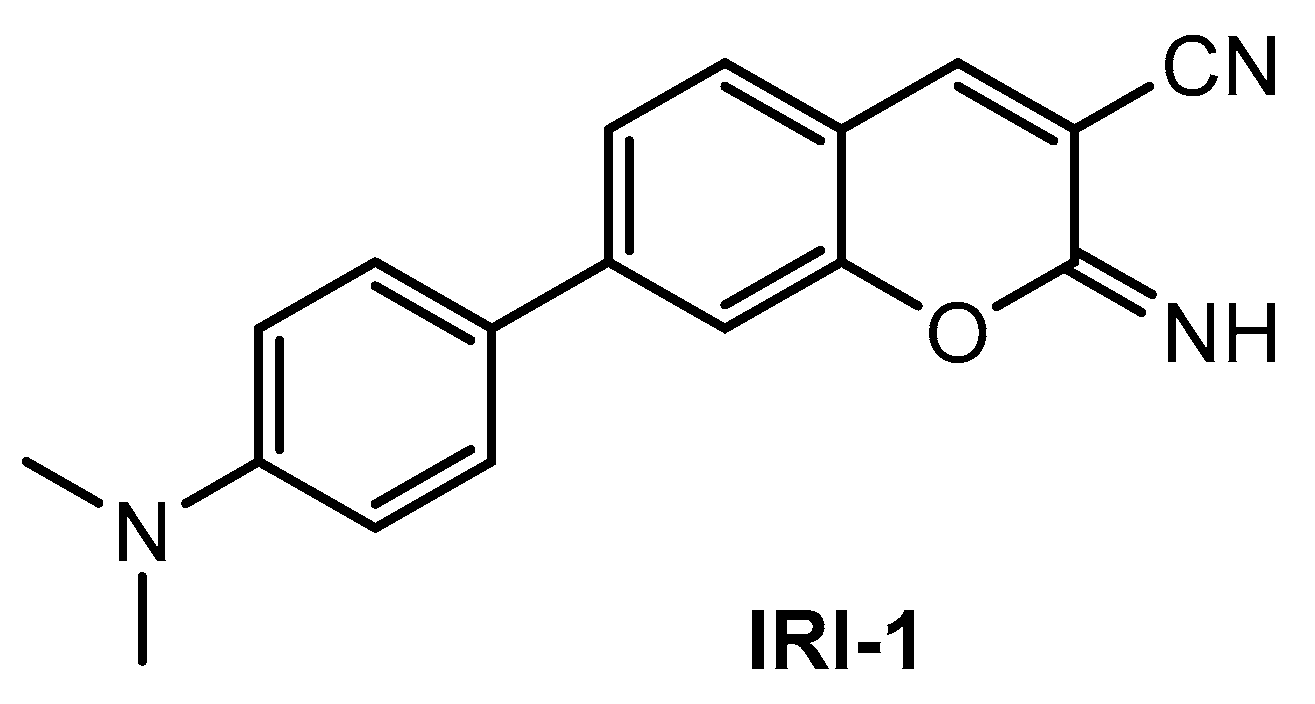
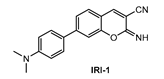
Kim and co-workers [88] described a new two-photon fluorescent probe for detection and imaging of Aβ42 plaques. Probe IRI-1 (Figure 11) was synthesized by Suzuki coupling reaction between 4-bromosalicylaldehyde and 4-(dimethylamino) phenylboronic acid, followed by condensation and cyclization reaction with malononitrile.
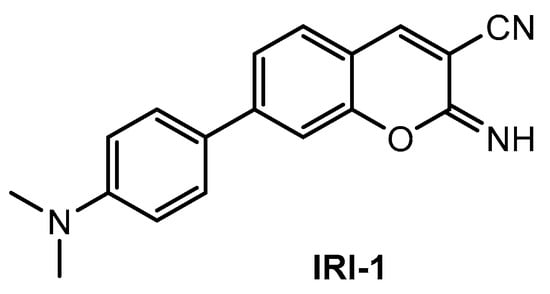
Figure 11.
Structure of probe IRI-1.
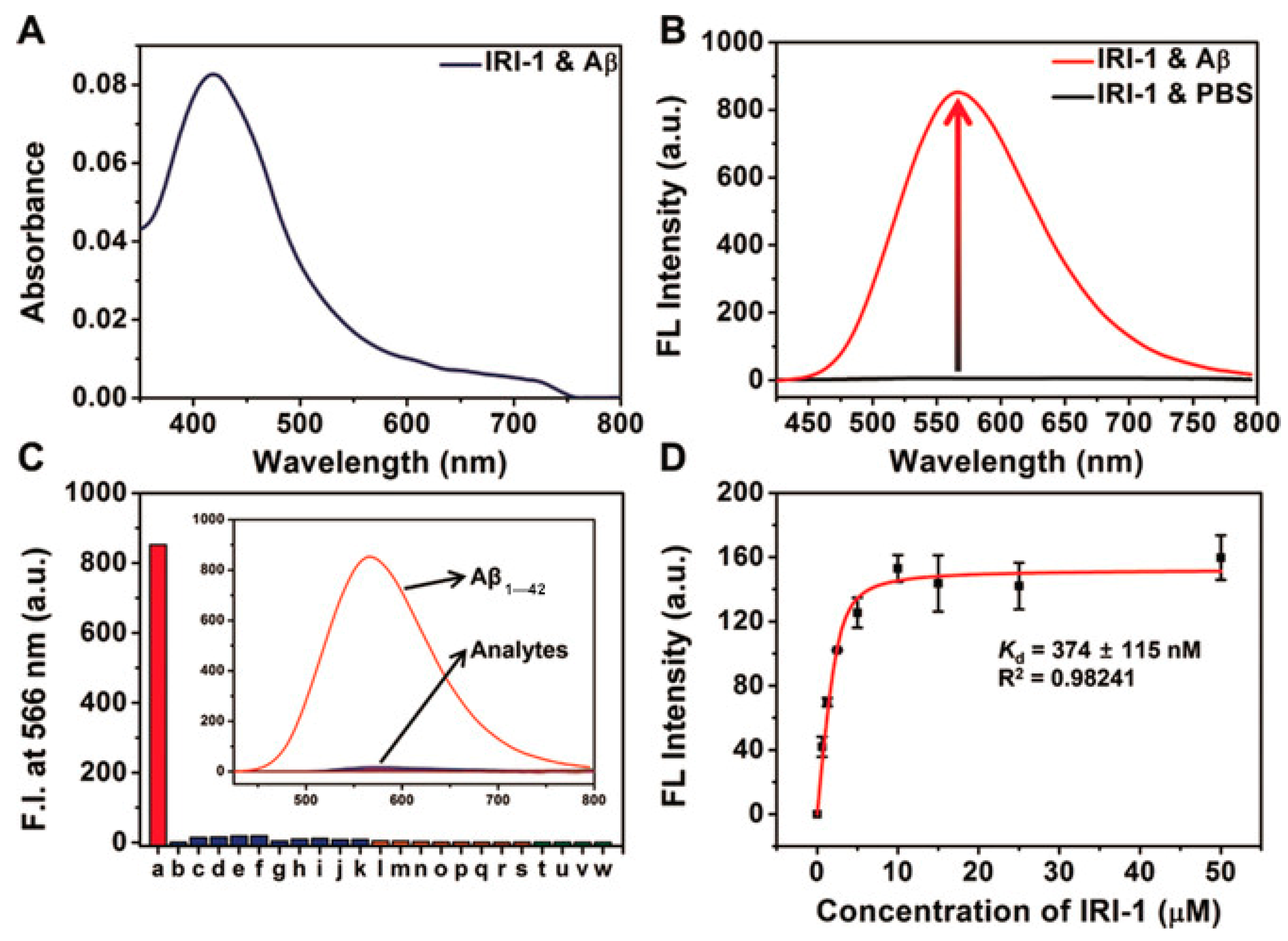
Probe IRI-1 exhibited absorption maximum at ~419 nm (Figure 12A). In the absence of Aβ aggregates, no emission was observed, while in the presence of Aβ aggregates in PBS (pH 7.4), a distinct enhanced fluorescence maximum at ~566 nm was detected (Figure 12B). The enhanced fluorescence resulted from two potential pathways: reduced polarity and conformational restriction at the protein binding site. Docking studies showed that there are two main locations for binding affinities of probe IRI-1 and Aβ aggregates. One is a tunnel along the aggregate axis, and the other is located on a groove along the aggregate axis; the tunnel-based interaction may be more kinetically stable [89]. In addition, a control experiment demonstrated that metal ions, amino acids, and thiols showed negligible interference (Figure 12C), only a weak fluorescence enhancement in the presence of BSA, HSA, or mouse brain homogenates. The binding affinity of probe IRI-1 toward Aβ aggregates is calculated to be Kd = 374 ± 115 nm (Figure 12D), and the δTPA value of IRI-1 is 111 GM at 880 nm.
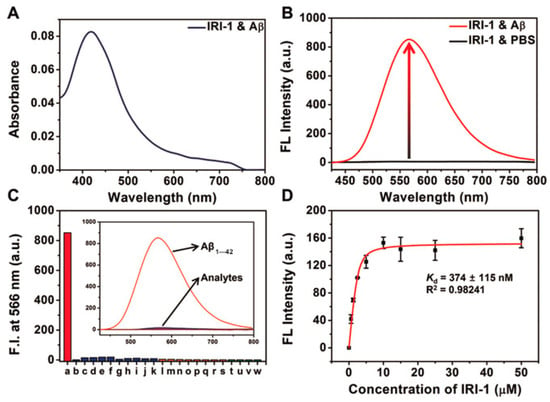
Figure 12.
Absorbance and fluorescence data of probe IRI-1 (10 µm). (A) Absorption spectra of IRI-1 in the presence of Aβ aggregates (20 µm). (B) Fluorescence spectra of IRI-1 in PBS and Aβ aggregates (20 µm). (C) Fluorescence response assays (λem = 566 nm) for IRI-1 and various potential interferents: a: Aβ aggregates (20 µm), b–k: metal ions (20 µm, from b to k: Al3+, Fe3+, Fe2+, Ca2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+), l–s: amino acids (20 µm, from l to s: Lys, Arg, Asp, Glu, His, Trp, Tyr, Phe), and t–w: thiols (20 µm, form t to w: DTT, Hcy, GSH, Cys), in PBS. (D) Saturation binding curve of Aβ aggregates (10 µm) as a function of IRI-1 (0–50 µm) in PBS; error bars represent SD (n = 3). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [88]. Copyright 2019 Wiley-VCH.
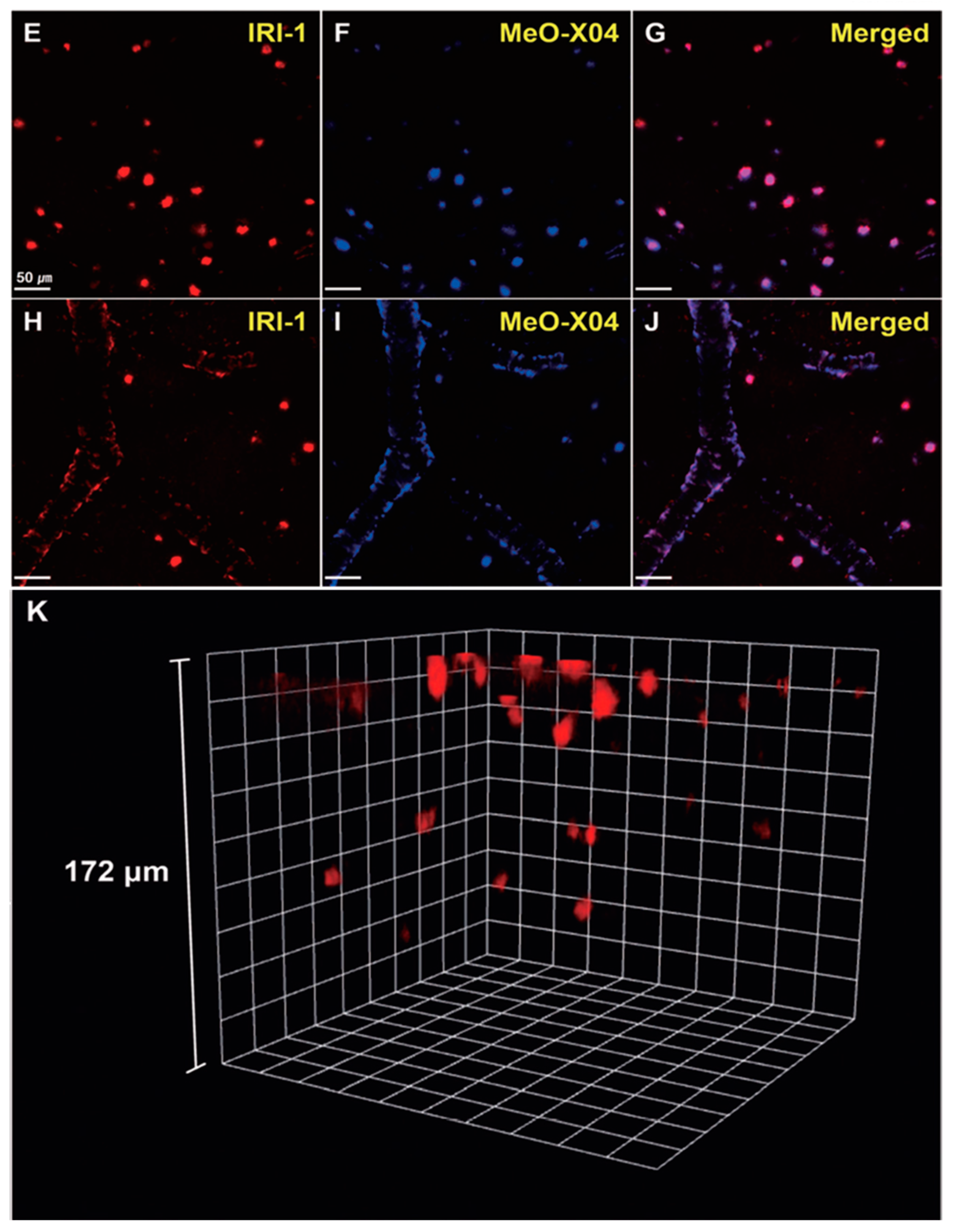
In vivo TPM imaging showed that a bright fluorescence in the frontal cortex of 10–12-month old 5XFAD-Tg mice was observed after IRI-1 was injected into the peritoneal cavity and excitation at 920 nm (Figure 13E). The bright fluorescence is the result of combining lower tissue background emission and large two-photon cross-sections of IRI-1. Co-staining experiments (Figure 13E–G) revealed well-merged fluorescence images by using MeO-X04, confirming that IRI-1 efficiently images Aβ plaques. Moreover, a clear visualization of Aβ deposits on cerebral blood vessels associated with CAA was also found (Figure 13H–J). Finally, 3D TPM imaging showed that individual Aβ plaques could be detected up to a depth of 172 µm (Figure 13K).
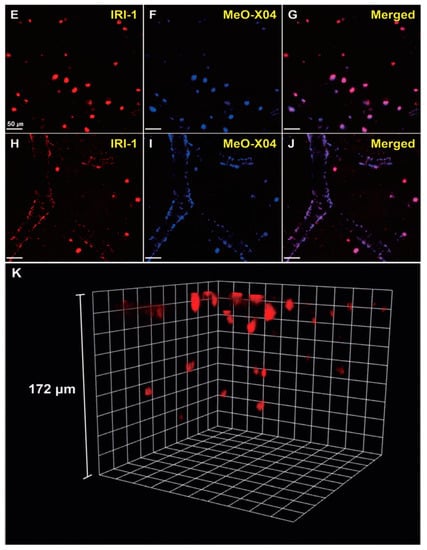
Figure 13.
In vivo TPM imaging of Aβ plaques in the frontal cortex of transgenic mice (5xFAD-Tg, 10–12-monthold). Dyes were administered intraperitoneally (5 mg kg−1) and imaged with a laser power of around 30 mW at the focal point. (E–J) Co-staining with IRI-1 and MeO-X04 of Aβ plaques (E–G) and CAA near the blood vessel walls (H–J). Fluorescence images were acquired under excitation at 920 nm (E,H) and 780 nm (F,I). Scale bars = 50 mm. (K) 3D in vivo imaging of IRI-1-stained Aβ plaques. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [88]. Copyright 2019 Wiley-VCH.
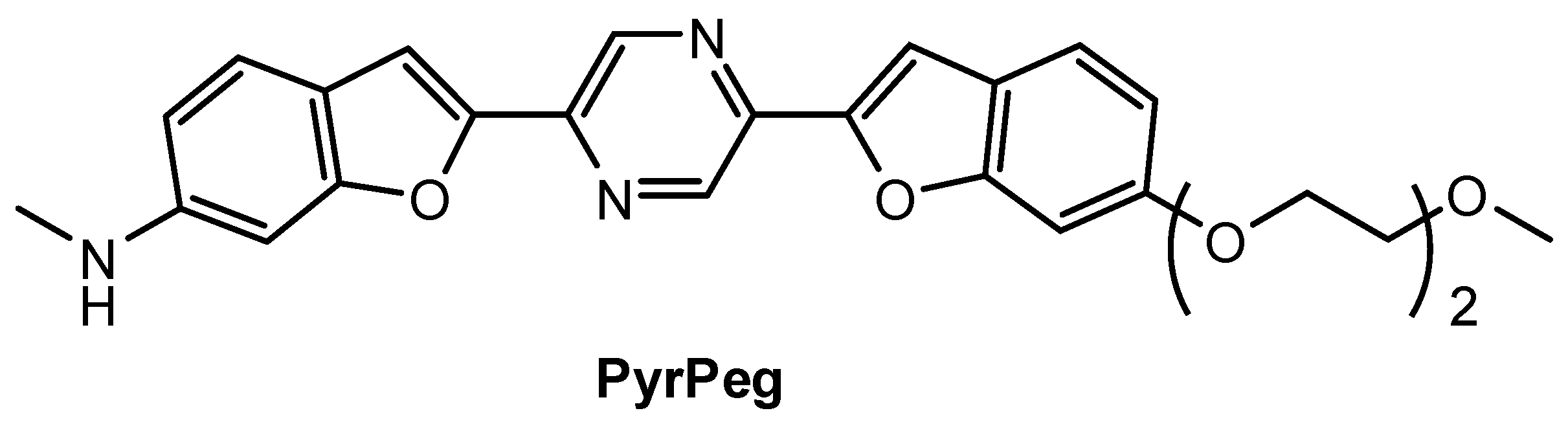
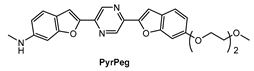
Lee and co-workers [90] prepared a new NIR fluorescent probe for two-photon imaging of Aβ42 plaques. Probe PyrPeg (Figure 14) was synthesized in total of five steps starting from 3-methoxy-N-methylaniline. PyrPeg exhibited emission in organic solvents, but almost no emission in PBS solution. A broad two-photon emission in the range of 450–650 nm with a maximum emission at 560 nm was detected when PyrPeg was excited with 740 nm excitation in SH-SY5Y cells. Control experiments demonstrated that PyrPeg is specific for detection of Aβ42 fibrils over other amyloidogenic proteins. The Kd values of PyrPeg for the binding to the Aβ42 aggregates and monomer were 63.8 and 799 nM, respectively. Such a large difference indicates that the affinity of PryPeg for Aβ42 aggregates is much stronger than that for the Aβ42 monomer. Both δTPA value and logP value of PyrPeg are 230 GM (at 740 nm) and 3.51, respectively.
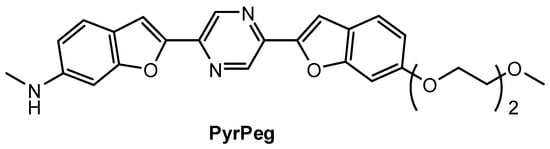
Figure 14.
Structure of probe PyrPeg.
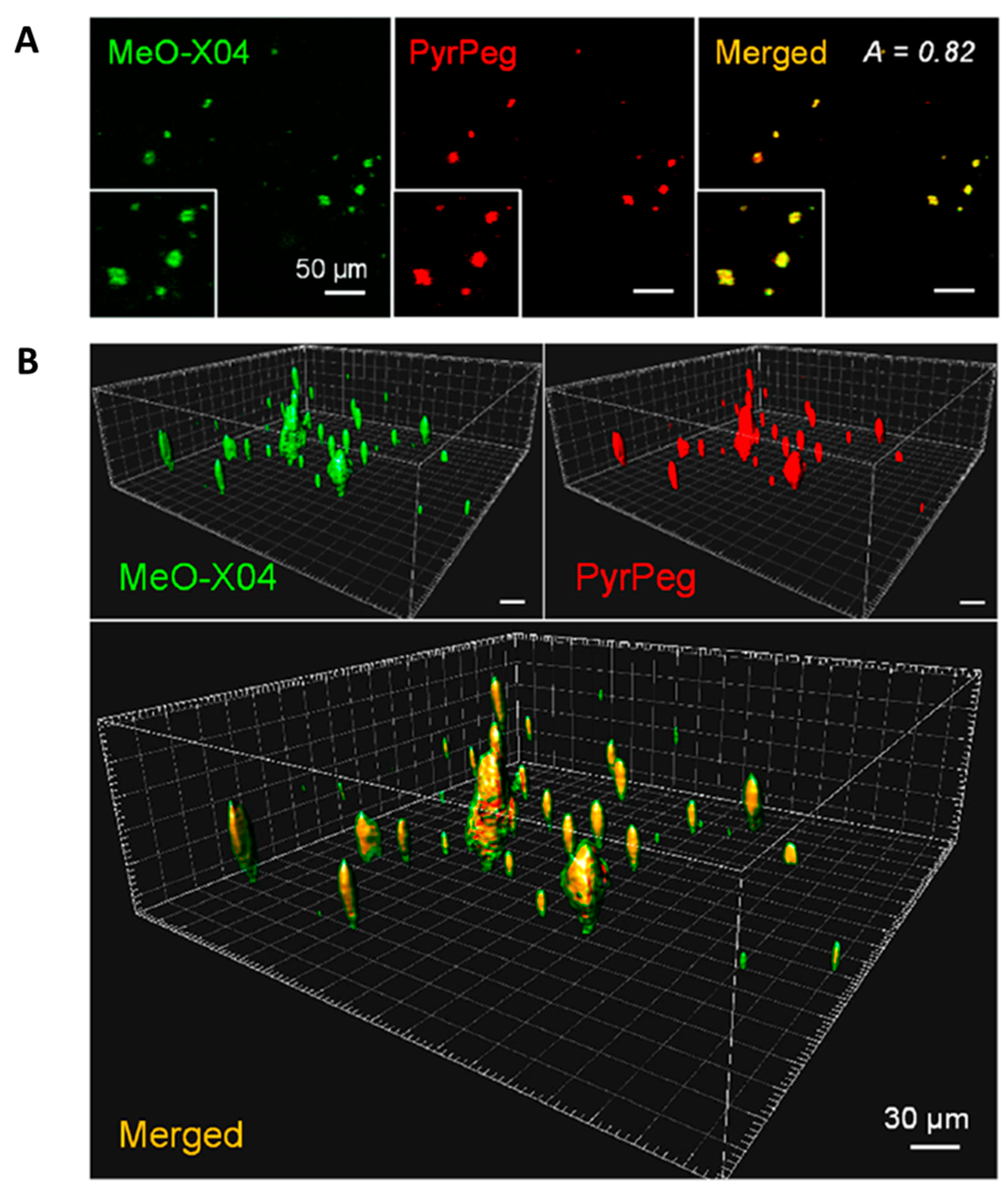
Co-staining experiments revealed well-merged fluorescence images. As shown in Figure 15, the sectional images captured in Ch1 (detection windows at 400–500 nm for MeO-X04) and Ch2 (detection windows at 530–640 nm for PyrPeg) at a depth of 220 μm overlapped well, with the A value of 0.82, which confirmed that probe PyrPeg efficiently images Aβ plaques. The 3D images were constructed from 200 sectional images. Both images from Ch1 and Ch2, respectively, overlapped well except for the green dots (MeOX04) scattered around the overlap region (yellow dots) that can be attributed to the tangles and cerebrovascular amyloids [91]. The result indicated that PyrPeg was localized in the dense core region of the neuritic Aβ plaque.
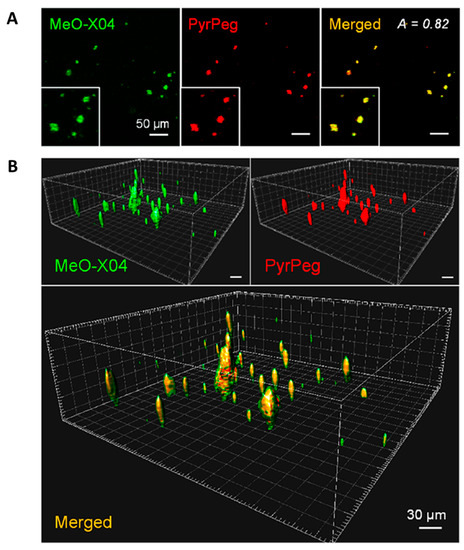
Figure 15.
Detection of neuritic plaques in APP/PS1 mice. (A) TPM images of an APP/PS1 mouse brain slice 1 day after ip injection with MeO-X04 (2 mg/kg) and iv injection with PyrPeg (2 mg/kg) and a merged image (yellow). The images were captured at 400–500 nm (MeO-X04, green) and 530–640 nm (PyrPeg, red) upon TP excitation at 750 nm at a depth of 200 μm. (B) 3D images constructed from 200 sectional images of the MeO-X04- and PyrPeg-injected tissues at a depth of 150–300 μm with 0.75 μm intervals along the z-direction and a merged image. The merged image shows green dots around the overlapping regions. Representative images from replicate experiments (n = 3) are presented. Scale bars: 30 and 50 μm. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [90]. Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society.
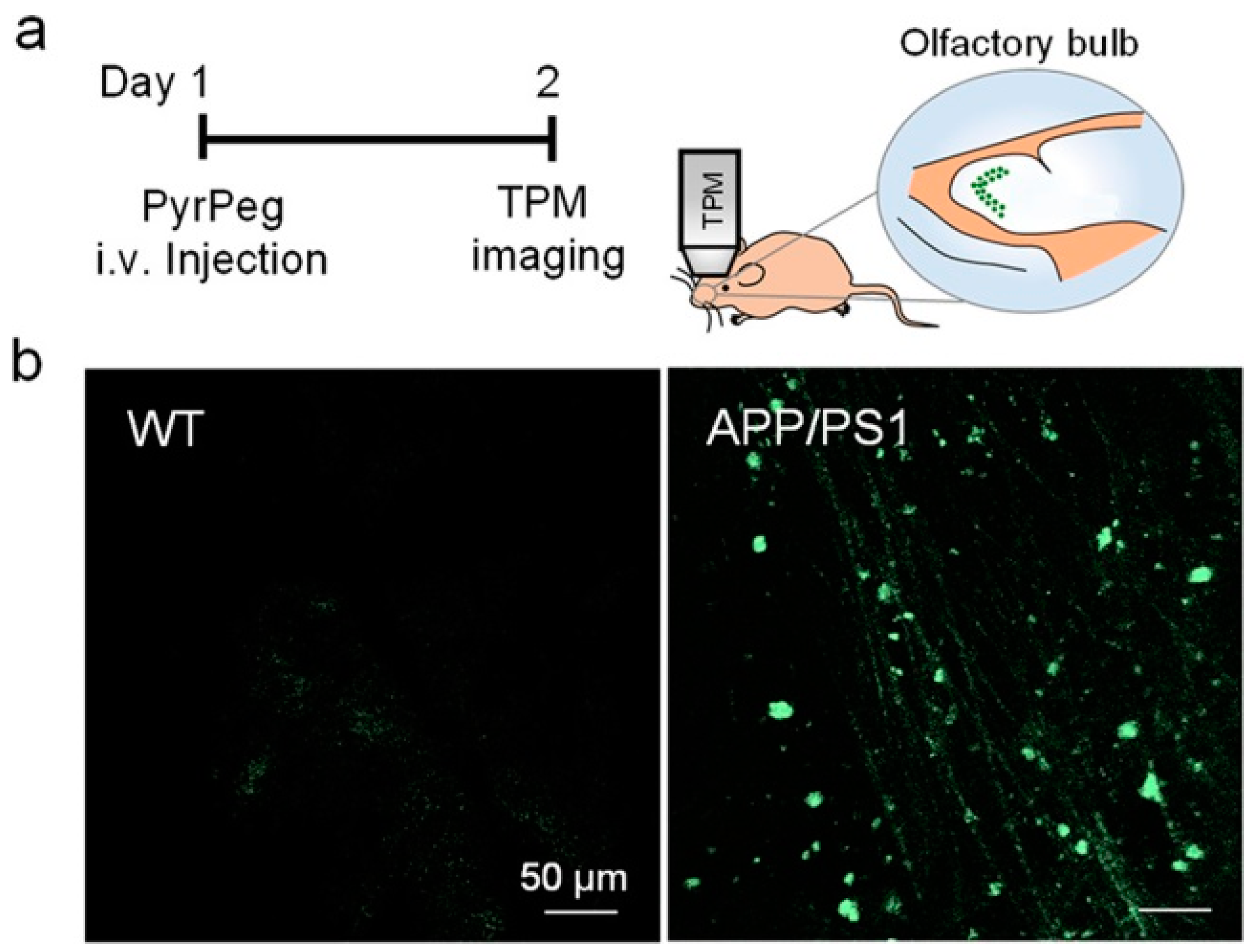
In vivo detection of Aβ plaques was carried out in the olfactory bulb of APP/PS1 mice by TPM imaging. The olfactory bulb is primarily affected in AD [92,93]. Both WT (wide-type) and APP/PS1 mice were injected with PyrPeg, respectively, and examined by TPM imaging. As shown in Figure 16, a bright fluorescence was observed in the APP/PS1 mice, but not in the WT mice, indicating that PyrPeg can selectively label Aβ plaques in the AD brain, and could be useful for AD diagnosis.
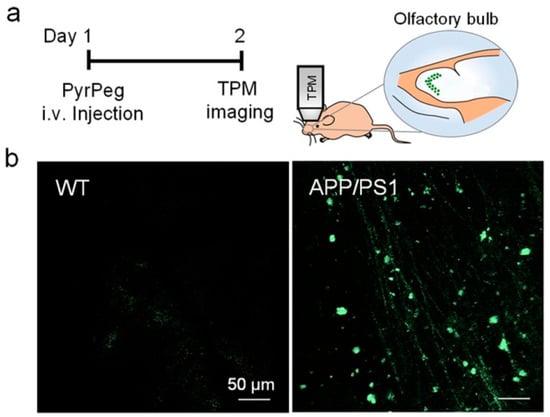
Figure 16.
In vivo TPM images of the olfactory bulb in mice. (a) Schematic diagram of TPM imaging of the olfactory bulbs of a tail-injected mouse. (b) TPM images of the olfactory bulbs of WT (left) and APP/PS1 mice (right) 1 day after injection with PyrPeg (1 mg/kg). Scale bar: 50 μm. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [90]. Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society.
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Fluorescence probes can directly detect and image Aβ plaques and other pathological markers in the brain, providing a powerful tool for AD diagnostics in situ during AD development. In this review, recent advances in two-photon Aβ-specific fluorescence probes are highlighted including design strategies and applications to the detection and imaging of Aβ in vivo (Table 1).

Table 1.
Highlights of fluorescent probes included in this review for two-photon imaging of Aβ in vivo.
To date, a class of two-photon NIR fluorescent probes for Aβ plaques has been developed, but several challenges remain for practical applications. First, sensitivity and selectivity are the basic requirements for accurate detection of AD. Efforts need not only increase the signal-to-noise contrast and improve the sensitivity, but also distinguish diffuse and neuritic plaques and enhance selectivity. Second, for in vivo detection and imaging, NIR or two-photon fluorescent probes should have large two-photon cross-sections and NIR emission as a consequence of their low-power laser excitation (≤5 mW at the focal point does not cause damage to the cells and tissues [94]) and deep penetration depth (>100 µm). Third, appropriate lipophilicity (log P = 2.0–3.5) [79] and good permeability of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) are needed for in vivo detection and imaging in brain tissues. In addition, stability, cytotoxicity, and mechanism are important factors in practical applications which also need to be tested and clarified. With more and more research, outstanding progress of two-photon NIR fluorescent probes for Aβ plaques is expected to be achieved, which will finally improve AD diagnoses and treatments in clinics.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the National Natural Science Foundation of China for the funding through project (No. 21572241).
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Mawuenyega, K.G.; Sigurdson, W.; Ovod, V.; Munsell, L.; Kasten, T.; Morris, J.C.; Yarasheski, K.E.; Randall, J.; Bateman, R.J. Decreased clearance of CNSb-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 2010, 330, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucke, L. Neuroscience: Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2009, 461, 895–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtzman, D.M.; Morris, J.C.; Goate, A.M. Alzheimer’s disease: The challenge of the second century. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 77sr1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFerla, F.M.; Green, K.N.; Oddo, S. Intracellular amyloid-β in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karran, E.; Mercken, M.; De Strooper, B. The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease: An appraisal for the development of therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 698–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittner, L.M.; Gotz, J. Amyloid-β and tau-a toxic pas de deux in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Frank, R.; Broich, K.; Teipel, S.J.; Katz, R.G.; Hardy, J.; Herholz, K.; Bokde, A.L.; Jessen, F.; Hoessler, Y.C. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: Academic, industry and regulatory perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 560–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K. Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease drug development. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J. Resolving controversies on the path to Alzheimer’s therapeutics. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Knopman, D.S.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; Weiner, M.W.; Aisen, P.S.; Shaw, L.M.; Vemuri, P.; Wiste, H.J.; Weigand, S.D.; et al. Tracking pathophysiological processes in Alzheimer’s disease: An updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, H.F.; Choi, S.R.; Qu, W.; Zhang, W.; Skovronsky, D. 18F Stilbenes and styrylpyridines for PET imaging of Aβ plaques in Alzheimer’s disease: A miniperspective. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Saji, H. Recent advances in molecular imaging probes for β-amyloid plaques. Med. Chem. Commun. 2015, 6, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlard, P.A.; Tran, B.A.; Finkelstein, D.I.; Desmond, P.M.; Johnston, L.A.; Bush, A.I.; Egan, G.F. A review of β-amyloid neuroimaging in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Choi, S.R.; Zhao, R.; Ploessl, K.; Alexoff, D.; Zhu, L.; Zha, Z.; Kung, H.F. A new highly deuterated [18F]AV-45, [18F]D15FSP, for imaging β-amyloid plaques in the brain. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molavipordanjani, S.; Emami, S.; Hosseinimehr, S.J. 99mTc-labeled small molecules for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease; past, recent and future perspectives. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Qu, Y.; Wang, X. Amyloid β-targeted metal complexes for potential applications in Alzheimer’s disease. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 679–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Cui, M. Recent progress in the development of metal complexes as β-amyloid imaging probes in the brain. Med. Chem. Commun. 2017, 8, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulanova, M.; Poljak, A.; Wen, W.; Bongers, A.; Gloag, L.; Gooding, J.J.; Tilley, R.D.; Sachdev, P.S.; Braidy, N. Nanoparticles as contrast agents for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1743–5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooyama, I.; Yanagisawa, D.; Taguchi, H.; Kato, T.; Hirao, K.; Shirai, N.; Sogabe, T.; Ibrahim, N.F.; Inubushi, T.; Morikawa, S. Amyloid imaging using fluorine-19 magnetic resonance imaging (19F-MRI). Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 30, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poduslo, J.F.; Wengenack, T.M.; Gurran, G.L.; Wisniewski, T.; Sigurdsson, E.M.; Macura, S.I.; Borowski, B.; Jack, C.R.J. Molecular targeting of Alzheimer’s amyloid plaques for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Neurobiol. Dis. 2002, 11, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staderini, M.; Martin, M.A.; Bolognesi, M.L.; Menendez, J.C. Imaging of β-amyloid plaques by near infrared fluorescent tracers: A new frontier for chemical neuroscience. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Zhang, X.; Tautiva, N.A.; Nyabera, A.N.; Owa, O.O.; Baidya, M.; Sung, H.C.; Taunk, P.S.; Abdollahi, S.; Charles, S. Small molecules and Alzheimer’s disease: Misfolding, metabolism and imaging. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2015, 12, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linke, R.P. Highly sensitive diagnosis of amyloid and various amyloid syndromes using Congo red fluorescence. Virchows Arch. 2000, 436, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, P.; Ye, F.; Liu, Y.; Du, Z.Y.; Zhang, K.; Dong, C.Z.; Meunier, B.; Chen, H. Development of phenothiazine-based theranostic compounds that act both as inhibitors of β-amyloid aggregation and as imaging probes for amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Tu, P.; Zhao, L.; Dai, J.; Liu, B.; Cui, M. Amyloid-β deposits target efficient near-infrared fluorescent probes: Synthesis, in vitro evaluation, and in vivo imaging. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1944–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.N.; Jeon, H.; Jung, Y.; Baek, S.; Lee, S.; Yoo, H.C.; Bae, G.H.; Park, K.; Yang, S.-H.; Han, J.M.; et al. Fluorescent 1,4-naphthoquinones to visualize diffuse and dense-core amyloid plaques in APP/PS1 transgenic mouse brains. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 3031–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, K.; Wang, J.; Tan, H.; Xu, Z.; Chen, S.; Lu, Y.; Cui, M.; Zhang, L. Neutral merocyanine dyes: For in vivo NIR fluorescence imaging of amyloid-β plaques. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 9910–9913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Zhang, J.; Peng, C.; Xiang, H.; Chen, J.; Peng, C.; Zhu, W.; Huang, R.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y. Fluorescent imaging of β-amyloid using BODIPY based near-infrared Off–On fluorescent probe. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 3459–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boländer, A.; Kieser, D.; Voss, C.; Bauer, S.; Schön, C.; Burgold, S.; Bittner, T.; Hölzer, J.; Heyny-von Haußen, R.; Mall, G.; et al. Bis(arylvinyl)pyrazines, -pyrimidines, and -pyridazines as imaging agents for Tau fibrils and β-amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease models. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 9170–9180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Cui, M.; Zhao, L.; Tu, P.; Zhou, K.; Dai, J.; Liu, B. Highly sensitive near-infrared fluorophores for in vivo detection of amyloid-β plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 6972–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, G.S.M.; Garai, K.; Rath, N.P.; Yan, P.; Cirrito, J.R.; Cairns, N.J.; Lee, J.-M.; Sharma, V. Characterization of a brain permeant fluorescent molecule and visualization of Aβ parenchymal plaques, using real-time multiphoton imaging in transgenic mice. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3640–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, H.-W.; Wong, M.S.; Luo, H.-B.; Xiao, L. Deep red blinking fluorophore for nanoscopic imaging and inhibition of β-amyloid peptide fibrillation. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 11341–11351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Dou, F.; Chen, Z. A near-infrared fluorescent probe quinaldine red lights up the β-sheet structure of amyloid proteins in mouse brain. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 153, 112048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliyan, A.; Cook, N.P.; Martí, A.A. Interrogating amyloid aggregates using fluorescent probes. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 11819–11856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, H.-W.; Wong, M.S. Versatile fluorescent probes for near-infrared imaging of amyloid-b species in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Ono, M.; Ariyoshi, T.; Katayanagi, R.; Saji, H. Novel benzothiazole derivatives as fluorescent probes for detection of β-amyloid and α-synuclein aggregates. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1656–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tian, X.; Ross, A.; Moir, R.D.; Sun, H.; Tanzi, R.E.; Moore, A.; Ran, C. Near-infrared fluorescence molecular imaging of amyloid beta species and monitoring therapy in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9734–9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanchuk, A.A.; Heyne, B.; Stys, P.K. Complex photophysical properties of K114 make for a versatile fluorescent probe for amyloid detection. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lv, J.; Ran, C.; Li, Y. Targeting β-amyloid plaq and ues oligomers: Development of near-IR fluorescence imaging probes. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhar, K.; Narayanaswamy, N.; Murugan, N.A.; Viccaro, K.; Lee, H.; Shah, K.; Govindaraju, T. Aβ plaque-selective NIR fluorescence probe to differentiate Alzheimer’s disease from tauopathies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Xu, D.; Poon, C.-Y.; Ho, S.-L.; Zheng, R.; Liu, Q.; Song, G.; Li, H.-W.; Wong, M.S. Effective theranostic cyanine for imaging of amyloid species in vivo and cognitive improvements in mouse model. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6812–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Fang, S.; Tang, Y.; Wang, C.; Luo, H.; Qu, L.; Zhao, J.; Shi, C.; Yin, F.; Wang, X. A hemicyanine derivative for near-infrared imaging of β-amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 179, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zeng, F.; Ge, Y.; Peng, k.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. Development of near-infrared fluorescent probes for use in Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Bioconjugate Chem. 2020, 31, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, C.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Advances in fluorescent probes for detection and imaging of amyloid-β peptides in Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2021, 103, 136–182. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, B.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, J. Design principles and fundamental understanding of biosensors for amyloid-β detection. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 6179–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhuang, D.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Li, R.; Wu, C.; Deng, Y.; Hu, G.; Guo, B. Recent advances in small molecular near-infrared fluorescence probes for a targeted diagnosis of the Alzheimer disease. Analyst 2022, 147, 4701–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Diao, W.; Li, J.; Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Mao, W. Strategic design of amyloid-β species fluorescent probes for Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, T.C.; Bolton, S.G.; Kenison, J.P.; Shangguan, J.; Otteson, C.E.; Civitci, F.; Nan, X.; Pluth, M.D.; Jasti, R. Subcellular targeted nanohoop for one- and two-photon live cell imaging. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15285–15293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Li, M.; Xing, Y.; Duan, T.; Zhou, X.; Yu, F. Bioimaging of glutathione with a two-photon fluorescent probe and its potential application for surgery guide in laryngeal cancer. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Tang, B.; James, T.D. Two-photon small-molecule fluorescence-based agents for sensing, imaging, and therapy within biological systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 702–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Cho, B.R. Small-molecule two-photon probes for bioimaging applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 5014–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juvekar, V.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, D.J.; Kim, H.M. Two-photon fluorescent probes for quantitative bio-imaging analysis in live tissues. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Xu, M.; Liang, S.H.; Xiang, H.; Tang, L.; Zhang, M.; Ding, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y. Discovery of a novel fluorescent probe for the sensitive detection of β-amyloid deposits. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhou, K.; Bai, H.; Feng, L.; Dai, J.; Cui, M. Smart D-π-A type near-infrared Aβ probes: Effects of a marked π bridge on optical and biological properties. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9432–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Gong, X.; Tian, C.; Fu, H.; Tan, H.; Dai, J.; Cui, M. Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probes with Rotatable Polyacetylene Chains for the Detection of Amyloid-β Plaques. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yuan, C.; Dai, B.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Ma, D.; Dai, J.; Liang, Y.; Tan, H.; Cui, M. Environment-sensitive near-infrared probe for fluorescent discrimination of Aβ and Tau fibrils in AD brain. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 6694–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Yan, C.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tian, H.; Zhu, W. Rational design of near-infrared aggregation-induced-emission-active probes: In situ mapping of amyloid-β plaques with ultrasensitivity and high-fidelity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3171–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; Sun, A.; Wang, M.; Wei, P.; Li, R.; Yi, T. A novel near-infrared fluorescent probe for detection of early-stage Aβ protofibrils in Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 1625–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Hu, J.; Nan, D.; Wang, S.; Li, H. Synthesis and biological evaluation of curcumin analogs as β-amyloid imaging agents. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, P.; Li, Y.; Yaseen, M.A.; Grutzendler, J.; Moore, A.; Ran, C. A bifunctional curcumin analogue for two-photon imaging and inhibiting crosslinking of amyloid beta in Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 11550–11553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Du, L.; Feng, H.; Tian, Y.; Cao, J.; Ran, C. Tuning the stereo-hindrance of a curcumin scaffold for the selective imaging of the soluble forms of amyloid beta species. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 7710–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Watanabe, H.; Kimura, H.; Saji, H. BODIPY-based molecular probe for imaging of cerebral β-amyloid plaques. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; Ono, M.; Matsumura, K.; Yoshimura, M.; Kimura, H.; Saji, H. Molecular imaging of β-amyloid plaques with near-infrared boron dipyrromethane (BODIPY)-based fluorescent probes. Mol. Imaging 2013, 12, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spzmen, F.; Kolemen, S.; Kumada, H.-O.; Ono, M.; Saji, H.; Akkaya, E.U. Designing BODIPY-based probes for fluorescence imaging of β-amyloid plaques. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 51032–51037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Peng, J.; Son, S.; Ji, M.S.; Won, M.; Kim, J.S. Fluorescent diagnostic probes in neurodegenerative diseases. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyasi, Y.I.; Pang, Y.; Li, X.; Gu, J.; Cheng, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, T.; Liu, Y. Biological applications of near infrared fluorescence dye probes in monitoring Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 187, 111982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ren, W.; Tang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H. Advances in development of fluorescent probes for detecting amyloid-β aggregates. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Lou, K.; Wang, W. Near-infrared fluorescent probes for imaging of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hou, J.; Wang, P.; Peng, X.; Ge, G. Coumarin-based near-infrared fluorogenic probes: Recent advances, challenges and future perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 480, 215020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamerlan, A.; An, S.S.A.; Hulme, J. Advances in amyloid beta oligomer detection applications in Alzheimer’s disease. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 129, 115919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yang, J.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Fluorescence detection and dissociation of amyloid-β species for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Therap. 2019, 2, 1900054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, H.; Gupta, S.; Kumar, S.; Yang, J.; Singh, S.K.; Ran, C.; Modi, G. Near-infrared fluorescent probes as imaging and theranostic modalities for amyloid-beta and Tau aggregates in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 8550–8595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Moon, H.; Baik, S.H.; Singha, S.; Jun, Y.W.; Wang, T.; Kim, K.H.; Park, B.S.; Jung, J.; Mook-Jung, I.; et al. Two-photon absorbing dyes with minimal autofluorescence in tissue imaging: Application to in vivo imaging of amyloid-β plaques with a negligible background signal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6781–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lim, C.S.; Tian, Y.S.; Han, J.H.; Cho, B.R. A two-photon fluorescent probe for thiols in live cells and tissues. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1216–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, C.-W.; Chen, G.Y.J.; Zhu, B.; Chai, C.; Xu, Q.-H.; Tan, E.-K.; Zhu, Q.; Lim, K.-L.; Yao, S.Q. A sensitive two-photon probe to selectively detect monoamine oxidase B activity in Parkinson’s disease models. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.S.; Kim, D.; Wang, T.; Kim, K.H.; Hwang, S.; Ahn, K.H. Reaction-based two-photon probes for mercury ions: Fluorescence imaging with dual optical windows. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 2598–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Ono, M.; Watanabe, H.; Kimura, H.; Liu, B.; Saji, H. Smart near-infrared fluorescence probes with donor–acceptor structure for in vivo detection of β-amyloid deposits. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3388–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maezawa, I.; Hong, H.S.; Liu, R.; Wu, C.Y.; Cheng, R.H.; Kung, M.P.; Kung, H.F.; Lam, K.S.; Oddo, S.; Laferla, F.M.; et al. Congo red and thioflavin-T analogs detect Aβ oligomers. J. Neurochem. 2008, 104, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klunk, W.E.; Bacskai, B.J.; Mathis, C.A.; Kajdasz, S.T.; McLellan, M.E.; Frosch, M.P.; Debnath, M.L.; Holt, D.P.; Wang, Y.M.; Hyman, B.T. Imaging Aβ plaques in living transgenic mice with multiphoton microscopy and methoxy-X04, a systemically administered Congo Red derivative. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 61, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, C.H.; Ranjan Sarkar, A.; Baik, S.H.; Jung, T.S.; Kim, J.J.; Kang, H.; Mook-Jung, I.; Kim, H.M. A quadrupolar two-photon fluorescent probe for in vivo imaging of amyloid-b plaques. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 4600–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, O.-K.; Lee, K.-S.; Woo, H.Y.; Kim, K.-S.; He, G.S.; Swiatkiewicz, J.; Prasad, P.N. New class of two-photon-absorbing chromophores based on dithienothiophene. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, H.; Cole, S.L.; Logan, S.; Maus, E.; Shao, P.; Craft, J.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.; Ohno, M.; Disterhoft, J.; Van Eldik, L.; et al. Intraneuronal β-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration, and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations: Potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10129–10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratim Bose, P.; Chatterjee, U.; Xie, L.; Johansson, J.; Göthelid, E.; Arvidsson, P.I. Effects of Congo red on Aβ1−40 fibril formation process and morphology. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2010, 1, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rensink, A.A.; de Waal, R.M.; Kremer, B.; Verbeek, M.M. Pathogenesis of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Brain Res. Rev. 2003, 43, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, B.; Li, X.; Lui, C.; Ip, N.Y.; Qu, J.Y. In vivo near-infrared two-photon imaging of amyloid plaques in deep brain of Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 3128–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Moore, A. Spectral unmixing imaging of wavelength-responsive fluorescent probes: An application for the realtime report of amyloid Beta species in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2012, 14, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Verwilst, P.; Choi, H.; Kang, S.; Han, J.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, J.G.; Oh, M.S.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, D.; et al. Harnessing intramolecular rotation to enhance two-photon imaging of Aβ plaques through minimizing background fluorescence. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Kuang, G.; Agren, H.; Nordberg, A.; Lngstrçm, B.; Tu, Y. Free energy profile for penetration of pittsburgh compound-B into the amyloid β fibril. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-W.; Ju, Y.H.; Choi, Y.; Hyeon, S.J.; Gadhe, C.G.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, M.S.; Baek, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, K.D.; et al. PyrPeg, a blood−brain-barrier-penetrating two-photon imaging probe, selectively detects neuritic plaques, not Tau aggregates. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Rodriguez, M.; Hou, S.S.; Snyder, A.C.; Dujardin, S.; Shirani, H.; Nilsson, K.P.R.; Bacskai, B.J. In vivo detection of tau fibrils and amyloid beta aggregates with luminescent conjugated oligothiophenes and multiphoton microscopy. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, T. Mechanisms of olfactory dysfunction in aging and neurodegenerative disorders. Ageing Res. Rev. 2004, 3, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, M.D.; Peabody, C.A.; Flattery, J.J.; Tinklenberg, J.R. Olfactory deficits and Alzheimer’s disease. Biol. Psychiatry 1986, 21, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.J.; Kim, E.S.; Cho, B.R. Scope and limitation of label-free multiphoton microscopy and probe-labeled two-photon microscopy for the endomicroscopic diagnosis. Scanning 2014, 36, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).