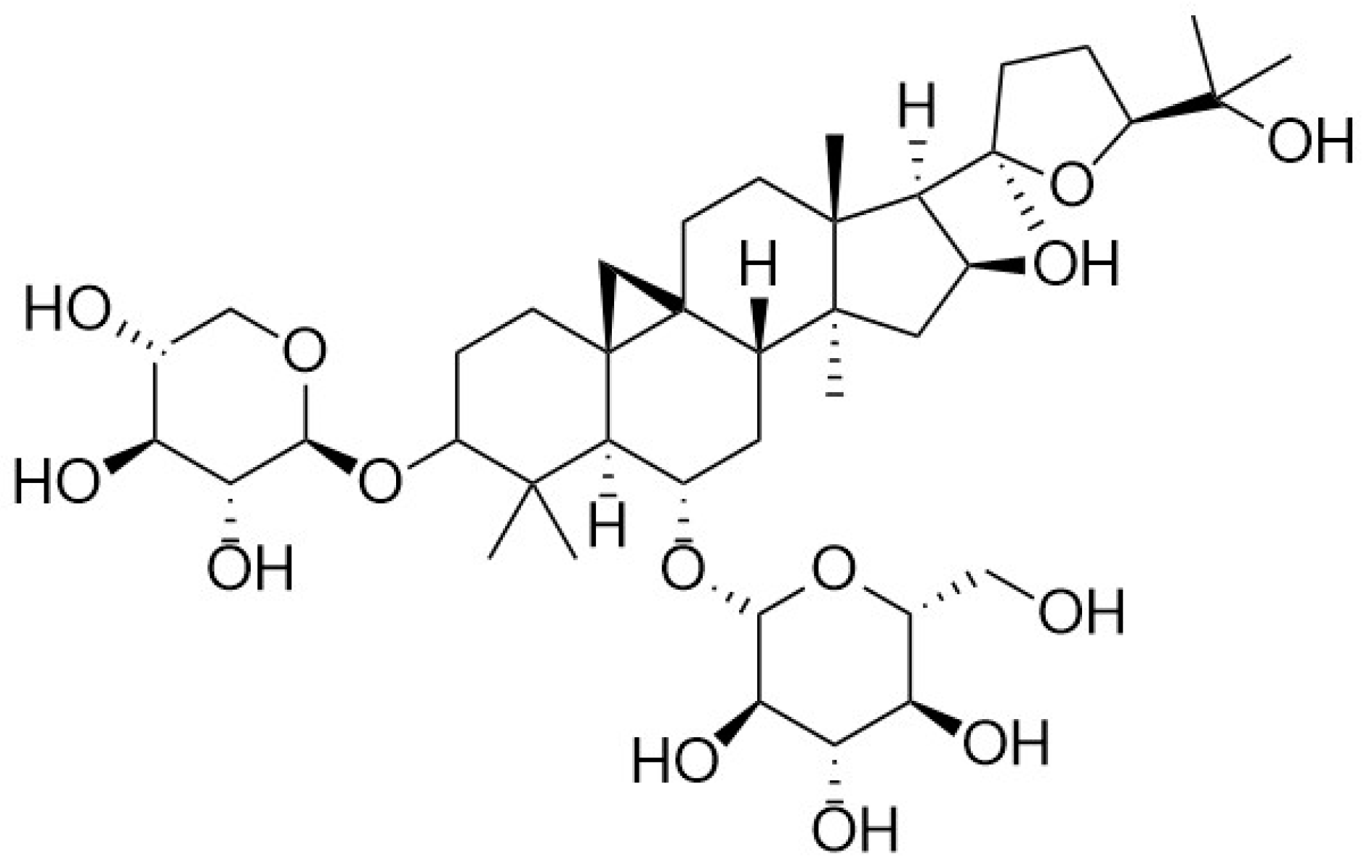
Pharmacological Effects of Astragaloside IV: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
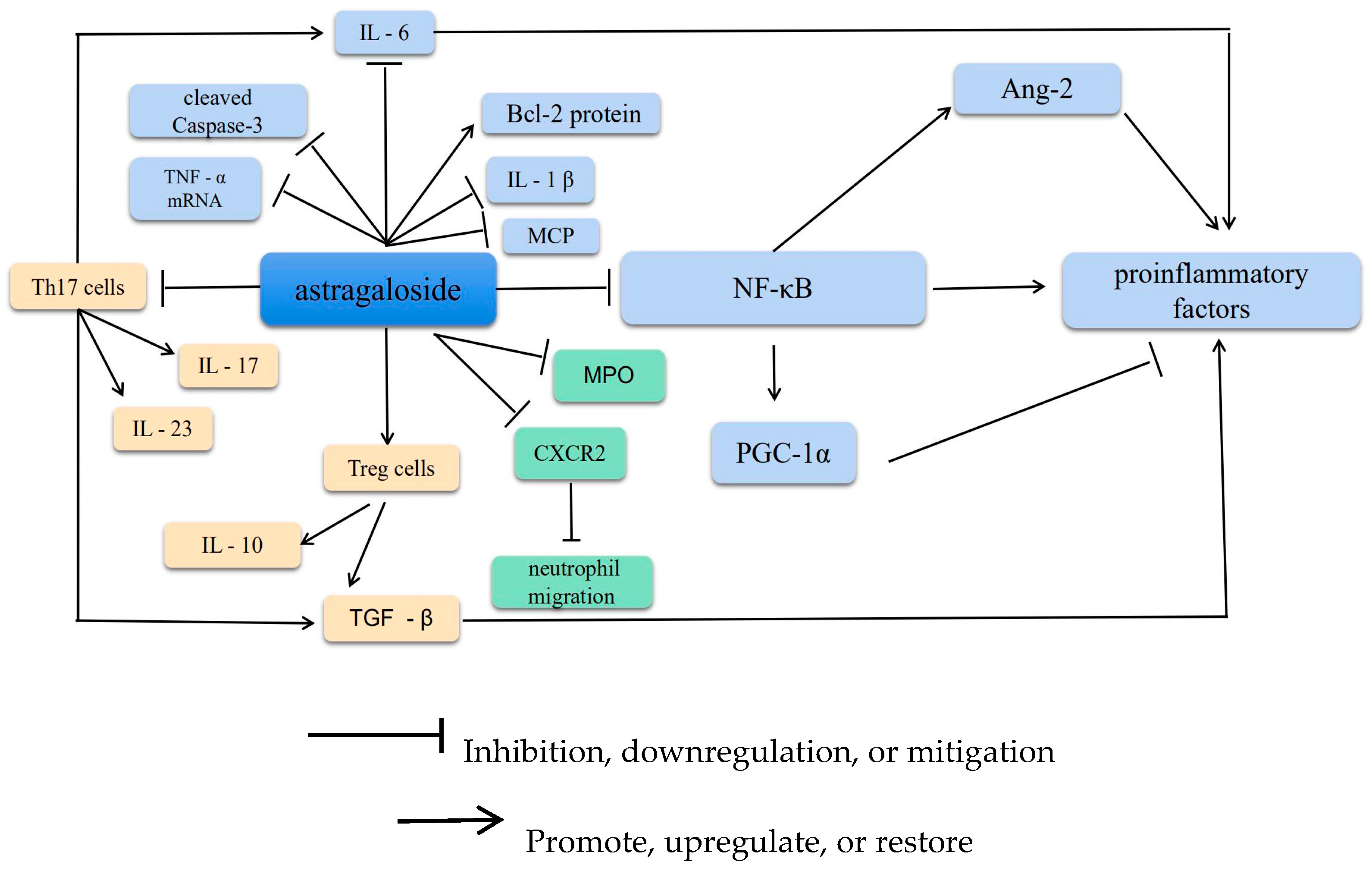
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
2.1. Suppression of Inflammatory Factors
2.2. Increasing T and B Lymphocyte Proliferation
2.3. Inhibiting Neutrophil Adhesion-Associated Molecules
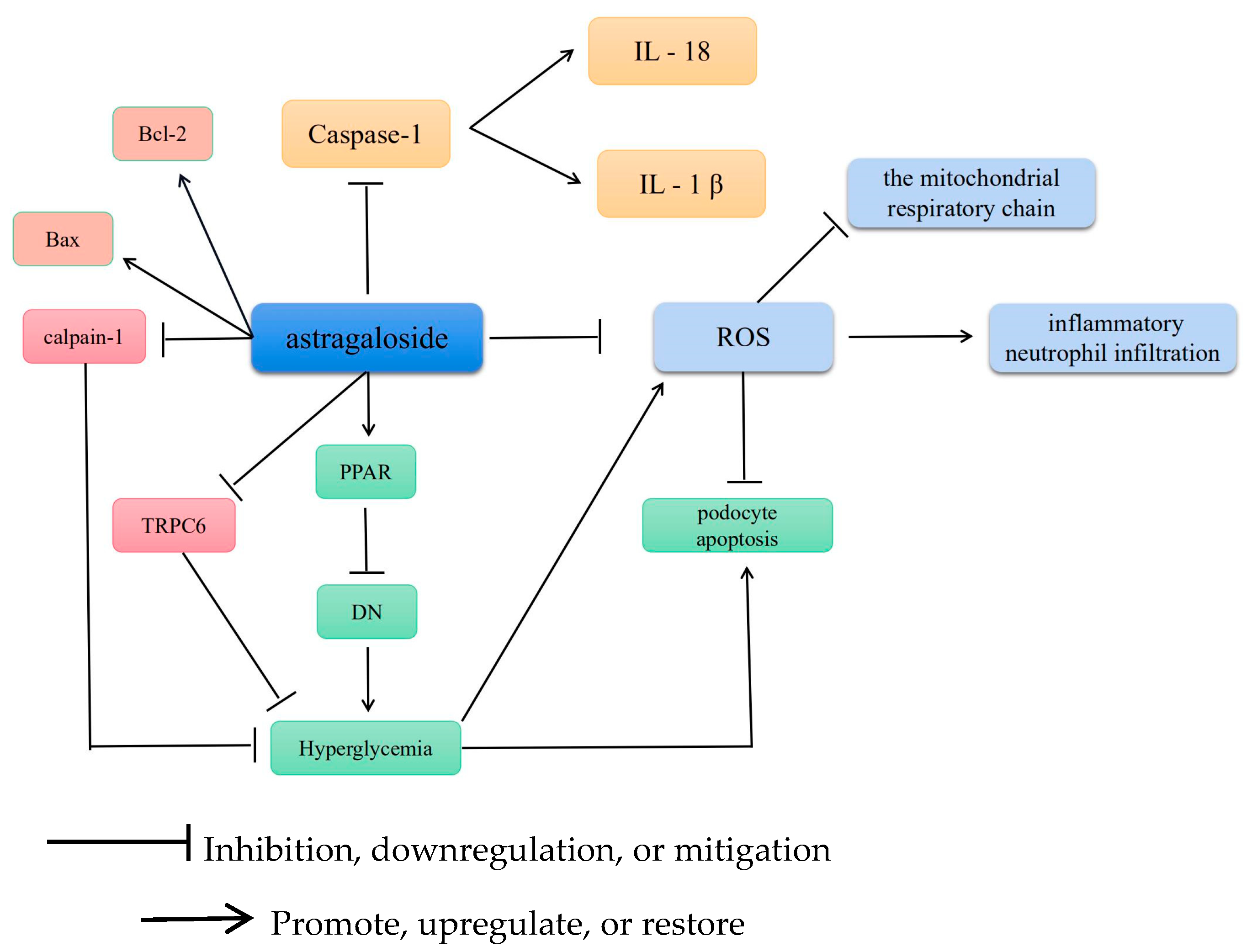
3. Antioxidative Effects
3.1. Antioxidative Stress
3.2. AS-IV Scavenges ROS and Alleviates Cellular Scorching
3.3. AS-IV Regulates Mitochondrial Gene Mutations
3.4. AS-IV Regulates Calcium Homeostasis
4. Neuroprotective Effects
4.1. Preventing Neuronal Loss
4.2. Action on Neural Stem Cells
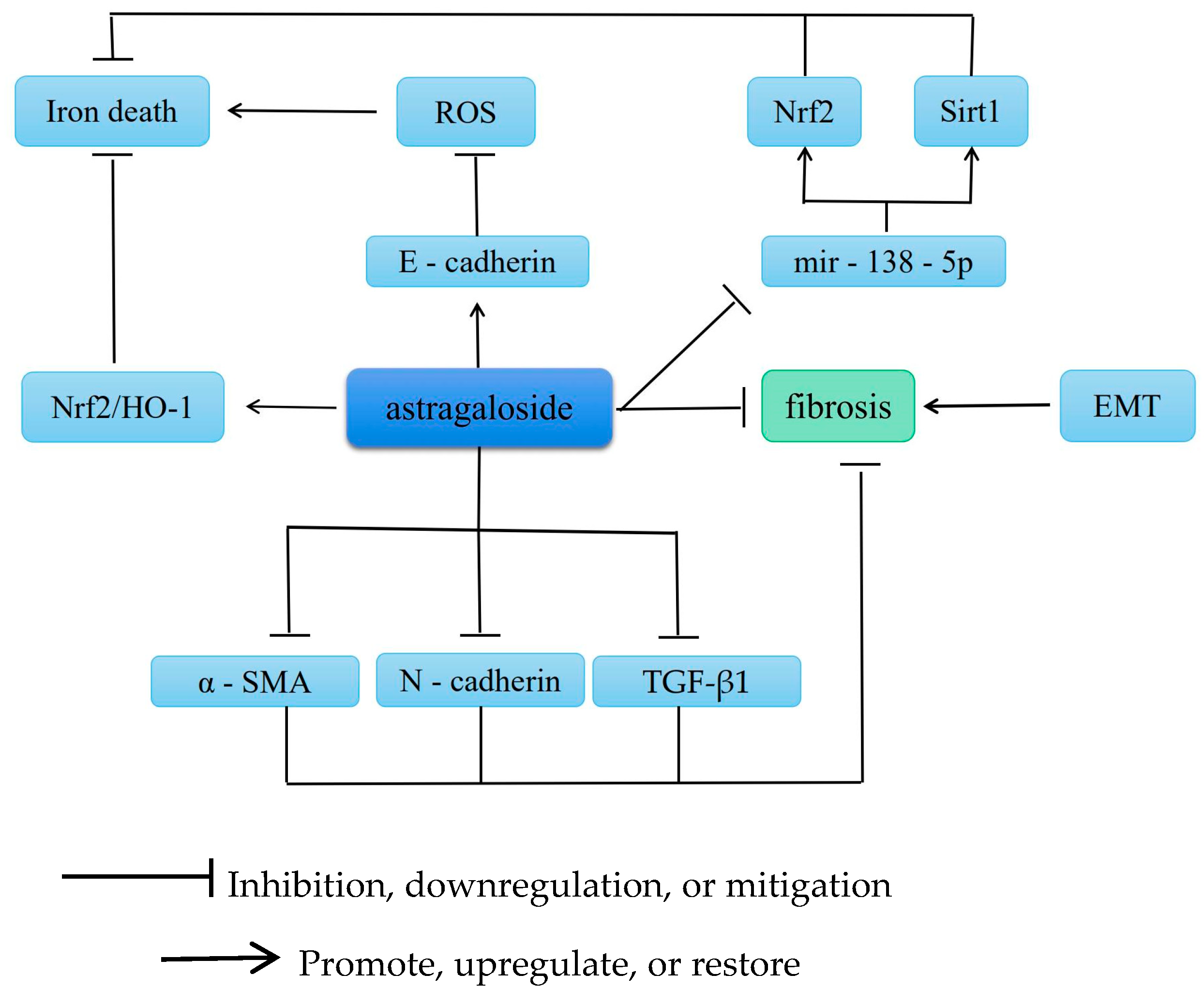
5. Antifibrotic Effects
5.1. Improvement of Renal Fibrosis
5.2. Improvement of Cardiac Fibrosis
5.3. Improvement of Liver Fibrosis
6. Antitumor Effects
6.1. Modulation of the Immune System
6.2. Control of EMT-Associated Autophagic Pathways for Tumor Suppression
6.3. Enhancing Sensitivity to Anticancer Drugs
6.4. Reduced Integrin-Linked Kinase (ILK)
7. Miscellaneous
8. Discussion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Gao, L.; Du, G.; Qin, X. Astragaloside IV derived from Astragalus membranaceus: A research review on the pharmacological effects. Adv. Pharmacol. San Diego Calif. 2020, 87, 89–112. [Google Scholar]
- Brouns, R.; De Deyn, P.P. The complexity of neurobiological processes in acute ischemic stroke. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, M. Astragaloside IV Suppresses High Glucose-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB and CaSR. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 1082497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Mercurio, F.; Karin, M. NF-κB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Jiao, J.; Qin, T.; Yu, J.; Fu, Q.; Deng, X.; Ma, S.; Ma, Z. A New Perspective on Ameliorating Depression-Like Behaviors: Suppressing Neuroinflammation by Upregulating PGC-1α. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Ma, W.; Liu, F.; Huang, P.; Wei, L.; Qian, Y. Astragaloside IV restores Th17/Treg balance via inhibiting CXCR4 to improve chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yin, T.; Chen, D.; Xu, S.; Ye, R.; Zhang, Y. Astragaloside IV regulates insulin resistance and inflammatory response of adipocytes via modulating miR-21/PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2023. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Jang, C.; Dharaneeswaran, H.; Li, J.; Bhide, M.; Yang, S.; Li, K.; Arany, Z. Endothelial pyruvate kinase M2 maintains vascular integrity. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4543–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothstein, D.M.; Camirand, G. New insights into the mechanisms of Treg function. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2015, 20, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.R. The Balance of Th17 versus Treg Cells in Autoimmunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, J.; Chen, R.; Xu, W.; Xiong, S. Remission of CVB3-induced myocarditis with Astragaloside IV treatment requires A20 (TNFAIP3) up-regulation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 850–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astragaloside IV Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis by Regulating the Balance of Th17/Treg Cells—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35752072/ (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Yang, L.; Xing, F.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Wu, H.; Shi, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, F.; Wu, X. Astragaloside IV regulates differentiation and induces apoptosis of activated CD4+ T cells in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 362, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Lu, X.; Yuan, B.; Liu, T.; Dai, L.; Liu, Y.; Yin, H. Astragaloside IV alleviates E. coli-caused peritonitis via upregulation of neutrophil influx to the site of infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 39, 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.C.; Sung, Y.J.; Chen, C.F. Magnolol inhibits Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18)-dependent neutrophil adhesion: Relationship with its antioxidant effect. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 343, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhesion Receptors of the Immune System—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1974032/ (accessed on 2 August 1990).
- Buras, J.A.; Stahl, G.L.; Svoboda, K.K.; Reenstra, W.R. Hyperbaric oxygen downregulates ICAM-1 expression induced by hypoxia and hypoglycemia: The role of NOS. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2000, 278, C292–C302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ma, R.N.; Li, L.H.; Qu, Y.Z.; Gao, G.D. Astragaloside IV reduces cerebral edema post-ischemia/reperfusion correlating the suppression of MMP-9 and AQP4. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 715, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambley, C.A.; Marsee, J.D.; Halper, N.; Miller, J.M. Characterization of Mitochondrial YME1L Protease Oxidative Stress-Induced Conformational State. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 1250–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Karakhanova, S.; Hartwig, W.; D’Haese, J.G.; Philippov, P.P.; Werner, J.; Bazhin, A.V. Mitochondria and Mitochondrial ROS in Cancer: Novel Targets for Anticancer Therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 2570–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, P.R.; Abramov, A.Y. Role of mitochondrial ROS in the brain: From physiology to neurodegeneration. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ke, J.; Wu, X.; Yan, Y. Astragaloside prevents UV-induced keratinocyte injury by regulating TLR4/NF-κB pathway. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Opdenbosch, N.; Lamkanfi, M. Caspases in Cell Death, Inflammation, and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poreba, M.; Strózyk, A.; Salvesen, G.S.; Drag, M. Caspase substrates and inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Liu, J.; Xing, F. ‘Hints’ in the killer protein gasdermin D: Unveiling the secrets of gasdermins driving cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; She, Y.; Sun, Q.; Shi, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, D.-C.; Shao, F. Erratum: Pore-forming activity and structural autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature 2016, 540, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qu, H.; Yang, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, H. Astragaloside IV attenuate MI-induced myocardial fibrosis and cardiac remodeling by inhibiting ROS/caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 2309–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbecki, J.; Bobiński, R.; Dutka, M. Self-regulation of the inflammatory response by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Inflamm. Res. Off. J. Eur. Histamine Res. Soc. 2019, 68, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.T.; Yudell, B.E.; Loor, J.J. Regulation of energy metabolism by long-chain fatty acids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 53, 124–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, Y.I.; Kitamura, T.; Kruse, J.P.; Raum, J.C.; Stein, R.; Gu, W.; Accili, D. FoxO1 protects against pancreatic beta cell failure through NeuroD and MafA induction. Cell Metab. 2005, 2, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Fang, J.; Zhu, B.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Yao, X. Astragaloside IV protects against podocyte apoptosis by inhibiting oxidative stress via activating PPARγ-Klotho-FoxO1 axis in diabetic nephropathy. Life Sci. 2021, 269, 119068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittler, R.; Zandalinas, S.I.; Fichman, Y.; Van Breusegem, F. Reactive oxygen species signalling in plant stress responses. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2022, 23, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L.; Leng, B.; Wang, H. Astragaloside IV protects against hyperglycemia-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction by inhibiting oxidative stress and Calpain-1 activation. Life Sci. 2019, 232, 116662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Effect of Astragalus as an Adjuvant Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A (Preliminary) Meta-Analysis—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27269392/ (accessed on 3 June 2016).
- Qi, W.; Niu, J.; Qin, Q.; Qiao, Z.; Gu, Y. Astragaloside IV attenuates glycated albumin-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by inhibiting oxidative stress in renal proximal tubular cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 2014, 19, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.-L.; Xie, X.-H.; Ding, J.-H.; Du, R.-H.; Hu, G. Astragaloside IV inhibits astrocyte senescence: Implication in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Gao, C.; Sun, X. Astragaloside IV Exerts Cognitive Benefits and Promotes Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Stroke Mice by Downregulating Interleukin-17 Expression via Wnt Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chu, W.; Shang, S.; Ma, L.; Jiang, C.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Shao, B. Preliminary study on the anti-apoptotic mechanism of Astragaloside IV on radiation-induced brain cells. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 2058738420954594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, D.; Huang, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, N. Astragaloside IV ameliorates renal injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammatory genes expression. Cytokine 2013, 61, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Suo, C.; Zhou, H.; Gu, M.; Wang, Z.; Tan, R. Therapeutic Implications of Ferroptosis in Renal Fibrosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 890766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Han, W. Astragaloside-IV alleviates high glucose-induced ferroptosis in retinal pigment epithelial cells by disrupting the expression of miR-138-5p/Sirt1/Nrf2. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 8240–8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Tian, N.; Wang, T.; Shi, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, B. Astragaloside IV inhibits glucose-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of podocytes through autophagy enhancement via the SIRT-NF-κB p65 axis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. New insights into epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2010, 21, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tang, W.; Liu, W.; Hu, Z.; Pan, C. Astragaloside IV Alleviates Renal Tubular Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via CX3CL1-RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 1605–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ma, K.; Ju, Y.; Ji, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Li, W. Astragaloside IV inhibits palmitate-mediated oxidative stress and fibrosis in human glomerular mesangial cells via downregulation of CD36 expression. Pharmacol. Rep. 2019, 71, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Chen, C.; Liang, H.; Zhong, S.; Cheng, X.; Li, L. Astragaloside IV inhibits excessive mesangial cell proliferation and renal fibrosis caused by diabetic nephropathy via modulation of the TGF-β1/Smad/miR-192 signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 3053–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Cong, Y. Astragaloside IV attenuates renal fibrosis through repressing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by inhibiting microRNA-192 expression: In vivo and in vitro studies. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 5029–5038. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Tian, N.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Wu, B.; Zhang, N. Astragaloside IV represses high glucose-induced mesangial cells activation by enhancing autophagy via SIRT1 deacetylation of NF-κB p65 subunit. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 2971–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Han, P.; Sun, H.; Shao, M.; Yu, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Yi, W.; Ge, N.; Li, S.; et al. Astragaloside IV ameliorates early diabetic nephropathy by inhibition of MEK1/2-ERK1/2-RSK2 signaling in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 2883–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, X.; Gong, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Shan, G.; Yao, Q. Astragaloside IV from Astragalus membranaceus ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis by inhibiting inflammation via TLR4/NF-κB in vivo and in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 42, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.; Wang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Xu, W.; Shao, X.; Mou, S.; Ni, Z. Astragaloside IV suppresses transforming growth factor-β1 induced fibrosis of cultured mouse renal fibroblasts via inhibition of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chi, Y.F.; Yuan, Z.T.; Zhou, W.C.; Yin, P.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Peng, W.; Cai, H. Astragaloside IV inhibits renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis by blocking TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 1310–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shang, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, S.; Qu, L.; Cai, S.; Li, X. Astragaloside IV synergizes with ferulic acid to inhibit renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis in rats with obstructive nephropathy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yang, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Sun, J.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Niu, H.; Ma, R.; Wang, Y.; et al. Astragaloside IV reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a murine model of coxsackievirus B3-induced viral myocarditis. Exp. Anim. 2019, 68, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.-Q.; Shi, L.-P.; Chen, Z.-W.; Hu, J.-Y.; Zuo, B.; Xiong, Y.; Cao, W.-F. Astragaloside IV Ameliorates Isoprenaline-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis in Mice via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 836150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zeng, G.; Wang, T.; Ren, H.; An, H.; Lian, C.; Liu, J.; Guo, L.; Li, W. Astragaloside IV Ameliorates Myocardial Infarction Induced Apoptosis and Restores Cardiac Function. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 671255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.-F.; Guan, P.; Qin, L.-Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Wang, N.; Ji, E.-S. Astragaloside IV inhibits adriamycin-induced cardiac ferroptosis by enhancing Nrf2 signaling. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 2603–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, Y.; Feng, K.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, R.; Xu, H.; Tang, Y. Astragaloside IV inhibits cardiac fibrosis via miR-135a-TRPM7-TGF-β/Smads pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 249, 112404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, X.-C.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Ma, Y.-T.; Tang, Y.-Q. AstragalosideIV against cardiac fibrosis by inhibiting TRPM7 channel. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2017, 30, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Leng, B.; Wang, H.; Dai, H. Inhibition of cardiotrophin-1 overexpression is involved in the anti-fibrotic effect of Astrogaloside IV. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 8365–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Jia, G.; Lu, M.; Liang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Astragaloside IV inhibits isoprenaline-induced cardiac fibrosis by targeting the reactive oxygen species/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xie, Y.; Shen, E.; Li, G.G.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.B.; Yang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Ge, J.; Chen, R.; et al. Astragaloside IV attenuates myocardial fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β1 signaling in coxsackievirus B3-induced cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 658, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginès, P.; Krag, A.; Abraldes, J.G.; Solà, E.; Fabrellas, N.; Kamath, P.S. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2021, 398, 1359–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Liu, H.; Chen, R.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, T. Astragaloside IV combating liver cirrhosis through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 393–397. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Hou, S.; Shi, Z.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; He, Y.; Gong, Y.; Fang, Z.; Yang, Y. Astragaloside IV inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma by continually suppressing the development of fibrosis and regulating pSmad3C/3L and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, L.; Kong, L.; Hou, S.; Wan, Y.; Ma, C.; Chen, J.; Xing, X.; Xing, C.; et al. Hepatocyte leukotriene B4 receptor 1 promotes NAFLD development in obesity. Hepatology 2022, 78, 562–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Guo, T.; Li, J. Research progress on the antitumor effects of astragaloside IV. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 938, 175449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-P.; Ding, H.; Lu, J.D.; Tang, Y.H.; Deng, B.X.; Deng, C.Q. Effects of the Combination of the Main Active Components of Astragalus and Panax notoginseng on Inflammation and Apoptosis of Nerve Cell after Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 1419–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Cui, W.-Q.; Wei, Y.; Cui, J.; Qiu, J.; Hu, L.-L.; Gong, W.-Y.; Dong, J.-C.; Liu, B.-J. Astragaloside IV inhibits lung cancer progression and metastasis by modulating macrophage polarization through AMPK signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zheng, Y.; Que, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, S.; Le, V.; Liu, J.; Tian, J. Astragaloside IV inhibits progression of lung cancer by mediating immune function of Tregs and CTLs by interfering with IDO. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-P.; Li, X.-Y.; Song, C.-Q.; Hu, Z.-B. Effect of astragaloside IV on T, B lymphocyte proliferation and peritoneal macrophage function in mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2002, 23, 263–266. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ye, Y.; Chen, H. Astragaloside IV inhibits cell migration and viability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppressing long noncoding RNA ATB. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Chen, H.; Wang, D. Protective role of astragaloside IV in gastric cancer through regulation of microRNA-195-5p-mediated PD-L1. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2021, 43, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Lei, Y.-H.; Yao, N.; Wang, C.-R.; Hu, N.; Ye, W.-C.; Zhang, D.-M.; Chen, Z.-S. Autophagy and multidrug resistance in cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2017, 36, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astragaloside IV Enhances cisplatin Chemosensitivity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Suppressing MRP2—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32259679/ (accessed on 30 May 2020).
- Xie, T.; Li, Y.; Li, S.-L.; Luo, H.-F. Astragaloside IV Enhances Cisplatin Chemosensitivity in Human Colorectal Cancer via Regulating NOTCH3. Oncol. Res. 2016, 24, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Dedhar, S. Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) and its interactors: A new paradigm for the coupling of extracellular matrix to actin cytoskeleton and signaling complexes. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gui, D.; Chen, Y.; Mou, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J. Astragaloside IV improves high glucose-induced podocyte adhesion dysfunction via alpha3beta1 integrin upregulation and integrin-linked kinase inhibition. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.-M.; Liu, Y.-J.; Wang, Y.-M.; Wang, H.; Zhu, B.-B.; Liang, Y.-P.; Yao, W.-G.; Yu, H.; Wang, N.-S.; Zhang, X.-M.; et al. Astragaloside IV prevents high glucose-induced podocyte apoptosis via downregulation of TRPC6. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 5149–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-M.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Y.-N.; Niu, Y.-C. Astragaloside IV Synergizes with Ferulic Acid to Alleviate Hepatic Fibrosis in Bile Duct-Ligated Cirrhotic Rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 2925–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yao, L.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Peng, S.; Wan, G.; Cheng, J.; Wang, J.; Cao, W. Astragaloside IV regulates NF-κB-mediated cellular senescence and apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells to suppress PDGF-BB-induced activation. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 3741–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Gong, Z.; Wang, B.; Guo, X.; Yang, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y. Astragaloside Inhibits Hepatic Fibrosis by Modulation of TGF-β1/Smad Signaling Pathway. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. ECAM 2018, 2018, 3231647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Liu, Z.-L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, Z.-M.; Liu, C.-H. A combination of astragaloside I, levistilide A and calycosin exerts anti-liver fibrosis effects in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Xiang, M.; Zhang, F.; Wei, D.; Wen, Z.; Zhou, Y. Astragaloside Alleviates Hepatic Fibrosis Function via PAR2 Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Rats. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 41, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yongping, M.; Zhang, X.; Xuewei, L.; Fan, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, G.; Liu, C.; Liu, P. Astragaloside prevents BDL-induced liver fibrosis through inhibition of notch signaling activation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 169, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Han, C.; Xing, G.; Zhou, L.; Li, G.; Niu, Y. Astragaloside IV suppresses collagen production of activated hepatic stellate cells via oxidative stress-mediated p38 MAPK pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 60, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wei, W.; Sun, W.; Li, X. Protective effects of astragaloside IV on porcine-serum-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats and in vitro effects on hepatic stellate cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Qian, H.; Kong, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Chai, Y.; Xu, J.; Kang, Q. Accelerated Bone Regeneration by Astragaloside IV through Stimulating the Coupling of Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1821–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Du, J.; Ren, H.; Yang, G.; Wang, W.; Du, J. Astragaloside IV protects against iron loading-induced abnormal differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs). FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Han, C.; Huang, L.; Yang, H.; Hu, J.; Chen, H.; Dou, R.; Ren, D.; Lin, H. Astragaloside IV alleviates mouse slow transit constipation by modulating gut microbiota profile and promoting butyric acid generation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 9349–9361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Luo, P.; Liu, Y. The Astragaloside IV Derivative LS-102 Ameliorates Obesity-Related Nephropathy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 647–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Research Subject | Induction Methods | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| T2DM | Alleviates renal tubular epithelial–mesenchymal transdifferentiation through the CX3CL1-RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway | [45] | |
| Male diabetes nephropathy rats and | High-fat diet consisting of 8% lard, 10% yolk powder, 18% sucrose, and 0.5% sodium cholate | Downregulation of CD36 expression mediates FFA uptake and lipid accumulation | [46] |
| diabetic nephropathy rats | using streptozotocin administration in vivo | Inhibiting the excessive proliferation of HG-induced RMCs decreased TGF-β1, Smad3, col1, α-SMA mRNA and protein expression, and increased Smad7 mRNA and protein expression in vitro and in vivo | [47] |
| Male C57BL/6 mice with renal fibrosis | Unilateral ureteral occlusion (UUO) | Inhibition of TGF-β1 induced EMT | [48] |
| diabetic KK-Ay mice | Feeding KK-Ay mice a high-fat diet | Inducing autophagy and inhibiting MC activation through the SIRT1-NF-κB pathway | [49] |
| Male C57BL/6 mice with diabetes | Streptozotocin-induced | Inhibition of the activation of the MEK1/2ERK1/2-RSK2 signaling pathway | [50] |
| UUO mice | Unilateral ureteral obstruction | Inhibiting inflammation via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway | [51] |
| Primary renal fibroblasts of BALB/c mice | Treated with TGF-b1 | Inhibition of the C and NF-κB signaling pathways | [52] |
| Male Sprague–Dawley rats with renal fibrosis | Unilateral ureteral obstruction in vivo and TGF-b1-stimulated | Inhibition of TGF-b1, CTGF, a-SMA, and collagen matrix expression, decrease in serum creatinine and urea nitrogen, and upregulation of Smad7, thereby blocking upregulation of TGF-b1, CTGF, and a-SMA, and activation of phosphorylated-Smad2/3 | [53] |
| Male SPF Wistar rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction | Unilateral ureteral obstruction | Inhibition of tubular epithelial–mesenchymal transdifferentiation, fibroblast activation, and an increase in NO production in the kidney | [54] |
| Research Subject | Induction Methods | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male C57BL-6J mice with cardiac fibrosis | Isoprenaline | Increase of Akkermansia, Defluviitaleaceae_UCG-011, and Rikenella abundance and modulation of amino acid metabolism | [56] |
| Diabetic rats | High glucose/high fat and hypoxia culture condition | Prevented apoptosis and restored cardiac function in MI | [57] |
| Sprague–Dawley male rats with cardiomyopathy | Adriamycin | Suppressed oxidative stress to counter type I and III collagens, TGF-β, NOX2, and NOX4 expression, and SMAD2/3 activity in the left ventricles | [58] |
| Cardiac fibrosis rats | Isoprenaline | Inhibited cardiac fibrosis by targeting the miR-135a-TRPM7-TGF-β/Smads pathway | [59] |
| Male BALB/c mice with cardiac fibrosis | Isoprenaline | Inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway | [59] |
| Cardiac fibrosis rats | Isoprenaline | Inhibited hypoxia-induced cardiac fibrosis in vivo and in vitro is associated with reduced expression of TRPM7 | [60] |
| Male healthy Sprague-Dawley rats with cardiac fibroblast | Isoprenaline | Inhibited ISO-induced cardiac fibrosis proliferation and collagen production through negative regulation of ROS-mediated CT-1 upregulation | [61] |
| Sprague–Dawley rat pups (age, 1–3 days; weight, 7 ± 2 g) | Isoprenaline | Inhibited ISO-induced cardiac fibrosis by suppressing ROS-mediated MAPK activation | [62] |
| CVB3-induced inbred male BALB/c mice | CVB3 | Downregulated TGF-β1-Smad signaling | [63] |
| Acute viral myocarditis BALB/c mice | CVB3 | Downregulated TGF-β1-Smad signaling | [63] |
| Research Subject | Induction Methods | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary liver cancer mice | DEN/CCl4/C2H5OH (DCC) | Regulates reversibility and antagonism of pSmad3C and pSmad3L and promotes the phosphorylation of Nrf2 | [66] |
| Male Wistar rats with bile duct ligated | UUO | Induced accumulation of Nrf2 in the nucleus, synthesized antioxidant enzymes through negative regulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β, scavenged reactive oxygen species, and suppressed hepatic stellate cell activation in bile duct-ligated rats | [82] |
| HSC rat line HSC-T6 | Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) family | Promoted cellular senescence and apoptosis by activating the NF-κB pathway to suppress PDGF-BB-induced HSC-T6 activation | [83] |
| Liver fibrosis mice | Administered carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) to rats | Inhibition of HSC activation and modulation of the TGF-𝛽1/Smad signaling pathway | [84] |
| Hepatic stellate cells of rats | CCL4 | Inhibition of HSC activation and modulation of the TGF-𝛽1/Smad signaling pathway | [84] |
| Liver fibrosis C57BL/6 mice | Injection with DMN | Decreased collagen deposition, hydroxyproline content, and α-SMA expression levels in the liver tissues | [85] |
| Diabetic-CCL4 rats | CCL4 | Inhibited PAR2 signaling expression | [86] |
| Male Sprague–Dawley) rats with Cholestatic liver fibrosis | Common bile duct ligation (BDL) | Inhibition of the Notch signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting the abnormal proliferation of biliary epithelial cells | [87] |
| Hepatic stellate cells of normal male Sprague–Dawley rats | Sequential Pronase and collagenase perfusion | Inhibits HSC activation by inhibiting the generation of oxidative stress and associated p38 MAPK activation | [88] |
| Hepatic stellate cells of rats | Porcine serum | Inhibitory effects on collagen synthesis and proliferation in HSCs | [89] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Chen, B.; Liang, D.; Quan, X.; Gu, R.; Meng, Z.; Gan, H.; Wu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Pharmacological Effects of Astragaloside IV: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 6118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166118
Liang Y, Chen B, Liang D, Quan X, Gu R, Meng Z, Gan H, Wu Z, Sun Y, Liu S, et al. Pharmacological Effects of Astragaloside IV: A Review. Molecules. 2023; 28(16):6118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166118
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yutong, Biqiong Chen, Di Liang, Xiaoxiao Quan, Ruolan Gu, Zhiyun Meng, Hui Gan, Zhuona Wu, Yunbo Sun, Shuchen Liu, and et al. 2023. "Pharmacological Effects of Astragaloside IV: A Review" Molecules 28, no. 16: 6118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166118
APA StyleLiang, Y., Chen, B., Liang, D., Quan, X., Gu, R., Meng, Z., Gan, H., Wu, Z., Sun, Y., Liu, S., & Dou, G. (2023). Pharmacological Effects of Astragaloside IV: A Review. Molecules, 28(16), 6118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166118






