Discrimination of Radix Astragali from Different Growth Patterns, Origins, Species, and Growth Years by an H1-NMR Spectrogram of Polysaccharide Analysis Combined with Chemical Pattern Recognition and Determination of Its Polysaccharide Content and Immunological Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Information on the Collected Herb RA
2.2. Establishment of Data for Chemical Pattern Recognition
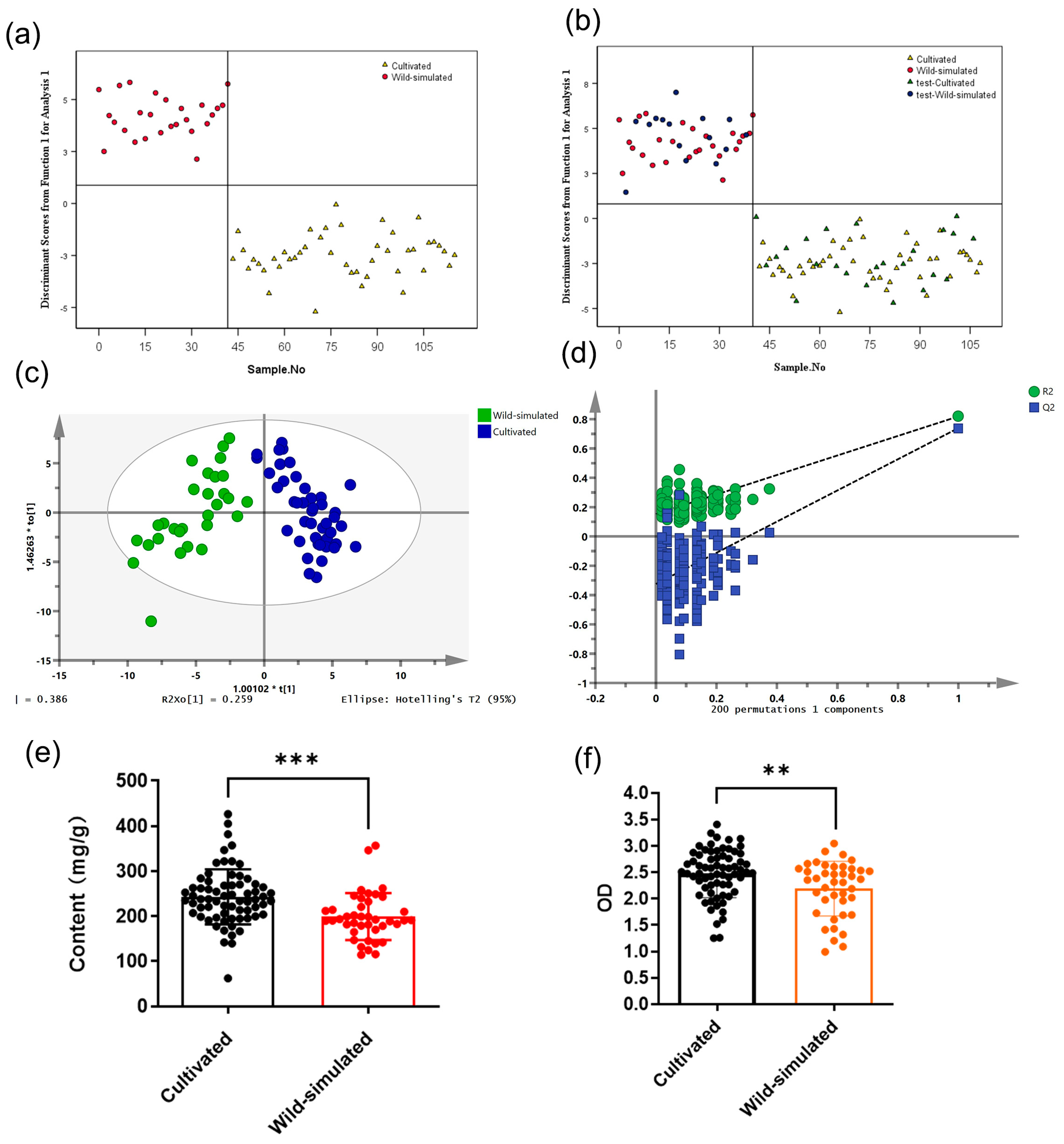
2.3. Identification and Analysis of Different Growth Patterns
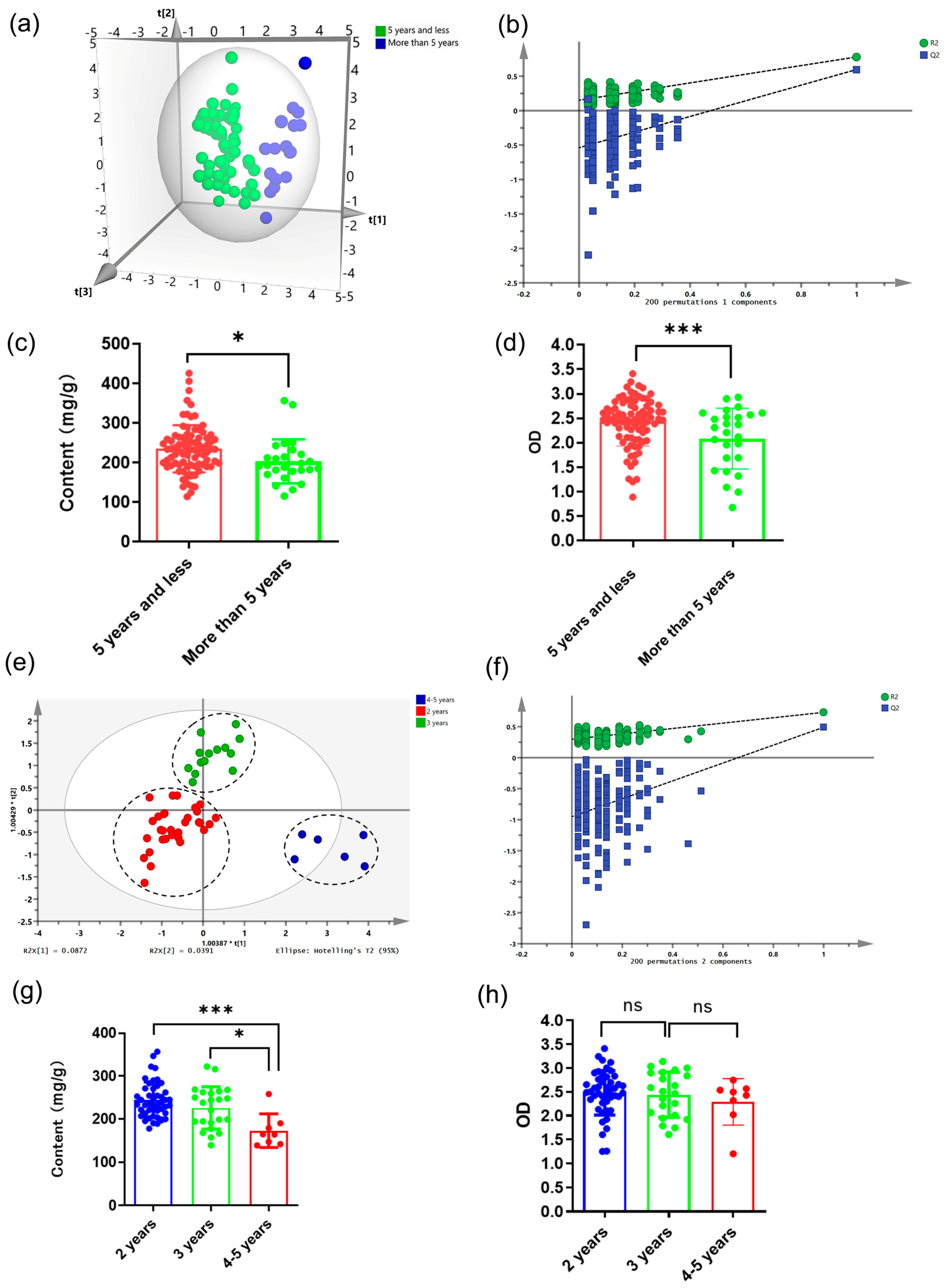
2.4. Identification and Analysis of Different Growth Years
2.5. Identification and Analysis of Different Species
2.6. Identification and Analysis of Different Origins
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals, Reagents, and Materials
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. NMR Measurements
3.4. Determination of the Polysaccharide Content
3.5. Cellular Phagocytosis of Neutral Red
3.6. Data Processing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Bi, Y.; Bao, H.; Zhang, C.; Yao, R.; Li, M. Quality control of Radix astragali (the root of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus) along its value chains. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 562376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z.; Huang, L. Application of Invigorating Qi and Moistening Intestines Method in Qi Deficiency Constipation. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. Res. 2022, 6, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medicine Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Liang, Y.; Fu, F. Effect of Shenqi Fuzheng Injection on leukopenia and T-cell subsets in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing radiotherapy. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 2832739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chiang, B. Anti-tumor activity of the fermentation broth of Cordyceps militaris cultured in the medium of Radix astragali. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleebrahim-Dehkordi, E.; Heidari-Soureshjani, E.; Aryan, A.; Ganjirad, Z.; Soveyzi, F.; Hoseinsalari, A.; Derisi, M.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Antiviral Compounds Based on Natural Astragalus polysaccharides (APS): Research and Foresight in the Strategies for Combating SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 2299–2307. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Niu, J.; Zhang, S.; Si, X.; Bian, T.; Wu, H.; Li, D.; Sun, Y.; Jia, J.; Xin, E.; et al. Comparative study on the gastrointestinal-and immune-regulation functions of Hedysari Radix Paeparata Cum Melle and Astragali Radix Praeparata cum Melle in rats with spleen-qi deficiency, based on fuzzy matter-element analysis. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 1237–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Yu, Q.; Yi, L.; Ren, M.; Een, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, P. Simultaneous determination of 15 marker constituents in various Radix Astragali preparations by solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Qi, L.; Liu, E.; Li, B.; Gao, W.; Li, P. Radix Astragali (Astragalus): Latest advancements and trends in chemistry, analysis, pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Curr. Org. Chem. 2010, 14, 1792–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, D.; Mai, Y.; Wei, B.; Wang, X. Concordance between antioxidant activities in vitro and chemical components of Radix Astragali (Huangqi). Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 1050–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Yang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Yi, T.; Chen, H. Comparison of the immunoregulatory function of different constituents in radix astragali and radix hedysari. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 479426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.; Sun, C. Natural polysaccharides and their derivates: A promising natural adjuvant for tumor immunotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 621813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Lai, J. Astragalus polysaccharide: A review of its immunomodulatory effect. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2022, 45, 367–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Cao, Y.; Jiao, S.; Du, G.; Du, Y.; Qin, X. Structural characterization and immune activity screening of polysaccharides with different molecular weights from Astragali Radix. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 582091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Jin, Q.; Wang, Q.; Shao, C.; Zhang, L.; Gan, Y.; Tian, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y. Effects of soil quality on effective ingredients of Astragalus mongholicus from the main cultivation regions in China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Mu, X.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Liiu, H.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, P. Plant metabolomics: A new strategy and tool for quality evaluation of Chinese medicinal materials. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Lai, Y.; Yang, Q.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y. Sustainable utilization of traditional chinese medicine resources: Systematic evaluation on different production modes. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 218901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Q. Recent advances in qualitative and quantitative analysis of polysaccharides in natural medicines: A critical review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 220, 115016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Zhao, K.; Huang, Q.; Shang, P. Structural features and biological activities of the polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L. The structures and biological functions of polysaccharides from traditional Chinese herbs. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 163, 423–444. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, X.; Su, M.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, J.; Zang, H.; Jiang, H.; Nie, L. A calibration method based on model updating strategy for the quantitative model of Radix Astragali extract. Microchem. J. 2022, 181, 107690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wan, H.; Huang, P.; Yang, J.; He, Y. A critical review of Astragalus polysaccharides: From therapeutic mechanisms to pharmaceutics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomin, V.H. NMR chemical shifts in structural biology of glycosaminoglycans. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Li, Z.; Jia, J.; Qin, X. Chemical comparison of coat and kernel of mung bean by nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolic spectrum approach. Spectrosc. Lett. 2016, 49, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yao, C.; Guo, D. Quality assessment of herbal medicines based on chemical fingerprints combined with chemometrics approach: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 185, 113215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, M.; Ren, X.; Jiang, M.; Deng, Y. Rapid authentication and differentiation of herbal medicine using 1H NMR fingerprints coupled with chemometrics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 160, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venditti, A.; Frezza, C.; Celona, D.; Sciubba, F.; Foddai, S.; Delfini, M.; Serafini, M.; Bianco, A. Phytochemical comparison with quantitative analysis between two flower phenotypes of Mentha aquatica L.: Pink-violet and white. AIMS Mol. Sci. 2017, 4, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, R.L.; Feng, Q.; Li, A. Status and analysis of Astragali Radix resource in China. J. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2013, 38, 3234–3238. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla-González, G.; Frey, M.; Gómez-Zeledón, J.; Da Costa, F.; Spring, O. Metabolomic and gene expression approaches reveal the developmental and environmental regulation of the secondary metabolism of yacón (Smallanthus sonchifolius, Asteraceae). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T/CACM 1021.4-2018; Commercial grades for Chinese materia medica–ASTRAGALI RADIX 中药材商品规格等级 黄芪. China Association of Chinese Medicine: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Qian, X.; Ciao, Q.; Zhang, R.; Li, K.; Li, A.; Liu, Y. Research progress on quality evaluation and product specification level of Mongolian Astragalus membranaceus. J. Shanxi. Med. Univ. 2019, 50, 854–859. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Zheng, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S. Review of the botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi). Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Guo, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J. Chemical discrimination of Astragalus mongholicus and Astragalus membranaceus based on metabolomics using UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS approach. Molecules 2019, 24, 4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Guo, B.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, Z.; Yi, T. Study of the relationship between genetics and geography in determining the quality of Astragali Radix. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.; Rui, W. Multi-fingerprint profiling combined with chemometric methods for investigating the quality of Astragalus polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, C.; Muhammad, S.; Ng, J.; Aziz, F.; Nasir, F.; Adenan, M.; Moosa, S.; Othman, Z.; Abdullah, S.; Muhammad, S.; et al. Detection of adulteration activities in edible bird’s nest using untargeted 1H-NMR metabolomics with chemometrics. Food Control 2022, 132, 108542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, H.; Peng, D.; Cheng, M.; Zha, L.; Huang, L. Evolution and characteristics of system, assessing quality by distinguishing features of traditional Chinese medicinal materials, of Dao-di herbs of Astragali Radix. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2017, 42, 1646–1651. [Google Scholar]


| Sample No. | Cultivation Patterns | Species | Origins (Province) | Growth Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Shanxi | 2 |
| S2 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Heilongjiang | 2 |
| S3 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Inner Mongolia | 1.5 |
| S4–S9 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Inner Mongolia | 2 |
| S10 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Inner Mongolia | 2.5 |
| S11–S14 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Inner Mongolia | 3 |
| S15–S19 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Inner Mongolia | 3.5 |
| S20 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Inner Mongolia | 4 |
| S21–S23 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Gansu | 1 |
| S24 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Gansu | 1.5 |
| S25–S38 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Gansu | 2 |
| S39–S41 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Gansu | 2.5 |
| S42–S44 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Gansu | 3 |
| S45–S48 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Gansu | 3.5 |
| S49–S50 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus | Xinjiang | 2 |
| S51–S58 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus | Shanxi | 2 |
| S59–S60 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus | Qinghai | 2 |
| S61–S68 | Cultivated | A. membranaceus | Gansu | 2 |
| S69–S71 | Wild-simulated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Shaanxi | 1 |
| S72–S74 | Wild-simulated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Shaanxi | 2 |
| S75–S77 | Wild-simulated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Shaanxi | 3 |
| S78–S81 | Wild-simulated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Shaanxi | 4 |
| S82–S84 | Wild-simulated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Shaanxi | 5 |
| S85–S91 | Wild-simulated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Shaanxi | 6 |
| S92–S99 | Wild-simulated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Shaanxi | 7 |
| S100–S104 | Wild-simulated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Shaanxi | 8 |
| S105–S106 | Wild-simulated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Shaanxi | 9 |
| S107–S109 | Wild-simulated | A. membranaceus var. Mongholicus | Shaanxi | 10 |
| Items of Model | Categories | Number of Samples | R2X | R2Y | Q2 | Number of Correct Classification (%) | Permutation Test (200 Permutations) | LOOCV Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Testing Set | Training Set | Testing Set | |||||||
| LDA | Cultivated | 44 | 24 | − | − | − | 70 (100%) | 39 (100%) | − | 100% |
| Wild-simulated | 26 | 15 | ||||||||
| OPLS-DA | Cultivated | 43 | 25 | 0.714 | 0.819 | 0.74 | 71 (100%) | 38 (100%) | 0.149 | − |
| Wild-simulated | 28 | 13 | ||||||||
| Items of OPLS-DA | Categories | Number of Samples | R2X | R2Y | Q2 | Number of Correct Classification (%) | Permutation Test (200 Permutations) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Testing Set | Training Set | Testing Set | ||||||
| Growth years | 5 years and less | 55 | 29 | 0.643 | 0.769 | 0.596 | 71 (100%) | 35 (92.1%) | 0.158 |
| More than 5 years | 16 | 9 | |||||||
| Growth years (5 years and less) | 2 years | 31 | 9 | 0.911 | 0.806 | 0.518 | 51 (100%) | 23 (92%) | 0.298 |
| 3 years | 14 | 14 | |||||||
| 4~5 years | 6 | 2 | |||||||
| Items of Model | Categories | Number of Samples | R2X | R2Y | Q2 | Number of Correct Classification (%) | Permutation Test (200 Permutations) | LOOCV Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Testing Set | Training Set | Testing Set | |||||||
| LDA | MG | 64 | 26 | − | − | − | 77 (100%) | 32 (100%) | − | 96.1% |
| MJ | 13 | 6 | ||||||||
| OPLS-DA | MG | 60 | 30 | 0.847 | 0.823 | 0.699 | 72 (100%) | 36 (97.3%) | 0.115 | − |
| MJ | 12 | 7 | ||||||||
| Items of Model | Categories | Number of Samples | R2X | R2Y | Q2 | Number of Correct Classification (%) | Permutation Test (200 Permutations) | LOOCV Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Testing Set | Training Set | Testing Set | |||||||
| LDA | Inner Mongolia | 12 | 7 | − | − | − | 61 (100%) | 26 (92.9%) | − | 100% |
| Gansu | 20 | 9 | ||||||||
| Shaanxi | 29 | 12 | ||||||||
| OPLS-DA | Inner Mongolia | 10 | 9 | 0.805 | 0.808 | 0.685 | 59 (100%) | 29 (96.6%) | 0.154 | − |
| Gansu | 20 | 9 | ||||||||
| Shaanxi | 29 | 12 | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Wang, B.; Gu, L.; Yin, G.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.-A.; Wang, T. Discrimination of Radix Astragali from Different Growth Patterns, Origins, Species, and Growth Years by an H1-NMR Spectrogram of Polysaccharide Analysis Combined with Chemical Pattern Recognition and Determination of Its Polysaccharide Content and Immunological Activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 6063. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166063
Guo Y, Wang B, Gu L, Yin G, Wang S, Li M, Wang L, Yu X-A, Wang T. Discrimination of Radix Astragali from Different Growth Patterns, Origins, Species, and Growth Years by an H1-NMR Spectrogram of Polysaccharide Analysis Combined with Chemical Pattern Recognition and Determination of Its Polysaccharide Content and Immunological Activity. Molecules. 2023; 28(16):6063. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166063
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yali, Bing Wang, Lifei Gu, Guo Yin, Shuhong Wang, Meifang Li, Lijun Wang, Xie-An Yu, and Tiejie Wang. 2023. "Discrimination of Radix Astragali from Different Growth Patterns, Origins, Species, and Growth Years by an H1-NMR Spectrogram of Polysaccharide Analysis Combined with Chemical Pattern Recognition and Determination of Its Polysaccharide Content and Immunological Activity" Molecules 28, no. 16: 6063. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166063
APA StyleGuo, Y., Wang, B., Gu, L., Yin, G., Wang, S., Li, M., Wang, L., Yu, X.-A., & Wang, T. (2023). Discrimination of Radix Astragali from Different Growth Patterns, Origins, Species, and Growth Years by an H1-NMR Spectrogram of Polysaccharide Analysis Combined with Chemical Pattern Recognition and Determination of Its Polysaccharide Content and Immunological Activity. Molecules, 28(16), 6063. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166063







