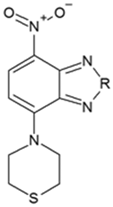
A New and Fast-Response Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Hypochlorous Acid Derived from Myeloperoxidase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
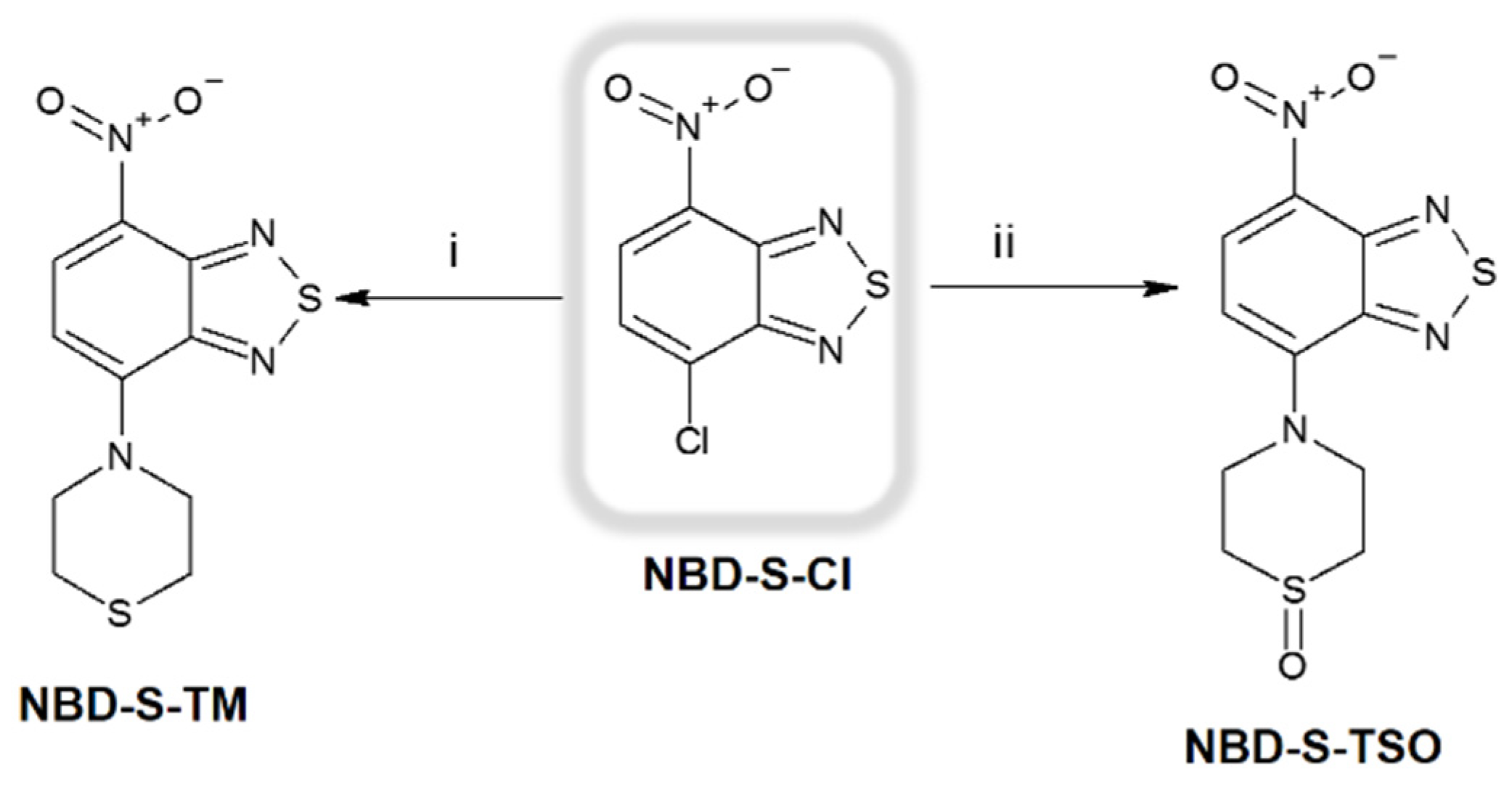
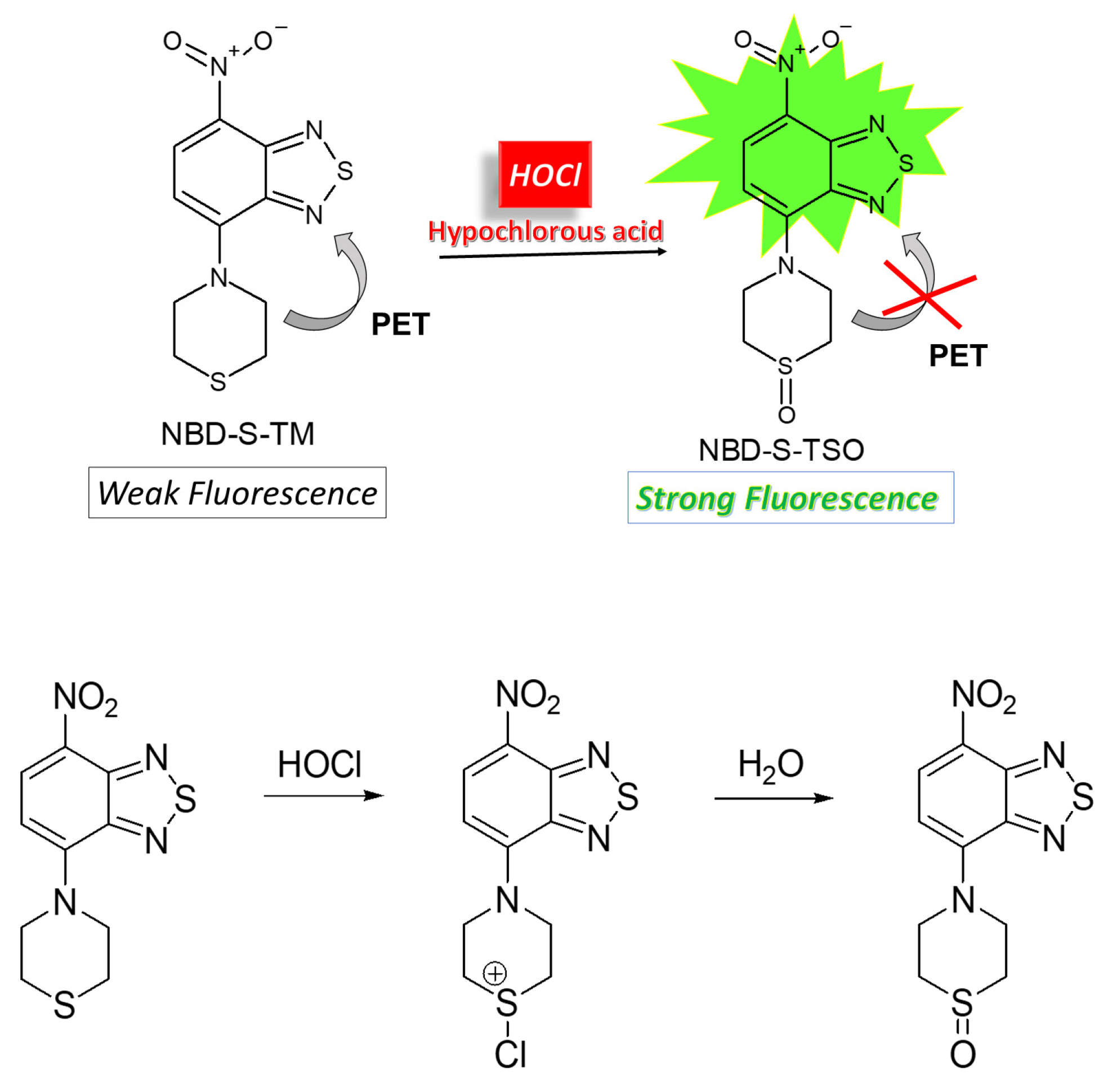
2.1. Molecular Design and Synthesis
2.2. Spectroscopic Characterization of the Probe and its Oxidation Product
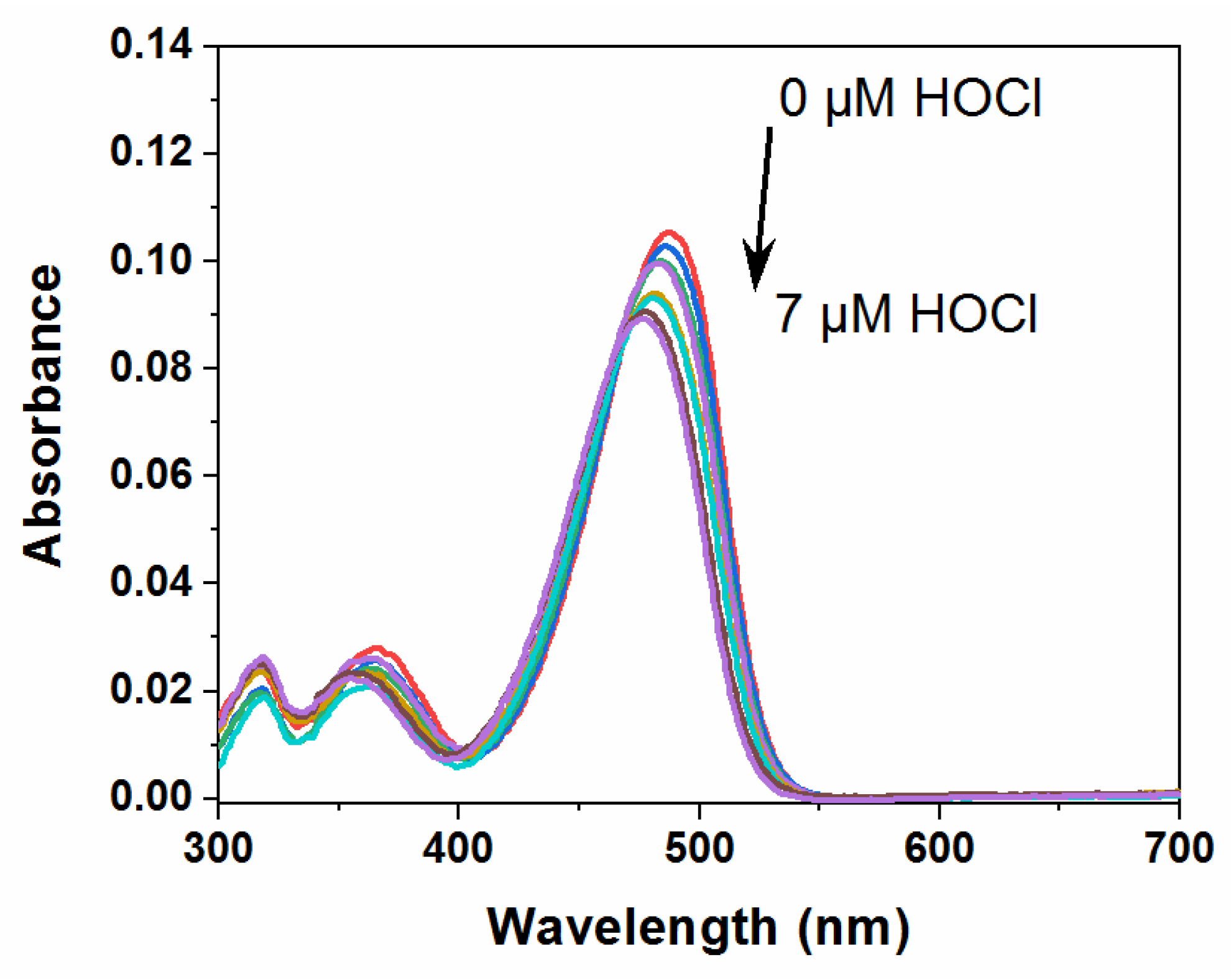
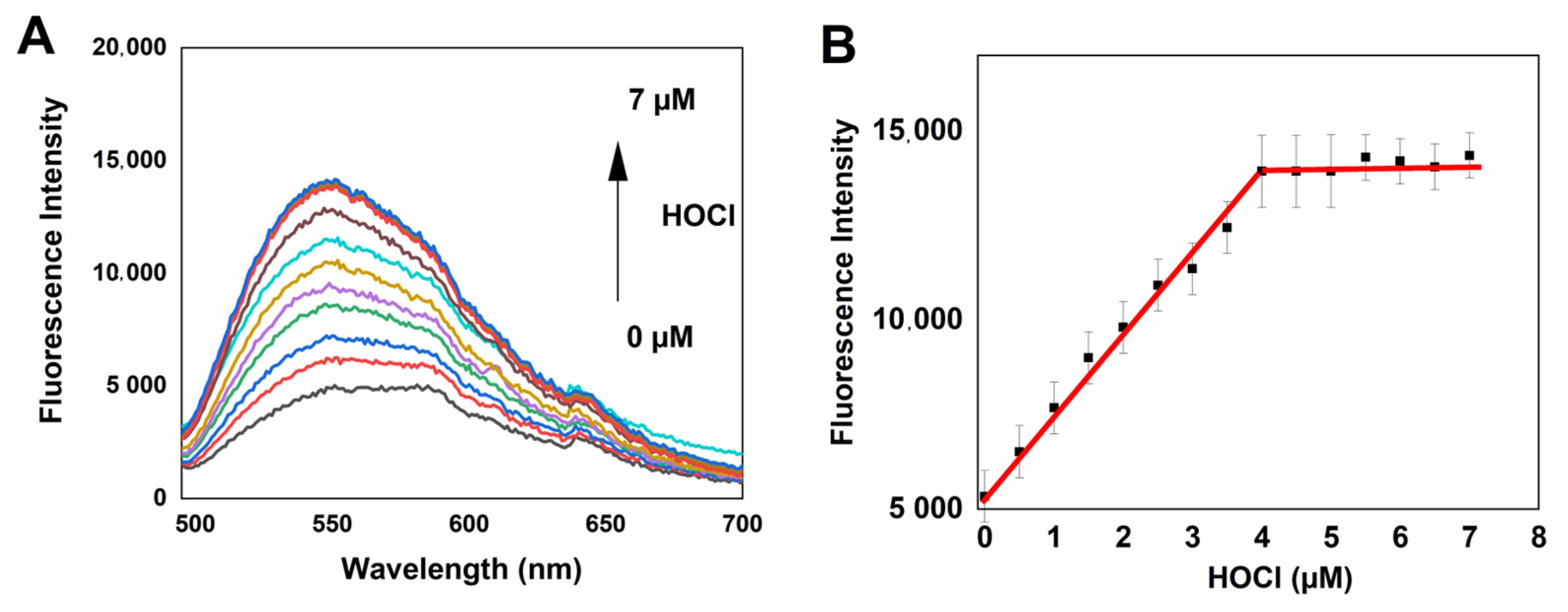
2.3. Spectral Response of NBD-S-TM to HOCl
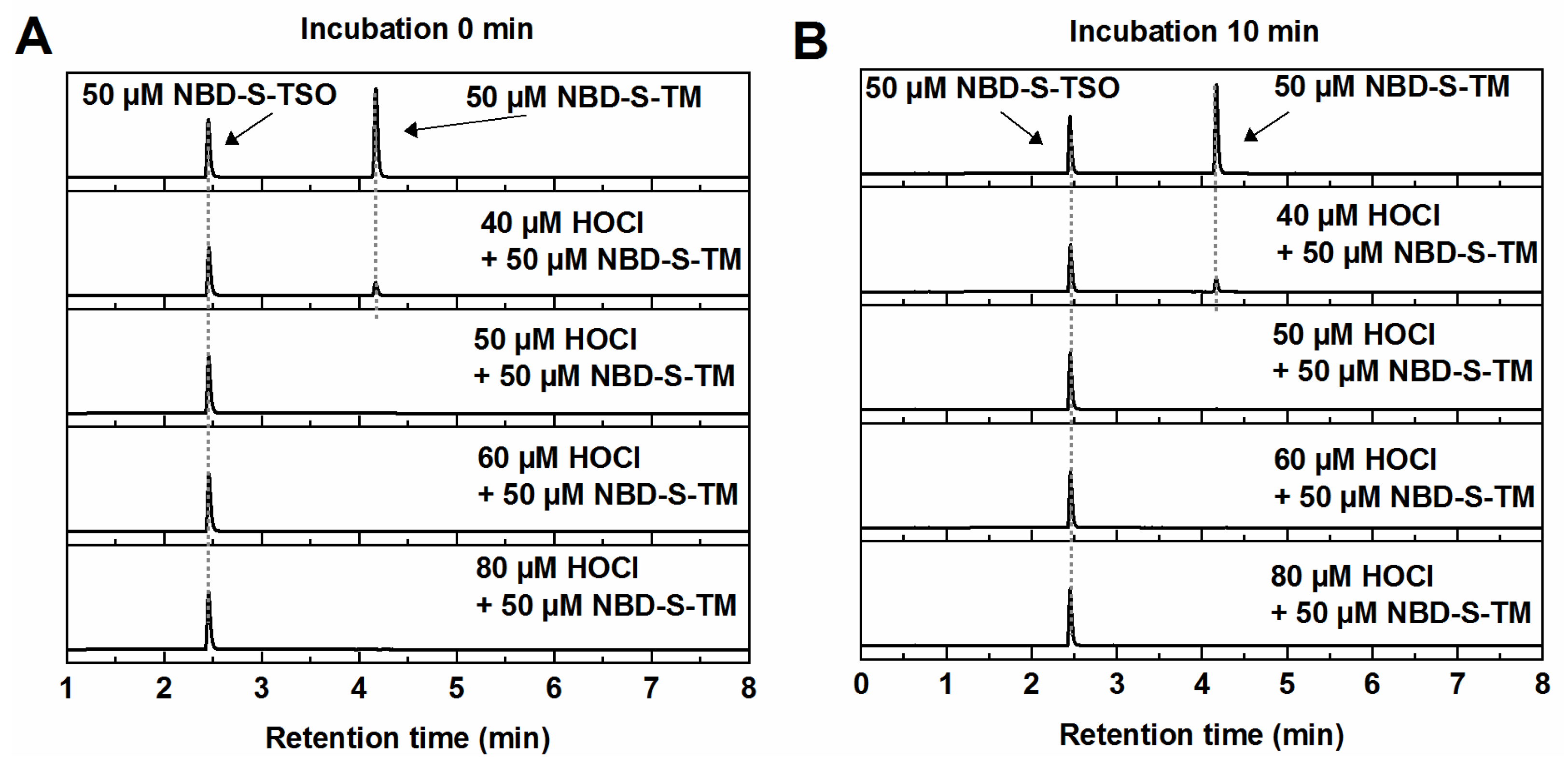
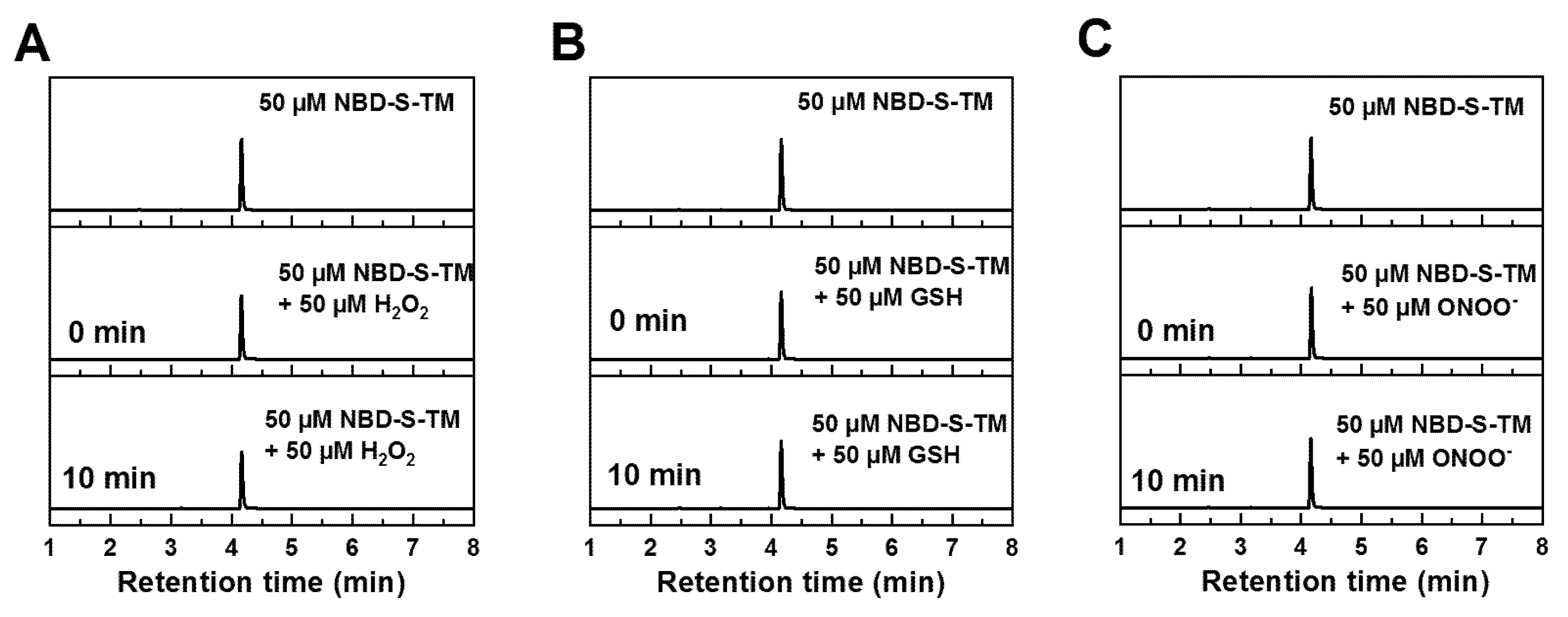
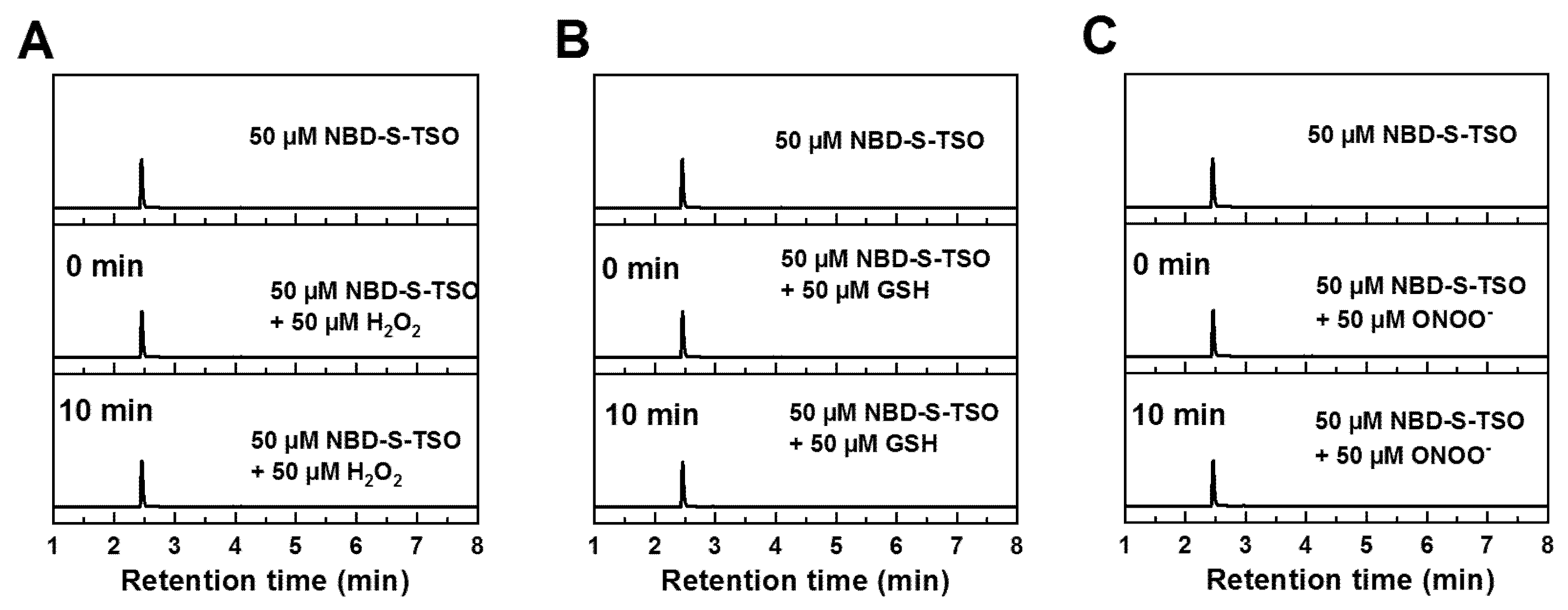
2.4. HPLC Titration
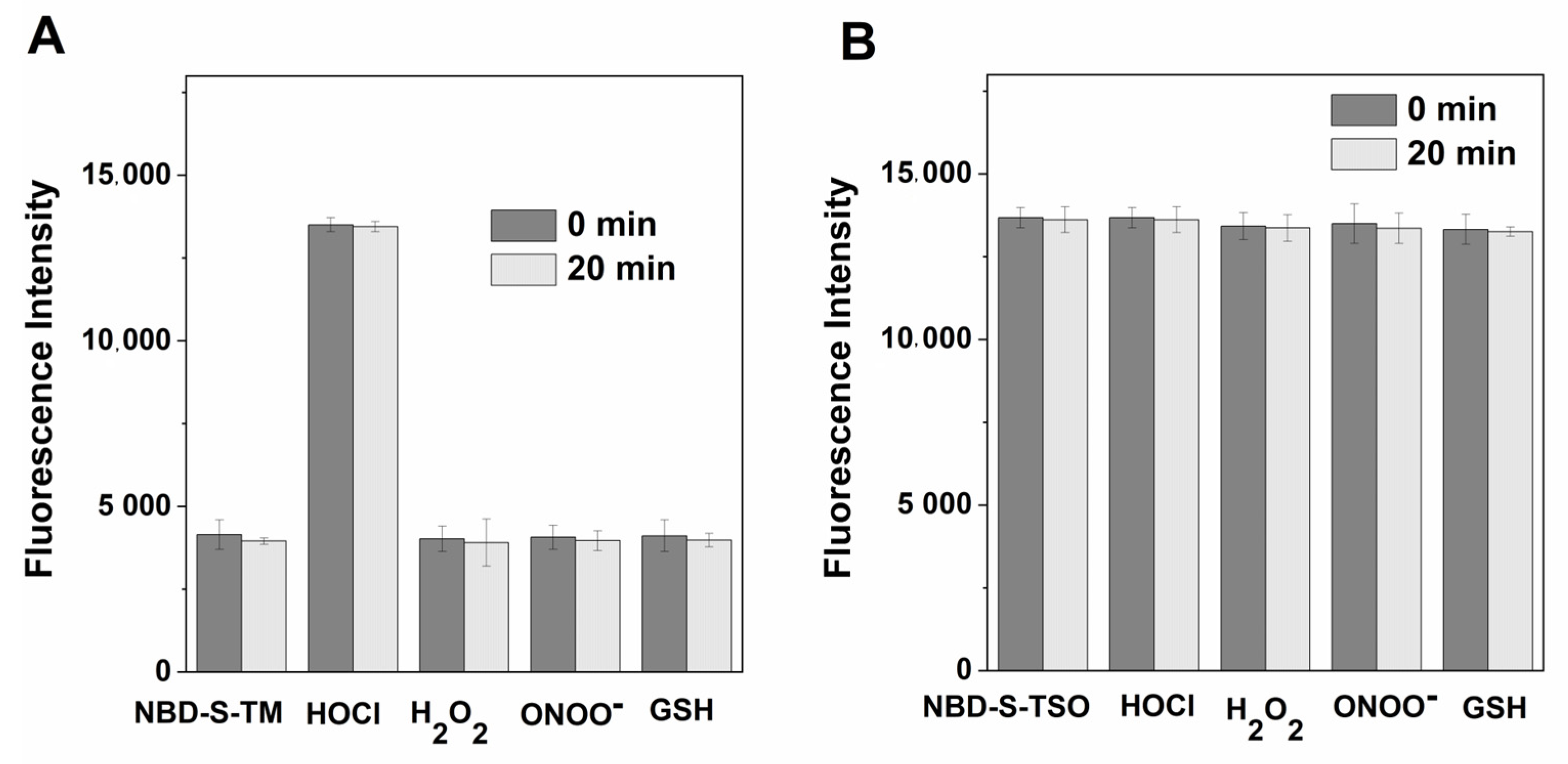
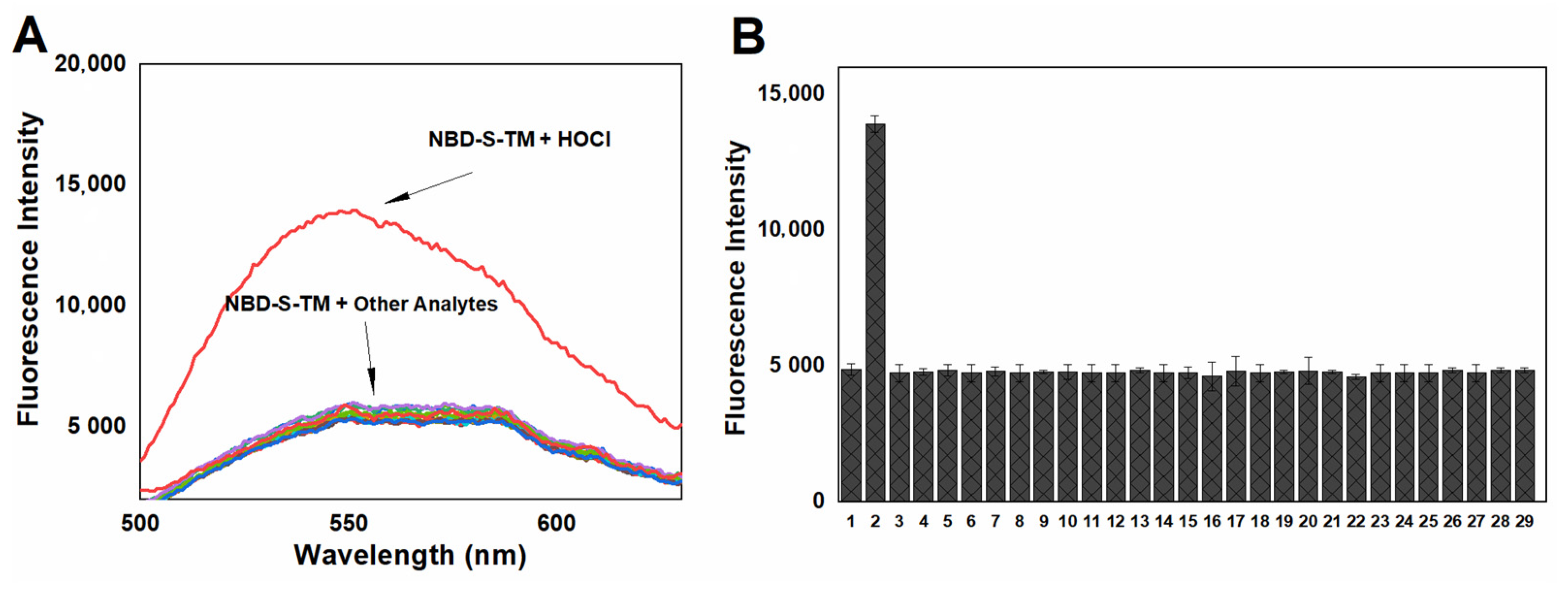
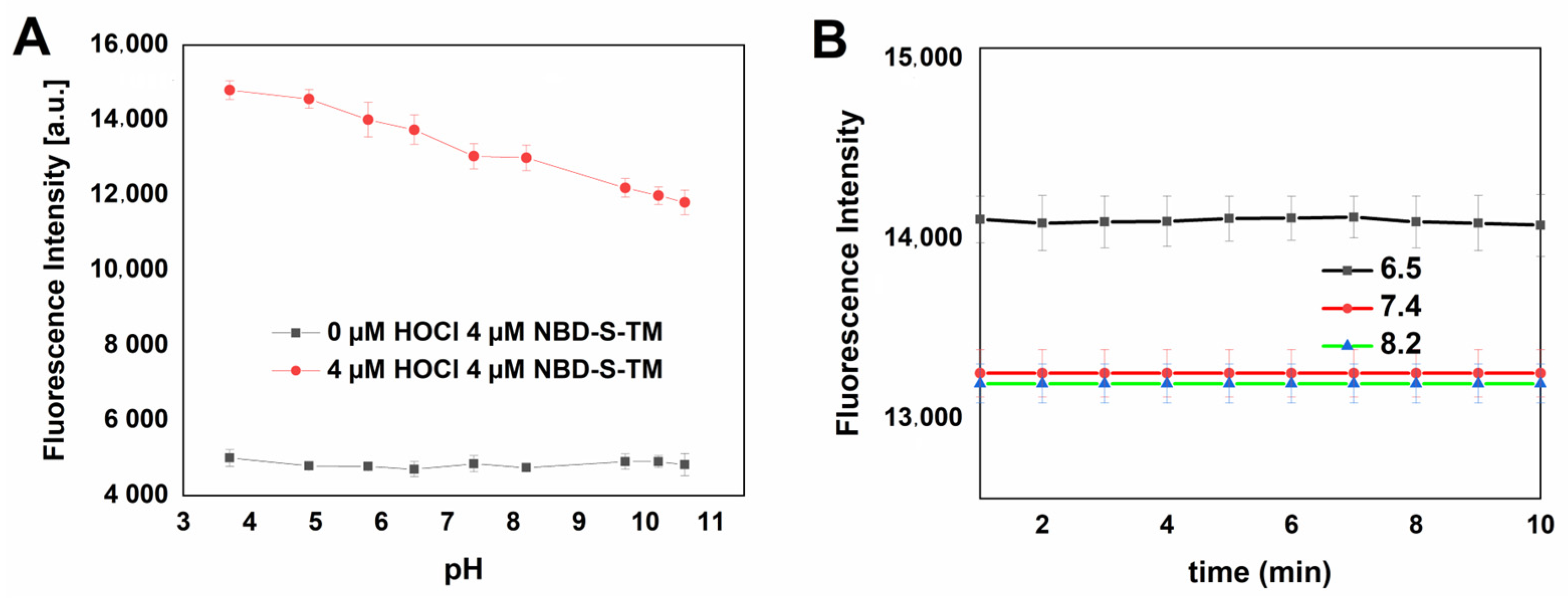
2.5. Stability and Selectivity Studies
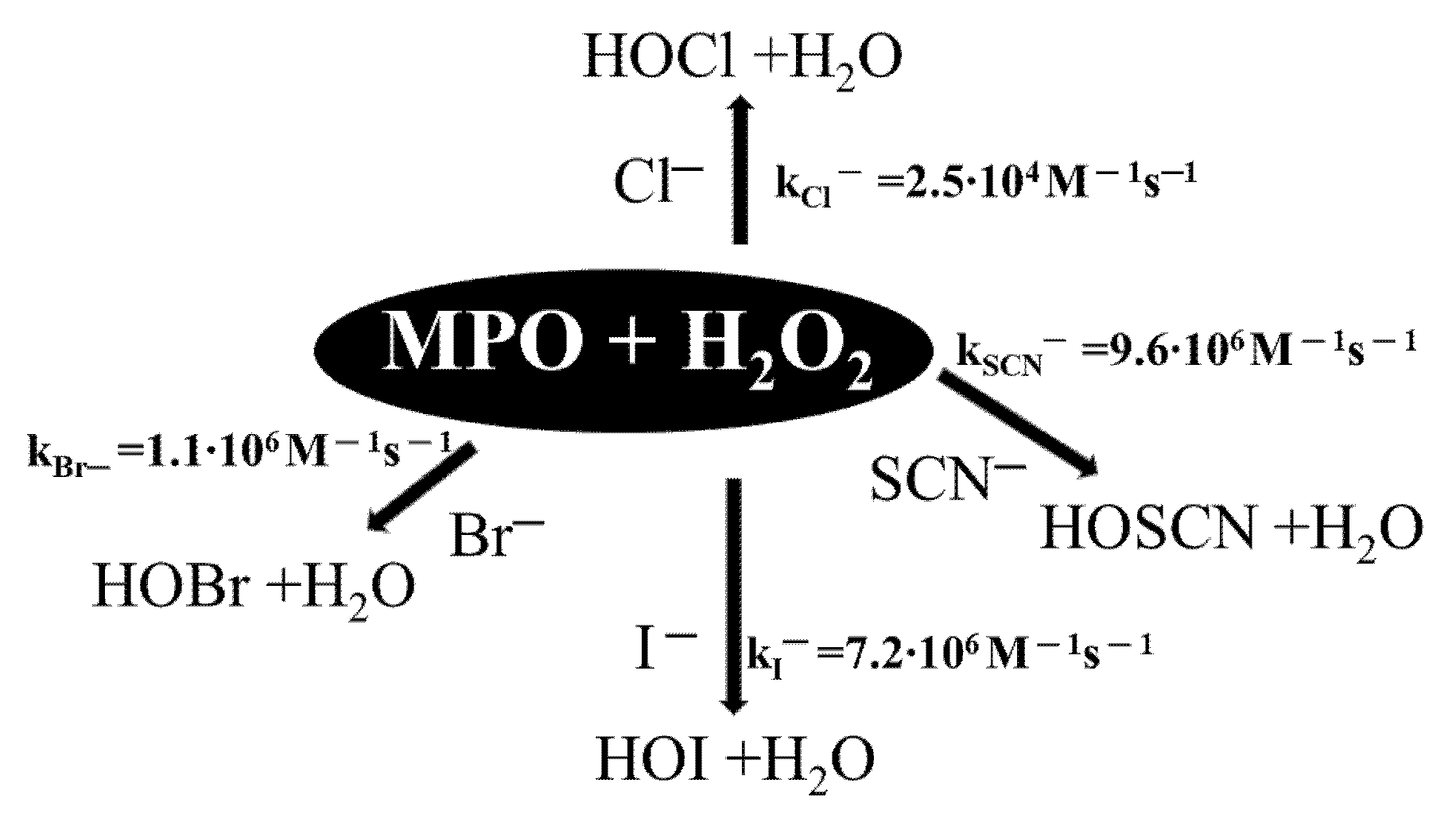
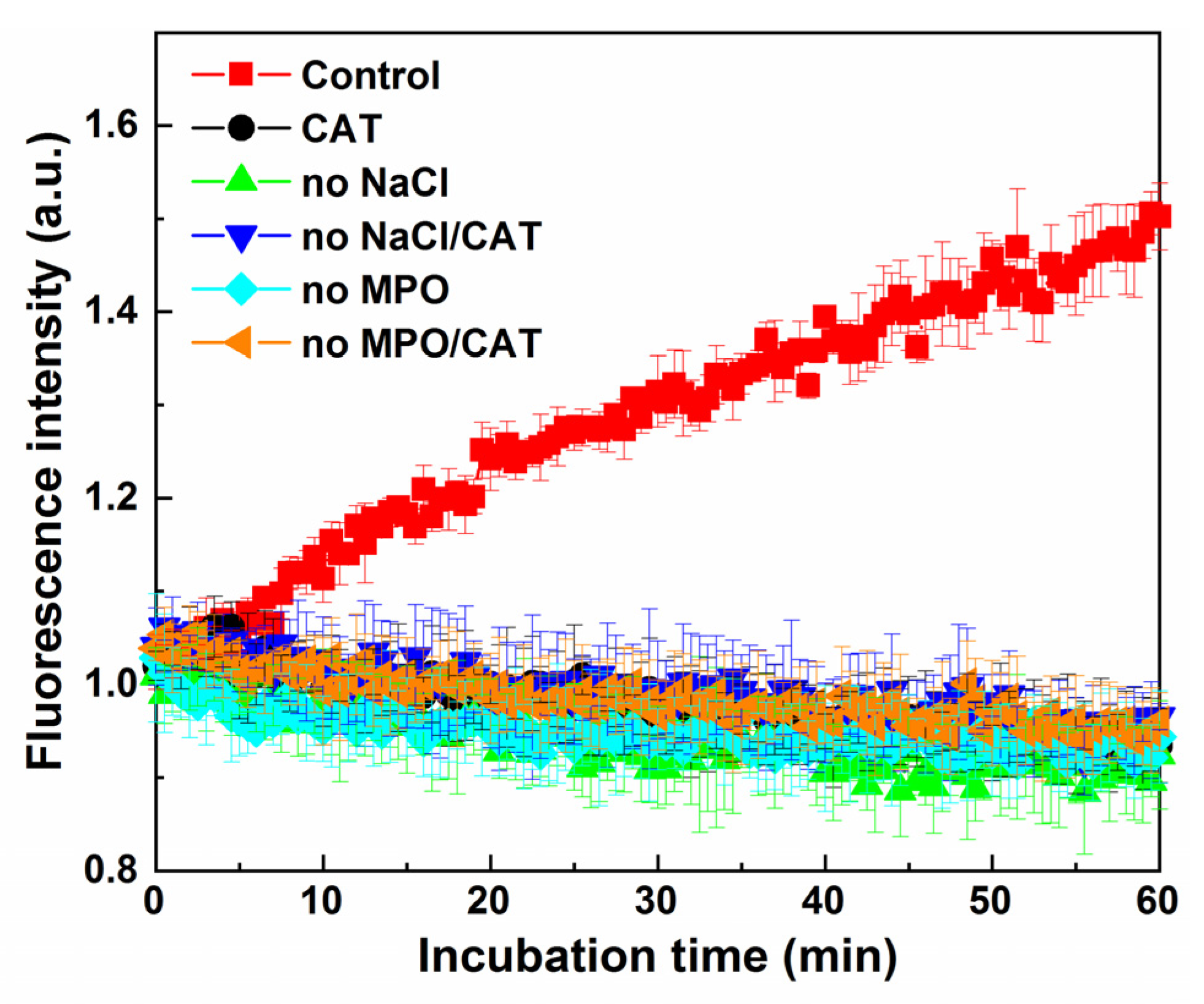
2.6. Oxidation of NBD-S-TM via the MPO/H2O2 System
2.7. Kinetic Measurements
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3.2. Synthesis
3.3. Solutions Preparation
3.4. Spectral Measurements
3.5. HPLC Analyses
3.6. Plate Reader Measurements
3.7. Kinetic Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Davies, M.J. Myeloperoxidase: Mechanisms, Reactions and Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy in Inflammatory Diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 218, 107685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, C.L.; Davies, M.J. Role of Myeloperoxidase and Oxidant Formation in the Extracellular Environment in Inflammation-Induced Tissue Damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 172, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterbourn, C.C. Reconciling the Chemistry and Biology of Reactive Oxygen Species. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulfig, A.; Leichert, L.I. The Effects of Neutrophil-Generated Hypochlorous Acid and Other Hypohalous Acids on Host and Pathogens. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 385–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Hawkins, C.L.; Pattison, D.I.; Rees, M.D. Mammalian Heme Peroxidases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Health Implications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 1199–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Chuang, C.Y.; Malle, E.; Gamon, L.F.; Hawkins, C.L.; Davies, M.J. Influence of Plasma Halide, Pseudohalide and Nitrite Ions on Myeloperoxidase-Mediated Protein and Extracellular Matrix Damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 188, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Yu, P.; Zhuang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, L.; Ping, Y.; Liu, W.; Tao, Z. High Concentrations of Hypochlorous Acid-Based Disinfectant in the Environment Reduced the Load of SARS-CoV-2 in Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, C.M.C.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Juan, C.A.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. Hypochlorous Acid Chemistry in Mammalian Cells-Influence on Infection and Role in Various Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Hawkins, C.L. The Role of Myeloperoxidase in Biomolecule Modification, Chronic Inflammation, and Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 32, 957–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, D.I.; Davies, M.J. Reactions of Myeloperoxidase-Derived Oxidants with Biological Substrates: Gaining Chemical Insight into Human Inflammatory Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 3271–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Crossett, B.; Cordwell, S.J.; Pattison, D.I.; Davies, M.J. Characterization of Disulfide (Cystine) Oxidation by HOCl in a Model Peptide: Evidence for Oxygen Addition, Disulfide Bond Cleavage and Adduct Formation with Thiols. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 154, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattison, D.I.; Davies, M.J. Absolute Rate Constants for the Reaction of Hypochlorous Acid with Protein Side Chains and Peptide Bonds. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hammer, A.; Hoefler, G.; Malle, E.; Hawkins, C.L.; Chuang, C.Y.; Davies, M.J. Hypochlorous Acid and Chloramines Induce Specific Fragmentation and Cross-Linking of the G1-IGD-G2 Domains of Recombinant Human Aggrecan, and Inhibit ADAMTS1 Activity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flouda, K.; Gammelgaard, B.; Davies, M.J.; Hawkins, C.L. Modulation of Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) Induced Damage to Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells by Thiocyanate and Selenium Analogues. Redox Biol. 2021, 41, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, G.-J.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Dong, W.-P.; Meng, H.-M.; Wang, Q.-Q.; Luo, X.-F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. A Lysosome-Targetable Two-Photon Excited near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe for Visualizing Hypochlorous Acid-Involved Arthritis and Its Treatment. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 249, 119326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Yang, R.; Chen, C.; Zhao, W. Imaging Endogenous HClO in Atherosclerosis Using a Novel Fast-Response Fluorescence Probe. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2598–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.; Qian, Y. A Novel Red-Emission Phenothiazine Fluorescent Protein Chromophore Based on Oxygen-chlorine Bond (O–Cl) Formation for Real-Time Detection of Hypochlorous Acid in Cells. Talanta 2021, 222, 121503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisic, B.; Miric, D.; Dragojevic, I.; Rasic, J.; Popovic, L. Role of Myeloperoxidase in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 1069743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Yu, H.; Zhu, W.; Yao, X.; Liu, W.; Yang, S.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y. Near Infrared Fluorescent Probe for in Vivo Bioimaging of Endogenous Hypochlorous Acid. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 188, 109218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantry, I.Q.; Waris, S.; Habib, S.; Khan, R.H.; Mahmood, R.; Ali, A. Hypochlorous Acid Induced Structural and Conformational Modifications in Human DNA: A Multi-Spectroscopic Study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravalika, K.; Sarmah, D.; Kaur, H.; Wanve, M.; Saraf, J.; Kalia, K.; Borah, A.; Yavagal, D.R.; Dave, K.R.; Bhattacharya, P. Myeloperoxidase and Neurological Disorder: A Crosstalk. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndrepepa, G. Myeloperoxidase—A Bridge Linking Inflammation and Oxidative Stress with Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 493, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aratani, Y. Myeloperoxidase: Its Role for Host Defense, Inflammation, and Neutrophil Function. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 640, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, M.; Wu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jia, P. A Highly Specific Far-Red Fluorescent Probe for Imaging Endogenous Peroxynitrite in the Mitochondria of Living Cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Li, Y.; Niu, J.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, B. Small-Molecule Fluorescent Probes for Imaging and Detection of Reactive Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Species in Biological Systems. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 533–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Huo, F.; Yin, C.; Escobedo, J.O.; Strongin, R.M. Recent Progress in Chromogenic and Fluorogenic Chemosensors for Hypochlorous Acid. Analyst 2016, 141, 1859–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Gao, Y.; Liu, T.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Du, L.; Li, M. Bioluminescent Probe for Detecting Endogenous Hypochlorite in Living Mice. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Guo, S.; Hu, C.; Fan, J.; Peng, X. Recent Development of Chemosensors Based on Cyanine Platforms. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7768–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.-T.; Ren, W.X.; Li, K.; Seo, J.; Sharma, A.; Yu, X.-Q.; Kim, J.S. Fluorescent Bioimaging of PH: From Design to Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2076–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, W.-T.; Han, H.-H.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Zhu, G.-B.; Zang, Y.; Yang, X.-R.; Yoon, J.; James, T.D.; Li, J.; He, X.-P. Fluorescent Probes for the Detection of Disease-Associated Biomarkers. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 853–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanaraman, B.; Darley-Usmar, V.; Davies, K.J.A.; Dennery, P.A.; Forman, H.J.; Grisham, M.B.; Mann, G.E.; Moore, K.; Roberts, L.J.; Ischiropoulos, H. Measuring Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species with Fluorescent Probes: Challenges and Limitations. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Huang, J.; Fang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Peng, C.; Dehaen, W. Fluorescent Probes for Ozone-Specific Recognition: An Historical Overview and Future Perspectives. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 38, e00201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sheng, Z.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.-Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y. Near-Infrared Fluorescence Probes for Monitoring and Diagnosing Nephron-Urological Diseases. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 486, 215137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Hou, S.; Zhao, N.; Finney, N.; Wang, Y. A Novel Colorimetric and Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Lysosomal HOCl in Real Time. Dye. Pigment. 2022, 204, 110394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świerczyńska, M.; Słowiński, D.; Grzelakowska, A.; Szala, M.; Romański, J.; Pierzchała, K.; Siarkiewicz, P.; Michalski, R.; Podsiadły, R. Selective, Stoichiometric and Fast-Response Fluorescent Probe Based on 7-Nitrobenz-2-Oxa-1,3-Diazole Fluorophore for Hypochlorous Acid Detection. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 193, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świerczyńska, M.; Słowiński, D.; Michalski, R.; Romański, J.; Podsiadły, R. A Thiomorpholine-Based Fluorescent Probe for the Far-Red Hypochlorous Acid Monitoring. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 289, 122193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierzchała, K.; Pięta, M.; Rola, M.; Świerczyńska, M.; Artelska, A.; Dębowska, K.; Podsiadły, R.; Pięta, J.; Zielonka, J.; Sikora, A.; et al. Fluorescent Probes for Monitoring Myeloperoxidase-Derived Hypochlorous Acid: A Comparative Study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Qiu, X.; Xi, Z.; Yi, L. Investigation of Thiolysis of NBD Amines for the Development of H2S Probes and Evaluating the Stability of NBD Dyes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 11117–11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, M. Multi-Responsive Fluorescence Sensing Based on a Donor-Acceptor-Donor Molecule for Highly Sensitive Detection of Water and Cyanide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 245, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, G.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Jin, D. Highly Responsive Hydrazine Sensors Based on Donor–Acceptor Perylene Diimides: Impact of Electron-Donating Groups. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 19037–19044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldeab, A.O.; Li, L.; Cekli, S.; Abboud, K.A.; Schanze, K.S.; Castellano, R.K. Pyridine-Terminated Low Gap π-Conjugated Oligomers: Design, Synthesis, and Photophysical Response to Protonation and Metalation. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 3170–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madushani, B.; Mamada, M.; Goushi, K.; Nguyen, T.B.; Nakanotani, H.; Kaji, H.; Adachi, C. Multiple Donor–Acceptor Design for Highly Luminescent and Stable Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Emitters. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudim, N.S.; Knyazeva, E.A.; Mikhalchenko, L.V.; Golovanov, I.S.; Popov, V.V.; Obruchnikova, N.V.; Rakitin, O.A. Benzothiadiazole vs. Iso-Benzothiadiazole: Synthesis, Electrochemical and Optical Properties of D–A–D Conjugated Molecules Based on Them. Molecules 2021, 26, 4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storkey, C.; Davies, M.J.; Pattison, D.I. Reevaluation of the Rate Constants for the Reaction of Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) with Cysteine, Methionine, and Peptide Derivatives Using a New Competition Kinetic Approach. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 73, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Huang, X.-Q.; Lin, Y.; Yang, D.-Y.; Lv, Y.-J.; Cao, X.-Q.; Zhang, G.-X.; Dong, J.; Shen, S.-L. A New Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Sensing Lysosomal HOCl Based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Strategy. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 223, 117355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.-S.; Thirumalaivasan, N.; Lin, T.-C.; Wu, S.-P. Ultrasensitive and Specific Two-Photon Fluorescence Detection of Hypochlorous Acid by a Lysosome-Targeting Fluorescent Probe for Cell Imaging. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 190, 113545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umberger, J.Q.; LaMer, V.K. The Kinetics of Diffusion Controlled Molecular and Ionic Reactions in Solution as Determined by Measurements of the Quenching of Fluorescence1,2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1945, 67, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, A.; Zielonka, J.; Dębowska, K.; Michalski, R.; Smulik-Izydorczyk, R.; Pięta, J.; Podsiadły, R.; Artelska, A.; Pierzchała, K.; Kalyanaraman, B. Boronate-Based Probes for Biological Oxidants: A Novel Class of Molecular Tools for Redox Biology. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 580899. [Google Scholar]
- Słowiński, D.; Świerczyńska, M.; Grzelakowska, A.; Szala, M.; Kolińska, J.; Romański, J.; Podsiadły, R. Hymecromone Naphthoquinone Ethers as Probes for Hydrogen Sulfide Detection. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 196, 109765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słowiński, D.; Świerczyńska, M.; Romański, J.; Podsiadły, R. HPLC Study of Product Formed in the Reaction of NBD-Derived Fluorescent Probe with Hydrogen Sulfide, Cysteine, N-Acetylcysteine, and Glutathione. Molecules 2022, 27, 8305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, X.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent and Colorimetric Probes for Detection of Thiols. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 2120–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noctor, G.; Queval, G.; Mhamdi, A.; Chaouch, S.; Foyer, C.H. Glutathione. Arab. Book 2011, 9, e0142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, K.; Jakob, U. The Role of Thiols in Antioxidant Systems. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 140, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashoka, A.H.; Ali, F.; Tiwari, R.; Kumari, R.; Pramanik, S.K.; Das, A. Recent Advances in Fluorescent Probes for Detection of HOCl and HNO. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 1730–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Y.; Ding, C.; Lu, C. Luminescent Probes for Hypochlorous Acid in Vitro and in Vivo. Analyst 2020, 145, 5068–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-R.; Wu, S.-P. Hypochlorous Acid Turn-on Fluorescent Probe Based on Oxidation of Diphenyl Selenide. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 878–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, S.; Kong, X.; Cui, J.; Su, S.; Shu, W.; Jing, J.; Zhang, X. Revealing the Redox Status in Endoplasmic Reticulum by a Selenium Fluorescence Probe. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 2660–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radi, R. Oxygen Radicals, Nitric Oxide, and Peroxynitrite: Redox Pathways in Molecular Medicine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5839–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Murfin, L.C.; Wu, L.; Lewis, S.E.; James, T.D. Fluorescent Small Organic Probes for Biosensing. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 3406–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, N. Recent Advances in Fluorescent Probes for the Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-L.; Gan, H.-Q.; Meng, F.-D.; Han, H.-H.; Shi, D.-T.; Zhang, S.; Zou, L.; He, X.-P.; James, T.D. Fluorescent Probes and Functional Materials for Biomedical Applications. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 1425–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reut, V.E.; Gorudko, I.V.; Grigorieva, D.V.; Sokolov, A.V.; Panasenko, O.M. Fluorescent Probes for HOCl Detection in Living Cells. Russ. J. Bioorganic Chem. 2022, 48, 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Chen, Z.; Yang, M.; Lv, J.; Li, H.; Gao, J.; Yuan, Z. A Hydroxytricyanopyrrole-Based Fluorescent Probe for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Hypochlorous Acid. Molecules 2022, 27, 7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.J.; Wong, N.-K.; Lu, M.-Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, S.; Zhao, A.Q.; Gao, P.; Kao, R.Y.-T.; Shen, J.; Yang, D. HKOCl-3: A Fluorescent Hypochlorous Acid Probe for Live-Cell and in Vivo Imaging and Quantitative Application in Flow Cytometry and a 96-Well Microplate Assay. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Chen, J.; Yu, S.; Liu, Z.; Ma, M. The Development of a 4-Aminonaphthalimide-Based Highly Selective Fluorescent Probe for Rapid Detection of HOCl. J. Fluoresc. 2022, 32, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohle, D.S.; Glassbrenner, P.A.; Hansert, B. Syntheses of Pure Tetramethylammonium Peroxynitrite. Methods Enzymol. 1996, 269, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Goshisht, M.; Tripathi, N.; Kumar Patra, G.; Chaskar, M. Organelle-Targeting Ratiometric Fluorescent Probes: Design Principles, Detection Mechanisms, Bio-Applications, and Challenges. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 5842–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Yang, T.; Han, Y. A TICT-Based Fluorescent Probe for Hypochlorous Acid and Its Application to Cellular and Zebrafish Imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 392, 134041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, S.; Bing, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Zou, X.; Qu, Z. A Simple ICT-Based Fluorescent Probe for HOCl and Bioimaging Applications. Biosensors 2023, 13, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, X.; Fang, M.; Xu, Y. In Vivo Bioimaging and Detection of Endogenous Hypochlorous Acid in Lysosome Using a Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 3188–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Yang, B.; Guo, T.; Tian, R.; Qiu, S.; Chen, X.; Geng, Z.; Wang, Z. A Dual-Response Mitochondria-Targeted NIR Fluorescent Probe with Large Stokes Shift for Monitoring Viscosity and HOCl in Living Cells and Zebrafish. Analyst 2023, 148, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Z.; Yang, X.; Meng, Q.; Tian, S.; Zhang, Z. A Ratiometric Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe for the Detection and Monitoring of Hypochlorous Acid in Rheumatoid Arthritis Model and Real Water Samples. Smart Mol. 2023, e20220007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
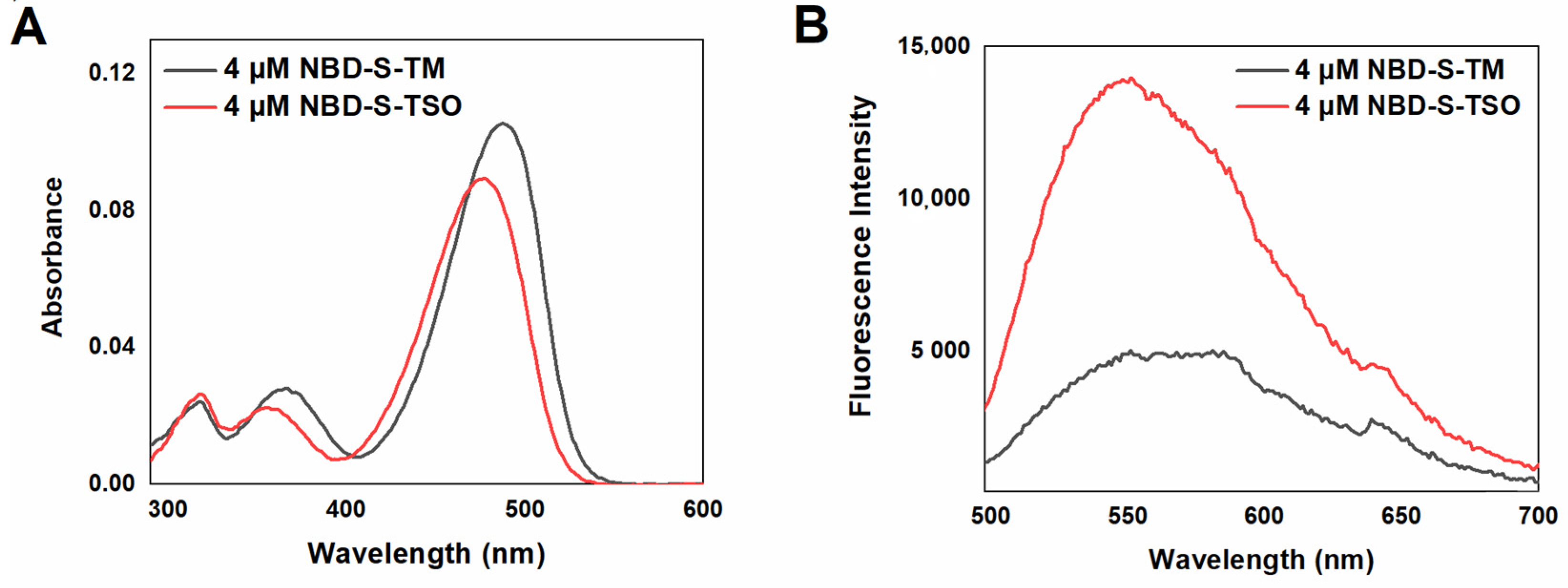


| Compound | λabs (nm) (ε (103 M−1cm−1)) | λem (nm) (Φem (%)) | λexc (nm) | Stokes Shift (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBD-S-TM 1 | 490 (26.3), 365 (7) | 550 (1.00) | 490 | 60 |
| NBD-TM 2 | 350 (7.8), 500 (22) | 550 (0.2) | 500 | 50 |
| NBD-Se-TM 3 | 345, 520 (18) | 620 (0.06) | 520 | 100 |
| NBD-S-TSO 1 | 475 (22.2) | 550 (3.35) | 475 | 75 |
| NBD-TSO 2 | 485 (23.3) | 550 (2.4) | 485 | 65 |
| NBD-Se-TSO 3 | 500 (16.7) | 620 (0.49) | 500 | 120 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Świerczyńska, M.; Słowiński, D.; Michalski, R.; Romański, J.; Podsiadły, R. A New and Fast-Response Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Hypochlorous Acid Derived from Myeloperoxidase. Molecules 2023, 28, 6055. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166055
Świerczyńska M, Słowiński D, Michalski R, Romański J, Podsiadły R. A New and Fast-Response Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Hypochlorous Acid Derived from Myeloperoxidase. Molecules. 2023; 28(16):6055. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166055
Chicago/Turabian StyleŚwierczyńska, Małgorzata, Daniel Słowiński, Radosław Michalski, Jarosław Romański, and Radosław Podsiadły. 2023. "A New and Fast-Response Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Hypochlorous Acid Derived from Myeloperoxidase" Molecules 28, no. 16: 6055. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166055
APA StyleŚwierczyńska, M., Słowiński, D., Michalski, R., Romański, J., & Podsiadły, R. (2023). A New and Fast-Response Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Hypochlorous Acid Derived from Myeloperoxidase. Molecules, 28(16), 6055. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166055