Suppression of Inflamm-Aging by Moringa oleifera and Zingiber officinale Roscoe in the Prevention of Degenerative Diseases: A Review of Current Evidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Causes of Inflamm-Aging
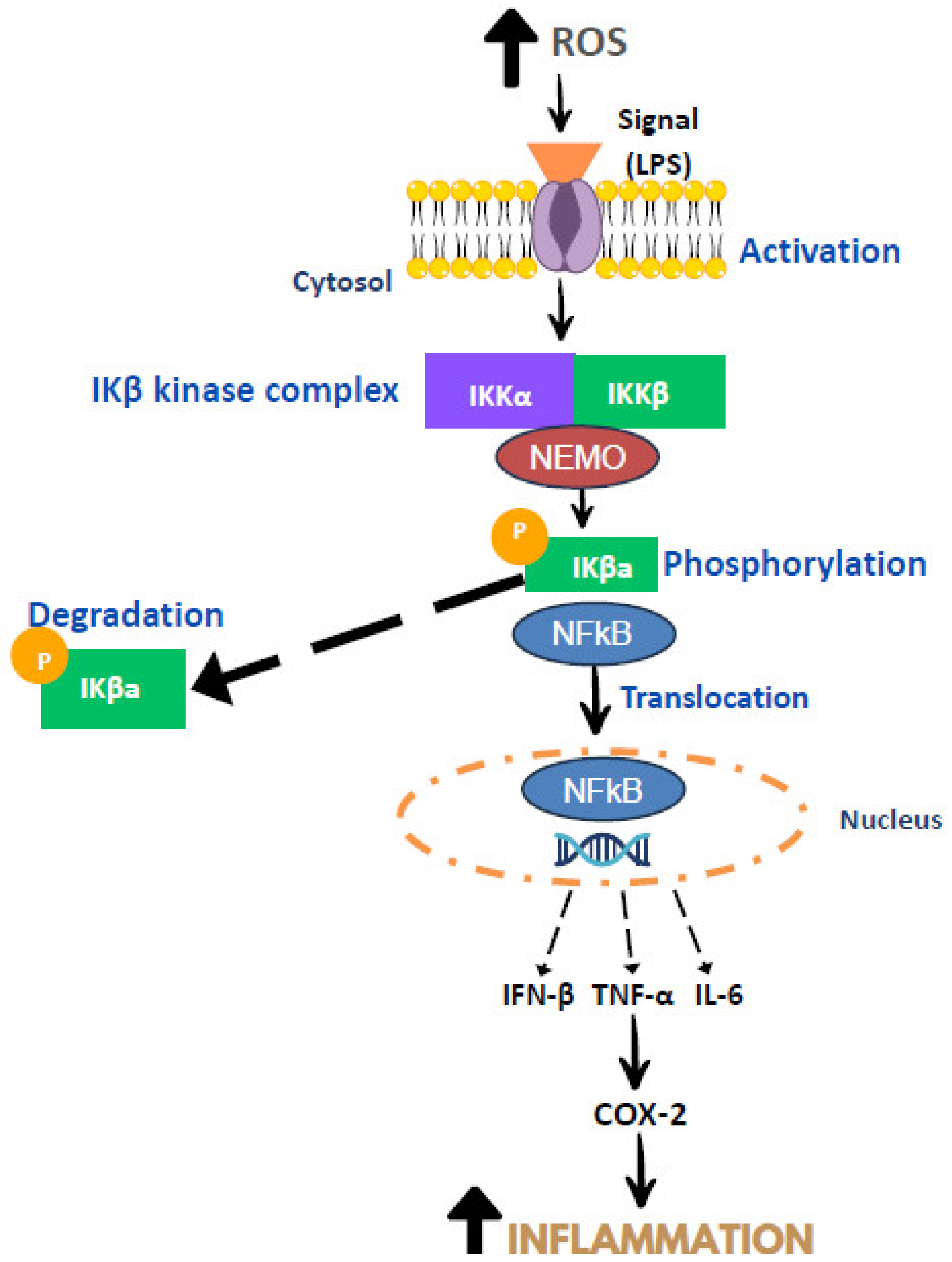
3. Mechanism of Inflammation
4. Moringa oleifera and Zingiber officinale Roscoe
5. The Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Moringa oleifera and Ginger
6. The Role of MO and Ginger in Preventing Age-Related Degenerative Diseases
6.1. Effect of MO and Ginger on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
6.2. Effect of MO and Ginger on Cardiovascular Disease
6.3. Effect of MO and Ginger on Neurodegenerative Disease
6.4. Effect of MO and Ginger on Cancer
6.5. Effect of MO and Ginger on Kidney Disease
7. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooke, J.P. Inflammation and Its Role in Regeneration and Repair. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1166–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczyk-Sowa, M.; Nowak-Kiczmer, M.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Berger, T. Immunosenescence and multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2022, 56, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.A.; Vago, J.P.; Perretti, M.; Teixeira, M.M. Mediators of the Resolution of the Inflammatory Response. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feehan, K.T.; Gilroy, D.W. Is Resolution the End of Inflammation? Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, I.M.; Gibson, D.S.; McGilligan, V.; McNerlan, S.E.; Alexander, H.D.; Ross, O.A. Age and age-related diseases: Role of inflammation triggers and cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daenen, K.; Andries, A.; Mekahli, D.; Van Schepdael, A.; Jouret, F.; Bammens, B. Oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative stress: Harms and benefits for human health. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.T.; Green, E.R.; Mecsas, J. Neutrophils to the ROScue: Mechanisms of NADPH oxidase activation and bacterial resistance. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-P.; Peng, Y.-B.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Wang, Y.; Yu, W.-R.; Yao, M.; Fu, X.-J. Reactive oxygen species mediated prostaglandin E2 contributes to acute response of epithelial injury. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4123854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilienbaum, A. Relationship between the proteasomal system and autophagy. Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 4, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.S.; Seo, Y.-K.; Kwon, K.-S. Sarcopenia targeting with autophagy mechanism by exercise. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, R.; Vasilaki, A. Age-related changes in skeletal muscle: Changes to life-style as a therapy. Biogerontology 2018, 19, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Segura, A.; Nehme, J.; Demaria, M. Hallmarks of Cellular Senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 436–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, P.; Cui, Z.Y.; Huang, X.F.; Zhang, D.D.; Guo, R.J.; Han, M. Inflammation and atherosclerosis: Signaling pathways and therapeutic intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandia, R.; Munjal, A. Interplay between inflammation and cancer. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2020, 119, 199–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohm, T.V.; Meier, D.T.; Olefsky, J.M.; Donath, M.Y. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity 2022, 55, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T. IL-6 in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer. Int. Immunol. 2021, 33, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zheng, L.; Chen, L.; Luo, N.; Yang, W.; Qu, X.; Liu, M.; Cheng, Z. Lipopolysaccharide activated TLR4/NF-κβ signaling pathway of fibroblasts from uterine fibroids. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 10014. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, B.; Hochreiter, B.; Basílio, J.; Gleitsmann, V.; Panhuber, A.; Pardo-Garcia, A.; Hoesel, B.; Salzmann, M.; Resch, U.; Noreen, M.; et al. The inflammatory kinase IKKα phosphorylates and stabilizes c-Myc and enhances its activity. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, T.G. Role of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signalling in neurodegenerative diseases: An mechanistic approach. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 918–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakad, A.K.; Ikram, M.; Sharma, S.; Khan, S.; Pandey, V.V.; Singh, A. Biological, nutritional, and therapeutic significance of Moringa oleifera Lam. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2870–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Kumar, M.; Waghmare, R.; Suhag, R.; Gupta, O.P.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Prakash, S.; Radha; Rais, N.; Sampathrajan, V.; et al. Moringa (Moringa oleifera Lam.) polysaccharides: Extraction, characterization, bioactivities, and industrial application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, C.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Optimization of extraction method to obtain a phenolic compounds-rich extract from Moringa oleifera Lam leaves. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 66, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landázuri, A.C.; Gualle, A.; Castañeda, V.; Morales, E.; Caicedo, A.; Orejuela-Escobar, L.M. Moringa oleifera Lam. leaf powder antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity in human primary fibroblasts. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 6194–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, S.; Thiagarajan, K.; Varghese, S.; Kumar, R.; Karthick, B.P.; Varadarajan, S.; Balaji, T.M. Assessing the In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Moringa oleifera Crude Extract. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2022, 23, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y. Moringa oleifera Lam. seed extract protects kidney function in rats with diabetic nephropathy by increasing GSK-3β activity and activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Phytomedicine 2022, 95, 153856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alia, F.; Putri, M.; Anggraeni, N.; Syamsunarno, M. The Potency of Moringa oleifera Lam. as Protective Agent in Cardiac Damage and Vascular Dysfunction. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 724439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, P.; Cerdá, B.; Arcusa, R.; Marhuenda, J.; Yamedjeu, K.; Zafrilla, P. Effect of Ginger on Inflammatory Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, F.; Tzvetkov, N.T.; Horbanczuk, J.O.; Li, Y.; Atanasov, A.G.; Wang, D. Vasculoprotective effects of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) and underlying molecular mechanisms. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1897–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Mirghazanfari, S.M.; Hazrati, E.; Hadi, S.; Milajerdi, A. The effect of ginger supplementation on metabolic profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2022, 65, 102802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C. Ginger for Migraine. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2021, 82, 21f14325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebi, M.; İlgün, S.; Ebrahimi, V.; Talebi, M.; Farkhondeh, T.; Ebrahimi, H.; Samarghandian, S. Zingiber officinale ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease and Cognitive Impairments: Lessons from preclinical studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 111088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyama, R. Nutritional implications of ginger: Chemistry, biological activities and signaling pathways. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 86, 108486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Q.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Cao, S.Y.; Gan, R.Y.; Corke, H.; Beta, T.; Li, H.B. Bioactive Compounds and Bioactivities of Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Foods 2019, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, R.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, S.; Lu, F.; Peng, W.; Wu, C. Ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) and its bioactive components are potential resources for health beneficial agents. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 711–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unuofin, J.O.; Masuku, N.P.; Paimo, O.K.; Lebelo, S.L. Ginger from Farmyard to Town: Nutritional and Pharmacological Applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 779352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.-C.; Lai, M.-H.; Hsu, K.-P.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Chen, J.; Tsai, M.-C.; Li, C.-X.; Yin, X.-J.; Jeyashoke, N.; Chao, L.K.-P. Identification of β-sitosterol as in vitro anti-inflammatory constituent in Moringa oleifera. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10748–10759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sul, O.J.; Ra, S.W. Quercetin Prevents LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation by Modulating NOX2/ROS/NF-κβ in Lung Epithelial Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Khalil, S.R.; Awad, A.; Abu Zeid, E.H.; El-Aziz, R.A.; El-Serehy, H.A. Ethanolic Extract of Moringa oleifera Leaves Influences NF-κβ Signaling Pathway to Restore Kidney Tissue from Cobalt-Mediated Oxidative Injury and Inflammation in Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrok, H.B.; Mohamed, M.S. Induction of COX-1, suppression of COX-2 and pro-inflammatory cytokines gene expression by moringa leaves and its aqueous extract in aspirin-induced gastric ulcer rats. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 4213–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.S.; Arulselvan, P.; Karthivashan, G.; Fakurazi, S. Moringa oleifera flower extract suppresses the activation of inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages via NF-κB pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 720171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, S.M.; Ezzat, M.I.; Okba, M.M.; Menze, E.T.; Abdel-Naim, A.B. The hidden mechanism beyond ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) potent in vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 214, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinyemi, A.J.; Thomé, G.R.; Morsch, V.M.; Bottari, N.B.; Baldissarelli, J.; de Oliveira, L.S.; Goularte, J.F.; Bello-Klein, A.; Duarte, T.; Duarte, M. Effect of ginger and turmeric rhizomes on inflammatory cytokines levels and enzyme activities of cholinergic and purinergic systems in hypertensive rats. Planta Medica 2016, 82, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, D.M.; Kim, J.Y. Ginger extract suppresses inflammatory response and maintains barrier function in human colonic epithelial Caco-2 cells exposed to inflammatory mediators. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.A.; Heeba, G.H.; Hamza, S.; Abdalla, A.; Amin, A. Standardized extract of ginger ameliorates liver cancer by reducing proliferation and inducing apoptosis through inhibition oxidative stress/ inflammation pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarruel-López, A.; López-de la Mora, D.A.; Vázquez-Paulino, O.D.; Puebla-Mora, A.G.; Torres-Vitela, M.R.; Guerrero-Quiroz, L.A.; Nuño, K. Effect of Moringa oleifera consumption on diabetic rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omodanisi, E.I.; Aboua, Y.G.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Assessment of the anti-hyperglycaemic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of the methanol extract of Moringa oleifera in diabetes-induced nephrotoxic male wistar rats. Molecules 2017, 22, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaliani, B.; Setiasih, N.; Winaya, I. Histopathological kidney overview of experimental diabetes mellitus Wistar rats given ethanol extract of Moringa leaf. Bul. Vet. Udayana 2019, 11, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Siahaan, S.; Santoso, B.; Widjiati. Effectiveness of Moringa oleifera Leaves on TNF-α Expression, Insulin Levels, Glucose Levels and Follicle Count in Rattus norvegicus PCOS Model. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 3255–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaja-Chimedza, A.; Zhang, L.; Wolff, K.; Graf, B.L.; Kuhn, P.; Moskal, K.; Carmouche, R.; Newman, S.; Salbaum, J.M.; Raskin, I. A dietary isothiocyanate-enriched moringa (Moringa oleifera) seed extract improves glucose tolerance in a high-fat-diet mouse model and modulates the gut microbiome. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y. Integrated Network Pharmacology Analysis and Experimental Validation to Reveal the Mechanism of Anti-Insulin Resistance Effects of Moringa oleifera Seeds. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 4069–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veisi, P.; Zarezade, M.; Rostamkhani, H.; Ghoreishi, Z. Renoprotective effects of the ginger (Zingiber officinale) on Diabetic kidney disease, current knowledge and future direction: A systematic review of animal studies. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostamkhani, H.; Veisi, P.; Niknafs, B.; Jafarabadi, M.A.; Ghoreishi, Z. The effect of Zingiber officinale on prooxidant-antioxidant balance and glycemic control in diabetic patients with ESRD undergoing hemodialysis: A double-blind randomized control trial. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.C.N.; Lira-Neto, J.C.G.; Araújo, M.F.M.; Freitas, R.; Zanetti, M.L.; Damasceno, M.M.C. Effectiveness of ginger in reducing metabolic levels in people with diabetes: A randomized clinical trial. Rev. Lat. Am. Enferm. 2020, 28, e3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hroob, A.M.; Abukhalil, M.H.; Alghonmeen, R.D.; Mahmoud, A.M. Ginger alleviates hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis and protects rats against diabetic nephropathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marefati, N.; Abdi, T.; Beheshti, F.; Vafaee, F.; Mahmoudabady, M.; Hosseini, M. Zingiber officinale (Ginger) hydroalcoholic extract improved avoidance memory in rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes by regulating brain oxidative stress. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2021, 43, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Santos, J.M.; Dufour, J.M.; Stephens, E.R.; Miranda, J.M.; Washburn, R.L.; Hibler, T.; Kaur, G.; Lin, D.; Shen, C.L. Ginger Root Extract Improves GI Health in Diabetic Rats by Improving Intestinal Integrity and Mitochondrial Function. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randriamboavonjy, J.I.; Loirand, G.; Vaillant, N.; Lauzier, B.; Derbré, S.; Michalet, S.; Pacaud, P.; Tesse, A. Cardiac protective effects of Moringa oleifera seeds in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2016, 29, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aju, B.Y.; Rajalakshmi, R.; Mini, S. Protective role of Moringa oleifera leaf extract on cardiac antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randriamboavonjy, J.I.; Rio, M.; Pacaud, P.; Loirand, G.; Tesse, A. Moringa oleifera seeds attenuate vascular oxidative and nitrosative stresses in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4129459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randriamboavonjy, J.I.; Heurtebise, S.; Pacaud, P.; Loirand, G.; Tesse, A. Moringa oleifera seeds improve aging-related endothelial dysfunction in wistar rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2567198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.C.; Horng, C.T.; Tsai, S.C.; Lee, Y.L.; Hsu, S.C.; Tsai, Y.J.; Tsai, F.J.; Chiang, J.H.; Kuo, D.H.; Yang, J.S. Relaxant and vasoprotective effects of ginger extracts on porcine coronary arteries. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2420–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirpoor, A.; Zerehpoosh, M.; Ansari, M.H.K.; Kheradmand, F.; Rasmi, Y. Ginger extract mitigates ethanol-induced changes of alpha and beta—Myosin heavy chain isoforms gene expression and oxidative stress in the heart of male wistar rats. DNA Repair 2017, 57, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaman, Y.A.R.; Huang, F.; Wu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Bao, J.; Salissou, M.T.M.; Ke, D.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R.; et al. Moringa oleifera Alleviates Homocysteine-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Pathology and Cognitive Impairments. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 63, 1141–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacoppo, S.; Rajan, T.S.; De Nicola, G.R.; Iori, R.; Rollin, P.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. The isothiocyanate isolated from Moringa oleifera shows potent anti-inflammatory activity in the treatment of murine subacute Parkinson’s disease. Rejuvenation Res. 2017, 20, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Burgos, E.; Ureña-Vacas, I.; Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Nutritional value of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaf powder extracts and their neuroprotective effects via antioxidative and mitochondrial regulation. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, W.-s.; Suo, D.-q.; Li, Y.; Peng, L.; Xu, L.-x.; Zeng, K.-y.; Ren, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Moringa oleifera Seed Extract Alleviates Scopolamine-Induced Learning and Memory Impairment in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onasanwo, S.A.; Adamaigbo, V.O.; Adebayo, O.G.; Eleazer, S.E. Moringa oleifera-supplemented diet protect against cortico-hippocampal neuronal degeneration in scopolamine-induced spatial memory deficit in mice: Role of oxido-inflammatory and cholinergic neurotransmission pathway. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 2445–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.Y.; Seo, Y.; Lee, C.; Park, G.H.; Jang, J.H. Neuroprotective Effect and Molecular Mechanism of [6]-Gingerol against Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia in C57BL/6 Mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 8941564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, J.-Y.; Song, K.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, S.; Kwon, J. Sortilin-related receptor 1 interacts with amyloid precursor protein and is activated by 6-shogaol, leading to inhibition of the amyloidogenic pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 484, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, E.; Lim, S.; Kim, H.G.; Ha, S.K.; Park, H.-Y.; Huh, Y.; Oh, M.S. Ginger fermented with Schizosaccharomyces pombe alleviates memory impairment via protecting hippocampal neuronal cells in amyloid beta 1–42 plaque injected mice. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, J.Y.; Song, K.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, S.; Kwon, J. 6-Shogaol has anti-amyloidogenic activity and ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease via CysLT1R-mediated inhibition of cathepsin B. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Qian, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.; Peng, L.J.; Mao, J.Y.; Yang, M.R.; Tian, Y.; Sheng, J. Isothiocyanate From Moringa oleifera Seeds Inhibits the Growth and Migration of Renal Cancer Cells by Regulating the PTP1B-dependent Src/Ras/Raf/ERK Signaling Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 790618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, S.; Upadhyay, S.; Ahmad, I.; Hussain, A.; Ahamed, M. Cytotoxicity of Moringa oleifera fruits on human liver cancer and molecular docking analysis of bioactive constituents against caspase-3 enzyme. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuellar-Núñez, M.L.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E.; Loarca-Piña, G. Moringa oleifera leaves alleviated inflammation through downregulation of IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α in a colitis-associated colorectal cancer model. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Pandey, P.; Ahmad, V.; Upadhyay, T.K. Moringa oleifera methanolic leaves extract induces apoptosis and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest via downregulation of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in human prostate PC-3 cancer cells. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Fisall, U.F.; Ismail, N.Z.; Adebayo, I.A.; Arsad, H. Dichloromethane fraction of Moringa oleifera leaf methanolic extract selectively inhibits breast cancer cells (MCF7) by induction of apoptosis via upregulation of Bax, p53 and caspase 8 expressions. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 4465–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.R.; Choi, W.G.; Kwon, M.J.; Woo, J.H.; Kim, B.J. [6]-Gingerol induces Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis in Bladder Cancer cells via MAPK and ROS Signaling. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.D.; He, Z.L.; Yao, H.L.; Xiao, J.S.; Li, L.; Gu, J.Z.; Shi, P.Z.; Wang, J.H.; Jiang, L.H. 6-Shogaol from ginger shows anti-tumor effect in cervical carcinoma via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 2781–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, M.; Makuch, S.; Winograd, K.; Wiśniewski, J.; Ziółkowski, P.; Agrawal, S. 6-Shogaol enhances the anticancer effect of 5-fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan via increase of apoptosis and autophagy in colon cancer cells in hypoxic/aglycemic conditions. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajeigbe, O.F.; Maruf, O.R.; Anyebe, D.A.; Opafunso, I.T.; Ajayi, B.O.; Farombi, E.O. 6- shogaol suppresses AOM/DSS-mediated colorectal adenoma through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in mice. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, M.M.; Aldhahrani, A.; Alkhedaide, A.Q.; Nassan, M.A.; Althobaiti, F.; Mohamed, W.A. The ameliorative impacts of Moringa oleifera leaf extract against oxidative stress and methotrexate-induced hepato-renal dysfunction. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedapo, A.A.; Etim, U.; Falayi, O.O.; Ogunpolu, B.S.; Omobowale, T.O.; Oyagbemi, A.A.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Methanol stem extract of Moringa oleifera mitigates glycerol-induced acute kidney damage in rats through modulation of KIM-1 and NF-κβ signaling pathways. Sci. Afr. 2020, 9, e00493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Choi, E.J.; Han, W.C.; Oh, M.; Kim, J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Park, P.J.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, E.K. Moringa oleifera from Cambodia Ameliorates Oxidative Stress, Hyperglycemia, and Kidney Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinrinde, A.S.; Oduwole, O.; Akinrinmade, F.J.; Bolaji-Alabi, F.B. Nephroprotective effect of methanol extract of Moringa oleifera leaves on acute kidney injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Afr. Health Sci. 2020, 20, 1382–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirpoor, A.; Rezaei, F.; Fard, A.A.; Afshari, A.T.; Gharalari, F.H.; Rasmi, Y. Ginger extract protects rat’s kidneys against oxidative damage after chronic ethanol administration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Rashid, S.M.; Rasool, S.; Shakeel, S.; Ahmad, B.; Ahmad, S.B.; Madkhali, H.; Ganaie, M.A.; Majid, S.; Bhat, S.A. Zingerone (4-(4-hydroxy-3-methylphenyl) butan-2-one) ameliorates renal function via controlling oxidative burst and inflammation in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 125, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, S.A.; Alghadir, A.H.; Ghoniem, G.A. Biological activities of ginger against cadmium-induced renal toxicity. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D.; Srivastav, S.K.; Belemkar, S.; Dixit, V.A. Zingiber officinale and 6-gingerol alleviate liver and kidney dysfunctions and oxidative stress induced by mercuric chloride in male rats: A protective approach. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, W.A.; Ayoade, T.E.; Akhigbe, T.M.; Akhigbe, R.E. Moringa oleifera seed oil partially abrogates 2,3-dichlorovinyl dimethyl phosphate (Dichlorvos)-induced cardiac injury in rats: Evidence for the role of oxidative stress. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 32, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
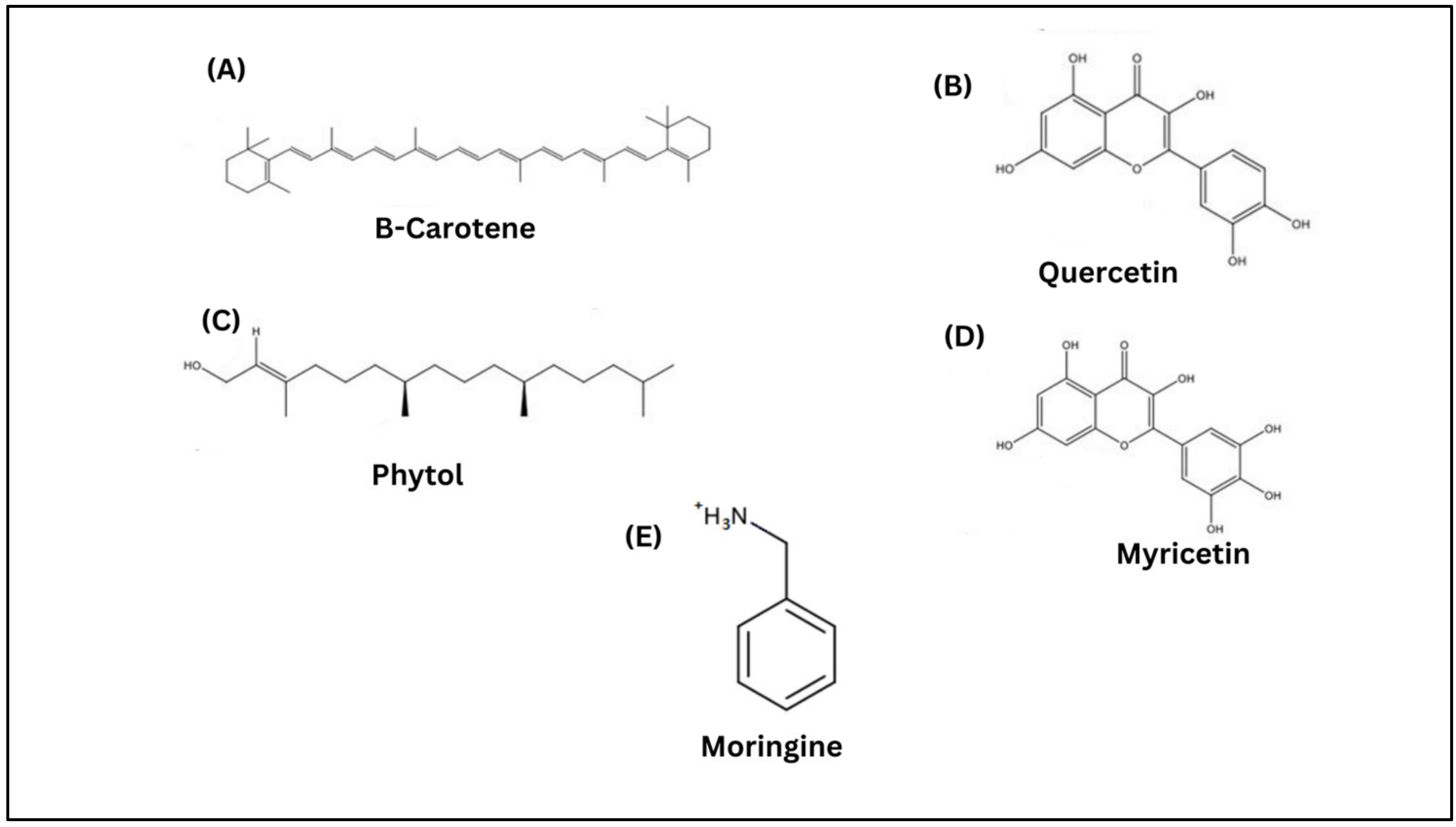
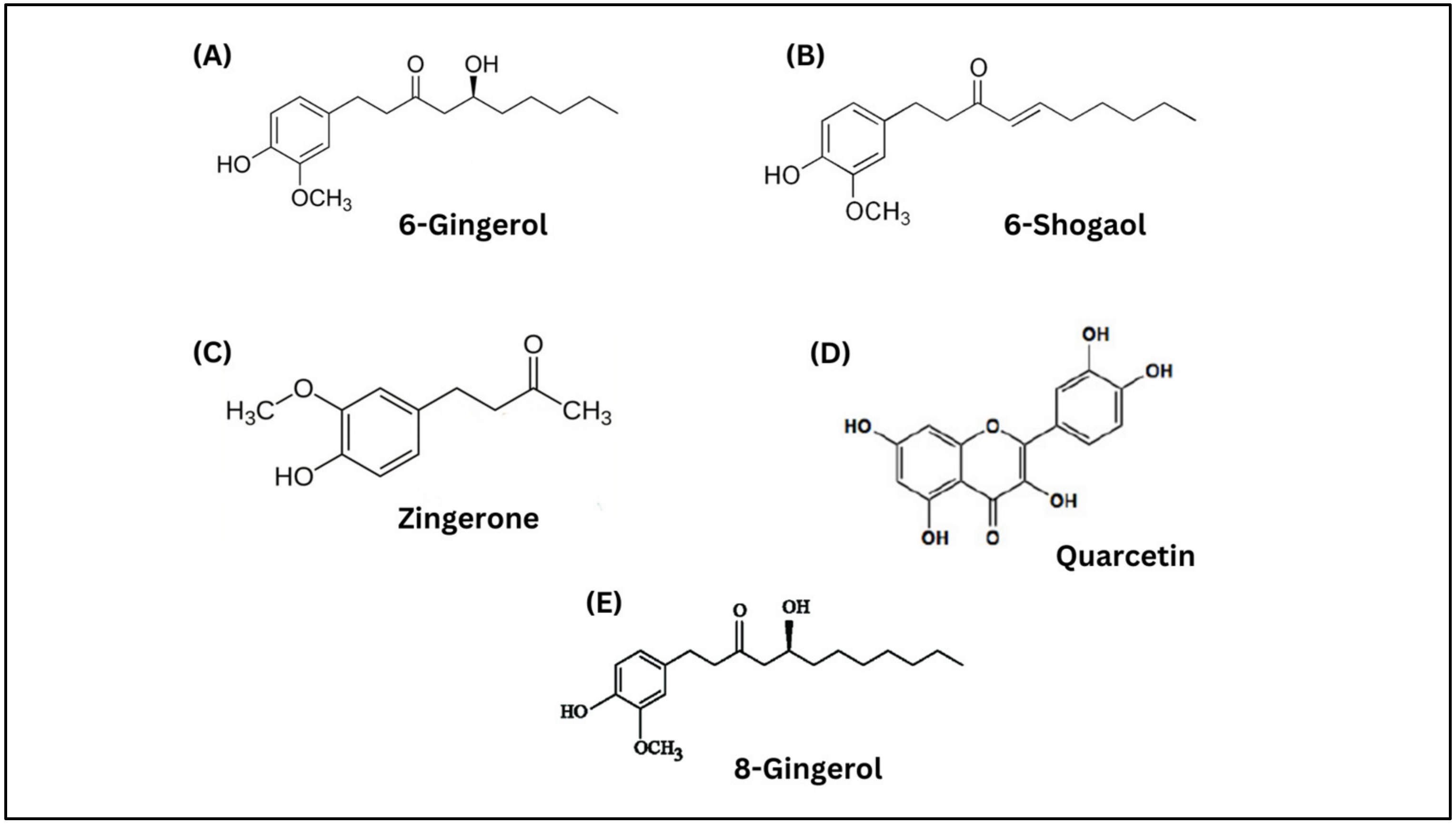
| Items | Moringa | Ginger | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific name | Moringa oleifera Lam | Zingiber officinale Roscoe | [21,34] |
| Family and genus | Moringaceae family and Moringa genus | Zingiberaceae family and Zingiber genus | [21,34] |
| Plant parts | Seed, root, leaves and flower | Rhizome | [22,35] |
| Bioactive compounds | Beta-carotene, quercetin, phytol, myricetin and moringine | 6-gingerol, 8-gingerol, 6-shogaol, quercetin, and zingerone | [22,35] |
| Biological activities | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, antidiabetic, antiproliferative and cardioprotective activities | Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anticancer, antidiabetic, gastro-protective, antioxidant, and neuroprotective effects | [24,25,26,27,34,35,36] |
| Related Disease | Constituent | Study Type | Potential Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes mellitus type 2 | Methanolic extract of Moringa oleifera | In vivo study |
| [47] |
| Moringa oleifera leaf | In vivo study |
| [49] | |
| Aqueous leaf decoction of Moringa oleifera | In vivo study |
| [48] | |
| Moringa oleifera isothiocyanate-rich seed extract | In vivo study |
| [50] | |
| Moringa oleifera seed | In silico study |
| [51] | |
| Cardiovascular disease | Moringa oleifera seed | In vivo study |
| [58] |
| Moringa oleifera seed | In vivo study |
| [60] | |
| Moringa oleifera leaf extract | In vivo study |
| [59] | |
| Moringa oleifera seed oil | In vivo study |
| [90] | |
| Moringa oleifera seed oil | In vivo study |
| [61] | |
| Neurodegenerative disease | Moringa oleifera leaf powder | In vivo study |
| [64] |
| Moringa oleifera active compound; isothiocyanate | In vitro and in vivo study |
| [65] | |
| Moringa oleifera leaf | In vitro study |
| [66] | |
| Moringa oleifera seed | In vivo study |
| [67] | |
| Moringa oleifera extract | In vivo study |
| [68] | |
| Cancer | Moringa oleifera active compound; 4-[(α-L-Rhamnosyloxy) benzyl] isothiocyanate | In vitro and in vivo study |
| [73] |
| Moringa oleifera fruit | In vitro study |
| [74] | |
| Moringa oleifera leaf | In vivo study |
| [75] | |
| Moringa oleifera methanolic leaf extract | In vitro study |
| [76] | |
| Moringa oleifera methanolic leaf extract | In vitro study |
| [77] | |
| Kidney disease | Moringa oleifera leaf extract | In vivo study |
| [47] |
| Moringa oleifera leaf extract | In vivo study |
| [82] | |
| Moringa oleifera stem extract | In vivo study |
| [83] | |
| Moringa oleifera leaf extract | In vivo study |
| [84] | |
| Moringa oleifera leaf extract | In vivo study |
| [85] |
| Related Disease | Constituent | Study Type | Potential Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes mellitus type 2 | Ginger extract | Human study |
| [54] |
| Ginger rhizome extract | In vivo study |
| [55] | |
| Ginger extract | In vivo study |
| [56] | |
| Gingerol-enriched ginger | In vivo study |
| [57] | |
| Cardiovascular disease | Ginger crude extract | In vitro study |
| [62] |
| Ginger extract | In vitro study |
| [43] | |
| Ginger extract | In vivo study |
| [63] | |
| Neurodegenerative disease | Ginger active compound; Gingerol | In vivo study |
| [69] |
| Ginger active compound; 6-shogaol | In vitro and in vivo study |
| [70] | |
| Ginger fermented with Schizosaccharomyces pombe | In vivo study |
| [71] | |
| Ginger active compound; 6-shogaol | In vitro and in vivo study |
| [72] | |
| Cancer | Ginger active compound; 6-Gingerol | In vitro study |
| [78] |
| Ginger active compound; 6-Shogaol | In vitro and in vivo study |
| [79] | |
| Ginger active compound; 6-Shogaol | In vitro study |
| [80] | |
| Ginger active compound; 6-Shogaol | In vivo study |
| [81] | |
| Kidney disease | Ginger rhizome extract | In vivo study |
| [55] |
| Ginger extract | In vivo study |
| [86] | |
| Zingerone | In vivo study |
| [87] | |
| Ginger extract | In vivo study |
| [88] | |
| 6-Gingerol | In vivo study |
| [89] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohd Sahardi, N.F.N.; Makpol, S. Suppression of Inflamm-Aging by Moringa oleifera and Zingiber officinale Roscoe in the Prevention of Degenerative Diseases: A Review of Current Evidence. Molecules 2023, 28, 5867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155867
Mohd Sahardi NFN, Makpol S. Suppression of Inflamm-Aging by Moringa oleifera and Zingiber officinale Roscoe in the Prevention of Degenerative Diseases: A Review of Current Evidence. Molecules. 2023; 28(15):5867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155867
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohd Sahardi, Nur Fatin Nabilah, and Suzana Makpol. 2023. "Suppression of Inflamm-Aging by Moringa oleifera and Zingiber officinale Roscoe in the Prevention of Degenerative Diseases: A Review of Current Evidence" Molecules 28, no. 15: 5867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155867
APA StyleMohd Sahardi, N. F. N., & Makpol, S. (2023). Suppression of Inflamm-Aging by Moringa oleifera and Zingiber officinale Roscoe in the Prevention of Degenerative Diseases: A Review of Current Evidence. Molecules, 28(15), 5867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155867