Molecular Mechanism of Male Sterility Induced by 60Co γ-Rays on Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Quantitative Proteomics Analysis
2.2. Analysis of Differential Protein in P. xylostella after Irradiation
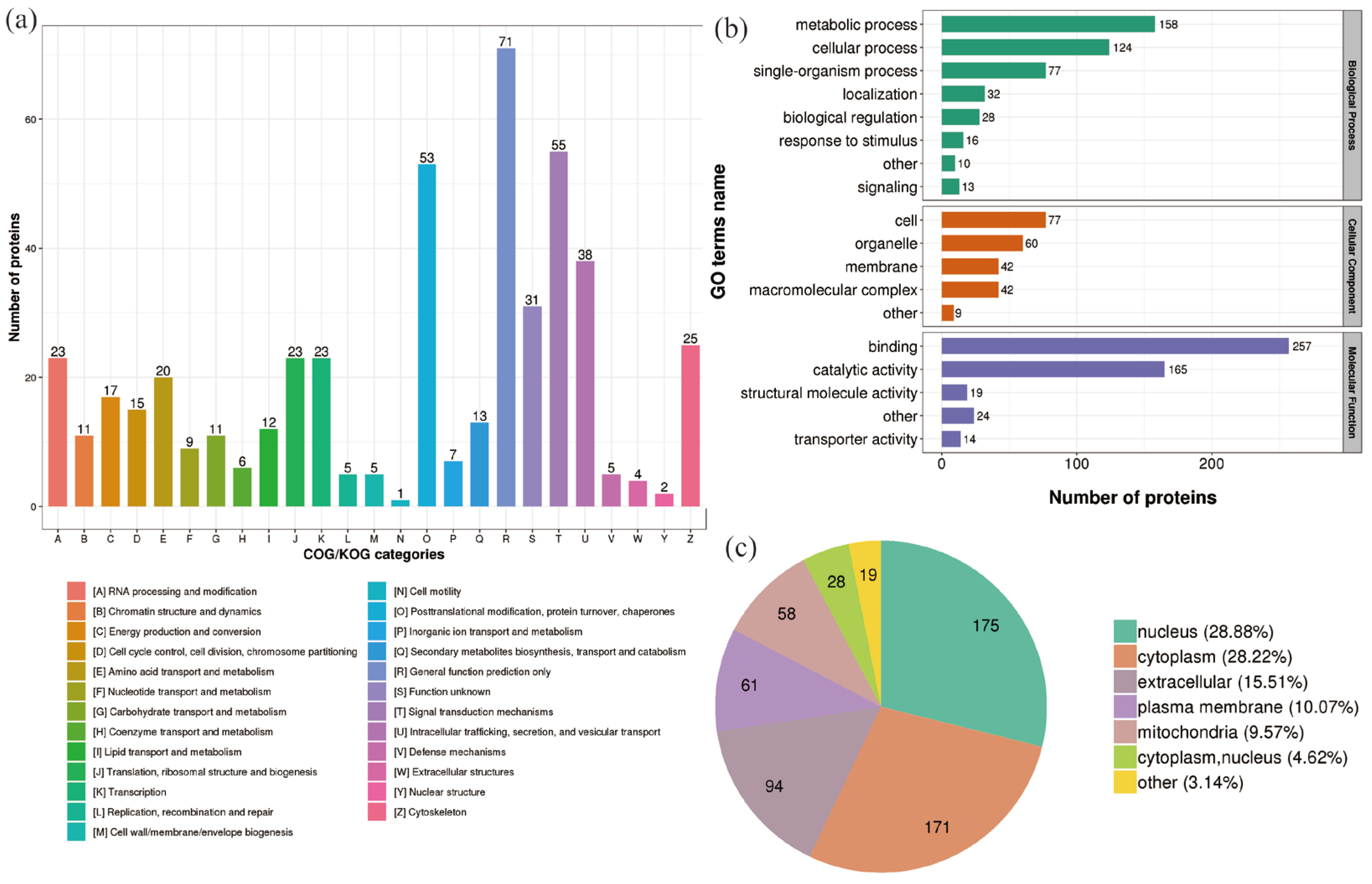
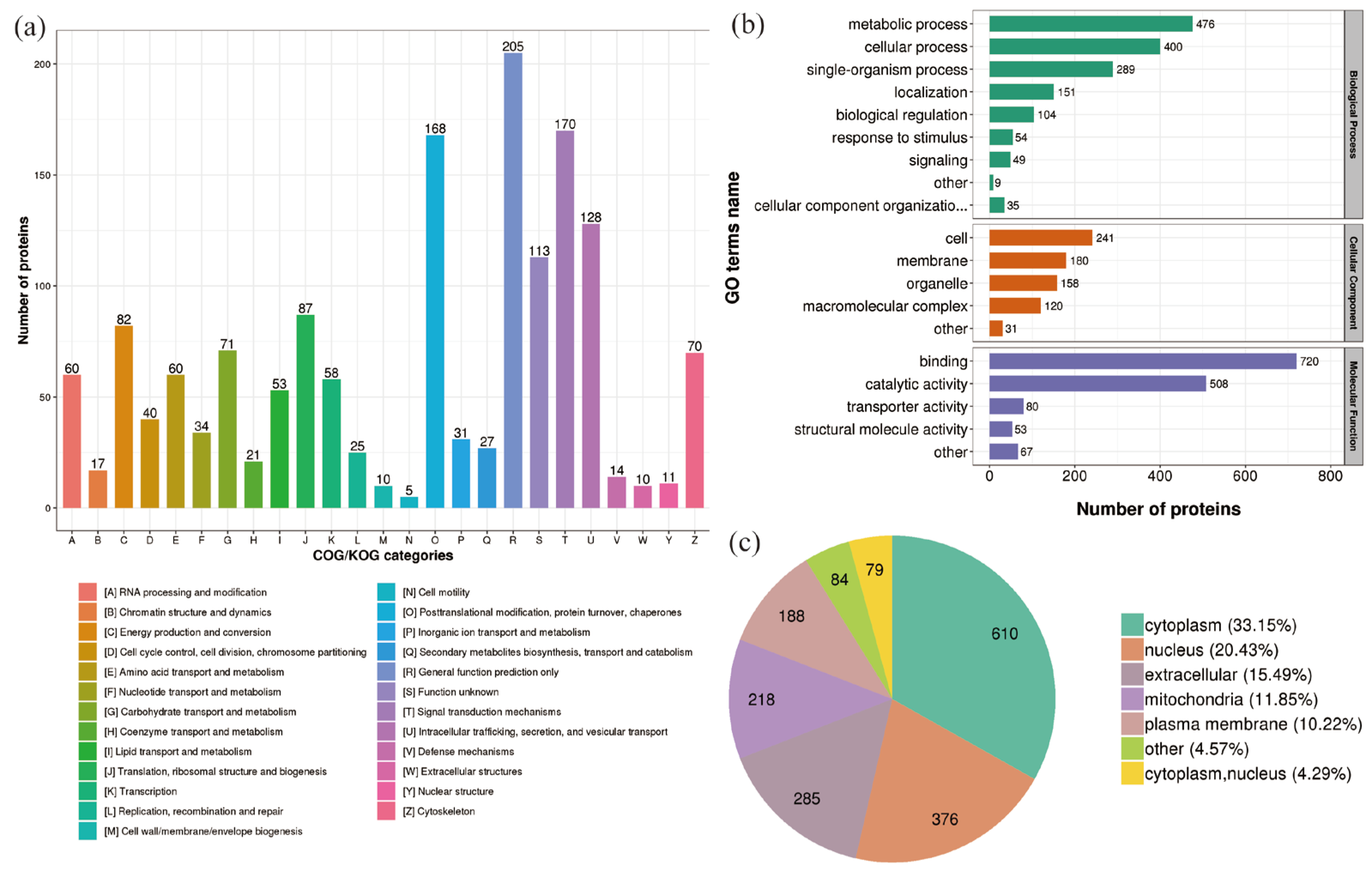
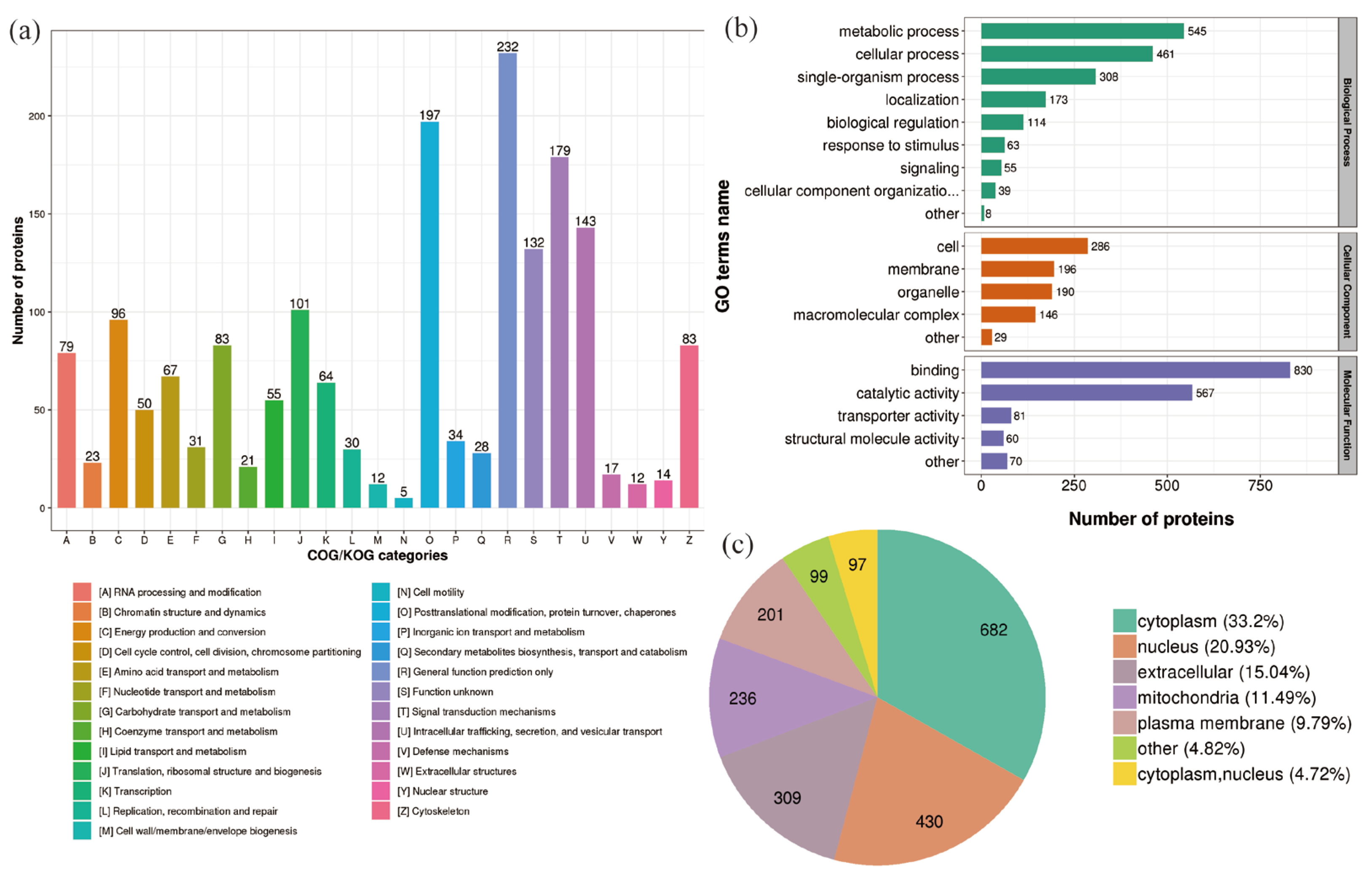
2.3. Classification of DEPs in P. xylostella after Irradiation
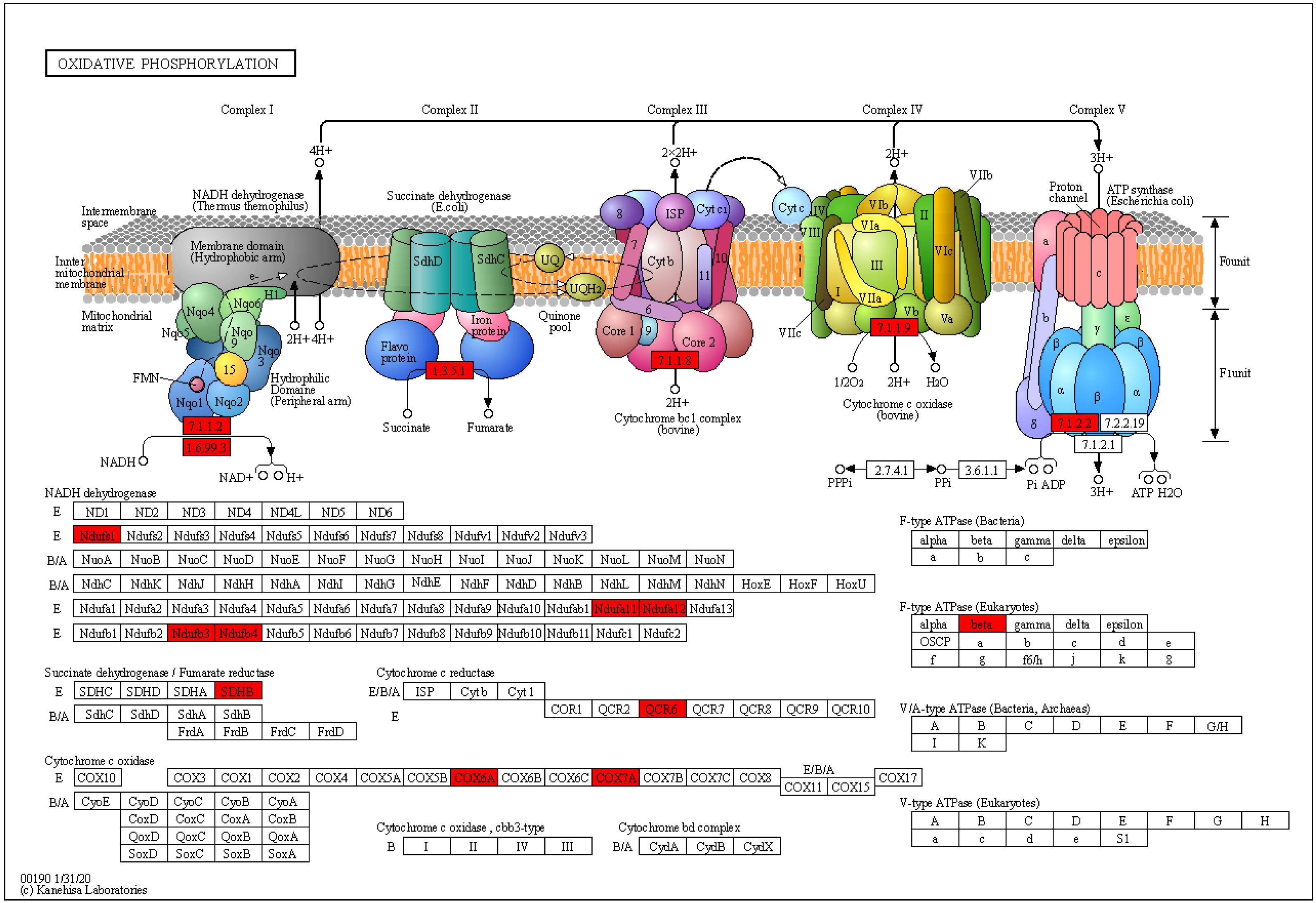
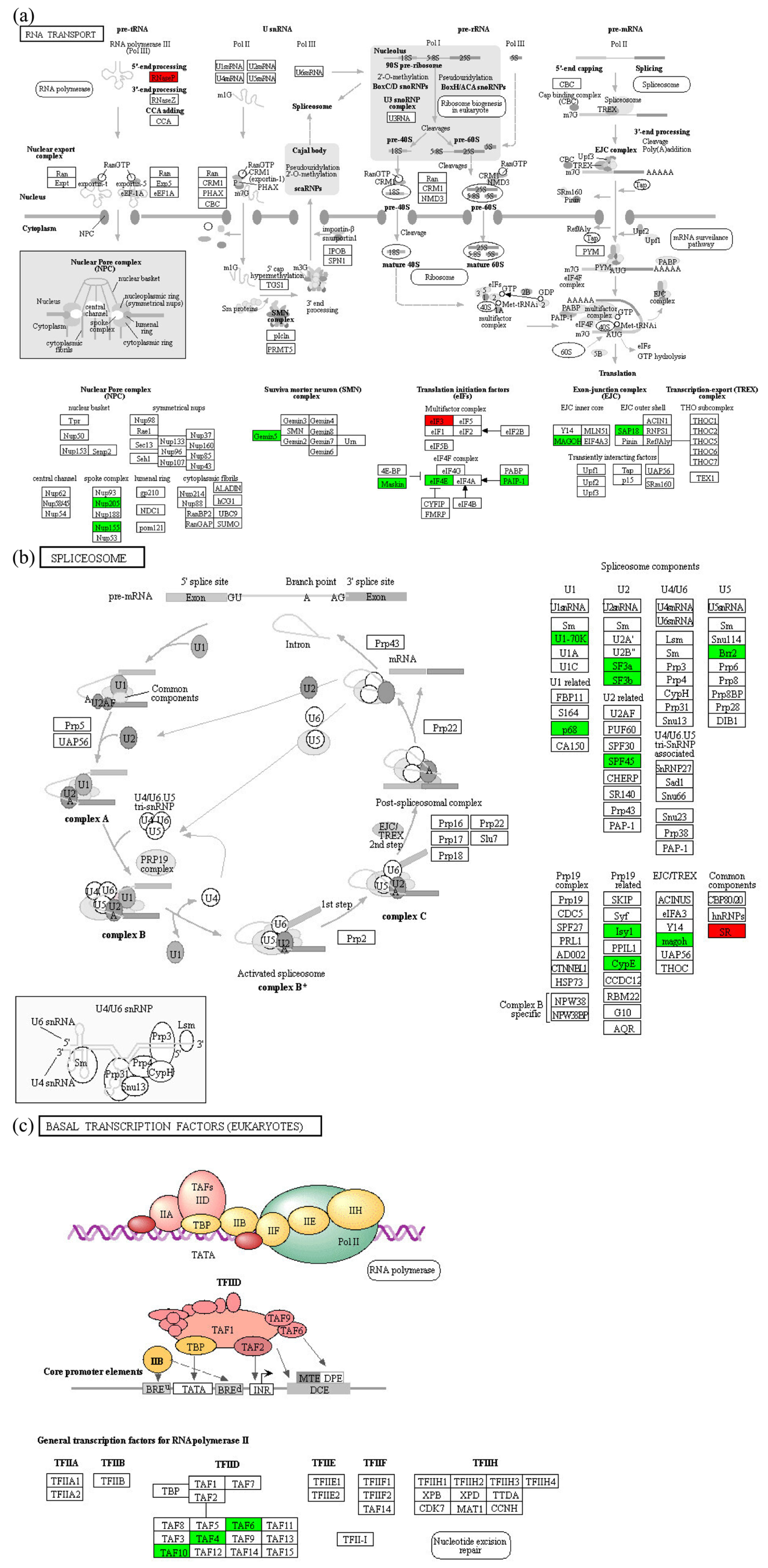
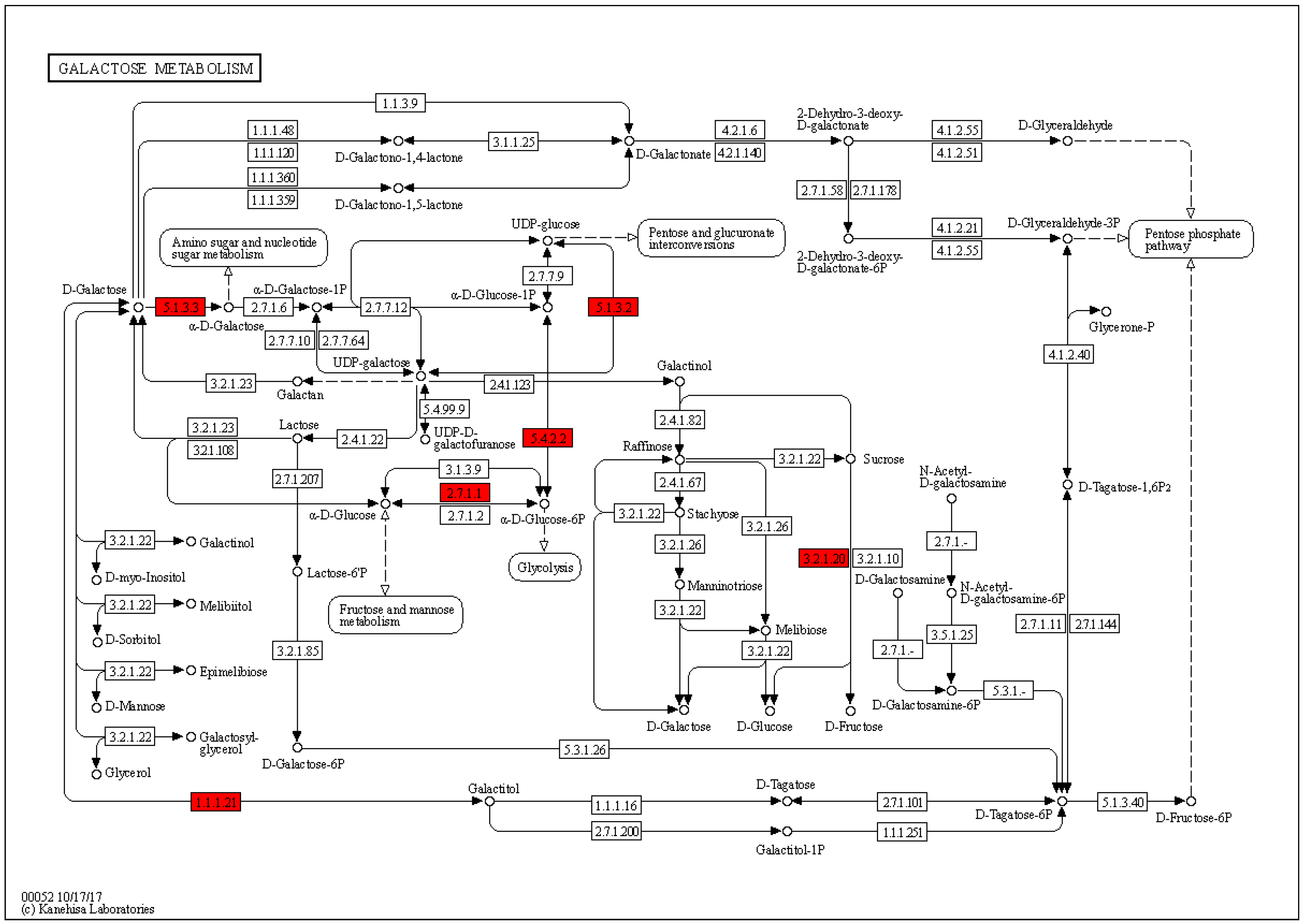
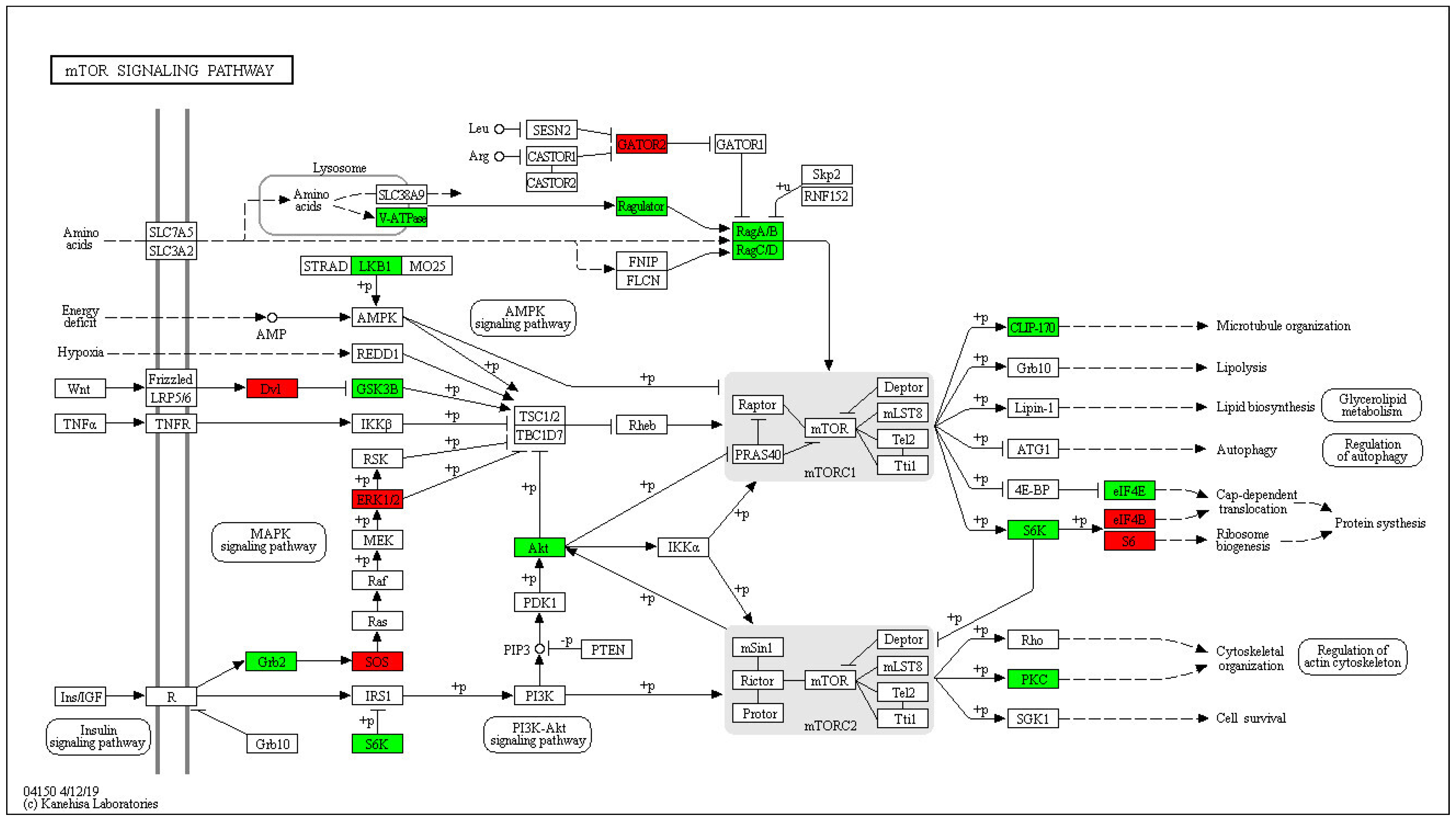
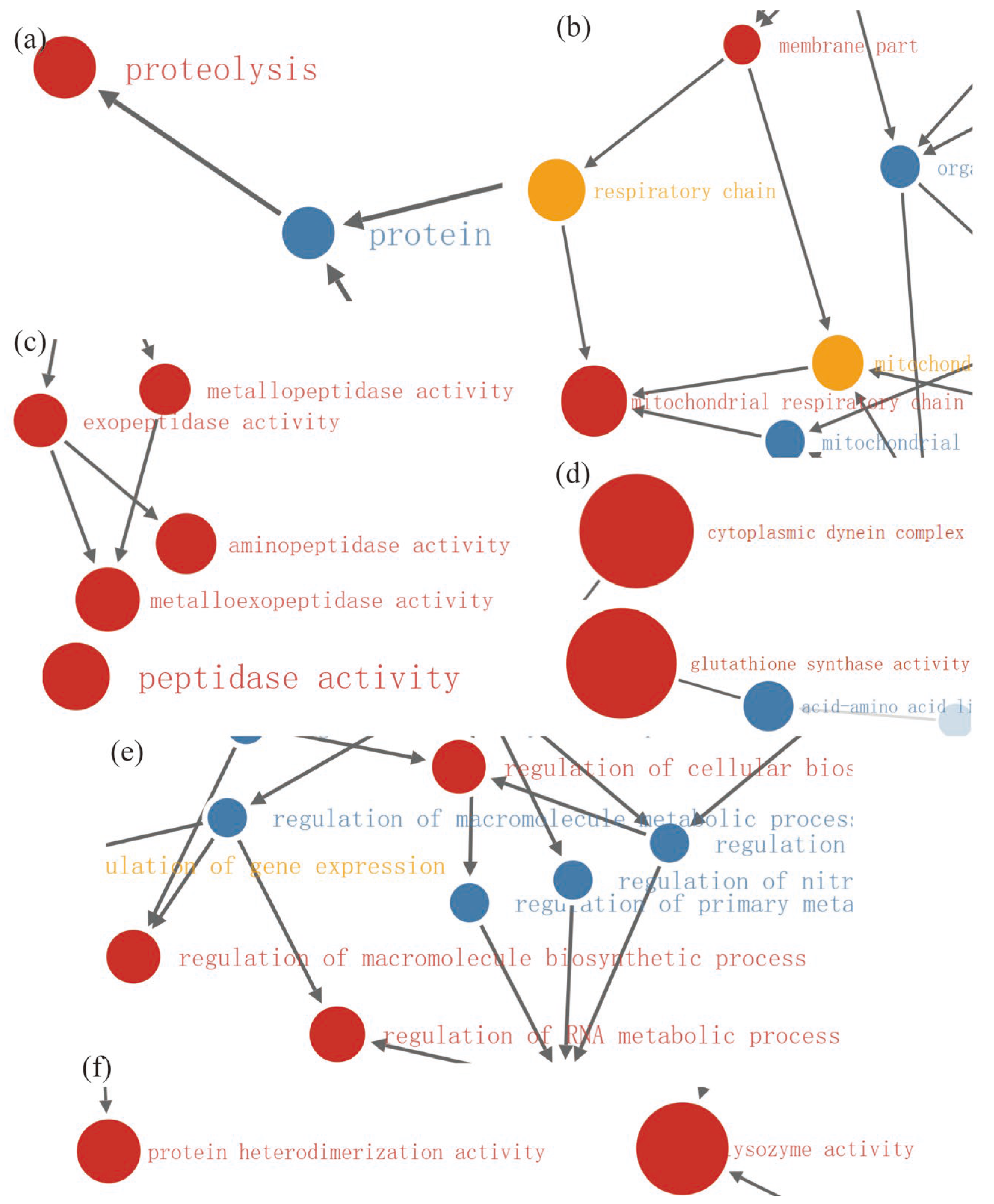
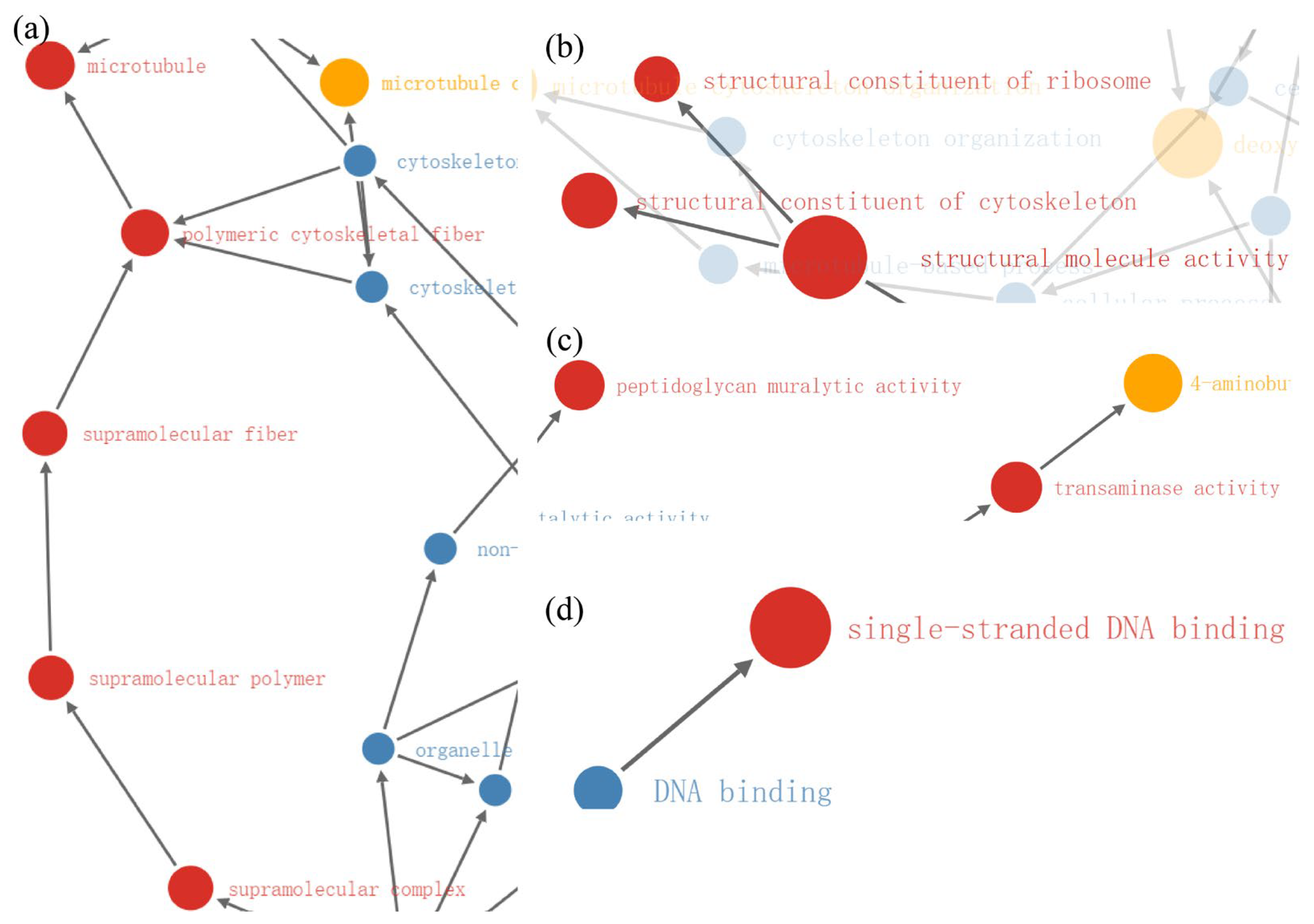
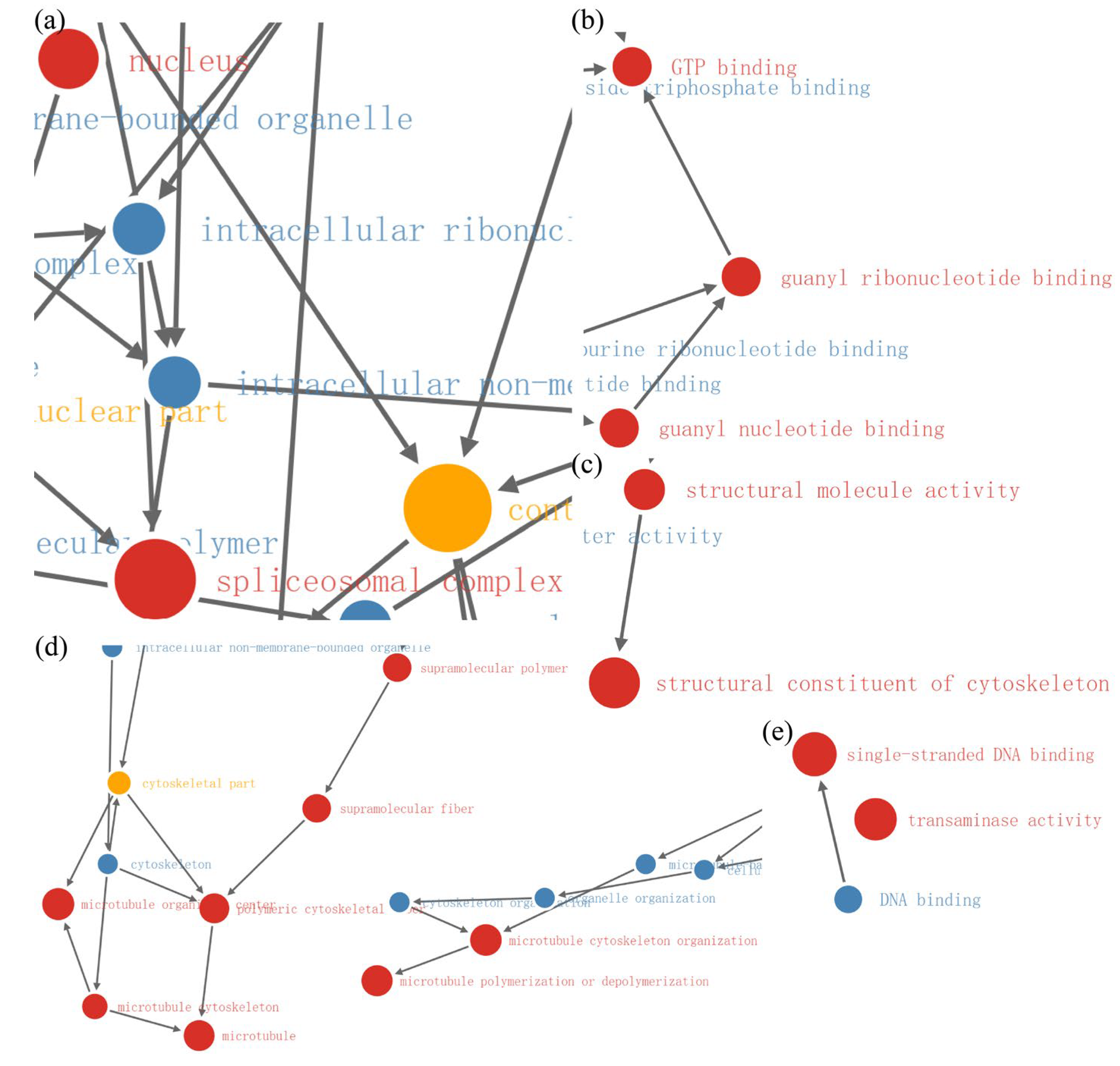
2.4. Enrichment Analysis of DEPs in P. xylostella after Irradiation
2.5. Functional Enrichment
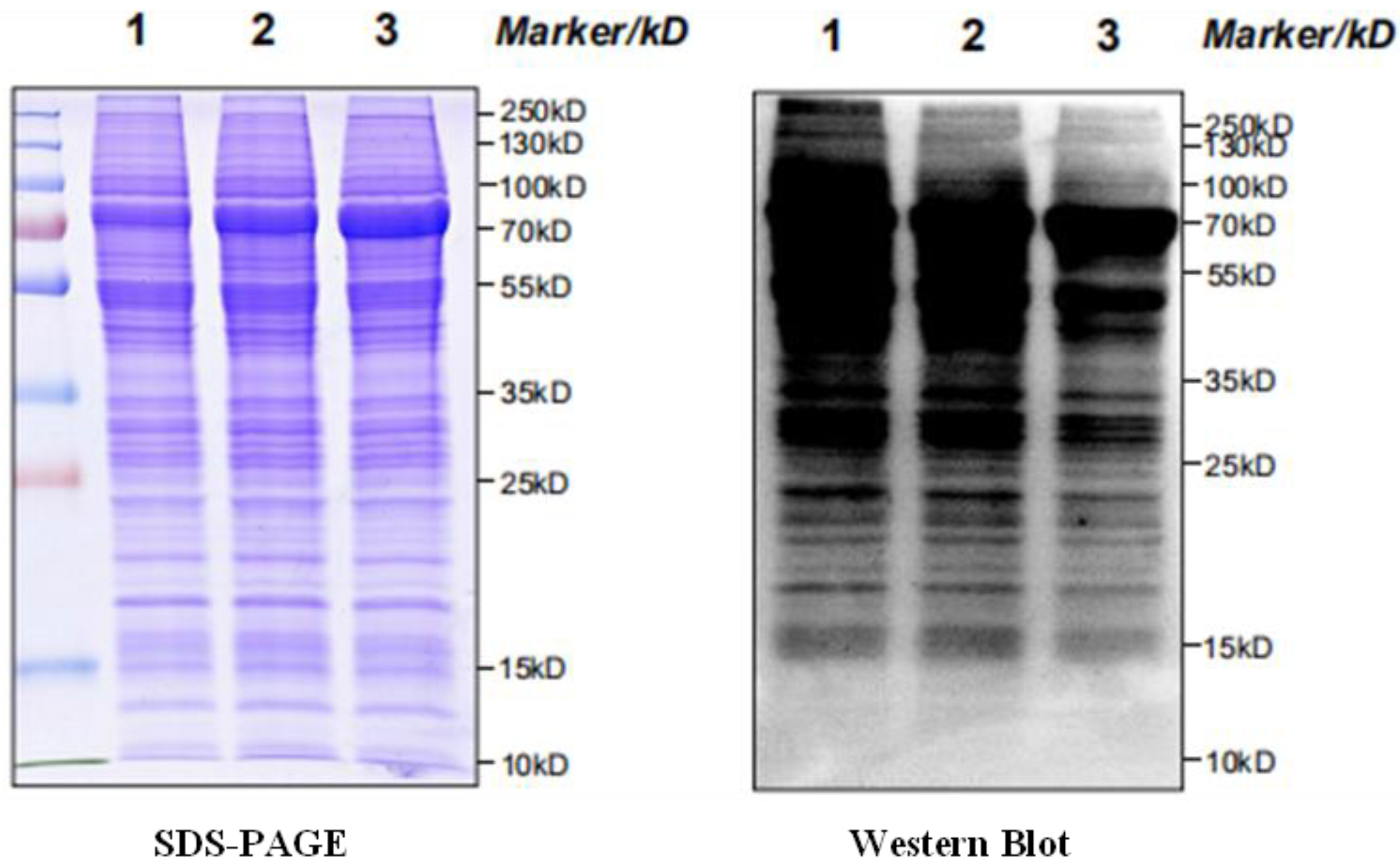
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Effect of 200 Gy/CK Group on the Spermial Tissue of P. xylostella
3.2. Effect of 400 Gy/CK Group on the Spermial Tissue of P. xylostella
3.3. Effect of 400 Gy/200 Gy Group on the Spermial Tissue of P. xylostella
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Rearing and Irradiation Treatment of P. xylostella
4.2. Anatomy of P. xylostella Testis and Extraction of Testis Protein
4.3. Protein Concentration Determination
4.4. SDS-PAGE Electrophoresis Detection
4.5. Trypsin Digestion and TMT Labeling
4.6. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Fractionation
4.7. Mass Spectrum (MS) Analysis
4.8. Database Search
4.9. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.10. Western Blot
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Li, Z.; Feng, X.; Liu, S.-S.; You, M.; Furlong, M.J. Biology, Ecology, and Management of the Diamondback Moth in China. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlong, M.J.; Wright, D.J.; Dosdall, L.M. Diamondback Moth Ecology and Management: Problems, Progress, and Prospects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 517–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalucki, M.P.; Shabbir, A.; Silva, R.; Adamson, D.; Shu-Sheng, L.; Furlong, M.J. Estimating the Economic Cost of One of the World’s Major Insect Pests, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae): Just How Long Is a Piece of String? J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1115–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckel, D.G.; Gahan, L.J.; Liu, Y.-B.; Tabashnik, B.E. Genetic Mapping of Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Toxins in Diamondback Moth Using Biphasic Linkage Analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8373–8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Huang, F.; Ghimire, M.N.; Leonard, B.R.; Siegfried, B.D.; Rangasamy, M.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gahan, L.J.; Heckel, D.G.; et al. Efficacy of Genetically Modified Bt Toxins against Insects with Different Genetic Mechanisms of Resistance. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 1128–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Shen, A.; Wu, Y. Baseline Susceptibility of the Diamondback Moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) to Chlorantraniliprole in China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Desneux, N.; Sonoda, S.; Liang, P.; Han, P.; Gao, X.-W. Sublethal and Transgenerational Effects of Chlorantraniliprole on Biological Traits of the Diamondback Moth, Plutella xylostella L. Crop Prot. 2013, 48, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Neto, J.E.; Amaral, M.H.P.; Siqueira, H.A.A.; Barros, R.; Silva, P.A.F. Resistance Monitoring of Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) to Risk-Reduced Insecticides and Cross Resistance to Spinetoram. Phytoparasitica 2016, 44, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, S.W.; Badenes-Pérez, F.R.; Morrison, A.; Vogel, H.; Crickmore, N.; Kain, W.; Wang, P.; Heckel, D.G.; Jiggins, C.D. Parallel Evolution of Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin Resistance in Lepidoptera. Genetics 2011, 189, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabashnik, B.E. Implications of Gene Amplification for Evolution and Management of Insecticide Resistance. J. Econ. Entomol. 1990, 83, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.; Bezuidenhout, C.C.; Van den Berg, J. An Overview of Mechanisms of Cry Toxin Resistance in Lepidopteran Insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikbal, C.; Pavela, R. Essential Oils as Active Ingredients of Botanical Insecticides against Aphids. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, V.A.D.; Jorge Hendrichs, A.S. Sterile Insect Technique: Principles and Practice in Area-Wide Integrated Pest Management, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-00-303557-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.M.; Moustafa, H.Z.; Sayed, R.M. Alterations in Biomarkers Associated with Sterility in Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) Induced by Gamma Irradiation. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2017, 60, e17160634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphey, L.; Benedict, M.; Bellini, R.; Clark, G.G.; Dame, D.A.; Service, M.W.; Dobson, S.L. Sterile-Insect Methods for Control of Mosquito-Borne Diseases: An Analysis. Vector-Borne Zoonot. 2010, 10, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botto, E.; Glaz, P. Potential for Controlling Codling Moth Cydia pomonella (Linnaeus) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in Argentina Using the Sterile Insect Technique and Egg Parasitoids. J. Appl. Entomol. 2010, 134, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, D.; Song, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Bai, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, C. Fractionated Irradiation of Right Thorax Induces Abscopal Damage on Testes Leading to Decline in Fertility. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, C.; Dihazi, H. Introduction to Proteomics Technologies. In Statistical Analysis in Proteomics, 1st ed.; Jung, K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1362, pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, R.; Shi, L.; Chu, X. Unraveling Proteome Changes of Irradiated Goat Meat and Its Relationship to Off-Flavor Analyzed by High-Throughput Proteomics Analysis. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 127806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Jung, J.W.; Han, D.; Cha, M.-J.; Chang, J.H. One-Week Dynamic Changes in Cardiac Proteomes After Cardiac Radioablation in Experimental Rat Model. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 898222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pan, H.; Li, J.; Pan, D.; Liu, P.; Hu, H. Effects of Irradiated Sterile Male and Mating Sequence on the Fertility of Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). J. Insect Sci. 2022, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.; Zahran, N.; Sawires, S. Impact of Substerilizing Dose on Histological Changes in Gonads and Ovaries of Ephestia cautella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) by Gamma Radiation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannkuk, E.L.; Laiakis, E.C.; Authier, S.; Wong, K.; Fornace, A.J. Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics of Urine and Serum from Nonhuman Primates Exposed to Ionizing Radiation: Impacts on the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle and Protein Metabolism. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 2091–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.; Sun, C.; Di, C.; Si, J.; Gan, L.; Yan, J. Mitochondrial Proteomics Reveals the Mechanism of Spermatogenic Cells Apoptosis Induced by Carbon Ion Radiation in Zebrafish. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 22439–22449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtuszkiewicz, A.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Maas, M.J.; Kaspers, G.J.; Jansen, G.; Cloos, J. Pre-MRNA Splicing in Cancer: The Relevance in Oncogenesis, Treatment and Drug Resistance. Expert Opin. Drug Met. 2015, 11, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Fayos, A.C.; Pérez-Gómez, J.M.; García, G.M.E.; Jiménez-Vacas, J.M.; Blanco-Acevedo, C.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Solivera, J.; Breunig, J.J.; Gahete, M.D.; Castaño, J.P.; et al. SF3B1 Inhibition Disrupts Malignancy and Prolongs Survival in Glioblastoma Patients through BCL2L1 Splicing and MTOR/ß-Catenin Pathways Imbalances. J. Exp. Clin. Canc. Res. 2022, 41, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampoelz, B.; Andres-Pons, A.; Kastritis, P.; Beck, M. Structure and Assembly of the Nuclear Pore Complex. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2019, 48, 515–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, P.; Dang, T.; Pané, N.; Shevchenko, A.; Mann, M.; Forbes, D.; Hurt, E. Nup93, a Vertebrate Homologue of Yeast Nic96p, Forms a Complex with a Novel 205-KDa Protein and Is Required for Correct Nuclear Pore Assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell 1997, 8, 2017–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.; Bachorik, J.L.; Dreyfuss, G. Gemin5-SnRNA Interaction Reveals an RNA Binding Function for WD Repeat Domains. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Morcillo, M.; Francisco-Velilla, R.; Embarc-Buh, A.; Fernández-Chamorro, J.; Ramón-Maiques, S.; Martinez-Salas, E. Structural Basis for the Dimerization of Gemin5 and Its Role in Protein Recruitment and Translation Control. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollmann, F.; Fechir, K.; Nowag, S.; Koch, K.; Art, J.; Kleinert, H.; Pautz, A. Human Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (INOS) Expression Depends on Chromosome Region Maintenance 1 (CRM1)- and Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4E (ElF4E)-Mediated Nucleocytoplasmic MRNA Transport. Nitric Oxide-Biol. Ch. 2013, 30, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, G.; De Crescenzo, G.; Khaleghpour, K.; Kahvejian, A.; O’Connor-McCourt, M.; Sonenberg, N. Paip1 Interacts with Poly(A) Binding Protein through Two Independent Binding Motifs. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 3769–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.; Shuvalova, E.; Egorova, T.; Shuvalov, A.; Sokolova, E.; Bizyaev, N.; Shatsky, I.; Terenin, I.; Alkalaeva, E. Polyadenylate-Binding Protein–Interacting Proteins PAIP1 and PAIP2 Affect Translation Termination. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 8630–8639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, A.; Xiao, Y.; Shu, W.-J.; Du, H.; Zhang, T. Upregulation of PAIP1 Promotes the Gallbladder Tumorigenesis through Regulating PLK1 Level. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.K.; Erkelenz, S.; Rattay, S.; Dehof, A.K.; Hildebrandt, A.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Schaal, H.; Schwerk, C. Human SAP18 Mediates Assembly of a Splicing Regulatory Multiprotein Complex via Its Ubiquitin-like Fold. RNA 2010, 16, 2442–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.-F.; Nowak, N.J.; Shows, T.B.; Aplan, P.D. MAGOH Interacts with a Novel RNA-Binding Protein. Genomics 2000, 63, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Di Giammartino, D.C.; Taylor, D.; Sarkeshik, A.; Rice, W.J.; Yates, J.R.; Frank, J.; Manley, J.L. Molecular Architecture of the Human Pre-MRNA 3′ Processing Complex. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, I.; Martin, G.; Friedlein, A.; Langen, H.; Keller, W. Human Fip1 Is a Subunit of CPSF That Binds to U-Rich RNA Elements and Stimulates Poly(A) Polymerase. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daxinger, L.; Whitelaw, E. Understanding Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance via the Gametes in Mammals. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg Effect: The Metabolic Requirements of Cell Proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras-Rubio, A.; Perucho, L.; Paciucci, R.; Vilardell, J.; LLeonart, M.E. Ribosomal Proteins as Novel Players in Tumorigenesis. Cancer Metast. Rev. 2014, 33, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, H.; Nadano, D.; Hidaka, E.; Higuchi, K.; Kawakubo, M.; Sato, T.-A.; Nakayama, J. Differential Expression of Ribosomal Proteins in Human Normal and Neoplastic Colorectum. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2003, 51, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimoto, Y.; Shimizu, S. Another Way to Die: Autophagic Programmed Cell Death. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanida, I.; Yamasaki, M.; Komatsu, M.; Ueno, T. The FAP Motif within Human ATG7, an Autophagy-Related E1-like Enzyme, Is Essential for the E2-Substrate Reaction of LC3 Lipidation. Autophagy 2012, 8, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, L. Regulation of ATG and Autophagy Initiation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1206, 41–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupack, D.G. Caspase-8 as a Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, V.S.; O’Connor, L.; O’Reilly, L.A.; Silke, J.; Metcalf, D.; Ekert, P.G.; Huang, D.C.S.; Cecconi, F.; Kuida, K.; Tomaselli, K.J.; et al. Apoptosis Initiated by Bcl-2-Regulated Caspase Activation Independently of the Cytochrome c/Apaf-1/Caspase-9 Apoptosome. Nature 2002, 419, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, J.; Meirow, D.; Lewis-Roness, H.; Ornoy, A. Genetic and Teratogenic Effects of Cancer Treatments on Gametes and Embryos. Hum. Reprod. Update 2001, 7, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, S.; Al-Sadaan, M.; Agarwal, A. Spermatogenesis, DNA Damage and DNA Repair Mechanisms in Male Infertility. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2015, 31, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavattam, K.G.; Kato, Y.; Sin, H.-S.; Maezawa, S.; Kowalski, I.J.; Zhang, F.; Pang, Q.; Andreassen, P.R.; Namekawa, S.H. Elucidation of the Fanconi Anemia Protein Network in Meiosis and Its Function in the Regulation of Histone Modifications. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1141–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Deng, Y.; He, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, G.; Hu, Q.; Weng, Q. Effects of 60Co-γ Radiation on Testis Physiological Aspects of Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus). Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2019, 169, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, G.E.; Young, J.C.; Horvay, K.; Abud, H.E.; Loveland, K.L. Regulated Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling Sustains Adult Spermatogenesis in Mice. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 90, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deb, A.; Zhang, Z.; Pachori, A.; He, W.; Guo, J.; Pratt, R.; Dzau, V.J. Secreted Frizzled Related Protein 2 Protects Cells from Apoptosis by Blocking the Effect of Canonical Wnt3a. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2009, 46, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Deng, G.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, J.; Ma, C.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. A Caspase-Dependent Pathway Is Involved in Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Promoted Apoptosis in Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Infected RAW264.7 Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5045–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appenzeller-Herzog, C.; Hall, M.N. Bidirectional Crosstalk between Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and MTOR Signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahran, A.M.; Mosad, E.; Abdel-Raheem, M.A.; Ahmed, E.H.; Abdel Motaleb, A.A.; Hofny, E.R. The Correlation between Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (MTOR) Gene Expression and Sperm DNA Damage among Infertile Patients with and without Varicocele. Andrologia 2019, 51, e13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, A.; Girard, M.; Thimmanahalli, D.S.; Levasseur, A.; Céleste, C.; Paquet, M.; Duggavathi, R.; Boerboom, D. MTOR Regulates Gap Junction Alpha-1 Protein Trafficking in Sertoli Cells and Is Required for the Maintenance of Spermatogenesis in Mice. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 95, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Diaz, E.S.; Kong, M. Proteasome Activity and Its Relationship with Protein Phosphorylation during Capacitation and Acrosome Reaction in Human Spermatozoa. Soc. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 2007, 65, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, J.L. Factors Regulating Sperm Capacitation. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2010, 56, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardilha, M.; Esteves, S.L.C.; Korrodi-Gregório, L.; Vintém, A.P.; Domingues, S.C.; Rebelo, S.; Morrice, N.; Cohen, P.T.W.; e Silva, O.A.D.C.; e Silva, E.F.D.C. Identification of the Human Testis Protein Phosphatase 1 Interactome. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffone, M.G.; Calamera, J.C.; Verstraeten, S.V.; Doncel, G.F. Capacitation-Associated Protein Tyrosine Phosphorylation and Membrane Fluidity Changes Are Impaired in the Spermatozoa of Asthenozoospermic Patients. Reproduction 2005, 129, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Substance | Serial Number | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| Bovine serum albumin standard solution (μL) | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| PBS buffer (μL) | 20 | 18 | 16 | 14 | 12 | 10 |
| Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 solution (μL) | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Protein content (μg) | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| OD562 | 0.3705 | 0.4970 | 0.6125 | 0.7695 | 0.8580 | 0.9240 |
| Analyze Project | Software/ Method | Website |
|---|---|---|
| Mass spectrum data analysis | MaxQuant | http://www.maxquant.org/ (accessed on 3 April 2022) |
| Motif analysis | MoMo | http://meme-suite.org/tools/momo (accessed on 6 April 2022) |
| GO annotation | InterProScan | http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/ (accessed on 6 April 2022) |
| Domain annotation | InterProScan | http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/ (accessed on 6 April 2022) |
| KEGG annotation | KEGG Mapper | http://www.kegg.jp/kegg/mapper.html (accessed on 6 April 2022) |
| KAAS | http://www.genome.jp/kaas-bin/kaas_main (accessed on 6 April 2022) | |
| Subcellular localization | Wolfpsort | http://www.genscript.com/psort/wolf_psort.html (accessed on 6 April 2022) |
| CELLO | http://cello.life.nctu.edu.tw/ (accessed on 6 April 2022) | |
| Enrichment analysis | Perl module | https://metacpan.org/pod/Text::NSP::Measures::2D::Fisher (accessed on 8 April 2022) |
| Clustering heat map | R Package pheatmap | https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/cluster/ (accessed on 8 April 2022) |
| Protein interaction | Blast | http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 8 April 2022) |
| R package networkD3 | https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/networkD3/ (accessed on 8 April 2022) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Zhang, K.; Wen, J.; Zeng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Hu, Q.; Weng, Q. Molecular Mechanism of Male Sterility Induced by 60Co γ-Rays on Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus). Molecules 2023, 28, 5727. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155727
Li S, Zhang K, Wen J, Zeng Y, Deng Y, Hu Q, Weng Q. Molecular Mechanism of Male Sterility Induced by 60Co γ-Rays on Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus). Molecules. 2023; 28(15):5727. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155727
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shifan, Ke Zhang, Jiaqi Wen, Yuhao Zeng, Yukun Deng, Qiongbo Hu, and Qunfang Weng. 2023. "Molecular Mechanism of Male Sterility Induced by 60Co γ-Rays on Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus)" Molecules 28, no. 15: 5727. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155727
APA StyleLi, S., Zhang, K., Wen, J., Zeng, Y., Deng, Y., Hu, Q., & Weng, Q. (2023). Molecular Mechanism of Male Sterility Induced by 60Co γ-Rays on Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus). Molecules, 28(15), 5727. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155727







