Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Canagliflozin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
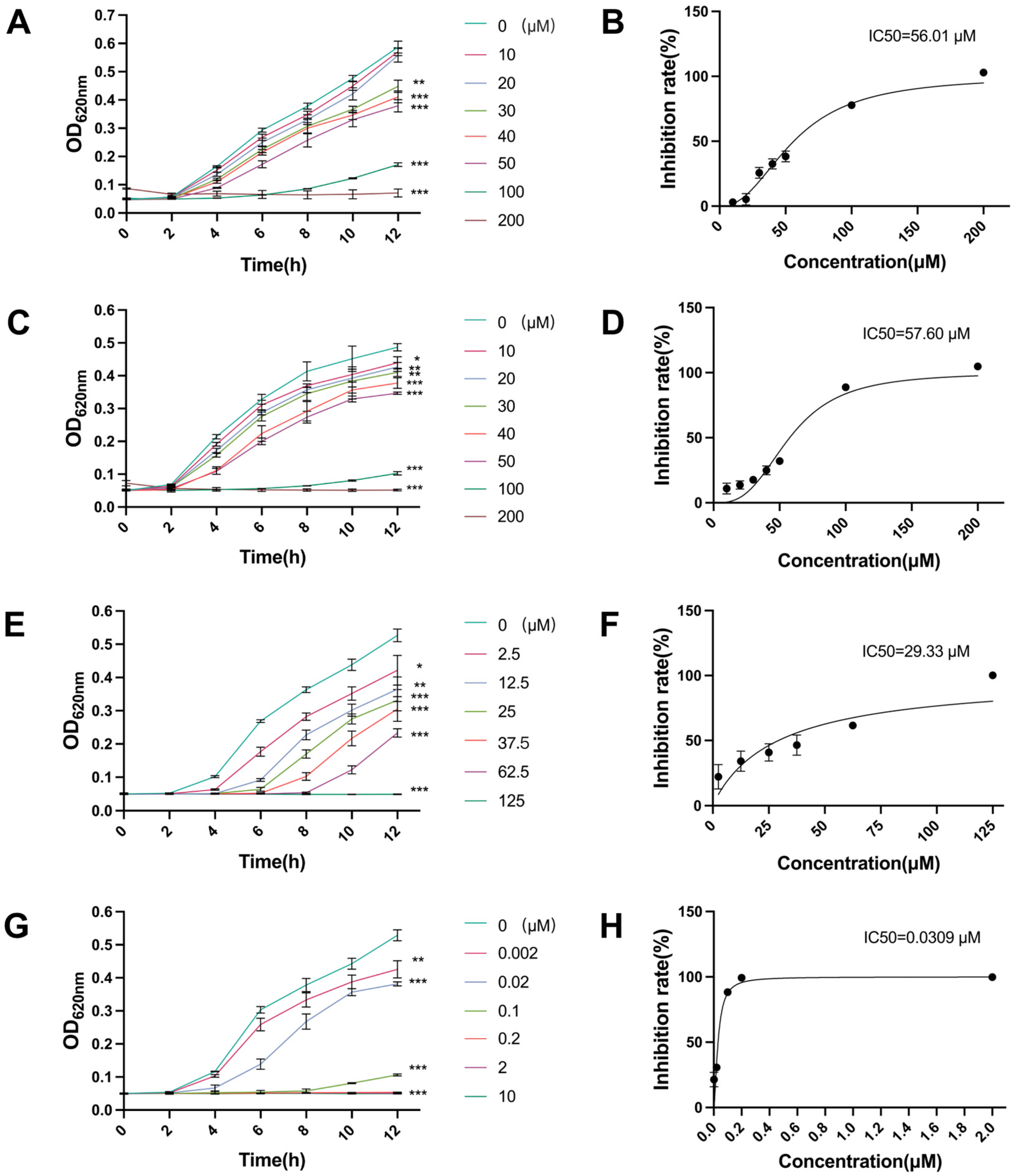
2.1. Antibacterial Activity of Canagliflozin, Penicillin and Doxycycline and Their IC50 Values
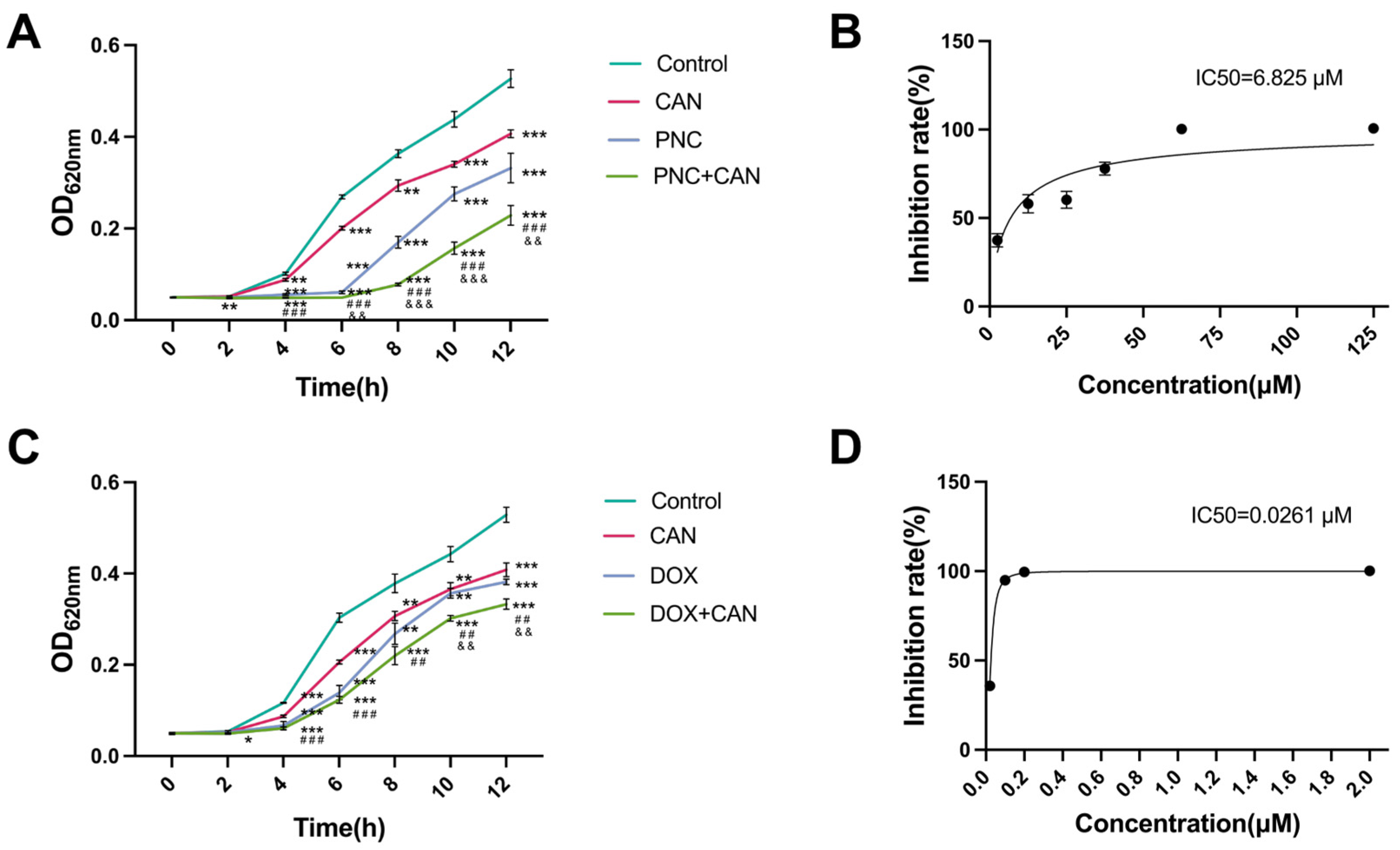
2.2. Antibacterial Effect of CAN Combined with PNC and DOX
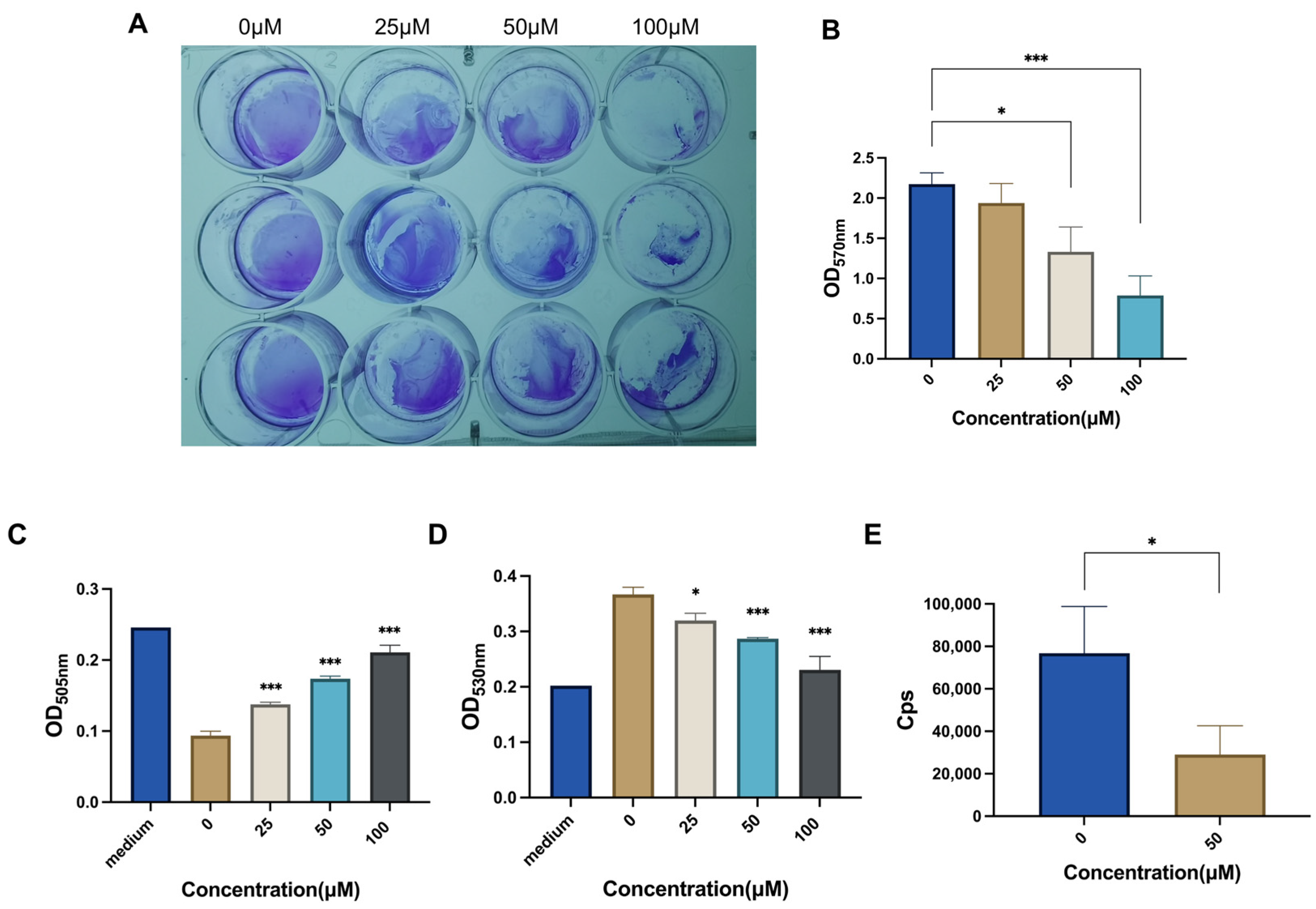
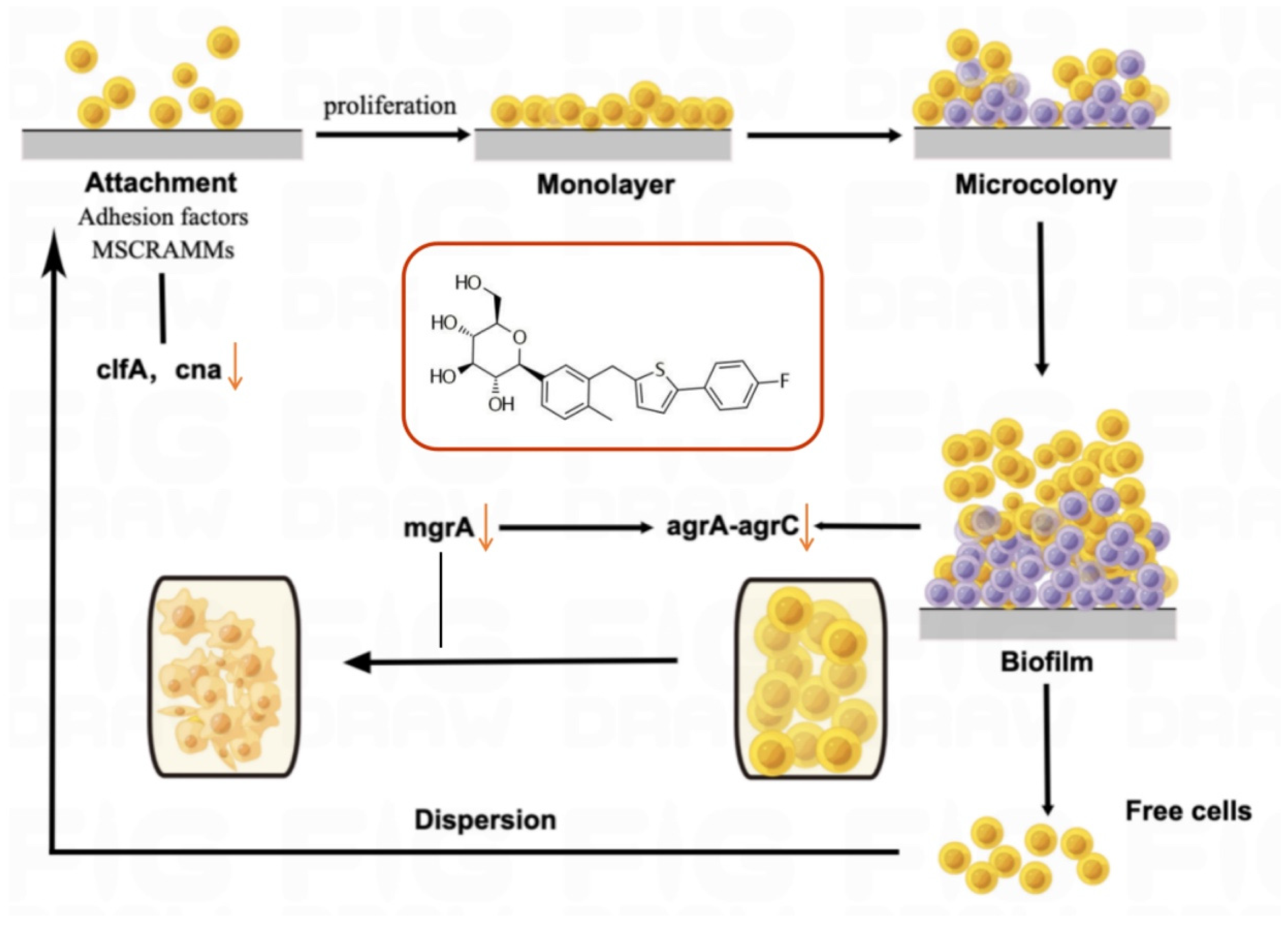
2.3. CAN Inhibits Bacterial Biofilm and Metabolism
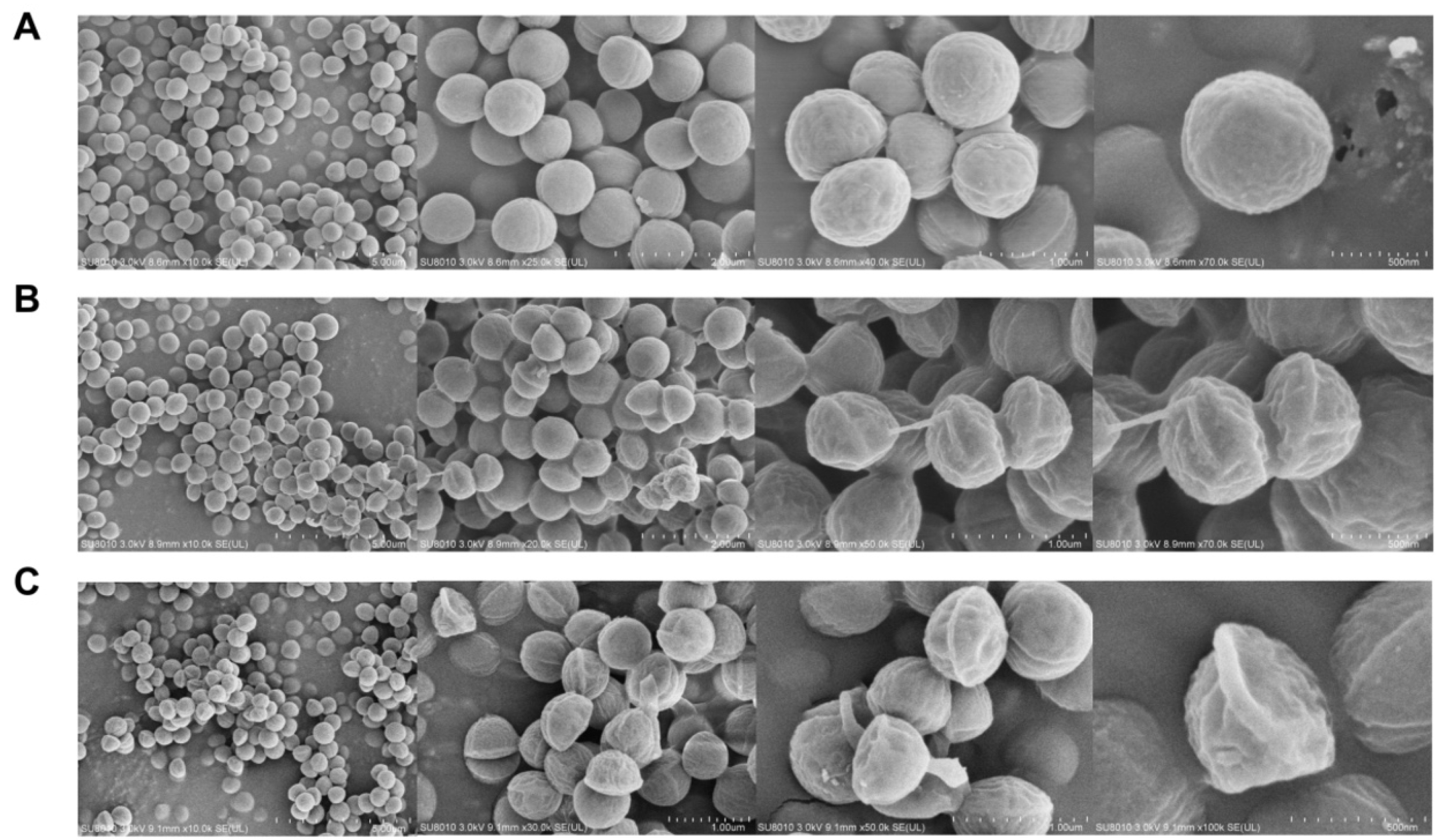
2.4. Field-Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
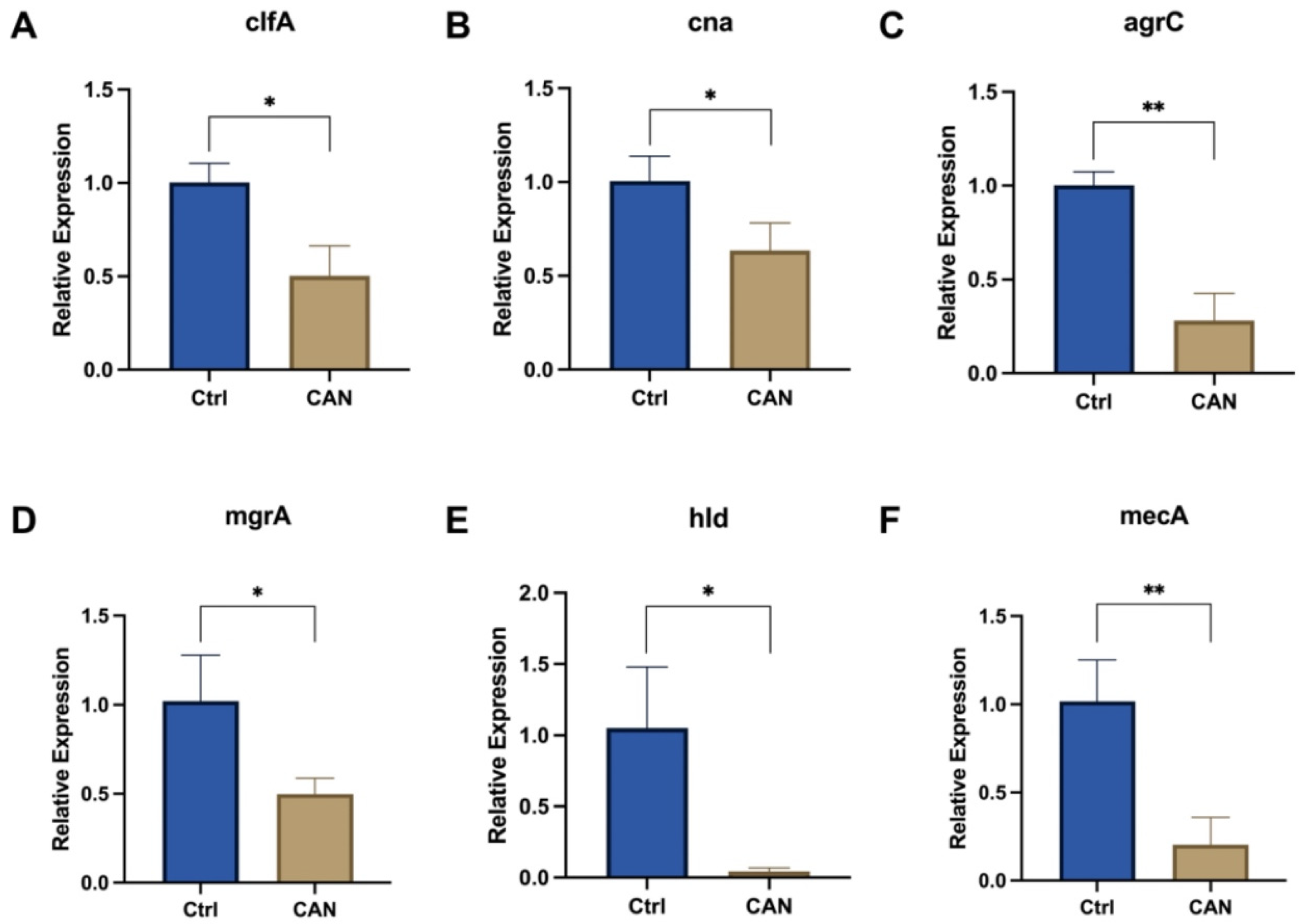
2.5. CAN Affects Biofilm-Related Signaling Pathways in MRSA
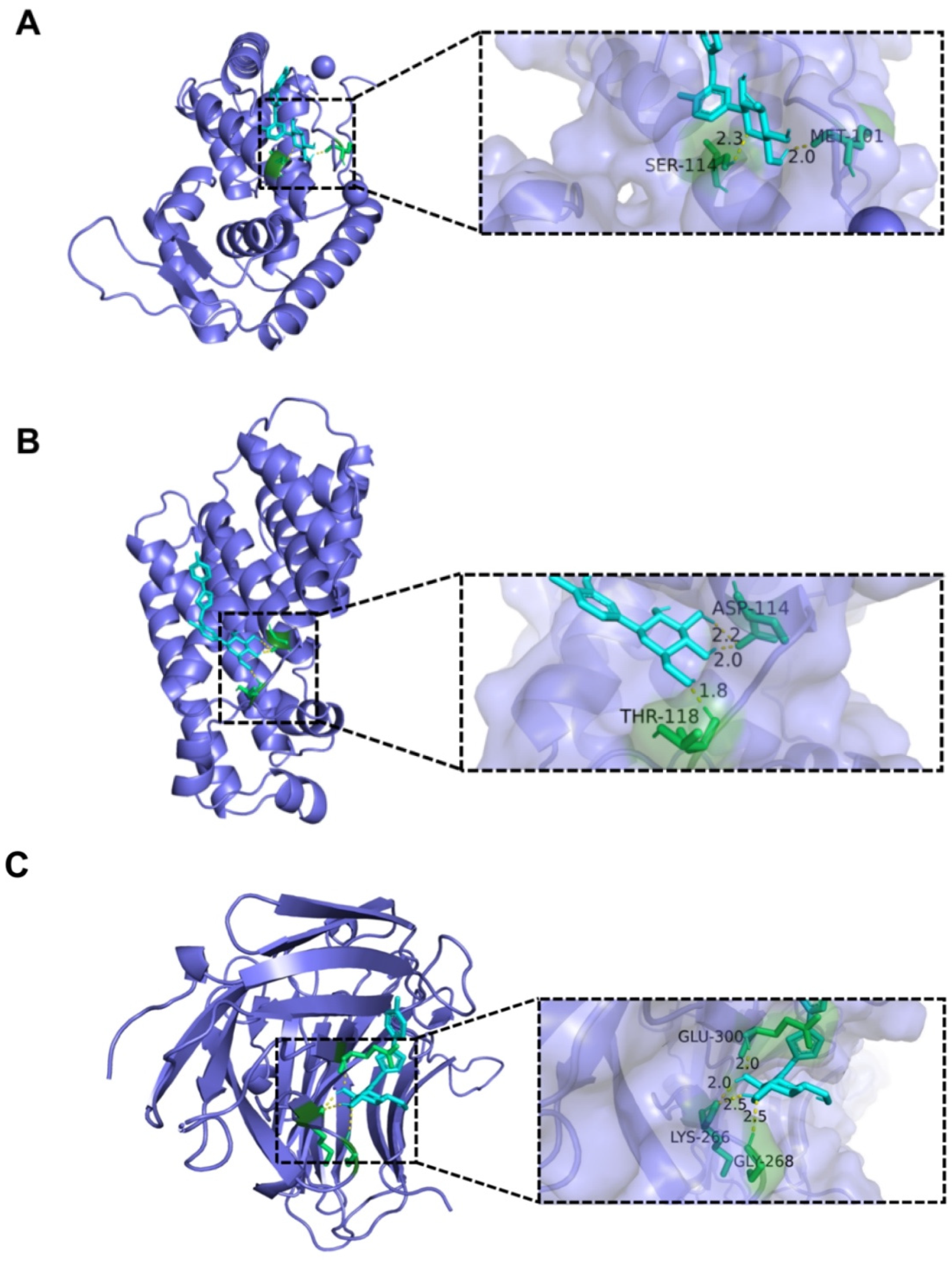
2.6. Analysis of Interaction between CAN and Bacterial Protein
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Determination of Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentrations (IC50)
4.2.1. Canagliflozin (CAN)
4.2.2. Penicillin (PNC)
4.2.3. Doxycycline (DOX)
4.3. Growth Curve and Fractional Inhibitory Concentration Index (FICI)
4.4. Biofilm Growth
4.5. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
4.6. ATP Detection
4.7. Glucose Detection
4.8. Lactic Acid Detection
4.9. Field-Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
4.10. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
4.11. Molecular Docking
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Mottola, C.; Matias, C.S.; Mendes, J.J.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Tavares, L.; Cavaco-Silva, P.; Oliveira, M. Susceptibility patterns of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in diabetic foot infections. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, R.; Simring, D.; Kim, B.; Mortensen, J.; Williams, D.; Leslie, A. The diabetic foot ulcer. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2020, 49, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Panero, A.J.; Ruiz-Muñoz, M.; Cuesta-Vargas, A.I.; Gónzalez-Sánchez, M. Prevention, assessment, diagnosis and management of diabetic foot based on clinical practice guidelines: A systematic review. Medicine 2019, 98, e16877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xia, L.; Fu, X.; Xu, Z.; Ran, X.; Yan, L.; Li, Q.; Mo, Z.; Yan, Z.; et al. A cohort study of diabetic patients and diabetic foot ulceration patients in China. Wound Repair. Regen. 2015, 23, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitocco, D.; Spanu, T.; Di Leo, M.; Vitiello, R.; Rizzi, A.; Tartaglione, L.; Fiori, B.; Caputo, S.; Tinelli, G.; Zaccardi, F.; et al. Diabetic foot infections: A comprehensive overview. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, D.G.; Tan, T.W.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Bus, S.A. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. JAMA 2023, 330, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghotaslou, R.; Memar, M.Y.; Alizadeh, N. Classification, microbiology and treatment of diabetic foot infections. J. Wound Care 2018, 27, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shettigar, K.; Murali, T.S. Virulence factors and clonal diversity of Staphylococcus aureus in colonization and wound infection with emphasis on diabetic foot infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 2235–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, K.E.; Boeckh, S.; Stacey, H.J.; Jones, J.D. The microbiology of diabetic foot infections: A meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherardi, G. Staphylococcus aureus Infection: Pathogenesis and Antimicrobial Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobanovska, M.; Pilla, G. Penicillin’s Discovery and Antibiotic Resistance: Lessons for the Future? Yale J. Biol. Med. 2017, 90, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Khanna, D.; Kalra, S. Minocycline and Doxycycline: More Than Antibiotics. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 1046–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftheriadou, I.; Tentolouris, N.; Argiana, V.; Jude, E.; Boulton, A.J. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in diabetic foot infections. Drugs 2010, 70, 1785–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, S.J.; Wylam, M.E. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection and Treatment Options. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2069, 229–251. [Google Scholar]
- Parikh, M.P.; Octaria, R.; Kainer, M.A. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infections and Injection Drug Use, Tennessee, USA, 2015–2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.; Uthman, O.; Cummins, E.; Clar, C.; Royle, P.; Colquitt, J.; Tan, B.K.; Clegg, A.; Shantikumar, S.; Court, R.; et al. Canagliflozin, dapagliflozin and empagliflozin monotherapy for treating type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. 2017, 21, 1–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, P.; Gao, T.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W. Canagliflozin Attenuates Lipotoxicity in Cardiomyocytes by Inhibiting Inflammation and Ferroptosis through Activating AMPK Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, W.; Wang, B.; Xu, T.; Wang, J.; Wei, D. Canagliflozin Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Inhibiting Inflammation through Induction of Autophagy. Yonsei Med. J. 2022, 63, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, W.; Zhong, J.; Lei, F.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W. Canagliflozin exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting intracellular glucose metabolism and promoting autophagy in immune cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 152, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, P.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Ding, Y.; Xie, W. Intragastric and atomized administration of canagliflozin inhibit inflammatory cytokine storm in lipopolysaccharide-treated sepsis in mice: A potential COVID-19 treatment. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Hao, W.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Xie, W. Canagliflozin Ameliorates NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Inflammation Through Inhibiting NF-κB Signaling and Upregulating Bif-1. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 820541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Shan, W.; Wan, F.; Luo, J.; Niu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, N.; Xie, W. Canagliflozin Delays Aging of HUVECs Induced by Palmitic Acid via the ROS/p38/JNK Pathway. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Sun, P.; Zhang, X.; Lin, G.; Xin, Q.; Niu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W. Canagliflozin Modulates Hypoxia-Induced Metastasis, Angiogenesis and Glycolysis by Decreasing HIF-1α Protein Synthesis via AKT/mTOR Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, B.J.; Blagih, J.; Ponce-Garcia, F.M.; Canavan, M.; Gudgeon, N.; Eastham, S.; Hill, D.; Hanlon, M.M.; Ma, E.H.; Bishop, E.L.; et al. Canagliflozin impairs T cell effector function via metabolic suppression in autoimmunity. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1132–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Jiang, H.; Cai, C.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Canagliflozin Prevents Lipid Accumulation, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Mice with Diabetic Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 839640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, A.; Yoshifuji, A.; Irie, J.; Tajima, T.; Uchiyama, K.; Itoh, T.; Wakino, S.; Itoh, H. Canagliflozin protects the cardiovascular system through effects on the gut environment in non-diabetic nephrectomized rats. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2023, 27, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yao, Y.; Wei, P.; Song, C.; Wan, S.; Yang, S.; Zhu, G.M.; Liu, H.M. Housefly Phormicin inhibits Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA by disrupting biofilm formation and altering gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1424–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsinwar, S.; Jayaraman, A.; Mahapatra, S.K.; Vellingiri, V. Anti-virulence properties of catechin-in-cyclodextrin-in-phospholipid liposome through down-regulation of gene expression in MRSA strains. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 167, 105585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.; Kalra, R.; Ponnan, P.; Jayaweera, J.; Kumbukgolla, W.W. Inhibition of penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a) in methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) by combination of oxacillin and a bioactive compound from Ramalinaroesleri. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, Y.H.E.; Manukumar, H.M.; Rakesh, K.P.; Karthik, C.S.; Mallu, P.; Qin, H.L. Vision for medicine: Staphylococcus aureus biofilm war and unlocking key’s for anti-biofilm drug development. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 123, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergara, A.; Normanno, G.; Di Ciccio, P.; Pedonese, F.; Nuvoloni, R.; Parisi, A.; Santagada, G.; Colagiorgi, A.; Zanardi, E.; Ghidini, S.; et al. Biofilm Formation and Its Relationship with the Molecular Characteristics of Food-Related Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2364–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosch, A.; Haefner, S.; Jude, E.; Lobmann, R. Diabetic foot infections: Microbiological aspects, current and future antibiotic therapy focusing on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. Wound J. 2011, 8, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Shapouri Moghaddam, A.; Derakhshan, S.; Hashemipour, S.M.A.; Hadadi-Fishani, M.; Pirouzi, A.; Khaledi, A. Correlation Between Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in MRSA and MSSA Isolated from Clinical Samples in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhang, H.; Fareed, M.S.; He, Y.; Su, J.; Wang, P.; Shen, Z.; Yan, W.; et al. A carrier-free, dual-functional hydrogel constructed of antimicrobial peptide Jelleine-1 and 8Br-cAMP for MRSA infected diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2022, 151, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, W.; Che, S.; Li, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, H.; Xie, W. Synthesis of Berberine and Canagliflozin Chimera and Investigation into New Antibacterial Activity and Mechanisms. Molecules 2022, 27, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, S.; Fan, B.; Wan, F.; Gao, T.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, D.; Xie, W. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Canagliflozin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2023, 28, 5668. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155668
Gu S, Fan B, Wan F, Gao T, Qi Y, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Gu D, Xie W. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Canagliflozin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules. 2023; 28(15):5668. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155668
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Siyao, Bing Fan, Fang Wan, Tong Gao, Yuanyuan Qi, Jin Zhou, Yaou Zhang, Dayong Gu, and Weidong Xie. 2023. "Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Canagliflozin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus" Molecules 28, no. 15: 5668. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155668
APA StyleGu, S., Fan, B., Wan, F., Gao, T., Qi, Y., Zhou, J., Zhang, Y., Gu, D., & Xie, W. (2023). Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Canagliflozin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules, 28(15), 5668. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155668






