Abstract
Adsorption has become the most popular and effective separation technique that is used across the water and wastewater treatment industries. However, the present research direction is focused on the development of various solid waste-based adsorbents as an alternative to costly commercial activated carbon adsorbents, which make the adsorptive separation process more effective, and on popularising the sustainable options for the remediation of pollutants. Therefore, there are a large number of reported results available on the application of raw or treated agricultural biomass-based alternatives as effective adsorbents for aqueous-phase heavy metal ion removal in batch adsorption studies. The goal of this review article was to provide a comprehensive compilation of scattered literature information and an up-to-date overview of the development of the current state of knowledge, based on various batch adsorption research papers that utilised a wide range of raw, modified, and treated agricultural solid waste biomass-based adsorbents for the adsorptive removal of aqueous-phase heavy metal ions. Metal ion pollution and its source, toxicity effects, and treatment technologies, mainly via adsorption, have been reviewed here in detail. Emphasis has been placed on the removal of heavy metal ions using a wide range of agricultural by-product-based adsorbents under various physicochemical process conditions. Information available in the literature on various important influential physicochemical process parameters, such as the metal concentration, agricultural solid waste adsorbent dose, solution pH, and solution temperature, and importantly, the adsorbent characteristics of metal ion removal, have been reviewed and critically analysed here. Finally, from the literature reviewed, future perspectives and conclusions were presented, and a few future research directions have been proposed.
1. Introduction
The sustainable and cost-effective remediation of water pollutants to produce clean water is a challenging task for scientists, researchers, and engineers worldwide. As per the United Nations World Water Development Report in 2020 [1], around four billion people face severe water scarcity for at least one month per year [2]. Environmental water contamination due to the large release of various potential and toxic pollutants from human activities, such as increased industrialisation, urbanisation, populations, and agricultural activities, into water bodies present a high risk to human life and aquatic environments [3]. The commonly found heavy metals ions include Cu2+, Ni2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, and Hg2+ ions [3,4,5]. Among them, Cd2+, Pb2+, Hg2+, and As3+ ions are the most dangerous heavy metal ions that have been identified by the World Health Organisation (WHO) [5]. Heavy metals are not biodegradable and are carcinogenic in nature. About 40% of Earth’s surface water, comprising mainly river and lake water, is being polluted by heavy metal ions primarily from the industrial and agricultural activities [6].
The major sources of heavy metal ion pollution comprise discharge from various untreated industrial effluents from refineries, coal-fired power plants, mining industries, alumina refineries, metallurgical industries, heavy chemicals, chloro-alkali industries, battery industries, dyes and pigments, fertilisers, metal smelters, paints and ceramics, tanneries, textiles, etc. [3,7]. The metal ions Cd2+, Pb2+, Hg2+ Cr3+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Fe3+, and Zn2+ are significantly toxic and pose risks to both humans and the environment [7,8,9]. There are various adverse health effects, such as diarrhoea, disorderedness, stomach problems, paralysis, various skin deceases, haemoglobinuria, vomiting, etc., that occur due to heavy metal ion contamination [3,10]. Heavy metal ions are highly toxic, hazardous to health, and non-biodegradable, and pose a high threat to the ecosystem if they are left untreated [3,11,12]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop ecofriendly, economically feasible technology to remove these potential pollutants from the aqueous phase [11]. Detailed information on heavy metal ion classifications, sources, and their toxicity effects have been detailed in our own previous publications [3].
A number of conventional technologies, such as chemical precipitation, oxidation, advanced oxidation, coagulation/flocculation, electrocoagulation, photo catalysis, membrane processes, reverse osmosis (RO), filtration, adsorption, solvent extraction, electroplating, ion exchange, activated sludge, and aerobic and anaerobic treatment, have been used to remove these potential pollutants from water and wastewater with varying levels of success [2,3,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. All these treatment technologies have their own advantages and disadvantages. Various researchers, including the current author’s in their own reported review publication, have critically discussed the advantages and disadvantages of these different metal ion treatment technologies [7,19,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. Among these methods, adsorption-based separation technology is one of the most effective but widely used treatment technologies for heavy metal-contaminated water and wastewater. This is due to its simple operation, design simplicity, high separation efficiency, efficiency at lower pollutant concentrations, high selectivity at the molecular level, low energy consumption, and ability to separate multiple pollutant components with minimal secondary pollution, making it a form of sustainable development [3,20,21,28]. In their previous review article, Afroze and Sen [3] reported statistical data (Figure 1) on the increasing trend of published research papers on inorganic and organic adsorption using various adsorbents since the year of 1995. The adsorptive removal of heavy metals from water and wastewater has become an essential and widely used separation technique in recent times [12].
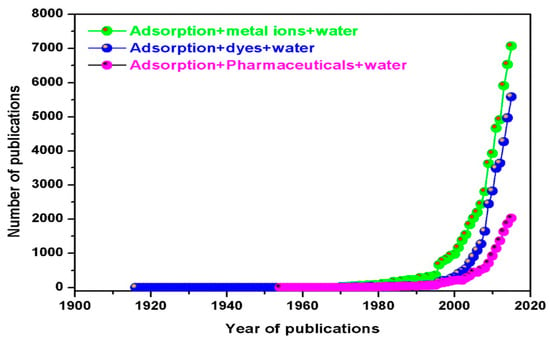
Figure 1.
Number of adsorption publications for metal ions and organics removal. Source: taken from [3] with written permission.
Adsorption may be defined as the transfer of one or more solute molecules from the bulk fluid phase to the solid adsorbent surface and getting retained there. The solid that adsorbs a solute component is called the adsorbent, and the solute component that is adsorbed is termed the adsorbate. When the adsorption arises as a result of weak Van der Waals or short-range forces, it is called physical adsorption. In contrast, in the case of chemical adsorption, a chemical covalent or ionic bond formation takes place between the adsorbate and the adsorbent via electronic transfer, which is irreversible in nature [7]. There are three major steps involved at the solid/liquid interface of the adsorption process. These mechanistic steps are as follows: (a) diffusion of the solute adsorbate from the bulk aqueous phase to the surface of the adsorbent by film diffusion; (b) the adsorption at the solid/liquid interface means on the active sites of adsorbent surface; and then (c) the internal diffusion of the solute molecules within the solid adsorbent via pore diffusion or surface diffusion, or both. In simple terms, the adsorption of aqueous phase heavy metal ions involves a solid adsorbent phase and a liquid solvent phase, wherein metal ions are in the dissolved solute adsorbate molecules and are therefore part of the solid/liquid interfacial adsorption separation process. The mechanism underlying this adsorptive separation process involves chemisorption, complexation formation at the solid/liquid interface, adsorption on surface and interior pore structure of the adsorbent, ion exchange, etc., and this is due to the presence of the mass transfer concentration gradient and diffusional processes [3,14,29].
To predict the rate of adsorption and to identify the mechanisms underlying adsorption and the adsorbent’s capacity, it is vital to understand the various reported adsorption kinetic models and isotherm model equations [3,29]. In terms of the adsorption process design, the determination of various kinetic parameters is a particularly critical design parameter. Numerous kinetic models, such as the first-order and second-order reversible or irreversible kinetic models, along with the pseudo-first-order or pseudo-second-order adsorption models, have been reported and applied to batch adsorption experimental results by various researchers [2,3,30,31]. The most reported kinetic models are the pseudo-first order (PFO) and pseudo-second order (PSO) kinetic models, in which batch experimental data are fitted to these PFO and PSO models. In their critical review article, Tan and Hameed [30] mentioned that Ho [32] reviewed the applications of second-order models for adsorption systems, while Liu and Liu [33] summarised the useful kinetic models for biosorption. Surface reaction mechanism-based adsorption models have been reviewed by Plazinski et al. [34]. Alberti et al. discussed the batch and dynamic adsorption models [35]. Afroze and Sen [3] presented a compilation of reported batch adsorption results on the applicability of pseudo-second-order kinetic models for heavy metal and dye adsorption using several agricultural solid wastes, and readers are encouraged to go through this review article.
Adsorption isotherm studies are crucial for understanding the mechanisms of adsorption and for finding the maximum adsorption capacity of the adsorbent. Several adsorption isotherm models have been reported in the literature, such as the Langmuir, Freundlich, Redlich–Peterson, Tempkin, and Toth isotherm models. Of these isotherm models, the Freundlich 1906 [36] and Langmuir (1918) [37] models have been widely used in the evaluation of the adsorption process. From this research, readers are encouraged to go through the review article by Afreza and Sen [3], where the applicability of various isotherm models on the batch heavy metal adsorption process using wide ranges of agricultural solid waste-based adsorbents have been reported.
The adsorption process depends on the nature and the types of the adsorbent and adsorbate characteristics. The adsorbate characteristics, such as molecular weight, structure, size, charge, and solution concentration, and the adsorbent characteristics, such as particle size, surface area, surface charge, and surface functional groups are all responsible for effective adsorption [22,38]. Apart from these adsorbent-adsorbate characteristics, many physicochemical process parameters, such as the initial metal ion concentration, adsorbent dosage, contact time, solution pH, temperature, and salt concentration all significantly affect the adsorption process [3,4,27]. In the adsorptive separation process, four commonly used important adsorbents are activated carbon, zeolites or molecular sieves, natural inorganic clay minerals, silica gel, and activated alumina [39,40]. However, commercial activated carbon (CAC) is most used in the water and wastewater treatment industry due to its large porous structure, large surface area, high capacity, and the hydrophobic nature of activated carbon [3,12,38]. But coal-based CAC is costly and possesses significant regeneration issues. Therefore, the current focus of research has been shifted towards the use of various carbonaceous, lignocellulosic, and agricultural by-product solid wastes, such as fruit and vegetable wastes, leaves, seeds, tree waste, fibres, fruit peels, dates, sawdust, bark, etc., for the development of an effective adsorbent alternative to costly coal-based activated carbon. Agricultural biomasses materials, like the shells of wheat, orange peels, sunflower leaves, biochar from plant residues, activated carbon from plant residues, wood waste, bark residues, fruit wastes, and manures have been successfully used in heavy metal ion removal from water by adsorption [31]. Figure 2 shows a few agricultural by-products that are cost-effective, and function as alternative adsorbents that can be used in the adsorption of heavy metal ions.

Figure 2.
Several examples of agricultural biomass alternative adsorbents that are used in the adsorption of metal ions. Source: taken from [41] with written permission.
Modified agricultural solid waste has been widely used as an effective adsorbent in the removal of various contaminations from wastewater, and this has ben attributed to their surface properties improvements. Raw biomass can be modified using acids, such as hydrochloric, phosphoric, sulfuric, nitric, citric acids etc., or alkaline solutions, such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, zinc chloride, calcium chloride, ammonia etc., or cross-linked with other materials [3]. Chemical treatment removes natural fats, waxes, and low-molecular-weight lignin compounds from agricultural adsorbent surfaces. In recent years, the production of activated carbon, biochar, and charcoal from agricultural solid residuals is emerging as an alternative and cost-effective adsorbent with a high selectivity, porosity, and surface area, and these waste materials have naturally been available in large quantities, requires less processing time, are a renewable source, and have little or no commercial value [3,31]. Biochar is produced via the pyrolysis of biomass residues. The production and properties of these valuable adsorbents depend on the production and treatment methods, which are presented in Figure 3. Figure 4 shows a flowchart for the overall adsorption process for the removal of inorganic/organic compounds using agricultural wastes as adsorbents under various physicochemical process conditions.
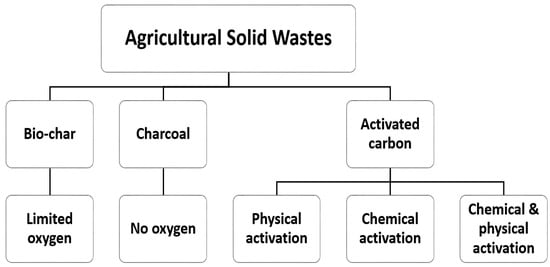
Figure 3.
Various treatments of adsorbent materials.
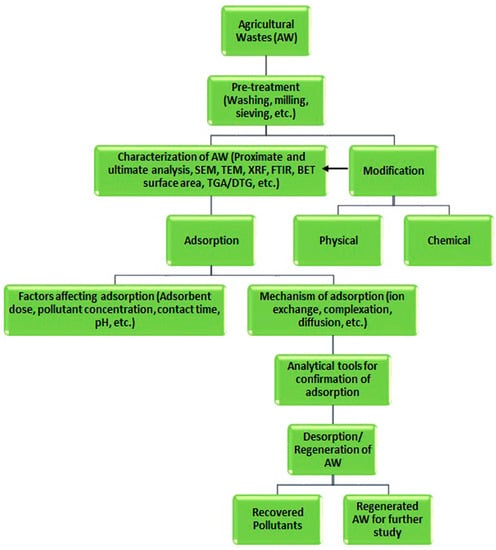
Figure 4.
A flowchart presenting the overall adsorption process for pollutant removal from waste water. Source: taken from Ogunlalu et al. [31] with written permission.
In recent times, these agricultural by-products have raised environmental awareness about their safe disposal, and therefore any kind of their utilisation is considered as a win-win situation for effective solid waste management as well. Hence, this review article will provide a comprehensive compilation of all the up-to-date developments of the current state of knowledge on various batch adsorption results using a wide range of raw and modified agricultural solid waste adsorbents in the removal of heavy metal ions from water and wastewater. The significance of this review is not only the compilation and up-to-date developments of the current state of knowledge, but also the critical analysis of the recent research articles that have been published in the directions of agricultural solid waste and modified agricultural solid waste adsorbents. In this review, we have also reported and compiled the various batch heavy metal ion adsorption results under various physicochemical process parameters. Therefore, the structure of this review article began with a general introduction section comprising heavy metal ion water pollution and their sources, toxicity, and treatment methods. Emphasis has been given to agricultural by-product-based adsorbents for the removal of aqueous phase heavy metal ions through adsorption under various process conditions. Finally, the knowledge gap between the future perspectives and the future directions have been presented.
2. Characteristics of the Role of Adsorbents and Agricultural Waste-Based Adsorbents in Heavy Metal Adsorption
The current research has primarily been driven towards using lignocelluloses, and carbonaceous, agricultural, and forest-based adsorbents for water decontamination, including metal decontamination using an adsorption alternative to the costly CAC. These materials are available locally in large quantities and are almost priceless, with a minimum pre-treatment cost for improvements in terms of their effectiveness, efficiency, and environmental friendliness, and are an alternative adsorbent to the costly CAC. Further, agricultural solid waste adsorbent materials require minimal pre-treatment operations, such as washing, drying, grinding, or minor chemical treatments [42]. The adsorption capacity of an adsorbent plays a vital role in the selection of effective adsorbents in the removal of aqueous phase pollutants, which is either determined experimentally or theoretically using various isotherms and kinetic models. The metal adsorption at the solid/liquid interface is highly dependent on many physicochemical process parameters, such as metal ion concentration, solution pH, temperature, adsorbent dose etc., and hence the adsorption capacity was discussed and reviewed in the next section. For example, Gumus et al. [43] reported that the leaf biomass of Laurus nobilis is an effective adsorbent in the removal of Cd2+, Cu2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+ toxic metal ions from its aqueous solution and strong functions of temperature and solution pH with the adsorption capacity as the pH increases. A theoretical maximum Cr6+ adsorption capacity of 70.49 mg/g for data palm empty fruit bunch biomass was obtained at an optimum solution pH of 2 and a temperature of 30 °C [44]. Rice bran and rice straw adsorbents were successfully used to remove aqueous phase Cu2+ metal ions and their reported maximum adsorbent capacities were found to be 21 mg/g and 18.4 mg/g, respectively [45]. Similarly, the metal ions Pb2+ and Cr6+ were also effectively removed from water using the peanut shell residue adsorbent [46,47]. The same peanut shell residue biomass was effectively used to remove the aqueous phase from the Cr3+, Cu2+, and Pb2+ ions with an adsorption capacity of 7.7 mg/g, 10.2 mg/g, and 29.1 mg/g, respectively [48]. Afroze et al. [49] successfully developed a eucalyptus bark-based adsorbent for the removal of heavy metal ions from water. Ahmed and Danish [50] reviewed the raw and treated avocado waste-based effective adsorbents used in heavy metal ion removal under various conditions. Anastopoulos et al. [51] reviewed and compiled various coffee adsorbents, such as coffee grounds, coffee residues, spent coffee grains, and coffee husks in the removal of aqueous phase heavy metal ions under various experimental conditions. Hence, while a large number of reported metal adsorption results through various raw or treated/modified agricultural solid waste-based processes have been deemed as effective, cost-effective alternative adsorbents include fruit wastes, such as lemon peel [52], durian peel [53], banana peel, Kuwai peel [54], raw pomegranate peel [55], watermelon shell [56], and coconut coir [57], along with various tree leaves, such as Artocarpus odoratissimus leaves [58], and Colocation esculenta leaves [59]. All these articles have also reported on the effects of various factors on heavy metal ion adsorption kinetics and equilibrium adsorption by agricultural wastes and their maximum adsorption capacity. Raw and chemically activated various agricultural wastes, such as jackfruit, rice husk, pecan shell, bamboo, pine leaves, pinecone, eucalyptus bark, hazelnut shell, maize cob or husk, castor hull etc., are also reported effective adsorbents in the removal of aqueous phase heavy metal ions [3,31]. There are a couple of reported review articles available in the literature, such as those by Ahmed and Danesh, [50]; Saukat et al. [42]; Ogunlalu et al. [31]; Afroze and Sen; [3]; and Sulyman et al. [60] on aqueous phase heavy metal ion removal through selective agricultural solid waste-derived adsorbents. Their maximum adsorbent capacities have been reported, and readers are encouraged to go through these articles. Table 1 presents the compilation of various reported results on the maximum adsorption capacity of various agricultural by-products in the removal of heavy metals from water during the last 10-year period of 2012–2022.

Table 1.
Adsorption capacities qm (mg/g) of several recently reported raw and modified agricultural waste materials for heavy metal ion adsorption.
The effectiveness and adsorbent capacity depend on the adsorbent’s size, shape, and morphological and chemical structure, including surface characteristics such as the surface area, pore volume, point of zero charge (pHpzc), bulk density, and the presence of surface functional groups [49,97]. The presence of surface functional groups in agricultural by-product adsorbent surfaces, such as carbonyl, phenolic, acetamido, alcoholic, amino groups etc., undergo strong interactions with heavy metal ions under physicochemical process conditions to form metal complexes or chelates. Adsorption is a reaction, and the rate of adsorption increases with the adsorbent surface area, shape, and surface charge, respectively. Table 2 represents the effects of various adsorbent characteristic parameters on heavy metal ion adsorption from some of the more recently published research articles [3].

Table 2.
The effects of several agricultural solid waste-based adsorbent characteristics on heavy metal ion adsorption.
3. Batch Metal Ion Adsorption by Agricultural Solid Waste Biomass Adsorbents under Various Physicochemical Process Parameters
In this section, the effects of the important process parameters, such as metal ion concentration, contact time, adsorbent load, pH, and temperature on the adsorbent capacity towards metal ion adsorption has been reviewed and discussed below. The identification and optimisation of these process parameters were generally determined through batch adsorption studies prior to pilot-scale continuous adsorption operation.
3.1. The Effects of the Initial Metal Ion Concentration and the Contact Time
To understand the adsorbate load and their optimum load concentration, a wide range of initial adsorbate metal ion concentrations has been examined across various reported batch adsorption studies [3,104]. Generally, with the increase in the initial adsorbate heavy metal ion concentration, the percentage removal efficiency of the carbon-based adsorbents initially increased up to a certain level and then decreased [20,105,106]. A higher solute concentration increases the competition due to the presence of excess solutes in the system to adhere with an adsorbent surface, which subsequently reduces the overall removal efficiency of the system [4,27,49,100,107]. The adsorbate or solute offers the driving force in terms of the concentration gradient to overcome the mass transfer resistance. Increasing the initial adsorbate concentration leads to the decrease in the percentage of adsorbate metal removal and an increase in the amount of heavy metal ions adsorbed per gram of adsorbent (qt). At lower concentration ranges, the available adsorbent sites are occupied by adsorbate molecules and hence increase the adsorption capacity [49]. Sometimes the adsorption process slows down due to the steric repulsion between the solute molecules [108]. Generally, the higher percentage of heavy metal removal decreases with the metal ion concentration; in this research direction, readers are encouraged to go through these various recently reported review articles [3,11,20,69,104]. The percentage removal of Zn2+ metal ions by the sorghum hull adsorbent was found to have decreased from 50.98% to 12.8% for the metal ion concentration range of 10–50 mg/L, respectively [86]. With the increase in the initial metal ion concentration from 25 to 150 mg/L, the percentage of adsorption of the rice husk decreased from 90.8% to 60.85% for Cr2+, 96.12% to 65.42% for Pb2+, and from 94.36% to 66.83% for Zn2+, respectively [20,109]. Similarly, it was reported by Ding et al. [110] that the maximum hickory wood biochar adsorbent capacity for the Cd2+, Zn2+, Ni2+, and Cu2+ metal ions was increased with the metal ion concentrations of 2–100 mg/L, respectively [7]. Yargic et al. [111] reported on the batch Cu2+ adsorption studies by the chemically-treated tomato waste where the percentage of metal ion removal decreased with the increase in the initial metal ion concentration, and the adsorbed amount of metal (qe) per gram of adsorbent increased with the initial metal ion concentration. Similarly, Kilic et al. [112] presented the variation between the adsorptive capacities of Ni2+ and Co2+, qe (mg/g), by almond shell biochar with the Ni2+ and Co2+ metal ion concentration ranges of 50–150 ppm and 100–200 ppm, respectively, under various temperatures, which are presented in Figure 5. As shown in Figure 5, the metal ion adsorption increased with time and followed the three step process with an initial fast reaction rate period followed by a slow rate, ending with the attainment of an equilibrium stage at 240 min [112]. A further amount of metal ion adsorption (qe (mg/g)) was increased with the increased temperature, which is also shown in Figure 5. The adsorption capacity of the Hass avocado shell (HAS) adsorbent for Ni2+ increased from 5.63 to 107.26 mg per gram, respectively, with the increase in the metal ion concentration [50].
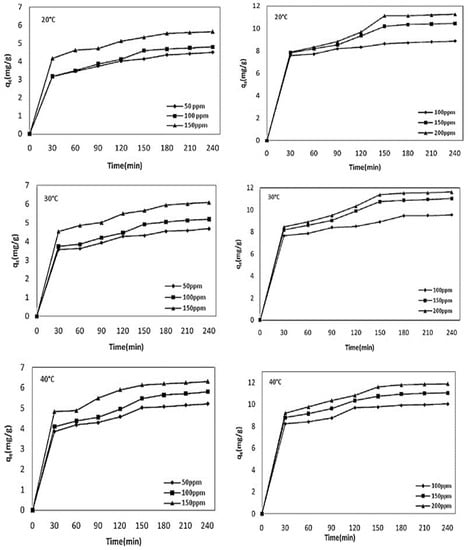
Figure 5.
The effects of the contact time and initial metal ion concentrations of Ni2+ and Co2+ on the amount of adsorption by the almond shell biochar adsorbent at temperatures of 20, 30, and 40 °C, respectively. Source: taken from [112] with written permission.
Generally, the percentage removal of aqueous phase pollutants by initial adsorption increases with the contact time, and then slowly reaches a steady-state saturation level. It may present in the form of either a two-stage or multistage adsorption process [3,4,14,49,63]. Therefore, adsorption kinetic studies are important for obtaining crucial knowledge on the speed of the reaction and the equilibrium time for maximum adsorption achievement, as well as to know the kinetic parameters required for the adsorber design.
3.2. Effects of the Adsorbent Dose
For the successful design, development, and scale-up of a continuous adsorption column, the knowledge of the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent is essential. The effect of an adsorbent dose on heavy metal adsorption in a solution indicates its adsorption capacity, which also depends on the available active sites on the adsorbent’s surface for adsorption [63,97]. In general, the adsorption capacity qe (mg/g) decreases with the increase in the adsorbent dose, whereas the percentage removal of metal ions increases along with the increase in the adsorbent dose [97,113]. A high adsorption capacity indicates that the adsorption process is running with a lower adsorbent dose/load. At higher adsorbent doses, there are maximum available active sites for adsorption and hence higher percentage removals of the adsorptive metal ions takes place at higher adsorbent dosages [3]. However, with a lower adsorption capacity, the removal percentage of pollutants increases rapidly and then slows down as the dose is reduced [50,114]. Much of the information presented in the literature supports these findings, such as Kılıç et al. [112], who reported from their batch adsorption study that the percentage adsorptive removal of the Ni2+ and Co2+ metal ions by the almond shell biochar increased from 10% to 38%, and from 25% to 50%, with the increase in the adsorbent doses from 1 to 10 g/L, respectively. In contrast, Ni2+ and Co2+ adsorbent’s capacities, qe (mg/g), were decreased from 10 mg/g to 3 mg/g, and from 24 mg/g to 7 mg/g, respectively, for which their results are presented in Figure 6.
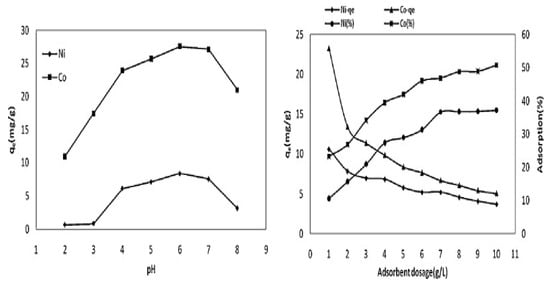
Figure 6.
Effects of the solution pH and adsorbent dosages on Ni2+ and Co2+ adsorption. Source: taken from Kilic et al. [112] with written permission.
Afroze et al. [49] also reported similar results for Zn2+ adsorption by modified eucalyptus sheathiana bark biomass, and it was found that their adsorbent capacity, qe (mg/g), decreased from 72.52 mg g−1 to 17.57 mg g−1 with the increase in the adsorbent doses from 0.01 g to 0.03 g, respectively [4]. There are also a few reported results on the same trends, i.e., with increases in the adsorbent dose accompanied with a decrease in the percentage of metal adsorption [115]. Imran-Shaukat et al. [42] reviewed and presented a compilation list on the variation of the adsorptive capacities of various amounts/loads of different agricultural biomass groups (such as bark, husk, leaves, peels, seeds, and straw) towards heavy metal ion (including Cd2+, Co2+, Cr2+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+) adsorption, and critically analysed their comparative results at high, medium, and low adsorbent doses. When the amount of adsorbent mass in a fixed-volume solution is below the optimum value, the removal of metal ions is also low due to the lower number of available active sites for adsorption [69]. Table 3 presents an updated compilation of the selected reported results on the effect of adsorbent dosage in the removal of aqueous phase heavy metals using agricultural waste biomass during the last 10-year period [3].

Table 3.
The selected reported list on the effect of changes in the adsorbent dosages on the percentage of adsorptive metal ion removal using several agricultural wastes as adsorbents during the last 10-year period.
3.3. Influential Effect of the Solution pH
The variation of solution pH plays a major role in changing the adsorbent surface charges, degree of ionisation, and metal speciation in solution, and hence causes changes to the adsorption capacity during the adsorption process [98,123]. Therefore, changes in the solution pH facilitate the adsorbent site dissociation and adsorbate solution chemistry, such as hydrolysis, surface complex formation, redox reactions, and precipitation, which are all strongly influenced by the pH [124]. The protonation and deprotonation of both functional groups in the adsorbent and adsorbate compound will produce different surface charges/zeta potential in the solution depending on the system’s pH [125]. Adsorbent capacity depends on its point of zero charge (pHpzc), and hence the surface charge. The point of zero charge (pzc) or the isoelectric point (iep) is defined as a particular pH where the surface charge becomes zero, i.e., where the extent of the adsorption of the positively charged species equals that of the negatively charged species. The point of zero charge (pHpz) of various raw, treated, or modified agricultural biomass-based adsorbents was determined by many investigators to obtain a better understanding of the adsorptive removal mechanism [49,126,127,128]. Generally, at lower acidic solutions, where pH < pHpzc, the adsorbent surface becomes positively charged and hence less metal cation adsorption takes place due to electrostatic repulsion between the positive cations and the positive surface-binding sites. Whereas, at pH > pHpzc, the surface becomes negatively charged and favours metal cation adsorption. However, at a higher basic pH, metal complex formation occurs resulting in precipitative separation instead of adsorptive metal ion separation [60]. For example, at a solution pH < 6.0, Pb (NO3)2 in solution predominately exists as Pb2+ ions. Meanwhile, with an increasing solution pH, for example at pH = 8, Pb (OH)+ formation occurs, and at pH = 11, it will precipitate as Pb (OH)2 [49,129]. Therefore, cationic species adsorption is favoured at pH > pHpzc due to the presence of the functional groups, such as the OH−, and COO− groups, while anionic adsorbate adsorption is favoured at pH < pHpzc due to the presence of H+ ions [113,130]. An electrical double layer at the solid/liquid interface is formed by the adsorbing counter ions from the aqueous solution to its adsorbent surface. Overall, the adsorbent surface functional groups/surface charges and the chemical nature of adsorbates at a solution pH strongly influence the adsorption behaviour and capacity. In their review article, Ahmad and Danish [50] mentioned that Mallampati et al. [72,131] reported the results of the solution pH effect on the adsorptive removal of the aqueous phase Pb2+, Ni2+, and Cr2O72− ions with the avocado peel adsorbent. They found that the percentage removal of the cationic Pb2+ and Ni2+ adsorption was increased with the increase in the solution pH, whereas the adsorption of anionic Cr2O72− was decreased with the same increasing solution pH. Abbar et al. [79] presented the batch adsorption experimental results on the effects of the solution pH on Cu2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ adsorption by the flax fibre tows (FFTs) adsorbent in the solution pH range from 1.6 to 8.5, respectively, for all metal ions. To investigate the effects of the solution pH on metal ion precipitation, Abbar et al. [79] presented the experimental results without adsorbent. It was found that the percentage removal of all three metal cations increased with the solution pH and attained a maximum value at an optimum pH, and thereafter decreased with the further increase in the solution pH. The maximum percentage removal of the Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions occurred in the solution pH range of 4–6, whereas for Zn2+ metal ions, the maximum values were observed at the solution pH of 7, respectively. At a higher pH, lead, copper, and zinc metal ions precipitate as hydroxides and reduce the rate of adsorption and hence reduce their removal capacity as well [79]. Similarly, Kilic et al. [112] reported that the amount of Ni2+ and Co2+ adsorption, qe (mg/g), by the almond shell biochar was increased from solution pH 2 to 6, and then decreased with the increasing solution pH, as shown in Figure 6. The deprotonation of the agricultural solid waste-based adsorbent typically takes place at a solution pH higher than pHzpc, and the surface becomes more negatively charged due to the presence of the stretching hydroxyl (–OH) and carboxyl (–COOH) functional groups [4]. Therefore, more adsorption of the cationic metal ions takes place mainly through the electrostatic force of attraction mechanism. Dawood and Sen [4], reported a similar trend in Ni2+ adsorption using the pinecone biochar adsorbent. At a low solution, the pH tends to decrease the adsorption capacity of the cations onto the adsorbent due to the presence of hydronium (H3O+) ions competing with the cationic metal ions for the available adsorption sites [7], accompanied with the fact that similar charges repel each other [50]. However, a lower, acidic solution pH favours anionic ion adsorption more, and this is because of the positively charged adsorbent surface and the opposite counter anions adsorption mechanism.
3.4. Effects of the Temperature and Thermodynamics of Adsorption
Temperature plays an important role in the adsorption of metal ions associated with the thermodynamics of the adsorption process. Temperature was found to be another significant physiochemical process parameter that influences the adsorption/biosorption mechanism and hence the equilibrium adsorbent capacity [3,42,132]. Different metal ions and different adsorbents have different responses to the system’s temperature [7,42,133]. Temperature induces various changes in the thermodynamic parameters, such as changes in the Gibb’s free energy (ΔG0), enthalpy (ΔH0), and entropy (ΔS0), for the heavy metal ion adsorption by the agricultural solid waste-based adsorbents, which can be determined by the following two equations [134]:
and
where qe is the amount of metal ion adsorbed per unit mass adsorbent (mg/g), Ce is the equilibrium concentration (mg/L), T is the temperature in K, and R is the universal gas constant (8.314 J/molK).
Shaukat et al. [42] recently reviewed and reported the temperature effects on the agricultural waste biomass adsorption efficiency for various heavy metal ions under three temperature levels: high: 45 °C < x ≤ 60 °C, medium: 30 °C < x ≤ 45 °C, and low: 20 °C ≤ x ≤ 30 °C, respectively. At low-temperature levels, the metal ion adsorption increases in the order of Mn2+ > Pb2+ > Cu2+ > Cr6+ > Co2+ > Zn2+ > Ni2+ > Cd2+ and in the order of Pb2+ > Cd2+ > Zn2+ at the medium level, respectively. Meanwhile, for the high level of temperature, the order was Cd2+ > Pb2+ > Cr2+ > Cu2+. Temperature is an important indicator of the exothermic or endothermic nature of the adsorption reaction process [135]. The solution viscosity is reduced with the increase in the solution’s temperature and hence increases the diffusive transport of adsorbate species from the bulk phase to the solid/liquid interface and through pore diffusion [136]. An increase in the adsorption capacity at higher solution temperatures indicates the endothermic nature of the adsorption reaction due an increase in the kinetic transport of adsorbate solutes and a higher diffusional rate [38]. However, a decrease in the adsorption capacity with an increase in the temperature indicates that the reaction has become exothermic, and this is due to the heat-induced decrease in the attractive adsorptive forces between the adsorbate and the adsorbent’s surface [137].
The temperature effect on the agricultural adsorbent’s capacity depends on the surface functional groups [138]. They reviewed and reported the results of many studies, such as mango leaf powder [139], rice husk [139], orange peel [140], and coconut shell [141]), which were all found to increase the percentage adsorption of metal ions with the increase in the temperature range (25–40 °C). In comparison, the adsorption of Cd2+ on the cashew nut shell was decreased from 80.13% to 74.32% with the rise in temperature from 30 °C to 60 °C, respectively. Many studies have also reported that metal ion uptake by some adsorbents is reduced with an increasing temperature [133,142].
4. Future Perspectives and Future Challenges
To overcome the high costs of commercial activated carbon (CAC) and to overcome the other operational issues that have been associated with the use of CAC as the adsorbent, raw and modified agricultural biomass residue-based adsorbents have gained a significant level of attention as an alternative, carbon-containing, easily accessible, and cost-effective adsorbent in the removal of aqueous phase heavy metal ions with a high degree of binding capacity. From the extensive literature review on adsorption-based wastewater treatment technology, the following points presented are the challenges and future directions that need to be addressed so that adsorption-based technology may be more effective and popularize this technology for the future remediation of water pollution.
Overall economy: the overall economically feasible operation of an adsorption-based treatment plant depends on many factors. Various costs associated with the operating costs, fixed costs, including the installation cost, adsorbent pre-treatment/preparation costs, and cost of adsorbent regeneration are all especially important for determining the feasibility of the full process. Among them, the adsorbent cost alone, including its procession, is above 60% of the total operating cost. Therefore, the adsorbent material selection is crucial for the adsorptive separation process. Various non-conventional solid waste-based adsorbents may be an alternative, cost-effective solution to this process.
Industrial scale problems and lab-based experiments: due to the introduction of various environmental protection laws and regulations, industries have imposed the discharge of waste into the environment. However, industries sometimes discharge harmful chemical waste at a higher than prescribed limit. Therefore, the industry always looks into some low-cost technology like adsorption, and many industries have already adopted this technology. However, the effectiveness of this adsorption-based technology is mainly judged using the laboratory-based batch adsorption results with limited continuous experimental results. Therefore, more continuous adsorption operation results, if possible, along with the pilot-scale results are required before commercial implementation.
Batch and continuous column analysis: based on the literature review over the last two decades, it has been found that more than 80% of adsorption-based studies are of the batch scale. The challenge of adsorption-based studies lies here. These batch studies are confined to various kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamic analysis with a very small lab scale. The batch-scale study results cannot be adopted directly for industrial use without continuous operation. Several recent studies have come up with some lab or bench-scale continuous studies of adsorption in a packed bed, fluidised bed, and semi-fluidised system to help in the scale up of this process. More research is required in the field of continuous adsorption systems and scale-up processes.
Adsorption modelling: For large-scale operation and process design adsorption modelling, the procedure for the accurate estimation of various kinetic parameters, isotherm models, and the thermodynamic parameters for the multicomponent system are essential.
Adsorbent regeneration and reuse: it has been mentioned previously in that the 60% cost of an adsorption-based system depends on the cost of the adsorbent. Therefore, in the age of sustainable development, adsorbent regeneration must be given significant priority. To reduce waste production, secondary pollution, and operating costs, and to make the overall technology more cost-effective for further reuse, regeneration of the loaded adsorbents is an essential process. Moreover, the capture adsorbate must be recovered as they may be valuable products or to aid in minimising secondary pollution. Hence, an eco-friendly and low-cost alternative regeneration method must be developed to reduce waste production and cost, as well as maximise the cycle number to use for a greater number of times under industrial operations.
Process optimisation: in adsorption-based studies, process optimisation is required under controlled conditions and for further applications in real-field situations. In most cases, the actual process effluents are multicomponent and compete with the adsorbates. The multicomponent systems always reduce the ideal adsorption capacity, meaning therefore that the modelling and optimisation of these multicomponent systems will be quite complex.
5. Conclusions
Water pollution due to heavy metal ion contamination resulting from various sources, including untreated industrial effluent discharge and agricultural activities, is of global concern and to find out an efficient but sustainable and cost-effective remediation solution to these important global problems imposes a challenging task on scientists, researchers, and practising engineers. Among the various conventional remediation techniques, adsorption-based separation technology is considered to be one of the most effective approaches widely used in treating heavy metal contaminated water and wastewater due to its simple operation, design simplicity, high separation efficiency, efficiency at lower pollutant concentrations, high selectivity at the molecular level, low energy consumption, ability to separate multiple pollutant components, and minimize secondary pollution. This review article presented a compilation of various scattered literature data along with the up-to-date development batch metal cation adsorption results using a wide range of non-conventional and cost-effective agricultural solid waste-based adsorbents under various process conditions. It is clear from the present literature survey in that non-conventional raw or modified agricultural solid waste-based adsorbents are emerging as effective, but low-cost adsorbents for heavy metal ions present decontamination problems. The utilisation of this large amount of agricultural solid waste-based effective adsorbents in the water and wastewater treatment industries is a sustainable and cost-effective pollution control option alternative to the costly CAC adsorbents. The literature has also revealed that in some cases, the modification of the adsorbent increased the removal efficiency of adsorption. The effective metal removal efficiency from the aqueous phase mainly depends on the adsorbent’s characteristics and various physicochemical process parameters. Therefore, this review article was compiled to critically analyse the large batch adsorption results on heavy metal ion adsorption by the wide ranges of agricultural solid waste-based adsorbents, specifically the adsorbent’s characteristics, and under various influential process parameters, such as the initial adsorbate metal ion concentration, the initial solution pH, the adsorbent doses, and the temperature, respectively.
Funding
This work was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia (GRANT-3804).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate, Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia supported this work [GRANT3804]. The author also acknowledges Sharmeen Afroze and Sara Dawood for their minor assistance in literature information collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- UNWWDR. United Nations World Water Development Report 2020. Available online: https://www.unwater.org/publications/un-world-water-development-report-2020 (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Tee, G.T.; Gok, X.Y.; Yong, W.F. Adsorption of pollutants in wastewater via biosorbents, nanoparticles and magnetic biosorbents: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afroze, S.; Sen, T.K. A Review on Heavy Metal Ions and Dye Adsorption from Water by Agricultural Solid Waste Adsorbents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.; Sen, T.K.; Phan, C. Synthesis and characterization of slow pyrolysis pinecone biochar in the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from aqueous solution by adsorption: Kinetic, equilibrium, mechanism and thermodynamic. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisi, S.D.; Lofrano, G.; Grassi, M.; Notarnicola, M. Characteristics and adsorption capacities of low-cost sorbents for wastewater treatment: A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2016, 9, 10–40. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, H.X. Modified biochar adsorbents (MBAs) for heavy metal ions adsorption: A critical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Biomass and Clay Minerals-Based Adsorbents for the Removal of Cationic Dye and Metal Ion from Wastewater by Adsorption. Ph.D. Thesis, Curtin University Library, Bentley, WA, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, I.; Chandra, G. Biosorption of heavy metals from industrial wastewater by Geobacillus thermodenitrificans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of copper (II), chromium (III), nickel (II) and lead (II) ions from aqueous solutions by meranti sawdust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duruibe, J.; Ogwuegbu, M.; Egwurugwu, J. Heavy metal pollution and human biotoxic effects. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2007, 2, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, R.; Garg, R.; Sillanpää, M.; Alimuddin Khan, M.A.; Mubarak, N.M.; Tan, Y.H. Rapid adsorptive removal of chromium from wastewater using walnut-derived biosorbents. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Priya, A.K.; Kumar, P.S.; Hoang, T.K.; Sekar, K.; Chong, K.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Ng, H.S.; Show, P.L. A critical and recent developments on adsorption technique for removal of heavy metals from wastewater—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Han, Z.; Li, W.; Ji, T.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, S. Adsorption properties of heavy metals and antibiotics by chitosan from larvae and adulty trypoxylus dichotonus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 276, 118735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, T.K. Air, Gas and Water Pollution Control Using Industrial and Agricultural Solid Wastes Adsorbents, 1st ed.; CRC-Press/Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 13:978-1-138-19673-5. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, J.; Song, T.; Liang, J.; Bai, X.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Huang, S.; Dong, L.; Jin, Y. Adsorption of lead (Ⅱ) from aqueous solution by modified Auricularia matrix waste: A fixed-bed column study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, N.; Guo, X.; Liang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J. Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by chemically modified orange peel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, K.; Shah, M.; Limbachiya, N. Adsorption of Copper Cu (2+) Metal Ion From Wastewater Using Sulphuric Acid Treated Sugarcane Bagasse as Adsorbent. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2014, 1, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sahari, M.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Mohamed, R.M.S.R.; Noman, E.; Naushad, M.; Rizuan, M.B.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Ismail, N. Green approach and strategies for wastewater treatment using bioelectrochemical systems: A critical review of fundamental concepts, applications, mechanism, and future trends. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Natasha; Mosa, A.; El-Naggar, A.; Hossain, F.; Abdelrahman, H.; Niazi, N.K.; Shahid, M.; Zhang, T.; Tsang, Y.F.; et al. Manganese oxide modified biochar: Production, characterization and application for the removal of pollutants from aqueous environments: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hossain, F.; Duan, C.; Lu, J.; Tsang, Y.F.; Islam, S.; Zhou, Y. Isotherm models for adsorption of heavy metals from water—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, N.; Bhuiyan, M.A.; Pramanik, B.K.; Nizamuddin, S.; Griffin, G. Waste Materials for Wastewater Treatment and Waste Adsorbents for Biofuel and Cement Supplement Applications: A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naef, A.; Qasem, A.; Ramy, H.M.; Dahiru, U.L. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhao, X.; Cao, J. Advanced nanomaterials for degrading persistent organic pollutants. In Advanced Nanomaterials for Pollutant Sensing and Environmental Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 249–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Pathak, B. Zinc oxide based photocatalytic degradation of persistent pesticides: A comprehensive review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 13, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D.; Kimura, S.Y. Emerging environmental contaminants: Challenges facing our next generation and potential engineering solutions. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2017, 8, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divyapriya, G.; Singh, S.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Scaria, J.; Karim, A.V.; Nidheesh, P.V. Treatment of real wastewater by photoelectrochemical methods: An overview. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Meikap, B.C.; Sen, T.K. Adsorptive Removal of Aqueous Phase Copper (Cu2+) and Nickel (Ni2+) Metal Ions by Synthesized Biochar–Biopolymeric Hybrid Adsorbents and Process Optimization by Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Guan, S.-S. Adsorption Kinetics of Lead and Zinc Ions by Coffee Residues. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sud, D.; Mahajan, G.; Kaur, M.P. Agricultural waste material as potential adsorbent for sequestering heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6017–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Hameed, B.H. Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlalu, O.; Oyekunle, I.P.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Aderibigbe, A.D.; Emenike, E.C. Trends in the mitigration of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using unmodified and chemically modified agricultural waste adsorbents. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S. Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.J. Biosorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 61, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazinski, W.; Rudzinski, W. A novel two-resistance model for description of the adsorption kinetics onto porous particles. Langmuir 2010, 26, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G.; Amendola, V.; Pesavento, M.; Biesuz, R. Beyond the synthesis of novel solid phases: Review on modelling of sorption phenomena. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica, platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, K.P.; Vo, D.-V.; Prakash, D.G.; Joseph, A.; Viswanathan, S.; Arun, J. Environmental applications of carbon-based materials: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 557–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.K. Principles of Mass Transfer and Separation Processes, 1st ed.; Prentice Hall of India: New Delhi, India, 2007; Chapter 12; pp. 609–677. [Google Scholar]
- Galamboš, M.; Suchánek, P.; Rosskopfová, O. Sorption of anthropogenic radionuclides on natural and synthetic inorganic sorbents. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2012, 293, 613–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Asthana, A.; Singh, A.K.; Jain, B.; Susan, A.B.H. Adsorption of heavy metal ions by various low-cost adsorbents: A review. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 342–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, M.I.; Wahi, R.; Ngaini, Z. The application of agricultural wastes for heavy metals adsorption: A meta-analysis of recent studies. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 17, 100902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümüş, D.; Gümüş, F. Modeling heavy metal removal by retention on Laurusnobilis leaves biomass: Linear and nonlinear isotherms and design. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2020, 22, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambabu, K.; Banat, F.; Pham, Q.M.; Ho, S.H.; Ren, N.Q.; Show, P.L. Biological remediation of acid mine drainage: Review of past trends and current outlook. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2020, 2, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, B.; Das, S.K. Adsorptive removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solution and industrial effluent using natural/agricultural wastes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 107, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Ghazi, Z.A.; Saeed, M.; Ilyas, M.; Ahmad, R.; Muqsit Khattak, A.; Iqbal, A. A comparative study of the removal of Cr(vi) from synthetic solution using natural biosorbents. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 10799–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşar, Ş.; Kaya, F.; Özer, A. Biosorption of lead (II) ions from aqueous solution by peanut shells: Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhai, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Zhou, J. Kinetic studies of adsorption of Pb(II), Cr(III) and Cu(II) from aqueous solution by sawdust and modified peanut husk. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afroze, S.; Sen, T.K.; Ang, H.M. Adsorption removal of zinc (II) from aqueous phase by raw and base modified Eucalyptus sheathiana bark: Kinetics, mechanism and equilibrium study. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 102, 336–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Danish, M. A review of avocado waste-derived adsorbents: Characterizations, adsorption characteristics, and surface mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 134036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Bhatnagar, A.; Hameed, B.H.; Ok, Y.S.; Omirou, M. A review on waste-derived adsorbents from sugar industry for pollutant removal in water and wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 240, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, K.; Chowdhury, M.A.K.; Chowdhury, M.A.H.; Rahman, A.; Mohiuddin, K.M. Heavy metals in handloom-dyeing effluents and their biosorption by agricultural by products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7954–7967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngabura, M.; Hussain, S.A.; Ghani, W.A.; Jami, M.S.; Tan, Y.P. Utilization of renewable durian peels for biosorption of zinc from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2528–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, K.M. Water purification using different waste fruit cortexes for the removal of heavy metals. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2016, 10, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ali, S.; Jaouali, I.; Souissi-Najar, S.; Ouederni, A. Characterization and adsorption capacity of raw pomegranate peel biosorbent for copper removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3809–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Gogate, P.R. Intensified removal of copper from wastewater using activated watermelon based biosorbent in the presence of ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 30, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asim, N.; Amin, M.H.; Samsudin, N.A.; Badiei, M.; Razali, H.; Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Sopian, K. Development of effective and sustainable adsorbent biomaterial from an agricultural waste material: Cu (II) removal. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 249, 123128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, N.A.H.M.; Lim, L.B.L.; Usman, A. Enhancing adsorption of Pb (II) from aqueous solution by NaOH and EDTA modified Artocarpus odoratissimus leaves. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7172–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakkeeran, E.; Saranya, N.; Giri, M.; Nandagopal, S.; Santhiagu, A.; Selvaraju, N. Hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solutions by a novel powder prepared from Colocasia esculenta leaves. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2016, 18, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulyman, M.; Namiesnik, J.; Gierak, A. Low-cost Adsorbents Derived from Agricultural By-products/Wastes for Enhancing Contaminant Uptakes from Wastewater: A Review. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 479–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, A.V.; Becerra, M.G.; Guerrero-Amaya, H.; Ballesteros, L.M.; Mercado, D.F. Sulfate radical anion activated agro-industrial residues for Cr (VI) adsorption: Is this activation process technically and economically feasible? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.I. Optimization process for removing of copper ions from groundwater of Iraq. Using watermelon shell as natural adsorbent. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 737, 012195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayob, S.; Othman, N.; Ali, W.; Altowayti, H.; Khalid, F.S.; Bakar, N.A. A Review on Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Wood-Industrial Wastewater by Oil Palm. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.; Agarwal, T. Removal of Cr(VI) from water using pineapple peel derived biochars: Adsorption potential and re-usability assessment. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, R.; Qiblawey, H.; EI-Naas, M.H. Adsorption as a Process for Produced Water Treatment: A Review. Process 2020, 8, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.C., Jr.; da Paz Schiller, A.; Conradi, E., Jr.; Manfrin, J.; Schwantes, D.; Zimmermann, J.; Klassen, G.J.; Campagnolo, M.A. Removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from Contaminated Water using Activated Carbon from Canola Seed Wastes. In Proceedings of the 5th World Congress on New Technologies (NewTech’19), Lisbon, Portugal, 18–20 August 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, K.; Huma, R.; Shahbaz, A.; Jamal, J.; Rehman, M.Z.U.; Sharif, A.; Ahmed, E.; Begum, R.; Irfan, A.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; et al. Extraction of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Medium by Husk Biomass: Adsorption Isotherm, Kinetic and Thermodynamic study. Z. Phys. Chem. 2018, 233, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devani, M.A.; Oubagaranadin, J.U.K.; Munshi, B.; Lal, B.B.; Mandal, S. BP-ANN Approach for Modeling Cd (II) Bio-Sorption from Aqueous Solutions Using Cajanus cajan Husk. Iran. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 38, 110–124. [Google Scholar]
- Sazali, N.; Harun, Z. A Review on Batch and Column Adsorption of Various Adsorbent Towards the Removal of Heavy Metal. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2020, 67, 66–88. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Huang, S. Four different kinds of peels as adsorbents for the removal of Cd (II) from aqueous solution: Kinetics, isotherm, and mechanism. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 88, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, Z.; Yu, Q.J.; El Hanandeh, A. Competitive adsorption of heavy metal ions (Pb2+, Cu2+, and Ni2+) onto date seed biochar: Batch and fixed bed experiments. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 888–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallampati, R.; Xuanjun, L.; Adin, A.; Valiyaveettil, S. Fruit peels as efficient renewable adsorbents for removal of dissolved heavy metals and dyes from water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.; Dahiya, S. An Experimental and Quantum Chemical Study of Removal of Utmostly Quantified Heavy Metals in Wastewater Using Coconut Husk: A Novel Approach to Mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuan, T.V.; Phuong, B.B.; Nguyen, D. Response surface methodology approach for optimization of Cu2+, Ni2+ and Pb2+ adsorption using KOH-activated carbon from banana peel. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, T.; Zuo, J.; Liu, F. Performance and mechanism for cadmium and lead adsorption from water and soil by corn straw biochar. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Yu, W.; Yang, T.; Li, Q.; Guo, J. The Adsorption of Corn Stalk Biochar for Pb and Cd: Preparation, Characterization, and Batch Adsorption Study. Separations 2022, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Cai, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Shao, J. Evaluation and Prediction of Cadmium Removal from Aqueous Solution by Phosphate-Modified Activated Bamboo Biochar. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 4469–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiza, S. Biosorption of heavy metal from aqueous solution using cellulosic waste orange peel. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbar, B.; Alem, A.; Pantet, A.; Marcotte, S.; Ahfir, N.D.; Duriatti, D. Removal of dissolved and particulate contaminants from aqueous solution using natural flex fibres. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 35, 656–661. [Google Scholar]
- Asuquo, E.D.; Martin, A.D. Sorption of cadmium (II) ion from aqueous solution onto sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) peel adsorbent: Characterisation, kinetic and isotherm studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4207–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, A.; Fathy, I.; Sayed, A.; Almedolab, A.; Aboelghait, K.M. Biosorption of heavy metals ions in real industrial wastewater using peanut husk as efficient and cost-effective adsorbent. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2016, 6, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinyelu, E. Use of unmodified orange peel for the adsorption of Cd (II), Pb (II) and Hg(II) ions in aqueous solutions. Am. J. Phys. Chem. 2015, 4, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutha, Y.; Munagapati, V.S.; Naushad, M.; Abburi, K. Removal of Ni (II) from aqueous solution by Lycopersicum esculentum (Tomato) leaf powder as a low-cost biosorbent. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 54, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paduraru, C.; Tofan, L.; Teodosiu, C.; Bunia, I.; Tudorachi, N.; Toma, O. Biosorption of zinc (II) on rapeseed waste: Equilibrium studies and thermogravimetric investigations. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 94, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruah, P.; Sarma, A.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Removal of Ni (II) ions from aqueous solution by using low cost biosorbent prepared from jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) leaf powder. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2015, 22, 322–327. [Google Scholar]
- Imaga, C.; Abia, A.; Igwe, J. Adsorption Isotherm Studies of Ni (II), Cu (II) and Zn (II) Ions on Unmodified and Mercapto-Acetic Acid (MAA) Modified Sorghum Hulls. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 5, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utomo, H.D.; Hunter, K.A. Adsorption of divalent copper, zinc, cadmium, and lead ions from aqueous solution by waste tea and coffee adsorbents. Environ. Technol. 2006, 27, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singha, A.S.; Guleria, A. Utility of chemically modified agricultural waste okra biomass for removal of toxic heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Eng. Agric. Environ. Food 2015, 8, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moubarik, A.; Grimi, N. Valorization of olive stone and sugar cane bagasse by-products as biosorbents for the removal of cadmium from aqueous solution. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamohan, N. Biosorption of Mercury onto Protonated Pistachio Hull Wastes–Effect of Variables and Kinetic Experiments. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2014, 5, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, W.P.; Kamari, A.; Yusoff, S.N.M.; Ishak, C.F.; Mohamed, A.; Hashim, N.; Isa, I.M. Biosorption of Cu (II), Pb (II) and Zn (II) ions from aqueous solutions using selected waste materials. J. Encapsulation Adsorpt. Sci. 2014, 4, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.-T.; Saman, N.; Johari, K.; Mat, H. Surface chemistry modifications of rice husk toward enhancement of Hg (II) adsorption from aqueous solution. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Mudhoo, A.; Lofrano, G.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Biomass-derived biosorbents for metal ions sequestration: Adsorbent modification and activation methods and adsorbent regeneration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husein, D.Z. Adsorption and removal of mercury ions from aqueous solution using raw and chemically modified Egyptian mandarin peel. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 6761–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoramzadeh, E.; Nasernejad, B.; Halladj, R. Mercury biosorption from aqueous solution by Sugarcane Bagasse. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Aguilar, D.L.; Miranda, J.P.-R.; Salcedo-Parra, O.J. Fruit Peels as a Sustainable Waste for the Biosorption of Heavy Metals in Wastewater: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.; Sen, T.K.; Phan, C. Synthesis and characterisation of novel-activated carbon from waste biomass pine cone and its application in the removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution by adsorption. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwa, B.A.; Khaled, W.; Victoria, S. Valorisation of Pine Cone as an Efficient Biosorbent for the Removal of Pb (II), Cd (II), Cu(II), and Cr(VI). Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2021, 2021, 6678530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzo, A.; Adebayo, M.A.; Dias, S.L.P.; Lima, E.C.; Vaghetti, J.C.P.; de Oliveira, E.R.; Leite, A.J.B.; Pavan, F.A. Avocado seed powder: Characterization and its application for crystal violet dye removal from aqueous solutions. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 15873–15888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, A.J.B.; Carmalin, S.A.; Thue, P.S.; Reis, G.; Dias, S.; Lima, E.C.; Vaghetti, J.C.; Pavan, F.A.; De Alencar, W.S. Activated carbon from avocado seeds for the removal of phenolic compounds from aqueous solutions. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 71, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.-A.; Cristiani-Urbina, E. Effect of pH on hexavalent and total chromium removal from aqueous solutions by avocado shell using batch and continuous systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3157–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.A.; Sreejalekshmi, K.; Vimexen, V.; Dev, V.V. Evaluation of adsorption properties of sulphurised activated carbon for the effective and economically viable removal of Zn (II) from aqueous solutions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 124, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahby, A.; Abdelouahab-Reddam, Z.; El Mail, R.; Stitou, M.; Silvestre-Albero, J.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, F. Mercury removal from aqueous solution by adsorption on activated carbons prepared from olive stones. Adsorption 2011, 17, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Ang, M. Removal of cationic dye methylene blue (MB) from aqueous solution by ground raw and base modified pine cone powder. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, B.; Maleki, A.; Najafi, F.; Daraei, H.; Gharibi, F.; McKay, G. Super High Removal Capacities of Heavy Metals (Pb2+ and Cu2+) Using CNT Dendrimer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 336, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Kumari, U.; Meikap, B.C.; Sen, T.K. Batch and continuous closed circuit semi-fluidized bed operation: Removal of MB dye using sugarcane bagasse biochar and alginate composite adsorbents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamari, S.; Shahbazi, A. Biocompatible Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 nanocomposite as a green nanofiller embedded in PES–nanofiltration membrane matrix for salts, heavy metal ion and dye removal: Long–term operation and reusability tests. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, B.H.; Rahman, A.A. Removal of phenol from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from biomass material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, A.; Yogeshwaran, V.; Rajendran, S.; Hoang, T.K.; Soto-Moscoso, M.; Ghfar, A.A.; Bathula, C. Investigation of mechanism of heavy metals (Cr6+, Pb2+& Zn2+) adsorption from aqueous medium using rice husk ash: Kinetic and thermodynamic approach. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Hu, X.; Wan, Y.; Wang, S.; Gao, B. Removal of lead, copper, cadmium, zinc, and nickel from aqueous solutions by alkali-modified biochar: Batch and column tests. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 33, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yargic, A.S.; Yarbay, R.Z.; Sahin, N.; Onal, O.E. Assessment of toxic copper (II) biosorption from aqueous solution by chemically treated tomato waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 88, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, M.; Kırbıyık, Ç.; Çepelioğullar, Ö.; Pütün, A.E. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by bio-char, a by-product of pyrolysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 283, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, D.K.; Karim, W.A.; Idris, A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngulube, T.; Gumbo, J.R.; Masindi, V.; Maity, A. An update on synthetic dyes adsorption onto clay-based minerals. A state-of-art review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 191, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Palaniyappan, M.; Priyadharshini, M.; Vignesh, A.M.; Thanjiappan, A.; Sebastina Anne Fernando, P.; Tanvir Ahmed, R.; Srinath, R. Adsorption of basic dye onto raw and surface-modified agricultural waste. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2014, 33, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, R.B.; Saifullah, B.; Rehman, F. Greener Method for the Removal of Toxic Metal Ions from the Wastewater by Application of Agricultural Waste as an Adsorbent. Water 2018, 10, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M.; Noreen, S.; Sadaf, S. Biocomposite efficiency for Cr (VI) adsorption: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamics studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayebi, O.O.; Olagboye, S.A.; Olatoye, R.A.; Olufemi, A.S. Agricultural Waste Adsorbents for Heavy Metals Removal from Wastewater. J. Phys. Chem. Sci. 2017, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Chen, H.; Xi, J.; Yao, D.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, Y. Biochars with excellent Pb (II) adsorption property produced from fresh and dehydrated banana peels via hydrothermal carbonization. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torab-Mostaedi, M.; Asadollahzadeh, M.; Hemmati, A.; Khosravi, A. Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies for biosorption of cadmium and nickel on grapefruit peel. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandharipande, S.; Kalnake, R.P. Tamarind fruit shell adsorbent synthesis, characterization and adsorption studies for Cr (VI) & Ni(II) ions from aqueous solution. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 4, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Hegazi, H.A. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using agricultural and industrial wastes as adsorbents. HBRC J. 2013, 9, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Siafaka, P.I.; Pavlidou, E.G.; Chrissafis, K.J.; Bikiaris, D.N. Synthesis and adsorption application of succinyl-grafted chitosan for the simultaneous removal of zinc and cationic dye from binary hazardous mixtures. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahalya, N.; Chandraprabha, M.N.; Kanamli, R.D.; Ramchandran, T.P. Adsorption of fast green onto coffee husk. J. Chem. Eng. Res. 2014, 2, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Karmaker, S.; Uddin, M.N.; Ichikawa, H.; Fukumori, Y.; Saha, T.K. Adsorption of reactive orange 13 onto jackfruit seed flakes in aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Jayaram, R.V. Removal of basic dyes from aqueous solution by low-cost adsorbent: Wood apple shell (Feronia acidissima). Desalination 2010, 250, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Sharif, M.; Iqbal, M. Application potential of grapefruit peel as dye sorbent: Kinetics, equilibrium, and mechanism of crystal violet adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, F.A.; Camacho, E.S.; Lima, E.C.; Dotto, G.L.; Branco, V.T.; Dias, S.L. Formosa papaya seed powder (FPSP): Preparation, characterization, and application as an alternative adsorbent for the removal of crystal violet from aqueous phase. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Mckay, G. Removal of Heavy Metals, Lead, Cadmium, and Zinc, Using Adsorption Processes by Cost-Effective Adsorbents. In Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment and Purification, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, A. Preparation of Chitosan/Calcium Alginate/Bentonite Composite Hydrogel and Its Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption Properties. Polymers 2021, 13, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Lopes, L.; Macena, M.; Esteves, B.; Guine, R.P. Ideal pH for the adsorption of metal ions Cr6+, Ni2+, Pb2+ in aqueous solution with different adsorbent materials. Open Agric. 2021, 6, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.; Sen, T.K. Removal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous solution by raw pine and acid-treated pine cone powder as adsorbent: Equilibrium, thermodynamic, kinetics, mechanism and process design. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Rastogi, A.; Nayak, A. Biosorption of nickel onto treated alga (Oedogonium hatei): Application of isotherm and kinetic models. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 342, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, T.K. Adsorptive Removal of Dye (Methylene Blue) Organic Pollutant from Water by Pine Tree Leaf Biomass Adsorbent. Processes 2023, 11, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.; Mukherjee, R.; Sinha, A.; Sarkar, S.; De, S. Removal of cyanide from steel plant effluent using coke breeze, a waste product of steel industry. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 28, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Krishni, R.R.; Sata, S.A. A novel agricultural waste adsorbent for the removal of cationic dye from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, H.; Rai, J.P.N. Agricultural waste materials as biosorbents for the removal of heavy metals and synthetic dyes—A review. Octa J. Environ. Res. 2016, 4, 208–229. [Google Scholar]
- Kamsonlian, S.; Suresh, S.; Ramanaiah, V.; Majumder, C.; Chand, S.; Kumar, A. Biosorptive behaviour of mango leaf powder and rice husk for arsenic (III) from aqueoussolutions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 9, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamsonlian, S.; Balomajumder, C.; Chand, S.; Suresh, S. Biosorption of Cd (II)andAs (III) ions from aqueous solution by teawaste biomass. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Okafor, P.C.; Okon, P.U.; Daniel, E.F.; Ebenso, E.E. Adsorption Capacity of Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) Shell for Lead, Copper, Cadmium and Arsenic from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 12354–12369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzen, M.; Sari, A.; Mendil, D.; Uluozlu, O.D.; Soylak, M.; Dogan, M. Characterization of biosorption process of As (III) on green algae Ulothrix cylindricum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).