Short Review on the Biological Activity of Cyclodextrin-Drug Inclusion Complexes Applicable in Veterinary Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chemistry and Pharmacology Aspects of CDs and Their Inclusion Complexes
3. The Benefits of Inclusion Complexes (CD–Antibiotic) in Anti-Bacterial Therapy
4. Benefits of Inclusion Complexes (CD–Antifungal) in Antifungal Therapy
5. Benefits of Inclusion Complexes (CD–NSAIDs; CD–SAIDs) in Pain Therapy
| Active Compound | Pharmacological Activity | Treated Species | CD Types | Characterization | Stoichiometry Guest: Host | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ketoprofen | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties; acute or chronic inflammation | horse, cattle, sheep and goats, pigs | β-CD | XRD, Dissolution Studies | 1:1 | [62,63] |
| Tolfenamic acid | Acute and chronic inflammatory conditions, fever, postoperative pain | cattle, pig, dog and cat | HP-β-CD | XRD, FT-IR | 1:1 | [64] |
| Meloxicam | Acute and chronic musculoskeletal pain, post-operative inflammation; acute respiratory infection and postoperative pain | dog, cat and cattle | β-CD | HPLC, Dissolution Studies | 1:1 | [65] |
| Carprofen | Acute and chronic musculoskeletal disorders (osteoarthritis); post-operative analgesic; acute respiratory infections | dog, cat and cattle | HP-β-CD | TEM, HPLC, DSC | 1:1 | [67] |
| Piroxicam | us ‘off label’ or ‘extra label’ in bladder transitional cell carcinoma, as well as other cancers | dog and cat | β-CD | DSC; XRD; HPLC | 1:2.5 | [68] |
| Dexamethasone | Anti-inflammatory effect in inflammatory and immune-mediated disease; diagnostic test of adrenal function | all animal species | HP-β-CD | UV-spectroscopy, Dissolution Studies | 1:1 | [77,80] |
| Hydrocortisone-acetate | Adrenal-gland dysfunction (Addison’s disease); Inflammatory conditions | dogs and cat | β-CD HP-β-CD | XRD, DSC | 1:1 | [76,81] |
| Methyl-prednisolone | Supportive treatment in ketosis, rheumatoid arthritis, bursitis inflammatory and allergic conditions | large and small animals | β-CD γ-CD | DTA; XRD, H-NMR | 1:2 2:3 | [78,82] |
6. Other Inclusion Complexes Used in Veterinary Therapy
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1H-NMR: 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance; | NSAID: Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug |
| C: carbon atom | SAID: Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug |
| CD: cyclodextrin | SBE-β-CD: sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin; |
| DSC: Differential Scanning Calorimetry; | SEM: Scanning Electron Microscopy; |
| DTA: Differential Thermal Analysis | TEM: Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| FT-IR: Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy; | TGA: Thermogravimetric Analysis; |
| HPLC: High Performance Liquid Chromatography | UV–VIS: Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy; |
| HP-β-CD: hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin; | XRD: X-ray Diffraction Analysis; |
| IMC: Isothermal Microcalorimetry; | α-CD: alpha-cyclodextrin; |
| MDS: Middle Distillate Synthesis; | β-CD: beta-cyclodextrin; |
| MM: Molecular Modelling; | γ-CD: gamma-cyclodextrin; |
| n/a: not available; |
References
- Han, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Qiu, S.; Zhong, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, J. Cyclodextrin-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks (CD-MOFs) in Pharmaceutics and Biomedicine. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, R.M.; McDonnell, G. Superbugs on Duodenoscopes: The Challenge of Cleaning and Disinfection of Reusable Devices. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3118–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical Applications of Cyclodextrins: Effects on Drug Permeation through Biological Membranes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 1119–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T. Pharmaceutical Applications of β-Cyclodextrin. Pharm. Technol. Eur. 1999, 23, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jambhekar, S.S.; Breen, P. Cyclodextrins in Pharmaceutical Formulations I: Structure and Physicochemical Properties, Formation of Complexes, and Types of Complex. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, R.; Verma, R.; Budhwar, V.; Kaushik, D. An Overview of Recent Patents and Future Perspective Based on Cyclodextrin Complexation. Recent Adv. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2023, 17, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajewski, R.A.; Stella, V.J. Pharmaceutical Applications of Cyclodextrins. 2. In Vivo Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 1142–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.B.; Patel, J.K. Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex To Enhance Solubility Of Poorly Water Soluble Drugs: A Review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia Appleton, S.; Navarro-Orcajada, S.; Martínez-Navarro, F.J.; Caldera, F.; López-Nicolás, J.M.; Trotta, F.; Matencio, A. Cyclodextrins as Anti-Inflammatory Agents: Basis, Drugs and Perspectives. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, J.; Adeoye, O.; Cabral-Marques, H.M.; Lobo, J.M.S. Cyclodextrins as Excipients in Tablet Formulations. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Cyclodextrins as Functional Excipients: Methods to Enhance Complexation Efficiency. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 3019–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Lu, S.; Bardelang, D.; Wang, R. Recent Advances in Supramolecular Antidotes. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Rai, A.K. Cyclodextrins in Delivery Systems: Applications. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muankaew, C.; Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrin-Based Formulations: A Non-Invasive Platform for Targeted Drug Delivery. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puskás, I.; Szente, L.; Szőcs, L.; Fenyvesi, É. Recent List of Cyclodextrin-Containing Drug Products. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2023, 67, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczar, D.; Michalska, K. Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes with Antibiotics and Antibacterial Agents as Drug-Delivery Systems-A Pharmaceutical Perspective. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astakhova, A.V.; Demina, N.B. Modern Drug Technologies: Synthesis, Characterization, and Use of Inclusion Complexes Between Drugs and Cyclodextrins (A Review). Pharm. Chem. J. 2004, 38, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.M.; Buchanan, N.L.; Edgar, K.J.; Ramsey, M.G. Solubilty and Dissolution Studies of Antifungal Drug:Hydroxybutenyl-β-Cyclodextrin Complexes. Cellulose 2006, 14, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical Applications of Cyclodextrins. 1. Drug Solubilization and Stabilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, E.M.M. Cyclodextrins and Their Uses: A Review. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Konrádsdóttir, F.; Másson, M. Influence of Aqueous Diffusion Layer on Passive Drug Diffusion from Aqueous Cyclodextrin Solutions through Biological Membranes. Die Pharm. -Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 61, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero, A.; Arena, R.; Battista, A.; Rizzo, D.; Attinà, G.; Riccardi, R. Azole Interactions with Multidrug Therapy in Pediatric Oncology. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Duchêne, D. Cyclodextrins and Their Pharmaceutical Applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 329, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challa, R.; Ahuja, A.; Ali, J.; Khar, R.K. Cyclodextrins in Drug Delivery: An Updated Review. AAPS PharmSciTech 2005, 6, E329–E357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehatta, I. Cyclodextrins as Enhancers of the Aqueous Solubility of the Anthelmintic Drug Mebendazole: Thermodynamic Considerations. Monatshefte Chem. Chem. Mon. 2002, 133, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uekama, K. Recent Aspects of Pharmaceutical Application of Cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2002, 44, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virmani, T.; Parvez, N.; Yadav, S.; Pathak, K. Solid Inclusion Complexes Of Class Ii Imidazole Derivative With Β—Cyclodextrin. Cont. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rouveix, B. Clinical Implications of Multiple Drug Resistance Efflux Pumps of Pathogenic Bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 1208–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levison, M.E.; Levison, J.H. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Antibacterial Agents. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 23, 791–vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Persistence of Antibiotic Resistance in Bacterial Populations. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, A.; Grudniak, A.M.; Kraczkiewicz-Dowjat, A.; Wolska, K.I. New Antibacterial Therapeutics and Strategies. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, M.-H.; Bao, Y.; Yang, X.-Z.; Zhu, Y.-H.; Wang, J. Delivery of Antibiotics with Polymeric Particles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 78, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhai, S.; Tan, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Dai, T. Enrofloxacin/Florfenicol Loaded Cyclodextrin Metal-Organic-Framework for Drug Delivery and Controlled Release. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Pang, Y.; Vara Prasad, C.V.N.S.; Wang, B. Formation of Inclusion Complex of Enrofloxacin with 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chierentin, L.; Garnero, C.; Chattah, A.K.; Delvadia, P.; Karnes, T.; Longhi, M.R.; Salgado, H.R.N. Influence of β-Cyclodextrin on the Properties of Norfloxacin Form A. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Y.; Shu, G.; Yuan, Z.; Lin, J.; Zhang, W.; Peng, G.; Zhong, Z.; Yin, L.; et al. Comparative Muscle Irritation and Pharmacokinetics of Florfenicol-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex Freeze-Dried Powder Injection and Florfenicol Commercial Injection in Beagle Dogs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, R.S. (Ed.) The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy, 20th ed.; Merck: Rahway, NJ, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-911910-42-1. [Google Scholar]
- Elad, D. Therapy of Non-Dermatophytic Mycoses in Animals. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedmousavi, S.; Wiederhold, N.P.; Ebel, F.; Hedayati, M.T.; Rafati, H.; Verweij, P.E. Antifungal Use in Veterinary Practice and Emergence of Resistance. In Emerging and Epizootic Fungal Infections in Animals; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 359–402. ISBN 978-3-319-72091-3. [Google Scholar]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Fourmentin, S.; Fenyvesi, É.; Lichtfouse, E.; Torri, G.; Fourmentin, M.; Crini, G. 130 Years of Cyclodextrin Discovery for Health, Food, Agriculture, and the Industry: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2581–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, L.; Mares, M.; Nastasa, V.; Spulber, M.; Fifere, A.; Pinteala, M.; Harabagiu, V.; Simionescu, B.C. Water Soluble Sulconazole-β-Cyclodextrin Complex: Physico-Chemical Characterization and Preliminary Pharmacological Studies. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2009, 63, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spulber, M.; Miron, L.; Mares, M.; Nastasa, V.; Pinteala, M.; Fifere, A.; Harabagiu, V.; Simionescu, B.C. Water Soluble 5 FC Complexes, Preliminary Pharmacological Studies. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2009, 65, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Usman, F.; Naseem, M.; Aati, H.Y.; Ahmad, H.; Manee, S.; Khalil, R.; ur Rehman Khan, K.; Qureshi, M.I.; Umair, M. Voriconazole Cyclodextrin Based Polymeric Nanobeads for Enhanced Solubility and Activity: In Vitro/In Vivo and Molecular Simulation Approach. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Kwon, J.-C.; Park, C.; Han, S.; Yim, D.-S.; Choi, J.-K.; Cho, S.-Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, S.H.; Choi, S.-M.; et al. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Safety of Intravenous Voriconazole Formulated with Sulfobutylether β-Cyclodextrin in Haematological Patients with Renal Impairment. Mycoses 2016, 59, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, D.S.; Trepanier, L.A. Antifungal Treatment of Small Animal Veterinary Patients. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 40, 1171–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, C.E. Antifungal Chemotherapy. In Infectious Diseases of the Dog and Cat; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 579–587. ISBN 978-0-323-26621-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, H.A.; Al-Marzouqi, A.H.; Jobe, B.; Hamza, A.A.; Ramadan, G.A. Enhancement of Dissolution Amount and in Vivo Bioavailability of Itraconazole by Complexation with Beta-Cyclodextrin Using Supercritical Carbon Dioxide. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossche, H.V.; Engelen, M.; Rochette, F. Antifungal Agents of Use in Animal Health—Chemical, Biochemical and Pharmacological Aspects. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 26, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Am, L.; Bw, R.; Rl, T.; Mg, R.; Ll, G.; Jb, J. Treatment of Blastomycosis with Itraconazole in 112 Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1996, 10, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubach, T.M.P.; Schubach, A.; Okamoto, T.; Barros, M.B.L.; Figueiredo, F.B.; Cuzzi, T.; Fialho-Monteiro, P.C.; Reis, R.S.; Perez, M.A.; Wanke, B. Evaluation of an Epidemic of Sporotrichosis in Cats: 347 Cases (1998–2001). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 224, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Shan, Q.; Zhong, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Cao, C.; Zeng, Z. Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability of Itraconazole Oral Solution in Cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2016, 18, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boothe, D.M.; Herring, I.; Calvin, J.; Way, N.; Dvorak, J. Itraconazole Disposition after Single Oral and Intravenous and Multiple Oral Dosing in Healthy Cats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1997, 58, 872–877. [Google Scholar]
- Hasbach, A.E.; Langlois, D.K.; Rosser, E.J.; Papich, M.G. Pharmacokinetics and Relative Bioavailability of Orally Administered Innovator-Formulated Itraconazole Capsules and Solution in Healthy Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Odaguiri, J.; Larsson, C.E. Retrospective Assessment of the Treatment of Sporotrichosis in Cats and Dogs Using Itraconazole. Acta Sci. Vet. 2013, 41, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Willems, L.; van der Geest, R.; de Beule, K. Itraconazole Oral Solution and Intravenous Formulations: A Review of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2001, 26, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minea, B.; Nastasa, V.; Moraru, R.F.; Kolecka, A.; Flonta, M.M.; Marincu, I.; Man, A.; Toma, F.; Lupse, M.; Doroftei, B.; et al. Species Distribution and Susceptibility Profile to Fluconazole, Voriconazole and MXP-4509 of 551 Clinical Yeast Isolates from a Romanian Multi-Centre Study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Tomé, V.; García-Otero, X.; Varela-Fernández, R.; Martín-Pastor, M.; Conde-Penedo, A.; Aguiar, P.; González-Barcia, M.; Fernández-Ferreiro, A.; Otero-Espinar, F.J. In Situ Forming and Mucoadhesive Ophthalmic Voriconazole/HPβCD Hydrogels for the Treatment of Fungal Keratitis. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 597, 120318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başaran, E.; Aykaç, K.; Yenilmez, E.; Büyükköroğlu, G.; Tunali, Y.; Demirel, M. Formulation and Characterization Studies of Inclusion Complexes of Voriconazole for Possible Ocular Application. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2022, 27, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, J.; Stewart, A.J. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Associated Toxicities in Horses. Animals 2022, 12, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro-Steagall, B.P.; Steagall, P.V.M.; Lascelles, B.D.X. Systematic Review of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Induced Adverse Effects in Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, G.M.; Santos, V.O.R.E.; Bessa, J.R.; Teles, Y.C.F.; Yahouédéhou, S.C.M.A.; Goncalves, M.S.; Ribeiro-Filho, J. Inclusion Complexes of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs with Cyclodextrins: A Systematic Review. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grecu, M.; Năstasă, V.; Ilie, C.; Miron, L.; Mareş, M. Comparative Assessment of Effectiveness of Ketoprofen and Ketoprofen/Beta-Cyclodextrin Complex in Two Experimental Models of Inflammation in Rats. Lab. Anim. 2014, 48, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-L.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Wang, H.; Li, R.-Y.; Zhang, L.-F.; Shen, W.-B.; Tu, X.-D. Antipyretic, Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Ketoprofen Beta-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes in Animals. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiłowicz, A.; Tykarska, E.; Rosiak, N.; Sałat, K.; Furgała-Wojas, A.; Plech, T.; Lewandowska, K.; Pikosz, K.; Pawłowicz, K.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. The Inclusion of Tolfenamic Acid into Cyclodextrins Stimulated by Microenvironmental PH Modification as a Way to Increase the Anti-Migraine Effect. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorab, M.M.; Abdel-Salam, H.M.; El-Sayad, M.A.; Mekhel, M.M. Tablet Formulation Containing Meloxicam and β-Cyclodextrin: Mechanical Characterization and Bioavailability Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004, 5, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaidat, A.A.; Obaidat, R.M. Development and Evaluation of Fast-Dissolving Tablets of Meloxicam-β-Cyclodextrin Complex Prepared by Direct Compression. Acta Pharm. Zagreb Croat. 2011, 61, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, A.; Clares, B.; Rosselló, A.; Garduño-Ramírez, M.L.; Abrego, G.; García, M.L.; Calpena, A.C. Ex Vivo Permeation of Carprofen from Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Study through Human, Porcine and Bovine Skin as Anti-Inflammatory Agent. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 501, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpignato, C. Piroxicam-β-Cyclodextrin: A GI Safer Piroxicam. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2415–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsarra, I.A.; Ahmed, M.O.; Alanazi, F.K.; ElTahir, K.E.H.; Alsheikh, A.M.; Neau, S.H. Influence of Cyclodextrin Complexation with NSAIDs on NSAID/Cold Stress-Induced Gastric Ulceration in Rats. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 7, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, P.K.; Gaud, R.S.; Bakal, R.; Patil, D. Effect of Inclusion Complexation of Meloxicam with β-Cyclodextrin- and β-Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges on Solubility, in Vitro Release and Stability Studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Chawla, V.; Chawla, P. Pectin, Beta-Cyclodextrin, Chitosan and Albumin Based Gastroprotective Systems for Piroxicam Maleate: Synthesis, Characterization and Biological Evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestrelli, F.; Mura, P.; Cirri, M.; Mennini, N.; Ghelardini, C.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L. Development and Characterization of Fast Dissolving Tablets of Oxaprozin Based on Hybrid Systems of the Drug with Cyclodextrins and Nanoclays. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.L.; Brito, R.G.; Quintans, J.S.S.; Araujo, A.A.S.; Menezes, I.R.A.; Brogden, N.K.; Quintans-Junior, L.J. Cyclodextrins as Complexation Agents to Improve the Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Profile: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 2096–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, S.D.; Amouret, A.; Muzzi, C.; Vettorazzi, S.; Tuckermann, J.P.; Lühder, F.; Reichardt, H.M. The Role of Glucocorticoids in Inflammatory Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, D.H.; Engelke, A.; Wenz, G. Solubilizing Steroidal Drugs by β-Cyclodextrin Derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, L. Synthesis and Characterization of β-Cyclodextrin-Conjugated Alginate Hydrogel for Controlled Release of Hydrocortisone Acetate in Response to Mechanical Stimulation. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2015, 30, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, K.; Kant, S.; Singh, P.N.; Pandit, J.K. Effect of Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin on the Ocular Bioavailability of Dexamethasone from a PH-Induced Mucoadhesive Hydrogel. Curr. Eye Res. 2011, 36, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uekama, K.; Otagiri, M.; Uemura, Y.; Fujinaga, T.; Arimori, K.; Matsuo, N.; Tasaki, K.; Sugii, A. IMPROVEMENT OF ORAL BIOAVAILABILITY OF PREDNISOLONE BY β-CYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEXATION IN HUMANS. J. Pharmacobiodyn. 1983, 6, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopcha, M.; Kaneene, J.B.; Shea, M.E.; Miller, R.; Ahl, A.S. Use of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Food Animal Practice. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1992, 201, 1868–1872. [Google Scholar]
- Usayapant, A.; Karara, A.H.; Narurkar, M.M. Effect of 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin on the Ocular Absorption of Dexamethasone and Dexamethasone Acetate. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović-Grčić, J.; Voinovich, D.; Moneghini, M.; Bećirević-Laćan, M.; Magarotto, L.; Jalšenjak, I. Chitosan Microspheres with Hydrocortisone and Hydrocortisone–Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 9, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uekama, K.; Fujinaga, T.; Hirayama, F.; Otagiri, M.; Yamasaki, M. Inclusion Complexations of Steroid Hormones with Cyclodextrins in Water and in Solid Phase. Int. J. Pharm. 1982, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Benedetti, I.-C.; Bublot, I.; Ribas, T.; Fourel, I.; Vogl, C.; Dubois, C.; Milani, M.; Ida, K.K.; Portier, K. Pharmacokinetics of Intramuscular Alfaxalone and Its Echocardiographic, Cardiopulmonary and Sedative Effects in Healthy Dogs. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittem, T.; Pasloske, K.S.; Heit, M.C.; Ranasinghe, M.G. The Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Alfaxalone in Cats after Single and Multiple Intravenous Administration of Alfaxan at Clinical and Supraclinical Doses. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 31, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambros, B.; Duke-Novakovski, T.; Pasloske, K.S. Comparison of the Anesthetic Efficacy and Cardiopulmonary Effects of Continuous Rate Infusions of Alfaxalone-2-Hydroxypropyl-Beta-Cyclodextrin and Propofol in Dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2008, 69, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferré, P.J.; Pasloske, K.; Whittem, T.; Ranasinghe, M.G.; Li, Q.; Lefebvre, H.P. Plasma Pharmacokinetics of Alfaxalone in Dogs after an Intravenous Bolus of Alfaxan-CD RTU. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2006, 33, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasloske, K.; Ranasinghe, M.G.; Sauer, S.; Hare, J. The Bioequivalence of a Single Intravenous Administration of the Anesthetic Alfaxalone in Cyclodextrin versus Alfaxalone in Cyclodextrin plus Preservatives in Cats. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 41, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Mocholí, D.; Escudero, E.; Belda, E.; Laredo, F.G.; Hernandis, V.; Marín, P. Pharmacokinetics and Effects of Alfaxalone after Intravenous and Intramuscular Administration to Cats. N. Z. Vet. J. 2018, 66, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP). CVMP Assessment Report for Cerenia New Route of Administration (Intravenous Use) for the Solution for Injection (EMEA/V/C/000106/X/0023); European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, K.A.; Lamont, L.A.; Tranquilli, W.J.; Greene, S.A.; Robertson, S.A. (Eds.) Veterinary Anesthesia and Analgesia, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-118-52623-1. [Google Scholar]
- Le, K. MAROPITANT. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2017, 26, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narishetty, S.T.; Galvan, B.; Coscarelli, E.; Aleo, M.; Fleck, T.; Humphrey, W.; McCall, R.B. Effect of Refrigeration of the Antiemetic Cerenia (Maropitant) on Pain on Injection. Vet. Ther. Res. Appl. Vet. Med. 2009, 10, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, T.-T.; Kraus, B.L.H. The Effect of Intravenous Maropitant on Blood Pressure in Healthy Awake and Anesthetized Dogs. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folger, M.; Lehner, S. Liquid Preparation Comprising Pimobendan. US9107952B2, 18 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
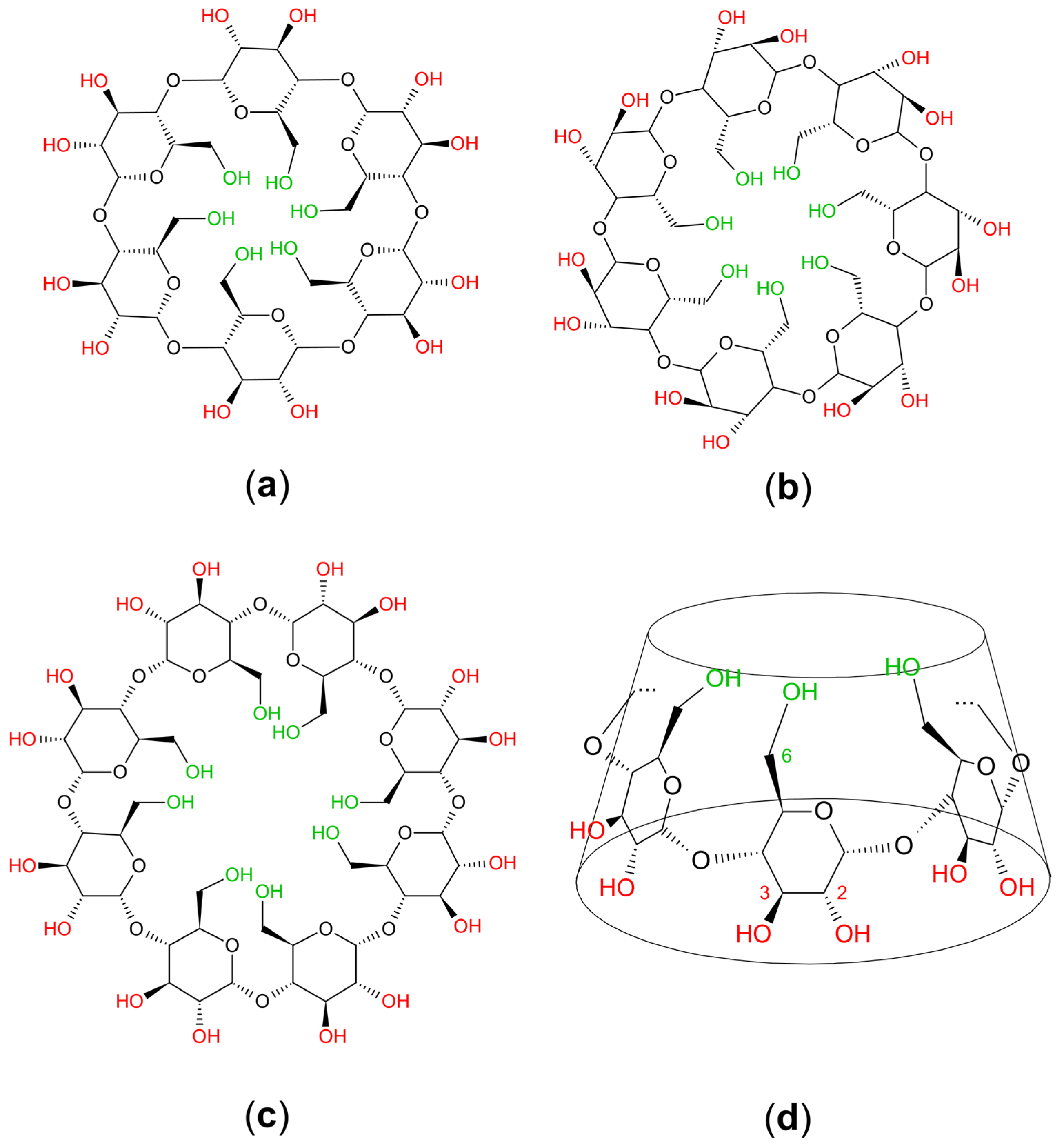
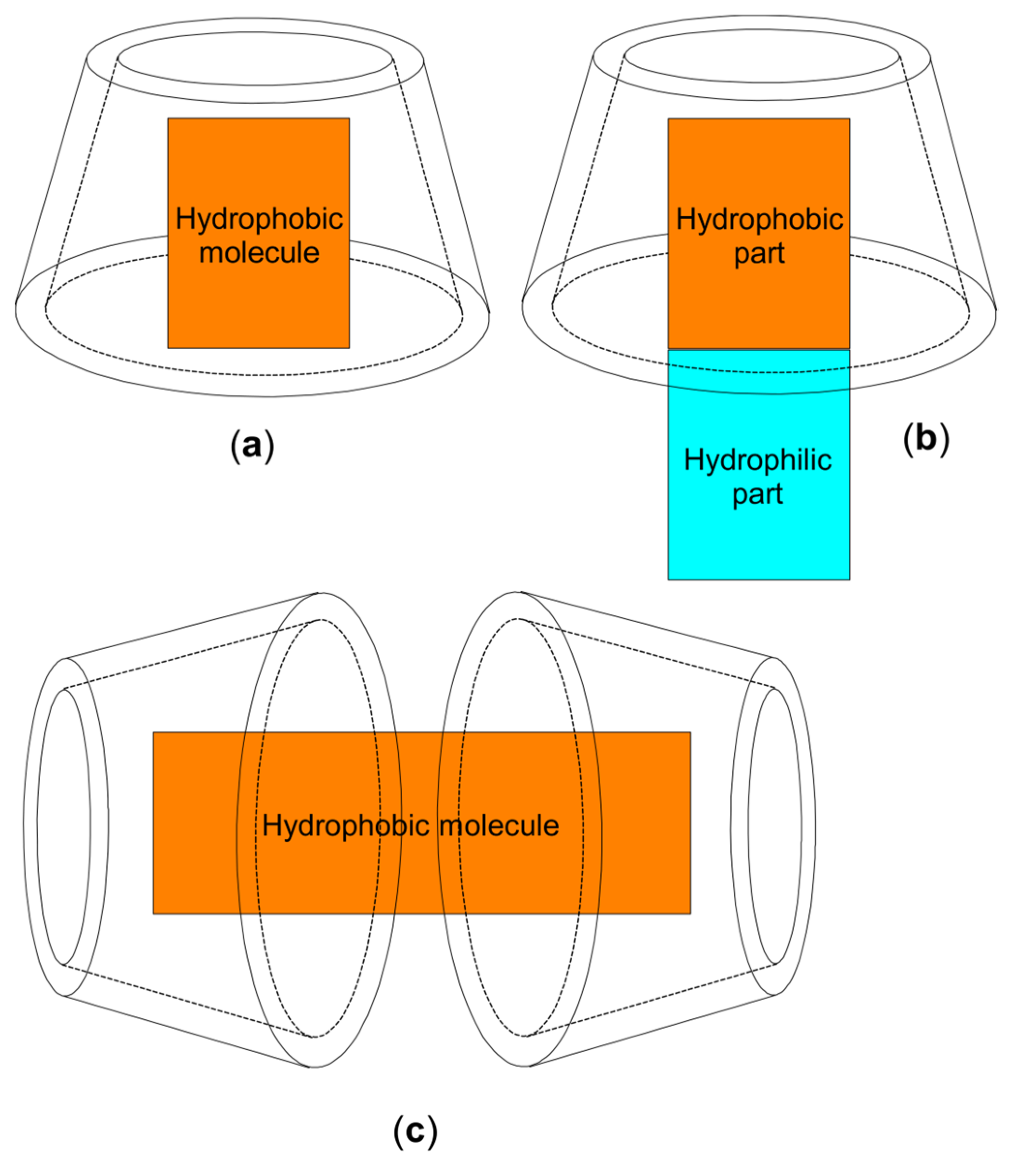
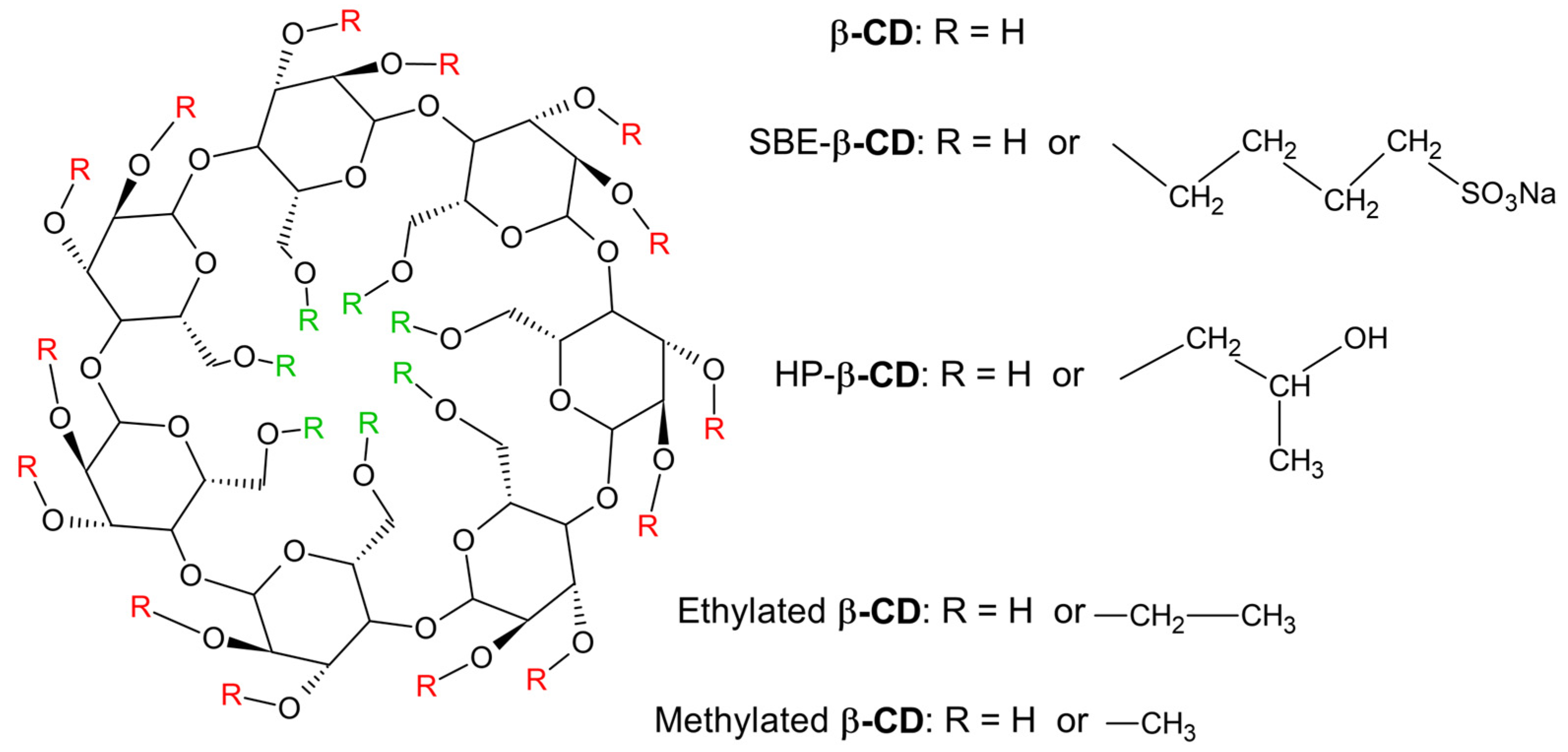
| Active Compound | Activity Spectrum | Treated Species | CD Type | Characterization | Stoichiometry Guest: Host | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrofloxacin | Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, Pasteurella multocida, Pseudomonas, Rickettsia, Chlamydophila felis, Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Haemophilus parasuis, and Streptococcus suis, Mannheimia haemolytica and Haemophilus somni | all animal species | γ-CD | FT-IR, 1H-NMR, SEM, UV spectroscopy, HPLC, Dissolution Studies | 1:1 | [34,37] |
| Norfloxacin | Mycoplasma, Gram-positive (staphylococci, streptococci, etc.) and Gram-negative (colibacilli, Pasteurella spp., Salmonella spp.) | cattle, sheep, goats, pigs and birds | β-CD | DSC, TGA, FT-IR, XRD, SEM, NMR spectrometry, HPLC, Dissolution Studies | 1:1 | [35,37] |
| Florfenicol | Gram-positive bacilli and Gram-negative cocci and Mycoplasma | cattle, sheep and pigs | HP-β-CD | SEM, XRD, DSC, FT-IR, 1H-NMR | 1:1 | [36,37] |
| Amoxicillin | Gram-positive bacteria, in particular streptococcal bacteria causing upper respiratory tract infections | all animal species | HP-β-CD | MDS, IMC, MM, HPLC | 1:1 | [16,37] |
| Gentamicin sulphate | Aerobic Gram-negative bacteria (e.g., Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Serratia spp. and Enterobacter spp.), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and some strains of Neisseria, Moraxella, and Haemophilus | horse, foal, cattle, calf, pig, dog, cat | β-CD | SEM, FT-IR, TGA | n/a | [16,37] |
| Metronidazole | Protozoans (Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia and Trichomonas vaginalis) and most Gram-negative (Bacteroides and Fusobacterium) and Gram-positive (pepto-streptococci and Clostridia spp.) anaerobic bacteria | dogs and cats | HP-β-CD | Rheology, SEM, NMR, FT-IR, DSC, TGA, XRD, Dissolution Studies | n/a | [16,37] |
| Active Compound | Activity Spectrum | Treated Species | CD Type | Characterization | Stoichiometry Guest: Host | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flucytosine | Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida spp. and filamentous fungi like Aspergillus spp. | dog and cat | β-CD HP-β-CD | UV–VIS, 1H-NMR, Dissolution Studies, DSC, SEM, FT-IR, XRD | 1:1 | [37,42] |
| Sulconazole nitrate | Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton floccosum, and Microsporum canis and Malassezia furfur | dog | β-CD | 1H-NMR, DSC, TGA, SEM, XRD | 1:1 | [37,41] |
| Voriconazole | Blastomyces spp., Cryptococcus neoformans and C. gattii and aspergillosis (A. fumigatus, A. terreus, A. flavus, f A. nidulans) | dog, rarely in cat, horse, cow ferret, deer, bird, many wildlife species | HP-β-CD SBE-β-CD γ-CD | SEM, FT-IR, DSC, XRD, Dissolution Studies | Variable, from 1:2 to 1:4 | [37,43,44,57,58] |
| Itraconazole | Cryptococcus neoformans and C. gattii, Microsporum canis, Trichophyton spp., T. terrestre and Microsporum gypseum. | dog, horse, bird, small mammals, and reptiles. | β-CD HP-β-CD | FT-IR, DSC, UV spectroscopy, Dissolution Studies | 1:2 | [37,47,48] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grecu, M.; Minea, B.; Foia, L.-G.; Bostanaru-Iliescu, A.-C.; Miron, L.; Nastasa, V.; Mares, M. Short Review on the Biological Activity of Cyclodextrin-Drug Inclusion Complexes Applicable in Veterinary Therapy. Molecules 2023, 28, 5565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145565
Grecu M, Minea B, Foia L-G, Bostanaru-Iliescu A-C, Miron L, Nastasa V, Mares M. Short Review on the Biological Activity of Cyclodextrin-Drug Inclusion Complexes Applicable in Veterinary Therapy. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145565
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrecu, Mariana, Bogdan Minea, Liliana-Georgeta Foia, Andra-Cristina Bostanaru-Iliescu, Liviu Miron, Valentin Nastasa, and Mihai Mares. 2023. "Short Review on the Biological Activity of Cyclodextrin-Drug Inclusion Complexes Applicable in Veterinary Therapy" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145565
APA StyleGrecu, M., Minea, B., Foia, L.-G., Bostanaru-Iliescu, A.-C., Miron, L., Nastasa, V., & Mares, M. (2023). Short Review on the Biological Activity of Cyclodextrin-Drug Inclusion Complexes Applicable in Veterinary Therapy. Molecules, 28(14), 5565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145565











