Highly Sensitive Voltammetric Method for Quinoline Yellow Determination on Renewable Amalgam Film Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
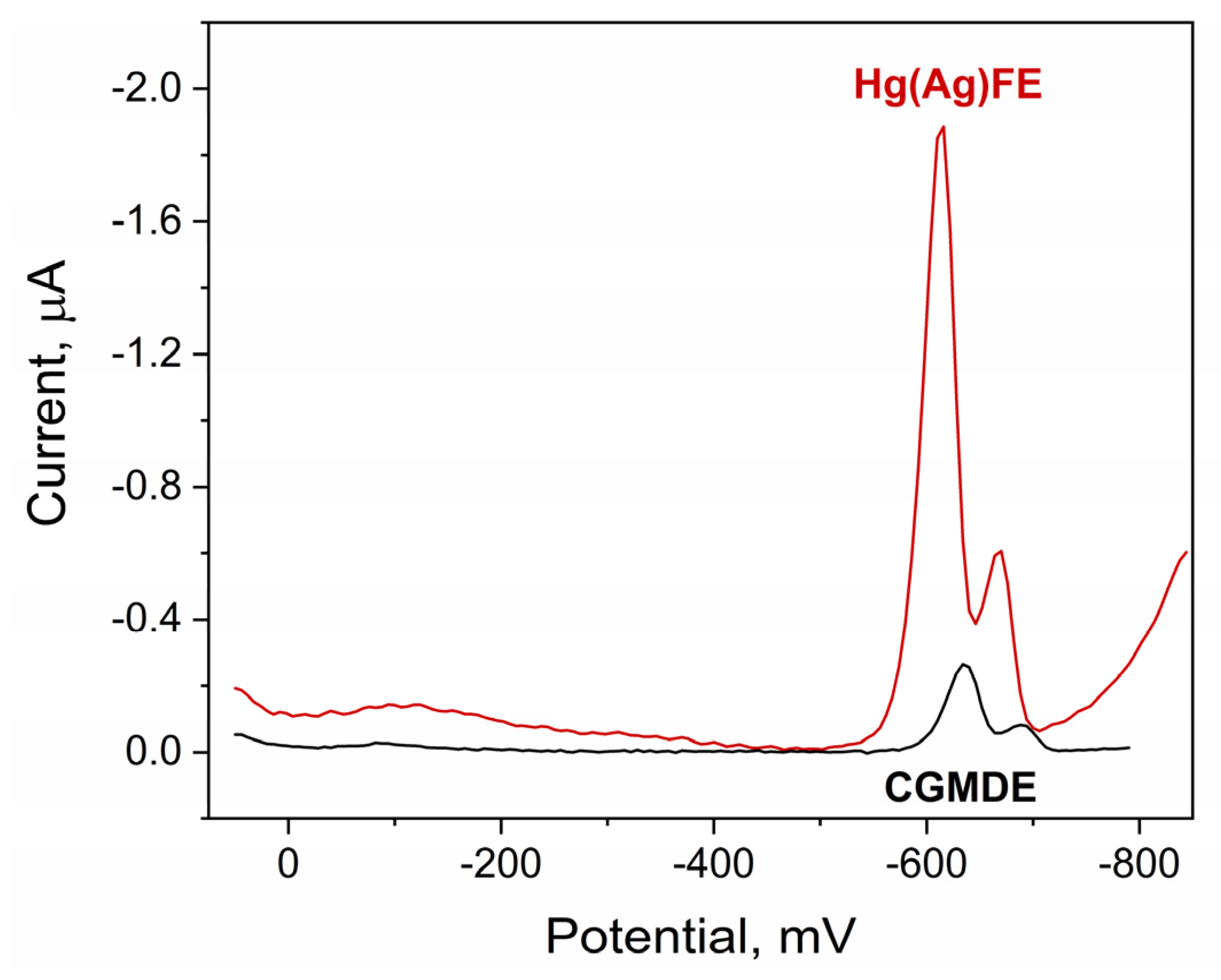
2.1. Quinoline Yellow Behavior on Hg(Ag)FE
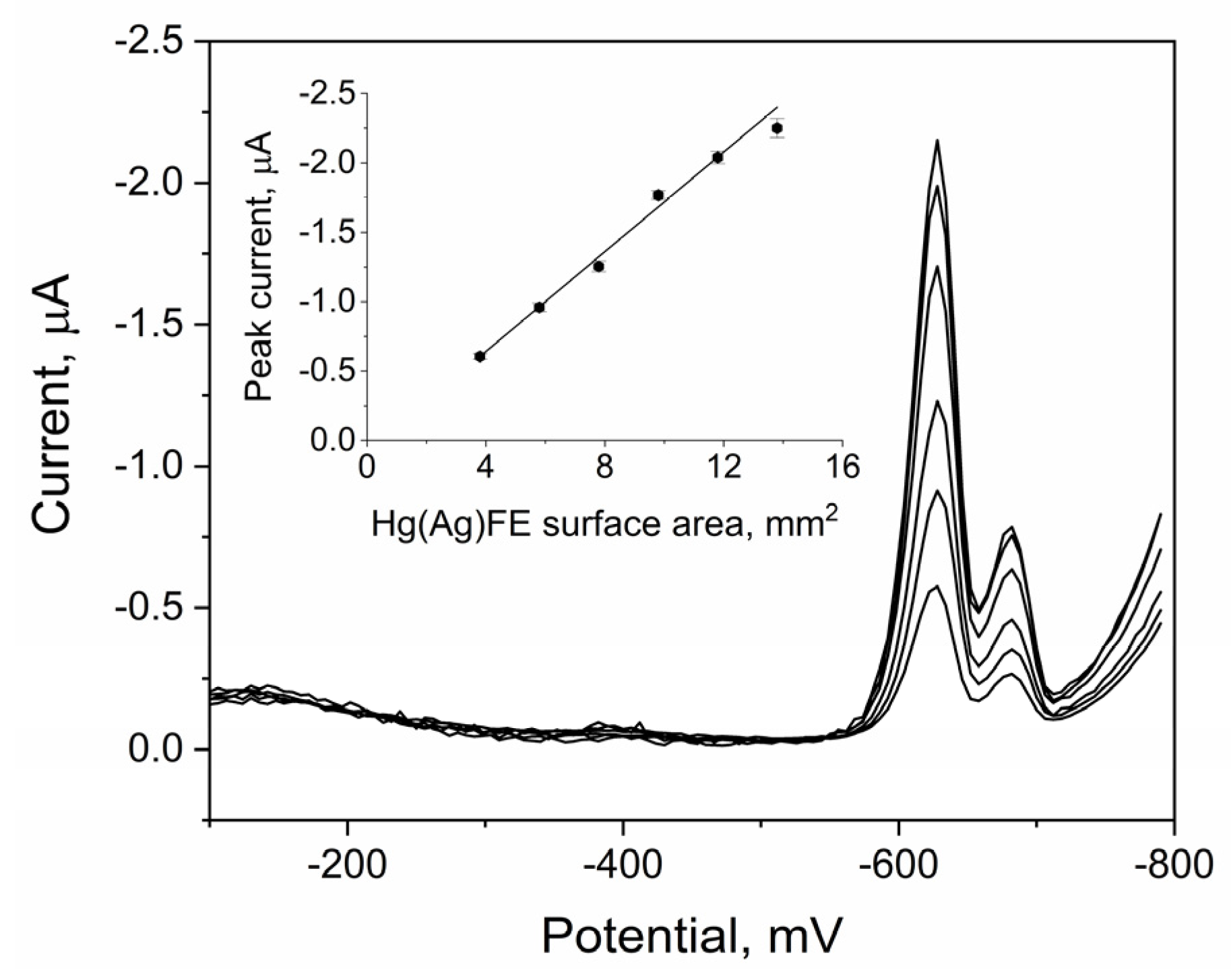
2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry
2.3. DPV Parameters Optimization
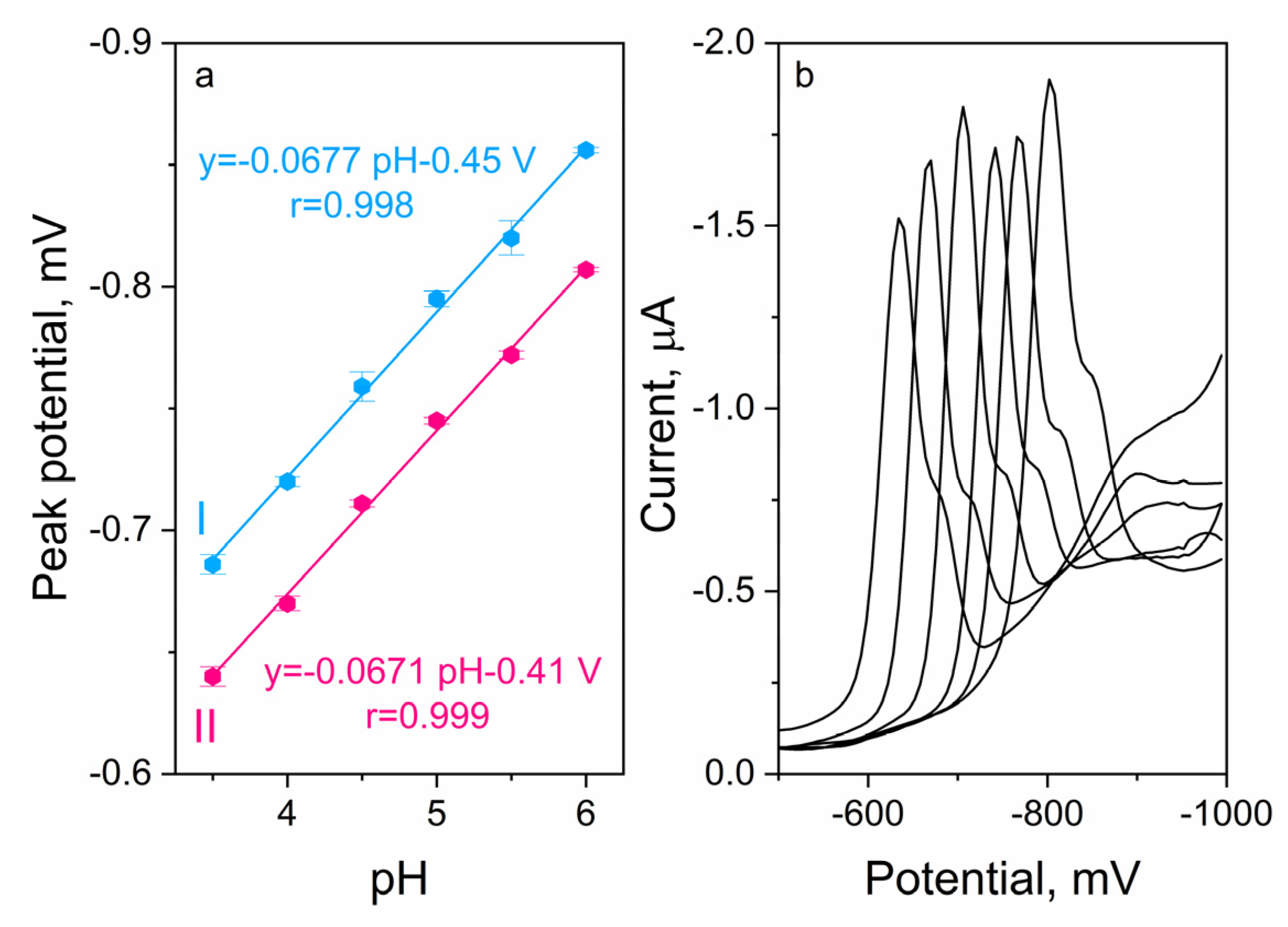
2.4. Supporting Electrolyte Optimization
2.4.1. Type of Supporting Electrolyte
2.4.2. Concentration of Supporting Electrolyte
2.5. Preconcentration Potential and Time Optimization
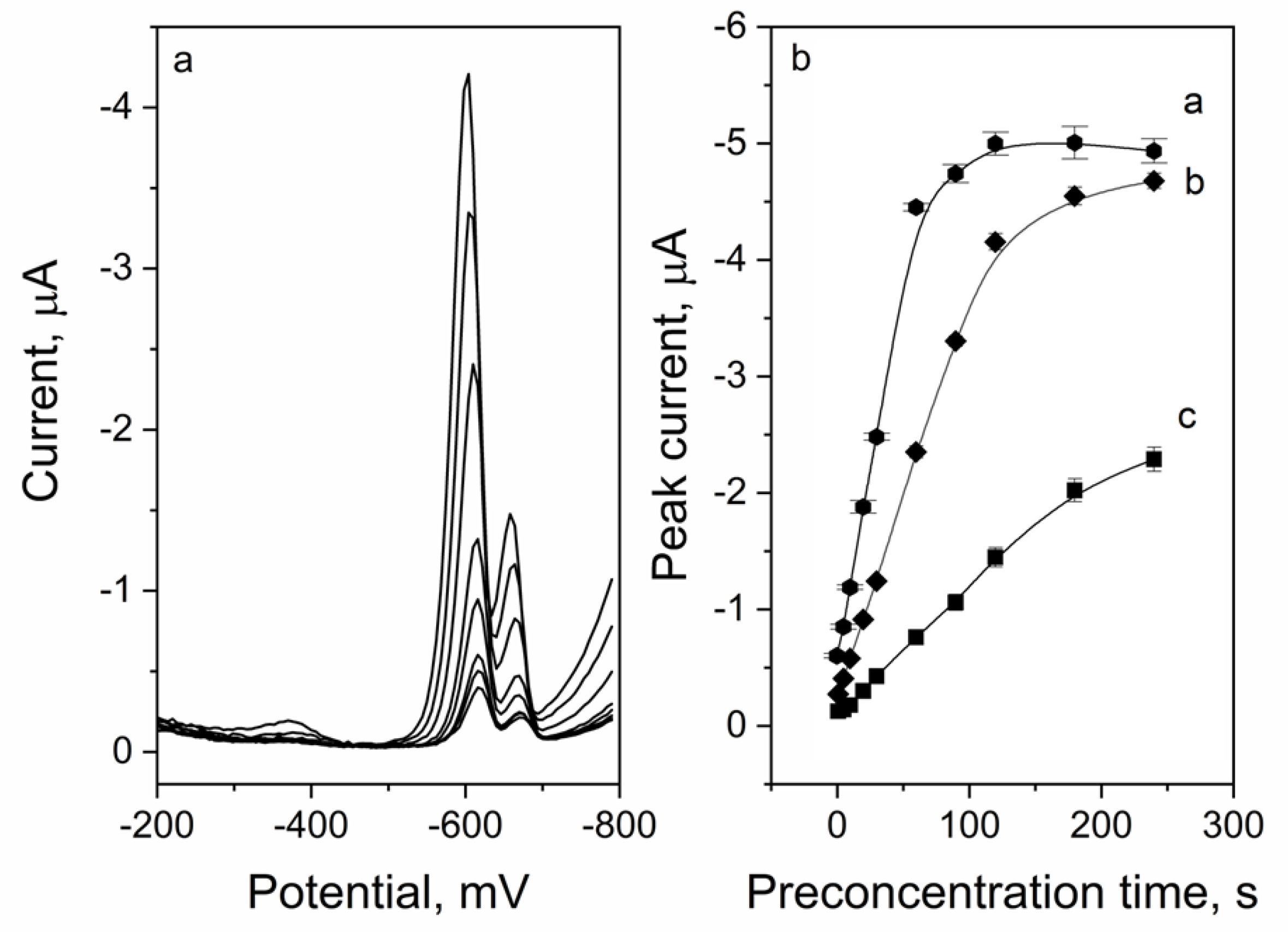
2.5.1. Preconcentration Potential
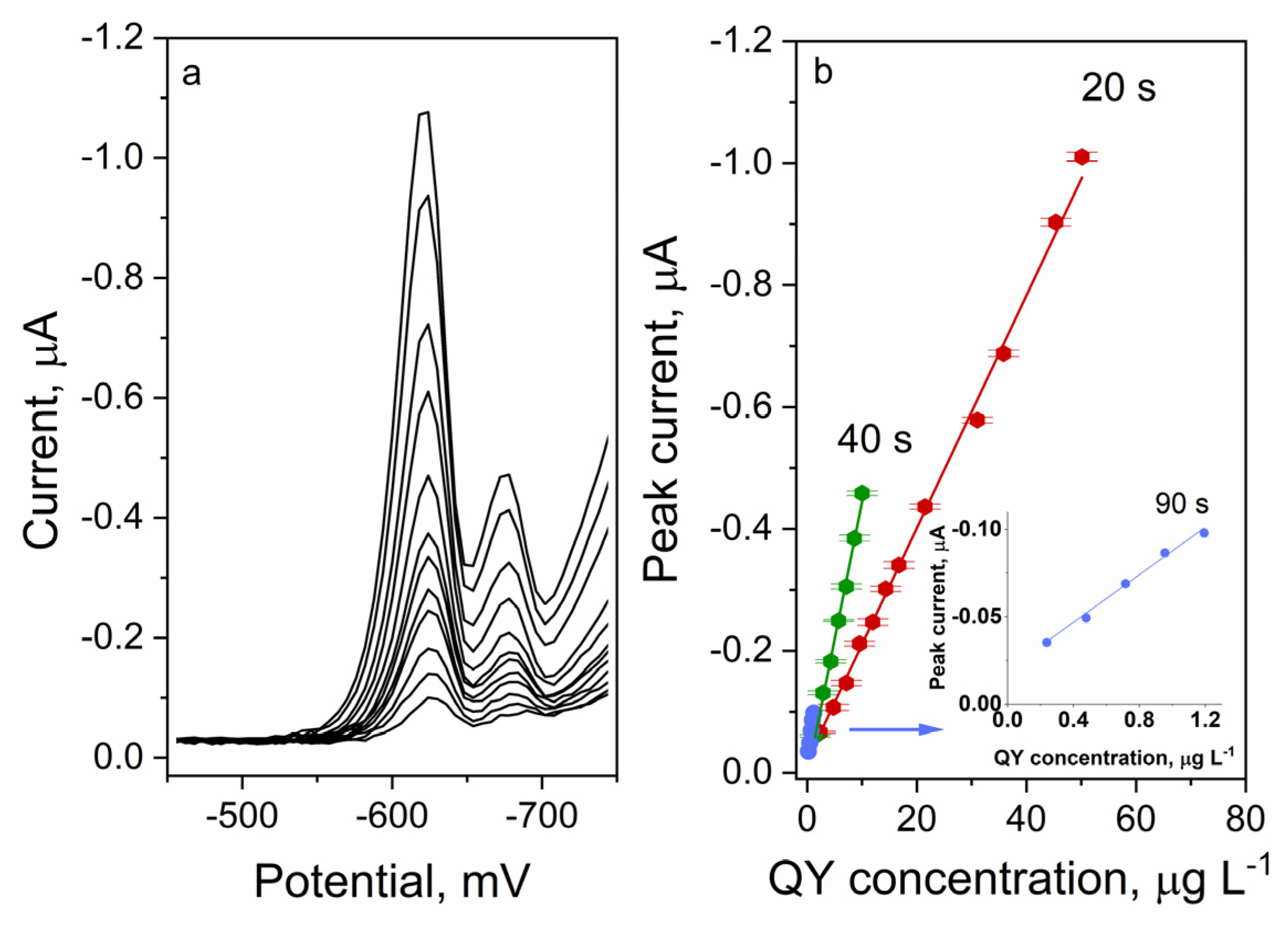
2.5.2. Preconcentration Time
2.6. Interference Study
2.7. Analytical Performance
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Apparatus
3.2. Chemicals and Glassware
3.3. Samples Preparation
3.3.1. Liquid Samples
3.3.2. Powder
3.3.3. Tablet
3.4. Measurement Procedure
- Cleaning of the working electrode’s surface: −1000 mV
- Preconcentration of QY: tacc = 20 s, Eacc = 50 mV
- Rest period: 3 s
- Voltammogram registration in the range from 50 mV to −850 mV
3.5. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Björkner, B.; Niklasson, B. Contact Allergic Reaction to D & C Yellow No. 11 and Quinoline Yellow. Contact Derm. 1983, 9, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.; McLean, W.G.; Williams, D.P.; Howard, C.V. Synergistic Interactions between Commonly Used Food Additives in a Developmental Neurotoxicity Test. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 90, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macioszek, V.K.; Kononowicz, A.K. The Evaluation of the Genotoxicity of Two Commonly Used Food Colors: Quinoline Yellow (E 104) and Brilliant Black (E 151). Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2004, 9, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asadpour-Zeynali, K.; Manafi-Khoshmanesh, S. Simultaneous Spectrophotometric Determination of Sunset Yellow and Quinoline Yellow in a Single Step. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2015, 62, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzas Nevado, J.J.; Rodríguez Flores, J.; Villaseñor Llerena, M.J.; Rodríguez Fariñas, N. Rapid Spectrophotometric Method to Resolve Ternary Mixtures of Tartrazine, Quinoline Yellow and Patent Blue V in Commercial Products. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1999, 365, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitán-Vallvey, L.F.; Fernández, M.D.; De Orbe, I.; Vilchez, J.L.; Avidad, R. Simultaneous Determination of the Colorants Sunset Yellow FCF and Quinoline Yellow by Solid-Phase Spectrophotometry Using Partial Least Squares Multivariate Calibration. Analyst 1997, 122, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitán-Vallvey, L.F.; Iglesias, N.N.; De Orbe Paya, I.; Castaneda, R.A. Simultaneous Determination of Quinoline Yellow and Brilliant Blue FCF in Cosmetics by Solid-Phase Spectrophotometry. Talanta 1996, 43, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedpour, V.; Amjadi, M. Application of Box-Behnken Design in the Optimization of In Situ Surfactant-Based Solid Phase Extraction Method for Spectrophotometric Determination of Quinoline Yellow in Food and Water Samples. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, H.; Başkan, D.; Yaşar, A.; Yaylı, N.; Ocak, Ü.; Ocak, M. Simultaneous Determination of Sunset Yellow FCF, Allura Red AC, Quinoline Yellow WS, and Tartrazine in Food Samples by RP-HPLC. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 6486250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinç Zor, Ş.; Aşçl, B.; Aksu Dönmez, Ö.; Ylldlrlm Küçükkaraca, D. Simultaneous Determination of Potassium Sorbate, Sodium Benzoate, Quinoline Yellow and Sunset Yellow in Lemonades and Lemon Sauces by HPLC Using Experimental Design. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Hristova, L.; Martínez-Moro, R.; Vázquez, L.; Ellis, G.J.; Sánchez, L.; del Pozo, M.; Petit-Domínguez, M.D.; Casero, E.; Quintana, C. A 2D Tungsten Disulphide/Diamond Nanoparticles Hybrid for an Electrochemical Sensor Development towards the Simultaneous Determination of Sunset Yellow and Quinoline Yellow. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 324, 128731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, A.; Cai, W.; Lin, H. Sensitive Determination of Quinoline Yellow Using Poly (Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride) Functionalized Reduced Graphene Oxide Modified Grassy Carbon Electrode. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, J. Rapid Detection of Quinoline Yellow in Soft Drinks Using Polypyrrole/Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Composites Modified Glass Carbon Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 735, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, K.; Roushani, M.; Farzadfar, F.; Goicoechea, H.C.; Jalalvand, A.R. Developing a Four-Dimensional Voltammetry as a Powerful Electroanalytical Methodology for Simultaneous Determination of Three Colorants in the Presence of an Uncalibrated Interference. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2019, 189, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Deng, P.; Tian, Y.; Magesa, F.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; He, Q. Construction of Effective Electrochemical Sensor for the Determination of Quinoline Yellow Based on Different Morphologies of Manganese Dioxide Functionalized Graphene. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 84, 103280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shi, Z.; Wang, J. Sensitive and Rapid Determination of Quinoline Yellow in Drinks Using Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Modified Electrode. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y. Electrochemical Sensor for Hazardous Food Colourant Quinoline Yellow Based on Carbon Nanotube-Modified Electrode. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, F.; Fu, L. One-Pot Synthesis of ZnO-Pd Nanocomposite with High Electrocatalytic Activity towards Quinoline Yellow. Inorg. Nano-Metal Chem. 2017, 47, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Fu, L.; Wang, A.; Cai, W. Electrochemical Detection of Quinoline Yellow in Soft Drinks Based on Layer-by-Layer Fabricated Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 3530–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankaran, U.; Radecki, J.; Radecka, H.; Girish Kumar, K. Copper Nanoclusters: An Efficient Fluorescence Sensing Platform for Quinoline Yellow. Luminescence 2019, 34, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, S.; Haji-Ghasemi, T. Novel PVC-Based Coated Graphite Electrode for Selective Determination of Quinoline Yellow. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2009, 6, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baś, B.; Baś, S. Rapidly Renewable Silver Amalgam Annular Band Electrode for Voltammetry and Polarography. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | Detection Limit | Source |
|---|---|---|
| HPLC | 92.2 pmol L−1 | [10] |
| RP-HPLC | 0.16 µmol L−1 | [9] |
| Spectrophotometry | 0.34 µmol L−1 | [4] |
| Spectrophotometry | 34.4 µmol L−1 | [5] |
| Spectrophotometry | 4.4 nmol L−1 | [8] |
| Spectrophotometry | 28.1 nmol L−1 | [7] |
| Fluorescence | 0.11 µmol L−1 | [20] |
| Potentiometry | 40 µmol L−1 | [21] |
| DPV (GC) | 0.25 mmol L−1 | [14] |
| CV (MWCNT/ITO) | 4 nmol L−1 | [19] |
| DPV (PDDA-RGO) | 2 nmol L−1 | [12] |
| SDLSV (MnO2/GR/GC) | 0.04 µmol L−1 | [15] |
| DPV (PVP/CPE) | 27 nmol L−1 | [16] |
| DPV (MWCNT/GC) | 1.0 µmol L−1 | [17] |
| DPV (ZnO-Pd/GC) | 4 nmol L−1 | [18] |
| DPV (WS2/DNPs/GC) | 3.4 µmol L−1 | [11] |
| SWV (PPy–SWCNT/GC) | 0.08 µmol L−1 | [13] |
| DPV (Hg(Ag)FE) | 0.48 nmol L−1 | This work |
| Voltammetry | Spectrophotometry | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | QY Added, mg L−1 | QY Found ± s, mg L−1, (Recovery, %) | QY Found, mg L−1 |
| Drink 1 | 0 | 21 ± 2 | 22 ± 2 |
| 19 | 40 ± 4 (96) | - | |
| 38 | 59 ± 2 (100) | - | |
| 57 | 78 ± 7 (106) | - | |
| Drink 2 | 0 | 18 ± 3 | 20 ± 2 |
| 19 | 37 ± 1 (99) | - | |
| 38 | 56 ± 1 (99) | - | |
| 57 | 75 ± 1 (96) | - | |
| Drink 3 | 0 | ND | ND |
| 19 | 19 ± 1 (102) | - | |
| 38 | 40 ± 1 (105) | - | |
| 57 | 58 ± 1 (101) | - | |
| Sample | Added, mg kg−1 | Found ± s, mg kg−1 | Found ± s, mg kg−1 |
| Pre-workout supplement (powder) | 0 | 1.15 ± 0.06 | 1.17 ± 0.03 |
| 0.95 | 0.95 ± 0.02 (100) | - | |
| 1.9 | 1.9 ± 0.01 (101) | - | |
| 2.85 | 2.86 ± 0.01 (102) | - | |
| Throat lozenges (tablet) | 0 | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.04 |
| 0.95 | 0.92 ± 0.03 (97) | - | |
| 1.9 | 1.78 ± 0.07 (95) | - | |
| 2.85 | 2.81 ± 0.04 (98) | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Górska-Ratusznik, A.; Różańska, D.; Smajdor, J.; Paczosa-Bator, B.; Piech, R. Highly Sensitive Voltammetric Method for Quinoline Yellow Determination on Renewable Amalgam Film Electrode. Molecules 2023, 28, 5475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145475
Górska-Ratusznik A, Różańska D, Smajdor J, Paczosa-Bator B, Piech R. Highly Sensitive Voltammetric Method for Quinoline Yellow Determination on Renewable Amalgam Film Electrode. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145475
Chicago/Turabian StyleGórska-Ratusznik, Anna, Dominika Różańska, Joanna Smajdor, Beata Paczosa-Bator, and Robert Piech. 2023. "Highly Sensitive Voltammetric Method for Quinoline Yellow Determination on Renewable Amalgam Film Electrode" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145475
APA StyleGórska-Ratusznik, A., Różańska, D., Smajdor, J., Paczosa-Bator, B., & Piech, R. (2023). Highly Sensitive Voltammetric Method for Quinoline Yellow Determination on Renewable Amalgam Film Electrode. Molecules, 28(14), 5475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145475









