Facile Synthesis of MXene-Ti3C2/Co Nanosheet Hydrogel Sensor with the Assistance of a Smartphone for On-Site Monitoring of Glucose in Beverages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
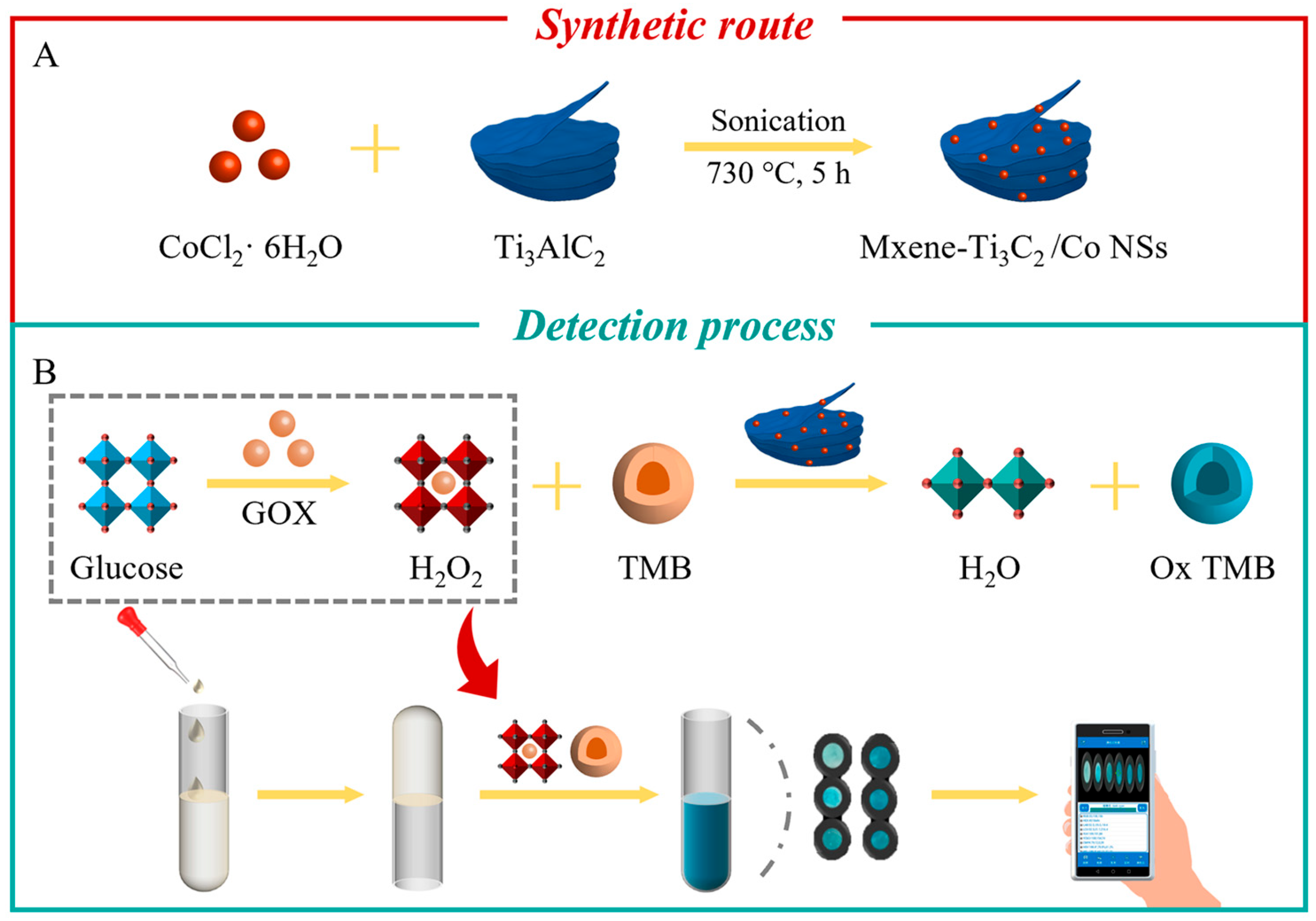
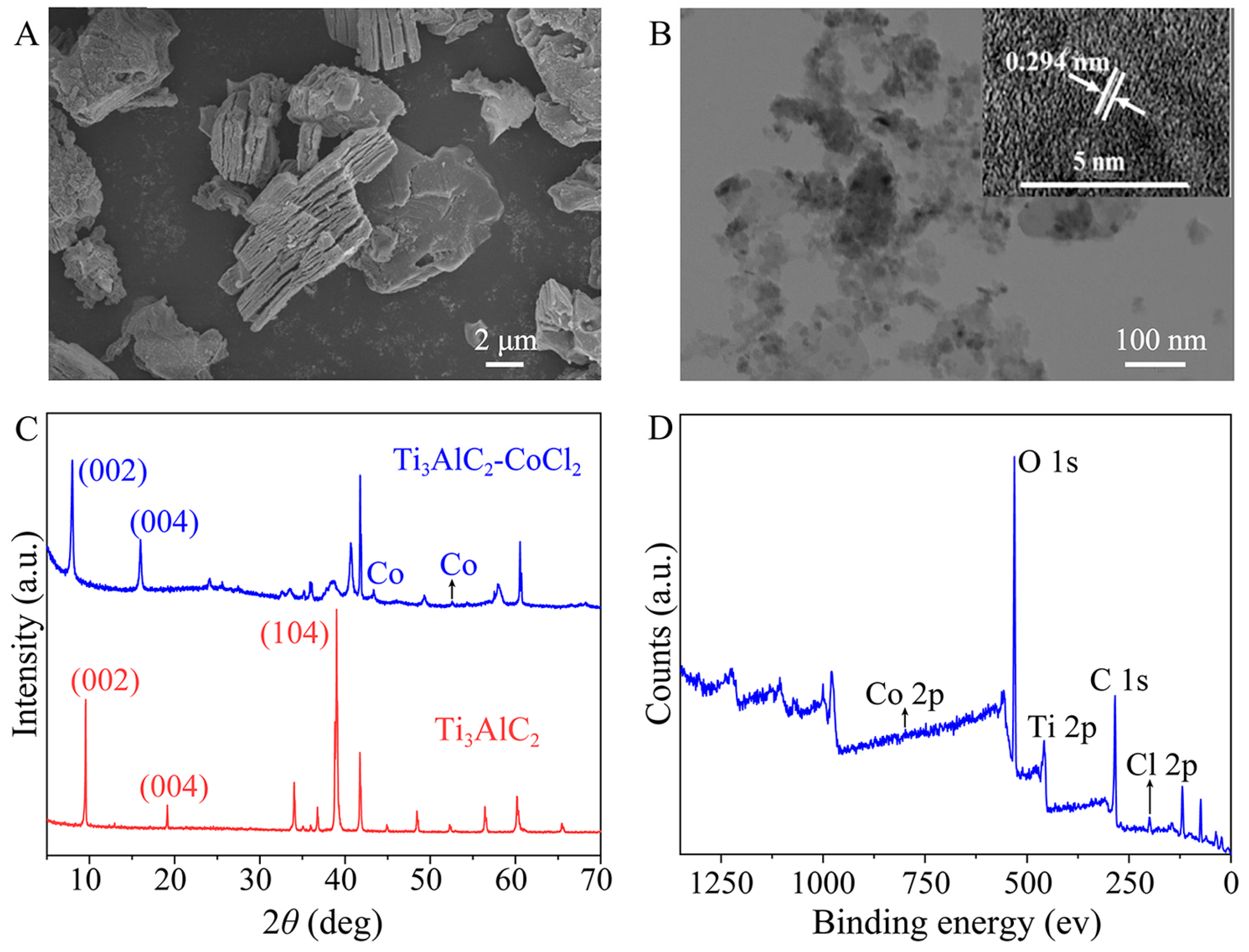
2.1. Characterization of MXene-Ti3C2/Co NSs
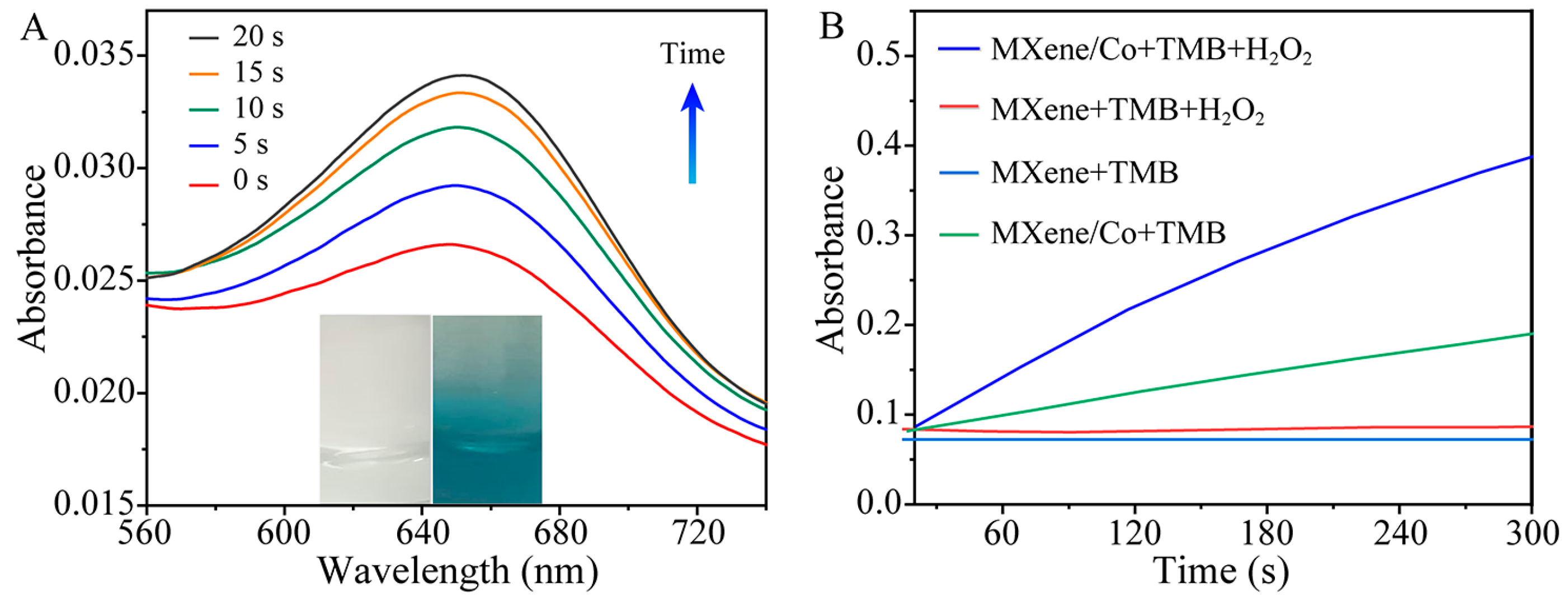
2.2. Study of Peroxidase-like Activity of MXene-Ti3C2/Co NSs
2.3. Kinetic Studies and Catalytic Mechanism of MXene-Ti3C2/Co NSs
2.4. Kinetic Studies and Catalytic Mechanism of MXene-Ti3C2/Co NSs
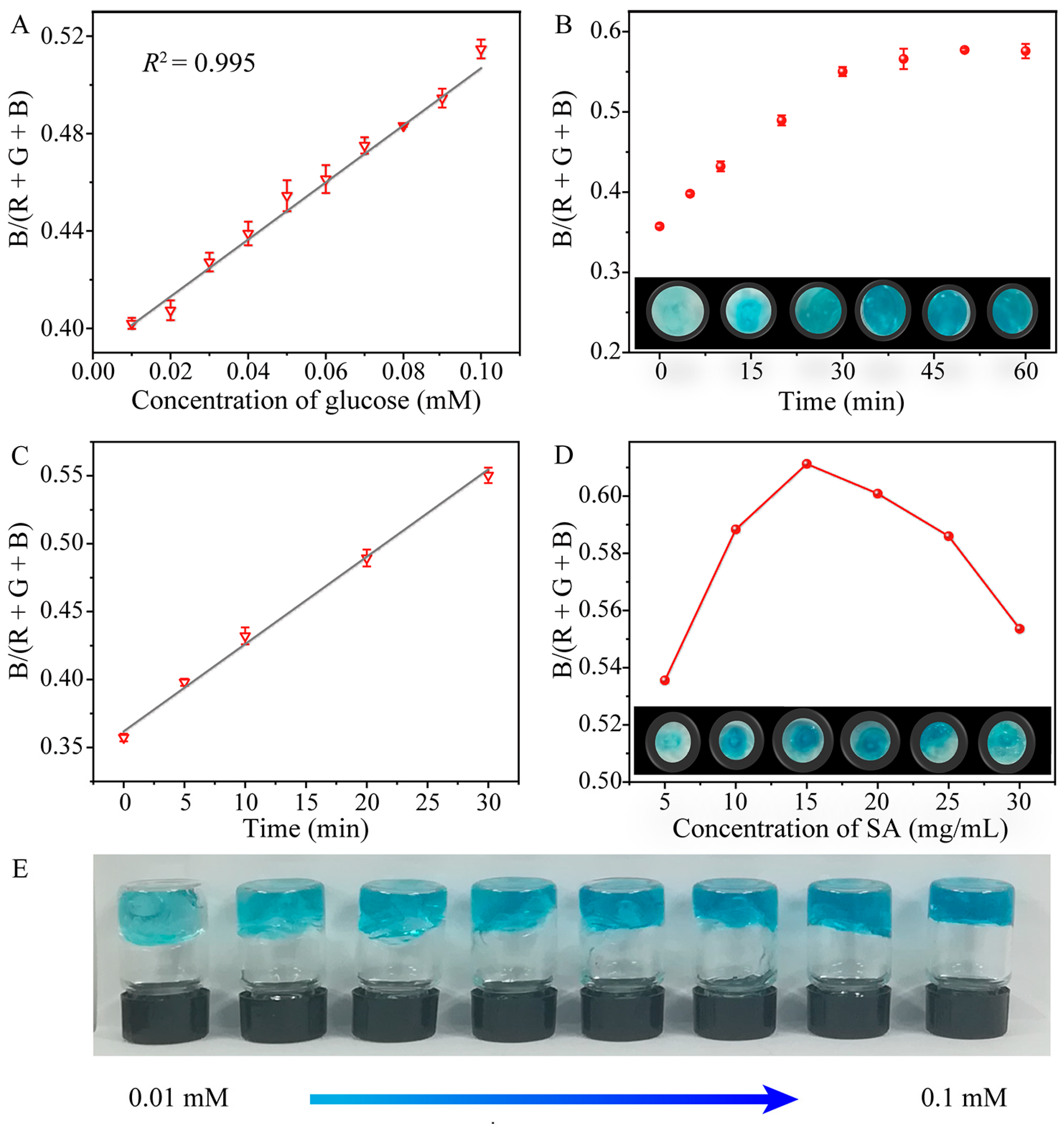
2.5. Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) for Glucose
2.6. Selectivity for Glucose
2.7. Real Sample Detection of Glucose
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Preparation of MXene-Ti3C2/Co NSs
3.4. Preparation of Hydrogel
3.5. Detection of Glucose and H2O2
3.6. Intelligent Detection of Glucose by SA Hydrogel Sensor
3.7. Detection of Glucose in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Tan, H.L.; Huang, Z.Z. A turn-on fluorescent assay for glucose detection based on carbon dots/manganese dioxide assembly. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xia, C.L.; Lin, J.Q.; Garalleh, H.A.; Alalawi, A.; Pugazhendhi, A. Carbon nanomaterials: A growing tool for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus. Environ. Res. 2023, 221, 115250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.L.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, Z.; Haidry, A.A.; Yao, Z.J.; Haque, E.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, G.; Daeneke, T.; McConville, C.F.; et al. Low dimensional materials for glucose sensing. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 11017–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, A.; Darraj, A.; Khan, M.E.; Azmi, L.; Alalwan, A.; Alamri, O.; Tabish, M.; Khan, A.U. A nanotechnology-based approach to biosensor application in current diabetes management practices. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.; Amaram, V.; Natarajan, R. Linking diabetic vascular complications with LncRNAs. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 114, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assoc, A.D. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, S62–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Tang, G.E.; Xiong, X.W.; Cao, Y.L.; Chen, L.L.; Xu, F.G.; Tan, H.L. Carbon coated magnetite nanoparticles with improved water-dispersion and peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric sensing of glucose. Sensor. Actuators B-Chem. 2015, 215, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liang, L.; Chi, W.H.; Bai, Y.J.; Gao, W.Q.; Zhu, P.H.; Yu, J.H. Porphyrin-based covalent organic frameworks with donor-acceptor sructure for enhanced peroxidase-like activity as a colorimetric biosensing platform. BioSens. 2023, 13, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Segovia, L.C.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Rogers, J.A.; Rintoul, I. Catalytic effects of magnetic and conductive nanoparticles on immobilized glucose oxidase in skin Sens. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 375101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.; Liu, X.M.; Yang, W.L.; Lin, J.Q.; Li, X.; Wu, J. Cu NWs@Pd with controllable diameter: Synthesis and their enhanced sensor performances in the detection of glucose and H2O2. J. Nanopart. Res. 2022, 24, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Zhou, C.S.; Long, Y.Y.; Cai, H.L.; Yin, C.Y.; Yang, Q.F.; Xiao, D. An enhanced chemiluminescence bioplatform by confining glucose oxidase in hollow calcium carbonate particles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.F.; Chen, G.; Ding, M.Y.; Cao, H.Y.; Li, G.Y.; Fang, M.Q.; Shi, W.B. Constructing a novel strategy for one-step colorimetric glucose biosensing based on Co-Nx sites on porous carbon as oxidase mimetics. Microchem. J. 2023, 188, 108448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.S.; Chen, F.Y.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, H.; Ouyang, G.F.; Zhao, W.D.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhao, Y.F. Carboxyl-based CPMP tag for ultrasensitive analysis of disaccharides by negative tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 9557–9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.F.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, R.P. One-step synthesis of N, B-codoped carbon nanofiber as a novel matrix for high-throughput and efficient laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry analysis. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 105966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M.S.; Duerkop, A.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Optical methods for sensing glucose. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4805–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.M.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Duan, L.Y.; Jiang, J.H.; Yu, R.Q. Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for highly sensitive detection of H2O2 and glucose. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2016, 8, 33439–33445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.C. Glucose detection through surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2022, 1206, 339226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, X.H.; Seong, B.; Hahm, E.; Huynh, K.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.H.; Jun, B.H. Glucose detection of 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid-immobilized gold-silver core-shell assembled silica nanostructure by surface enhanced raman scattering nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Li, H.T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wei, H.L.; Li, J.Y.; Su, H.J. Nanoceria-based artificial nanozymes: Review of materials and applications. ACS Appl. Nano. Mater. 2022, 5, 14147–14170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, Q.; Lou, Z.P.; Li, S.R.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Qin, L.; Wei, H. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1004–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Yan, H.Y.; Wu, Y.; Gu, W.L.; Zhu, C.Z.; Du, D.; Lin, Y.H. When nanozymes meet single-atom catalysis. Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D.; Jana, D.; Zhao, Y.L. Metal-organic framework derived nanozymes in biomedicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.J.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, J.S.; Qu, X.G. Carbon nanozymes: Enzymatic properties, catalytic mechanism, and applications. Angew. Chem. 2018, 57, 9224–9237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.L.; Zhou, J.D.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Q.J. Facile synthesis of iridium nanoparticles with superior peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric determination of H2O2 and xanthine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, T.M.; Wu, X.J.; Yang, G.W. CuMnO2 nanoflakes as pH-switchable catalysts with multiple enzyme-like activities for cysteine detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 279, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeramareddygari, M.; Phanthong, C.; Krishnappa, M.; Somasundrum, M.; Surareungchai, W. Peroxidase mimic sulfur-rich CuO-carbon nitride core-shell nanorods for the colorimetric detection of aminophenol isomers. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202300073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.S.; Liu, Y.; Gan, Y.; Li, Y.T.; Sha, J.Q.; Cao, A.M. A template-free assembly of Cu,N-codoped hollow carbon nanospheres as low-cost and highly efficient peroxidase nanozymes. Analyst 2022, 147, 5419–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.X.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, F.X.; He, N.; Yu, R.; Liu, X.H. AgNPs doping the fold carbon nanoflower composite for highly sensitive electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 904, 115930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.M.; Huang, S.; Su, G.H.; Wang, X.X.; Lu, Z.W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, T.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Song, C.; Rao, H.B. Synthesis of pH-switchable Pt/Co3O4 nanoflowers: Catalytic mechanism, four-enzyme activity and smartphone biosensing applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 134414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Dong, Y.M.; Jiang, P.P.; Wang, G.L.; Zhang, J.J. Highly Dispersed CeO2 on TiO2 nanotube: A synergistic nanocomposite with superior peroxidase-like activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6451–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirala, N.R.; Pandey, S.; Bansal, A.; Singh, V.K.; Mukherjee, B.; Saxena, P.S.; Srivastava, A. Different shades of cholesterol: Gold nanoparticles supported on MoS2 nanoribbons for enhanced colorimetric sensing of free cholesterol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Kang, Z.W.; Kong, L.Y.; Shi, H.T.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Cui, M.L.; Yang, D.P. MXene-Ti3C2/CuS nanocomposites: Enhanced peroxidase-like activity and sensitive colorimetric cholesterol detection. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 104, 110000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Wen, Y.Y.; Zhu, X.X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, B.G. Novel heterostructure of a MXene@NiFe-LDH nanohybrid with superior peroxidase-like activity for sensitive colorimetric detection of glutathione. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.X.; Chen, Z.P.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Qu, C.L.; Chen, L.X.; Shen, D.Z. Fluorescent sensing of mercury (II) based on formation of catalytic gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2013, 138, 4280–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.J.; Chen, T.M.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G.W. Modified Ti3C2 nanosheets as peroxidase mimetics for use in colorimetric detection and immunoassays. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 2650–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.F.; Ding, Y.Y.; Jiang, Y.L.; Liu, Q.Y. Montmorillonite-loaded ceria nanocomposites with superior peroxidase-like activity for rapid colorimetric detection of H2O2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stets, E.G.; Lee, C.J.; Lytle, D.A.; Schock, M.R. Increasing chloride in rivers of the conterminous US and linkages to potential corrosivity and lead action level exceedances in drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Cen, Y.; Kong, X.J.; Wu, S.; Liu, C.L.; Yu, R.Q.; Chu, X. MnO2-nanosheet-modified upconversion nanosystem for sensitive turn-On fluorescence detection of H2O2 and glucose in blood. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10548–10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.Z.; Yuan, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.N.; Majeed, S. Copper nanoclusters as peroxidase mimetics and their applications to H2O2 and glucose detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 762, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.K.; Tan, R.; Li, L.B.; Liu, D. Dual-modal colorimetric and fluorometric method for glucose detection using MnO2 sheets and carbon quantum dots. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2019, 35, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalui, A.; Pradhan, B.; Thupakula, U.; Khan, A.H.; Kumar, G.S.; Ghosh, T.; Satpati, B.; Acharya, S. Insight into the mechanism revealing the peroxidase mimetic catalytic activityof quaternary CuZnFeS nanocrystals: Colorimetric biosensing of hydrogenperoxide and glucose. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9062–9074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Yang, Y.Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, R.R.; Shao, Q.; Yang, S.G.; Xu, J.J. NiO nanoparticles modified with 5,10,15,20-tetrakis (4-carboxyl pheyl)-porphyrin: Promising peroxidase mimetics for H2O2 and glucose detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | Km (mM) | Vmax (10−8M·S−1) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMB | H2O2 | TMB | H2O2 | ||
| HRP | 0.275 | 0.214 | 1.24 | 2.46 | [34] |
| Ti3C2 nanosheets | 0.433 | 0.015 | 12.1 | 1.44 | [35] |
| Ala-Ti3C2 | 0.281 | 0.012 | 10.37 | 1.43 | [35] |
| MXene/CuS | 0.072 | 2.08 | 4.63 | 6.34 | [36] |
| GO-Fe3O4 | 0.43 | 0.71 | 13.08 | 5.31 | [37] |
| MXene-Ti3C2/Co | 0.107 | 0.095 | 2.27 | 2.04 | This work |
| Sample | Spiked (µM) | Found (µM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wonki Fores | 25 | 25.23 | 100.92 | 1.8 |
| 50 | 47.78 | 95.56 | 4.5 | |
| 75 | 80.92 | 107.89 | 2.3 | |
| Alien electrolyte | 25 | 24.34 | 97.36 | 5.4 |
| 50 | 52.29 | 104.58 | 3.1 | |
| 75 | 75.91 | 101.21 | 1.7 | |
| Soda | 25 | 26.49 | 105.96 | 2.4 |
| 50 | 48.39 | 96.78 | 3.8 | |
| 75 | 70.71 | 94.28 | 2.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Lei, T.; Pei, T.; Chen, K.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, M.; He, Y. Facile Synthesis of MXene-Ti3C2/Co Nanosheet Hydrogel Sensor with the Assistance of a Smartphone for On-Site Monitoring of Glucose in Beverages. Molecules 2023, 28, 5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135075
Li Z, Lei T, Pei T, Chen K, Zhao Z, Wang M, He Y. Facile Synthesis of MXene-Ti3C2/Co Nanosheet Hydrogel Sensor with the Assistance of a Smartphone for On-Site Monitoring of Glucose in Beverages. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135075
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ziling, Tiantian Lei, Ting Pei, Keyan Chen, Zhidong Zhao, Manman Wang, and Yu He. 2023. "Facile Synthesis of MXene-Ti3C2/Co Nanosheet Hydrogel Sensor with the Assistance of a Smartphone for On-Site Monitoring of Glucose in Beverages" Molecules 28, no. 13: 5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135075
APA StyleLi, Z., Lei, T., Pei, T., Chen, K., Zhao, Z., Wang, M., & He, Y. (2023). Facile Synthesis of MXene-Ti3C2/Co Nanosheet Hydrogel Sensor with the Assistance of a Smartphone for On-Site Monitoring of Glucose in Beverages. Molecules, 28(13), 5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135075





