Evaluation of Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity of Isatin Derivatives in Activated Microglia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
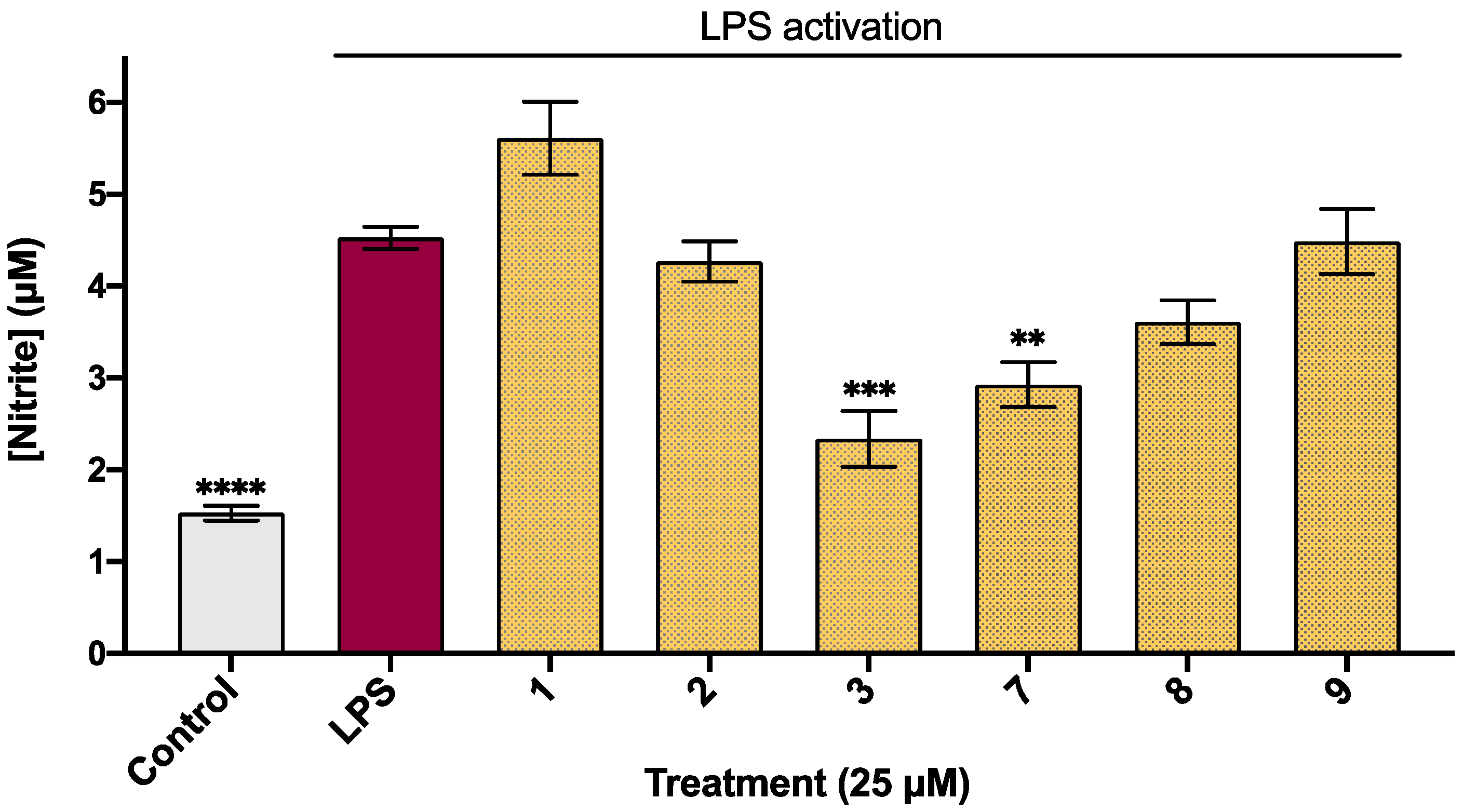
2.1. Biological Activity of Halogenated Isatin Derivatives
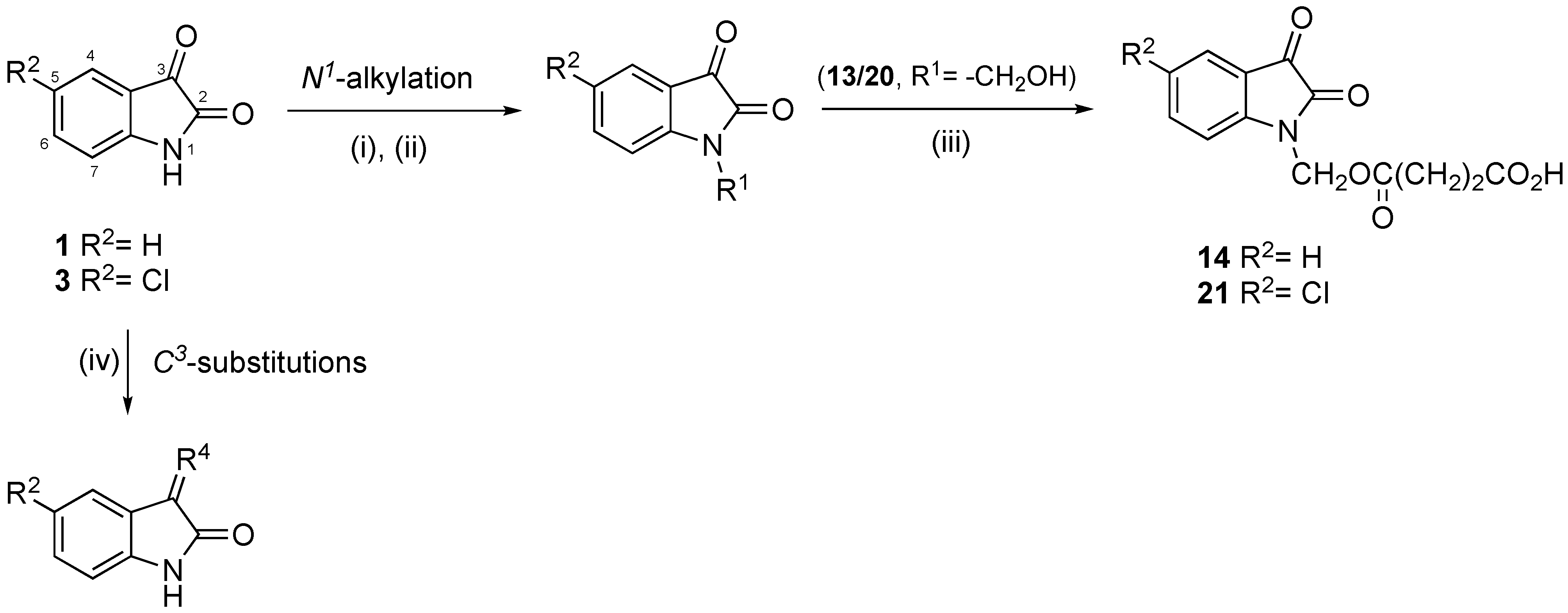
2.2. Chemical Synthesis
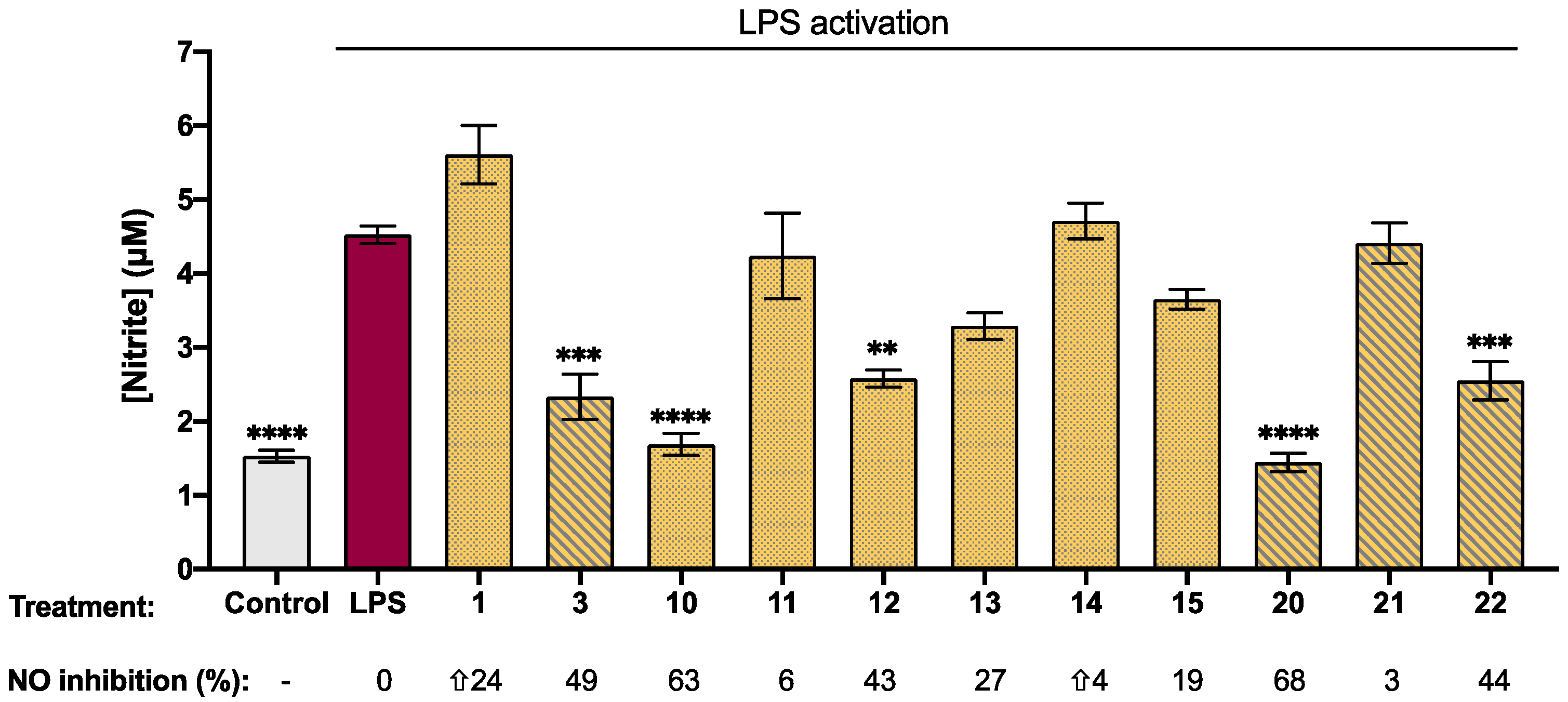
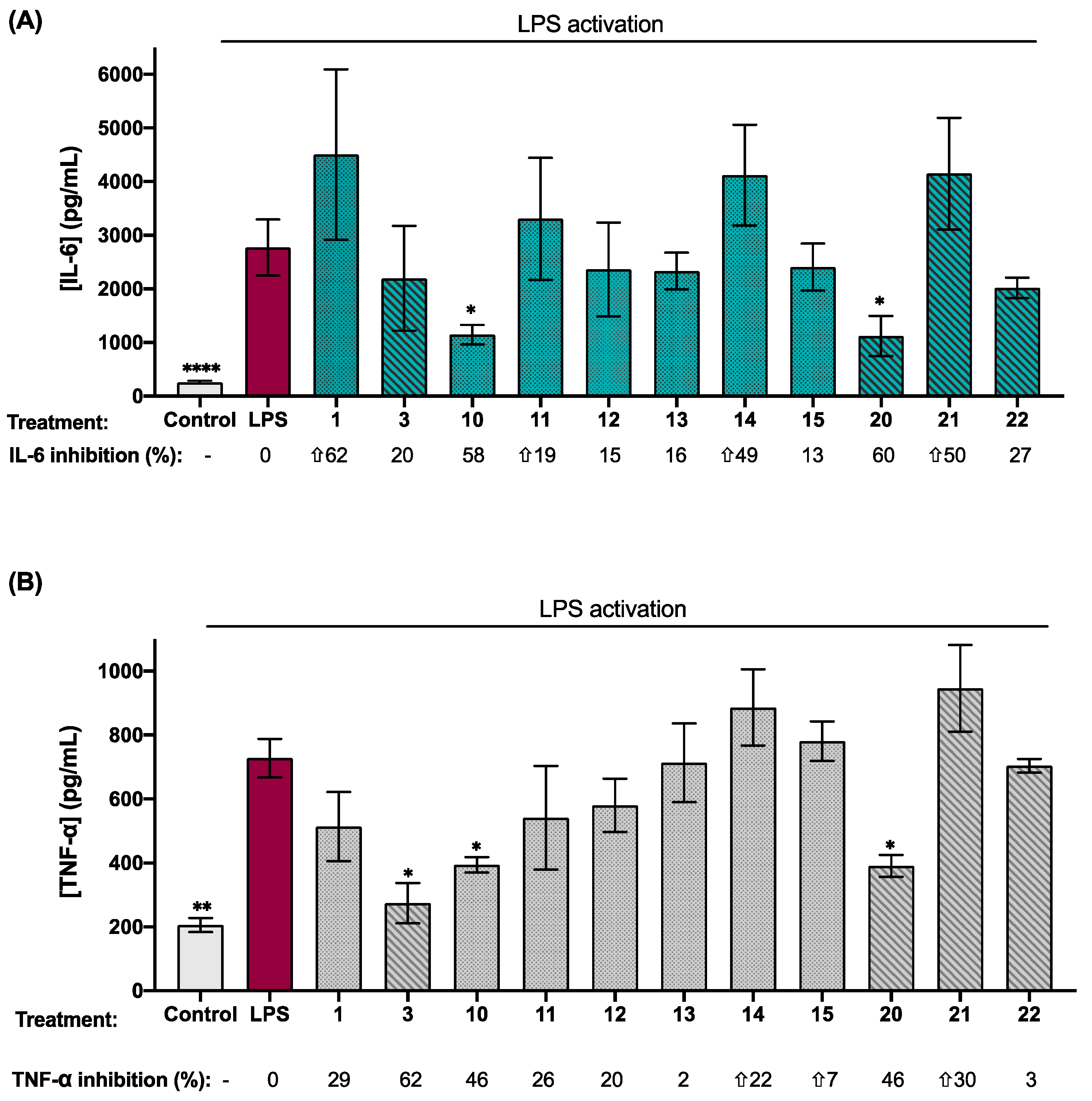
2.3. Biological Activity of Synthetic Isatin Derivatives
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials and Methods
4.2. Synthesis
4.2.1. Synthesis of the N-Derivatives
4.2.2. Synthesis of 1-(Hydroxymethyl)-Isatines
4.2.3. Synthesis of Isatin-Hydrazones
4.2.4. Synthesis of Target Compounds
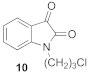
1-(3-chloropropyl)-1H-indole-2,3-dione (10)
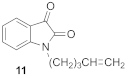
1-(pent-4-en-1-yl)-1H-indole-2,3-dione (11)
1-butyl-1H-indole-2,3-dione (12)
1-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-indole-2,3-dione (13)
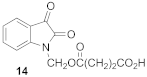
4-[(2,3-dioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-indole-1-yl)methoxy]-4-oxobutanoic Acid (14)
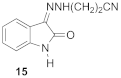
3-[(2Z)-2-(2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indole-3-ylidene)hydrazinyl]propanenitrile (15)
(3Z)-3-(2-phenylhydrazinylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-indole-2-one (16)
5-chloro-1-(3-chloropropyl)-1H-indole-2,3-dione (17)
5-chloro-1-(pent-4-en-1-yl)-1H-indole-2,3-dione (18)
1-butyl-5-chloro-1H-indole-2,3-dione (19)
5-cloro-1-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-indole-2,3-dione (20)
4-[(5-chloro-2,3-dioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-indole-1-yl)methoxy]-4-oxobutanoic Acid (21)
3-[(2Z)-2-(5-chloro-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indole-3ylidene)hydrazinyl] propanenitrile (22)
(3Z)-5-chloro-3-(2-phenylhydrazinylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-indole-2-one (23)
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.5. LPS-Activation of BV2 Cells
4.6. Nitric Oxide Release Determination
4.7. Measurement of IL-6 and TNF-α Levels
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Leng, F.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: Where do we go from here? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.S.; Koh, S.H. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, L.; Viotti, A.; Martino, G. Microglia in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration: From Understanding to Therapy. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 742065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, P.; Mukherjee, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Banerjee, S.; Das, S.; Banerjee, S. Isatin: A Scaffold with Immense Biodiversity. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 1096–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, P.; Kashanian, S.; Khodaei, M.M.; Harding, F.J. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of isatin and its derivatives: From structure to activity. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Singh, R.K. Medicinal Chemistry of indole derivaties: Current to future therapeutic prospectives. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 89, 103021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, E.; Hayallah, A.M.; Kovacic, S.; Abdelhamid, D.; Abdel-Aziz, M. Recent progress in biologically active indole hybrids: A mini review. Pharmacol. Rep. 2022, 74, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheke, R.S.; Patil, V.M.; Firke, S.D.; Ambhore, J.P.; Ansari, I.A.; Patel, H.M.; Shinde, S.D.; Pasupuleti, V.R.; Hassan, M.I.; Adnan, M.; et al. Therapeutic Outcomes of Isatin and Its Derivatives against Multiple Diseases: Recent Developments in Drug Discovery. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, A.; Lund, S.; Hedtjärn, M.; Schrattenholz, A.; Pörzgen, P.; Leist, M. The suitability of BV2 cells as alternative model system for primary microglia cultures or for animal experiments examining brain inflammation. ALTEX 2009, 26, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gegunde, S.; Alfonso, A.; Alvariño, R.; Pérez-Fuentes, N.; Botana, L.M. Anhydroexfoliamycin, a Streptomyces Secondary Metabolite, Mitigates Microglia-Driven Inflammation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 2336–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanguas-Casas, N.; Ojalvo-Sanz, A.C.; Martinez-Vazquez, A.; Goneau, M.F.; Gilbert, M.; Nieto-Sampedro, M.; Romero-Ramirez, L. Neurostatin and other O-acetylated gangliosides show anti-neuroinflammatory activity involving the NFκB pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 377, 114627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fang, J.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Xia, M.; Dong, J. Synthesis and Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity of 1,7-diphenyl-1,4-heptadien-3-ones in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Microglia via Inhibiting NF-κB/MAPK Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2022, 27, 3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, H.T.T.; Bui, B.P.; Sim, S.; Jung, J.K.; Lee, H.; Cho, J. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Migratory Activities of Isoquinoline-1-Carboxamide Derivatives in LPS-Treated BV2 Microglial Cells via Inhibition of MAPKs/NF-κB Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitnis, T.; Weiner, H.L. CNS inflammation and neurodegeneration. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3577–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Analysis of nitrite and nitrate in biological fluids by assays based on the Griess reaction: Appraisal of the Griess reaction in the L-arginine/nitric oxide area of research. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 851, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karali, N.; Güzel, O.; Ozsoy, N.; Ozbey, S.; Salman, A. Synthesis of new spiroindolinones incorporating a benzothiazole moiety as antioxidant agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggadi, V.; Kulandaivelu, U.; Sheshagiri, S.B.B.; Jupalli, V.R. Evaluation of Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Anticancer activity of Thiazole Tagged Isatin Hydrazones. J. Pharm. Chem. 2016, 3, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheus, M.E.; Violante Fde, A.; Garden, S.J.; Pinto, A.C.; Fernandes, P.D. Isatins inhibit cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase in a mouse macrophage cell line. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 556, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigan, M.; Jakusova, K.; Gaplovsky, M.; Filo, J.; Donovalova, J.; Gaplovsky, A. Isatin phenylhydrazones: Anion enhanced photochromic behaviour. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 2064–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodi, D.; Ishihara, Y. “Magic Chloro”: Profound Effects of the Chlorine Atom in Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 5305–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wei, N.; Guan, T.; Xu, H.; An, J.; Pritchard, K.A., Jr.; Shi, Y. Inhibition of CDKS by roscovitine suppressed LPS-induced *NO production through inhibiting NF-κB activation and BH4 biosynthesis in macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salem, H.S.; Arifuzzaman, M.; Alkahtani, H.M.; Abdalla, A.N.; Issa, I.S.; Alqathama, A.; Albalawi, F.S.; Rahman, A.F.M.M. A Series of Isatin-Hydrazones with Cytotoxic Activity and CDK2 Kinase Inhibitory Activity: A Potential Type II ATP Competitive Inhibitors. Molecules 2020, 25, 4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Martinez, L.; Maccioni, R.B.; Andrade, V.; Navarrete, L.P.; Pastor, M.G.; Ramos-Escobar, N. Neuroinflammation as a Common Feature of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, P.K.; Viengkhou, B.; Campbell, I.L.; Hofer, M.J. Microglia responses to interleukin-6 and type I interferons in neuroinflammatory disease. Glia 2019, 67, 1821–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Hao, X.; Mu, S.; Sun, Q. Simple isatin derivatives as free radical scavengers: Synthesis, biological evaluation and structure-activity relationship. Chem. Cent. J. 2011, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboul-Fadl, T.; Mohammed, F.A.; Hassan, E.A. Synthesis, antitubercular activity and pharmacokinetic studies of some Schiff bases derived from 1-alkylisatin and isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH). Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003, 26, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekircan, O.; Bektas, H. Synthesis of Schiff and Mannich bases of isatin derivatives with 4-amino-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5-ones. Molecules 2008, 13, 2126–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibinskaya, M.O.; Kutuzova, N.A.; Mazepa, A.V.; Lyakhov, S.A.; Andronati, S.A.; Zubritsky, M.J.; Galat, V.F.; Lipkowski, J.; Kravtsov, V.C. Synthesis of 6-aminopropyl-6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline derivatives. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2012, 49, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matcha, K.; Antonchick, A.P. Cascade multicomponent synthesis of indoles, pyrazoles, and pyridazinones by functionalization of alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilangovan, A.; Satish, G. Direct amidation of 2′-aminoacetophenones using I2-TBHP: A unimolecular domino approach toward isatin and iodoisatin. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, S.; Mohandossa, S.; Lee, Y.R. Indium(iii)-catalyzed efficient synthesis of 3-arylhydrazonoindolin-2-ones and their fluorescent metal sensing studies. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 3640–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damgaard, M.; Al-Khawaja, A.; Vogensen, S.B.; Jurik, A.; Sijm, M.; Lie, M.E.K.; Bæk, M.I.; Rosenthal, E.; Jensen, A.A.; Ecker, G.F.; et al. Identification of the first highly subtype-selective inhibitor of human GABA transporter GAT3. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratton, A.C.; Marshall, E.K.; Hendrickson, A.R. A new coupling component for sulfanilamide determination. J. Biol. Chem. 1939, 128, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.S.; McCabe, G.P. Introduction to the Practice of Statistics; W.H. Freeman & Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Royston, P. Remark AS R94: A Remark on Algorithm AS 181: The W-test for Normality. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 1995, 44, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | Log p b | [nitrite] c (µM) | NO Inhibition (%) d | Cell Viability (%) |
| Control e | - | - | - | - | 1.53 ± 0.08 **** | - | 100 ± 2 |
| LPS | - | - | - | - | 4.52 ± 0.12 | 0 | 100 ± 3 |
| 1 | H | H | H | 0.34 | 5.61 ± 0.40 | ⇧24 ± 2 | 106 ± 2 |
| 2 | H | F | H | 0.50 | 4.25 ± 0.20 | 6 ± 4 | 107 ± 3 |
| 3 | H | Cl | H | 0.90 | 2.33 ± 0.30 *** | 49 ± 6 | 90 ± 3 |
| 4 | H | Br | H | 1.17 | 2.71 ± 0.45 ** | - | 68 ± 3 *** |
| 5 | CH3 | Cl | H | 1.13 | 2.64 ± 0.04 ** | - | 68 ± 3 *** |
| 6 | CH3 | Br | H | 1.40 | 2.52 ± 0.10 ** | - | 55 ± 2 *** |
| 7 | H | H | Cl | 0.90 | 2.92 ± 0.22 ** | 33 ± 5 | 115 ± 4 |
| 8 | H | H | Br | 1.17 | 3.52 ± 0.25 | 22 ± 2 | 120 ± 4 |
| 9 | H | CH3 | Br | 1.40 | 4.36 ± 0.33 | 9 ± 1 | 115 ± 3 |
| Compound | Log p b | [nitrite] c (µM) | Viability (%) | Compound | Log p | [nitrite] (µM) | Viability (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
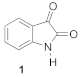 | 0.34 | 5.61 ± 0.40 | 106 ± 2 | 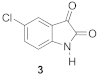 | 0.90 | 2.33 ± 0.30 *** | 90 ± 3 |
 | 1.39 | 1.70 ± 0.15 **** | 97 ± 2 |  | 1.95 | 1.16 ± 0.12 **** | 67 ± 1 *** |
 | 1.97 | 4.24 ± 0.60 | 100 ± 3 | 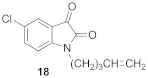 | 2.52 | 1.53 ± 0.30 **** | 82 ± 3 ** |
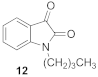 | 1.82 | 2.60 ± 12 ** | 92 ± 4 | 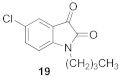 | 2.38 | 1.60 ± 0.07 **** | 85 ± 2 * |
 | 0.33 | 3.30 ± 0.20 | 110 ± 2 | 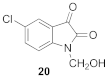 | 0.89 | 1.45 ± 0.12 **** | 106 ± 0.2 |
 | 0.23 | 4.71 ± 0.24 | 92 ± 1 | 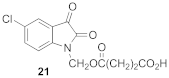 | 0.79 | 4.41 ± 0.30 | 110 ± 3 |
 | 0.35 | 3.65 ± 0.13 | 100 ± 2 |  | 0.91 | 2.55 ± 0.30 *** | 106 ± 3 |
 | 1.98 | 7.00 ± 1.00 | 85 ± 3 * |  | 2.53 | 11.10 ± 0.30 * | 83 ± 3 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cenalmor, A.; Pascual, E.; Gil-Manso, S.; Correa-Rocha, R.; Suárez, J.R.; García-Álvarez, I. Evaluation of Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity of Isatin Derivatives in Activated Microglia. Molecules 2023, 28, 4882. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124882
Cenalmor A, Pascual E, Gil-Manso S, Correa-Rocha R, Suárez JR, García-Álvarez I. Evaluation of Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity of Isatin Derivatives in Activated Microglia. Molecules. 2023; 28(12):4882. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124882
Chicago/Turabian StyleCenalmor, Alejandro, Elena Pascual, Sergio Gil-Manso, Rafael Correa-Rocha, José Ramón Suárez, and Isabel García-Álvarez. 2023. "Evaluation of Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity of Isatin Derivatives in Activated Microglia" Molecules 28, no. 12: 4882. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124882
APA StyleCenalmor, A., Pascual, E., Gil-Manso, S., Correa-Rocha, R., Suárez, J. R., & García-Álvarez, I. (2023). Evaluation of Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity of Isatin Derivatives in Activated Microglia. Molecules, 28(12), 4882. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124882







