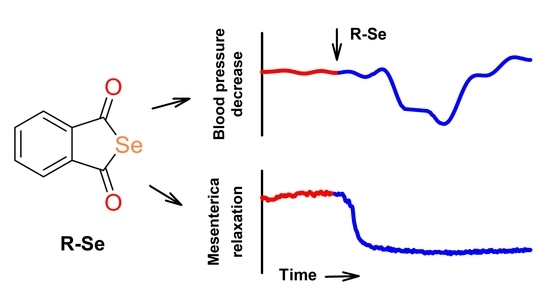
The Phthalic Selenoanhydride Decreases Rat Blood Pressure and Tension of Isolated Mesenteric, Femoral and Renal Arteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
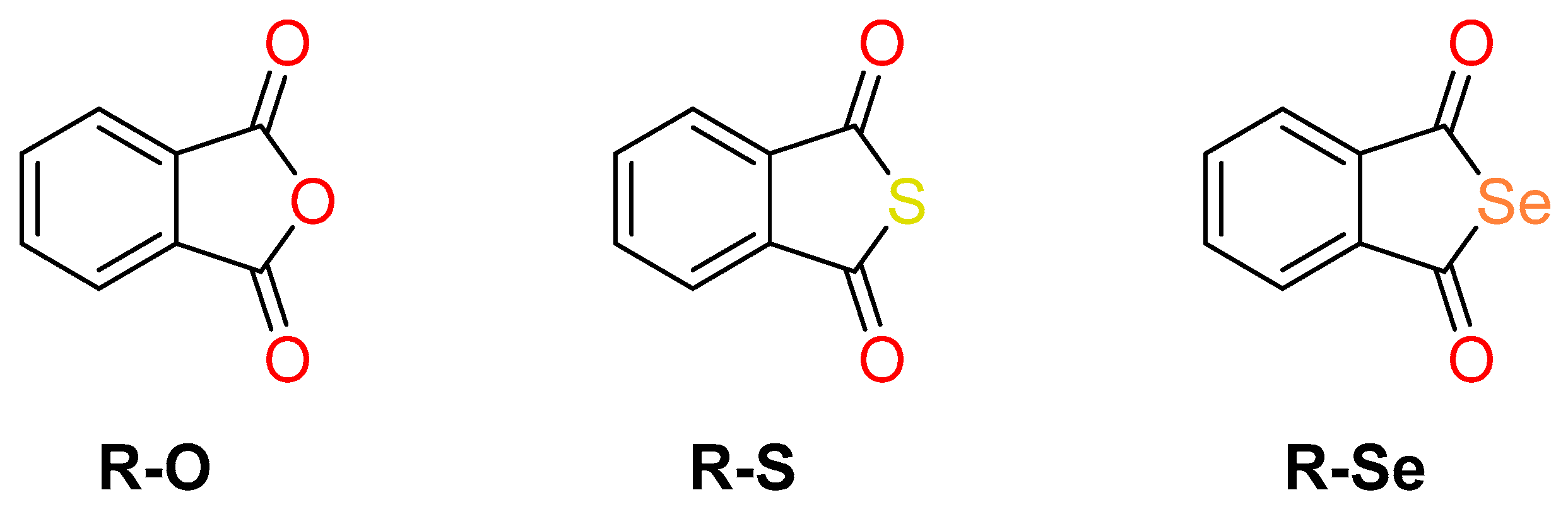
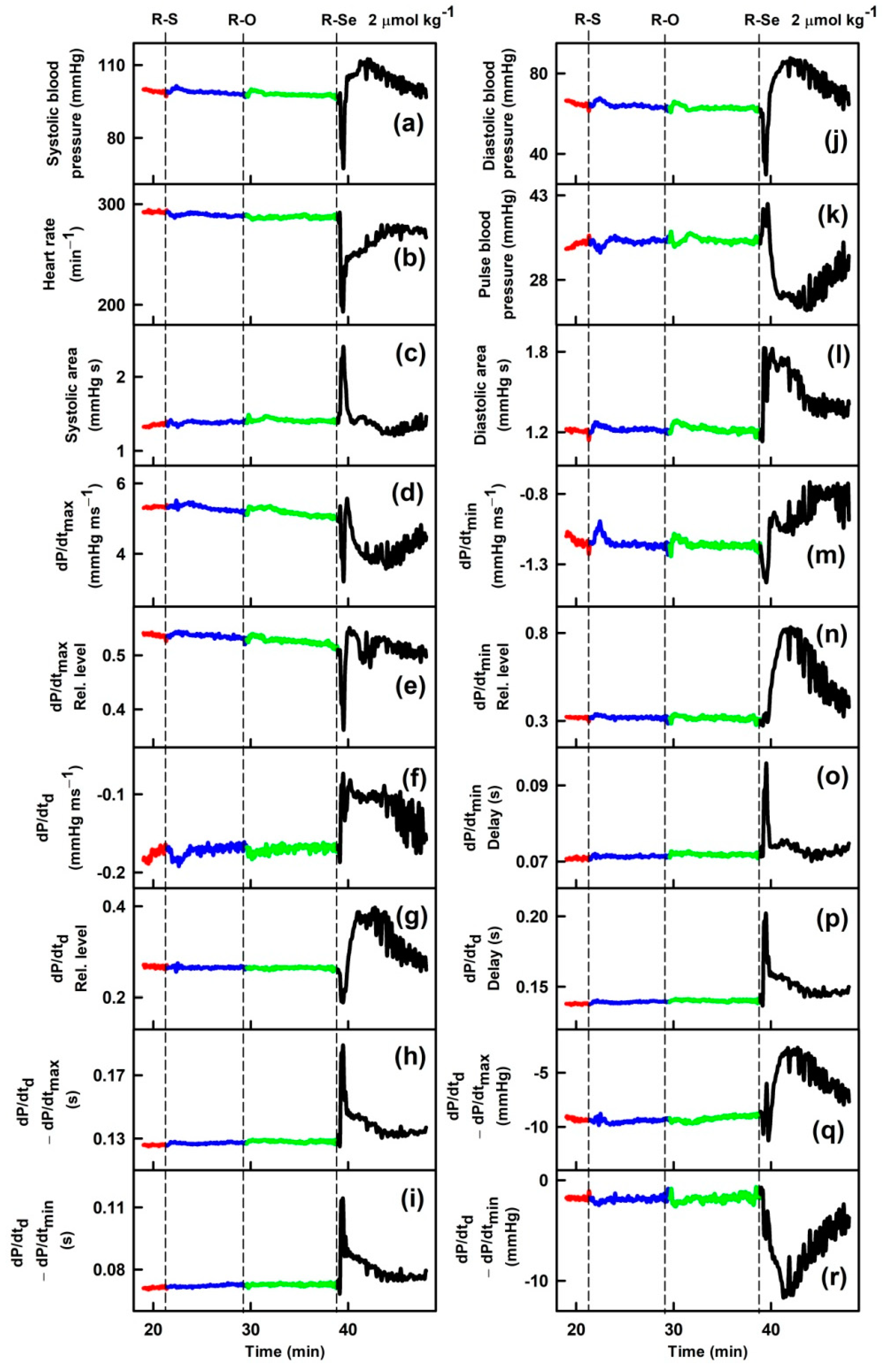
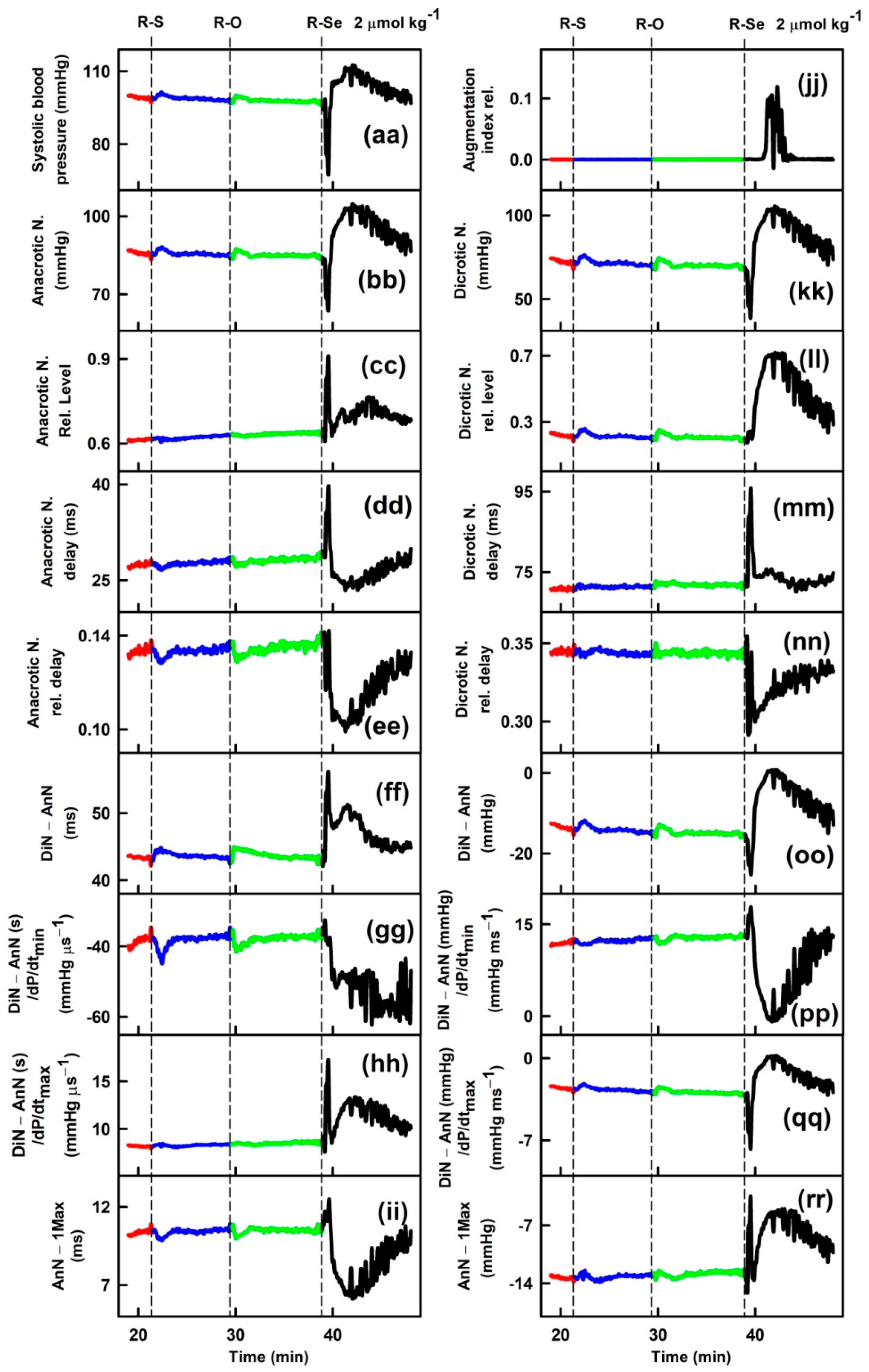
2.1. R-Se, but Not R-S or R-O Modulates Arterial Pulse Waveform
2.2. R-Se Decreased Tension of Isolated Mesenteric, Femoral and Renal Arteries
2.3. R-Se Had a Minor Effect on the Tension of the Isolated Thoracic Aorta
3. Discussion
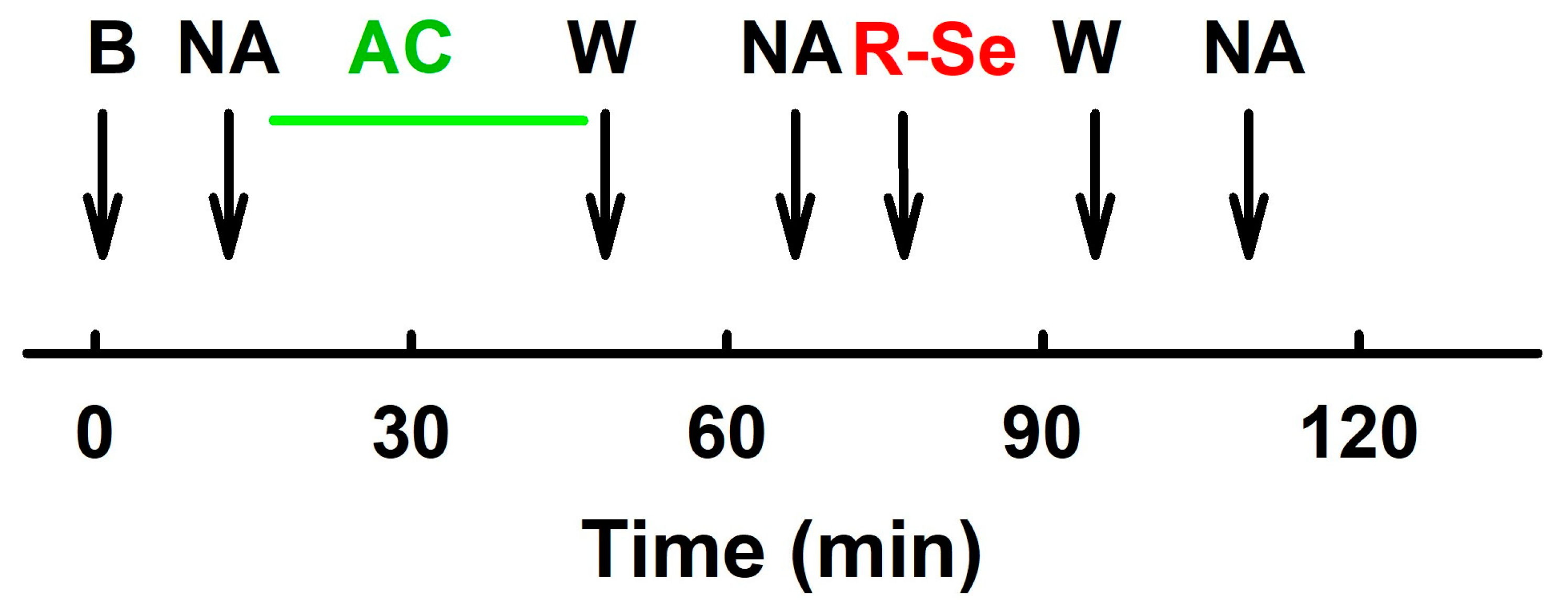
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.2. Guide for the Use and Care of Experimental Animals
4.3. APW Measurement and Data Evaluation
4.4. Measurement of the Vasoactive Effect of R-Se
4.4.1. Vascular Tissue Collection
4.4.2. Functional Study of Rat-Isolated Mesenteric, Femoral and Renal Arteries
4.4.3. Functional Study of the Isolated Thoracic Aorta
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Li, S.; Xiao, T.; Zheng, B. Medical geology of arsenic, selenium and thallium in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421–422, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrobel, J.K.; Power, R.; Toborek, M. Biological activity of selenium: Revisited. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stranges, S.; Marshall, J.R.; Natarajan, R.; Donahue, R.P.; Trevisan, M.; Combs, G.F.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Ceriello, A.; Reid, M.E. Effects of long-term selenium supplementation on the incidence of type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 147, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, D.L.; Yoo, M.H.; Carlson, B.A.; Gladyshev, V.N. Selenoproteins that function in cancer prevention and promotion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, J.C.; Hoffmann, P.R. Selenium, Selenoproteins, and Immunity. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, N.; Wang, X.; Shu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhao, L. The Functions of Selenium and Selenoproteins Relating to the Liver Diseases. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 1875–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.M.; Carlson, B.A.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Tsuji, P.A. Selenoproteins in colon cancer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 127, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandin, V.; Khalkar, P.; Braude, J.; Fernandes, A.P. Organic selenium compounds as potential chemotherapeutic agents for improved cancer treatment. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 127, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, N.; Kelishadi, M.R.; Asbaghi, O.; Naeini, F.; Afsharfar, M.; Mirzadeh, E.; kasra Naserizadeh, S. Selenium supplementation and oxidative stress: A review. PharmaNutrition 2021, 17, 100263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.A.Z.; Kerkadi, A.; Agouni, A. Selenium and Health: An Update on the Situation in the Middle East and North Africa. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchielli, G.; Capperucci, A.; Tanini, D. The Role of Selenium in Pathologies: An Updated Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.; Boylan, M.; Selvam, A.; Spallholz, J.E.; Björnstedt, M. Redox-active selenium compounds—From toxicity and cell death to cancer treatment. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3536–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.Y.; Jin, H.; Kim, S.J.; Kumar, A.P.; Lee, Y.I. Interaction of glutathione and sodium selenite in vitro investigated by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Biochem. 2008, 143, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennari, F.; Sharma, V.K.; Pettine, M.; Campanella, L.; Millero, F.J. Reduction of selenite by cysteine in ionic media. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 124, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenekeci, G.; Bilen, B.T.; Turkoz, Y.; Sahin, N.; Bulam, N.; Erdemli, M.E. The Effect of Selenium on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: An Experimental Study on a Transverse Rectus Abdominis Musculocutaneous Flap Model. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2016, 27, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomska, D.; Czarnomysy, R.; Radomski, D.; Bielawska, A.; Bielawski, K. Selenium as a Bioactive Micronutrient in the Human Diet and Its Cancer Chemopreventive Activity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Rácz, B.; Marć, M.A.; Nasim, M.J.; Szemerédi, N.; Viktorová, J.; Jacob, C.; Spengler, G. Selenium and tellurium in the development of novel small molecules and nanoparticles as cancer multidrug resistance reversal agents. Drug Resist. Updat. 2022, 63, 100844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørklund, G.; Shanaida, M.; Lysiuk, R.; Antonyak, H.; Klishch, I.; Shanaida, V.; Peana, M. Selenium: An Antioxidant with a Critical Role in Anti-Aging. Molecules 2022, 27, 6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Lee, J.; Wu, C.; Guo, X.; Lee, B.J.; Chun, J.S.; Kim, J.H. The role of selenium metabolism and selenoproteins in cartilage homeostasis and arthropathies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, M.; Szczyglowska, M.; Konieczka, P.; Namiesnik, J. Methods of Selenium Supplementation: Bioavailability and Determination of Selenium Compounds. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarze, A.; Dauplais, M.; Grigoras, I.; Lazard, M.; Ha-Duong, N.T.; Barbier, F.; Blanquet, S.; Plateau, P. Extracellular production of hydrogen selenide accounts for thiol-assisted toxicity of selenite against Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8759–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.P.; Gandin, V. Selenium compounds as therapeutic agents in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 1642–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marć, M.A.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Latacz, G.; Doroz-Płonka, A.; Sanmartín, C.; Spengler, G.; Handzlik, J. Pharmaceutical and Safety Profile Evaluation of Novel Selenocompounds with Noteworthy Anticancer Activity. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Plano, D.; Font, M.; Calvo, A.; Prior, C.; Jacob, C.; Palop, J.A.; Sanmartín, C. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of novel selenoester derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 73, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasim, M.J.; Ali, W.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; da Silva Júnior, E.N.; Saleem, R.S.Z.; Jacob, C. Reactive Selenium Species: Redox Modulation, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. In Organoselenium Compounds in Biology and Medicine: Synthesis, Biological and Therapeutic Treatments; Jain, V.K., Priyadarsini, K.I., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; pp. 277–302. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdács, M.; Spengler, G.; Sanmartín, C.; Marć, M.A.; Handzlik, J.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E. Selenoesters and selenoanhydrides as novel multidrug resistance reversing agents: A confirmation study in a colon cancer MDR cell line. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Gajdács, M.; Spengler, G.; Palop, J.A.; Marć, M.A.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; Amaral, L.; Molnár, J.; Jacob, C.; Handzlik, J.; et al. Identification of selenocompounds with promising properties to reverse cancer multidrug resistance. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2821–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, G.; Kincses, A.; Mosolygó, T.; Marć, M.A.; Nové, M.; Gajdács, M.; Sanmartín, C.; McNeil, H.E.; Blair, J.M.A.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E. Antiviral, Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity of Selenoesters and Selenoanhydrides. Molecules 2019, 24, 4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharma, A.; Misak, A.; Grman, M.; Brezova, V.; Kurakova, L.; Baráth, P.; Jacob, C.; Chovanec, M.; Ondrias, K.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E. Release of reactive selenium species from phthalic selenoanhydride in the presence of hydrogen sulfide and glutathione with implications for cancer research. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 11771–11783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, Y.; Shimizu-Furusawa, H.; Konishi, S.; Inaoka, T.; Ahmad, S.A.; Sekiyama, M.; Abdoellah, O.S.; Gunawan, B.; Parajuli, R.P.; Ikemoto, Y.; et al. Associations between urinary heavy metal concentrations and blood pressure in residents of Asian countries. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2021, 26, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot, T.S.; Staessen, J.A.; Roels, H.A.; Den Hond, E.; Thijs, L.; Fagard, R.H.; Dominiczak, A.F.; Struijker-Boudier, H.A. Blood pressure and blood selenium: A cross-sectional and longitudinal population study. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z. Selenium and Selenoproteins, from Structure, Function to Food Resource and Nutrition. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2017, 23, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaschler, M.M.; Stockwell, B.R. Lipid peroxidation in cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinola-Klein, C.; Rupprecht, H.J.; Bickel, C.; Schnabel, R.; Genth-Zotz, S.; Torzewski, M.; Lackner, K.; Munzel, T.; Blankenberg, S. Glutathione peroxidase-1 activity, atherosclerotic burden, and cardiovascular prognosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2007, 99, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.C.; Mahoney, C.E.; Coleman Anderson, L.; Ottaviano, F.; Croce, K.; Leopold, J.A.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Tang, S.S.; Handy, D.E.; Loscalzo, J. Glutathione peroxidase-3 deficiency promotes platelet-dependent thrombosis in vivo. Circulation 2011, 123, 1963–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laclaustra, M.; Navas-Acien, A.; Stranges, S.; Ordovas, J.M.; Guallar, E. Serum selenium concentrations and hypertension in the US Population. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2009, 2, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, M.M.; Locatis, C.; Maisiak, R.; Fontelo, P. Selenium, copper, zinc and hypertension: An analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2011–2016). BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhou, Q.; Mei, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, M.; Xu, J.; Ge, X.; Xu, Q. Novel Strategies for Assessing Associations between Selenium Biomarkers and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: Concentration, Visit-to-Visit Variability, or Individual Mean? Evidence from a Repeated-Measures Study of Older Adults with High Selenium. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 838613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruppu, D.; Hendrie, H.C.; Yang, L.; Gao, S. Selenium levels and hypertension: A systematic review of the literature. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.H.; Huang, Y.Q.; Liu, X.C.; Liu, L.; Lo, K.; Chen, J.Y.; Feng, Y.Q. A U-Shaped Relationship between Selenium Concentrations and All-Cause or Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with Hypertension. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 671618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Xian, J.; Zeng, M.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Z. Regional Difference in the Association between the Trajectory of Selenium Intake and Hypertension: A 20-Year Cohort Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Henkin, S.; Young, M.N. Renovascular Disease and Mesenteric Vascular Disease. Cardiol. Clin. 2021, 39, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, M.; Catena, F.; Kashuk, J.; De Simone, B.; Gomes, C.A.; Weber, D.; Sartelli, M.; Coccolini, F.; Kluger, Y.; Abu-Zidan, F.M.; et al. Acute mesenteric ischemia: Updated guidelines of the World Society of Emergency Surgery. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2022, 17, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serban, D.; Tribus, L.C.; Vancea, G.; Stoian, A.P.; Dascalu, A.M.; Suceveanu, A.I.; Tanasescu, C.; Costea, A.C.; Tudosie, M.S.; Tudor, C.; et al. Acute Mesenteric Ischemia in COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Liu, S.Y.; Man, R.Y. Enhancement of endothelium dependent relaxation in the rat aortic ring by selenium supplement. Cardiovasc. Res. 1994, 28, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günaldi, O.; Tuğcu, B.; Cöllüoğlu, B.; Güçlü, D.G.; Tanriverdi, O.; Akdemir, H.; Bayindir, C. Morphometric analysis of the influence of selenium over vasospastic femoral artery in rats. Acta Neurochir. 2010, 152, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swart, R.; Schutte, A.E.; van Rooyen, J.M.; Mels, C.M.C. Selenium and large artery structure and function: A 10-year prospective study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 3313–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grman, M.; Misak, A.; Kurakova, L.; Brezova, V.; Cacanyiova, S.; Berenyiova, A.; Balis, P.; Tomasova, L.; Kharma, A.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; et al. Products of Sulfide/Selenite Interaction Possess Antioxidant Properties, Scavenge Superoxide-Derived Radicals, React with DNA, and Modulate Blood Pressure and Tension of Isolated Thoracic Aorta. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9847650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüscher, T.F.; Dohi, Y.; Tschudi, M. Endothelium-dependent regulation of resistance arteries: Alterations with aging and hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1992, 19 (Suppl. 5), S34–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, G.A. Assessing vascular reactivity of arteries in the small vessel myograph. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1992, 19, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakova, L.; Misak, A.; Tomasova, L.; Cacanyiova, S.; Berenyiova, A.; Ondriasova, E.; Balis, P.; Grman, M.; Ondrias, K. Mathematical relationships of patterns of 35 rat haemodynamic parameters for conditions of hypertension resulting from decreased nitric oxide bioavailability. Exp. Physiol. 2020, 105, 312–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasova, L.; Grman, M.; Misak, A.; Kurakova, L.; Ondriasova, E.; Ondrias, K. Cardiovascular “Patterns” of H2S and SSNO−-Mix Evaluated from 35 Rat Hemodynamic Parameters. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharma, A.; Grman, M.; Misak, A.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Nasim, M.J.; Ondrias, K.; Chovanec, M.; Jacob, C. Inorganic Polysulfides and Related Reactive Sulfur–Selenium Species from the Perspective of Chemistry. Molecules 2019, 24, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bencze, M.; Behuliak, M.; Zicha, J. The impact of four different classes of anesthetics on the mechanisms of blood pressure regulation in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Physiol. Res. 2013, 62, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redfors, B.; Shao, Y.; Omerovic, E. Influence of anesthetic agent, depth of anesthesia and body temperature on cardiovascular functional parameters in the rat. Lab. Anim. 2014, 48, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobná, M.; Misak, A.; Holland, T.; Kristek, F.; Grman, M.; Tomasova, L.; Berenyiova, A.; Cacanyiova, S.; Ondrias, K. Captopril partially decreases the effect of H2S on rat blood pressure and inhibits H2S-induced nitric oxide release from S-nitrosoglutathione. Physiol. Res. 2015, 64, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.J.; Pfeffer, J.M.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Brenner, B.M. Systemic hemodynamic effects of endothelin in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 258, H787–H792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, S.M.; March, J.E.; Kemp, P.A.; Bennett, T. Bolus injection of human UII in conscious rats evokes a biphasic haemodynamic response. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, C.J.; Rademaker, M.T.; Richards, A.M. Apelin-13 induces a biphasic haemodynamic response and hormonal activation in normal conscious sheep. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 189, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Critchley, L.A.; Huang, L. Five algorithms that calculate cardiac output from the arterial waveform: A comparison with Doppler ultrasound. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; Jiang, H.; Chi, Z.; Wang, A.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Hao, D.; Zhang, L.; et al. Changes of Arterial Pulse Waveform Characteristics with Gestational Age during Normal Pregnancy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, M.; Venton, J.; Aston, P.J. A novel method to quantify arterial pulse waveform morphology: Attractor reconstruction for physiologists and clinicians. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 104008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, M.A.; Van Roon, A.M.; Bakker, J.T.; Bijen, H.T.J.; Mulder, D.J.; Brouwers, F.P.; Van Gilst, W.H.; Voors, A.A.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Bakker, S.J.L.; et al. Digital arterial pressure pulse wave analysis and cardiovascular events in the general population: The Prevention of Renal and Vascular End-stage Disease study. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misak, A.; Kurakova, L.; Berenyiova, A.; Tomasova, L.; Grman, M.; Cacanyiova, S.; Ondrias, K. Patterns and Direct/Indirect Signaling Pathways in Cardiovascular System in the Condition of Transient Increase of NO. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6578213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasova, L.; Misak, A.; Kurakova, L.; Grman, M.; Ondrias, K. Characterization of Rat Cardiovascular System by Anacrotic/Dicrotic Notches in the Condition of Increase/Decrease of NO Bioavailability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saugel, B.; Kouz, K.; Scheeren, T.W.L.; Greiwe, G.; Hoppe, P.; Romagnoli, S.; de Backer, D. Cardiac output estimation using pulse wave analysis-physiology, algorithms, and technologies: A narrative review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 126, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, H.; Geng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, T. The pulse waveform quantification method basing on contour and derivative. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 220, 106784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Chowienczyk, P.; Alastruey, J. Estimating pulse wave velocity from the radial pressure wave using machine learning algorithms. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morato, M.; Sousa, T.; Albino-Teixeira, A. Purinergic receptors in the splanchnic circulation. Purinergic Signal. 2008, 4, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, H.H.; Leo, C.H.; O’Sullivan, K.; Alexander, S.A.; Davies, M.J.; Schiesser, C.H.; Parry, L.J. 1,4-Anhydro-4-seleno-d-talitol (SeTal) protects endothelial function in the mouse aorta by scavenging superoxide radicals under conditions of acute oxidative stress. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 128, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharias, T.; Flouda, K.; Jepps, T.A.; Gammelgaard, B.; Schiesser, C.H.; Davies, M.J. Effects of a novel selenium substituted-sugar (1,4-anhydro-4-seleno-d-talitol, SeTal) on human coronary artery cell lines and mouse aortic rings. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 173, 113631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greasley, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Pei, Y.; Belzile, N.; Yang, G. H2S Protects against Cardiac Cell Hypertrophy through Regulation of Selenoproteins. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 6494306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Mu, J.; Ma, J.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, T.; Zhu, P.; Zheng, S.; Xie, J.; et al. Selenium Inhibits Homocysteine-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction and Apoptosis via Activation of AKT. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenyiova, A.; Balis, P.; Kluknavsky, M.; Bernatova, I.; Cacanyiova, S.; Puzserova, A. Age- and Hypertension-Related Changes in NOS/NO/sGC-Derived Vasoactive Control of Rat Thoracic Aortae. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 7742509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.T. Endothelium-derived Relaxing Factors of Small Resistance Arteries in Hypertension. Toxicol. Res. 2014, 30, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.Y.; Zhang, F.; Xie, W.M.; Fan, Y.F.; Duan, J.S.; et al. Endothelium-derived hydrogen sulfide acts as a hyperpolarizing factor and exerts neuroprotective effects via activation of large-conductance Ca(2+) -activated K(+) channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 4155–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, G.M.; da Silva, M.C.; Nascimento, D.V.G.; Lima Silva, E.M.; Gouvêa, F.F.F.; de França Lopes, L.G.; Araújo, A.V.; Ferraz Pereira, K.N.; de Queiroz, T.M. Nitric Oxide as a Central Molecule in Hypertension: Focus on the Vasorelaxant Activity of New Nitric Oxide Donors. Biology 2021, 10, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, D. Principles and standards for reporting animal experiments in The Journal of Physiology and Experimental Physiology. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 2547–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristek, F.; Grman, M.; Ondrias, K. In Vivo Measurement of H2S, Polysulfides, and “SSNO− Mix”-Mediated Vasoactive Responses and Evaluation of Ten Hemodynamic Parameters from Rat Arterial Pulse Waveform. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2007, 109–124. [Google Scholar]
- Cacanyiova, S.; Berenyiova, A.; Kristek, F.; Drobna, M.; Ondrias, K.; Grman, M. The adaptive role of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulphide in vasoactive responses of thoracic aorta is triggered already in young spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 67, 501–512. [Google Scholar]
- Cacanyiova, S.; Berenyiova, A.; Balis, P.; Kristek, F.; Grman, M.; Ondrias, K.; Breza, J.; Breza, J., Jr. Nitroso-sulfide coupled signaling triggers specific vasoactive effects in the intrarenal arteries of patients with arterial hypertension. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 68, 527–538. [Google Scholar]
- Balis, P.; Berenyiova, A.; Radosinska, J.; Kvandova, M.; Bernatova, I.; Puzserova, A. High concentration of uric acid failed to affect endothelial function of small mesenteric arteries, femoral arteries and aortas from aged Wistar-Kyoto rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 71, 99–408. [Google Scholar]
- Slezák, P.; Waczulíková, I.; Bališ, P.; Púzserová, A. Accurate normalization factor for wire myography of rat femoral artery. Physiol. Res. 2010, 59, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motulsky, H.; Christopoulos, A. Fitting curves with GraphPad Prism. In Fitting Models to Biological Data Using Linear and Nonlinear Regression: A Practical Guide to Curve Fitting; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
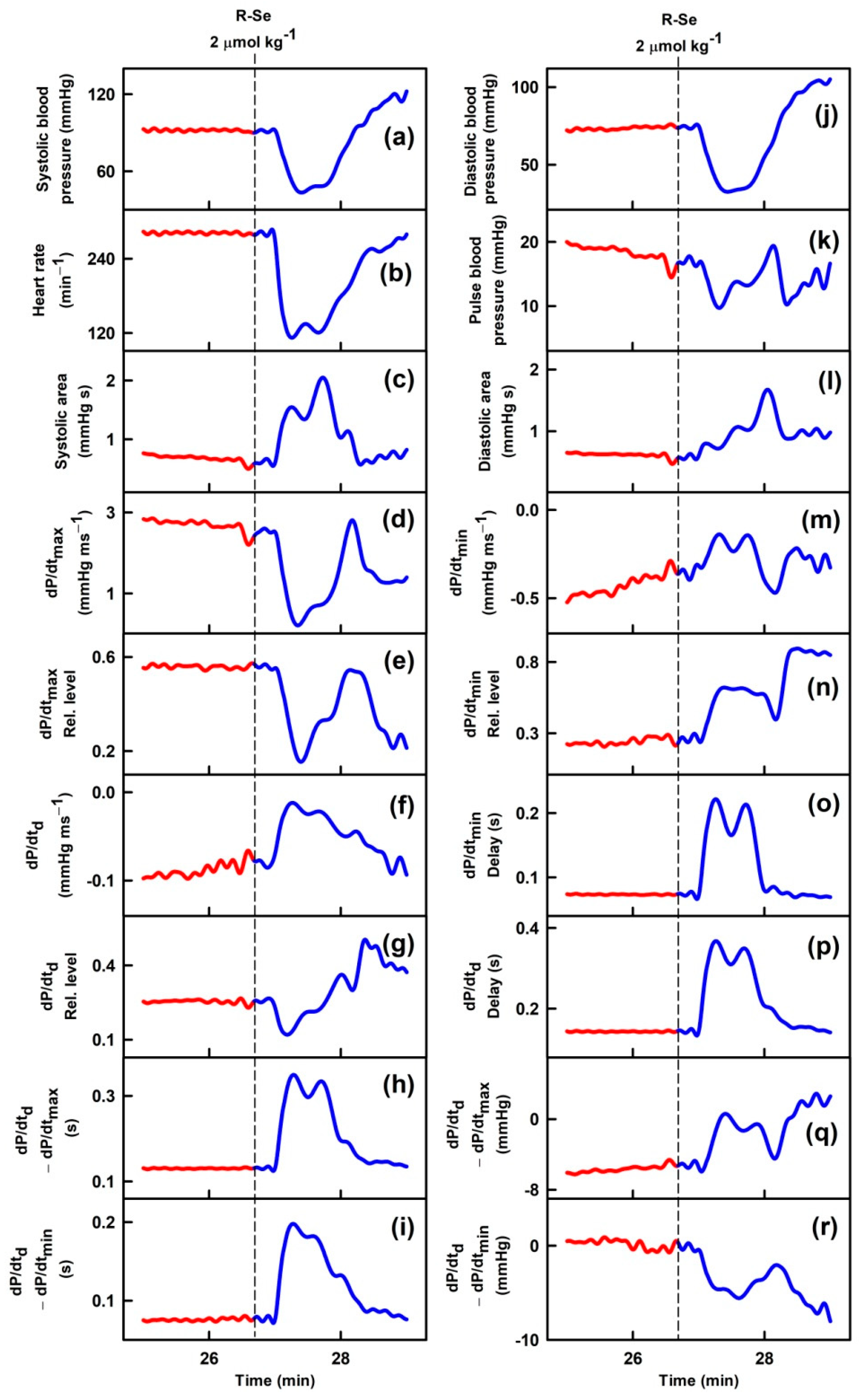
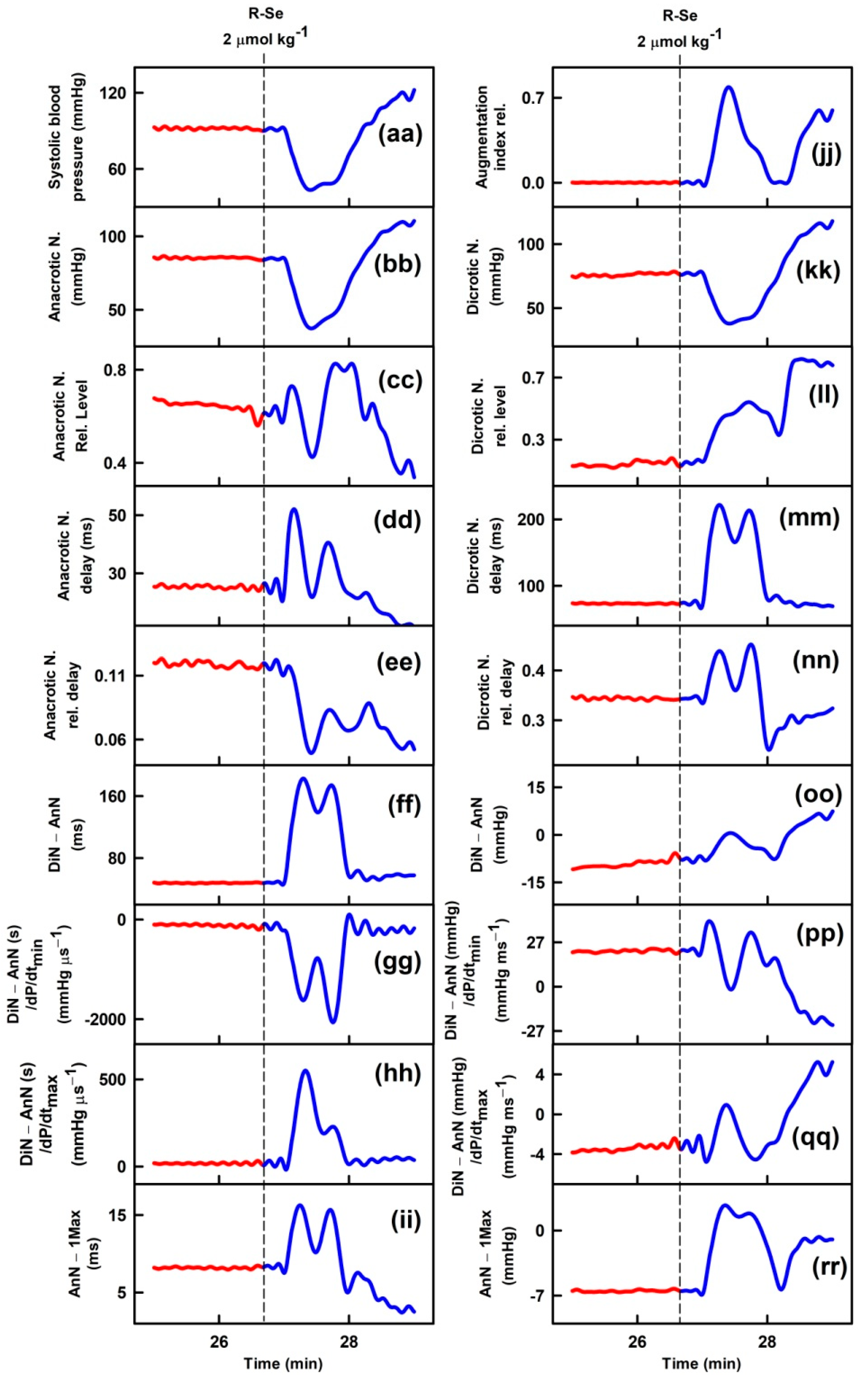


| APW-Ps | Variation | APW-Ps | Variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ↓ = 9 |
| ↓ = 9 |
| ↓ = 9 |
| ↓ = 9 |
| ↑ = 9 |
| ↑ = 9 |
| ↓ = 7 |
| ↑ = 9 |
| ↓ = 9 |
| ↓ = 7 |
| ↑ = 7 |
| ↑ = 9 |
| ↓ = 8 |
| ~ |
| ↑ = 9 |
| ↑ = 8 |
| ↑ = 9 |
| ↑ = 7 |
| ↓ = 9 |
| ~ |
| ↑ = 7 |
| ↓ = 9 |
| ↑ = 8 |
| ~ |
| ↓ = 6 |
| ↑ = 9 |
| ~ |
| ~ |
| ↑ = 9 |
| ↓ = 7 |
| ↑ = 9 |
| ↑ = 6 |
| ~ |
| ↓ = 6 |
| ~ |
| ↑ = 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balis, P.; Berenyiova, A.; Misak, A.; Grman, M.; Rostakova, Z.; Waczulikova, I.; Cacanyiova, S.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Ondrias, K. The Phthalic Selenoanhydride Decreases Rat Blood Pressure and Tension of Isolated Mesenteric, Femoral and Renal Arteries. Molecules 2023, 28, 4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124826
Balis P, Berenyiova A, Misak A, Grman M, Rostakova Z, Waczulikova I, Cacanyiova S, Domínguez-Álvarez E, Ondrias K. The Phthalic Selenoanhydride Decreases Rat Blood Pressure and Tension of Isolated Mesenteric, Femoral and Renal Arteries. Molecules. 2023; 28(12):4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124826
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalis, Peter, Andrea Berenyiova, Anton Misak, Marian Grman, Zuzana Rostakova, Iveta Waczulikova, Sona Cacanyiova, Enrique Domínguez-Álvarez, and Karol Ondrias. 2023. "The Phthalic Selenoanhydride Decreases Rat Blood Pressure and Tension of Isolated Mesenteric, Femoral and Renal Arteries" Molecules 28, no. 12: 4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124826
APA StyleBalis, P., Berenyiova, A., Misak, A., Grman, M., Rostakova, Z., Waczulikova, I., Cacanyiova, S., Domínguez-Álvarez, E., & Ondrias, K. (2023). The Phthalic Selenoanhydride Decreases Rat Blood Pressure and Tension of Isolated Mesenteric, Femoral and Renal Arteries. Molecules, 28(12), 4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124826