Exploring the Aroma Fingerprint of Various Chinese Pear Cultivars through Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Volatile Compounds Using HS-SPME and GC×GC-TOFMS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
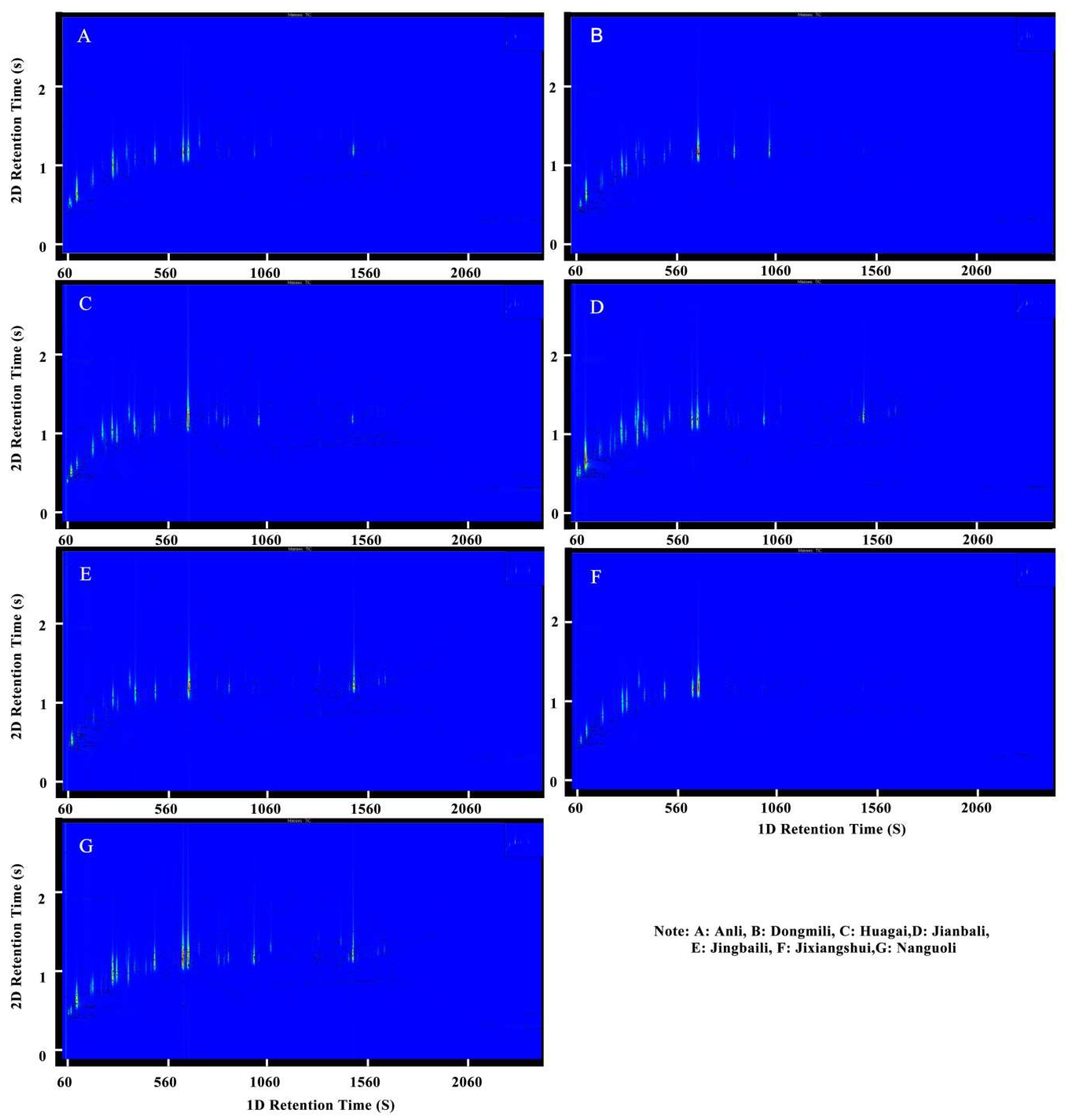
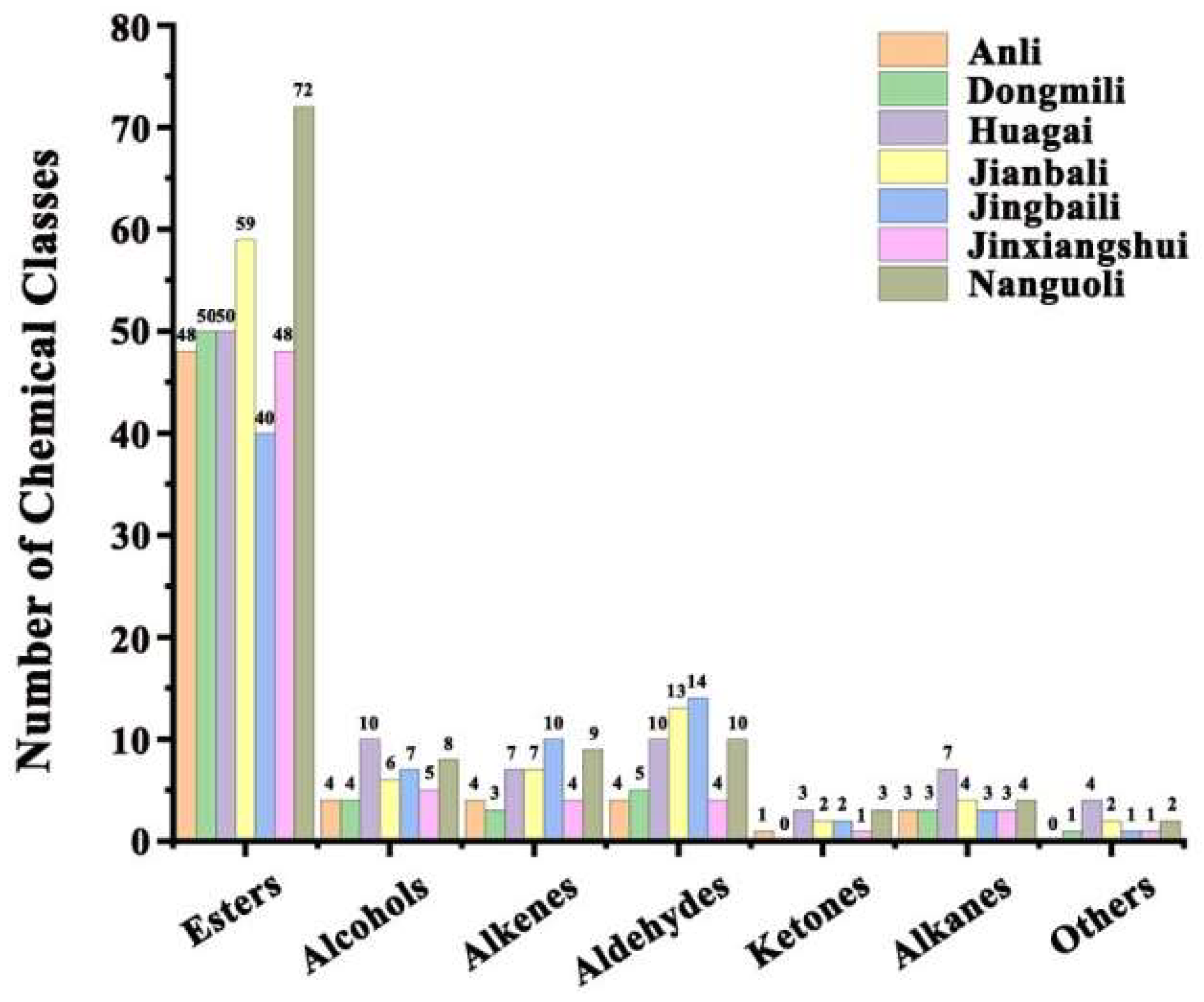
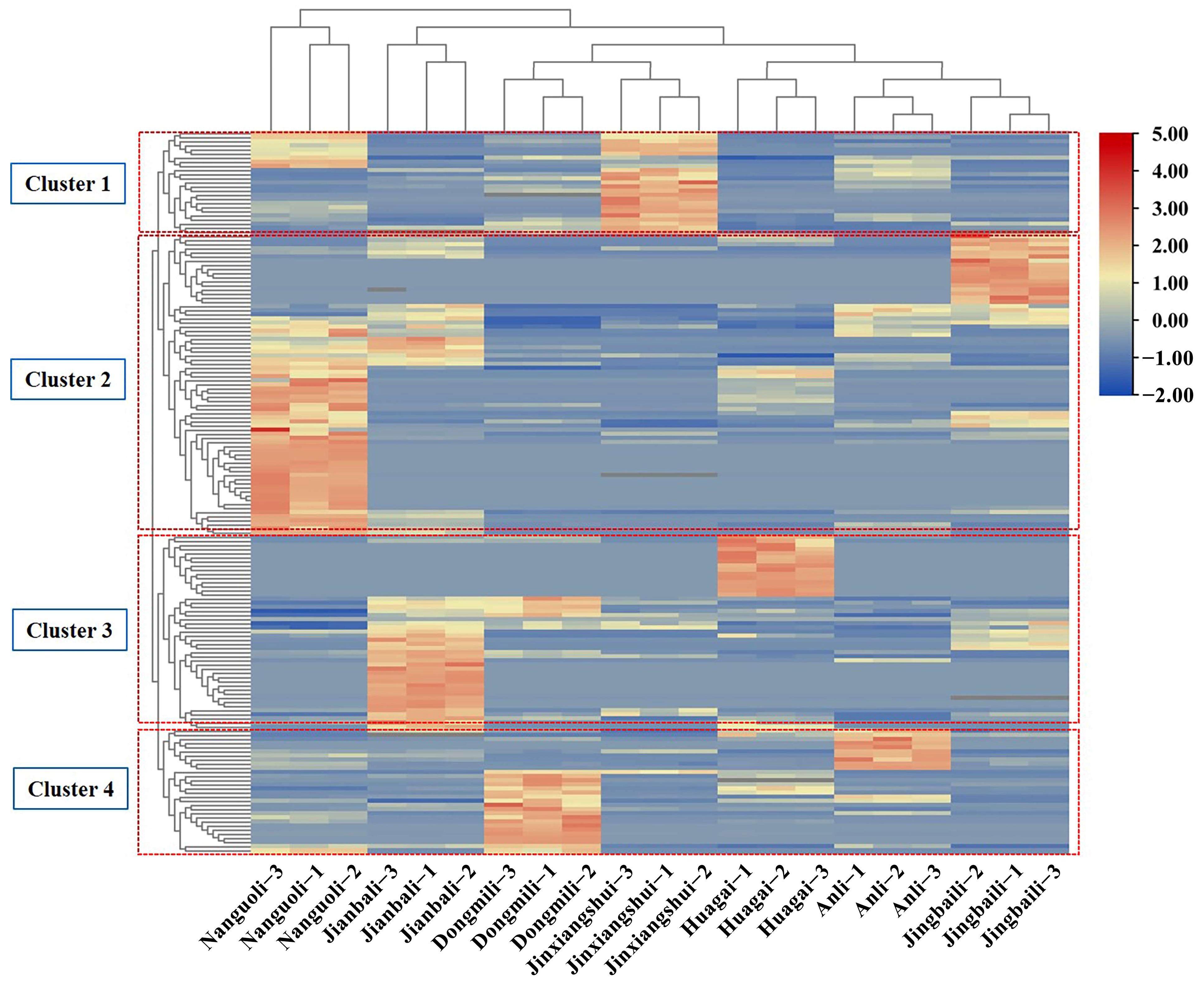
2.1. Analysis of Aroma Composition in Different Pear Fruits
2.2. Principal Component Analysis
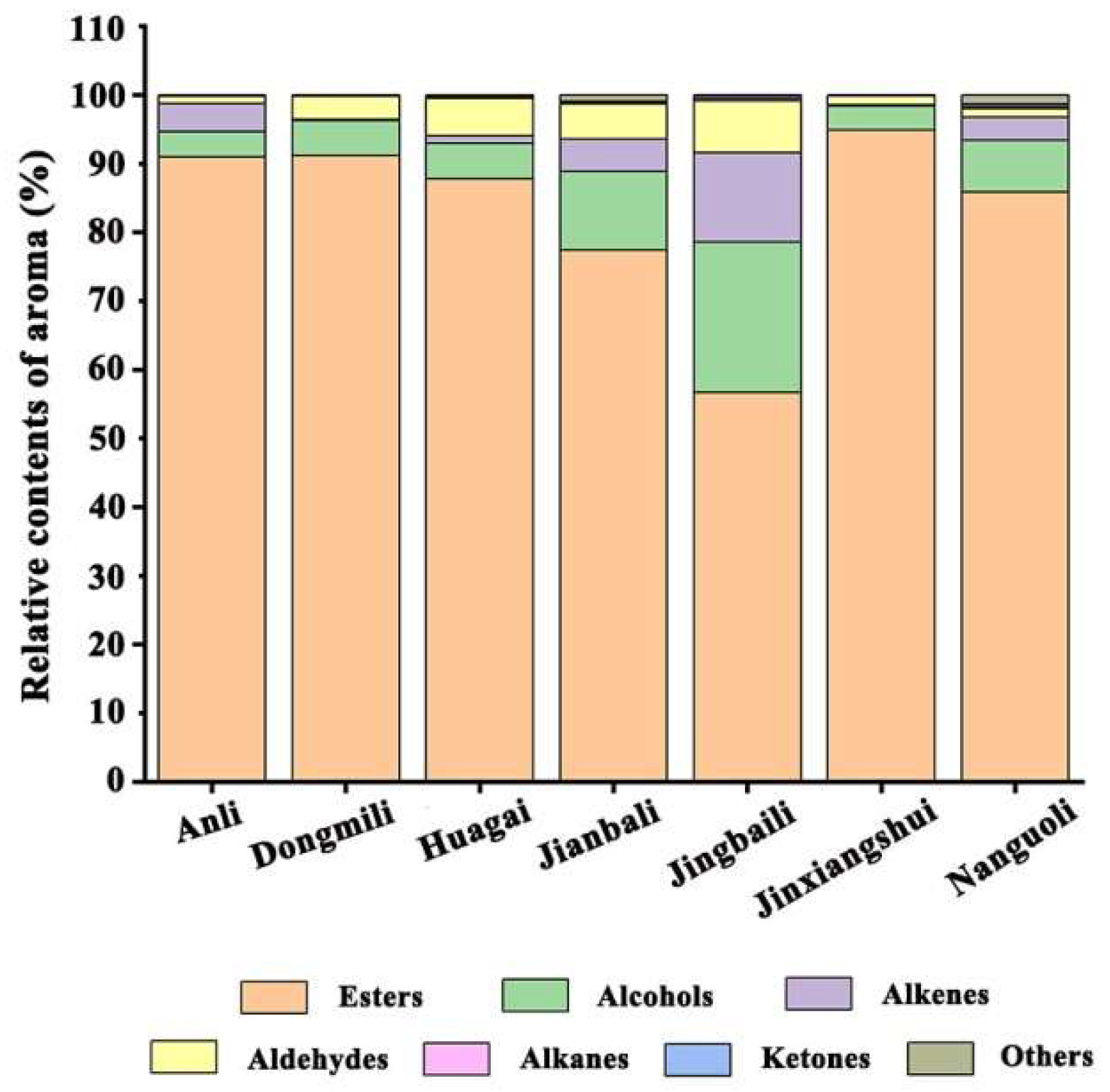
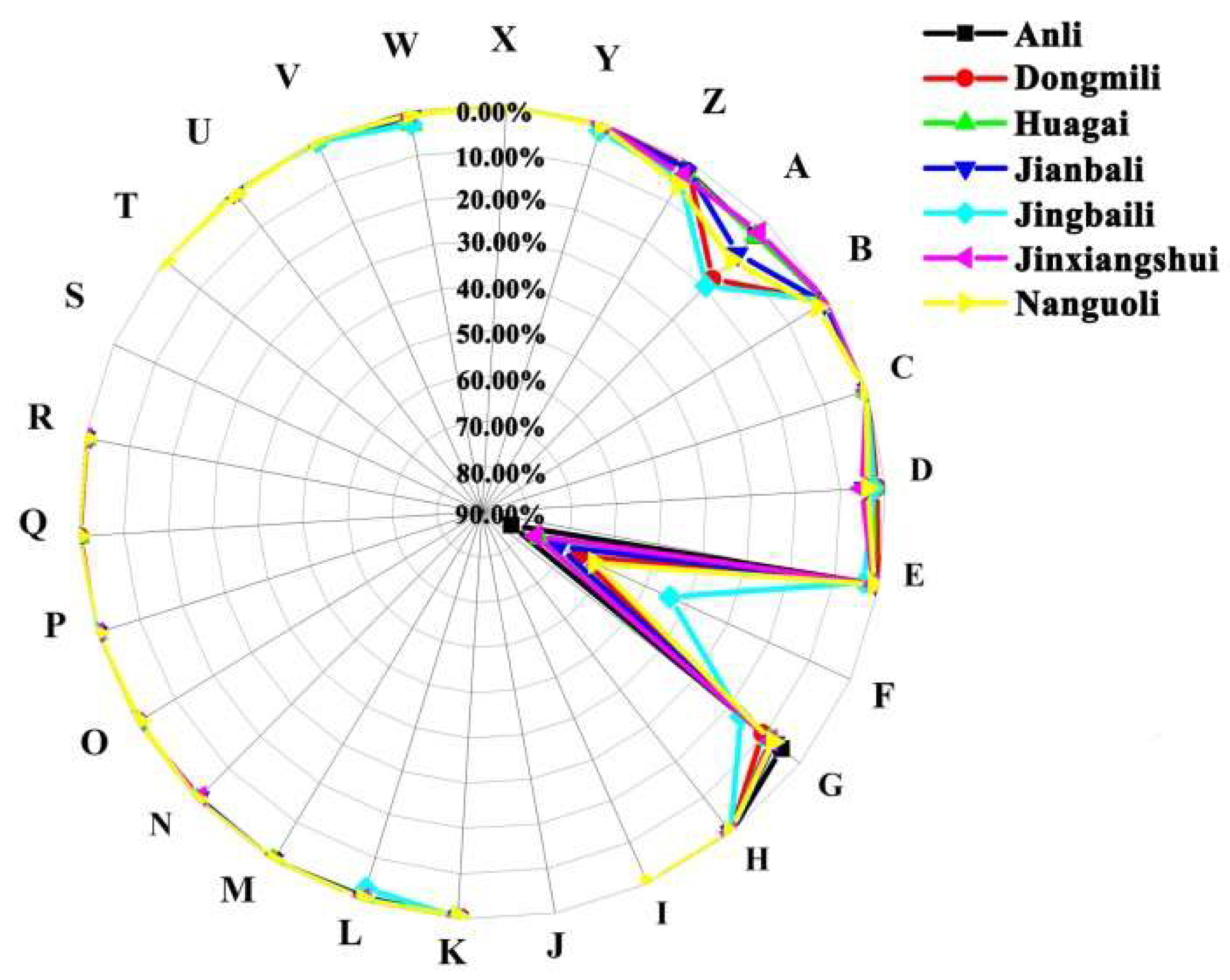
2.3. Analysis of Aroma Characteristic Percentage Distributions
2.4. Main Biosynthesis Pathway of Aroma Components
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Preparation of Standard Solution
4.2.2. GC×GC-TOFMS Conditions
4.2.3. Volatile Extraction
4.2.4. Analysis of Aroma Characteristic Distributions
4.2.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, M.Y.; Wu, C.H.; Wang, Q.; Yan, X.K.; Liu, M.H.; Zhang, M.J. Analysis of photosynthetic pigments and mineral elements content of leaves of wild Pyrus ussuriensis Maxin. with different color grown in saline alkali soil. Nonwood For. Res. 2021, 39, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, D.; Guo, J.; Yu, H.M.; Yan, J.; Yang, S.X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, J.J.; Cong, J.; He, S.L.; et al. Antioxidant phenolic compounds isolated from wild Pyrus ussuriensis Maxim. Fruit peels and leaves. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.H.; Jia, X.H.; Tong, W.; Wang, Z.H.; Yang, X.L. Evaluation of frozen fruit quality of different pear cultivars. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2017, 50, 3400–3412. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Zhang, Q.; Du, G.D.; Wang, X.Q.; Liu, Z. Present situation and countermeasures of pear industry development in Liaoning Province. North. Fruits 2018, 4, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.L. Physiological Differences and Regulation Mechanism of Different Pyrus ussuriensis Maxim Varieties during Softening. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, J.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Lee, H.S. Acaricidal activities of materials derived from Pyrus ussuriensis fruits against stored food mites. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.H.; Du, B.; Peng, F.; Wang, T.K.; Yang, Y.D. Optimization of triterpenoids extraction from Anli pears (Pyrus ussuriensis Maxim) by pressurized liquid extraction. Qual. Assur. Ssf. Crop 2016, 8, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, T.T.; Zhou, B.; Gao, W.Y.; Cao, J.G.; Huang, L.Q. Chemical composition and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of peels and flesh from 10 different pear varieties (Pyrus spp.). Food Chem. 2014, 152, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Q.; Hao, W.J.; Tang, X.Q.; Wang, K.C.; Zhang, S.L. Analysis of Characteristic Polyphenols and Triterpenic Acids in Ripe Pears of 36 Cultivars by UPLC-MS/MS. Food Sci. 2020, 41, 206–214. [Google Scholar]
- Goliáš, J.; Balík, J.; Létal, J. Identification of volatiles formed in Asian pear cultivars subjected to short-term storage using multinomial logistic regression. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 97, 103793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, B. Biogenesis of aroma compounds: Flavour formation in fruits and vegetables. In Flavor Development, Analysis and Perception in Food and Beverages; Parker, J.K., Elmore, J.S., Methven, L., Eds.; Woodhead Press: Sawston Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 127–149. [Google Scholar]
- Senoussi, A.; Rapisarda, T.; Schadt, I.; Chenchouni, H.; Saoudi, Z.; Senoussi, S.; Zitoun, O.A.; Zidoune, M.N.; Carpino, S. Formation and dynamics of aroma compounds during manufacturing ripening of Bouhezza goat cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 129, 105349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.H.; Tao, S.T.; Cao, Y.F.; Wu, J.Y.; Zhang, H.P.; Huang, W.J.; Zhang, S.L. Evaluation of the volatile profile of 33 Pyrus ussuriensis cultivars by HS–SPME with GC-MS. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 2367–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndikuryayo, C.; Ndayiragije, A.; Kilasi, N.; Kusolwa, P. Breeding for Rice Aroma and Drought Tolerance: A Review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Dokalahy, E.U.; Eissa, T.F.; Kamal, I.M.; Zayed, A. Chemometrics-Based Aroma Discrimination of 14 Egyptian Mango Fruits of Different Cultivars and Origins, and Their Response to Probiotics Analyzed via SPME Coupled to GC-MS. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 2377–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Du, G.Q. Analysis and evaluation of fruit quality and aroma components of ‘Yali’ pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.) pollinated with eighteen pollinizers. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 294–302. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Y. Analysis on Volatile Aroma Constituent Characteristics of Pears with Different Cultivars. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zlatić, E.; Zadnik, V.; Fellman, J.; Demšar, L.; Hribar, J.; Čejić, Ž.; Vidrih, R. Comparative analysis of aroma compounds in ‘Bartlett’ pear in relation to harvest date, storage conditions, and shelf-life. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 117, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.W.; Tao, S.T.; Qin, G.H.; Wang, S.M.; Tao, J.H.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.Y.; Zhang, S.L. Transcriptome profiling reveals the candidate genes associated with aroma metabolites and emission of pear (Pyrus ussuriensis cv.). Sci. Hortic. 2016, 206, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.P. Effects of Refrigeration and 1-Methylcyclopropene on the Metabolic of Volatile Aroma in Nanguo Pear and Control. Ph.D. Thesis, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Han, J.C.; Yang, S.M.; Wang, Y. GC-MS Analysis on aroma components of Huagaili Pear fruits. J. Hebei Agric. Sci. 2020, 24, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Farrapeira, R.O.; Andrade, Y.B.; Schena, T.; Schneider, J.K.; Muhlen, C.V.; Bjerk, T.R.; Krause, L.C.; Caramão, E.B. Characterization by Fast–GC×GC-TOFMS of the Acidic/Basic Neutral Fractions of Bio-Oils from Fast Pyrolysis of Green Coconut Fibers. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 61, 9567–9574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, T.; Yang, F.; Cui, X.Y.; Zou, T.T.; Song, H.L.; Liu, Y. Characterization of key aroma-active compounds in Hanyuan Zanthoxylum bungeanum by GC-O-MS and switchable GC×GC-O-MS. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welke, J.E.; Zanus, M.; Lazzarotto, M.; Pulgati, F.H.; Zini, C.A. Main differences between volatiles of sparkling and base wines accessed through comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometric detection and chemometric tools. Food Chem. 2014, 164, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, A.T.; Polyakova, O.V.; Mazur, D.M.; Artaev, V.B.; Canet, I.; Lallement, A.; Vaitilingom, M.; Deguillaume, L.; Delort, A.M. Detection of semivolatile compounds in cloud waters by GC×GC-TOF-MS. Evidence of phenols and phthalates as priority pollutants. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Lv, H.P.; Shao, C.Y.; Kang, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Dai, W.D.; Tan, J.F.; Peng, Q.H.; Lin, Z. Identification of key odorants responsible for chestnut-like aroma quality of green teas. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, H.D.; Mao, J.S.; Guo, C.Y.; Ding, R.Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, L.P.; Chen, Z.L.; Yang, G.S. Analysis of volatile compounds in pears by HS-SPME-GC×GC-TOFMS. Molecules 2019, 24, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.D. Study on Characteristic Aroma Compounds during the Process of Fu Brick Tea. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, X.Q.; Liang, Y.R.; Lin, Z. Multivariate statistical analysis of volatiles compounds in green teas from different harvesting seasons. Food Sci. 2018, 39, 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.N.; Jia, X.H.; Du, Y.M.; Wang, W.H.; Shu, Q. Comparation of fruit quality and aroma components among three red-skinned sand pear varieties. Food Sci. 2022, 39, 366–375. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.P.; Zheng, P.C.; Gong, Z.M.; Wang, S.P.; Teng, J.; Gao, S.W.; Wang, X.P.; Ye, F.; Zheng, L. Analysis of aroma components in Qingzhuan Dark Tea. Food Sci. 2017, 38, 164–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, Z.M.; Wang, J.T.; Guo, X. Comparative aroma components of fruits of four main Citrus varieties. Food Sci. 2017, 38, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.T.; Shi, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, W.J.; Yan, H.; Shao, C.Y.; Wang, M.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Q.H.; Chen, Y.Q.; et al. Insights into crucial odourants dominating the characteristic flavour of citrus-white teas prepared from citrus reticulata Blanco ‘Chachiensis’ and Camellia sinensis ‘Fudingdabai’. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 132048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.P.; Li, C.L.; Wang, H.R.; Zhang, S.W.; Yu, L.G.; Guo, C.X. Analysis of aroma compounds in Red Fragrant pear by headspace solid phase microextraction and gas chromatography–olfactometry–mass spectrometry. Food Res. Dev. 2020, 41, 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Campeloa, P.H.; Alves Filhob, E.G.; Silvac, L.M.A.; Britoc, E.S.; Rodriguesb, S.; Fernandesd, F.A.N. Modulation of aroma and flavor using dielectric barrier discharge plasma technology in a juice rich in terpenes and sesquiterpenes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 130, 109644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Study on Aroma Characterization of Mango Fruit. Master’s Thesis, Guangxi University, Nanning, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzolo, A.; Cambiaghi, P.; Grassi, M.; Zerbini, P.E. Influence of 1-methylcyclopropene and storage atmosphere on changes in volatile compounds and fruit quality of conference pears. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9781–9789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, W.; Davidovich-Rikanati, R.; Lewinsohn, E. Biosynthesis of plant-derived flavor compounds. Plant J. 2008, 54, 712–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeoka, G.; Buttery, R.G.; Flath, R.A.; Teranishi, R.; Wheeler, E.L.; Wieczorek, R.L.; Guentertet, M. Volatile constituents of pineapple (Ananas Comosus [L.] Merr.). In Flavor Chemistry Trends and Development; Teranishi, R., Buttery, R.G., Shahidi, F., Eds.; U.S. ACS Symposium Series Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 223–237. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, S.; Yan, S.J.; Ma, Y.K.; Hu, X.S. Analysis of aroma components of Fengshui, Dangshan and Nanguo pear by SPME/GC/MS. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2005, 32, 301–303. [Google Scholar]
- Hayaloglu, A.A.; Demir, N. Phenolic compounds, volatiles, and sensory characteristics of twelve sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars grown in Turkey. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiti, C.; Pandolfi, C.; Caparrotta, S.; Dei, M.; Giordani, E.; Mancuso, S.; Nencetti, V. Fruit aroma and sensorial characteristics of traditional and innovative Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.) cultivars grown in Italy. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 2655–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, F.; Noguera-Artiaga, L.; Burló, F.; Wojdyło, A.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Legua, P. Physico-chemical, nutritional, and volatile composition and sensory profile of Spanish jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) fruits. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2682–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.; Suh, J.H.; Chambers, A.H.; Crane, J.; Wang, Y. Relationship between Sensory Attributes and Chemical Composition of Different Mango Cultivars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5177–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.L.; Du, X.; Wallace, R.W. Investigating sensory properties of seven watermelon varieties and factors impacting refreshing perception using quantitative descriptive analysis. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, T.E.; Barker, A.; Pearson, W.; Barter, S.R.; de Barros Lopes, M.A.; Darriet, P.; Herderich, M.J.; Francis, I.L. Volatile Compounds Related to ‘Stone Fruit’ Aroma Attributes in Viognier and Chardonnay Wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2838–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
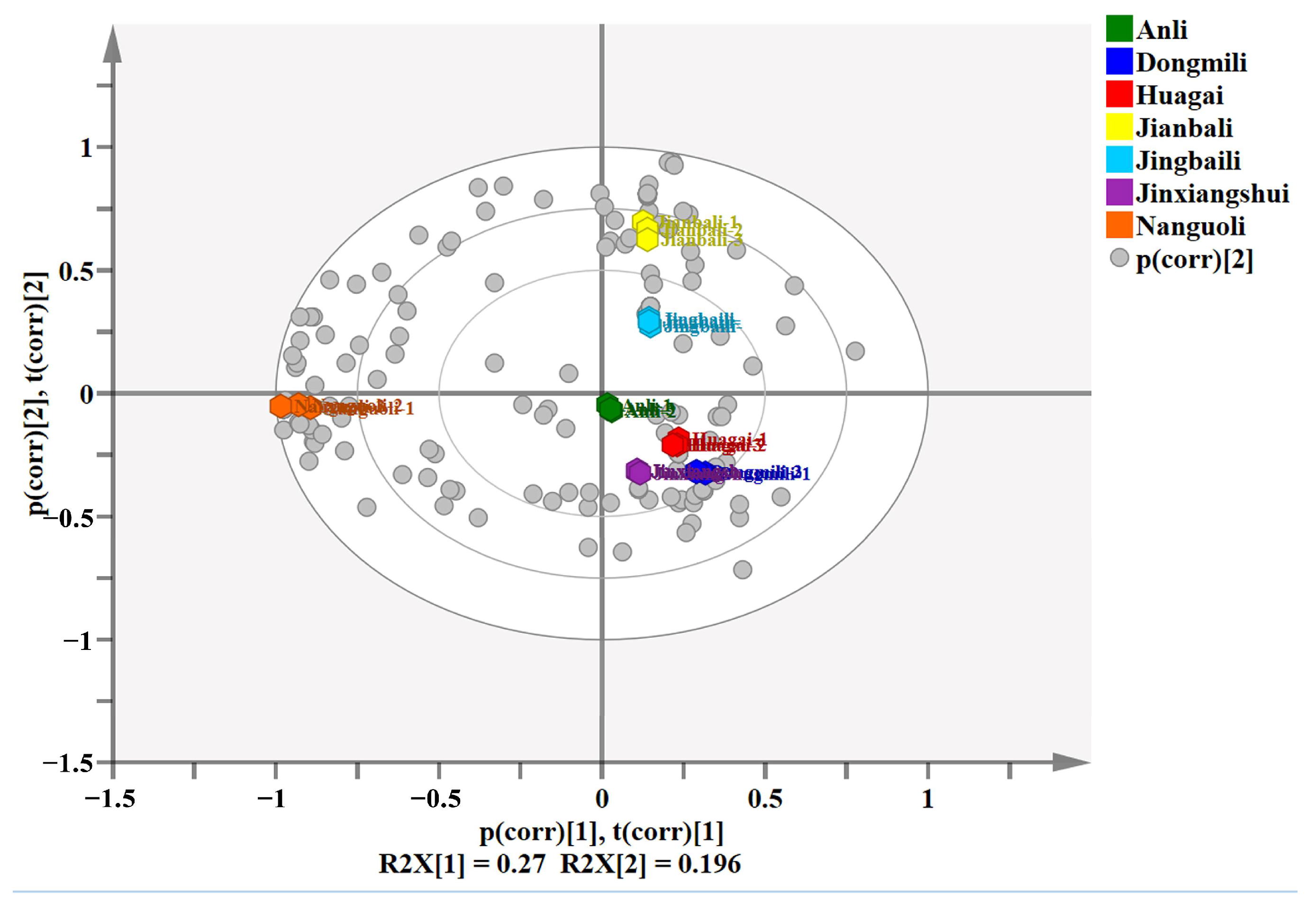
| Component | Proportion (%) | Cumulative (%) | Eigenvalue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 27.0 | 27.0 | 5.67 |
| 2 | 19.6 | 46.6 | 4.11 |
| 3 | 15.5 | 62.1 | 3.25 |
| 4 | 14.0 | 76.1 | 2.94 |
| 5 | 10.9 | 87.0 | 2.3 |
| 6 | 9.9 | 97.0 | 2.1 |
| Cultivars | Producing Region | Sampling Time |
|---|---|---|
| Anli | Huludaoshi city of Liaoning Province | 27 September 2020 |
| Dongmili | Huludaoshi city of Liaoning Province | 27 September 2020 |
| Huagai | Anshanshi city of Liaoning Province | 7 October 2020 |
| Jianbali | Huludaoshi city of Liaoning Province | 15 September 2020 |
| Jingbaili | Huludaoshi city of Liaoning Province | 24 August 2020 |
| Jinxiangshui | Huludaoshi city of Liaoning Province | 12 September 2020 |
| Nanguoli | Anshanshi city of Liaoning Province | 5 October 2020 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Yan, M.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Mao, J.; Qin, H.; Zhu, C.; Du, H.; Abd El-Aty, A.M. Exploring the Aroma Fingerprint of Various Chinese Pear Cultivars through Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Volatile Compounds Using HS-SPME and GC×GC-TOFMS. Molecules 2023, 28, 4794. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124794
Zhang W, Yan M, Zheng X, Chen Z, Li H, Mao J, Qin H, Zhu C, Du H, Abd El-Aty AM. Exploring the Aroma Fingerprint of Various Chinese Pear Cultivars through Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Volatile Compounds Using HS-SPME and GC×GC-TOFMS. Molecules. 2023; 28(12):4794. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124794
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenjun, Mengmeng Yan, Xinxin Zheng, Zilei Chen, Huidong Li, Jiangsheng Mao, Hongwei Qin, Chao Zhu, Hongxia Du, and A. M. Abd El-Aty. 2023. "Exploring the Aroma Fingerprint of Various Chinese Pear Cultivars through Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Volatile Compounds Using HS-SPME and GC×GC-TOFMS" Molecules 28, no. 12: 4794. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124794
APA StyleZhang, W., Yan, M., Zheng, X., Chen, Z., Li, H., Mao, J., Qin, H., Zhu, C., Du, H., & Abd El-Aty, A. M. (2023). Exploring the Aroma Fingerprint of Various Chinese Pear Cultivars through Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Volatile Compounds Using HS-SPME and GC×GC-TOFMS. Molecules, 28(12), 4794. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124794