Amphotericin B-Silver Hybrid Nanoparticles Help to Unveil the Mechanism of Biological Activity of the Antibiotic: Disintegration of Cell Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
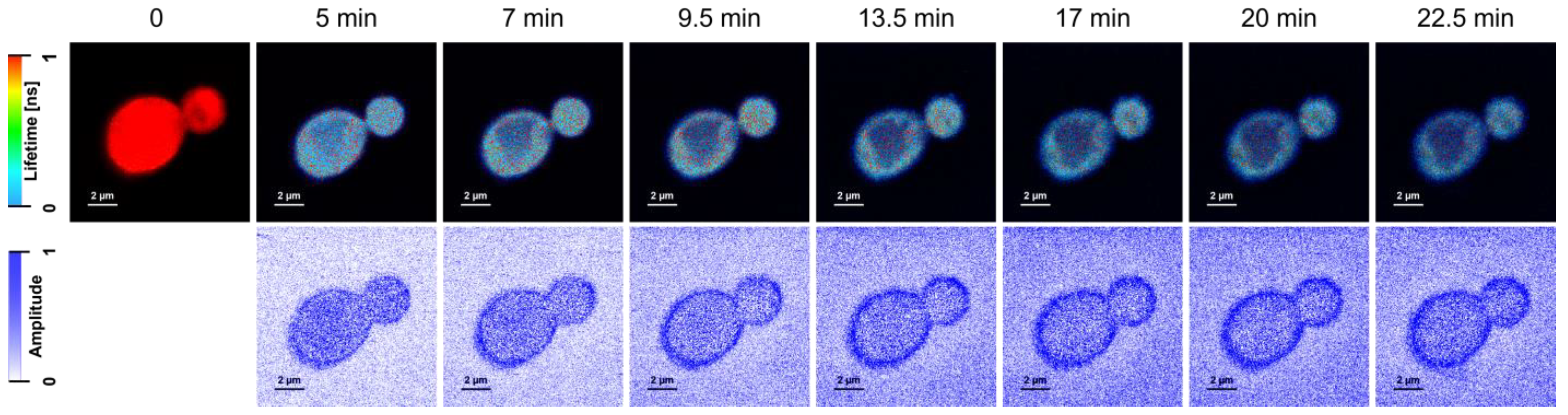
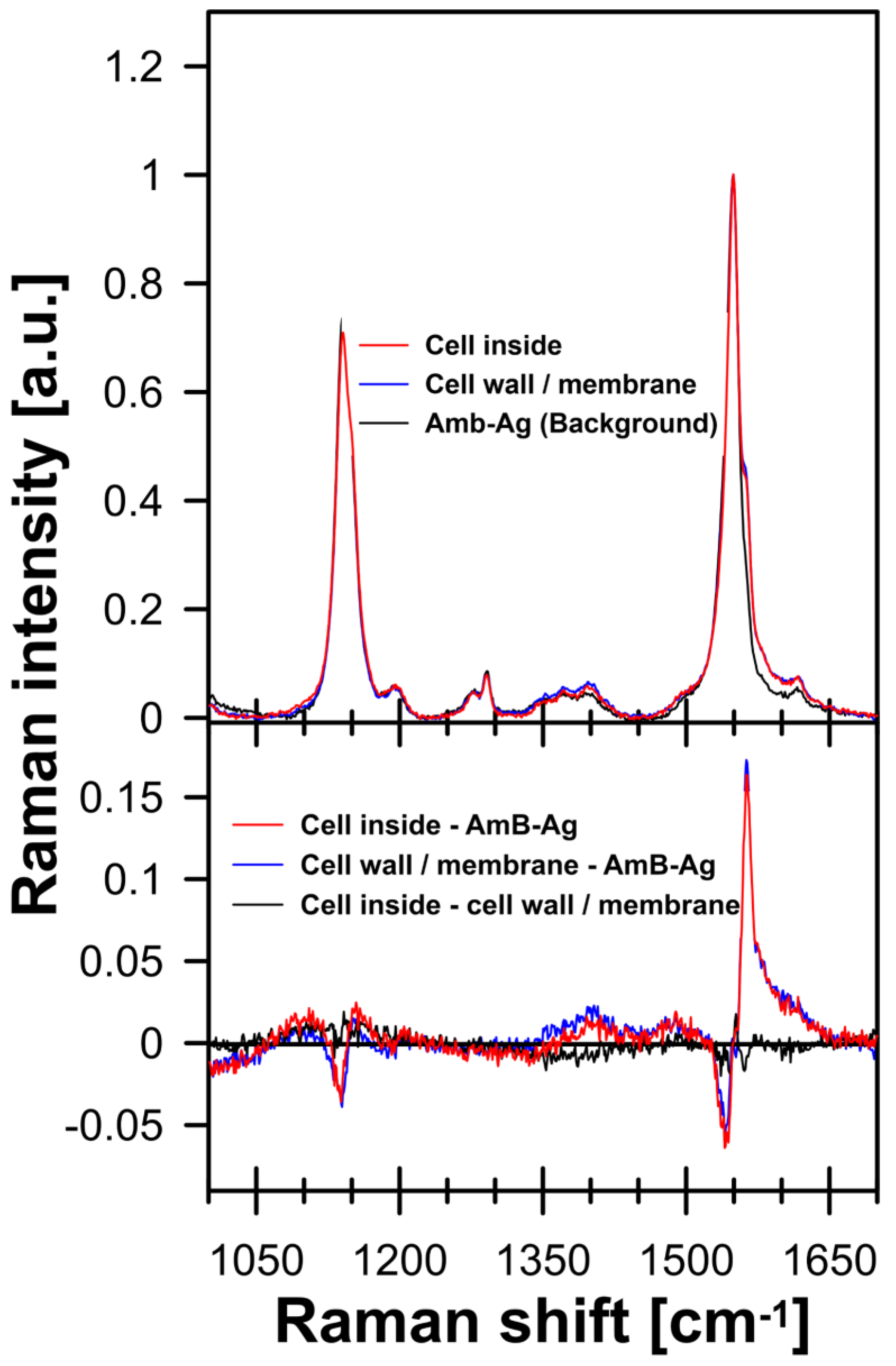
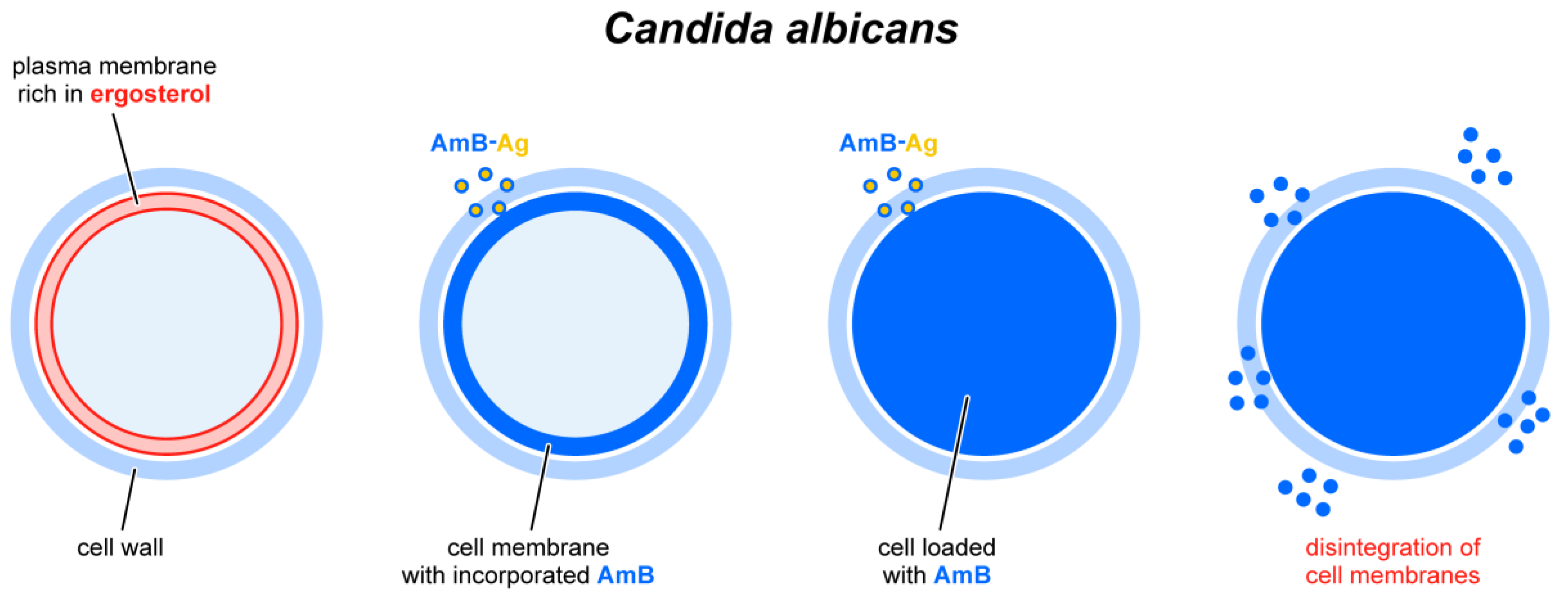
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Microorganism Cultivation
3.3. Viability Assay
3.4. Nanoparticles Synthesis
3.5. Giant Unilamellar Vesicles (GUV) Formation
3.6. Raman Spectroscopy and Imaging
3.7. Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Oura, M.; Sternberg, T.H.; Wright, E.T. A New Antifungal Antibiotic, Amphotericin B. Antibiot. Annu. 1955, 3, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavassin, F.B.; Baú-Carneiro, J.L.; Vilas-Boas, R.R.; Queiroz-Telles, F. Sixty Years of Amphotericin B: An Overview of the Main Antifungal Agent Used to Treat Invasive Fungal Infections. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 115–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carolus, H.; Pierson, S.; Lagrou, K.; Van Dijck, P. Amphotericin B and Other Polyenes—Discovery, Clinical Use, Mode of Action and Drug Resistance. JoF 2020, 6, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska, J.; Wieczór, M.; Chodnicki, P.; Grela, E.; Luchowski, R.; Nierzwicki, Ł.; Bączek, T.; Gruszecki, W.I.; Czub, J. Self-Assembly, Stability and Conductance of Amphotericin B Channels: Bridging the Gap between Structure and Function. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 3686–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umegawa, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Dixit, M.; Funahashi, K.; Seo, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Matsuoka, S.; Tsuchikawa, H.; Hanashima, S.; et al. Amphotericin B Assembles into Seven-Molecule Ion Channels: An NMR and Molecular Dynamics Study. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kruijff, B.; Demel, R.A. Polyene Antibiotic-Sterol Interactions in Membranes of Acholeplasma Laidlawii Cells and Lecithin Liposomes. III. Molecular Structure of the Polyene Antibiotic-Cholesterol Complexes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 1974, 339, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermishkin, L.N.; Kasumov, K.M.; Potzeluyev, V.M. Single Ionic Channels Induced in Lipid Bilayers by Polyene Antibiotics Amphotericin B and Nystatine. Nature 1976, 262, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, T.M.; Clay, M.C.; Cioffi, A.G.; Diaz, K.A.; Hisao, G.S.; Tuttle, M.D.; Nieuwkoop, A.J.; Comellas, G.; Maryum, N.; Wang, S.; et al. Amphotericin Forms an Extramembranous and Fungicidal Sterol Sponge. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuddihy, G.; Wasan, E.; Di, Y.; Wasan, K. The Development of Oral Amphotericin B to Treat Systemic Fungal and Parasitic Infections: Has the Myth Been Finally Realized? Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutaj, K.; Szlazak, R.; Szalapata, K.; Starzyk, J.; Luchowski, R.; Grudzinski, W.; Osinska-Jaroszuk, M.; Jarosz-Wilkolazka, A.; Szuster-Ciesielska, A.; Gruszecki, W.I. Amphotericin B-Silver Hybrid Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties and Antifungal Activity. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, A.; Siddiqui, R.; Shah, M.; Khan, N. Gold Nanoparticles Conjugation Enhances Antiacanthamoebic Properties of Nystatin, Fluconazole and Amphotericin B. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grela, E.; Stączek, S.; Nowak, M.; Pawlikowska-Pawlęga, B.; Zdybicka-Barabas, A.; Janik, S.; Cytryńska, M.; Grudzinski, W.; Gruszecki, W.I.; Luchowski, R. Enhanced Antifungal Activity of Amphotericin B Bound to Albumin: A “Trojan Horse” Effect of the Protein. J. Phys. Chem. B 2023, 127, 3632–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grela, E.; Wieczór, M.; Luchowski, R.; Zielinska, J.; Barzycka, A.; Grudzinski, W.; Nowak, K.; Tarkowski, P.; Czub, J.; Gruszecki, W.I. Mechanism of Binding of Antifungal Antibiotic Amphotericin B to Lipid Membranes: An Insight from Combined Single-Membrane Imaging, Microspectroscopy, and Molecular Dynamics. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4202–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grela, E.; Zdybicka-Barabas, A.; Pawlikowska-Pawlega, B.; Cytrynska, M.; Wlodarczyk, M.; Grudzinski, W.; Luchowski, R.; Gruszecki, W.I. Modes of the Antibiotic Activity of Amphotericin B against Candida Albicans. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, A.; Wieczor, M.; Zielinska, J.; Baginski, M.; Czub, J. Membrane Sterols Modulate the Binding Mode of Amphotericin B without Affecting Its Affinity for a Lipid Bilayer. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3452–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starzyk, J.; Gruszecki, M.; Tutaj, K.; Luchowski, R.; Szlazak, R.; Wasko, P.; Grudzinski, W.; Czub, J.; Gruszecki, W.I. Self-Association of Amphotericin B: Spontaneous Formation of Molecular Structures Responsible for the Toxic Side Effects of the Antibiotic. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 13821–13832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, I.; Barwicz, J.; Tancrède, P. The Structuring Effects of Amphotericin B on Pure and Ergosterol- or Cholesterol-Containing Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine Bilayers: A Differential Scanning Calorimetry Study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 1998, 1373, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hereć, M.; Islamov, A.; Kuklin, A.; Gagoś, M.; Gruszecki, W.I. Effect of Antibiotic Amphotericin B on Structural and Dynamic Properties of Lipid Membranes Formed with Egg Yolk Phosphatidylcholine. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2007, 147, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowa-Jasiłek, A.; Zdybicka-Barabas, A.; Stączek, S.; Wydrych, J.; Skrzypiec, K.; Mak, P.; Deryło, K.; Tchórzewski, M.; Cytryńska, M. Galleria Mellonella Lysozyme Induces Apoptotic Changes in Candida Albicans Cells. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 193, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grudzinski, W.; Sagan, J.; Welc, R.; Luchowski, R.; Gruszecki, W.I. Molecular Organization, Localization and Orientation of Antifungal Antibiotic Amphotericin B in a Single Lipid Bilayer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janik, S.; Grela, E.; Stączek, S.; Zdybicka-Barabas, A.; Luchowski, R.; Gruszecki, W.I.; Grudzinski, W. Amphotericin B-Silver Hybrid Nanoparticles Help to Unveil the Mechanism of Biological Activity of the Antibiotic: Disintegration of Cell Membranes. Molecules 2023, 28, 4687. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124687
Janik S, Grela E, Stączek S, Zdybicka-Barabas A, Luchowski R, Gruszecki WI, Grudzinski W. Amphotericin B-Silver Hybrid Nanoparticles Help to Unveil the Mechanism of Biological Activity of the Antibiotic: Disintegration of Cell Membranes. Molecules. 2023; 28(12):4687. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124687
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanik, Sebastian, Ewa Grela, Sylwia Stączek, Agnieszka Zdybicka-Barabas, Rafal Luchowski, Wieslaw I. Gruszecki, and Wojciech Grudzinski. 2023. "Amphotericin B-Silver Hybrid Nanoparticles Help to Unveil the Mechanism of Biological Activity of the Antibiotic: Disintegration of Cell Membranes" Molecules 28, no. 12: 4687. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124687
APA StyleJanik, S., Grela, E., Stączek, S., Zdybicka-Barabas, A., Luchowski, R., Gruszecki, W. I., & Grudzinski, W. (2023). Amphotericin B-Silver Hybrid Nanoparticles Help to Unveil the Mechanism of Biological Activity of the Antibiotic: Disintegration of Cell Membranes. Molecules, 28(12), 4687. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124687







