Abstract
Operation lifetime, as an important parameter, determines the performance of phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). Unveiling the intrinsic degradation mechanism of emission material is crucial for improving the operation’s lifetime. In this article, the photo-stabilities of tetradentate transition metal complexes, the popular phosphorescent materials, are explored by means of density functional theory (DFT) and time-dependent (TD)-DFT, aiming to illustrate the geometric signatures as important factors to control the photo-stabilities. Results indicate that for the tetradentate Ni(II), Pd(II), and Pt(II) complexes, the coordinate bonds of the Pt(II) complex exhibit stronger strength. It seems that the strengths of coordinate bonds are closely related to the atomic number of the metal center in the same group, which could be attributed to the various electron configurations. The effect of intramolecular and intermolecular interactions on ligand dissociation is also explored here. The large intramolecular steric hindrance and strong π-π interaction between the Pd(II) complexes caused by aggregation could effectively raise the energy barriers of the dissociation reaction, leading to an unfeasible reaction pathway. Moreover, the aggregation of Pd(II) complex can change the photo-deactivation mechanism as compared to that of monomeric Pd(II) complex, which is favored for avoiding the TTA (triplet-triplet annihilation) process.
1. Introduction
Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes have attracted more and more attention because of their excellent virtues. Essentially, the strong spin-orbital coupling (SOC) effect can facilitate the effective intersystem crossing (ISC) process and mixture of singlet and triplet excited states, causing the forbidden T1→S0 transition to become acceptable. The unique property of excited state transformation can promote the application of Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes in many hot fields. For instance, Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes can be regarded as phosphorescent emitters in the field of OLEDs. Over the past decades, substantial progress has been made in the development of high-performance Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes as a result of extensive research within the academic and industrial communities, which has enabled phosphorescent OLEDs to become a main component in state-of-the-art displays as well as in next-generation solid-state lighting [1,2,3,4,5]. Secondly, as a consequence of their efficient intersystem crossing derived from metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT), Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes have been developed as popular candidates [6,7]. Recently, Wong and co-workers proposed that well-designed J-aggregates of organometallic complex molecules are an efficient strategy to realize NIR-II phosphorescence-based hypoxia bioimaging [8]. Thirdly, the Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes can be used as antitumor drugs, which can exhibit cell-killing effects. In terms of antiproliferative activity, it has been revealed that the newly synthesized Pd(II) complex had stronger cytotoxic activity in the two tested human tumor cell lines than the remaining complexes, which suggests its promising potential as an antitumor drug [9]. Zhu et al. have reported Pt(IV) complex as an antitumor prodrug, and it can be controllably activated with the help of red light [10].
These complexes act as important functional components in the phosphorescence-based hypoxia bioimaging, antitumor prodrug, and phosphorescent OLEDs; undoubtedly, the photo-stability is crucial because it determines the performance in practical applications. Herein, we take complex applied as a phosphorescent emitter in the field of OLEDs as an example to illustrate the role of photo-stability. During the OLED’s operation, generally, once it possesses a high brightness range, it would experience a drastic drop in efficiency, that is, efficiency roll-off in phosphorescent emitters, which originates from triplet-triplet annihilation (TTA) and triplet-polaron quenching (TPQ) [11,12]. It is demonstrated that the TTA or TPQ processes in the emissive layer (EML) are closely related to the device’s operational stability because the TTA or TPQ processes can result in the generation of hot (multiply excited) excitons or polarons. The hot (multiply excited) excitons or polarons could induce chemical bond dissociation of the guest or host molecule; subsequently, an expedited device degradation process will occur, especially under conditions of high-brightness operation [13,14]. Thus far, enormous efforts have been made to improve the device lifetime of phosphorescent OLEDs, and some promising strategies have been provided: (I) Developing rigid phosphorescent dopants can improve the stability needed to sustain the excited state. The studies explored by Li and co-workers exhibited that the rigidity of molecules can be effectively promoted by employing a tetradentate core, which should be further investigated to enhance emitter stability [1,15,16]. (II) Developing suitably stable host materials is another strategy for addressing the short lifetime of phosphorescent OLEDs. For example, electron-transporting host materials, including a bulky triphenylsilyl unit, are usually applied to enhance the device’s lifetime [17,18].
Apart from the above-mentioned strategies, Kim and co-workers reported recently that the photochemical stability of the high-lying metal-centered triplet state can be effectively enhanced by adding bulky 3,5-di-tert-butyl-phenyl into the N-heterocyclic carbene moiety in the Pt(II) complex [19]. More importantly, the bulky substituent could prevent undesirable host-guest interactions to some extent. Both the high-lying metal-centered triplet state and the prevention of undesirable host-guest interactions contribute to a longer device lifetime. Li et al. illustrated that a host-free Pd(II)-based OLED had excellent performance and an ultra-long operational half-life. In their study, they declare that phosphorescent molecular aggregates can be feasible emitter candidates for lighting and display applications [20]. Due to the distinctive d8-configuration and square planar geometry, Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes can have a greater tendency to form π-π-stacking interactions, which is a significant signature of geometry. This aggregation can lead to the obvious change of properties of Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes, for example, the red shift of emission wavelength, phosphorescent efficiency, and operational stability [21,22,23].
As shown in these studies, it indicates that the photo-stabilities or operation lifetimes are closely related to the geometric signatures and intramolecular and intermolecular interactions of tetradentate Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes. However, a systematical theoretical investigation of the stabilities of tetradentate Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes so far is insufficient because they exhibit more rigidities as compared to those of their bi- and tridentate counterparts. In addition, some significant and meaningful questions can be provided in the investigations of the stabilities of Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes: (1) What is the relationship between structural signatures, including coordinated forms, aggregation, and intramolecular interaction, and the photostability of tetradentate Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes? (2) What is the role of aggregation in the photostabilities of Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes? (3) Can the molecular aggregation of complexes tune the photo-deactivation mechanism? For the sake of completely answering these questions, some Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes shown in Scheme 1 are chosen, which can explore the role of “metal-coordinate effect”, “aggregation effect”, and “steric hindrance effect” in the photo-stability. Therein, Pd-1, Pt-2, and Pt-3 are reported in Li and Kim’s studies, respectively [19,20]. This study can provide significant and meaningful information for designing stable Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes used in the fields of phosphorescent probes, prodrugs, and OLEDs.
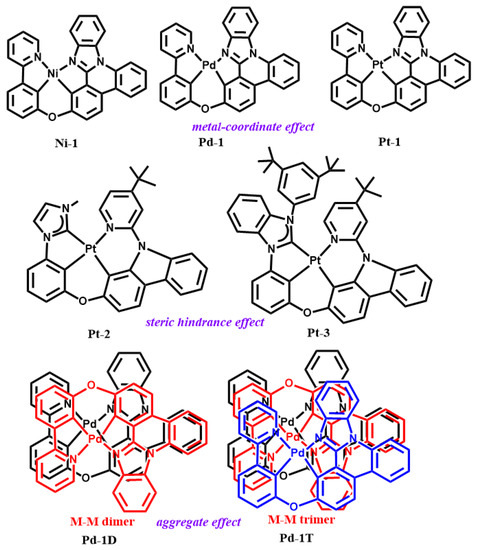
Scheme 1.
Chemical structures of studied Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes, along with the investigated topics.
2. Computational Details
In this paper, the geometry optimizations and vibrational frequency calculations of ground states (S0), lowest-lying triplet excited states (T1), cation states (+), anion states (−), and lowest-lying singlet excited states (S1) for all the tetradentate Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes are presented in the methodology of restricted, unrestricted, and time-dependent DFT (RDFT, UDFT, and TDDFT) with the B3LYP hybrid functional [24], respectively. As shown in the previous calculations of various Pt(II) complexes, the B3LYP hybrid functional can well reproduce the experimental results [25,26,27]. The D3BJ dispersion correction [28] was also taken into account. The mix basis sets, including the LANL2DZ basis set [29] and the 6-311G(d,p) basis set [30,31], were used to describe the heavy atoms Pt/Pd and the light atoms (C, H, O, and N). These calculations can be performed in the Gaussian 16 software [32].
In the application of optimized geometry to the T1 excited state, the spin-orbit coupling matrix elements were evaluated, which was realized by means of linear (single residue) response theories. The calculated protocol is the TDDFT with the B3LYP functional, as implemented in the Dalton program [33]. Moreover, the quadratic response theories in the methodology of TDDFT were used to obtain the radiative rate constants. During these computations, the LANL2DZ_ECP and 6-31G for Ir and light atoms are used to balance computational costs and accuracies. The other parameters, including topological parameters of the electron density and Laplacian bond orders, were calculated using Multiwfn_3.8 software [34]. The pictures of geometry, spin density, and interaction region indicator (IRI) analysis were drawn by combining the VMD [35] and Multiwfn_3.8 software.
The molecular dynamics (MD) simulation was performed using the GROMACS 2018.8 software [36] with periodic boundary conditions. A box containing one Pd-1 molecule and 30 mCBP molecules was built by the Packmol program [37]. The NPT ensemble was selected for a duration of 1 ns to obtain a reasonable density at 298 K and 1 bar pressure, followed by a 100 ns NVT production simulation under the same conditions. The GAFF force field [38] was adopted to describe the molecules. The Nosé-Hoover thermostat was used to control the temperature, and the pressure was controlled by the Parrinello-Rahman in an isotropic manner to reach equilibrium.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Influence of the “Metal-Coordinate Effect” on the Stability of Tetradentate Complexes
In order to explore the bonding nature between the Ni/Pd/Pt and the ligand, the electron localization function (ELF) was carried out here, and two-dimensional color-filled maps of S0 states are depicted in Figure 1. The two-dimensional color-filled maps of T1, S1, +, and − states for Ni-1, Pd-1, and Pt-1 are shown in Figures S1–S12. The two-dimensional color-filled ELF maps can be applied to show the coordination electron density localization. As shown in Figure 1, for all complexes, namely Ni-1, Pd-1, and Pt-1, the ELFs between Ni/Pd/Pt and N atoms are smaller than those between Ni/Pd/Pt and C atoms, indicating that the degree of electron localization between Ni/Pd/Pt-N bonds is smaller than that between Ni/Pd/Pt-C bonds. Moreover, from Ni-1 to Pd-1 and Pt-1, the ELF analysis can suggest that the electron between the Pt, N, and C atoms shows gradually localized features in the S0, T1, S1, +, and − states, respectively. In addition, for the Ni-1 complex, compared with the T1 and S1 states, it seems that the ELFs between Ni and ligand are smaller than those in the S0, +, and − states. On the basis of ELF analyses, one can speculate that, firstly, the electron-localized feature between N and Ni/Pd/Pt atoms could lead to decreased photo-stability of tetradentate Pt(II) complexes. Secondly, the coordinated bond could possess the tendency that, as the atomic number increases, the strengths should increase in the same group of periodic tables of the elements. Thirdly, for the Ni-1 complex, the smaller electron localization between N and Ni in T1 and S1 states as compared to those in S0, +, and − states imply that the unstable coordinated bonds may be causing the unsatisfactory photo-stability.
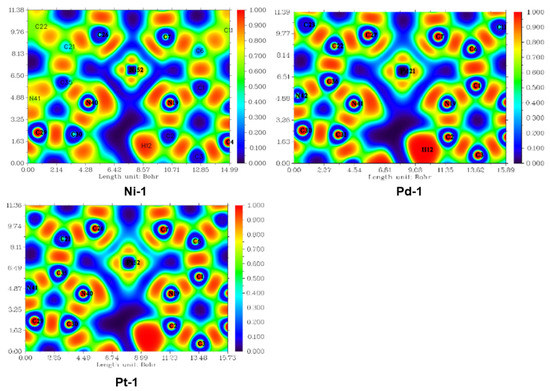
Figure 1.
Two-dimensional color-filled maps of ELF for Ni-1, Pd-1, and Pt-1 at the S0 states, respectively.
Next, a topological analysis was performed to investigate the properties of the coordinate bond further. The corresponding results were collected in Table S1. The parameters of the geometries are shown in Figure S13. The ρBCP of the Ni/Pd/Pt-N bonds are smaller than the others in the Ni-1 to Pd-1 and Pt-1, which indicates that the ρ(r) values between Ni/Pd/Pt and N are the smallest. Similarly, the ρ(r) values of all coordinate bonds tend to follow the trend in Ni-1 < Pd-1 < Pt-1 as a whole. In the case of Ni-1, the ρ(r) values of Ni-C and Ni-N bonds are also smaller than those in other states. These computed results are consistent with those of the ELF analyses. Here, all ∇2ρBCP were larger than 0, therefore indicating electron depletion at the BCP. Furthermore, the EBCP values are almost less than or close to 0, which is sufficient to contribute toward bond stabilization [39,40]. The Laplacian bond orders (LBO) of these coordinate bonds were calculated, and the results are summarized in Table 1. Obviously, the LBO of Ni/Pd/Pt-N bonds are considerably smaller than that of the other Ni/Pd/Pt-C bonds. For Ni-1, during the transition from S0 to T1 and S1, the Ni-N bonds would further weaken. These results demonstrated that the Ni/Pd/Pt-N bonds are the weakest bonds among all complexes, and the sequence of photostabilities may be as follows: Ni-1 < Pd-1 < Pt-1.

Table 1.
Laplacian bond orders of Ni/Pd/Pt-N and Ni/Pd/Pt-C bonds of Ni-1, Pd-1, and Pt-1.
Finally, the reaction pathways of the Ni/Pd/Pt-N bond breaking were computed to intuitively illustrate the photo-stabilities of Ni-1, Pd-1, and Pt-1, respectively. The corresponding vibration forms of TS are shown in Figures S14–S16. The calculated reaction steps are pictured in Figure 2. For the Ni-1 complex, the energy barriers are 27.06, 18.96, 16.61, 28.35, and 29.52 kcal/mol in the S0, T1, S1, +, and − states, respectively. Seen from these energy barriers, compared to the S0, +, and − states, the Ni-1 complex could exhibit weak photo-stability in the T1 and S1 states, which are the predominant states involved in the phosphorescent process. For the Pd-1 complex, the Pd-N bond breaking could need to overcome the energy barriers of 23.88, 22.71, 23.15, 27.80, and 24.11 kcal/mol, indicating that the stability of the Pd-1 complex, in comparison, is stronger than that of the Ni-1 complex. In the investigation of stability for Pt-1, larger energy barriers can be needed as compared to those of Ni-1 and Pd-1, and the corresponding values are 30.56, 31.76, 31.68, 35.06, and 30.56 in various states. Analyses of the energy barriers can indicate that, from a structural viewpoint, the stabilities of transition-metal complexes seem to be closely related to the atomic numbers of metal centers in the same group. Additionally, the calculated energy barriers agree with the conclusions of ELF, topological analysis, and Laplacian bond order.
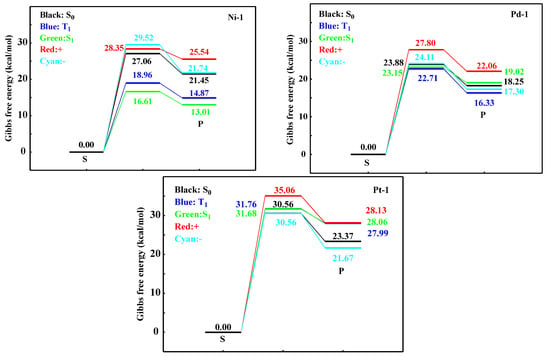
Figure 2.
The reaction pathways of the Ni/Pd/Pt-N bond breaking for Ni-1, Pd-1, and Pt-1 at different states, respectively.
3.2. The Effect of Steric Hindrance on the Stability of Tetradentate Metal Complexes
Here, the effect of intramolecular steric hindrance on the stability of tetradentate Pt(II) complexes, namely Pt-2 and Pt-3, is explored. In order to explore the bonding nature between the Pt and ligand, the ELF, topological analysis of the electron density, and Laplacian bond orders were first calculated, and the results of S0 states are shown in Figure 3, Figures S17–S24 and Tables S2–S3. The parameters of the geometries are shown in Figure S25. As polled in Figure 3, for Pt-2 and Pt-3, the ELFs between Pt, N, and C atoms are similar in different states, implying that the degree of electron localization between Pt-N and Pt-C atom bonds is comparable. Compared with the Pt-C bonds, a smaller electron localization between Pt and N can be found. The ρBCP and Laplacian bond orders of the Pt-C and N bonds are also applied to demonstrate the reliability of EFL analysis. On the basis of the results of ELF and topological analysis of the electron density and Laplacian bond orders, it can be indicated that the strength of Pt-N bonds, is weaker than that of Pt-C bonds and the substituent can have a negligible influence on the coordinate bonds.
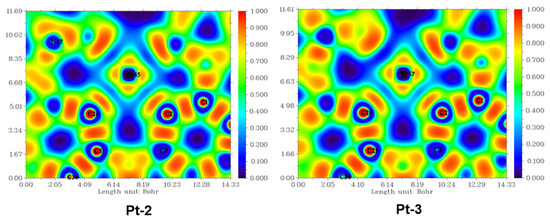
Figure 3.
Two-dimensional color-filled maps of ELF for Pt-2 and Pt-3 at the S0, T1, S1, cation states, and anion states, respectively. The zoom-in pictures are shown in the Supporting Information.
As shown in the results of ELF, topological analysis of the electron density and Laplacian bond orders revealed the reaction pathways of the Pt-N bond breaking for the Pt-2 and Pt-3 at different states, which are shown in Figure 4. The corresponding vibration forms of TS are shown in Figures S26 and S27. For Pt-2, the steps of Pt-N bond breaking would overcome the energy barriers of 22.77, 17.31, 24.56, and 18.80 kcal/mol S0, T1, +, and − states, respectively. In comparison to Pt-2, larger energy barriers can be achieved, and the corresponding values are 23.94, 19.17, 25.51, and 23.94 kcal/mol, respectively. Although the relative difference in energy barrier is not large enough, the tendency of energy barrier can illustrate that the Pt-N bond breaking of Pt-3 is more difficult than that of Pt-2. According to the experimental results [19], introducing bulky substituents in the Pt(II) complex can enhance the photochemical stability; hence, the calculated results are consistent with the experimental ones. To unveil the role of 3,5-di-tert-butyl-phenyl, only the isosurface map of the IRI of S0 states was computed because of the similar geometries in excited states. Figure 5 shows the isosurface map of the IRI of S0 states for Pt-2 and Pt-3 complexes, and sign(λ2)ρ is mapped on the isosurfaces according to the coloring method. The IRI analysis indicates that for the S0 state of Pt-2, there is a small interaction. Nevertheless, compared with Pt-2, a large intramolecular steric hindrance appears in the S0 states of Pt-3, which originates from the 3,5-di-tert-butyl-phenyl group.
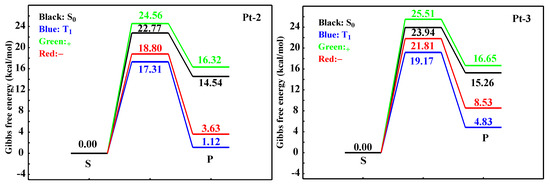
Figure 4.
The reaction pathways of the Pt-N bond breaking for the Pt-2 and Pt-3 at different states, respectively.
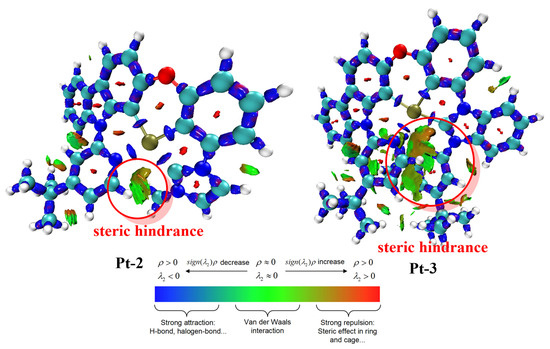
Figure 5.
Isosurface maps of IRI for Pt-2 and Pt-3 complexes at S0 states. The sign(λ2)ρ is mapped on the isosurfaces according to the coloring method. The isovalues of IRI are set to be 0.9.
3.3. The Effect of the “Aggregation Effect” on the Stability of Tetradentate Metal Complexes
The ELF, topological analysis of the electron density, and Laplacian bond orders were first calculated to illustrate the bonding nature between the Pd and ligand for the Pd-1D and Pd-1T at S0 and T1 states, and the results are shown in Figure S28 and Tables S4 and S5. As polled in Figure S8, for Pt-2 and Pt-3, the ELFs between Pt, N, and C atoms are similar in different states, implying that the degree of electron localization between Pt-N and Pt-C atomic bonds is comparable. Compared with the Pt-C bonds, a smaller electron localization between Pt and N can be found. The ρBCP and Laplacian bond orders of the Pt-C and N bonds are also applied to demonstrate the reliability of EFL analysis. On the basis of the results of ELF and topological analysis of the electron density and Laplacian bond orders, it can be indicated that the strength of Pt-N bonds is weaker than that of Pt-C bonds, and the aggregation can have a negligible influence on the coordinate bonds.
For the sake of exhibiting the “aggregation effect” on the stability of tetradentate metal complexes, the reaction pathways of the Pt-N bond breaking of Pd-1, Pd-1D, and Pd-1T are investigated with the help of a rigidity scan. Therein, the Pd-1 is trapped in the host materials, and the molecular dynamics (MD) simulation was performed using the GROMACS 2018.8 software. The corresponding results of rigidity scans for Pd-1, Pd-1D, and Pd-1T are shown in Figure 6. As plotted in Figure 6, the energy barriers of Pd-1D and Pd-1T in S0 and T1 states are far lager than those of Pd-1, indicating that the “aggregation effect” can cause the excellent stability of tetradentate metal complexes. This result is very much in accordance with the experimental investigation. In addition, the large energy barriers pictured in Figure 6 indicate that Pt-N bond breaking is almost impossible at room temperature.
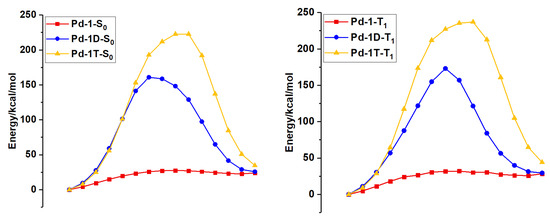
Figure 6.
The potential energy scans along the Pd-N bond break for the Pd-1, Pd-1D, and Pd-1T at S0 and T1 states, respectively.
The isosurface map of IRI states for Pd-1, Pd-1D, and Pd-1T complexes, based on the MD snapshot and geometric optimization, was also carried out to illustrate the intermolecular interaction. The corresponding results were plotted in Figure 7. As exhibited in Figure 7, for the host-guest system, the intermolecular interaction between Pd-1 and mCBP can be classified as π-π interaction and other weak interactions. Compared with the Pd-1 in the doped condition, the isosurface maps of IRI for Pd-1D and Pd-1T in Figure 7 exhibit that there is strong π-π interaction between the Pd(II) complexes. As shown in the Pd-1T complex, the π-π interaction and the middle Pd(II) complex can construct the “sandwich structure” to form the restricted region. This restricted region can effectively constrain the geometric change of the Pd-1T complex, which leads to a high energy barrier for the Pd-1T. In other words, the ligand is restricted in the special region to form the coordinate bonds with Pd, and the dissociation of complexes could originate from the bonds of the ligand, which may need a high energy barrier due to the property of covalent bonds.
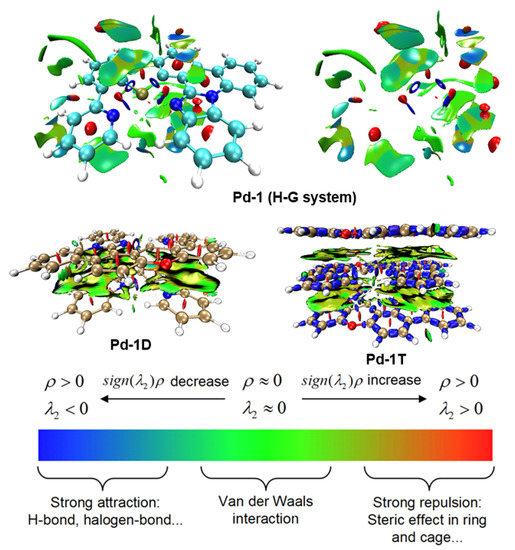
Figure 7.
Isosurface map of averaged RDG (reduced density gradient) for Pd-1 (H-G system) and isosurface maps of IRI for Pd-1D and Pd-1T complexes at S0 states.
3.4. Investigation of the Influence of Transformation between Singlet and Triplet Excited States on Stability
Apart from the investigations of the influence of intramolecular/intermolecular interactions and intrinsic properties on stability, the transformation between singlet and triplet excitons is also considered to explore the effect factor of stability. The calculations of adiabatic singlet and triplet excited states were carried out with the help of Tamm-Dancoff approximation density functional theory (TDA-DFT) in the protocol of B3LYP with LANL2DZ for Pd and6-311G** for C, H, N, and O. The calculated T1 energies of Pd-1 and Pd-1D are 2.55 eV and 1.98 eV, respectively. In order to further understand the intersystem crossing processes of Pd-1 and Pd-1D, the exploration of the energy-level alignment of singlet and triplet excited states is very significant since the transformation mechanism from singlet to triplet excited states may depend on the energy-level alignment. Hence, the S1 and T2 energy levels of Pd-1 and Pd-1D are further computed. As shown in Figure 8, the calculated S1/T2 energies of Pd-1 and Pd-1D in gas phase are calculated to be 2.81 eV/2.73 eV and 2.08 eV/2.33, respectively. It is interesting to note that the S1 energy of Pd-1 is higher than the T2 energy. In comparison, the calculated T2 energy of Pd-1D is higher than the S1 energy. For the calculated energy-level alignment of Pd-1, due to the competitive spin conversion process (S1 → T2 and S1 → T1), the intersystem crossing (ISC) may be inefficient. On the contrary, in the case of Pd-1D, because of the endothermic energy-level alignment, the ISC is only from S1 to T1, not from S1 to T2.
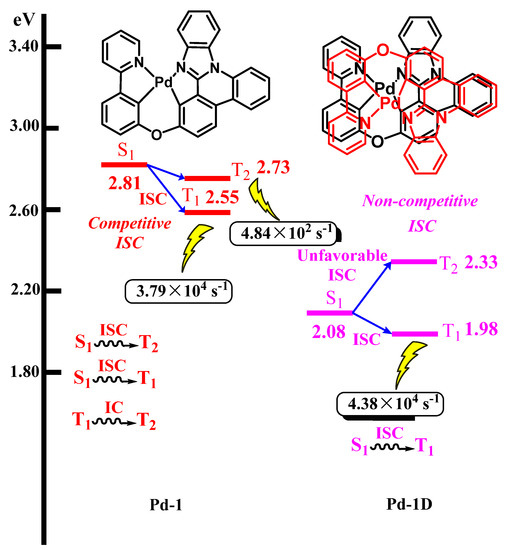
Figure 8.
Excited state energy levels (in eV) calculated in the gas phase and molecular structures of Pd-1 and Pd-1D, respectively.
To explore the transformation between singlet and triplet excited states in detail, the intersystem crossing (ISC) rates of Pd-1 (S1 → T2 and S1 → T1) and Pd-1D (S1 → T1) are calculated, which is plotted in Figure 7. The computed intersystem crossing (ISC) rates of Pd-1 (S1 → T2 and S1 → T1) are 1.00 × 1010 s−1 and 7.44 × 109 s−1, respectively. The computed results indicate that the intersystem crossing (ISC) from S1 to T2 is prior to that of S1 → T1. For the Pd-1D, the calculated intersystem crossing (ISC) from S1 to T1 is 5.45 × 109 s−1. The radiative decay rates for Pd-1 (T2 → S0 and T1 → S0) and Pd-1D (T1 → S0) are also computed, and the corresponding values are 4.84 × 102 s−1, 3.79 × 104 s−1, and 4.38 × 104 s−1, respectively. The computed radiative decay rates indicate that for Pd-1, the phosphorescence originated from the T1 excited state. In addition, compared with the Pd-1, the Pd-1D possesses a larger radiative decay rate, which is beneficial for facilitating the transition of the triplet exciton to the S0 state.
On the basis of the above-mentioned discussion, the phosphorescent process of Pd-1D could be identified as S1 → T1 → S0. However, in the case of the Pd-1 complex, the corresponding process is S1 → T2 →T1→ S0. In comparison to the Pd-1D complex, the complicated photo-physical process of Pd-1 can cause aggregation of triplet density in the emission layer (EML). The long excited state lifetime of triplet excitons is favored for resulting in a triplet-triplet quenching process. Triplet-triplet annihilation (TTA) and triplet-polaron annihilation (TPA) are the main degradation mechanisms. Surely, this conclusion needs to be confirmed via more investigation, and herein, only thinking is put forward in our study.
After exploration of the effect of the metal-N coordinate on the stability, the ligand dissociations of Ni-1, Pd-1, Pt-1, Pt-2, and Pt-3 are also investigated. As shown in Figure S6, the bond dissociation energy of Pd-1 is smaller than that of Ni-1. Among the Ni-1, Pd-1, and Pt-1, the Pt-1 possesses the largest bond dissociation energies in the S0, T1, S1, +, and − states, indicating that the different coordinate circumstances can induce the different stabilities. In the case of Pt-2 and Pt-3, the bond dissociation energies in the S0, T1, S1, +, and − states are comparable, implying that the substituent can cause a slight effect on the stability. In fact, for Ni-1, Pd-1, Pt-1, Pt-2, and Pt-3, the large bond dissociation energies could largely suppress the ligand dissociation. Hence, the investigation of breakage of the metal-N coordinate may be a reasonable strategy to unveil the stability of the tetradentate transition metal complex.
Finally, the dipole moment is also simulated. As shown in the previous study [41], the orientation of metal complexes is related to the dipole moment, and a molecular-scale simulation of the film formation suggested that dipole-dipole interactions tend to hinder alignment in organic films [42,43]. The dipole moments are computed here for Ni-1, Pd-1, Pt-1, Pt-2, and Pt-3, and the corresponding results are shown in Figure S29. For Ni-1, Pd-1, and Pt-1, the simulated dipole moment vectors are nearly identical, implying that the various mental centers can result in an ignorable effect. In the case of Pt-2, the dipole moment vector is parallel to the molecule. In comparison, for Pt-3, the dipole moment vector is pulled out of the molecular plane. On the basis of the simulated results, it can be inferred that the substituent added to the ligand can cause a distinct change in the dipole moment vector. In some situations, the dipole-dipole interactions do not play a significant role in the orientation of transition metal complexes [44]. Without doubt, the orientation of metal complexes in amorphous films is very complicated and should be explored using more methods.
4. Conclusions
In this investigation, a systematic investigation of the degradation mechanisms of tetradentate Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes has been performed to illustrate the geometric signatures as important factors to control the chemical stabilities. The corresponding conclusions can be put forward as follows:
- (I).
- Compared with the tetradentate Ni(II) and Pd(II) complexes, the Pt(II) complex possesses more strong coordinate bonds, which suggests that the strengths of coordinate bonds are closely related to the atomic number of the metal center in the same group.
- (II).
- The large intramolecular steric hindrance and strong π-π interaction between the complexes originated from aggregation can efficiently constrain the geometric change, raising the energy barriers of the ligand dissociation reaction.
- (III).
- In comparison to the monomeric Pd(II) complex, the aggregation of the Pd(II) complex can result in the essential change of the photo-deactivate mechanism and reduce the lifetime of triplet excitability, which is beneficial for avoiding triplet-triplet annihilation.
According to these conclusions, the effect factors of tetradentate metal complexes have been explored in detail. This study can provide meaningful strategies and information for designing high-stability transition metal complexes as phosphorescent materials.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules28124587/s1. Figures S1–S12: The two-dimensional color-filled maps of T1, S1, +, and − states for Ni-1, Pd-1, and Pt-1; Figure S13: Chemical geometries of Ni-1, Pd-1, and Pt-1 with key labels, respectively; Figure S14: Vibration forms of TS for Ni-1 at the S0, T1, S1, cation states, and anion states, respectively; Figure S15: Vibration forms of TS for Pd-1 at the S0, T1, S1, cation states, and anion states, respectively; Figure S16: Vibration forms of TS for Pt-1 at the S0, T1, S1, cation states, and anion states, respectively; Figures S17–S24: The two-dimensional color-filled maps of T1, S1, +, and – states for Pt-2, and Pt-3; Figure S25: Chemical geometries of Pt-2 and Pt-3 with key labels; Figure S26: Vibration forms for Pt-2 at the S0, T1, S1, cation states, and anion states, respectively; Figure S27: Vibration forms for Pt-3 at the S0, T1, S1, cation states, and anion states, respectively; Figure S28: Two-dimensional color-filled maps of ELF for Pd-1D and Pd-1T at the S0 and T1 states, respectively; Figure S29: Simulated dipole moment vectors for the Ni-1, Pd-1, Pt-1, Pt-2 and Pt-3, respectively; Table S1: Topological parameters of the electron density calculated at the bond critical point (BCP) (3, −1) of Pd/Pt-N and Pd/Pt-C bonds for Ni-1, Pd-1, and Pt-1 at the S0, T1, S1, +, and − states, respectively; Table S2: Topological parameters of the electron density calculated at the bond critical point (BCP) (3, −1) of Pd/Pt-N and Pd/Pt-C bonds for Pt-2 and Pt-3 at the S0, T1, S1, +, and − states, respectively; Table S3: Laplacian bond orders of Pt-N and Pt-C bonds of Pt-2 and Pt-3; Table S4: Topological parameters of the electron density calculated at the bond critical point (BCP) (3, −1) of Pd/Pt-N and Pd/Pt-C bonds for Pd-1D and Pd-1T at the S0 and T1 states; Table S5: Laplacian bond orders of Pt-N and Pt-C bonds of Pd-1D and Pd-1T;. Table S6: Bond dissociation energies of ligand dissociation for the Ni-1, Pd-1, Pt-1, Pt-2 and Pt-3, respectively.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, Y.L. and L.T.; writing—review and editing, Y.L. and L.T.; methodology, M.L.; formal analysis, Z.C.; investigation, Z.X.; data curation, Y.A.; supervision, J.H.; funding acquisition, D.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Spire Project of Chongqing University of Arts and Sciences (Grant No. P2019XY04), the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (Grant No. cstc2019jcyj-msxmX0469, cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0849, and cstc2021ycjh-bgzxm0170), and the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. KJQN202001310, KJZD-K202001305, and KJZD-M202101302).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Not available.
References
- Fleetham, T.B.; Huang, L.; Klimes, K.; Brooks, J.; Li, J. Tetradentate Pt(II) Complexes with 6-Membered Chelate Rings: A New Route for Stable and Efficient Blue Organic Light Emitting Diodes. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3276–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleetham, T.; Li, G.; Li, J. Phosphorescent Pt(II) and Pd(II) Complexes for Efficient, High-Color-Quality, and Stable OLEDs. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1601861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Miao, J.; Xiong, J.; Li, K.; Yang, C. Rigid Bridge-Confined Double-Decker Platinum(II) Complexes Towards High-Performance Red and Near-Infrared Electroluminescence. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113718. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Miao, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Zhu, W.; Yang, C. Red and near-infrared emissive palladium(II) complexes with tetradentate coordination framework and their application in OLEDs. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z.; Tang, B.Z. Critical Role of High-Lying Triplet States for Efficient Excitons Utilization in High-Performance Non-Doped Deep-Blue Fluorescent and Hybrid White Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2101724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, Q.; Shi, B.; Ge, F.; Liu, Y.; Mao, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S.; Yu, G.; Huang, F.; et al. Dual-Emissive Platinum(II) Metallacage with a Sensitive Oxygen Response for Imaging of Hypoxia and Imaging-Guided Chemotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 20208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, T.; Hirakawa, Y.; Hosaka, M.; Nangaku, M.; Tobita, S. Oxygen imaging of living cells and tissues using luminescent molecular probes. J. Photoch. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2017, 30, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Sun, P.; Ye, S.; Fan, Q.; Song, J.; Zeng, P.; Qu, J.; Wong, W.-Y. NIR-II J-Aggregated Pt(II)-Porphyrin-Based Phosphorescent Probe for Tumor-Hypoxia Imaging. Adv. Health. Mater. 2022, 11, 2200467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faihan, A.S.; Hatshan, M.R.; Kadhim, M.M.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Nasr, F.A.; Saleh, A.M.; Al-Jibori, S.A.; Al-Janabi, A.S. Promising bio-active complexes of platinum(II) and palladium(II) derived from heterocyclic thiourea: Synthesis, characterization, DFT, molecular docking, and anti-cancer studies. J. Mol. Struc. 2022, 1252, 132198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, N.; Cheng, S.-C.; Xu, K.; Deng, Z.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z.; Xie, K.; Tse, M.-K.; Shi, P.; et al. Phorbiplatin, a Highly Potent Pt(IV) Antitumor Prodrug That Can Be Controllably Activated by Red Light. Chem 2019, 5, 3151–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, M.A.; Adachi, C.; Forrest, S.R. Transient analysis of organic electrophosphorescence. II.Transient analysis of triplet-triplet annihilation. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 10967. [Google Scholar]
- Reineke, S.; Walzer, K.; Leo, K. Triplet-exciton quenching in organic phosphorescent light-emitting diodes with Ir-based emitters. Phy. Rev. B 2007, 75, 125328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, C.; Leo, K.; Gather, M.C. Efficiency Roll-Off in Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6801–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jeong, C.; Batagoda, T.; Coburn, C.; Thompson, M.E.; Forrest, S.R. Hot excited state management for long-lived blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimes, K.; Zhu, Z.-Q.; Li, J. Efficient Blue Phosphorescent OLEDs with Improved Stability and Color Purity through Judicious Triplet Exciton Management. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fleetham, T.; Turner, E.; Hang, X.-C.; Li, J. Highly Efficient and Stable Narrow-Band Phosphorescent Emitters for OLED Applications. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2015, 3, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, T. A bipolar host based high triplet energy electroplex for an over 10,000 h lifetime in pure blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.-H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-J. Exciplex-Forming Co-host for Organic Light-Emitting Diodes with Ultimate Efficiency. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4914–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ahn, H.; Kang, S.; Ko, S.-B.; Song, D.; Um, H.A.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.; Jeon, P.; Hwang, S.-H.; et al. Exceptionally stable blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes. Nat. Photon. 2022, 16, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Klimes, K.; Ji, Y.; Fleetham, T.; Li, J. Efficient and stable organic light-emitting devices employing phosphorescent molecular aggregates. Nat. Photon. 2021, 15, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fleetham, T.; Li, J. Efficient and Stable White Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Employing a Single Emitter. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2931–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleetham, T.; Huang, L.; Li, J. Tetradentate Platinum Complexes for Efficient and Stable Excimer-Based White OLEDs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6066–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleetham, T.; Ecton, J.; Wang, Z.; Bakken, N.; Li, J. Single-Doped White Organic Light-Emitting Device with an External Quantum Efficiency Over 20%. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2573–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, P.J.; Devlin, F.J.; Chabalowski, C.F.; Frisch, M.J. Ab Initio Calculation of Vibrational Absorption and Circular Dichroism Spectra Using Density Functional Force Fields. J. Phy. Chem. 1994, 98, 11623–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidanu, H.T. Planarity enhancement through effective π conjugation and interligand hydrogen bonding of hetrolipitic bipyrazolate Pt(II) complexes potentially applicable as a near infrared emitters: A DFT/TD-DFT study. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 28, 102574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, T.; Lee, J.Y. New design strategy for chemically-stable blue phosphorescent materials: Improving the energy gap between the T1 and 3MC states. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 3543–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tan, X.; Lv, A.; Yu, F.; Ma, H.; Shen, K.; Sun, Z.; Chen, F.; Chen, Z.-K.; Hang, X.-C. Triplet Excited-State Engineering of Phosphorescent Pt(II) Complexes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 5105–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Goerigk, L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, P.J.; Wadt, W.R. Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for K to Au including the outermost core orbitals. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, R.; Kari, R.; Csizmadia, I.G. Handbook of Gaussian Basis Sets; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Pople, J.A.; Binkley, J.S. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods 25. Supplementary functions for Gaussian basis sets. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 3265–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16; revision A. 03; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Angeli, C.; Bak, K.; Bakken, V.; Christiansen, O.; Cimiraglia, R.; Coriani, S.; Dahle, P.; Dalskov, E.; Enevoldsen, T.; Fernandez, B. Dalton, a Molecular Electronic Structure Program, Release Dalton 2011. 2011. Available online: http://daltonprogram.org (accessed on 17 April 2022).
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Grap. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.; Andrade, R.; Birgin, E.G.; Martínez, J.M. PACKMOL: A package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemin, D.; Escudero, D. The short device lifetimes of blue PhOLEDs: Insights into the photostability of blue Ir(III) complexes. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 7844–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavachari, K. Perspective on “Density functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange” Becke AD (1993) J. Chem. Phys. 98: 5648–5652. Theore. Chem. Acc. 2000, 103, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friederich, P.; Coehoorn, R.; Wenzel, W. Molecular Origin of the Anisotropic Dye Orientation in Emissive Layers of Organic Light Emitting Diodes. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 9528–9535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, C.-K.; Kim, K.-H.; Kim, J.-J. Unraveling the Orientation of Phosphors Doped in Organic Semiconducting Layers. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, A.; Liehm, P.; Murawski, C.; Hofmann, S.; Leo, K.; Gather, M.C. Correlating the Transition Dipole Moment Orientation of Phosphorescent Emitter Molecules in OLEDs with Basic Material Properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 10298–10304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Harms, K.; Degitz, C.; Morgenstern, T.; Hofmann, A.; Friederich, P.; Johannes, H.-H.; Wenzel, W.; Kowalsky, W.; Brütting, W. Optical and Electrical Measurements Reveal the Orientation Mechanism of Homoleptic Iridium-Carbene Complexes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 51709–51718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).