Insights into the Structural Conformations of the Tau Protein in Different Aggregation Status
Abstract
1. Introduction
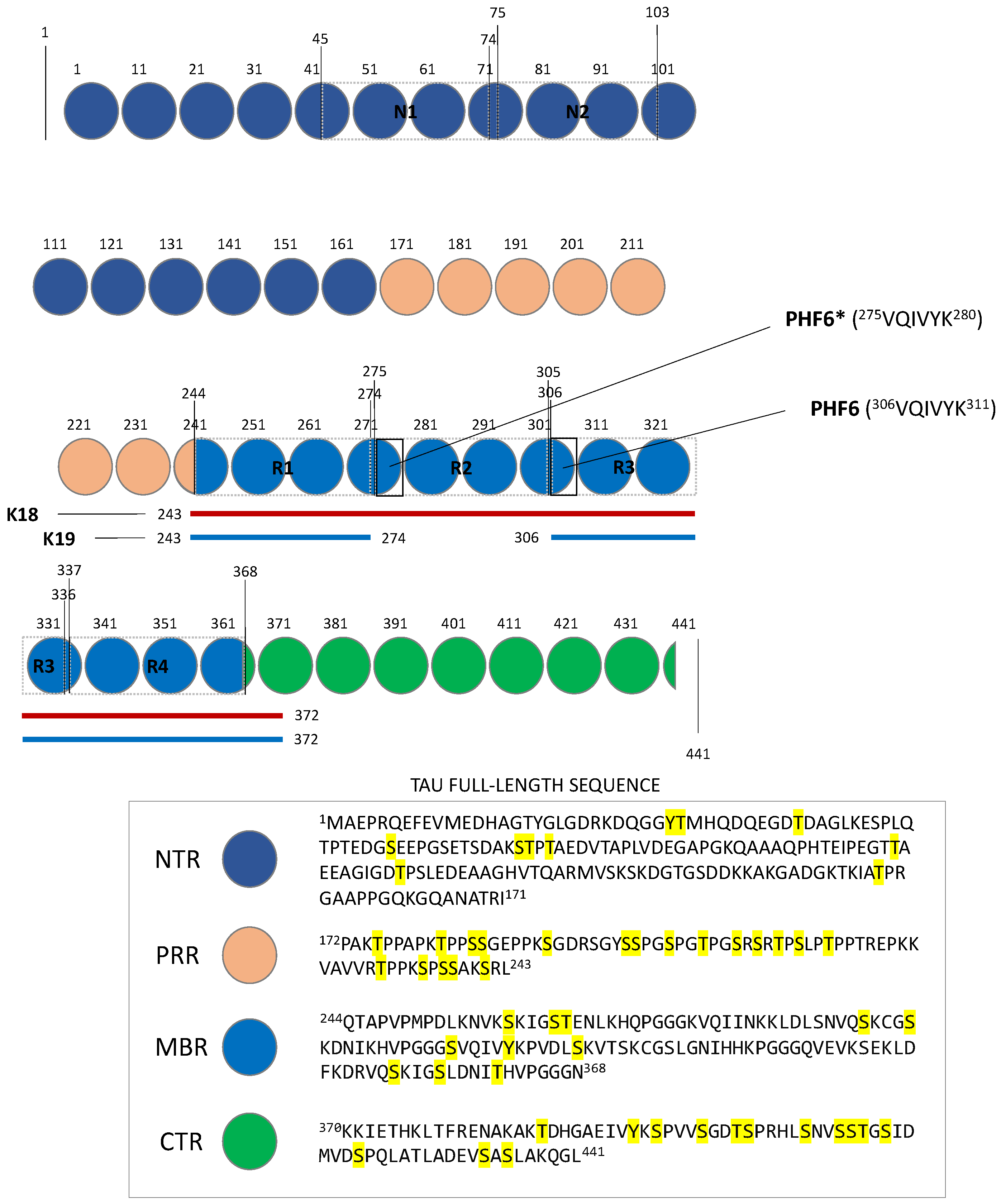
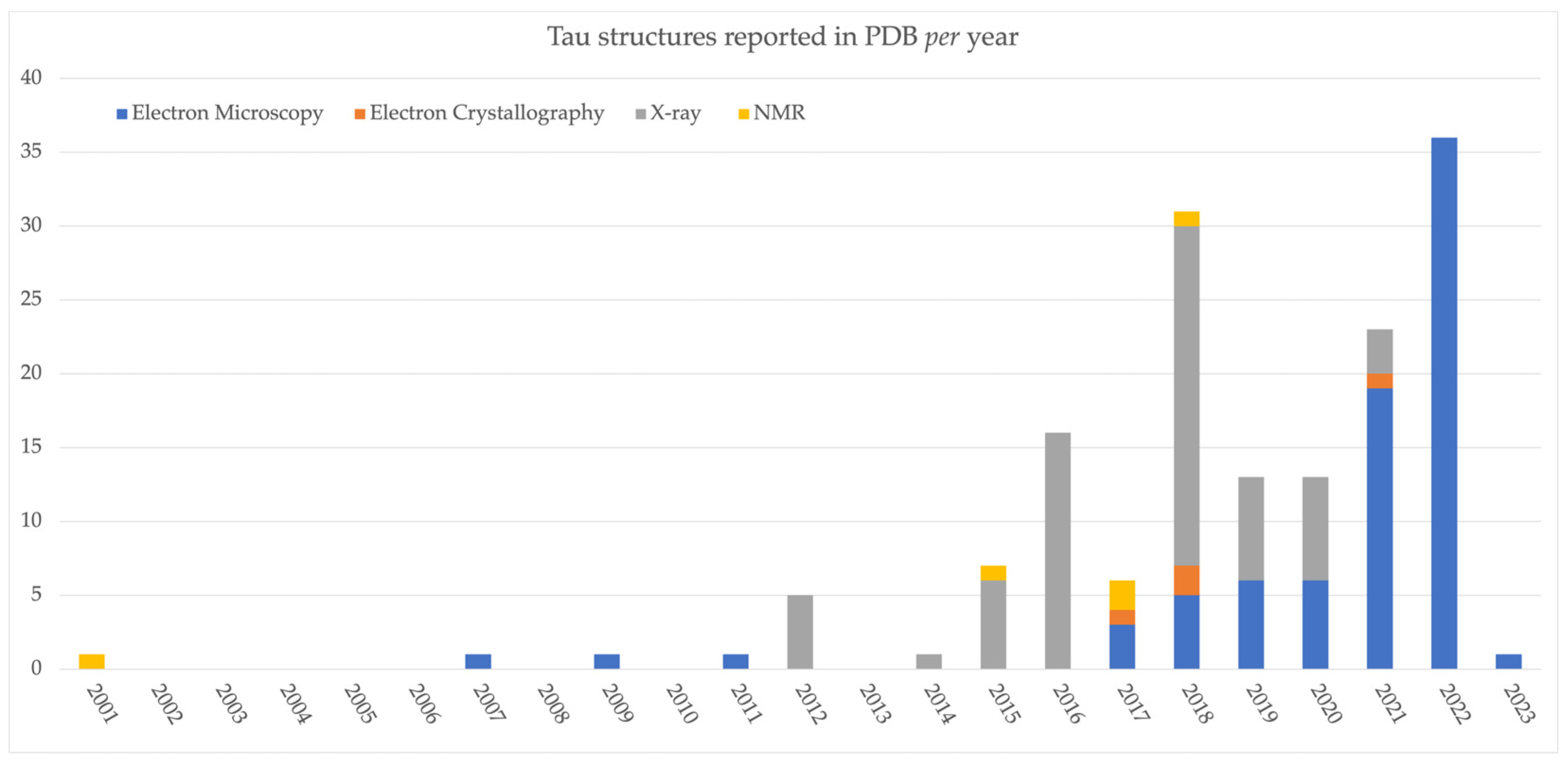
2. Tau Structures
| Title | Type of Structure * | Class ** | PDB Resolution (Å) | Publication Year | Experimental Method | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7P6D | 4R | AGD type 1 | 3.300 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [41] |
| 7P6E | 4R | AGD type 2 | 3.400 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [41] |
| 6TJX | 4R | CBD tau fibrils doublet | 3.000 | 2020 | Electron Microscopy | [42] |
| 6VH7 | 4R | CBD tau fibrils doublet | 3.800 | 2020 | Electron Microscopy | [43] |
| 6TJO | 4R | CDB tau fibrils singlet | 3.200 | 2020 | Electron Microscopy | [42] |
| 6VHA | 4R | CDB tau fibrils singlet | 4.300 | 2020 | Electron Microscopy | [43] |
| 6NWP | 4R–3R | CTE I | 2.300 | 2019 | Electron Microscopy | [44] |
| 8BYN | 4R–3R | CTE I | 2.600 | 2023 | Electron Microscopy | [45] |
| 7QL1 | 4R–3R | CTE I/II | 3.340 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 6NWQ | 4R–3R | CTE II | 3.400 | 2019 | Electron Microscopy | [44] |
| 7QJW | 4R–3R | CTE II | 2.810 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKX | 4R–3R | CTE II | 3.160 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QL0 | 4R–3R | CTE II | 3.130 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QL3 | 4R–3R | CTE III | 3.320 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QK5 | 4R (266/297–391) | CTE-like fold | 1.920 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKV | 4R (266/297–391) | CTE-like fold | 3.230 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7P66 | 4R | GGT I | 3.000 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [41] |
| 7P67 | 4R | GGT II | 3.100 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [41] |
| 7P68 | 4R | GGT III | 2.900 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [41] |
| 7QK3 | 4R (258–391) | GGT-like fold | 2.440 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QK6 | 4R (258–391) | GGT-like fold | 2.270 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKG | 4R (258–391) | GGT-like fold | 3.360 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7P6A | 4R | GPT type 1a | 1.900 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [41] |
| 7P6B | 4R | GPT type 1b | 2.200 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [41] |
| 7P6C | 4R | GPT type 2 | 2.500 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [41] |
| 6QJQ | 3R | Heparin-induced 3R | 3.700 | 2019 | Electron Microscopy | [47] |
| 6QJP | 4R | Heparin-induced 4R jagged | 3.500 | 2019 | Electron Microscopy | [47] |
| 6QJH | 4R | Heparin-induced 4R snake | 3.300 | 2019 | Electron Microscopy | [47] |
| 6QJM | 4R | Heparin-induced 4R twister | 3.300 | 2019 | Electron Microscopy | [47] |
| 6CVJ | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Model of synthetic Tau | 3.200 | 2018 | Electron Microscopy | [6] |
| 6CVN | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Model of synthetic Tau | 3.900 | 2018 | Electron Microscopy | [6] |
| 7QJY | 4R (266/297–391) | new I | 3.140 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7R4T | 4R (266/297–391) | new I | 2.750 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QJZ | 4R (266/297–391) | new II | 3.400 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QK2 | 4R (300–391) | new III | 2.610 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKZ | 4R (305–379) | new III | 2.650 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKL | 4R (266/297–391) | new IIX | 2.070 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKF | 4R (266/297–391) | new IV | 2.830 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKM | 4R (266–391, S356D) | new IX | 2.660 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKH | 4R (258–391) | new V | 3.170 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKI | 4R (297–408) | new VI | 3.130 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKJ | 4R (266/297–391) | new VII | 3.260 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKU | 4R (266/297–391) | new X | 2.570 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKW | 4R (266–391, S356D) | new XI | 2.320 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKY | 0N4R | new XII | 1.860 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QL2 | 4R (266/297–391) | new XIII | 2.950 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7R5H | 4R (266/297–391) | new XIV | 2.590 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7P65 | 4R | PSP | 2.700 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [41] |
| 7U0Z | 4R | PSP | 4.200 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [48] |
| 7KQK (chains ABC) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | pTau fragment in complex with anti-pTau C21-ABS Fab | 2.600 | 2020 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 7KQK (chains HLP) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | pTau fragment in complex with anti-pTau C21-ABS Fab | 2.600 | 2020 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 2MZ7 | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau bound to Microtubules | 2015 | Solution NMR (Model 1) | [49] | |
| 7PQC | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau bound to Microtubules | 4.100 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [50] |
| 7PQP | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau bound to Microtubules | 4.100 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [50] |
| 5O3L | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.400 | 2017 | Electron Microscopy | [35] |
| 5O3O | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.500 | 2017 | Electron Microscopy | [35] |
| 6HRE | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.200 | 2018 | Electron Microscopy | [51] |
| 6VHL | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.300 | 2020 | Electron Microscopy | [43] |
| 7MKF | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.000 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [52] |
| 7MKH | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.300 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [52] |
| 7NRQ | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 2.760 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [36] |
| 7NRV | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.000 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [36] |
| 7QJV | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.290 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QJX | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 2.990 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QK1 | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.030 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QKK | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 2.800 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7QL4 | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.200 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [46] |
| 7UPE | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.400 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [53] |
| 7UPF | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.300 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [53] |
| 7UPG | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.800 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [53] |
| 7YMN | 3R (266–391) | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—PHF | 3.460 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [54] |
| 5O3T | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—SF | 3.400 | 2017 | Electron Microscopy | [35] |
| 6HRF | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—SF | 3.300 | 2018 | Electron Microscopy | [51] |
| 6VI3 | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—SF | 3.300 | 2020 | Electron Microscopy | [43] |
| 7MKG | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—SF | 3.070 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [52] |
| 7NRS | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—SF | 2.680 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [36] |
| 7NRT | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—SF | 2.680 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [36] |
| 7NRX | 4R–3R | Tau fibril from Alzheimer’s Disease—SF | 3.550 | 2021 | Electron Microscopy | [36] |
| 6GX5 | 3R | Tau fibril from PICK’s Disease—NPF | 3.200 | 2018 | Electron Microscopy | [55] |
| 7YPG | 3R | Spindle-like fibril | 2.500 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [54] |
| 4FL5 | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 1.900 | 2015 | X-ray Diffraction | [12] |
| 4Y32 | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 1.700 | 2015 | X-ray Diffraction | [56] |
| 4Y3B | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 1.800 | 2015 | X-ray Diffraction | [56] |
| 4Y5I | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 1.400 | 2015 | X-ray Diffraction | [56] |
| 5BTV | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 1.700 | 2015 | X-ray Diffraction | [12] |
| 5HF3 | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 1.800 | 2015 | X-ray Diffraction | [56] |
| 6FAU | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 1.250 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [57] |
| 6FAV | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 1.400 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [57] |
| 6FAW | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 1.400 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [57] |
| 6FBW | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 1.450 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [57] |
| 6FBY | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 1.500 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [57] |
| 6FI4 | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 2.000 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [57] |
| 6FI5 | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with 14-3-3 | 1.700 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [57] |
| 7EYC (chains ABQ) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with antigen | 2.490 | 2021 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 7EYC (chains LHP) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with antigen | 2.490 | 2021 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 5ZIA (chains ABC) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with CBTAU-24.1 | 2.600 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [58] |
| 5ZIA (chains DEF) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with CBTAU-24.1 | 2.600 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [58] |
| 5ZIA (chains GLR) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with CBTAU-24.1 | 2.600 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [58] |
| 5ZIA (chains HIJ) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with CBTAU-24.1 | 2.600 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [58] |
| 5ZIA (chains KMN) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with CBTAU-24.1 | 2.600 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [58] |
| 5ZIA (chains OPQ) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with CBTAU-24.1 | 2.600 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [58] |
| 5ZV3 | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with CBTAU-24.1 | 2.090 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [59] |
| 6GK7 | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with CBTAU-27.1 | 2.950 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [59] |
| 6GK8 | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with CBTAU-28.1 | 2.850 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [59] |
| 5N5A | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with F-actin | 2017 | Solution NMR (Model 4) | [60] | |
| 5N5B | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with F-actin | 2017 | Solution NMR (Model 12) | [60] | |
| 5NVB | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with F-actin | 2018 | Solution NMR (Model 1) | ||
| 4GLR (chains AHI) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 1.900 | 2012 | X-ray Diffraction | [61] |
| 4GLR (chains BJK) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 1.900 | 2012 | X-ray Diffraction | [61] |
| 4TQE | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 1.600 | 2014 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 5DMG (chains CDZ) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.500 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | [62] |
| 5DMG (chains EFX) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.500 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | [62] |
| 5DMG (chains HLP) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.500 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | [62] |
| 5E2V | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 1.640 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | [63] |
| 5E2W | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 1.500 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | [63] |
| 5MO3 | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 1.690 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 5MP1 (chains AHL) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 3.100 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 5MP1 (chains BCD) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 3.100 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 5MP1 (chains EFG) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 3.100 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 5MP1 (chains IJK) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 3.100 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 5MP3 (chains ABC) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.750 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 5MP3 (chains DHL) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.750 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 5MP5 (chains ABK) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.310 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 5MP5 (chains CD) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.310 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 5MP5 (chains EFI) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.310 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 5MP5 (chains HJL) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.310 | 2016 | X-ray Diffraction | |
| 6BB4 (chains HLP) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.100 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [64] |
| 6BB4 (chains IMQ) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.100 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [64] |
| 6BB4 (chains JNR) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.100 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [64] |
| 6DC8 | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 1.800 | 2019 | X-ray Diffraction | [65] |
| 6DC9 (chains HLP) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 3.000 | 2019 | X-ray Diffraction | [65] |
| 6DC9 (chains IMQ) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 3.000 | 2019 | X-ray Diffraction | [65] |
| 6DCA (chains HLP) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.600 | 2019 | X-ray Diffraction | [65] |
| 6DCA (chains IMQ) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.600 | 2019 | X-ray Diffraction | [65] |
| 6DCA (chains JNR) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.600 | 2019 | X-ray Diffraction | [65] |
| 6LRA | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 1.900 | 2020 | X-ray Diffraction | [66] |
| 6PXR | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 1.560 | 2020 | X-ray Diffraction | [67] |
| 6XLI (chains ABE) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.000 | 2020 | X-ray Diffraction | [68] |
| 6XLI (chains CDF) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.000 | 2020 | X-ray Diffraction | [68] |
| 6XLI (chains HLP) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Fab | 2.000 | 2020 | X-ray Diffraction | [68] |
| 6H06 (chains ABK) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with FAB CBTAU-22.1 | 2.630 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [69] |
| 6H06 (chains CDG) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with FAB CBTAU-22.1 | 2.630 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [69] |
| 6H06 (chains EFJ) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with FAB CBTAU-22.1 | 2.630 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [69] |
| 6H06 (chains HIL) | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with FAB CBTAU-22.1 | 2.630 | 2018 | X-ray Diffraction | [69] |
| 1I8H | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with Pin1 WW domain | 2001 | Solution NMR (Model 1) | [70] | |
| 7SP1 | Tau fragment in complex with other proteins | Tau fragment in complex with RNA | 3.400 | 2022 | Electron Microscopy | [71] |
| 5V5B | Tau fragment | Tau fragment KVQIINKKL | 1.500 | 2018 | Electron Crystallography | [72] |
| 6NK4 | Tau fragment | Tau fragment KVQIINKKL | 1.990 | 2021 | Electron Crystallography | [73] |
| 6N4P | Tau fragment | Tau fragment RQEFEV | 1.850 | 2021 | X-ray Diffraction | [74] |
| 6ODG | Tau fragment | Tau fragment SVQIVY | 1.000 | 2019 | X-ray Diffraction | [75] |
| 4E0M | Tau fragment | Tau fragment SVQIVYK | 1.750 | 2012 | X-ray Diffraction | [76] |
| 4E0N | Tau fragment | Tau fragment SVQIVYK | 1.650 | 2012 | X-ray Diffraction | [76] |
| 4E0O | Tau fragment | Tau fragment SVQIVYK | 1.820 | 2012 | X-ray Diffraction | [76] |
| 5V5C | Tau fragment | Tau fragment VQIINK | 1.250 | 2018 | Electron Crystallography | [72] |
| 2ON9 | Tau fragment | Tau fragment VQIVYK | 1.510 | 2007 | X-ray Diffraction | [77] |
| 3OVL | Tau fragment | Tau fragment VQIVYK | 1.810 | 2011 | X-ray Diffraction | [78] |
| 4NP8 | Tau fragment | Tau fragment VQIVYK | 1.510 | 2009 | X-ray Diffraction | [79] |
| 5K7N | Tau fragment | Tau fragment VQIVYK | 1.100 | 2017 | Electron Crystallography | [80] |
3. Tau Structures in Different Neurodegenerative Diseases
4. Comparison of the Structural Features of Tau from Ex Vivo and In Vitro Samples
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Drubin, D.G.; Kirschner, M.W. Tau Protein Function in Living Cells. J. Cell Biol. 1986, 103, 2739–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Shala, A.; Bezginov, A.; Sljoka, A.; Audette, G.; Wilson, D.J. Hyperphosphorylation of Intrinsically Disordered Tau Protein Induces an Amyloidogenic Shift in Its Conformational Ensemble. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trushina, N.I.; Bakota, L.; Mulkidjanian, A.Y.; Brandt, R. The Evolution of Tau Phosphorylation and Interactions. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewidok, B.; Igaev, M.; Sündermann, F.; Janning, D.; Bakota, L.; Brandt, R. Presence of a Carboxy-Terminal Pseudorepeat and Disease-like Pseudohyperphosphorylation Critically Influence Tau’s Interaction with Microtubules in Axon-like Processes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 3537–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, R.; Trushina, N.I.; Bakota, L. Much More Than a Cytoskeletal Protein: Physiological and Pathological Functions of the Non-Microtubule Binding Region of Tau. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 590059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellogg, E.H.; Hejab, N.M.A.; Poepsel, S.; Downing, K.H.; DiMaio, F.; Nogales, E. Near-Atomic Model of Microtubule-Tau Interactions. Science 2018, 360, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanger, D.P.; Byers, H.L.; Wray, S.; Leung, K.-Y.; Saxton, M.J.; Seereeram, A.; Reynolds, C.H.; Ward, M.A.; Anderton, B.H. Novel Phosphorylation Sites in Tau from Alzheimer Brain Support a Role for Casein Kinase 1 in Disease Pathogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23645–23654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishima-Kawashima, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Takio, K.; Suzuki, M.; Yoshida, H.; Titani, K.; Ihara, Y. Proline-Directed and Non-Proline-Directed Phosphorylation of PHF-Tau. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier-Kemper, A.; Suárez Alonso, M.; Sündermann, F.; Niewidok, B.; Fernandez, M.-P.; Bakota, L.; Heinisch, J.J.; Brandt, R. Annexins A2 and A6 Interact with the Extreme N Terminus of Tau and Thereby Contribute to Tau’s Axonal Localization. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 8065–8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanoska, K.; Volkerling, A.; Bertz, J.; Poljak, A.; Ke, Y.D.; Ittner, L.M.; Ittner, A. An N-Terminal Motif Unique to Primate Tau Enables Differential Protein-Protein Interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 3710–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugaeva, K.V.; Tsvetkov, P.O.; Sluchanko, N.N. Bacterial Co-Expression of Human Tau Protein with Protein Kinase A and 14-3-3 for Studies of 14-3-3/Phospho-Tau Interaction. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, Y.; Schumacher, B.; Landrieu, I.; Bartel, M.; Smet-Nocca, C.; Jang, A.; Choi, H.S.; Jeon, N.L.; Chang, K.-A.; Kim, H.-S.; et al. Involvement of 14-3-3 in Tubulin Instability and Impaired Axon Development Is Mediated by Tau. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 4133–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibille, N.; Sillen, A.; Leroy, A.; Wieruszeski, J.-M.; Mulloy, B.; Landrieu, I.; Lippens, G. Structural Impact of Heparin Binding to Full-Length Tau As Studied by NMR Spectroscopy. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 12560–12572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhilb, M.L.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Fulga, T.A.; Felch, D.L.; Feany, M.B. Tau Phosphorylation Sites Work in Concert to Promote Neurotoxicity In Vivo. MBoC 2007, 18, 5060–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouchlis, V.D.; Melagraki, G.; Zacharia, L.C.; Afantitis, A. Computer-Aided Drug Design of β-Secretase, γ-Secretase and Anti-Tau Inhibitors for the Discovery of Novel Alzheimer’s Therapeutics. IJMS 2020, 21, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, D.W.; Hwo, S.-Y.; Kirschner, M.W. Physical and Chemical Properties of Purified Tau Factor and the Role of Tau in Microtubule Assembly. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 116, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliezer, D.; Barré, P.; Kobaslija, M.; Chan, D.; Li, X.; Heend, L. Residual Structure in the Repeat Domain of Tau: Echoes of Microtubule Binding and Paired Helical Filament Formation. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, S.; Bell, M.; Klimek, J.; Zempel, H. Differential Effects of the Six Human TAU Isoforms: Somatic Retention of 2N-TAU and Increased Microtubule Number Induced by 4R-TAU. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 643115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G.; Jakes, R.; Rutherford, D.; Crowther, R.A. Multiple Isoforms of Human Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau: Sequences and Localization in Neurofibrillary Tangles of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 1989, 3, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azouz, M.; Feuillie, C.; Lafleur, M.; Molinari, M.; Lecomte, S. Interaction of Tau Construct K18 with Model Lipid Membranes. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 4244–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukrasch, M.D.; Biernat, J.; Von Bergen, M.; Griesinger, C.; Mandelkow, E.; Zweckstetter, M. Sites of Tau Important for Aggregation Populate β-Structure and Bind to Microtubules and Polyanions. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24978–24986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabzuni, D.; Wray, S.; Vandrovcova, J.; Ramasamy, A.; Walker, R.; Smith, C.; Luk, C.; Gibbs, J.R.; Dillman, A.; Hernandez, D.G.; et al. MAPT Expression and Splicing Is Differentially Regulated by Brain Region: Relation to Genotype and Implication for Tauopathies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 4094–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M. Mutation-Specific Functional Impairments in Distinct Tau Isoforms of Hereditary FTDP-17. Science 1998, 282, 1914–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Prokop, S.; Giasson, B.I. “Don’t Phos Over Tau”: Recent Developments in Clinical Biomarkers and Therapies Targeting Tau Phosphorylation in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Tauopathies. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, F.X.; Luiken, J.A.; Bolhuis, P.G. Primary Fibril Nucleation of Aggregation Prone Tau Fragments PHF6 and PHF6 *. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 3250–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.R. Tauopathies: Classification and Clinical Update on Neurodegenerative Diseases Associated with Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau. Intern. Med. J. 2006, 36, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunello, C.A.; Merezhko, M.; Uronen, R.-L.; Huttunen, H.J. Mechanisms of Secretion and Spreading of Pathological Tau Protein. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1721–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lee, V.M.-Y. Characterization of Two VQIXXK Motifs for Tau Fibrillization In Vitro. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 15692–15701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, J.; Lucas, J.J.; Pérez, M.; Hernández, F. Role of Tau Protein in Both Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 361–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G. Propagation of Tau Aggregates. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Haque, M.M.; Kim, D.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, Y.K. Cell-Based Models To Investigate Tau Aggregation. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.-M.; Yang, L.; Dong, Q.; Yu, J.-T. Tauopathies: New Perspectives and Challenges. Mol. Neurodegener. 2022, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, W.; Hanger, D.P.; Miller, C.C.J.; Lovestone, S. The Importance of Tau Phosphorylation for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurol. 2013, 4, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A.W.P.; Falcon, B.; He, S.; Murzin, A.G.; Murshudov, G.; Garringer, H.J.; Crowther, R.A.; Ghetti, B.; Goedert, M.; Scheres, S.H.W. Cryo-EM Structures of Tau Filaments from Alzheimer’s Disease. Nature 2017, 547, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Murzin, A.G.; Falcon, B.; Epstein, A.; Machin, J.; Tempest, P.; Newell, K.L.; Vidal, R.; Garringer, H.J.; Sahara, N.; et al. Cryo-EM Structures of Tau Filaments from Alzheimer’s Disease with PET Ligand APN-1607. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, S.; Sasidharan, S.; Nag, N.; Saudagar, P.; Tripathi, T. Amyloid Cross-Seeding: Mechanism, Implication, and Inhibition. Molecules 2022, 27, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizynski, B.; Nieznanska, H.; Dec, R.; Boyko, S.; Dzwolak, W.; Nieznanski, K. Amyloidogenic Cross-Seeding of Tau Protein: Transient Emergence of Structural Variants of Fibrils. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.d.C.; Zaidi, T.; Novak, M.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K. Hyperphosphorylation Induces Self-Assembly of τ into Tangles of Paired Helical Filaments/Straight Filaments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6923–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2018-3: Maestro. Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2018. Available online: www.schrodinger.com (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Murzin, A.G.; Falcon, B.; Kotecha, A.; van Beers, M.; Tarutani, A.; Kametani, F.; Garringer, H.J.; et al. Structure-Based Classification of Tauopathies. Nature 2021, 598, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tarutani, A.; Newell, K.L.; Murzin, A.G.; Matsubara, T.; Falcon, B.; Vidal, R.; Garringer, H.J.; Shi, Y.; Ikeuchi, T.; et al. Novel Tau Filament Fold in Corticobasal Degeneration. Nature 2020, 580, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakhamia, T.; Lee, C.E.; Carlomagno, Y.; Kumar, M.; Duong, D.M.; Wesseling, H.; Kundinger, S.R.; Wang, K.; Williams, D.; DeTure, M.; et al. Posttranslational Modifications Mediate the Structural Diversity of Tauopathy Strains. Cell 2020, 180, 633–644.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcon, B.; Zivanov, J.; Zhang, W.; Murzin, A.G.; Garringer, H.J.; Vidal, R.; Crowther, R.A.; Newell, K.L.; Ghetti, B.; Goedert, M.; et al. Novel Tau Filament Fold in Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy Encloses Hydrophobic Molecules. Nature 2019, 568, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy Tau Filaments with PET Ligand Flortaucipir. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/8BYN (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Lövestam, S.; Koh, F.A.; van Knippenberg, B.; Kotecha, A.; Murzin, A.G.; Goedert, M.; Scheres, S.H. Assembly of Recombinant Tau into Filaments Identical to Those of Alzheimer’s Disease and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy. eLife 2022, 11, e76494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Falcon, B.; Murzin, A.G.; Fan, J.; Crowther, R.A.; Goedert, M.; Scheres, S.H. Heparin-Induced Tau Filaments Are Polymorphic and Differ from Those in Alzheimer’s and Pick’s Diseases. eLife 2019, 8, e43584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Xiang, X.; Wang, J.; Lee, C.; Arakhamia, T.; Simjanoska, M.; Wang, C.; Carlomagno, Y.; Zhang, G.; Dhingra, S.; et al. Homotypic Fibrillization of TMEM106B across Diverse Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cell 2022, 185, 1346–1355.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadavath, H.; Jaremko, M.; Jaremko, Ł.; Biernat, J.; Mandelkow, E.; Zweckstetter, M. Folding of the Tau Protein on Microtubules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10347–10351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotzakis, Z.F.; Lindstedt, P.R.; Taylor, R.J.; Rinauro, D.J.; Gallagher, N.C.T.; Bernardes, G.J.L.; Vendruscolo, M. A Structural Ensemble of a Tau-Microtubule Complex Reveals Regulatory Tau Phosphorylation and Acetylation Mechanisms. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcon, B.; Zhang, W.; Schweighauser, M.; Murzin, A.G.; Vidal, R.; Garringer, H.J.; Ghetti, B.; Scheres, S.H.W.; Goedert, M. Tau Filaments from Multiple Cases of Sporadic and Inherited Alzheimer’s Disease Adopt a Common Fold. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinan, G.I.; Hoq, M.R.; Ghosh, M.; Vago, F.S.; Fernandez, A.; Garringer, H.J.; Vidal, R.; Jiang, W.; Ghetti, B. Structure of Tau Filaments in Prion Protein Amyloidoses. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 142, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, P.M.; Murray, K.A.; Boyer, D.R.; Ge, P.; Sawaya, M.R.; Hu, C.J.; Cheng, X.; Abskharon, R.; Pan, H.; DeTure, M.A.; et al. Structure-Based Discovery of Small Molecules That Disaggregate Alzheimer’s Disease Tissue Derived Tau Fibrils in Vitro. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Tao, Y.; Xia, W.; Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Le, W.; Sun, B.; Li, D. Subtle Change of Fibrillation Condition Leads to Substantial Alteration of Recombinant Tau Fibril Structure. iScience 2022, 25, 105645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcon, B.; Zhang, W.; Murzin, A.G.; Murshudov, G.; Garringer, H.J.; Vidal, R.; Crowther, R.A.; Ghetti, B.; Scheres, S.H.W.; Goedert, M. Structures of Filaments from Pick’s Disease Reveal a Novel Tau Protein Fold. Nature 2018, 561, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milroy, L.; Bartel, M.; Henen, M.A.; Leysen, S.; Adriaans, J.M.C.; Brunsveld, L.; Landrieu, I.; Ottmann, C. Stabilizer-Guided Inhibition of Protein–Protein Interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15720–15724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrei, S.A.; Meijer, F.A.; Neves, J.F.; Brunsveld, L.; Landrieu, I.; Ottmann, C.; Milroy, L.-G. Inhibition of 14-3-3/Tau by Hybrid Small-Molecule Peptides Operating via Two Different Binding Modes. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 2639–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Pascual, G.; Wadia, J.S.; Keogh, E.; Hoozemans, J.J.; Siregar, B.; Inganäs, H.; Stoop, E.J.M.; Goudsmit, J.; et al. Structural Basis for Recognition of a Unique Epitope by a Human Anti-Tau Antibody. Structure 2018, 26, 1626–1634.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetri, A.; Crespo, R.; Juraszek, J.; Pascual, G.; Janson, R.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Keogh, E.; Holland, T.; Wadia, J.; et al. A Common Antigenic Motif Recognized by Naturally Occurring Human VH5–51/VL4–1 Anti-Tau Antibodies with Distinct Functionalities. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrales Fontela, Y.; Kadavath, H.; Biernat, J.; Riedel, D.; Mandelkow, E.; Zweckstetter, M. Multivalent Cross-Linking of Actin Filaments and Microtubules through the Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.H.; Tu, C.; Cao, W.; Klein, A.; Ramsey, R.; Fennell, B.J.; Lambert, M.; Ní Shúilleabháin, D.; Autin, B.; Kouranova, E.; et al. An Ultra-Specific Avian Antibody to Phosphorylated Tau Protein Reveals a Unique Mechanism for Phosphoepitope Recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 44425–44434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujotzek, A.; Lipsmeier, F.; Harris, S.F.; Benz, J.; Kuglstatter, A.; Georges, G. VH-VL Orientation Prediction for Antibody Humanization Candidate Selection: A Case Study. mAbs 2016, 8, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malia, T.J.; Teplyakov, A.; Ernst, R.; Wu, S.; Lacy, E.R.; Liu, X.; Vandermeeren, M.; Mercken, M.; Luo, J.; Sweet, R.W.; et al. Epitope Mapping and Structural Basis for the Recognition of Phosphorylated Tau by the Anti-tau Antibody AT8. Proteins 2016, 84, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukwu, J.E.; Pedersen, J.T.; Pedersen, L.Ø.; Volbracht, C.; Sigurdsson, E.M.; Kong, X.-P. Tau Antibody Structure Reveals a Molecular Switch Defining a Pathological Conformation of the Tau Protein. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukwu, J.E.; Congdon, E.E.; Sigurdsson, E.M.; Kong, X.-P. Structural Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting C-Terminal Ser 404 Region of Phosphorylated Tau Protein. mAbs 2019, 11, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T.; Susa, K.; Kibiki, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Miyamoto, K.; In, Y.; Minoura, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Ishida, T.; Tomoo, K. Crystal Structure of the Human Tau PHF Core Domain VQIINK Complexed with the Fab Domain of Monoclonal Antibody Tau2r3. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopko, R.; Golonzhka, O.; Arndt, J.; Quan, C.; Czerkowicz, J.; Cameron, A.; Smith, B.; Murugesan, Y.; Gibbons, G.; Kim, S.-J.; et al. Characterization of Tau Binding by Gosuranemab. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 146, 105120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kolen, K.; Malia, T.J.; Theunis, C.; Nanjunda, R.; Teplyakov, A.; Ernst, R.; Wu, S.-J.; Luo, J.; Borgers, M.; Vandermeeren, M.; et al. Discovery and Functional Characterization of HPT3, a Humanized Anti-Phospho Tau Selective Monoclonal Antibody. JAD 2020, 77, 1397–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ameijde, J.; Crespo, R.; Janson, R.; Juraszek, J.; Siregar, B.; Verveen, H.; Sprengers, I.; Nahar, T.; Hoozemans, J.J.; Steinbacher, S.; et al. Enhancement of Therapeutic Potential of a Naturally Occurring Human Antibody Targeting a Phosphorylated Ser422 Containing Epitope on Pathological Tau. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintjens, R.; Wieruszeski, J.-M.; Drobecq, H.; Rousselot-Pailley, P.; Buée, L.; Lippens, G.; Landrieu, I. 1H NMR Study on the Binding of Pin1 Trp-Trp Domain with Phosphothreonine Peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 25150–25156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abskharon, R.; Sawaya, M.R.; Boyer, D.R.; Cao, Q.; Nguyen, B.A.; Cascio, D.; Eisenberg, D.S. Cryo-EM Structure of RNA-Induced Tau Fibrils Reveals a Small C-Terminal Core That May Nucleate Fibril Formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119952119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, P.M.; Boyer, D.R.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Sawaya, M.R.; Cascio, D.; Murray, K.; Gonen, T.; Eisenberg, D.S. Structure-Based Inhibitors of Tau Aggregation. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipps, C.; Kelly, H.R.; Dahl, P.J.; Yi, S.M.; Vu, D.; Boyer, D.; Glynn, C.; Sawaya, M.R.; Eisenberg, D.; Batista, V.S.; et al. Intrinsic Electronic Conductivity of Individual Atomically Resolved Amyloid Crystals Reveals Micrometer-Long Hole Hopping via Tyrosines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2014139118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, D.R.; Eisenberg, D.S. A Structure-Based Model for the Electrostatic Interaction of the N-Terminus of Protein Tau with the Fibril Core of Alzheimer’s Disease Filaments. bioRxiv 2018, 484279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, P.M.; Boyer, D.R.; Murray, K.A.; Yang, T.P.; Bentzel, M.; Sawaya, M.R.; Rosenberg, G.; Cascio, D.; Williams, C.K.; Newell, K.L.; et al. Structure-Based Inhibitors Halt Prion-like Seeding by Alzheimer’s Disease–and Tauopathy–Derived Brain Tissue Samples. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 16451–16464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, M.; Jiang, L.; Cheng, P.-N.; Park, J.; Sawaya, M.R.; Pensalfini, A.; Gou, D.; Berk, A.J.; Glabe, C.G.; et al. Out-of-Register β-Sheets Suggest a Pathway to Toxic Amyloid Aggregates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20913–20918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaya, M.R.; Sambashivan, S.; Nelson, R.; Ivanova, M.I.; Sievers, S.A.; Apostol, M.I.; Thompson, M.J.; Balbirnie, M.; Wiltzius, J.J.W.; McFarlane, H.T.; et al. Atomic Structures of Amyloid Cross-β Spines Reveal Varied Steric Zippers. Nature 2007, 447, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, M.; Sawaya, M.R.; Faull, K.F.; Laganowsky, A.; Jiang, L.; Sievers, S.A.; Liu, J.; Barrio, J.R.; Eisenberg, D. Towards a Pharmacophore for Amyloid. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltzius, J.J.W.; Landau, M.; Nelson, R.; Sawaya, M.R.; Apostol, M.I.; Goldschmidt, L.; Soriaga, A.B.; Cascio, D.; Rajashankar, K.; Eisenberg, D. Molecular Mechanisms for Protein-Encoded Inheritance. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cruz, M.J.; Hattne, J.; Shi, D.; Seidler, P.; Rodriguez, J.; Reyes, F.E.; Sawaya, M.R.; Cascio, D.; Weiss, S.C.; Kim, S.K.; et al. Atomic-Resolution Structures from Fragmented Protein Crystals with the CryoEM Method MicroED. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Eisenberg, D.S.; Crowther, R.A. Propagation of Tau Aggregates and Neurodegeneration. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 40, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Ghetti, B.; Goedert, M. Classification of Diseases with Accumulation of Tau Protein. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobio. 2022, 48, e12792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglinger, G.U.; Respondek, G.; Kovacs, G.G. New Classification of Tauopathies. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 174, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G.; Jakes, R.; Crowtherp, R.A.; Vanmechelen, E.; Probst, A.; Götz, J.; Bürki, K.; Cohen, P. Molecular Dissection of the Paired Helical Filament. Neurobiol. Aging 1995, 16, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buée, L.; Delacourte, A. Comparative Biochemistry of Tau in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy, Corticobasal Degeneration, FTDP-17 and Pick’s Disease. Brain Pathol. 1999, 9, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, T.; Ikeda, K.; Akiyama, H.; Tsuchiya, K.; Iritani, S.; Ishiguro, K.; Yagishita, S.; Oda, T.; Odawara, T.; Iseki, E. Different Immunoreactivities of the Microtubule-Binding Region of Tau and Its Molecular Basis in Brains from Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease, Pick’s Disease, Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Degeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 2003, 105, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.C.; Roemer, S.; Petrucelli, L.; Dickson, D.W. Cellular and Pathological Heterogeneity of Primary Tauopathies. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, S.S.; Maina, M.B.; Marshall, K.E.; Al-Hilaly, Y.K.; Harrington, C.R.; Wischik, C.M.; Serpell, L.C. Tau Filament Self-Assembly and Structure: Tau as a Therapeutic Target. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 590754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, P.; Park, H.; Baumann, M.; Dunlop, J.; Frydman, J.; Kopito, R.; McCampbell, A.; Leblanc, G.; Venkateswaran, A.; Nurmi, A.; et al. Protein Misfolding in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Implications and Strategies. Transl. Neurodegener. 2017, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Arseni, D.; Zhang, W.; Huang, M.; Lövestam, S.; Schweighauser, M.; Kotecha, A.; Murzin, A.G.; Peak-Chew, S.Y.; Macdonald, J.; et al. Cryo-EM Structures of Amyloid-β 42 Filaments from Human Brains. Science 2022, 375, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M. Tau Filaments in Neurodegenerative Diseases. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 2383–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidenmüller, J.; Fath, T.; Hellwig, A.; Reed, J.; Sontag, E.; Brandt, R. Structural and Functional Implications of Tau Hyperphosphorylation: Information from Phosphorylation-Mimicking Mutated Tau Proteins. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 13166–13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.M.; Binder, L.I. Free Fatty Acids Stimulate the Polymerization of Tau and Amyloid Beta Peptides. In Vitro Evidence for a Common Effector of Pathogenesis in Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 150, 2181–2195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, K.M.; Carroll, E.C.; Thwin, A.C.; Quddus, A.Y.; Hodges, P.; Southworth, D.R.; Gestwicki, J.E. Chemical Features of Polyanions Modulate Tau Aggregation and Conformational States. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, jacs.2c08004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Congdon, E.E.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Kuret, J. Tau Isoform Composition Influences Rate and Extent of Filament Formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 20711–20719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

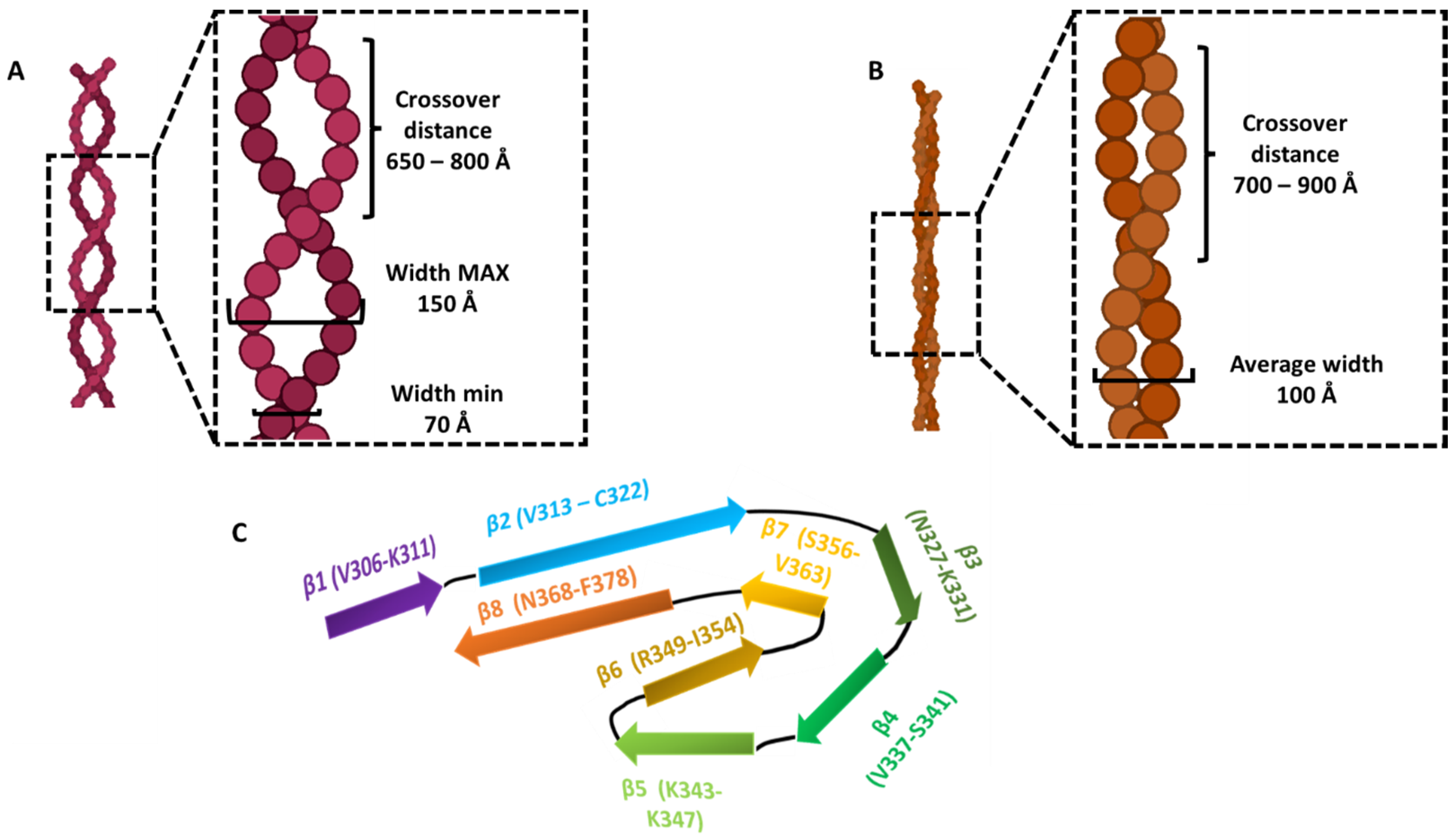
| Type of Filaments | Width | Crossover Distance | Helical Rise | Helical Twist | Core Residues | Tau Repeats | Secondary Structure Elements | Sample Type | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHF | 70–150 Å | 650–800 Å | 4.7 Å | −1° | V306–F378 | R3, R4 | 8 β-sheets | Ex vivo AD patient, tau full-length | [35,36,55] |
| SF | 100 Å | 700–900 Å | 4.7 Å | −1° | V306–F378 | R3, R4 | 8 β-sheets | Ex vivo AD patient, tau full-length | [35,36,55] |
| Twisted | - | 829 Å | 179.16° | 2.4° | E391-A426 | C-terminal | 5 β-sheets | In vitro (RNA induced aggregation), tau full-length | [71] |
| Not twisted | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | In vitro (RNA induced aggregation), tau full-length | [71] |
| Snake | 40–100 Å | 650 Å | - | −1.26° | G272–K330 | R2, R3 | 6 β-strands | In vitro (heparin induced aggregation), tau full-length | [47] |
| Twister | 80 Å | 250 Å | - | −3.38° | K274–K321 | R2, R3 (half) | 4 β-strands | In vitro (heparin induced aggregation), tau full-length | [47] |
| Hose | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | In vitro (heparin induced aggregation), tau full-length | [47] |
| Jagged | 50–90 Å | 450 Å | - | −2.03° | K274–K321 | R2, R3 (half) | 3 β-strands | In vitro (heparin induced aggregation), tau full-length | [47] |
| 2N3R tau filaments | 50–120 Å | 800 Å | - | −1.05° | K274–G330 and G272-G330 without V275–S305 | R3 | 4 β-strands | In vitro (heparin induced aggregation), tau 2N3R | [47] |
| 3R and tau 297–391 ribbon straight | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | In vitro 3R and tau 297–391 | [54] |
| 3R and tau 297–391 twisted type I | 140 Å | 790 Å | - | - | - | - | - | In vitro 3R and tau 297–391 | [54] |
| 3R and tau 297–391 twisted type II | - | 1300 Å | - | - | - | - | - | In vitro 3R and tau 297–391 | [54] |
| tau 297–391 ribbon straight | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | In vitro tau 297–391 | [54] |
| tau 297–391 twisted type I | 130 Å | 760 Å | - | - | - | - | - | In vitro tau 297–391 | [54] |
| tau 297–391 twisted type II | - | 1100–1860 Å | - | - | - | - | - | In vitro tau 297–391 | [54] |
| 3R and tau 297–391 PHF-like | - | 800 Å | 4.80 Å | - | - | - | - | In vitro 3R and tau 297–391 | [54] |
| tau 297–391 spindle-like | - | 750 Å | 4.82 Å | - | G304–H362 | R3, R4 | 7 β-strands | In vitro tau 297–391 | [54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinzi, L.; Bisi, N.; Sorbi, C.; Franchini, S.; Tonali, N.; Rastelli, G. Insights into the Structural Conformations of the Tau Protein in Different Aggregation Status. Molecules 2023, 28, 4544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114544
Pinzi L, Bisi N, Sorbi C, Franchini S, Tonali N, Rastelli G. Insights into the Structural Conformations of the Tau Protein in Different Aggregation Status. Molecules. 2023; 28(11):4544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114544
Chicago/Turabian StylePinzi, Luca, Nicolò Bisi, Claudia Sorbi, Silvia Franchini, Nicolò Tonali, and Giulio Rastelli. 2023. "Insights into the Structural Conformations of the Tau Protein in Different Aggregation Status" Molecules 28, no. 11: 4544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114544
APA StylePinzi, L., Bisi, N., Sorbi, C., Franchini, S., Tonali, N., & Rastelli, G. (2023). Insights into the Structural Conformations of the Tau Protein in Different Aggregation Status. Molecules, 28(11), 4544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114544








