Adsorption of Different Ionic Types of Polyacrylamide on Montmorillonite Surface: Insight from QCM-D and Molecular Dynamic Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. QCM-D Results
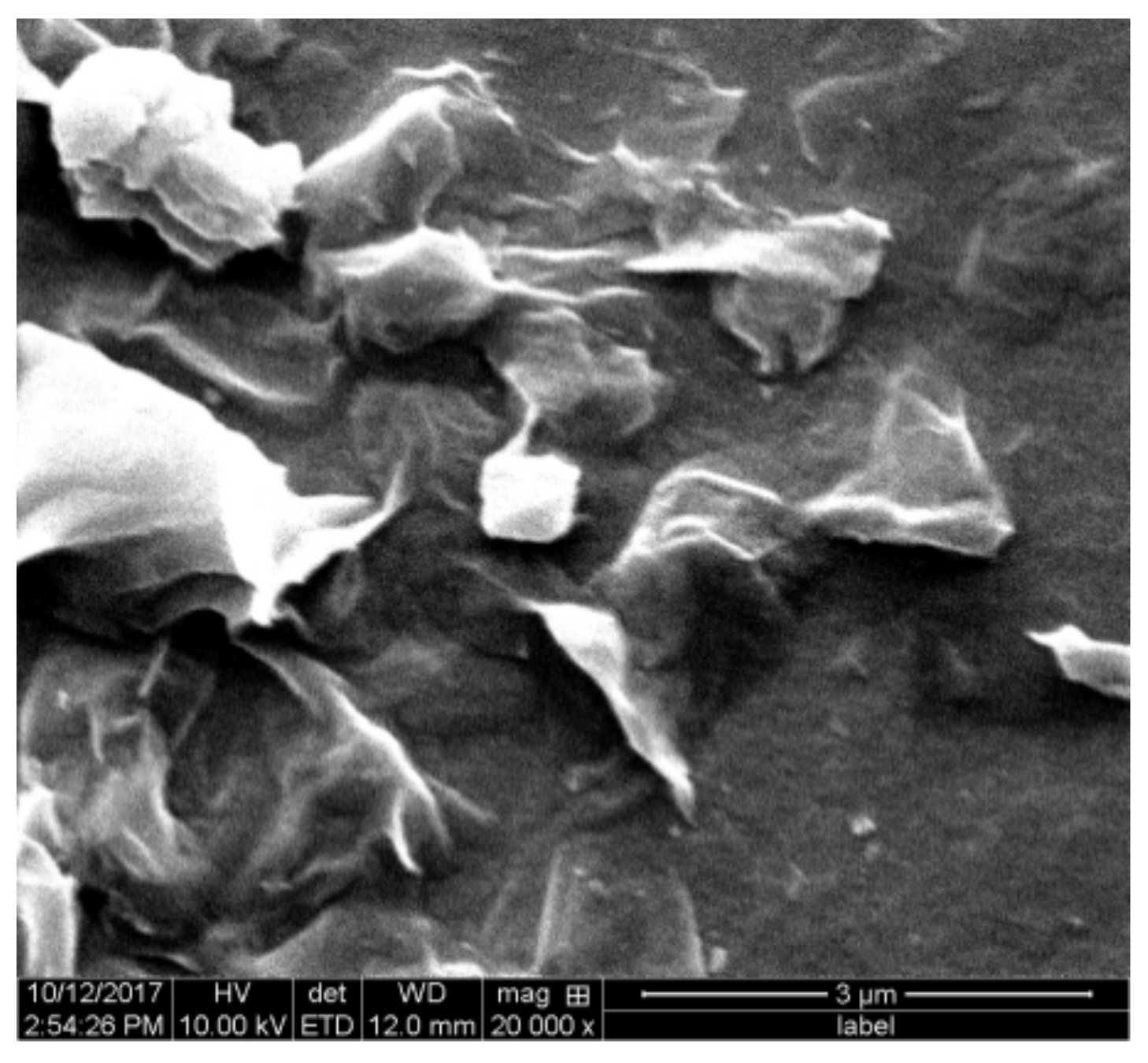
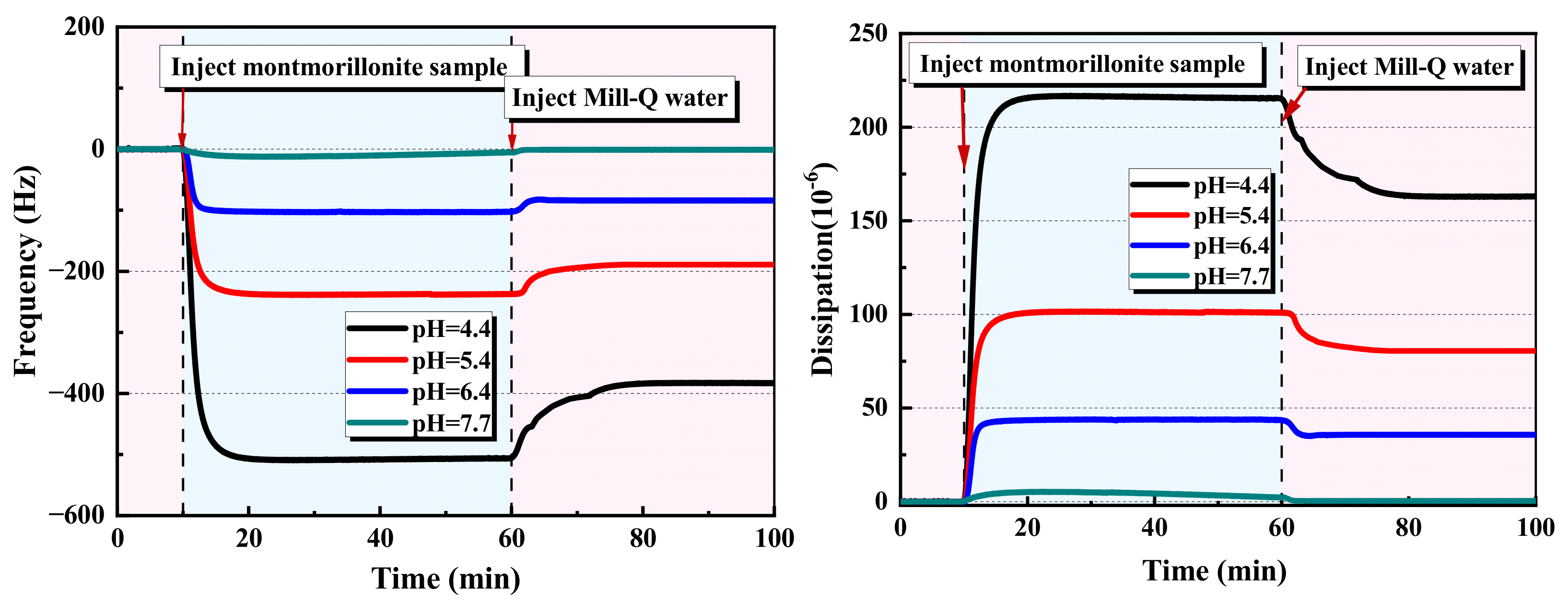
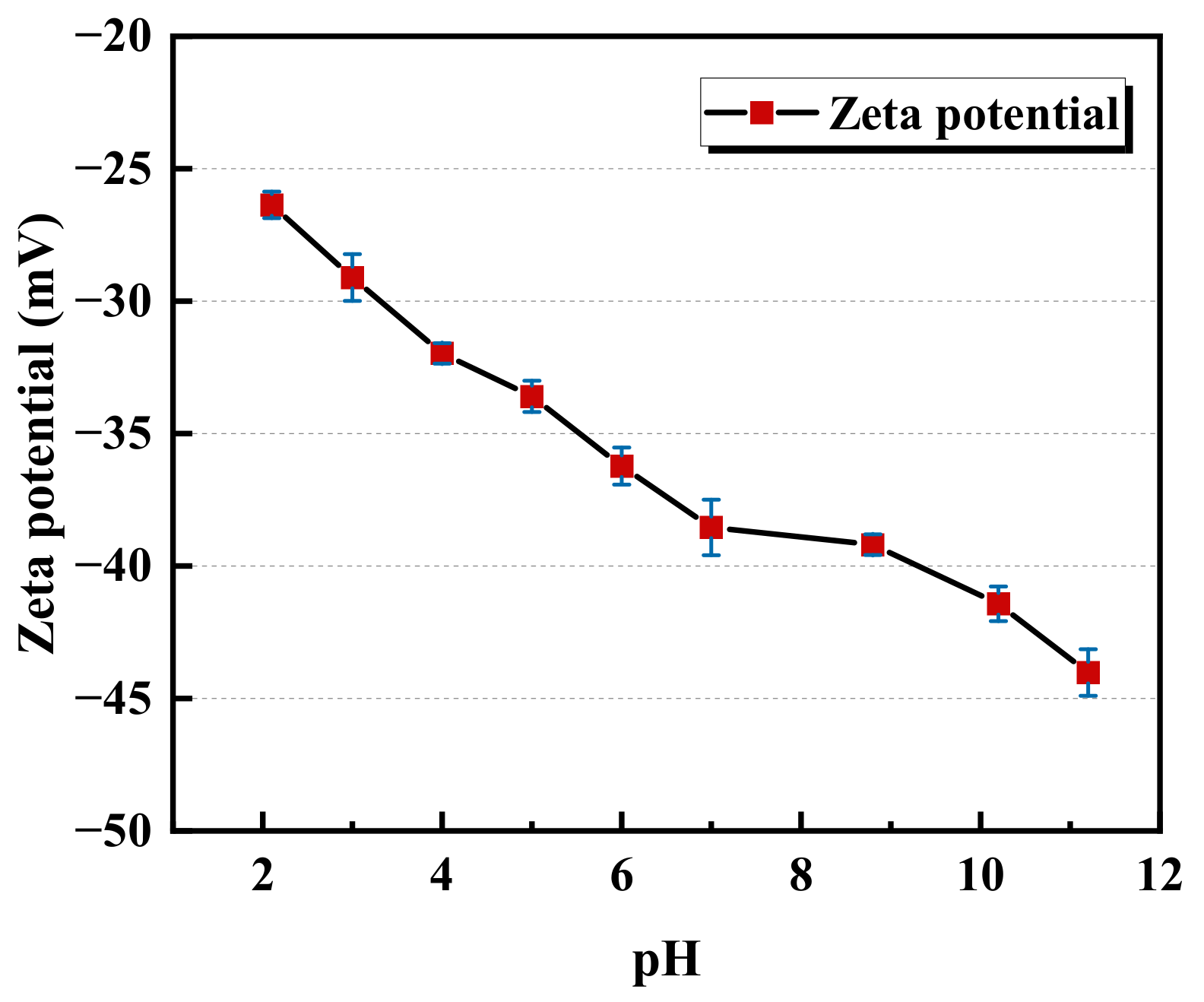
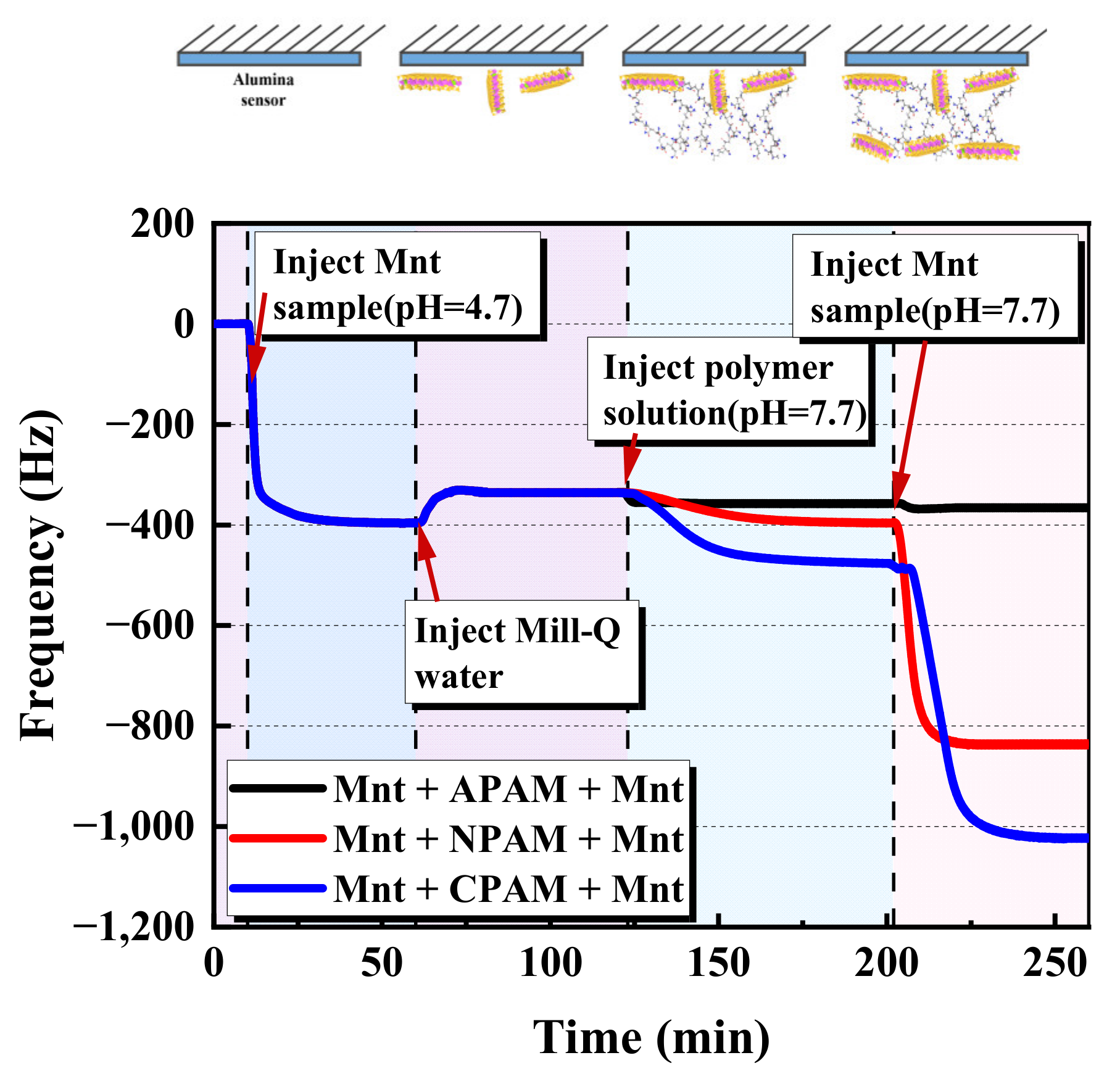
2.1.1. QCM-D Results of the Montmorillonite Adsorption on the Alumina Sensor
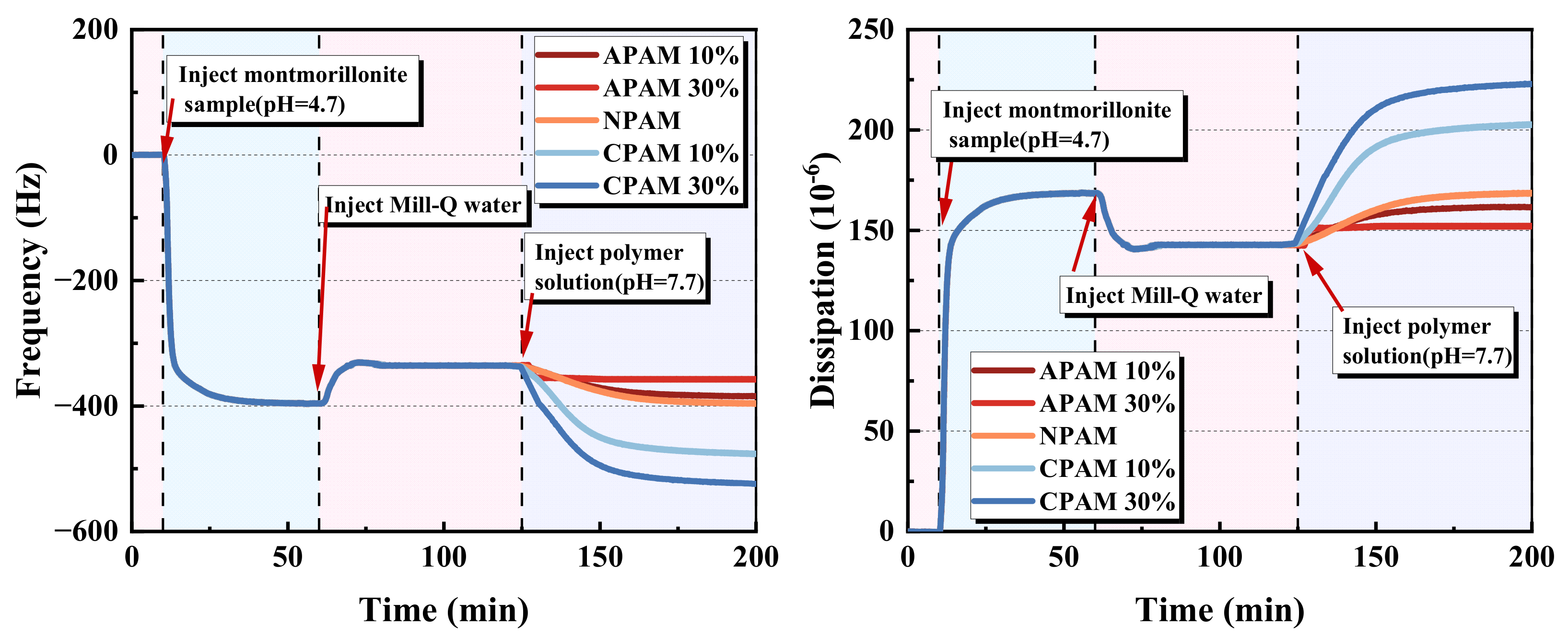
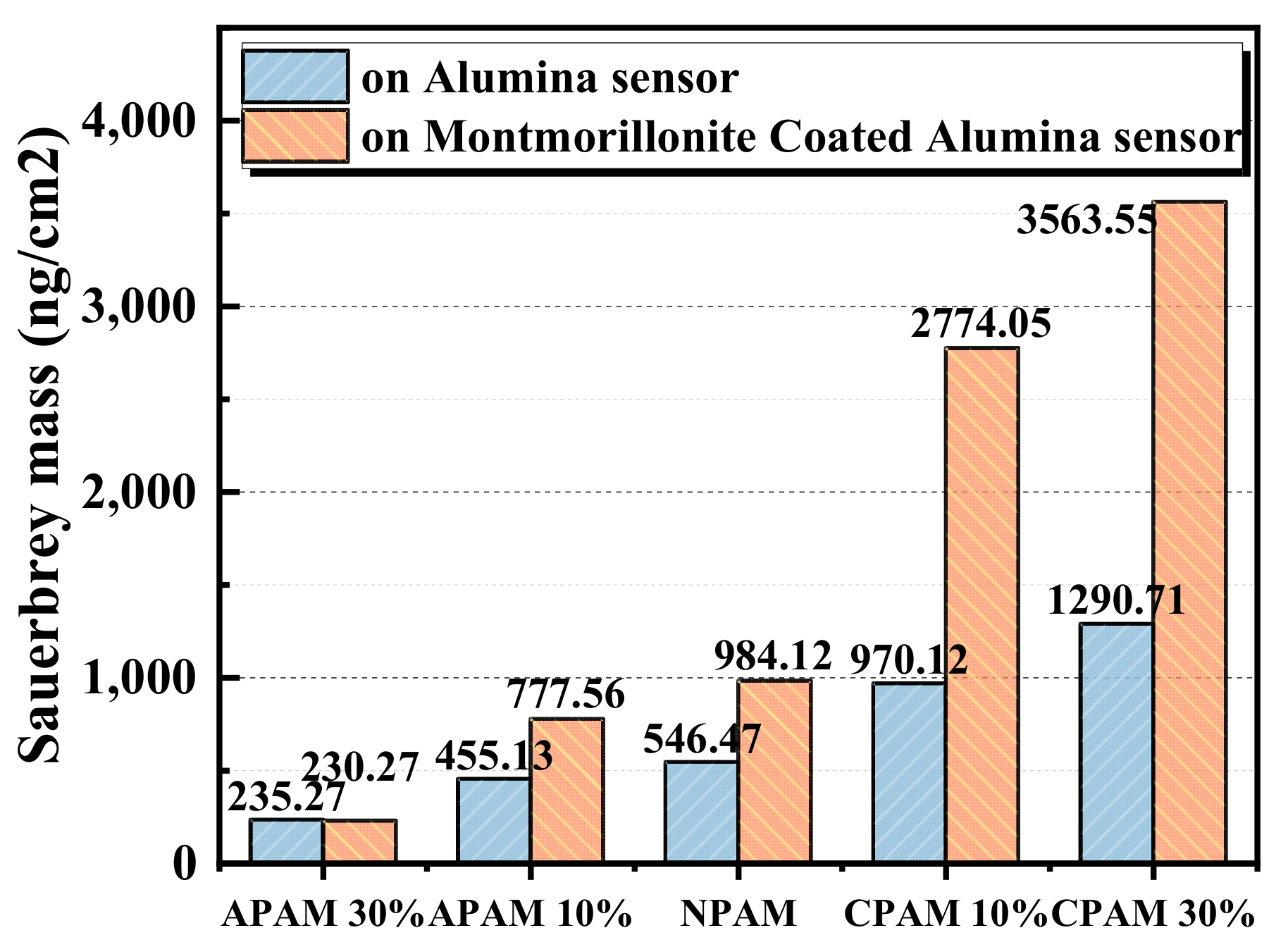
2.1.2. QCM-D Results of Polymers Adsorption on the Montmorillonite Pre-Adsorbed on the Alumina Sensor
2.1.3. QCM-D Results of the Bridging Effect of Polymers on the Montmorillonite Particles
2.2. MD Simulation Results
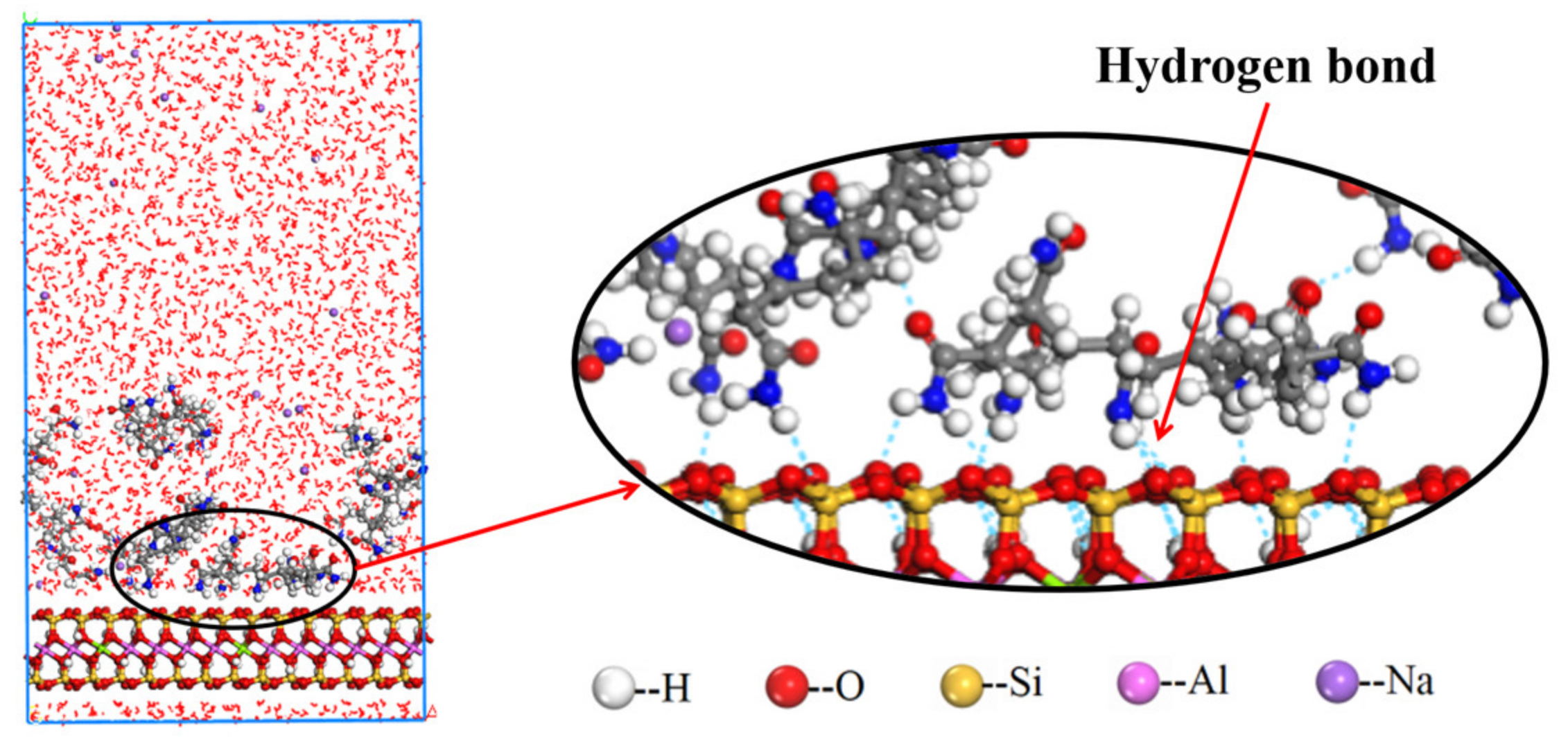
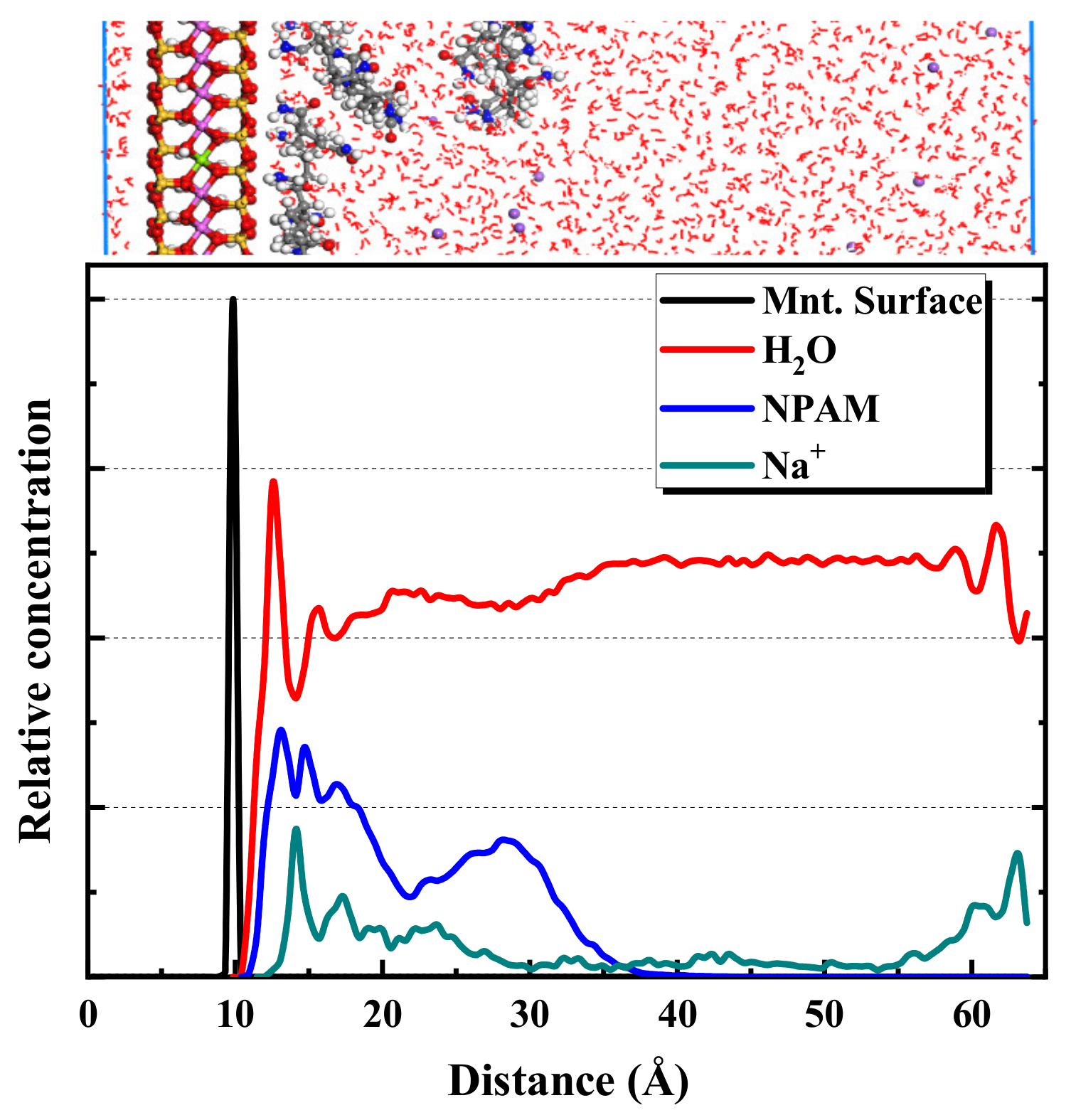
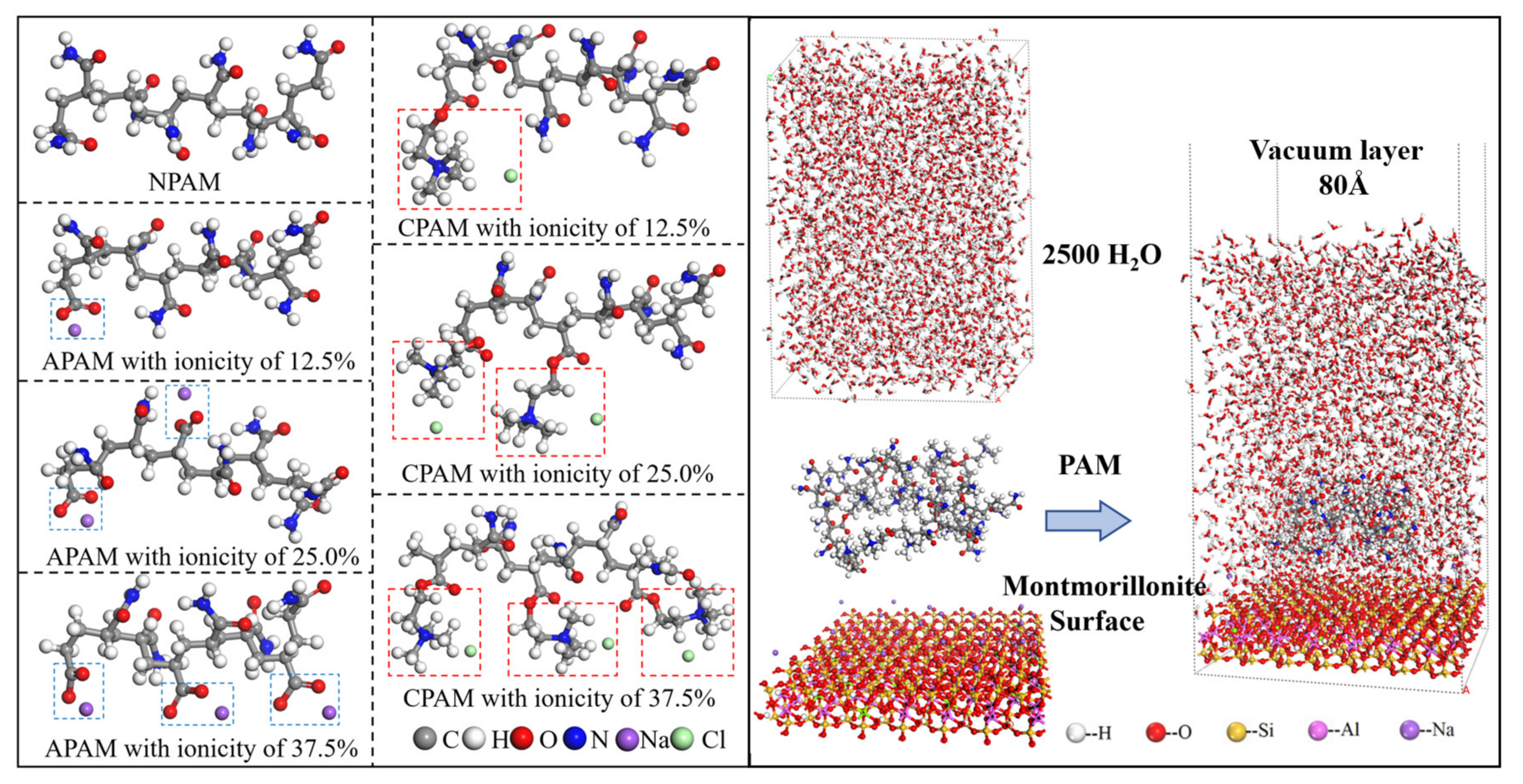
2.2.1. MD Simulation Results of NPAM Adsorption on Montmorillonite
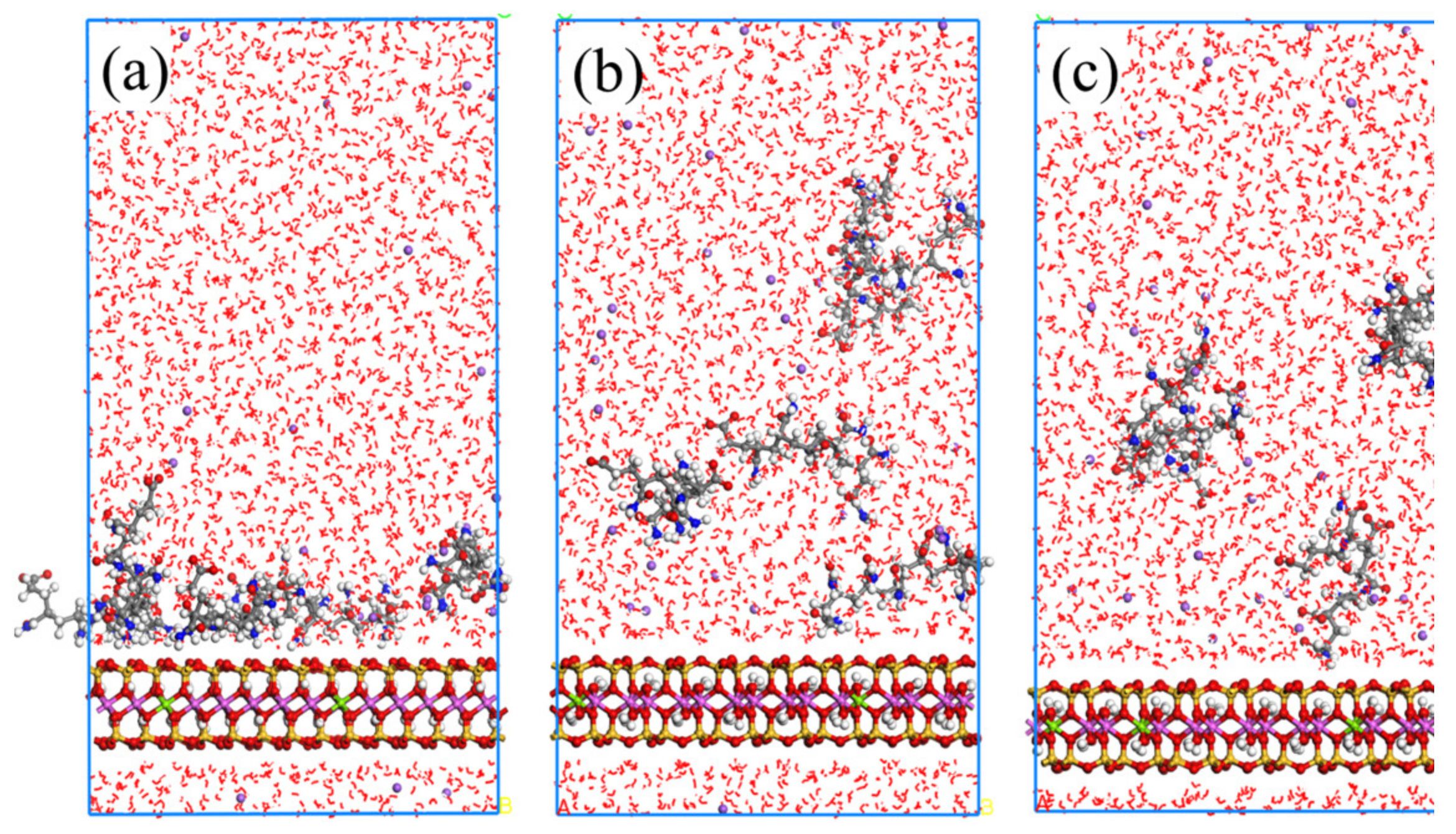
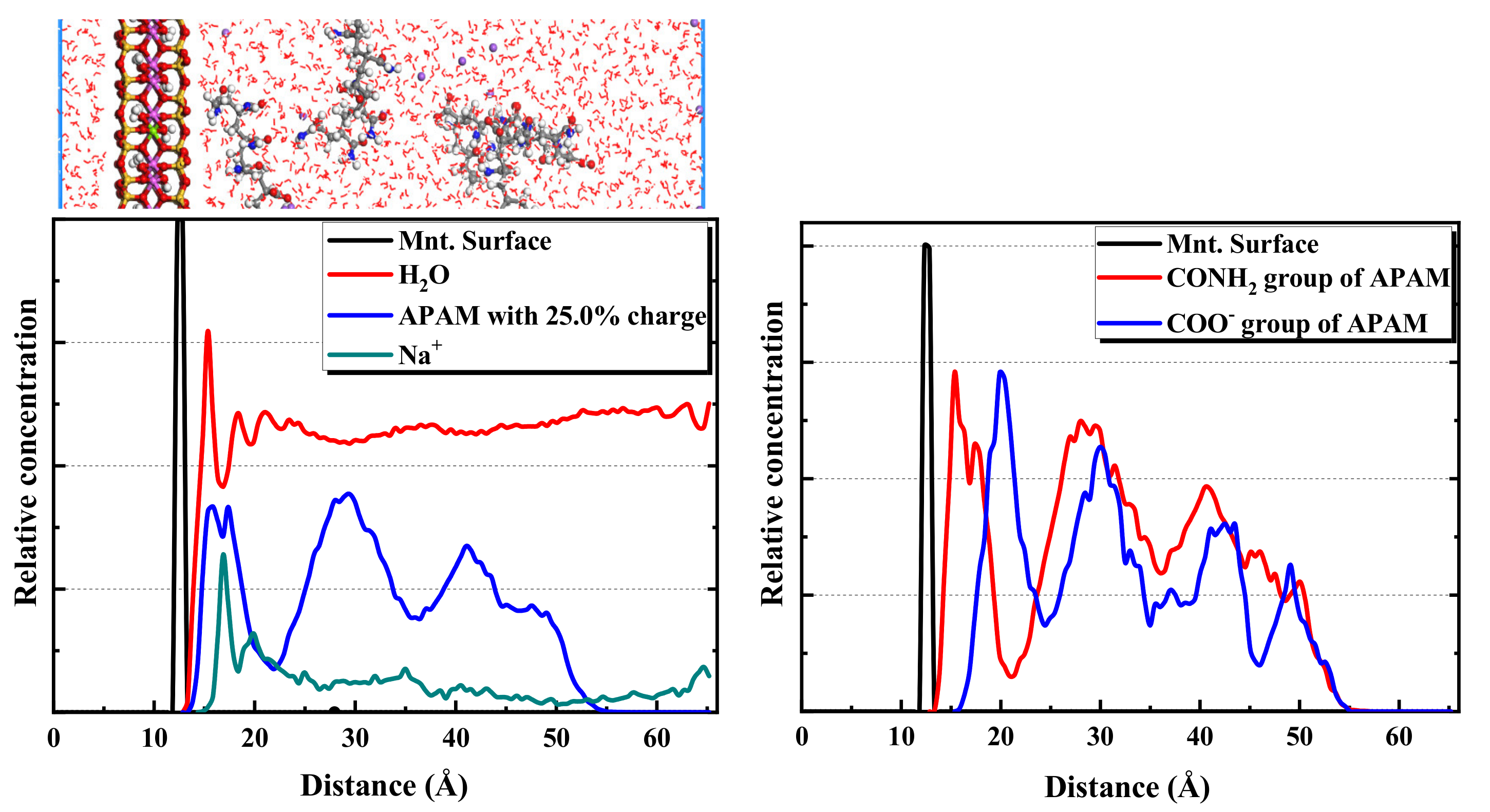
2.2.2. MD Simulation Results of APAM Adsorption on Montmorillonite
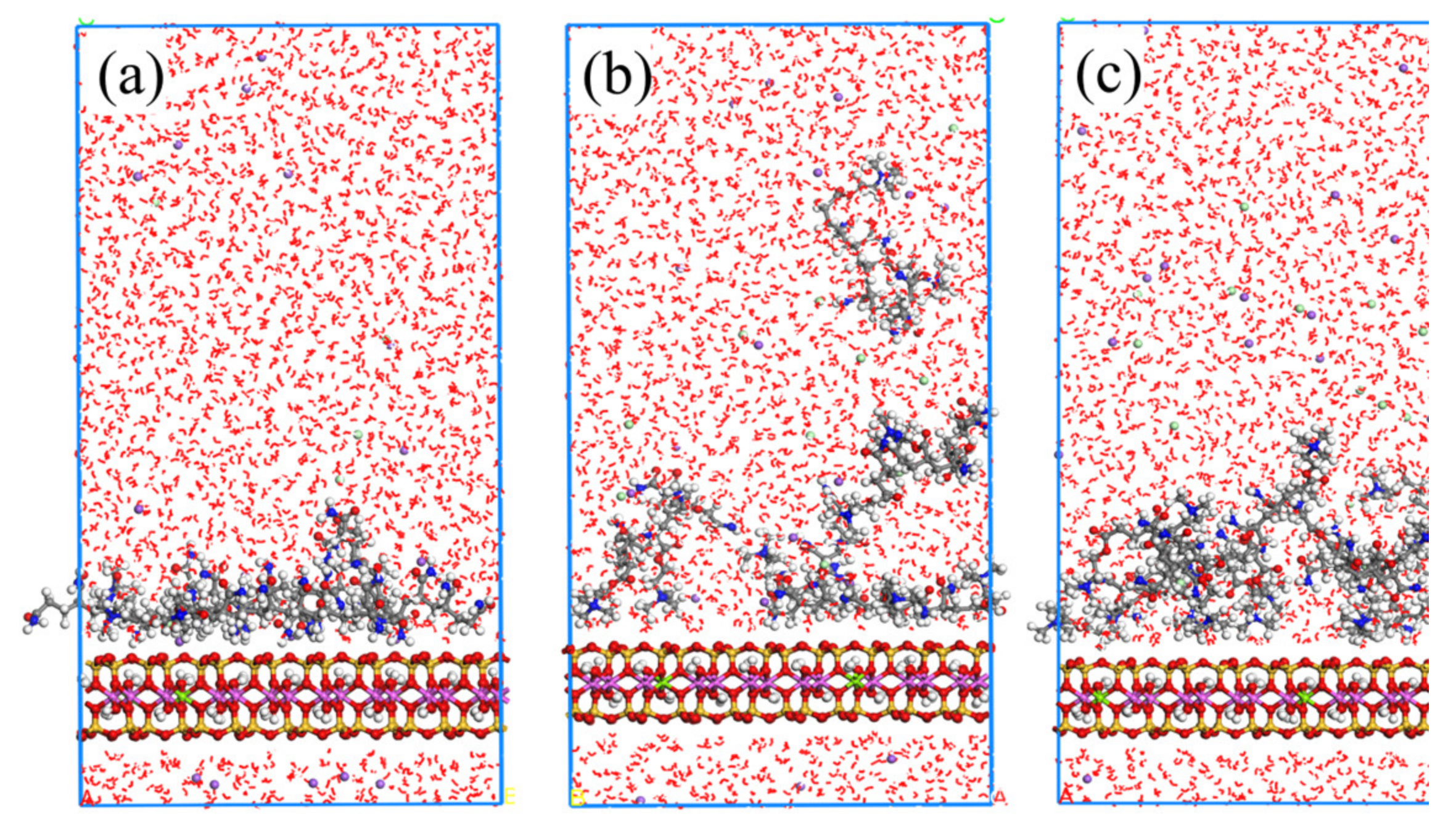
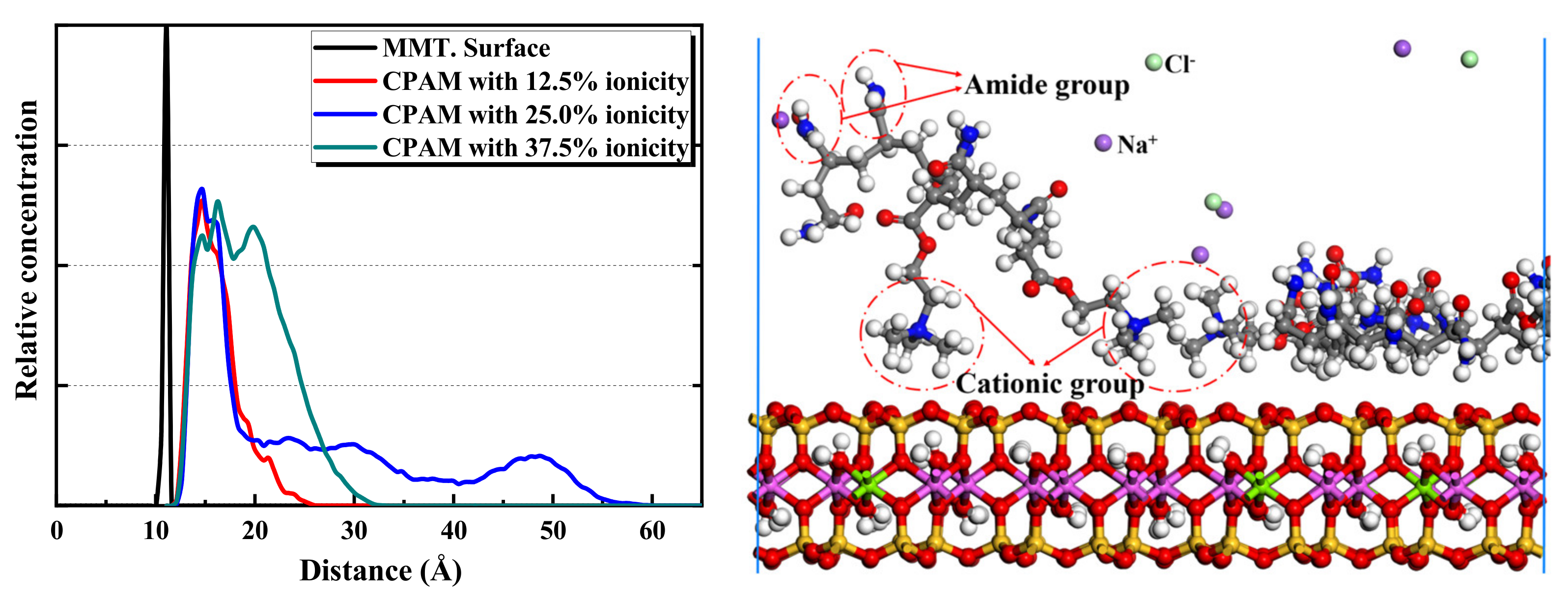
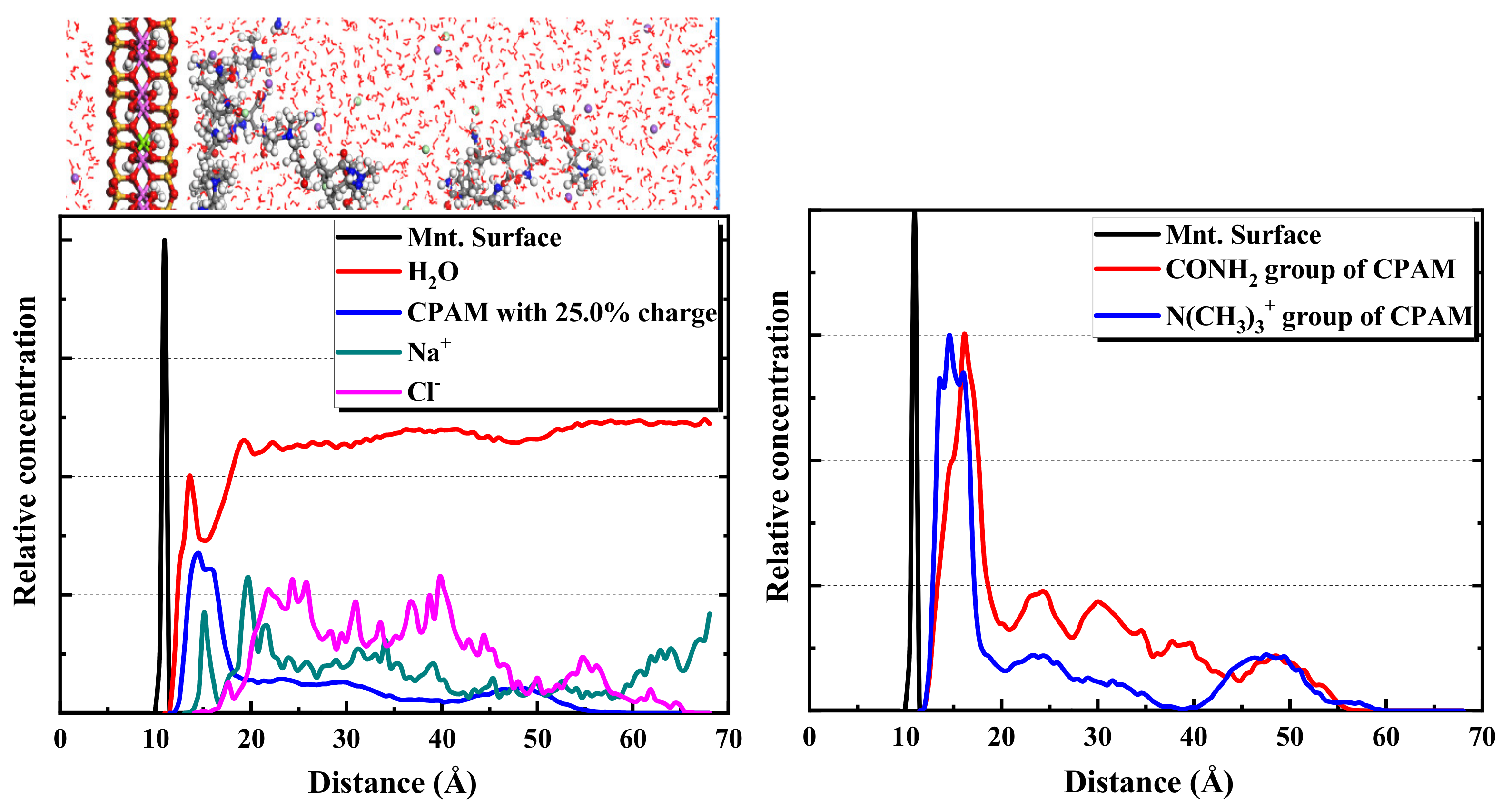
2.2.3. MD Simulation Results of CPAM Adsorption on Montmorillonite
3. Materials and Methods
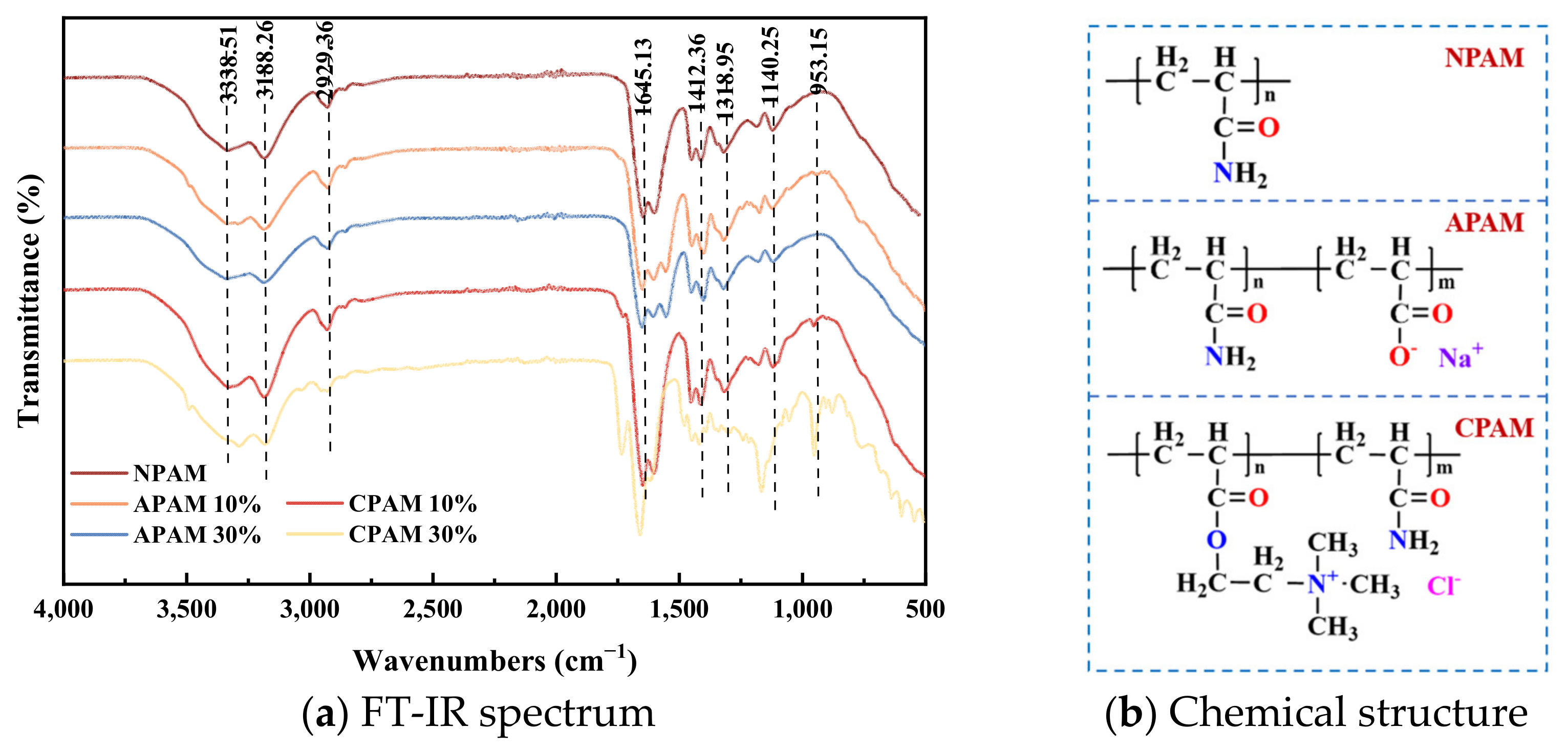
3.1. Materials
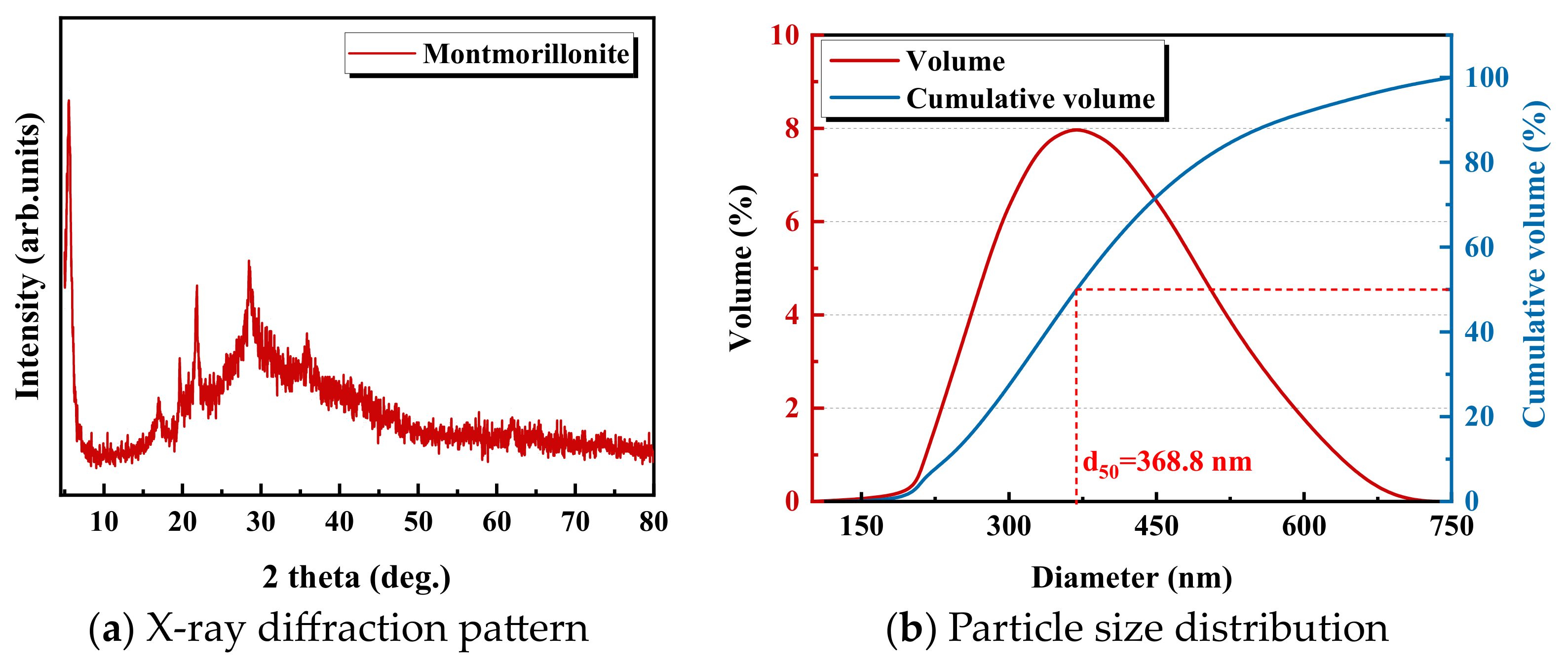
3.2. Preparing the Montmorillonite Suspension
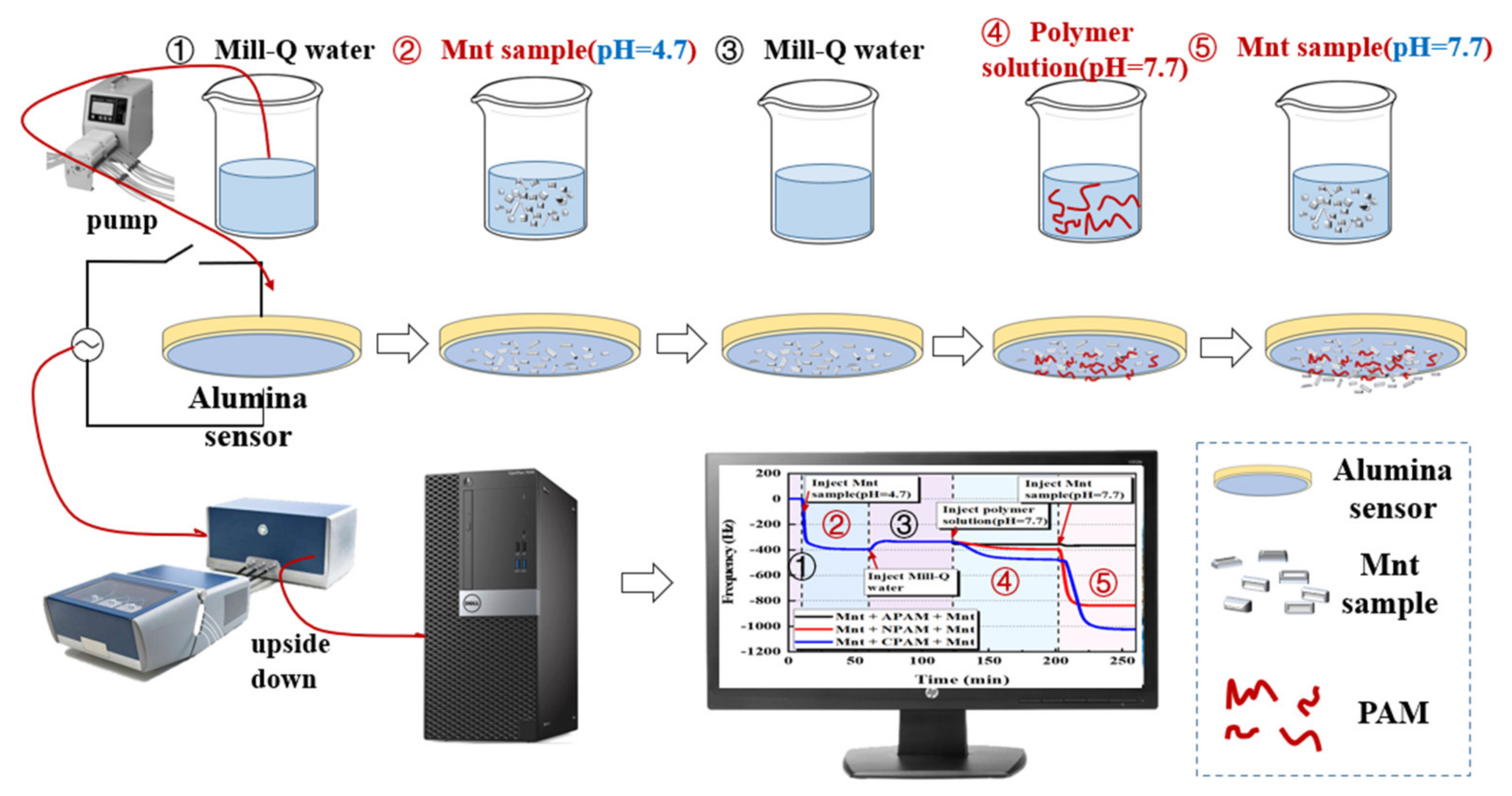
3.3. QCM-D Experiments
3.3.1. Adsorption Kinetic of the Montmorillonite on the Alumina Sensor
3.3.2. Adsorption Kinetic of Polymers on the Montmorillonite Pre-Adsorbed on the Alumina Sensor
3.4. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- A decreasing pH results in an increase in the adsorption mass of montmorillonite on the alumina surface. This contributes to the enhancement of the electrostatic attraction between the positive alumina surface and the negative montmorillonite particles caused by the change in the zeta potential. Considering the alumina and pre-adsorbed montmorillonite particles’ alumina surface, the adsorption mass of polymers is ranked as CPAM > NPAM >APAM.
- (2)
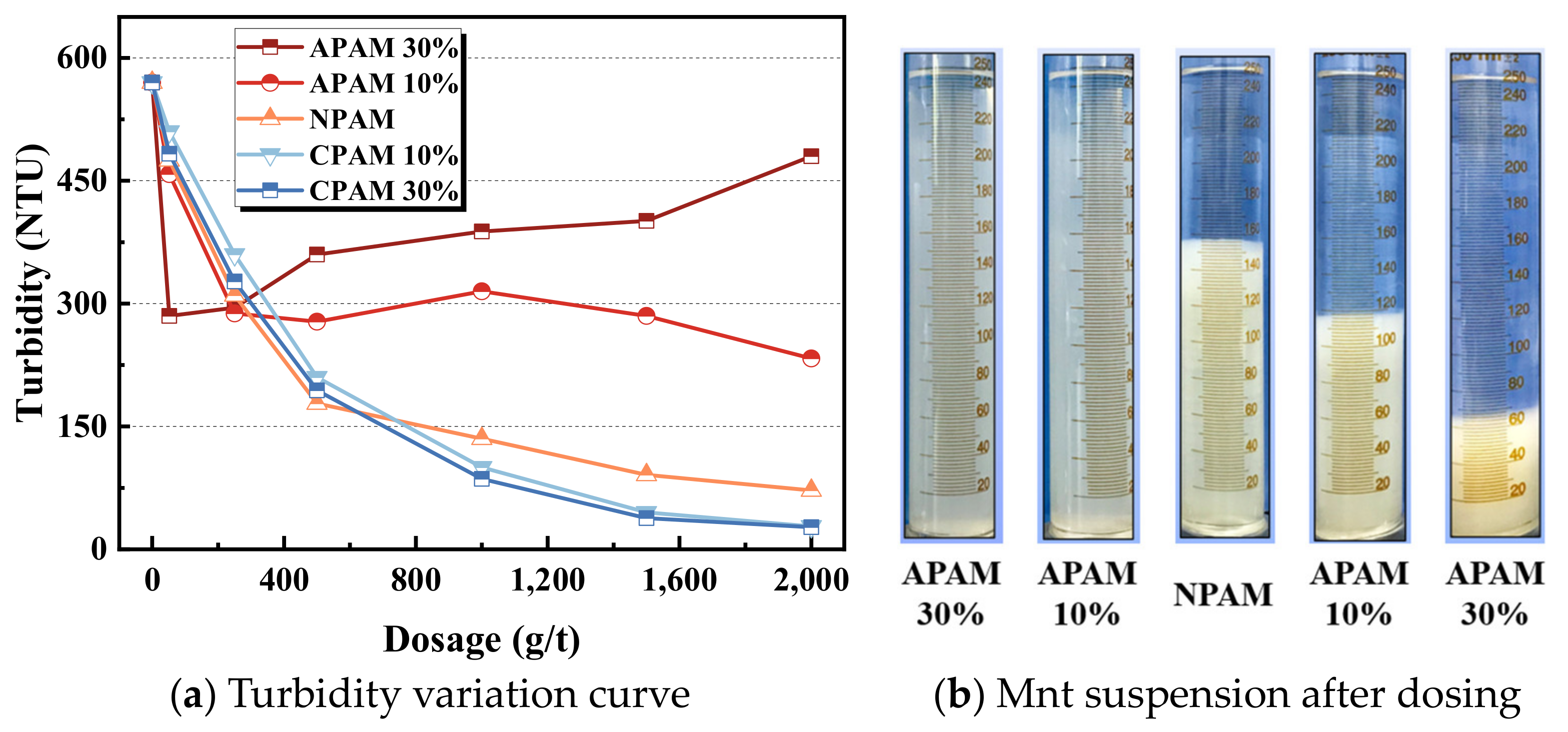
- Moreover, CPAM has the strongest bridging effect on montmorillonite nanoparticles, followed by NPAM, whereas APAM can hardly bridge the montmorillonite nanoparticles. The clarification test shows that when the dosage is high enough, the turbidity of CPAM is the lowest and the clarification effect is the best. This is consistent with the adsorption results from QCM-D.
- (3)
- The ionicity density has a great influence on the adsorption of polyacrylamides and their derivatives. The cationic functional group N(CH3)3+ has the strongest attraction interaction with the montmorillonite surface, followed by the hydrogen bonding interaction of the amide functional group CONH2. The anionic functional group COO- has a repulsive interaction.
- (4)
- Furthermore, CPAM with different ionicity densities can be adsorbed on the montmorillonite surface through the N(CH3)3+ and CONH2 functional groups. It is more interracially active and tends to concentrate near the montmorillonite surface than the water layer. Regarding APAM, when the ionicity is low, CONH2 is dominant, and it can be adsorbed on the montmorillonite. Although the ionicity is high, the anionic functional group is dominant; thus, the adsorption is weakened.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sun, W.; Zhou, S.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y. Synthesis and evaluation of cationic flocculant P(DAC-PAPTAC-AM) for flocculation of coal chemical wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejtemaei, M.; Ramli, S.; Osborne, D.; Nguyen, A.V. Synergistic effects of surfactant-flocculant mixtures on ultrafine coal dewatering and their linkage with interfacial chemistry. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Harbottle, D.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z. Current state of fine mineral tailings treatment: A critical review on theory and practice. Miner. Eng. 2014, 58, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, T.; Gao, X.; Liu, Q. Separation of ultra-fine hematite and quartz particles using asynchronous flocculation flotation. Miner. Eng. 2021, 164, 106817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didehban, K.; Mosadegh, M.; Adelkhan, H.; Hayasi, M.; Golikand, A.N.; Amirshaghaghi, A. New Superabsorbent Nanocomposites based on Polyacrylamide/clay: Synthesis, Characterization and Investigation of their Adsorption Properties. J. Polym. Mater. 2014, 31, 347–358. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Min, F.; Liu, L.; Chen, J. A periodic DFT study of adsorption of water on sodium-montmorillonite (001) basal and (010) edge surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Gan, Y.; Han, X.; Liu, W.; Xin, H. Micromechanism of partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide molecule agglomeration morphology and its impact on the stability of crude oil–water interfacial film. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 214, 110492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, G. The use of polyacrylamides in mineral processing. Miner. Eng. 1992, 5, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Robinson, J.; Chong, M.F. A review on application of flocculants in wastewater treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2014, 92, 489–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.; Barany, S. Adsorption and flocculation by polymers and polymer mixtures. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 169, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatat, R.S.; Niazi, S.K.; Batati, F.S.A. Synthetic Polyelectrolytes Based on Polyacrylamide: Non-ionic, Anionic and Cationic Polyacrylamides and Their Applications in Water and Wastewater Treatment: Literature Review. Chem. Sci. Int. J. 2019, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.M.R.; Nasser, M.S.; Hussein, I.; Benamor, A.; Onaizi, S.A.; Qiblawey, H. Influence of polyelectrolytes and other polymer complexes on the flocculation and rheological behaviors of clay minerals: A comprehensive review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 187, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Min, F.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Lv, K. Adsorption of different PAM structural units on kaolinite (0 0 1) surface: Density functional theory study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 504, 144324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sun, L.; Liu, X. Effect of degree of hydrolysis of polyacrylamide on the micromorphology of its solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverry, L.; Estrada, D.; Toledo, P.G.; Gutierrez, L. The depressing effect of an anionic polyacrylamide on molybdenite flotation and the importance of polymer anionicity. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 629, 127506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, H.; Keren, R. Anionic polyacrylamide polymer adsorption by pyrophyllite and montmorillonite. Clays Clay Miner. 2003, 51, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Dixon, J.B.; White, G.N. Adsorption of Polyacrylamide on Smectite, Illite, and Kaolinite. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Ye, L. In situ polymerization of cationic polyacrylamide/montmorillonite composites and its flocculation characteristics. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2016, 29, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimkhan, A.M. Adsorption of polyacrylic acid and polyacrylamide on montmorillonite. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A+ 2013, 87, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, H.; Keren, R. Anionic Polyacrylamide Polymers Effect on Rheological Behavior of Sodium-Montmorillonite Suspensions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohay, H.; Bilkis, I.I.; Mishael, Y.G. Effect of polycation charge density on polymer conformation at the clay surface and consequently on pharmaceutical binding. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2019, 552, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Min, F.; Chen, J.; Fang, F.; Liu, C. Adsorption mechanism insights into CPAM structural units on kaolinite surfaces: A DFT simulation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 197, 105719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Gong, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, C.; Zeng, H. Adsorption of hydrophobically modified polyacrylamide P(AM-NaAA-C(16)DMAAC) on model coal and clay surfaces and the effect on selective flocculation of fine coal. Miner. Eng. 2019, 142, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagha, L.; Wang, S.; Yan, L.; Xu, Z.; Masliyah, J. Probing Adsorption of Polyacrylamide-Based Polymers on Anisotropic Basal Planes of Kaolinite Using Quartz Crystal Microbalance. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3989–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zou, W.; Wang, T.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C. Adsorption and interaction mechanisms of Chi-g-P(AM-DMDAAC) assisted settling of kaolinite in a two-step flocculation process. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hashmi, A.R.; Luckham, P.F.; Heng, J.Y.Y.; Al-Maamari, R.S.; Zaitoun, A.; Al-Sharji, H.H.; Al-Wehaibi, T.K. Adsorption of High-Molecular-Weight EOR Polymers on Glass Surfaces Using AFM and QCM-D. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 2437–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zeng, H.; Tang, T. Synergetic adsorption of polymers on montmorillonite: Insights from molecular dynamics simulations. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 193, 105654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Lv, K.; Min, F.; Chen, J.; Liu, C. A new insight into the adsorption behavior of NPAM on kaolinite/water interface: Experimental and theoretical approach. Fuel 2021, 303, 121299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feke, D.L.; Prabhu, N.D.; Mann, J.A.; Mann, J.A. A formulation of the short-range repulsion between spherical colloidal particles. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 5735–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Kobayashi, M.; Adachi, Y. Interfacial characterization of α-alumina with small surface area by streaming potential and chromatography. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 436, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Gao, B.; Ren, J.; Li, A.; Yang, H. Coagulation/flocculation in dewatering of sludge: A review. Water Res. 2018, 143, 608–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, M.; Barbeau, B. Dual starch–polyacrylamide polymer system for improved flocculation. Water Res. 2017, 124, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabah, E.; Cengiz, I. An evaluation procedure for flocculation of coal preparation plant tailings. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedoy, D.R.L.; Soares, J.B.P. Water-soluble polymers for oil sands tailing treatment: A Review. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 93, 888–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabah, E.; Aciksoz, C. Flocculation Performance of Fine Particles in Travertine Slime Suspension. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2012, 48, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, I.; Sabah, E.; Ozgen, S.; Akyildiz, H. Flocculation of fine particles in ceramic wastewater using new types of polymeric flocculants. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Han, C.; Lin, Z.; Masliyah, J.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z. Role of Preconditioning Cationic Zetag Flocculant in Enhancing Mature Fine Tailings Flocculation. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 5223–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Rechendorff, K.; Hovgaard, M.B.; Foss, M.; Chevallier, J.; Besenbacher, F. Bovine serum albumin adsorption on nano-rough platinum surfaces studied by QCM-D. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 66, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Ma, X.; Fan, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, R.; Zhu, B. Adsorption of different valence metal cations on kaolinite: Results from experiments and molecular dynamics simulations. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 656, 130330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, H.; Lin, T.-J.; Kishore Mishra, R.; Emami, F.S. Thermodynamically Consistent Force Fields for the Assembly of Inorganic, Organic, and Biological Nanostructures: The INTERFACE Force Field. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Min, F.-f.; Liu, L.-y. The interactions between fine particles of coal and kaolinite in aqueous, insights from experiments and molecular simulations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467–468, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Polymers | Ionic Type | Ionicity Density | Molecular Weight | Code Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnafloc 155 | Anionic | low (~10%) | High | APAM 10% |
| Magnafloc 5250 | Anionic | Medium (~30%) [35] | High | APAM 30% |
| Magnafloc 351 | Nonionic | Nano | High | NPAM |
| Zetag 8110 | Cationic | Very low (~10%) | High | CPAM 10% |
| Zetag 8140 | Cationic | Medium (~30%) | High | CPAM 30% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Sun, X.; Chang, M.; Liu, Q.; Dong, X.; Fan, Y.; Chen, R. Adsorption of Different Ionic Types of Polyacrylamide on Montmorillonite Surface: Insight from QCM-D and Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Molecules 2023, 28, 4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114417
Ma X, Sun X, Chang M, Liu Q, Dong X, Fan Y, Chen R. Adsorption of Different Ionic Types of Polyacrylamide on Montmorillonite Surface: Insight from QCM-D and Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Molecules. 2023; 28(11):4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114417
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xiaomin, Xiaosong Sun, Ming Chang, Qingxia Liu, Xianshu Dong, Yuping Fan, and Ruxia Chen. 2023. "Adsorption of Different Ionic Types of Polyacrylamide on Montmorillonite Surface: Insight from QCM-D and Molecular Dynamic Simulation" Molecules 28, no. 11: 4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114417
APA StyleMa, X., Sun, X., Chang, M., Liu, Q., Dong, X., Fan, Y., & Chen, R. (2023). Adsorption of Different Ionic Types of Polyacrylamide on Montmorillonite Surface: Insight from QCM-D and Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Molecules, 28(11), 4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114417







