Anti-Photoaging Effects of Nanocomposites of Amphiphilic Chitosan/18β-Glycyrrhetinic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
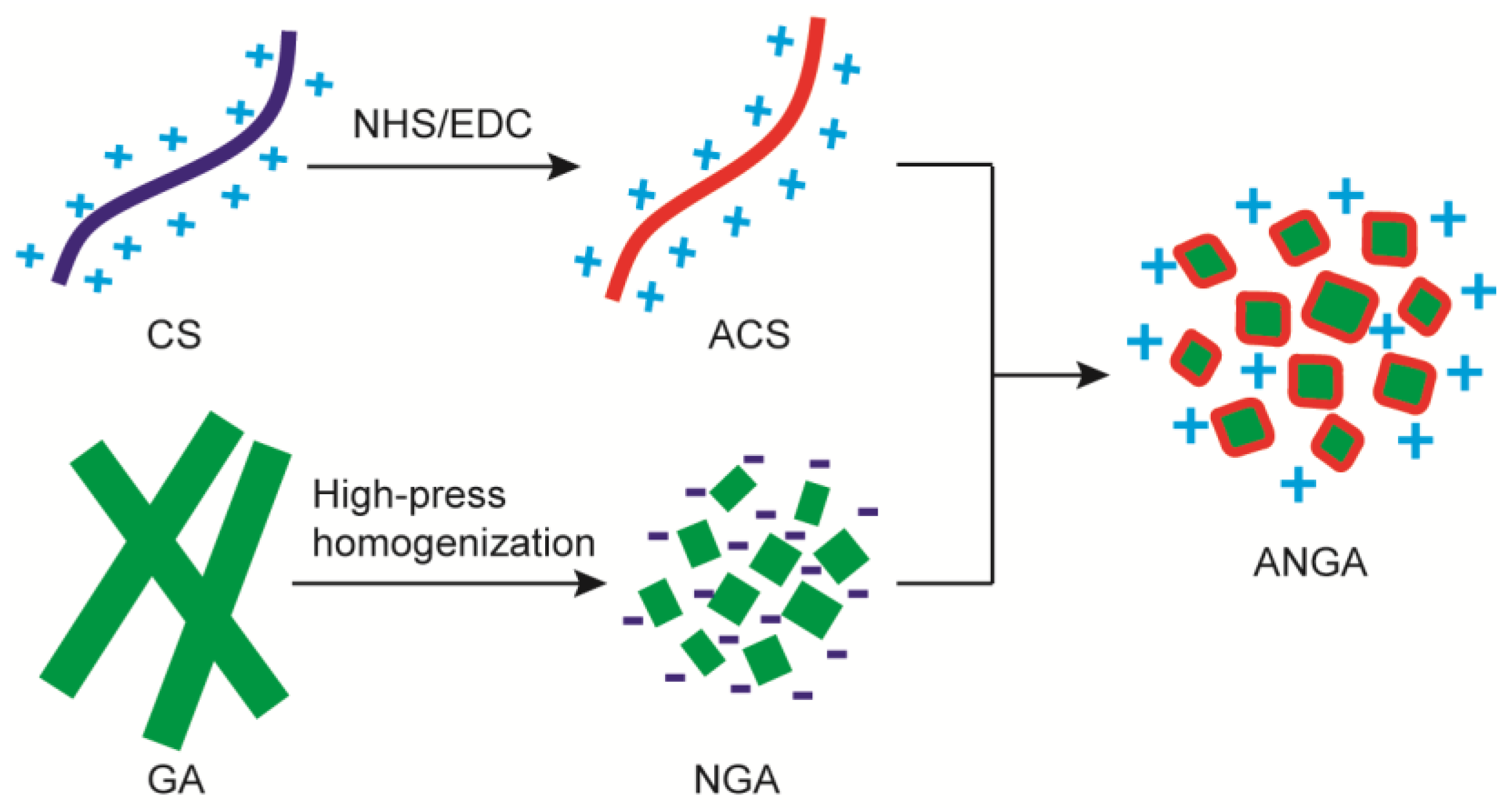
2.1. Preparation of ANGA Composites
2.2. Effects of Sterilization on the MPS and Zeta Potential
2.3. Cytotoxicity of ANGA Composites
2.4. Skin Penetration of the ANGA Hydrogel In Vitro
2.5. ANGA Hydrogel Ameliorated the Macroscopic Appearance of Photoaged Mouse Skin
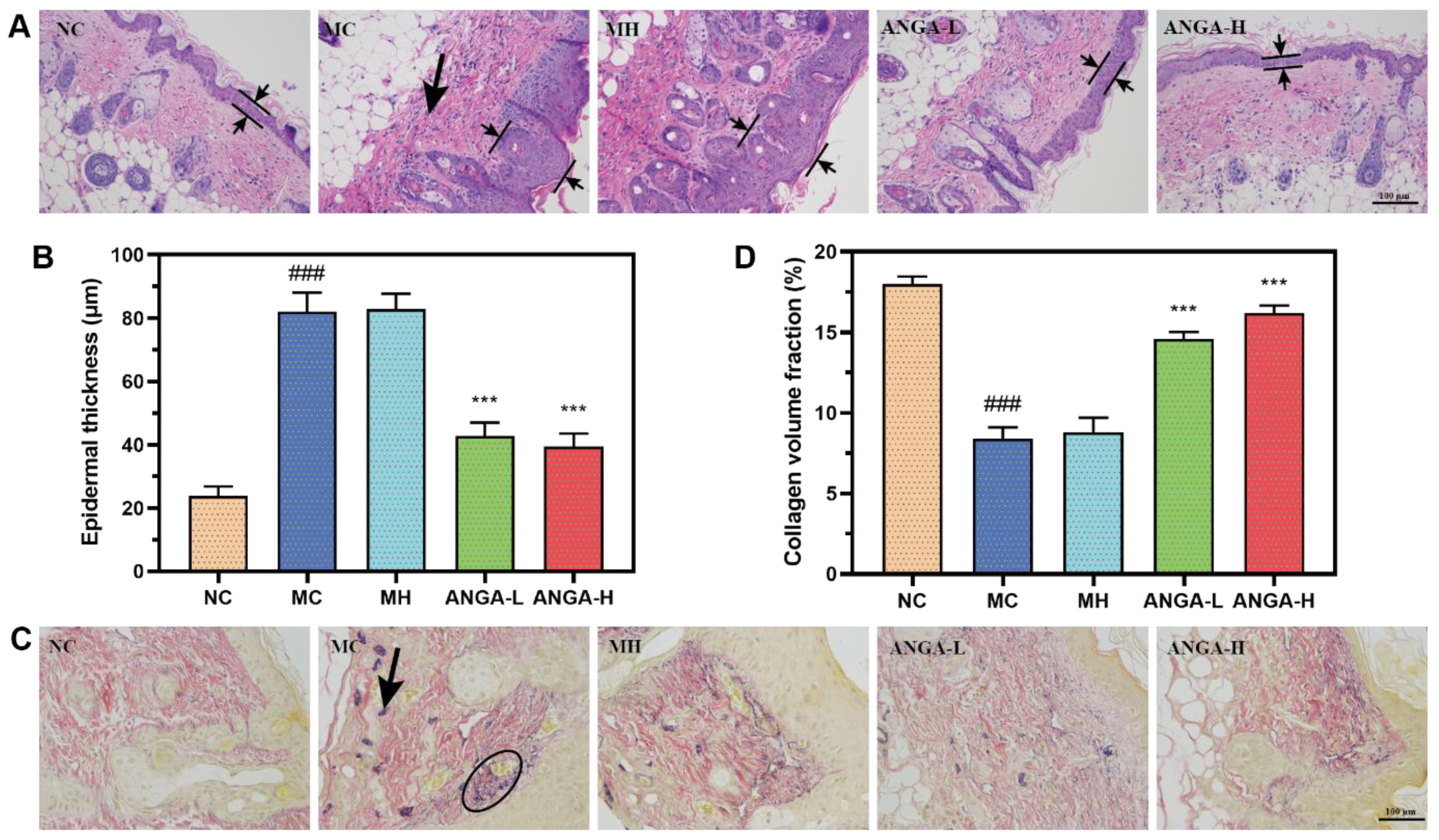
2.6. ANGA Hydrogel Prevented UV-Induced Damage to Skin Structure
2.7. ANGA Hydrogel Protected the Integrity of the Fiber Structure
2.8. ANGA Hydrogel Reversed the UV-Induced Increase in MMP Content
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Approval of the Study Protocol
4.2. Materials
4.3. Preparation of NGA and ANGA Suspension
4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Preparation of an ANGA Hydrogel
4.7. Skin Permeation Ex Vivo
4.8. Preparation of a Photoaged Mouse Model
4.9. Grouping of Experimental Animals and GA Treatment
4.10. Macroscopic Evaluation of Dorsal Skin
4.11. Determination of Skin Moisture Content
4.12. Histology
4.13. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.14. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ke, Y.; Wang, X.J. TGFβ signaling in photoaging and UV-induced skin cancer. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaid, A.N.; Al-Ramahi, R. Depigmentation and anti-aging treatment by natural molecules. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2292–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhu, D.; Xie, C.; Shi, Y.; Ni, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Lu, J.; Xiao, J.; Xia, W.; et al. 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in mouse chondrocytes and prevents osteoarthritic progression by activating Nrf2. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8399–8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.K.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xie, L.; Rong, F.; Zhu, X.Y.; Xie, J.; Zhou, H.; Xu, T. Progress in the treatment of drug-induced liver injury with natural products. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 183, 106361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, C.D.S.; Bonafé, G.A.; Carvalho Santos, J.; Martinez, C.A.R.; Ortega, M.M.; Ribeiro, M.L. The Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra)-Derived Compounds in Intestinal Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Chen, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Kang, X.; Li, W.; Huang, N.; Luo, H.; Su, Z.R. The protective effect of 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid against UV irradiation induced photoaging in mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 61, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhu, Z.; Hong, L.; Qian, Z.; Wang, F.; Mao, Z. ROS-responsive 18β-glycyrrhetic acid-conjugated polymeric nanoparticles mediate neuroprotection in ischemic stroke through HMGB1 inhibition and microglia polarization regulation. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 19, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kassas, R.; Bansal, M.; Shaw, J. Nanosizing techniques for improving bioavailability of drugs. J. Control. Release 2017, 260, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Zheng, A. Progress in the development of stabilization strategies for nanocrystal preparations. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Yang, W.; Feng, T.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Drug nanocrystals for cancer therapy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 10, e1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.S.; Elnahas, O.S.; Assar, N.H.; Gad, A.M.; Hosary, R.E. Nanocrystals of Fusidic Acid for Dual Enhancement of Dermal Delivery and Antibacterial Activity: In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Sharma, O.P.; Mehta, T. Nanocrystal: A novel approach to overcome skin barriers for improved topical drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, W.; Kong, S.; Ouyang, Q.Q.; Tao, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, H. Use of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid nanocrystals to enhance anti-inflammatory activity by improving topical delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 205, 111791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Jagtiani, T.; Liang, J.F. A new targeted delivery approach by functionalizing drug nanocrystals through polydopamine coating. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 114, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushirobira, C.Y.; Afiune, L.A.F.; Pereira, M.N.; Cunha-Filho, M. Dutasteride nanocapsules for hair follicle targeting: Effect of chitosan-coating and physical stimulus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liao, J.; Wu, F.; Shi, J. Mechanical strength improvement of chitosan/hydroxyapatite scaffolds by coating and cross-linking. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 114, 104169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ahmed, S. A review on chitosan and its nanocomposites in drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiris, K.; Brasinika, D.; Karatza, A.; Koumoulos, E.; Karoussis, I.K.; Kyriakidou, K.; Charitidis, C.A. Additive manufacturing of hydroxyapatite-chitosan-genipin composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 119, 111639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Qi, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Quan, W.; Luo, H.; Wu, K.; Li, S.; Ouyang, Q. Progress in Research of Chitosan Chemical Modification Technologies and Their Applications. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Araújo, M.; Novoa-Carballal, R.; Andrade, F.; Gonçalves, H.; Reis, R.L.; Lúcio, M.; Schwartz, S., Jr.; Sarmento, B. Novel amphiphilic chitosan micelles as carriers for hydrophobic anticancer drugs. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Wee, C.E.; Wai, L.K.; Zin, N.M.; Azmi, F. Biomimetic amphiphilic chitosan nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, W.; Kong, S.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Ouyang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Luo, H. Grafting of 18β-Glycyrrhetinic Acid and Sialic Acid onto Chitosan to Produce a New Amphipathic Chitosan Derivative: Synthesis, Characterization, and Cytotoxicity. Molecules 2021, 26, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.N.; Gil, C.H.; Kim, Y.R.; Shin, H.K.; Choi, B.T. Anti-photoaging properties of the phosphodiesterase 3 inhibitor cilostazol in ultraviolet B-irradiated hairless mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, G. Molecular mechanisms of skin ageing. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2002, 123, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.; Qin, Z.; Xia, W.; Shao, Y.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Matrix-Degrading Metalloproteinases in Photoaging. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2009, 14, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yuan, B.C.; Ma, Y.S.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Y. The anti-inflammatory activity of licorice, a widely used Chinese herb. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelikh, O.; Stahr, P.L.; Huang, J.; Gerst, M.; Scholz, P.; Dietrich, H.; Geisel, N.; Keck, C.M. Nanocrystals for improved dermal drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 128, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, I.S.; Hu, H.; Yin, L.; He, W. Drug nanocrystals: Fabrication methods and promising therapeutic applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 562, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilhar, A.; Etzioni, A. The nude mouse model for the study of human skin disorders. Dermatology 1994, 189, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; You, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chang, X. Hawthorn Polyphenol Extract Inhibits UVB-Induced Skin Photoaging by Regulating MMP Expression and Type I Procollagen Production in Mice. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8537–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, L.A.; Tanveer, M.A.; Umar, S.A.; Love, S.; Divya, G.; Tasduq, S.A. Inhibition of Ultraviolet-B Radiation Induced Photodamage by Trigonelline Through Modulation of Mitogen Activating Protein Kinases and Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling Axis in Skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2021, 97, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.H. Photoaging in Asians. Photoaging in Asians. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2003, 19, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Datta, S.C.; Varani, J.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Pathophysiology of Premature Skin Aging Induced by Ultraviolet Light. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittayapruek, P.; Meephansan, J.; Prapapan, O.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Photoaging and Photocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenneisen, P.; Sies, H.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. Ultraviolet-B Irradiation and Matrix Metalloproteinases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 973, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| ACS: NGA (w/w) | Zeta Potential (mV) | Mean Particle Size (nm) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −36.80 ± 0.70 | 290.6 ± 7.3 | 0.13 ± 0.06 |
| 1:20 | 14.96 ± 0.53 | 306.3 ± 4.2 | 0.19 ± 0.07 |
| 1:10 | 31.63 ± 0.76 | 314.3 ± 4.5 | 0.16 ± 0.05 |
| 1:5 | 33.56 ± 0.74 | 316.0 ± 3.6 | 0.19 ± 0.06 |
| 1:1 | 36.67 ± 0.72 | 320.3 ± 6.5 | 0.18 ± 0.05 |
| Before Sterilization | After Sterilization | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGA | ANGA | NGA | ANGA | |
| MPS (nm) | 290.6 ± 7.3 | 314.3 ± 4.5 | 360.2 ± 4.8 | 318.8 ± 5.4 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −36.80 ± 0.70 | 31.63 ± 0.76 | −35.45 ± 1.1 | 30.88 ± 1.4 |
| PDI | 0.13 ± 0.06 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 0.16 ± 0.08 | 0.17 ± 0.09 |
| Sample | Retention Rate (%) | Cumulative Permeability (%) |
|---|---|---|
| NGA hydrogel | 16.9 ± 1.7 | 56.5 ± 1.4 |
| ANGA hydrogel | 14.5 ± 1.4 | 75.3 ± 1.8 |
| Score | Features Used for Grading |
|---|---|
| 0 | No wrinkles or laxity; fine striations running the length of the body |
| 1 | Fine striations |
| 2 | Disappearance of all fine striations |
| 3 | Shallow wrinkles |
| 4 | A few deep wrinkles and laxity |
| 5 | Increased number of deep wrinkles |
| 6 | Severe wrinkles; development of lesions/tumors |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quan, W.; Kong, S.; Li, S.; Ouyang, Q.; Lu, S.; Guo, J.; Wu, K.; Zhao, W.; Luo, H. Anti-Photoaging Effects of Nanocomposites of Amphiphilic Chitosan/18β-Glycyrrhetinic Acid. Molecules 2023, 28, 4362. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114362
Quan W, Kong S, Li S, Ouyang Q, Lu S, Guo J, Wu K, Zhao W, Luo H. Anti-Photoaging Effects of Nanocomposites of Amphiphilic Chitosan/18β-Glycyrrhetinic Acid. Molecules. 2023; 28(11):4362. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114362
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuan, Weiyan, Songzhi Kong, Sidong Li, Qianqian Ouyang, Sitong Lu, Jiaqi Guo, Kefeng Wu, Wei Zhao, and Hui Luo. 2023. "Anti-Photoaging Effects of Nanocomposites of Amphiphilic Chitosan/18β-Glycyrrhetinic Acid" Molecules 28, no. 11: 4362. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114362
APA StyleQuan, W., Kong, S., Li, S., Ouyang, Q., Lu, S., Guo, J., Wu, K., Zhao, W., & Luo, H. (2023). Anti-Photoaging Effects of Nanocomposites of Amphiphilic Chitosan/18β-Glycyrrhetinic Acid. Molecules, 28(11), 4362. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114362






