Dummy Template-Based Molecularly Imprinted Membrane Coating for Rapid Analysis of Malachite Green and Its Metabolic Intermediates in Shrimp and Fish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
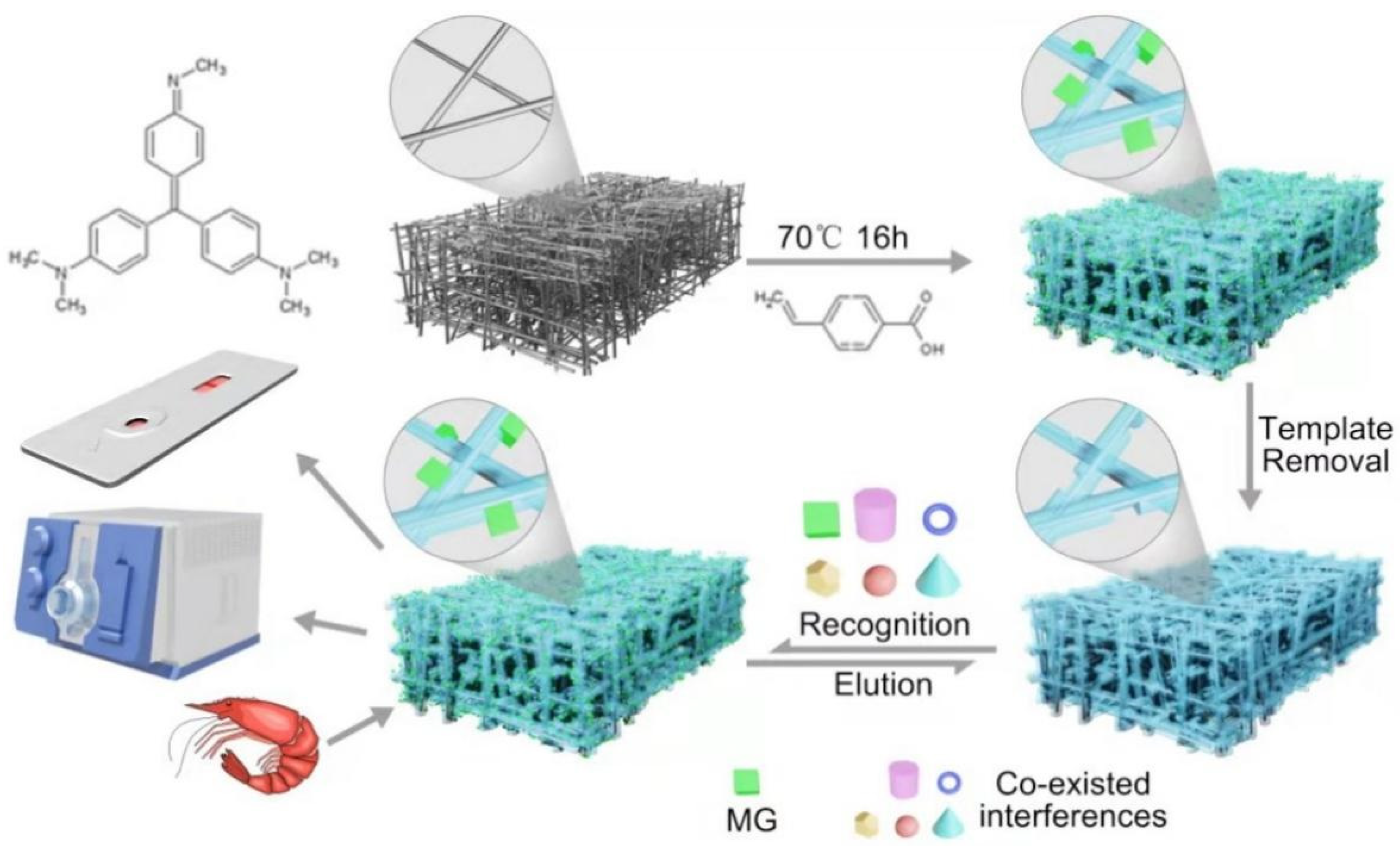
2.1. Synthesis of MG-MIM
2.2. Structural Characterization of the MIP
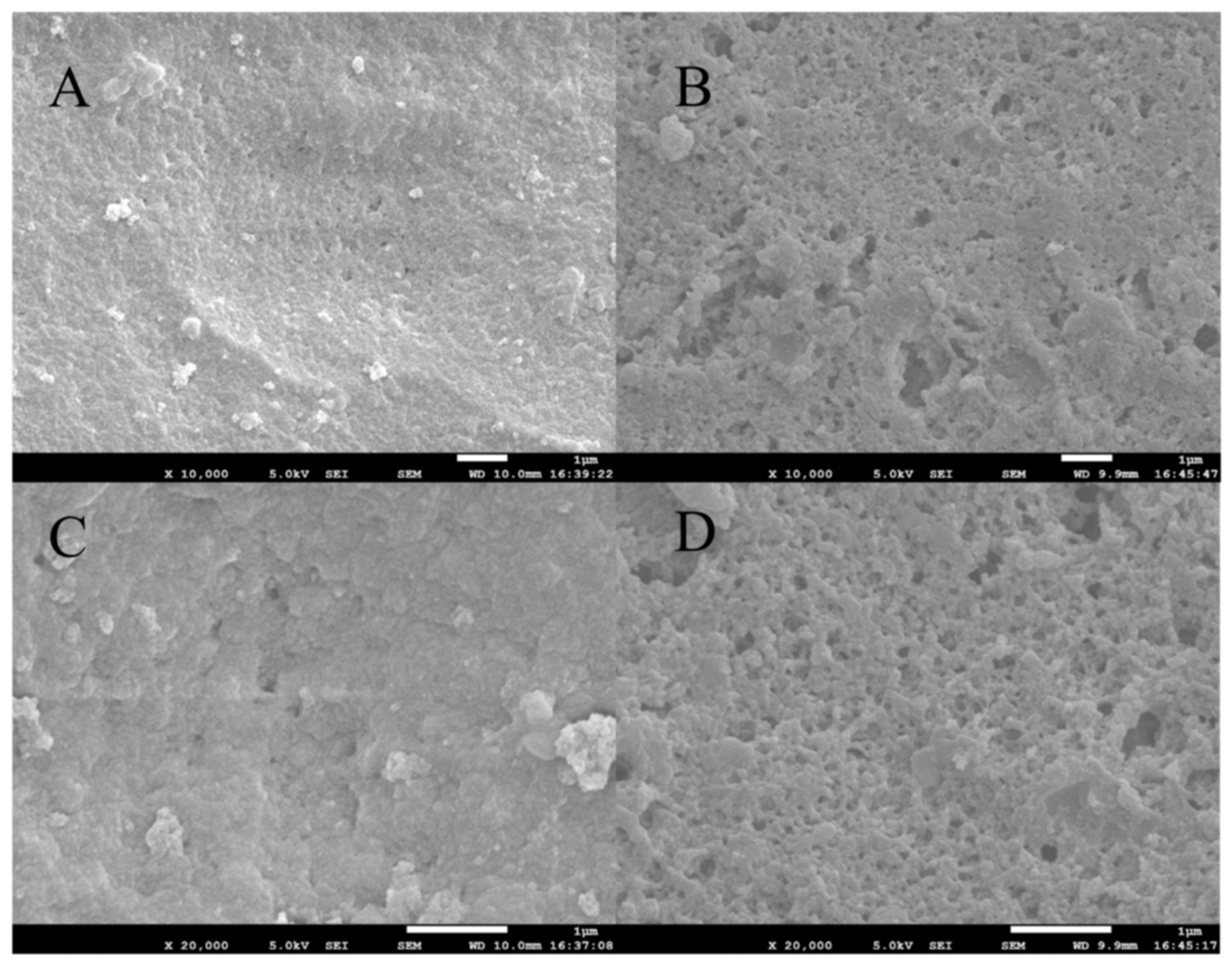
2.2.1. SEM Analysis
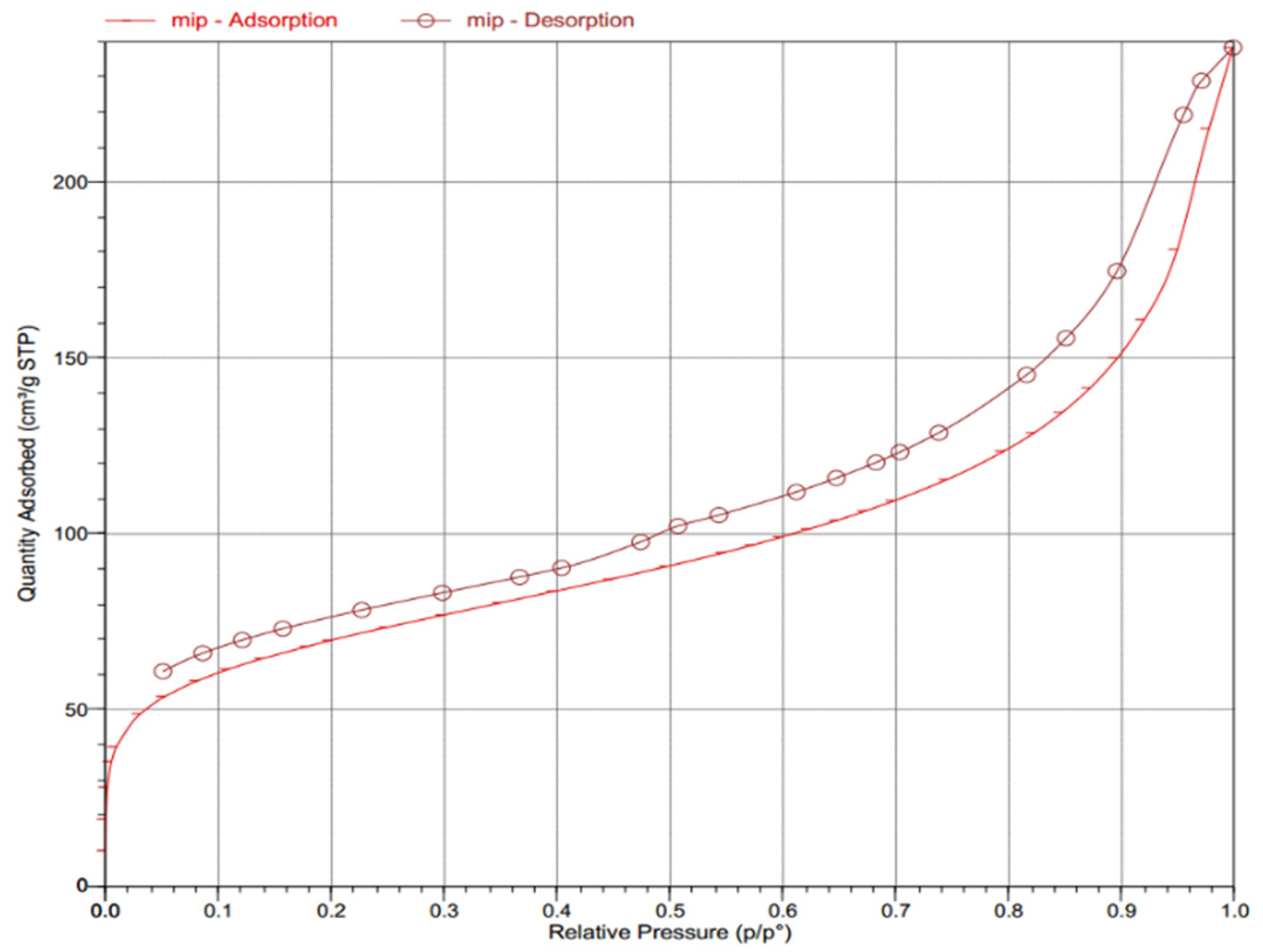
2.2.2. Specific Surface Area Analysis
2.2.3. FT-IR Analysis
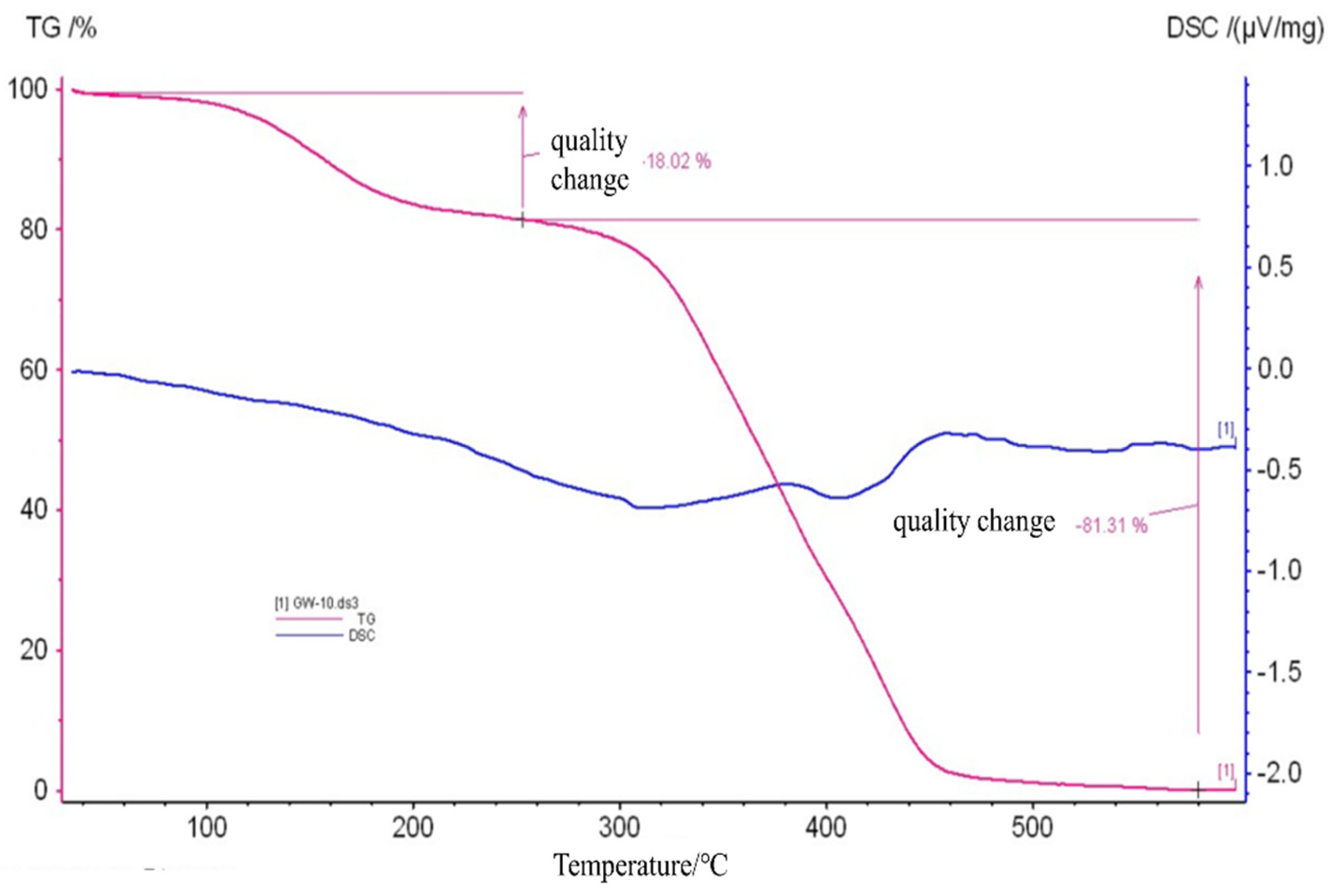
2.2.4. TGA-DSC Analysis
2.3. Adsorption Properties of the MIP
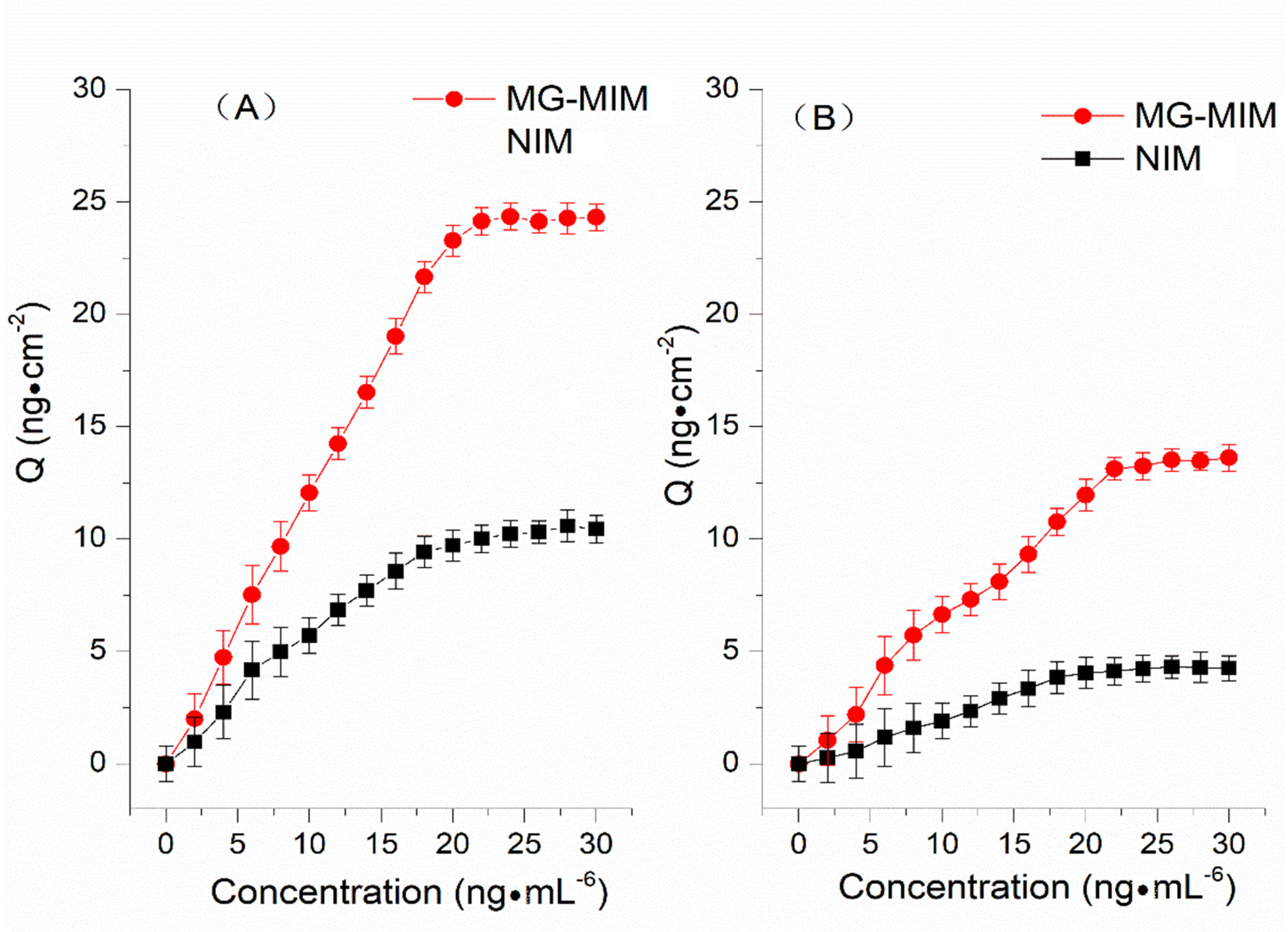
2.3.1. Adsorption Isotherms
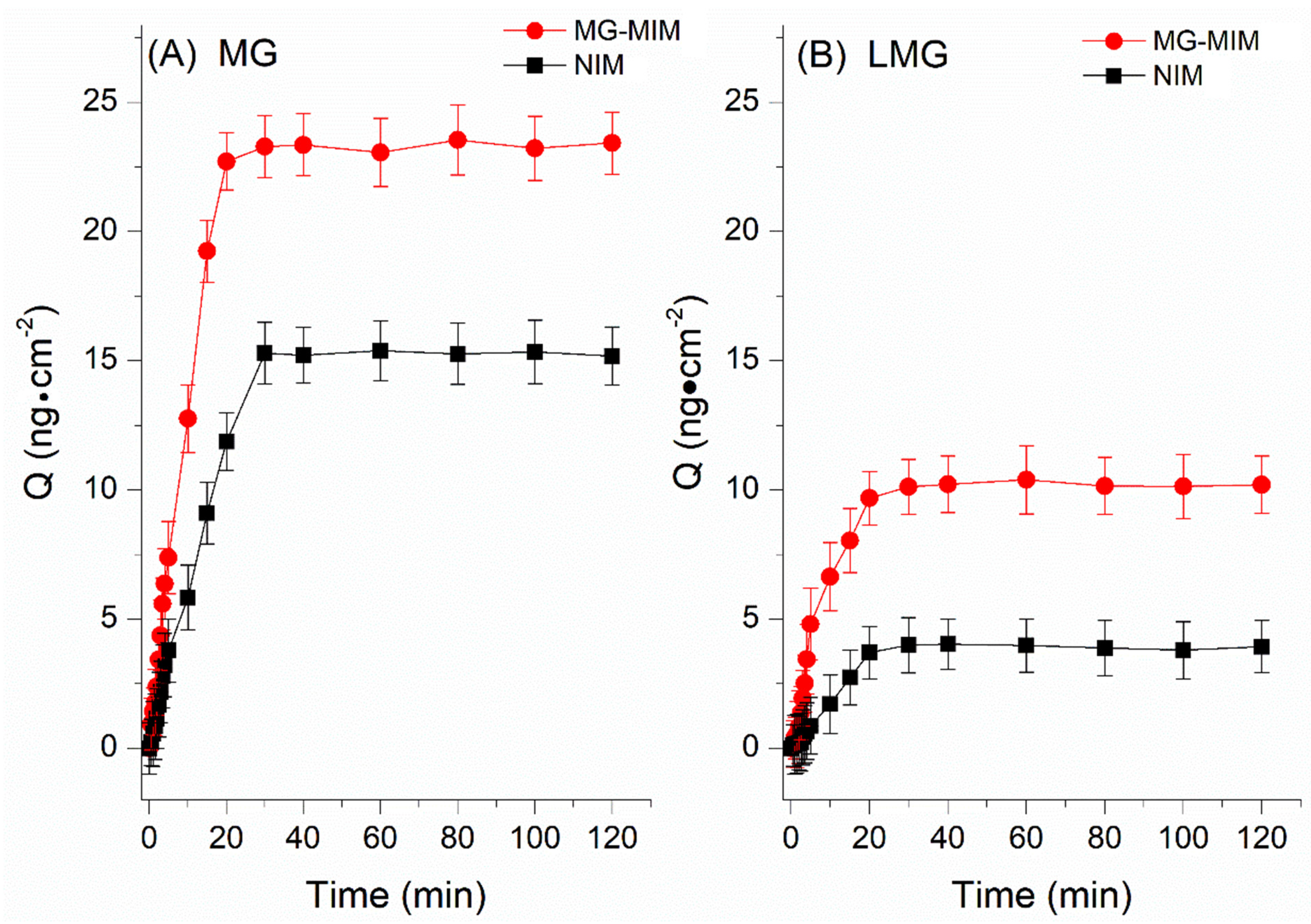
2.3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
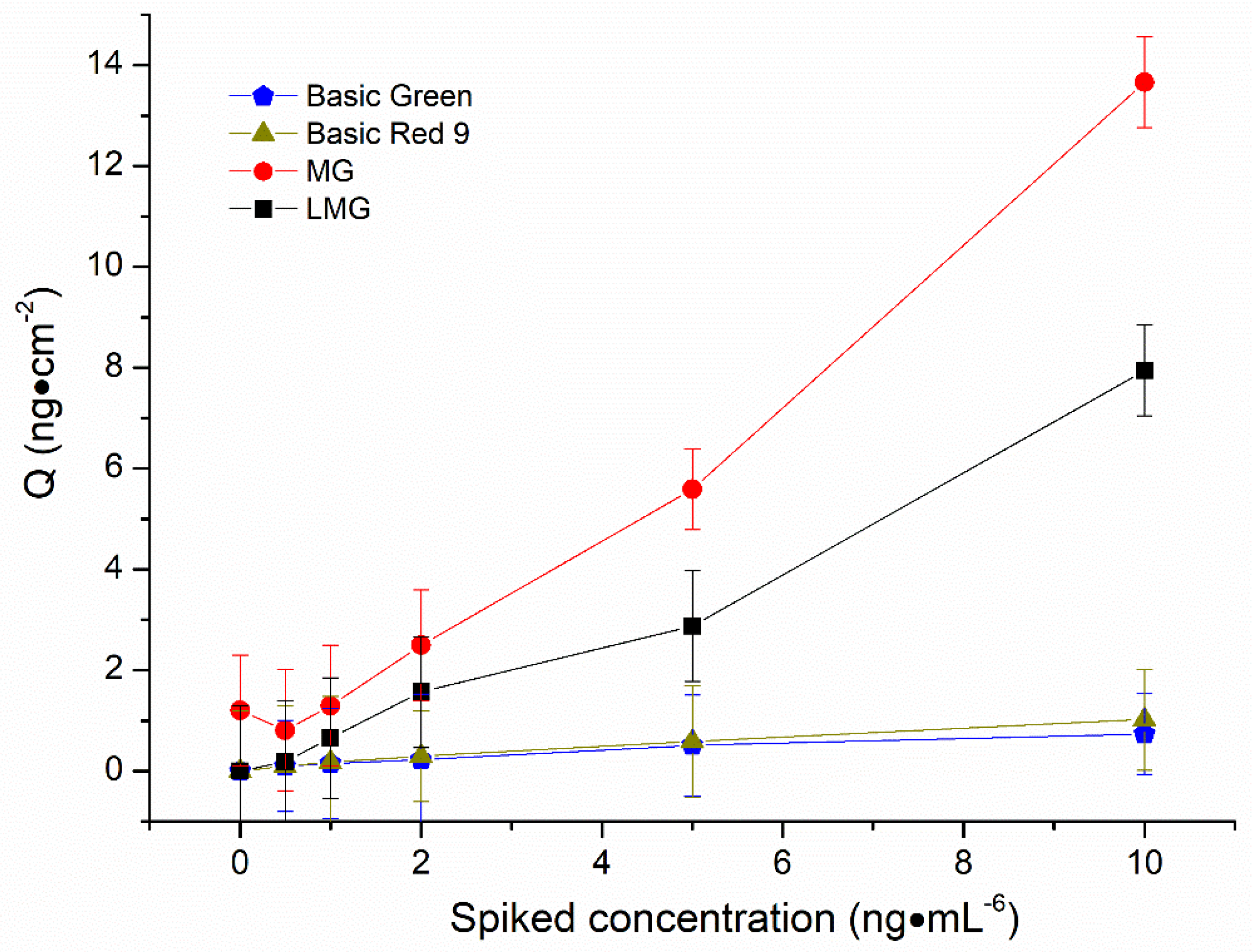
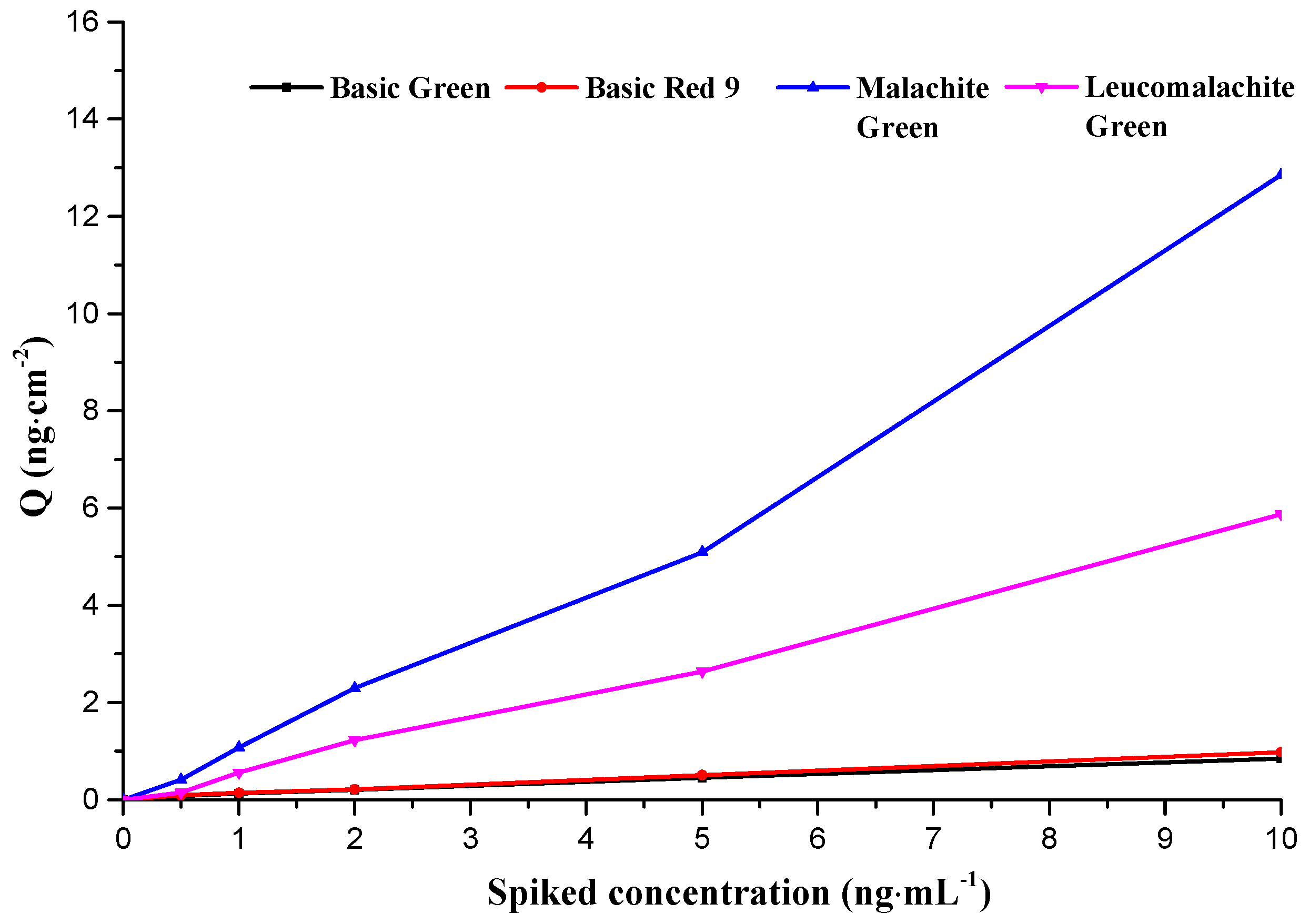
2.3.3. Interference, Stability and Reproducibility Studies
2.4. Evaluation of Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Evaluation of Instrument Method
Linearity Range, Limit of Detection (LOD), and Limit of Quantification (LOQ) Determination
Blank Sample Spiked Recovery and Precision
2.4.2. Evaluation of Rapid Detection Technology
2.5. Practical Sample Analysis
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. UPLC/MS Measurements
3.4. Preparation of Surface-Coated MIM
3.5. Adsorption Experiments
3.5.1. Static Adsorption Experiment
3.5.2. The Experiment of Adsorption Kinetics
3.6. Sample Pretreatment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, T.; Ibarra, I.; Silva, M.; Miranda, J.; Rodriguez, J. Use of modified henequen fibers for the analysis of malachite green and leuco-malachite green in fish muscle by d-SPE followed by capillary electrophoresis. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Chen, C.; Deng, J.; Wu, J.; He, K.; Xiang, Z.; Yang, Y. Analysis of trace malachite green, crystal violet, and their metabolites in zebrafish by surface-coated probe nanoelectrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Talanta 2020, 217, 121064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Sun, D.; Pu, H.; Wei, Q. A dynamically optical and highly stable pNIPAM @ Au NRs nanohybrid substrate for sensitive SERS detection of malachite green in fish fillet. Talanta 2020, 218, 121188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Xiao, Z.; Gee, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Wu, W.; Shen, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Enhanced sensitive immunoassay: Noncompetitive phage anti-immune complex assay for the determination of malachite green and leucomalachite green. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8752–8758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Bei, F.; Wang, M.; Ai, S. Electrochemical determination of malachite green at graphene quantum dots-gold nanoparticles multilayers–modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2013, 43, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.; Nematollahi, D. A comprehensive study on the electrocatalytic degradation, electrochemical behavior and degradation mechanism of malachite green using electrodeposited nanostructured beta-PbO2 electrodes. Water Res. 2018, 144, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilenko, N.; Volgina, T.; Pugachev, E.; Gavrilenko, M. Visual determination of malachite green in sea fish samples. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, J.; Xu, Z.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, Z. Bispecific Monoclonal Antibody-based Multi-analyte ELISA for Furaltadone Metabolite, Malachite Green and Leucomalachite Green in Aquatic Products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8054–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Luo, J. Fluorescence detection of malachite green in fish tissue using red emissive Se,N,Cl-doped carbon dots. Food Chem. 2020, 335, 127677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Mai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Xu, X.; Lu, L.; Zou, X. Determination of multi-residue for malachite green, gentian violet and their metabolites in aquatic products by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 2275–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, K.; Maleki, R.; Nezhad, N.; Samadi, N. Spectrophotometric Determination of Malachite Green Residue in Water Samples After Preconcentration on Surfactant-Coated Alumina. Spectrosc. Lett. 2010, 43, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Meng, Z.; Du, M.; Liu, C.; Song, M.; Wang, H. Pseudo-template molecularly imprinted polymer for selective screening of trace β-lactam antibiotics in river and tap water. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5420–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feas, X.; Seijas, J.; Vazquez-Tato, M.; Regal, P.; Cepeda, A.; Fente, C. Syntheses of molecularly imprinted polymers: Molecular recognition of cyproheptadine using original print molecules and azatadine as dummy templates. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 631, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y. Determination of methotrexate in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography combined with pseudo template molecularly imprinted polymer. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 7533–7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.; Nie, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, Z.; Li, J.; Bacha, S.; Mushtaq, A.; Zhang, H. Molecularly imprinted polymers’ application in pesticide residue detection. Analyst 2018, 143, 3971–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Li, W.; Cui, L.; Huang, J. Exploiting the application of l-aptamer with excellent stability: An efficient sensing platform for malachite green in fish samples. Analyst 2019, 144, 4204–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, G. Development of selective and chemically stable coating for stir bar sorptive extraction by molecularly imprinted technique. Talanta 2010, 82, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BelBruno, J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeyeva, T.; Yarynka, D.; Piletska, E.; Linnik, R.; Zaporozhets, O.; Brovko, O.; Piletsky, S.; El’skaya, A. Development of a smartphone-based biomimetic sensor for aflatoxin B1 detection using molecularly imprinted polymer membranes. Talanta 2019, 201, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, I.; Rodrigues, M.; Chaves, A.; Vaz, B. Molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) membrane assisted direct spray ionization mass spectrometry for agrochemicals screening in foodstuffs. Talanta 2018, 178, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Zhu, X.; Kang, A.; Li, X. Molecular imprinted electrospun chromogenic membrane for l-tyrosine specific recognition and visualized detection. Talanta 2019, 204, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Xu, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, M.; Xu, W. Molecularly Imprinted Membrane Electrospray Ionization for Direct Sample Analyses. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1453–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Guo, X.; Shi, X.; Sun, A.; Wang, L.; Xiao, T.; Tang, Z.; Pan, D.; Li, D.; Chen, J. Highly Permselective Membrane Surface Modification by Cold Plasma-Induced Grafting Polymerization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Recognition of Pyrethroid Insecticides in Fish. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11705–11713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Sun, M.; Guo, P.; Chang, C.; Fu, Q. Molecularly imprinted membrane extraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for selective analysis of cloxacillin from shrimp samples. Food Chem. 2018, 259, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamluyi, B.; Sadeghian, R.; Malek, F.; Boroushaki, M.T. Improved solid phase extraction for selective and efficient quantification of sunset yellow in different food samples using a novel molecularly imprinted polymer reinforced by FeO@UiO-66-NH. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedghi, R.; Ashrafzadeh, S.; Heidari, B. pH-sensitive molecularly imprinted polymer based on graphene oxide for stimuli actuated controlled release of curcumin. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 857, 157603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, X.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Zeng, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S. Fabrication of Multilayered Molecularly Imprinted Membrane for Selective Recognition and Separation of Artemisinin. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 7, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiliang, X.; Zhuomin, Z.; Gongke, L. Dummy template based molecularly imprinted solid-phase microextraction coating for analysis of trace disinfection by-product of 2,6-dichloro-1,4-benzoquinone using high-performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 2022, 239, 123065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajani, A.; Soheili, V.; Moosavi, F.; Ghodsi, R.; Alizadeh, T.; Bazzazac, S. Ultra selective and high-capacity dummy template molecular imprinted polymer to control quorum sensing and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1199, 339574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Pan, J.; Hu, Y.; Huo, Y.; Li, G. Preparation and evaluation of solid-phase microextraction fiber based on molecularly imprinted polymers for trace analysis of tetracyclines in complicated samples. J. ChromatograpHy A 2008, 1188, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segundo, J.; Moraes, M.; Brito, W.; d’Ávila, M. Incorporation of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles in electrospun polycaprolactone fibers. Mater. Lett. 2020, 275, 128088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; He, X.; Zhou, Y. A new magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer based on deep eutectic solvents as functional monomer and cross-linker for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1129, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Fu, Y. Synthesis and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres functionalized with POSS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 511, 145506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Lai, X.; Li, B.; Yang, X. Amido surface-functionalized magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the efficient extraction of Sibiskoside from Sibiraea angustata. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1109, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Muhammad, T.; Yang, J.; Yasen, A.; Chen, L. In-situ kinetic and thermodynamic study of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid adsorption on molecularly imprinted polymer based solid-phase microextraction coatings. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2020, 313, 112190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Matrix | Compound | Regression Equations | Correlation Coefficients (R2) | LOD (µg·kg−1) | LOQ (µg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard solution | MG | Y = −5.43901e + 006 + 1.64419e + 007X | 0.9998 | 0.005 | 0.020 |
| LMG | Y = 6.44322e + 007 + 5.53649e + 007X | 0.9994 | 0.005 | 0.010 | |
| Fish | MG | Y = 1.74e6 + 3.51e7X | 0.9997 | 0.005 | 0.020 |
| LMG | Y = 2.36e6 + 2.32e7X | 0.9995 | 0.020 | 0.050 | |
| Shrimp | MG | Y = −2.55e6 + 2.67e7X | 0.9993 | 0.005 | 0.020 |
| LMG | Y = 4.42e6 + 5.94e7X | 0.9991 | 0.020 | 0.050 |
| Sample | Target | 1 µg·kg−1 | 2 µg·kg−1 | 5 µg·kg−1 | 10 µg·kg−1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery% | RSD% | Recovery% | RSD% | Recovery% | RSD% | Recovery% | RSD% | ||
| Fish | MG | 76.31 | 1.49 | 87.25 | 0.96 | 86.02 | 1.12 | 81.85 | 1.30 |
| LMG | 80.75 | 1.28 | 93.26 | 0.78 | 85.65 | 2.18 | 82.04 | 2.33 | |
| Shrimp | MG | 85.35 | 0.79 | 89.16 | 2.76 | 96.26 | 0.70 | 84.69 | 0.73 |
| LMG | 79.53 | 3.62 | 93.32 | 1.73 | 86.12 | 3.72 | 82.70 | 2.43 | |
| Sample | Method | Blank | The Standard Concentration Level | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 ng·g−1 | 2.0 ng·g−1 | 5.0 ng·g−1 | |||||||||||
| Fish | C (ng·mL−1) | 0.000 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.843 | 1.183 | 0.858 | 1.868 | 1.806 | 1.720 | 4.527 | 4.696 | 4.491 |
| Quick test strip | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Shrimp | C (ng·mL−1) | 0.026 | NF | 0.021 | 0.815 | 1.036 | 1.052 | 1.784 | 1.741 | 1.850 | 4.849 | 4.775 | 4.759 |
| Quick test strip | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yue, Z.; Ouyang, L.; Zhao, F. Dummy Template-Based Molecularly Imprinted Membrane Coating for Rapid Analysis of Malachite Green and Its Metabolic Intermediates in Shrimp and Fish. Molecules 2023, 28, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010310
Zhang Y, Li S, Gu Y, Zhang J, Yue Z, Ouyang L, Zhao F. Dummy Template-Based Molecularly Imprinted Membrane Coating for Rapid Analysis of Malachite Green and Its Metabolic Intermediates in Shrimp and Fish. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010310
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yi, Shaofeng Li, Yurong Gu, Jianying Zhang, Zhenfeng Yue, Liao Ouyang, and Fengjuan Zhao. 2023. "Dummy Template-Based Molecularly Imprinted Membrane Coating for Rapid Analysis of Malachite Green and Its Metabolic Intermediates in Shrimp and Fish" Molecules 28, no. 1: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010310
APA StyleZhang, Y., Li, S., Gu, Y., Zhang, J., Yue, Z., Ouyang, L., & Zhao, F. (2023). Dummy Template-Based Molecularly Imprinted Membrane Coating for Rapid Analysis of Malachite Green and Its Metabolic Intermediates in Shrimp and Fish. Molecules, 28(1), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010310






