Effect of Heavy Metal Stress on Phenolic Compounds Accumulation in Winter Wheat Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Germination Test
2.2. Activity of the Phenylpropanoid Pathway Enzymes
2.2.1. PAL Activity
2.2.2. TAL Activity
2.3. Total Phenols
2.4. Flavonoids
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.1.1. Germination Experiment
4.1.2. Pot Experiment
4.2. Phenolic Compounds Analysis
4.2.1. Extraction of Phenolic Compounds
4.2.2. Total Phenols Determination
4.2.3. Flavonoids Determination
4.3. l-Phenylalanine (PAL) and l-Tyrosine Ammonia-Lyase (TAL) Activity
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Vitousek, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Lubchenco, J.; Melillo, J.M. Human domination of Earth’s ecosystems. Science 1997, 277, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Joia, J.; Sood, A.; Sood, R.; Sidhu, C.; Kaur, G. Microbes as potential tool for remediation of heavy metals: A review. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2016, 223, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Mitra, M.; Agarwal, P.; Mahapatra, K.; De, S.; Sett, U.; Roy, S. Oxidative and genotoxic damages in plants in response to heavy metal stress and maintenance of genome stability. Plant Signal. Behav. 2018, 13, 1460048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneviratne, M.; Rajakaruna, N.; Rizwan, M.; Madawala, H.M.S.P.; Vithanage, Y.S.O.M. Heavy metal-induced oxidative stress on seed germination and seedling development: A critical review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1813–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.A. Heavy metals of special concern to human health and environment. In Practical Food Safety: Contemporary Issues and Future Directions; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, R.; Khan, M.; Masab, M.; Rehman, H.U.; Rauf, N.U.; Shahab, S.; Ameer, N.; Sajed, M.; Ullah, M.; Rafeeq, M.; et al. Accumulation of heavy metals (Ni, Cu, Cd, Cr, Pb, Zn, Fe) in the soil, water and plants and analysis of physico-chemical parameters of soil and water collected from Tanda Dam kohat. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2015, 7, 89–97. Available online: https://www.jpsr.pharmainfo.in/Documents/Volumes/vol7issue03/jpsr07031501.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Giannakoula, A.; Therios, I.; Chatzissavvidis, C. Effect of lead and copper on photosynthetic apparatus in citrus (Citrus aurantium L.) plants. The role of antioxidants in oxidative damage as a response to heavy metal stress. Plants 2021, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, V.; Feller, U. Heavy metals in crop plants: Transport and redistribution processes on the whole plant level. Agronomy 2015, 5, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Sajad, M.A. Phytoremediation of heavy metals-concepts and applications. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirevska-Kepova, K.; Simova-Stoilova, L.; Stoyanova, Z.; Holzer, R.; Feller, U. Biochemical changes in barley plants after excessive supply of copper and manganese. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2004, 52, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K. Heavy metals toxicity in plants: An overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2010, 76, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Srivastava, S.; Tripathi, R.; Kumar, R.; Seth, C.S.; Gupta, D.K. Lead detoxification by coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum L.) involves induction of phytochelatins and antioxidant system in response to its accumulation. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nas, F.S.; Ali, M. The effect of lead on plants in terms of growing and biochemical parameters: A review. MOJ Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2018, 3, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, Z. Effects of lead stress on the growth, physiology, and cellular structure of privet seedlings. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alengebawy, A.; Abdelkhalek, S.T.; Qureshi, S.R.; Wang, M.-Q. Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: Ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadou, E.C.; Kowalska, E.; Patla, K.; Kulbat, K.; Smolińska, B.; Leszczyńska, J.; Fotopoulos, V. Influence of heavy metals (Ni, Cu, and Zn) on nitro-oxidative stress responses, proteome regulation and allergen production in basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghori, N.-H.; Ghori, T.; Hayat, M.Q.; Imadi, S.R.; Gul, A.; Altay, V.; Ozturk, M. Heavy metal stress and responses in plants. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1807–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Shri, M.; Gupta, A.; Rani, V.; Chakrabarty, D. Toxicity and detoxification of heavy metals during plant growth and metabolism. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1169–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdei, S.; Hegedus, A.; Hauptmann, G.; Szali, J.; Horvath, G. Heavy metal induced physiological changes in the antioxidative response system. Acta Biol. Szeged. 2002, 46, 89–90. Available online: https://www2.sci.u-szeged.hu/ABS/2002/Acta%20HPb/s2/erde.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2022).
- Sytar, O.; Kumar, A.; Latowski, D.; Kuczynska, P.; Strzałka, K.; Prasad, M.N.V. Heavy metal-induced oxidative damage, defense reactions, and detoxification mechanisms in plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013, 35, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, W.; Masoodi, K.Z.; Zaid, A.; Wani, S.H.; Shah, F.; Meena, V.S.; Wani, S.A.; Mosa, K.A. Engineering plants for heavy metal stress tolerance. Rend. Lincei. Sci. Fis. Nat. 2018, 29, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamás, L.; Mistrík, I.; Zelinová, V. Heavy metal-induced reactive oxygen species and cell death in barley root tip. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 140, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Roychoudhury, A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 00053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.M.; Liu, W.C.; Jin, Y.; Lu, Y.T. Role of ROS and auxin in plant response to metal-mediated stress. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, 24671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szpunar-Krok, E.; Jańczak-Pieniążek, M.; Skrobacz, K.; Bobrecka-Jamro, D.; Balawejder, M. Response of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Plants to Spraying by Hydrogen Peroxide. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorzynska-Polit, E.; Pawlikowska-Pawlȩga, B.; Szczuka, E.; Drązkiewicz, M.; Krupa, Z. The activity and localization of lipoxygenases in Arabidopsis thaliana under cadmium and copper stresses. Plant Growth Regul. 2006, 48, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Prasad, M.N.V.; Sytar, O. Lead toxicity, defense strategies and associated indicative biomarkers in Talinum triangulare grown hydroponically. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1056–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Jha, A.B.; Dubey, R.S.; Pessarakli, M. Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 217037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Shahzad, B.; Rehman, A.; Bhardwaj, R.; Landi, M.; Zheng, B. Response of phenylpropanoid pathway and the role of polyphenols in plants under abiotic stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiosi, R.; dos Santos, W.D.; Constantin, R.P.; de Lima, R.B.; Soares, A.R.; Finger-Teixeira, A.; Mota, T.R.; de Oliveira, D.M.; de Paiva Foletto-Felipe, M.; Abrahão, J.; et al. Biosynthesis and metabolic actions of simple phenolic acids in plants. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 865–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakihama, Y.; Cohen, M.F.; Grace, S.C.; Yamasaki, H. Plant phenolic antioxidant and pro-oxidant activities: Phenolicsinduced oxidative damage mediated by metals in plants. Toxicology 2002, 177, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrera, J.L.; Austin, M.B.; Stewart, C., Jr.; Noel, J.P. Structure and function of enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, J.; Serrani-Yarce, J.C.; Chen, F.; Baxter, D.; Venables, B.J.; Dixon, R.A. Role of bifunctional ammonia-lyase in grass cell wall biosynthesis. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Sánchez, M.; Guevara-González, R.G.; Castaño-Tostado, E.; Mercado-Silva, E.M.; Acosta-Gallegos, J.A.; Rocha-Guzmán, N.E.; Reynoso-Camacho, R. Effect of chemical stress on germination of cv Dalia bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as an alternative to increase antioxidant and nutraceutical compounds in sprouts. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitta, M.; Curto, S.L.; Salvo, F.; Di Bella, G.; Dugo, G. Gas chromatographic–tandem mass spectrometric identification of phenolic compounds in Sicilian olive oils. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 466, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, L.; Fernandez, M.T.; Santos, M.; Rocha, R.; Florencio, M.H.; Jennings, K.R. Interactions of flavonoids with iron and copper ions: A mechanism for their antioxidant activity. Free Radic. Res. 2002, 36, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Løvdal, T.; Olsen, K.M.; Slimestad, R.; Verheul, M.; Lillo, C. Synergetic effects of nitrogen depletion, temperature, and light on the content of phenolic compounds and gene expression in leaves of tomato. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R. Wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 1537–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Taghouti, M.; Gaboun, F.; Nsarellah, N.; Rhrib, R.; El-Haila, M.; Kamar, M.; Abbad-Andaloussi, F.; Udupa, S.M. Genotype x environment interaction for quality traits in durum wheat cultivars adapted to different environments. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 3054–3062. Available online: https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajb/article/view/80550 (accessed on 18 November 2022).
- Rozbicki, J.; Ceglińska, A.; Gozdowski, D.; Jakubczak, M.; Cacak-Pietrzak, G.; Mądry, W.; Golba, J.; Piechociński, M.; Sobczyński, G.; Studnicki, M.; et al. Influence of the cultivar, environment and management on the grain yield and bread-making quality in winter wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 61, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitford, R.; Fleury, D.; Reif, J.C.; Garcia, M.; Okada, T.; Korzun, V.; Langridge, P. Hybrid breeding in wheat: Technologies to improve hybrid wheat seed production. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 5411–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jańczak-Pieniążek, M.; Buczek, J.; Kaszuba, J.; Szpunar-Krok, E.; Bobrecka-Jamro, D.; Jaworska, G. A Comparative assessment of the baking quality of hybrid and population wheat cultivars. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.; Whitford, R. Hybrid wheat and abiotic stress. In Genomics Assisted Breeding of Crops for Abiotic Stresstolerance; Rajpal, V.R., Sehgal, D., Kumar, A., Raina, S.N., Eds.; Sustainable Development and Biodiversity; Springer: Cham, Switerland, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 211–224. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.K.; Balyan, H.S.; Gahlaut, V.; Saripalli, G.; Pal, B.; Basnet, B.R.; Joshi, A.K. Hybrid wheat: Past, present and future. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 2463–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, K.C.; Alsop, B.; Bell, E.; Goley, M.; Jenkinson, J.; Liu, B.; Martin, C.; Parrott, W.; Souder, C.; Sparks, O.; et al. Bringing new plant varieties to market: Plant breeding and selection practices advance beneficial characteristics while minimizing unintended changes. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 2906–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Mirdita, V.; Reif, J.C. Efficient strategies to assess yield stability in winter wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 1587–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jańczak-Pieniążek, M.; Buczek, J.; Kwiatkowski, C.A.; Harasim, E. The course of physiological processes, yielding, and grain quality of hybrid and population wheat as affected by integrated and conventional cropping systems. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muqaddasi, Q.H.; Reif, J.C.; Röder, M.S.; Basnet, B.R.; Dreisigacker, S. Genetic Mapping Reveals Large-Effect QTL for Anther Extrusion in CIMMYT Spring Wheat. Agronomy 2019, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Ji, S.; Ping, J.; Cui, D. Recent advances in metabolomics for studying heavy metal stress in plants. TRAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, J.; Starmans, D. Heavy metals balance in Polish and Dutch agronomy: Actual state and previsions for the future. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 107, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwalaba, J.L.W.; Louis, L.T.; Zvobgo, G.; Richmond, M.E.A.; Fu, L.; Naz, S.; Mwamba, T.M.; Mundende, R.P.M.; Zhang, G. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of cobalt and copper interaction in causing phyto-toxicity to two barley genotypes differing in Co tolerance. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.T.; Wu, P.; Wang, L.H.; Zhou, Q. Response of soybean seed germination to cadmium and acid rain. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 144, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Mohammad, A. Effect of lead and cadmium on germination and seedling growth of Leucaena leucocephala. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2008, 12, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamhamdi, M.; Galiou, O.E.; Bakrim, A.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.C.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Aarab, A.; Lafont, R. Effect of lead stress on mineral content and growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and spinach (Spinacia oleracea) seedlings. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 20, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamhamdi, M.; Bakrim, A.; Aarab, A.; Lafont, R.; Sayah, F. Effects of lead phytotoxicity on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seed germination and seedling growth. C. R. Biol. 2011, 334, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baruah, N.; Mondal, S.C.; Farooq, M.; Gogoi, N. Influence of heavy metals on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat, pea, and tomato. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethy, S.K.; Ghosh, S. Effect of heavy metals on germination of seeds. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. 2013, 4, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gu, M.; Lai, Z.; Fan, B.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Yu, J.-Q.; Chen, Z. Functional analysis of the arabidopsis PAL gene family in plant growth, development, and response to environmental stress. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1526–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feduraev, P.; Skrypnik, L.; Riabova, A.; Pungin, A.; Tokupova, E.; Maslennikov, P.; Chupakhina, G. Phenylalanine and tyrosine as exogenous precursors of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) secondary metabolism through PAL-associated pathways. Plants 2020, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Mendoza, D.; Troncoso-Rojas, R.; Gonzalez-Soto, T.; Grimaldo-Juarez, O.; Ceceña-Duran, C.; Duran-Hernandez, D.; Gutierrez-Miceli, F. Changes in the phenylalanine ammonia lyase activity, total phenolic compounds, and flavonoids in Prosopis glandulosa treated with cadmium and copper. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2018, 90, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.L.; Hammerschmidt, R. Phenolic compounds and their role in disease resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1992, 30, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfini, T.; Gabrielli, R.; Comparining, C. Nickel toxicity and peroxidase activity in seedlings of Triticum aestivum L. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerniewicz, P.; Sytykiewicz, H.; Durak, R.; Borowiak-Sobkowiak, B.; Chrzanowski, G. Role of phenolic compounds during antioxidative responses of winter triticale to aphid and beetle attack. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 118, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, H.; Geng, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S. Changes in defense-related enzymes and phenolics in resistant and susceptible common wheat cultivars under aphid stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2021, 43, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshamgan, E.S.; Sharifi, M.; Zarinkamar, F. Crosstalk among polyamines, phytohormones, hydrogen peroxide, and phenylethanoid glycosides responses in Scrophularia striata to Cd stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 143, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, W.; Prithiviraj, B.; Smith, D.L. Chitosan and chitin oligomers increase phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and tyrosine ammonia-lyase activities in soybean leaves. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 160, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, J.; Dixon, R.A. Plant phenylalanine/tyrosine ammonia-lyases. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlestkina, E.K. The adaptive role of flavonoids: Emphasis on cereals. Cereal Res. Commun. 2013, 41, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, K.L.; McGrath, S.P.; Lombi, E.; Stack, S.M.; Terry, N.; Pickering, I.J.; George, G.N.; Pilon-Smits, E.A. Molybdenum sequestration in Brassica species. A role for anthocyanins? Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, K.L.; Tufan, H.A.; Pickering, I.J.; George, G.N.; Terry, N.; Pilon, M.; Pilon-Smits, E.A.H. Anthocyanins facilitate tungsten accumulation in Brassica. Physiol. Plant. 2002, 116, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakihama, Y.; Yamasaki, H. Lipid peroxidation induced by phenolics in conjunction with aluminum ions. Biol. Plant. 2002, 45, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.H.; Chee Kong, Y.; Mohd Zain, N.A. Effect of cadmium and copper exposure on growth, secondary metabolites and antioxidant activity in the medicinal plant Sambung Nyawa (Gynura procumbens (Lour.) merr). Molecules 2017, 22, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Parmar, P.; Sharma, V. Differential gene expression in two contrasting wheat cultivars under cadmium stress. Biol. Plant. 2015, 59, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsova, E.; Dobrikova, A.; Stefanov, M.; Misheva, S.; Bardáčová, M.; Matušíková, I.; Žideková, L.; Blehová, A.; Apostolova, E. Effects of cadmium on two wheat cultivars depending on different nitrogen supply. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 155, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiafeng, J.; Xin, H.; Ling, L.; Jiangang, L.; Hanliang, S.; Qilai, X.; Renhong, Y.; Yuanhua, D. Effect of cold plasma treatment on seed germination and growth of wheat. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2014, 16, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSSWorking Group WRB. International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. In Word Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015; Word Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 172–173. Available online: https://www.iuss.org/archived-content/archived-int-year-of-soils-2015/archived-working-groups-for-iys/working-group-world-reference-base-for-soil-resources-wrb/ (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- BBCH Working Group. Growth Stages of Mono-and Dicotyledonous Plants, 2nd ed.; Meier, U., Ed.; Federal Biological Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry: Bonn, Germany, 2001; Available online: https://www.politicheagricole.it/flex/AppData/WebLive/Agrometeo/MIEPFY800/BBCHengl2001.pdf (accessed on 2 July 2010).
- Zhishen, J.; Mengcheng, T.; Jianming, W. The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem. 1999, 64, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

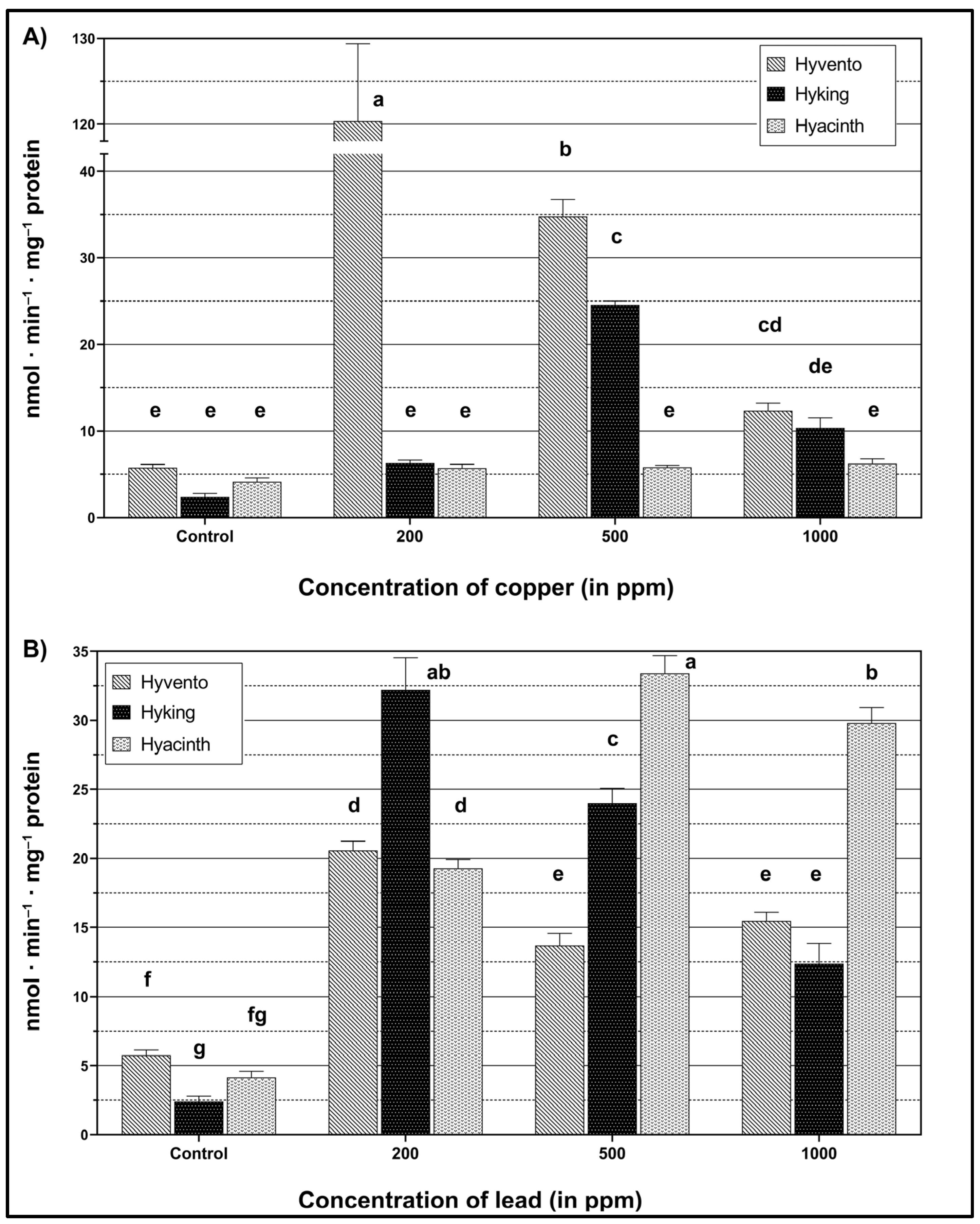
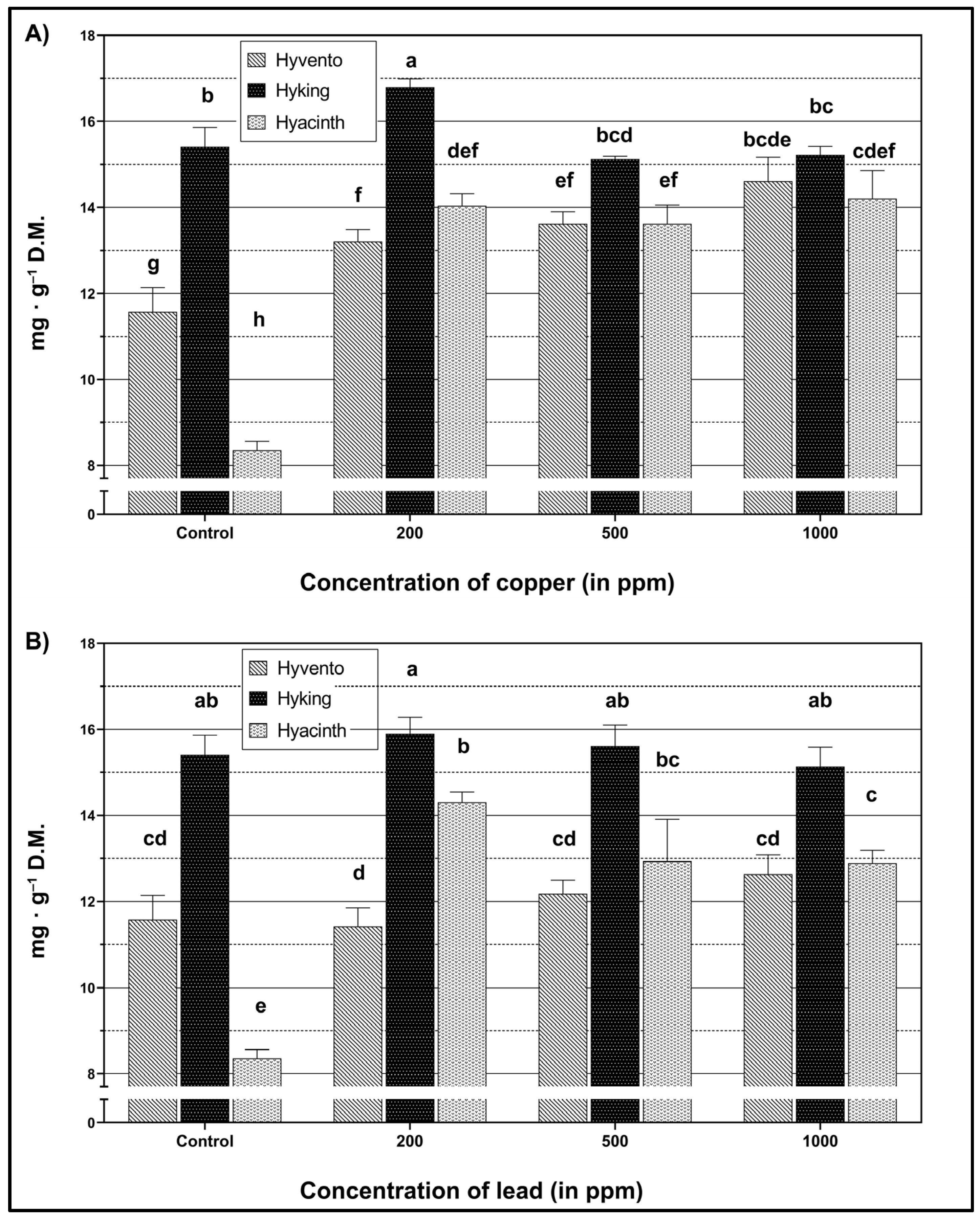
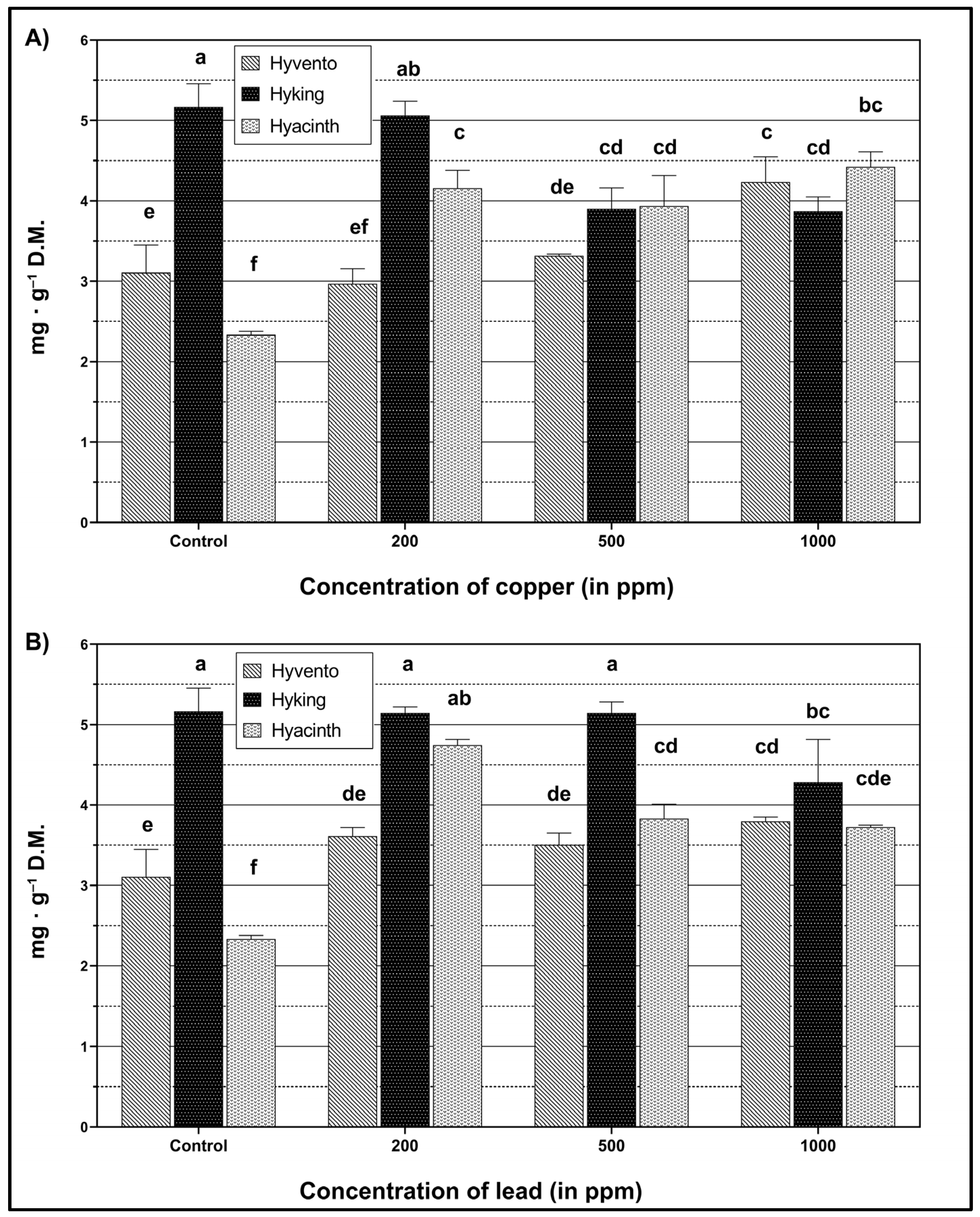
| Hybrid Wheat Cultivar | Heavy Metal Concentration | Copper (Cu) | Lead (Pb) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germination Rate (%) | Germination Potential (%) | Germination Rate (%) | Germination Potential (%) | ||
| Hyvento | Control | 66.00c * ± 5.29 | 92.00d ± 4.00 | 66.00d ± 5.29 | 92.00g ± 4.00 |
| 200 ppm | 4.00a ± 2.00 | 12.00c ± 2.00 | 56.00d ± 3.46 | 86.00g ± 4.00 | |
| 500 ppm | 0.67a ± 1.15 | 2.00ab ± 0.00 | 28.00bc ± 3.46 | 56.00bcd ± 2.00 | |
| 1000 ppm | 0.00a ± 0.00 | 0.00a ± 0.00 | 20.00b ± 2.00 | 46.00b ± 5.29 | |
| Hyking | Control | 58.00bc ± 6.00 | 90.00d ± 6.00 | 58.00d ± 6.00 | 90.00g ± 6.00 |
| 200 ppm | 2.00a ± 2.00 | 8.00bc ± 0.00 | 36.00c ± 2.00 | 84.00fg ± 5.29 | |
| 500 ppm | 2.00a ± 2.00 | 4.00ab ± 2.00 | 34.00c ± 4.00 | 64.00de ± 5.29 | |
| 1000 ppm | 0.00a ± 0.00 | 2.00ab ± 2.00 | 20.00b ± 4.00 | 50.00bc ± 3.46 | |
| Hyacinth | Control | 56.00b ± 3.46 | 88.00d ± 2.00 | 56.00d ± 3.46 | 88.00g ± 2.00 |
| 200 ppm | 0.67a ± 1.15 | 6.00abc ± 2.00 | 32.00c ± 3.46 | 74.00ef ± 4.00 | |
| 500 ppm | 0.00a ± 0.00 | 0.67a ± 1.15 | 28.00bc ± 2.00 | 58.00cd ± 2.00 | |
| 1000 ppm | 0.00a ± 0.00 | 0.00a ± 0.00 | 6.00a ± 3.46 | 16.00a ± 2.00 | |
| Mean | 15.78 ± 26.11 | 25.39 ± 38.05 | 36.67 ± 18.17 | 67.00 ± 22.61 | |
| Cultivar (Cv.) | F = 4.956 p < 0.05 | F = 4.491 p < 0.05 | F = 30.929 p < 0.0001 | F = 36.000 p < 0.0001 | |
| Concentration (Co.) | F = 1036.314 p < 0.0001 | F = 2750.127 p < 0.0001 | F = 228.381 p < 0.0001 | F = 307.347 p < 0.0001 | |
| Cv x Co | F = 2.564 p < 0.05 | ns | F = 9.024 p < 0.0001 | F = 12.980 p < 0.0001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jańczak-Pieniążek, M.; Cichoński, J.; Michalik, P.; Chrzanowski, G. Effect of Heavy Metal Stress on Phenolic Compounds Accumulation in Winter Wheat Plants. Molecules 2023, 28, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010241
Jańczak-Pieniążek M, Cichoński J, Michalik P, Chrzanowski G. Effect of Heavy Metal Stress on Phenolic Compounds Accumulation in Winter Wheat Plants. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010241
Chicago/Turabian StyleJańczak-Pieniążek, Marta, Jan Cichoński, Patrycja Michalik, and Grzegorz Chrzanowski. 2023. "Effect of Heavy Metal Stress on Phenolic Compounds Accumulation in Winter Wheat Plants" Molecules 28, no. 1: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010241
APA StyleJańczak-Pieniążek, M., Cichoński, J., Michalik, P., & Chrzanowski, G. (2023). Effect of Heavy Metal Stress on Phenolic Compounds Accumulation in Winter Wheat Plants. Molecules, 28(1), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010241






