In Situ Synthesis of C-N@NiFe2O4@MXene/Ni Nanocomposites for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption at an Ultralow Thickness Level
Abstract
1. Introduction
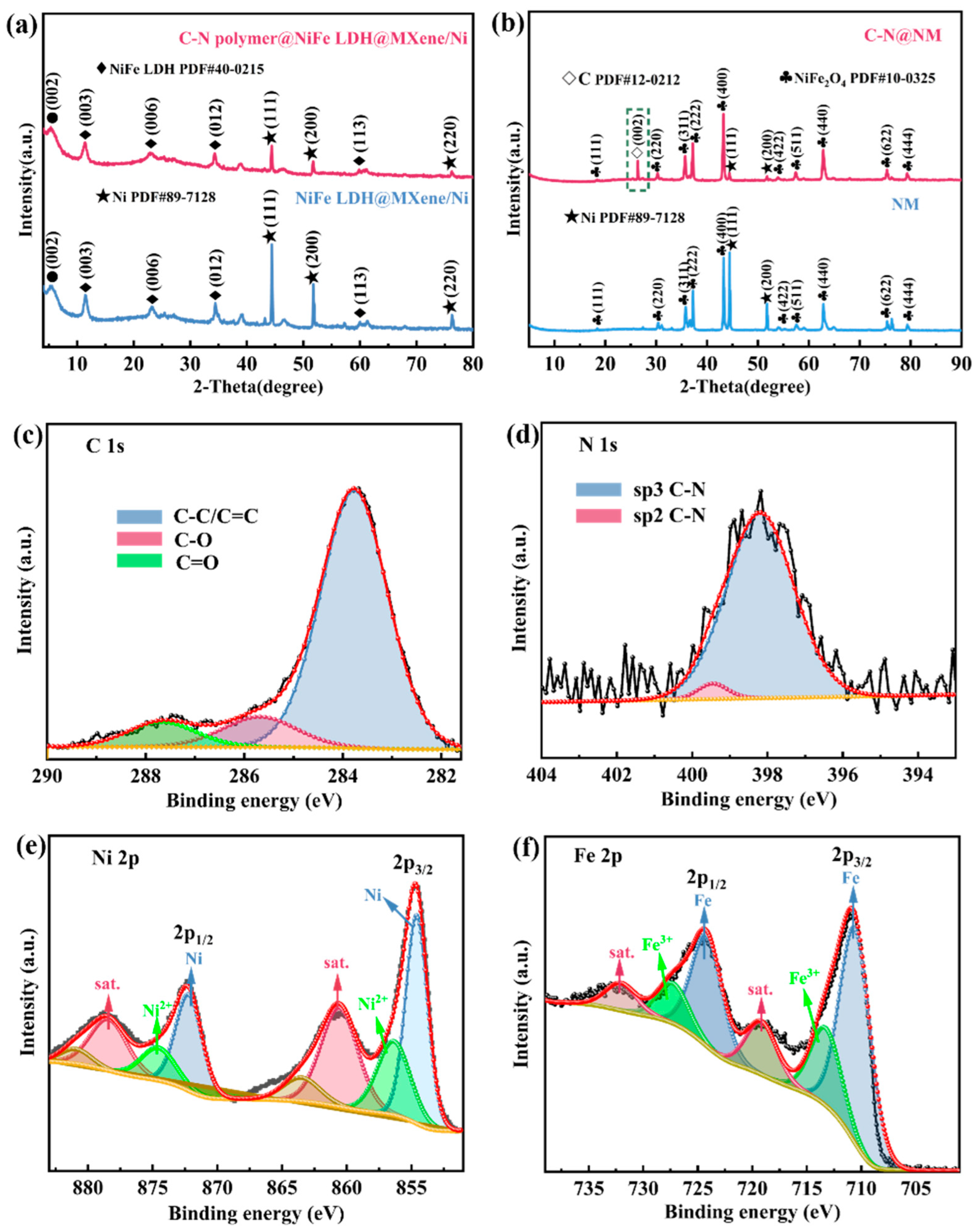
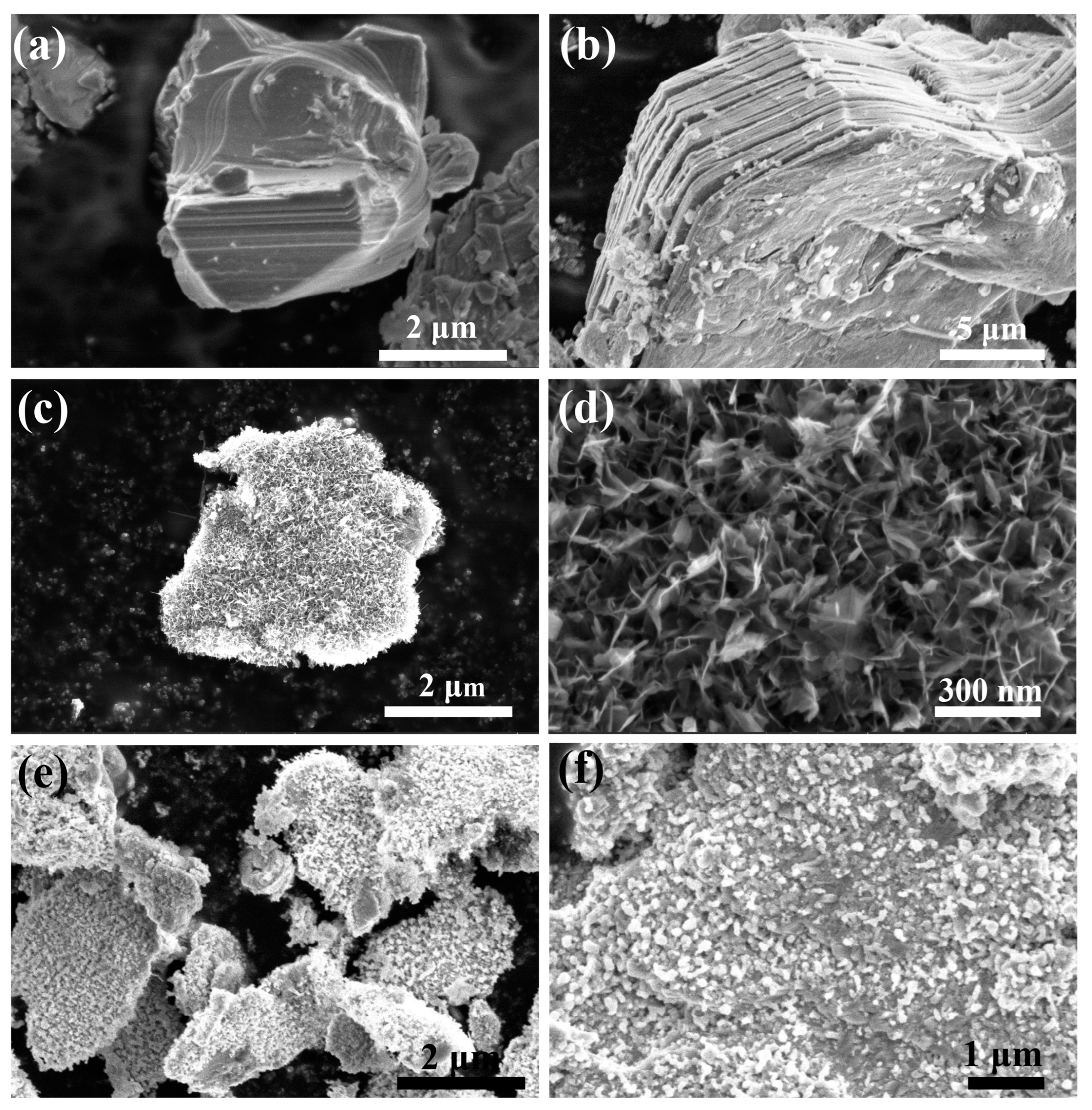
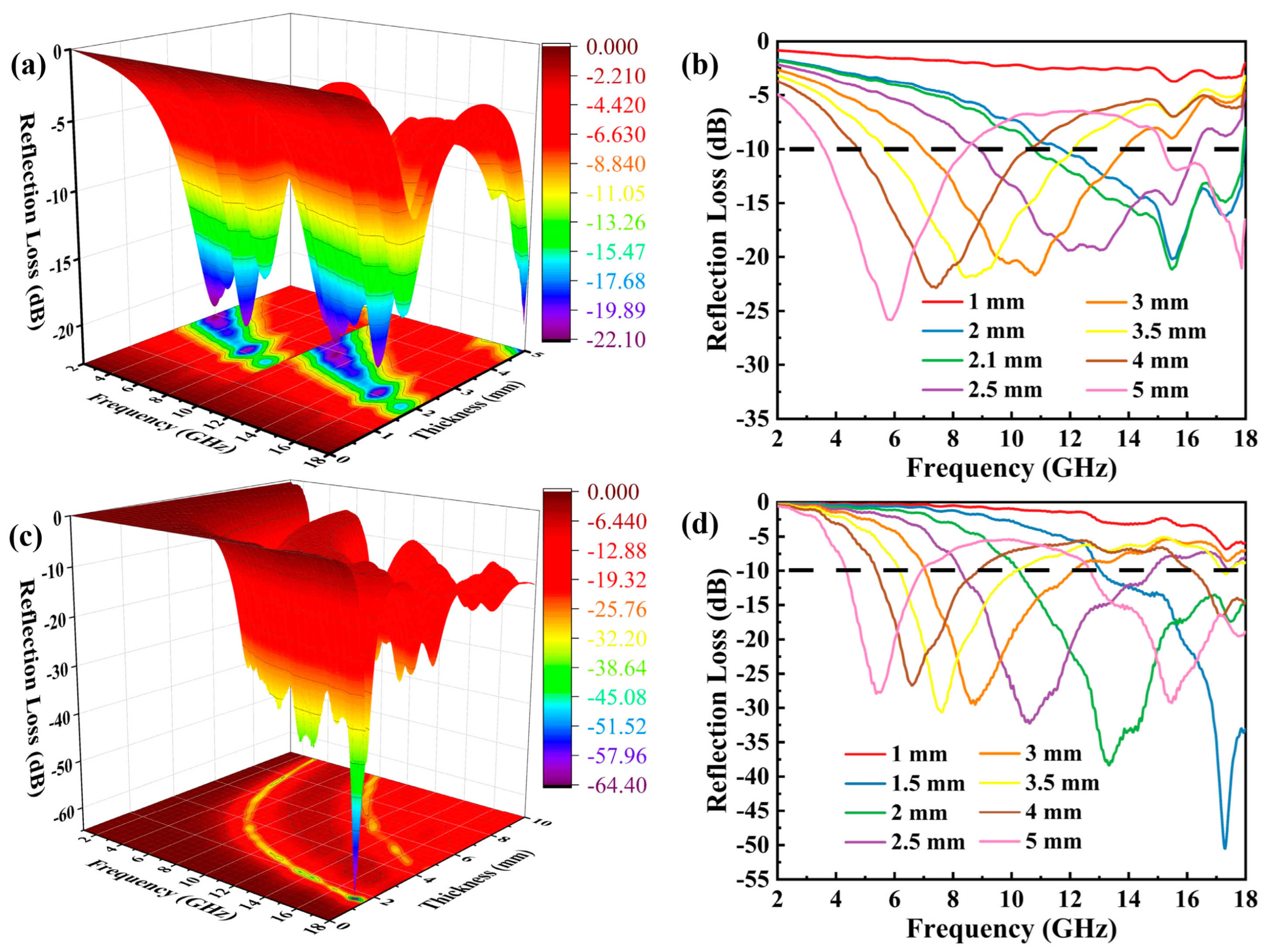
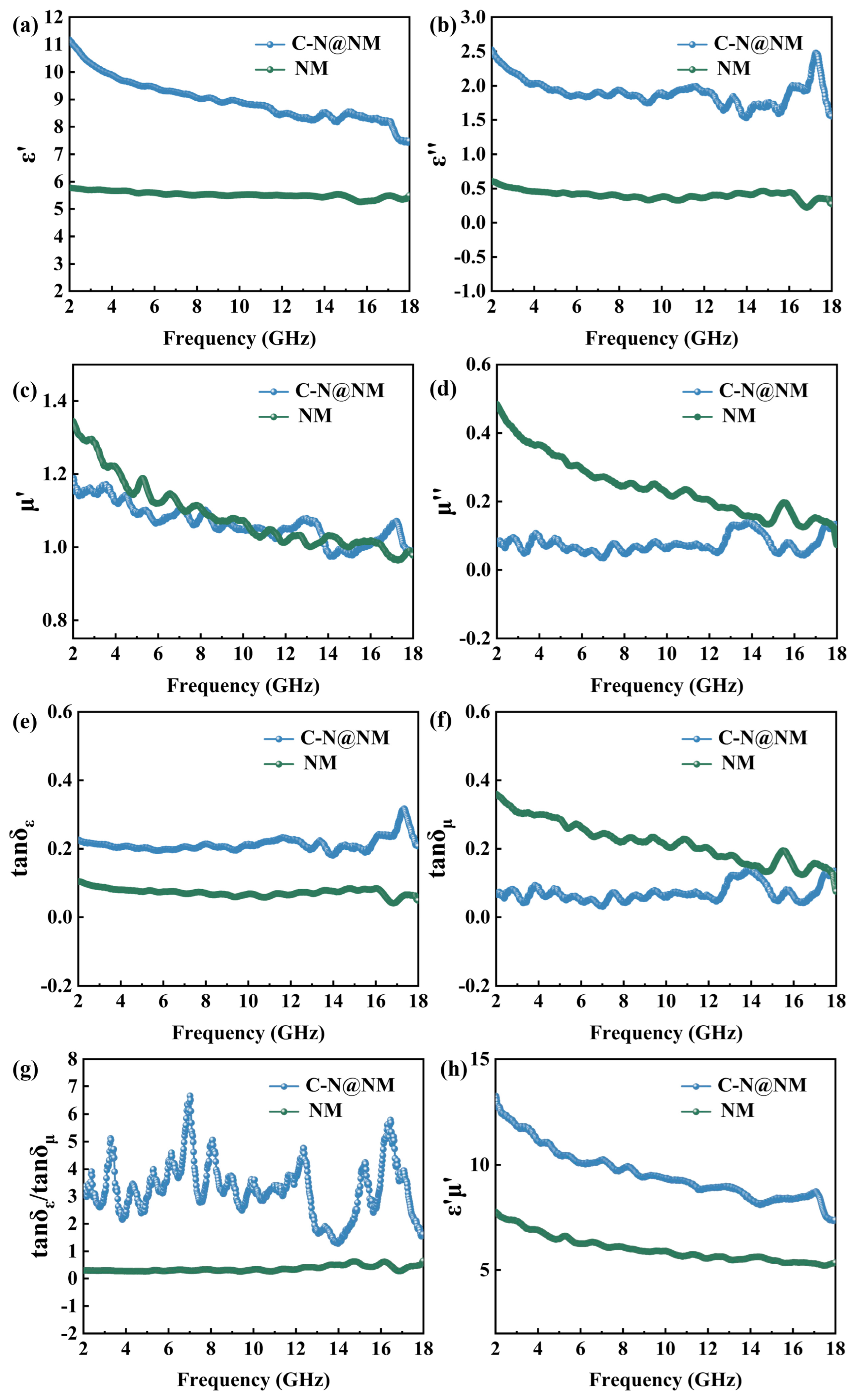
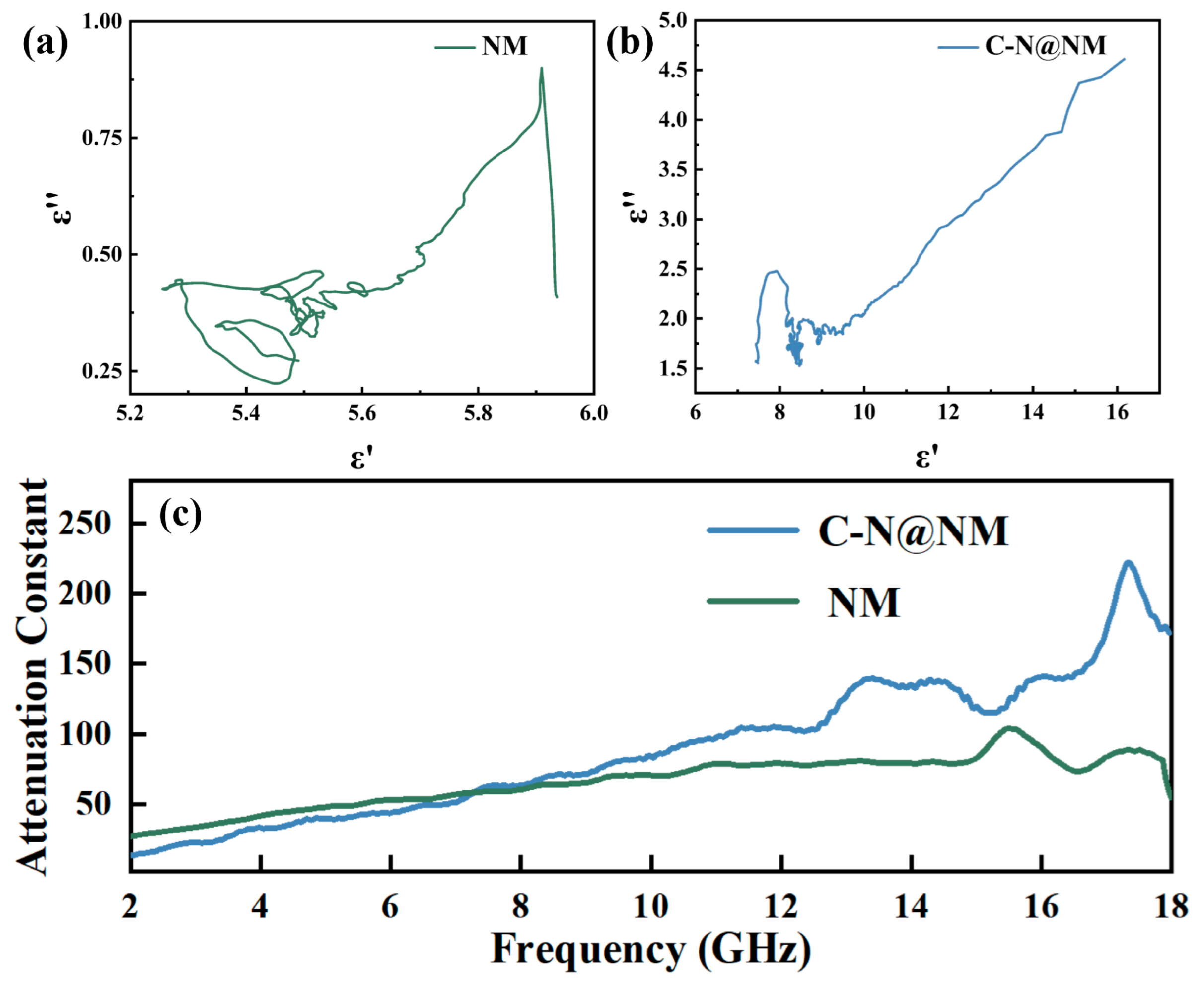
2. Results Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of MXene
3.3. Synthesis of NiFe LDH@MXene/Ni and C-N polymer@NiFe LDH@MXene/Ni
3.4. Synthesis of NiFe2O4@MXene/Ni and C-N@NiFe2O4@MXene/Ni
3.5. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Yang, X.; Shu, T.; Yang, X.; Qiao, M.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Rao, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P. MOFs-Derived Three-Phase Microspheres: Morphology Preservation and Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Molecules 2022, 27, 4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.; Ma, M.; Liao, Z.; Tong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Ma, Y.; Wu, G. One-dimensional Ni@Co/C@PPy composites for superior electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 605, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Di, X.; Fu, Y.; Wu, X.; Cao, J. Facile synthesis of the three-dimensional flower-like ZnFe2O4@MoS2 composite with heterogeneous interfaces as a high-efficiency absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 587, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plyushch, A.; Macutkevic, J.; Svirskas, S.; Banys, J.; Plausinaitiene, V.; Bychanok, D.; Maksimenko, S.; Selskis, A.; Sokal, A.; Lapko, K. Silicon carbide/phosphate ceramics composite for electromagnetic shielding applications: Whiskers vs. particles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 183105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, X.; Zeng, M.; Yu, R.; Wang, G.-S. Flexible nanocomposites with enhanced microwave absorption properties based on Fe3O4/SiO2 nanorods and polyvinylidene fluoride. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 12197–12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Song, H.; Liu, H.; Luo, C.; Ren, Y.; Ding, T.; Khan, M.A.; Young, D.P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Polypyrrole-interface-functionalized nano-magnetite epoxy nanocomposites as electromagnetic wave absorbers with enhanced flame retardancy. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 5334–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.-J.; Sui, G.-X. Lightweight spongy bone-like graphene@ SiC aerogel composites for high-performance microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karataş, Y.; Çetin, T.; Akkuş, İ.N.; Akinay, Y.; Gülcan, M. Rh (0) nanoparticles impregnated on two-dimensional transition metal carbides, MXene, as an effective nanocatalyst for ammonia-borane hydrolysis. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 11411–11423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Huyan, W.; Yang, F.; Yao, J.; Tan, R.; Chen, P.; Tao, X.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, P. Achieving ultra-wideband and elevated temperature electromagnetic wave absorption via constructing lightweight porous rigid structure. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastin, H.; Zhang, B.; Mazinani, A.; Hassan, K.; Bi, J.; Tung, T.T.; Losic, D. 3D bioprinting of cell-laden electroconductive MXene nanocomposite bioinks. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 16069–16080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, P.; Zhang, T.; Ye, X.; Yang, Y.; Gu, W. Confining tiny MoO2 clusters into reduced graphene oxide for highly efficient low frequency microwave absorption. Small 2020, 16, 2001686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Luo, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, S.; Deng, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Peng, S. Ti3C2 MXene: A promising microwave absorbing material. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 2398–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Han, G.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, B.; Feng, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, C. Promising Ti3C2T x MXene/Ni chain hybrid with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption and shielding capacity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25399–25409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Lin, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Highly efficient microwave-assisted Fenton degradation bisphenol A using iron oxide modified double perovskite intercalated montmorillonite composite nanomaterial as catalyst. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 594, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yao, Z.; Ng, V.M.H.; Zhou, J.; Kong, L.B.; Yue, K. Facile synthesis of ultrasmall Fe3O4 nanoparticles on MXenes for high microwave absorption performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 115, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Mohamed, A.M.; Mousavi, M.; Akinay, Y. Poly (pyrrole-co-styrene sulfonate)-encapsulated MWCNT/Fe–Ni alloy/NiFe2O4 nanocomposites for microwave absorption. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 259, 124169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinay, Y.; Hayat, F.; Kanbur, Y.; Gokkaya, H.; Polat, S. Comparison of microwave absorption properties between BaTiO3/Epoxy and NiFe2O4/Epoxy composites. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, E2143–E2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Xiang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, L.; Cui, E.; Deng, B.; Liu, Z.; Liu, R.; Lu, W. Layered NiCo alloy nanoparticles/nanoporous carbon composites derived from bimetallic MOFs with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Carbon 2019, 154, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Hu, R.; Huang, C.; Zhong, W.; Pan, L.; Feng, Y.; Qiu, T.; Zhang, C.J.; Yang, J. Novel solvothermal preparation and enhanced microwave absorption properties of Ti3C2Tx MXene modified by in situ coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 484, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Luo, H.; Deng, L.; Wang, S.; Wei, S.; Zheng, Y.; Jia, Q.; Liu, J. Interfacial design of sandwich-like CoFe@ Ti3C2Tx composites as high efficient microwave absorption materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 494, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; You, W.; Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Che, R. 3D seed-germination-like MXene with in situ growing CNTs/Ni heterojunction for enhanced microwave absorption via polarization and magnetization. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, L. Hierarchical Ti3C2T x MXene/Ni chain/ZnO array hybrid nanostructures on cotton fabric for durable self-cleaning and enhanced microwave absorption. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8634–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yin, X.; Duan, W.; Hao, B.; Kong, L.; Liu, X. Dielectric and microwave absorption properties of polymer derived SiCN ceramics annealed in N2 atmosphere. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, C.; Jia, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Zhang, D.; Wu, G. FeNi nanoparticles embedded reduced graphene/nitrogen-doped carbon composites towards the ultra-wideband electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 584, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Li, Q.; Yan, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.-B.; Zhou, X.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Xie, X. Multifunctional magnetic Ti3C2T x MXene/graphene aerogel with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6622–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shao, H.; Lin, Z.; Lu, J.; Liu, L.; Duployer, B.; Persson, P.O.; Eklund, P.; Hultman, L.; Li, M. A general Lewis acidic etching route for preparing MXenes with enhanced electrochemical performance in non-aqueous electrolyte. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, S.; Deng, L.; Shan, D.; Cao, C.; Luo, H.; Yan, S. Tunable electromagnetic and enhanced microwave absorption properties in CoFe2O4 decorated Ti3C2 MXene composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 504, 144210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, F.; Zuo, L.; Wu, J.; Sun, L.; Li, Z.; Hou, H. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon/Co3O4 nanocomposites as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7117–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhl, S.; Méndez, J.M. A review of the preparation of carbon nitride films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1999, 8, 1809–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Rodil, S.; Robertson, J. Interpretation of infrared and Raman spectra of amorphous carbon nitrides. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 155306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, W.; Wei, B.; Zu, J.; Yan, K. Hydrangea-like Ni/NiO/C composites derived from metal-organic frameworks with superior microwave absorption. Carbon 2021, 173, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faid, A.Y.; Barnett, A.O.; Seland, F.; Sunde, S. Ni/NiO nanosheets for alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction: In situ electrochemical-Raman study. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 361, 137040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, M.A.; Forse, A.C.; Griffith, K.J.; Lukatskaya, M.R.; Ghidiu, M.; Gogotsi, Y.; Grey, C.P. NMR reveals the surface functionalisation of Ti3C2 MXene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 5099–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Li, W.; Tong, Z.; Ma, Y.; Bi, Y.; Liao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wu, G.; Li, M.; Yue, J. NiCo2O4 nanosheets decorated on one-dimensional ZnFe2O4@SiO2@C nanochains with high-performance microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 578, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Shah, T.; Ahmad, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B. Fabrication of magnetic tubular fiber with multi-layer heterostructure and its microwave absorbing properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 577, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Wen, B. Hollow Ni/C microspheres derived from Ni-metal organic framework for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, X.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Nie, X.; Yu, R.; Shui, J. Magnetically aligned Co–C/MWCNTs composite derived from MWCNT-interconnected zeolitic imidazolate frameworks for a lightweight and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 30850–30861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-X.; Ma, T.; Shu, J.-C.; Cao, M.-S. Confinedly tailoring Fe3O4 clusters-NG to tune electromagnetic parameters and microwave absorption with broadened bandwidth. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G. Nitrogen-doped Co-C/MWCNTs nanocomposites derived from bimetallic metal–organic frameworks for electromagnetic wave absorption in the X-band. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.-S.; Yang, J.; Song, W.-L.; Zhang, D.-Q.; Wen, B.; Jin, H.-B.; Hou, Z.-L.; Yuan, J. Ferroferric oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube vs polyaniline/ferroferric oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube multiheterostructures for highly effective microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6949–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Han, X.; Xu, P.; Zhang, X.; Du, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. The electromagnetic property of chemically reduced graphene oxide and its application as microwave absorbing material. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 072906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C. Facile synthesis of RGO/Co@ Fe@ Cu hollow nanospheres with efficient broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xia, L.; Ma, S.; Yin, Z.; Wang, R.; Cao, Y. The recent progress of MXene-Based microwave absorption materials. Carbon 2021, 174, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Wang, Y.; Di, X.; Lu, Z.; Wang, P.; Wu, X. Heterostructure design of MOFs derived Co9S8/FeCoS2/C composite with efficient microwave absorption and waterproof functions. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Pu, F.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Bai, J. Interfacial interactions and synergistic effect of CoNi nanocrystals and nitrogen-doped graphene in a composite microwave absorber. Carbon 2016, 104, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Q.; Yang, X.; Shu, T.; Yang, X.; Qiao, M.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Rao, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. In Situ Synthesis of C-N@NiFe2O4@MXene/Ni Nanocomposites for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption at an Ultralow Thickness Level. Molecules 2023, 28, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010233
Sun Q, Yang X, Shu T, Yang X, Qiao M, Wang D, Liu Z, Li X, Rao J, Zhang Y, et al. In Situ Synthesis of C-N@NiFe2O4@MXene/Ni Nanocomposites for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption at an Ultralow Thickness Level. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010233
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Qing, Xin Yang, Tie Shu, Xianfeng Yang, Min Qiao, Dashuang Wang, Zhaohui Liu, Xinghua Li, Jinsong Rao, Yuxin Zhang, and et al. 2023. "In Situ Synthesis of C-N@NiFe2O4@MXene/Ni Nanocomposites for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption at an Ultralow Thickness Level" Molecules 28, no. 1: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010233
APA StyleSun, Q., Yang, X., Shu, T., Yang, X., Qiao, M., Wang, D., Liu, Z., Li, X., Rao, J., Zhang, Y., Yang, P., & Yao, K. (2023). In Situ Synthesis of C-N@NiFe2O4@MXene/Ni Nanocomposites for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption at an Ultralow Thickness Level. Molecules, 28(1), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010233







