Marine-Based Candidates as Potential RSK1 Inhibitors: A Computational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehbub, M.F.; Lei, J.; Franco, C.; Zhang, W. Marine sponge-derived natural products between 2001 and 2010: Trends and opportunities for discovery of bioactives. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4539–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghareeb, M.A.; Tammam, M.A.; El-Demerdash, A.; Atanasov, A.G. Insights about clinically approved and preclinically investigated marine natural products. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2020, 2, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C. Marine Natural Products in Medicinal Chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaspar, M.; de Pascale, D.; Andersen, J.; Reyes, F.; Crawford, A.; Ianora, A. The marine biodiscovery pipeline and ocean medicines of tomorrow. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2016, 96, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, A.L.; Olivier Peraud, O.; Kasanah, N.; Sim, J.W.; Kothalawala, N.; Anderson, M.A.; Abbas, S.H.; Rao, K.V.; Jupally, V.R.; Kelly, M.; et al. An analysis of the sponge Acanthostrongylophora igens microbiome yields an actinomycete that produces the natural product manzamine A. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Shigemori, H.; Kikuchi, Y.; Ishibashi, M.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Ircinals A and B from the Okinawan marine sponge Ircinia sp.: Plausible biogenetic precursors of manzamine alkaloids. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 2480–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlTarabeen, M.; Daletos, G.; Ebrahim, W.; Müller, W.E.G.; Hartmann, R.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Ircinal E, a New Manzamine Derivative from the Indonesian Marine Sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1951–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Watanabe, D.; Kawasaki, N.; Tsuda, M. Nakadomarin A, a novel hexacyclic manzamine-related alkaloid from Amphimedon sponge. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 9236–9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, M.; Hanora, A.; Khalifa, S.; Abou-El-Ela, S.H. Manzamines: A potential for novel cures. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.; Donia, M.S.; Peng, J.; Garcia-Palomero, E.; Alonso, D.; Martinez, A.; Medina, M.; Franzblau, S.G.; Tekwani, B.L.; Khan, S.I.; et al. Manzamine B and E and ircinal A related alkaloids from an Indonesian Acanthostrongylophora sponge and their activity against infectious tropical parasitic, and Alzheimer’s diseases. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 69, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Kamijyo, Y.; Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Fromont, J.; Gonoi, T.; Kobayashi, J. Zamamiphidin A, a new manzamine related alkaloid from an Okinawan marine sponge Amphimedon sp. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Takahashim, Y.; Kubota, T.; Fromont, J.; Ishiyama, A.; Otoguro, K.; Yamada, H.; Ōmura, S.; Kobayashi, J. Zamamidine C, 3,4-dihydro-6- hydroxy-10,11-epoxymanzmine A, and 3,4-dihydromanzamine J N-oxide, new manzamine alkaloids from sponge Amphimedon sp. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 2313–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edrada, R.A.; Proksch, P.; Wray, V.; Witte, L.; Müller, W.E.G.; Van Soest, R.W.M. Four new manzamine-type alkaloids from Philippine marine sponge Xestospongia ashmorica. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, A.E.; Fromentin, Y.; Zou, Y.; Hamman, M.T. Acantholactone, a new manzamine related alkaloid with an unprecedented δ-lactone and εlactam ring system. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 6329–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousaf, M.; Hammond, N.L.; Peng, J.; Wahyuono, S.; McInstosh, K.A.; Charman, W.N.; Mayer, A.M.S.; Hamann, M.T. New manzamine alkaloids from an Indo-Pacific sponge. Pharmacokinetics, oral availability, and the significant activity of several manzamines against HIV-I, AIDS opportunistic infections, and inflammatory diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 3512–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Hayashida, A.; Horlad, H.; Kato, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Takeya, M.; et al. Manzamine A, a marine-derived alkaloid, inhibits accumulation of cholesterol ester in macrophages and suppresses hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis in vivo. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3831–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Eguchi, K.; Kawabata, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Takeya, M.; Yokosawa, H.; et al. Acantholactam and pre-neo-kauluamine, manzamine-related alkaloids from the Indonesian marine sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusato, A.; Kato, H.; Nehira, T.; Eguchi, K.; Kawabata, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Takeya, M.; et al. Acanthomanzamines A−E with new manzamine frameworks from the marine sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3888–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, R.; Higa, T.; Jefford, C.W.; Bernardinelli, G. Manzamine A, a novel antitumor alkaloid from a sponge. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 6404–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallifatidis, G.; Hoepfner, D.; Jaeg, T.; Guzman, E.A.; Wright, A.E. The marine natural product manzamine A targets vacuolar ATPases and inhibits autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3500–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, M.; Alonso, D.; Martin-Aparicio, E.; Fuertes, A.; Perez-Puerto, M.J.; Castro, A.; Morales, S.; Navarro, M.L.D.; Monte-Millan, M.; Medina, M.; et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) inhibitory activity and structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies of the manzamine alkaloids. Potential for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Hall, M.L.; Lach, J.; Clifford, J.; Chandrasena, K.; Canton, C.; Kontoyianni, M. Effect of the marine β-carboline alkaloid Manzamine A on RSK1 vs RSK2 inhibition: A biochemical and computational study. Comms 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Roux, P.P. Regulation and function of the RSK family of protein kinases. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffron, D.; Mandell, J.W. Differential localization of MAPK-activated protein kinases RSK1 and MSK1 in mouse brain. Brain Res. Mol. 2005, 136, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasena, K.; Hall, M.L.; Mayer, A.M.S. The mechanism of the marine β-carboline thromboxane B2 inhibitor Manzamine A: Possible involvement of rat brain microglia p90 ribosomal S6 kinase 1 (RSK1). FASEB J. 2021, 27, 888.1. [Google Scholar]
- AlTarabeen, M.; El-Neketi, M.; Albohy, A.; Müller, W.E.G.; Rasheed, M.; Ebrahim, W.; Proksch, P.; Ebada, S.S. Isolation and Molecular Docking of Cytotoxic Secondary Metabolites from Two Red Sea Sponges of the Genus Diacarnus. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Albohy, A.; Abdulrazik, B.S.; Bayoumi SA, L.; Malak, L.G.; Khallaf IS, A.; Bringmann, G.; Farag, S.F. Natural coumarins as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents supported by docking analysis. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 16970–16979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, S.A.; Zahran, E.M.; Abdel Fadeel, M.R.; Albohy, A.; Safwat, M.A. New Acaciin-Loaded Self-Assembled Nanofibers as M(Pro) Inhibitors Against BCV as a Surrogate Model for SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 1789–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.W.; Zhang, Y. DockRMSD: An open-source tool for atom mapping and RMSD calculation of symmetric molecules through graph isomorphism. J. Cheminform. 2019, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
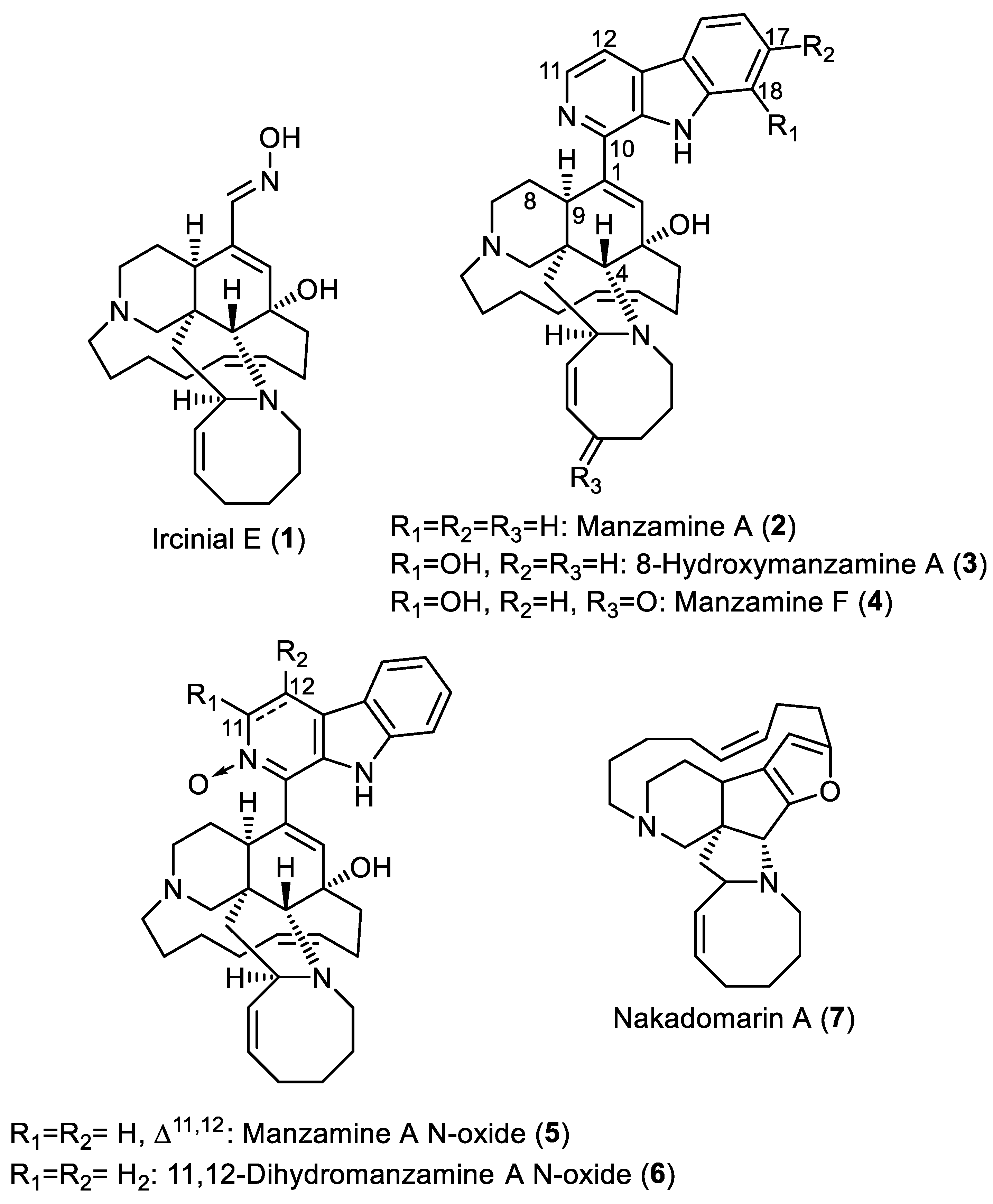

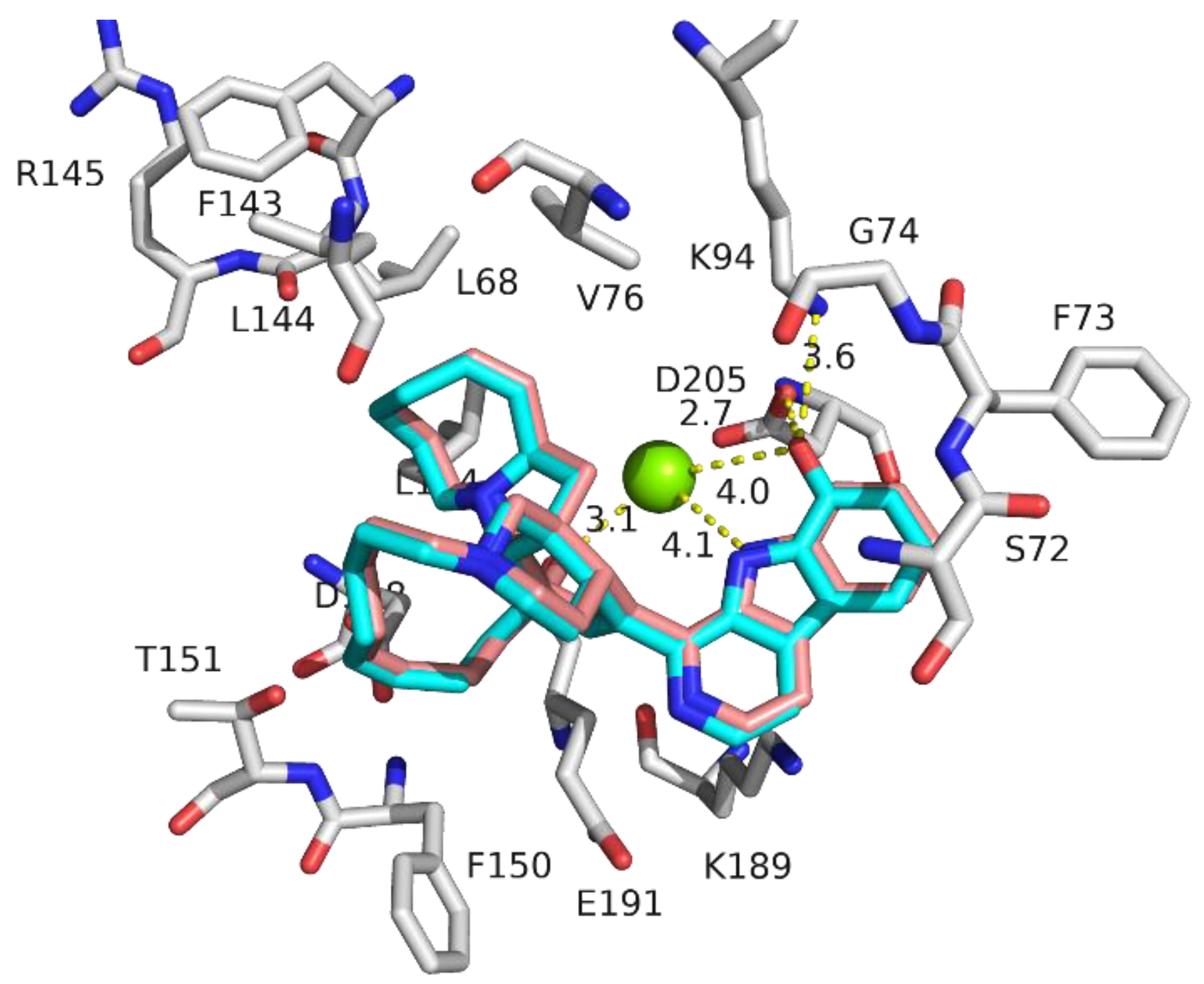
| Name | IC50 (µM) | Docking Score (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Ircinial E (1) | 21.7 | −7.5 |
| Manzamine A (2) | 3.3 | −9.9 |
| 8-Hydroxymanzamine A (3) | 3 | −10.2 |
| Manzamine F (4) | 4.1 | −10.3 |
| Manzamine A N-oxide (5) | 3.1 | −10.6 |
| 3,4-Dihydromanzamine A N-oxide (6) | 2.8 | −9.8 |
| Nakadomarin A (7) | - | −8.0 |
| AMP-PCP Ligand | −8.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlTarabeen, M.; Al-Balas, Q.; Albohy, A.; Müller, W.E.G.; Proksch, P. Marine-Based Candidates as Potential RSK1 Inhibitors: A Computational Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010202
AlTarabeen M, Al-Balas Q, Albohy A, Müller WEG, Proksch P. Marine-Based Candidates as Potential RSK1 Inhibitors: A Computational Study. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010202
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlTarabeen, Mousa, Qosay Al-Balas, Amgad Albohy, Werner Ernst Georg Müller, and Peter Proksch. 2023. "Marine-Based Candidates as Potential RSK1 Inhibitors: A Computational Study" Molecules 28, no. 1: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010202
APA StyleAlTarabeen, M., Al-Balas, Q., Albohy, A., Müller, W. E. G., & Proksch, P. (2023). Marine-Based Candidates as Potential RSK1 Inhibitors: A Computational Study. Molecules, 28(1), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010202







