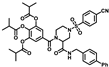
Abstract
The Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and dengue fever (DF) pandemics both remain to be significant public health concerns in the foreseeable future. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs and vaccines are both indispensable to eliminate the epidemic situation. Here, two piperazine-based polyphenol derivatives DF-47 and DF-51 were identified as potential inhibitors directly blocking the active site of SARS-CoV-2 and DENV RdRp. Data through RdRp inhibition screening of an in-house library and in vitro antiviral study selected DF-47 and DF-51 as effective inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2/DENV polymerase. Moreover, in silico simulation revealed stable binding modes between the DF-47/DF-51 and SARS-CoV-2/DENV RdRp, respectively, including chelating with Mg2+ near polymerase active site. This work discovered the inhibitory effect of two polyphenols on distinct viral RdRp, which are expected to be developed into broad-spectrum, non-nucleoside RdRp inhibitors with new scaffold.
1. Introduction
Coronavirus and flavivirus both encode single-stranded positive sense RNA (+RNA), containing some viruses seriously threatening human health. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) of β-coronavirus, as the causative pathogen of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), is now still spreading worldwide [1]. The clinical manifestations of COVID-19 vary from asymptomatic to common fever, and up to more severe symptoms such as pneumonia, respiratory failure, multiorgan failure, and eventually death [2]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there were over 630 million confirmed infections and 6.6 million deaths globally in mid-November 2022 [3]. The emergence of the Omicron variant, which is highly infectious and resistant to the vaccines, has reduced the effectiveness of the vaccine by at least 40% [4]. Dengue virus (DENV) belongs to a serotype subgroup of flavivirus which is mainly insect-borne, causing dengue fever (DF), dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF), and dengue shock syndrome, with high incidence rate and mortality. Currently, in some underdeveloped countries and areas, the regular outbreaks of dengue fever form a double threat along with COVID-19 pandemic [5,6]. Among these territories, the DENV-SARS-CoV-2 co-infection has been a serious situation, which has been one of the focus issues on COVID-19 epidemiology. Thus, developing broad-spectrum antiviral agents blocking both SARS-CoV-2 and DENV is a promising strategy to alleviate the public health burden in certain areas around the world [7,8]. Although supportive therapy of dengue fever remarkably reduced the mortality rate, no specific therapy agents towards DENV were approved. To end the global pandemic and prevent future outbreaks of highly contagious RNA viruses, antivirals are expected to act as essential complements to vaccines.
RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase (RdRp) acts as a critical component in the life cycle of both SARS-CoV-2 and DENV. In the two viruses, RdRp adapts the “Finger-Palm-Thumb” conformation formed by several conserved motifs, and utilizes two sequential aspartate residues coordinated with Mg2+ ions as their catalytic centers [9,10,11,12,13]. The conservation of RdRp among evolutionary distant RNA viruses and the absence of host homologs apparently make it an ideal target for the development of potential antivirus drug candidates to multiple viruses.
RdRp inhibitors can be classified into nucleoside inhibitors (Nis) and non-nucleoside inhibitors (NNIs), based on their structures. Nucleoside inhibitors bind to RdRp active center and could be incorporated into elongating RNA chain, causing chain termination or lethal mutagenesis. Four repurposed SARS-CoV-2 RdRp inhibitors: Remdesivir, favipiravir, molnupiravir, and bemnifosbuvir (AT-527) were investigated for their anti-COVID-19 activity (Figure 1) [14]. Among them, remdesivir (EC50 = 0.77 μM) was the first drug urgently approved to treat COVID-19 in 2020 by the FDA. However, several clinical trials have demonstrated that the time point of efficacy of remdesivir was not significantly earlier than that of placebo group [15], and it has failed to significantly improve mortality, cure rate, recovery time, and other indicators [16,17,18]. Favipiravir, as a pyrazinecarboxamide derivative, requires in vivo conversion to ribosylated triphosphate favipiravir, to act as an antiviral agent. The complex structure of favipiravir and SARS-CoV-2 RdRp was revealed by electron cryomicroscopy, demonstrated the unexpected base pairing pattern between favipiravir and pyrimidine residues, and explained its ability to mimic adenine and guanine nucleotides [19]. Early studies showed favipiravir could alleviate symptoms and shorten hospitalization; thus, it has been approved in India and Russia. However, FUJIFILM Toyama Chemical Co., Ltd. announced the cessation of the development of the anti-influenza drug Avigan for COVID-19 infection on October 14, 2022 [20]. Molnupiravir (EC50 = 0.3 µM) induces lethal mutagen in SARS-CoV-2 genome. By the end of 2021, FDA issued emergency use authorization for molnupiravir for it led to a 50% decrease of hospitalization or death in a clinical trial, but only for non-hospitalized patients when no other therapies are available [21]. Bemnifosbuvir (EC90 = 0.47 µM) is a repurposed SARS-CoV-2 RdRp inhibitor, but failed in phase II clinical trial of treating COVID-19 [22]. Further phase II and III trials are setting out to evaluate whether bemnifosbuvir could be applied in the future [23]. Meanwhile, bemnifosbuvir was also reported to effectively inhibit DENV2/DENV3 in vitro (EC50 = 0.48/0.77 µM) and in vivo [24]. The current situation urgently calls for more RdRp inhibitors with definite therapeutic effect.
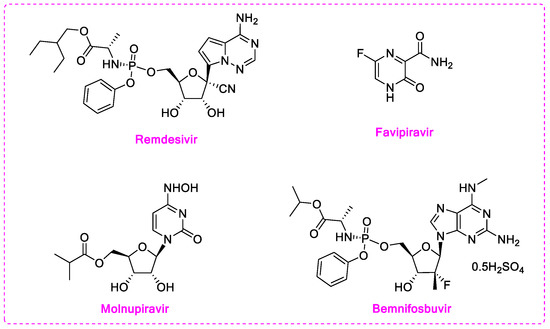
Figure 1.
Structures of current nucleoside or nucleoside precursors RdRp inhibitors.
Non-nucleoside inhibitors may act directly on RdRp active site or bind to its potential allosteric sites, thus impairing polymerase function [14]. Compared with nucleoside inhibitors, NNIs do not incorporate into RNA chains, therefore can evade the exonuclease (Nsp14) excision mechanism, and have greater potential of modification and development. Meanwhile, targeting the catalytic metal ions by chelators has been proved successful in inhibiting HIV, HCV, and influenza virus [25,26,27]. The strategy of utilizing catalytic Mg2+ of SARS-CoV-2/DENV RdRp as an anchoring point of metal chelating agents had been reported. Flavonoids with polyphenol moiety display potent inhibition towards SARS-CoV-2 RdRp in computational simulation or experiments. Cyanidin 3-O-rutinoside and petunidin 3′5-O-diglucoside exhibited outstanding binding affinity in virtual screening [28], while Baicalein (EC50 = 4.5 μM) and Baicalin (EC50 = 9.0 μM) are potent SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors in both RdRp enzymatic assay and cellular assay (Figure 2) [29]. Docking results highlighted that the pyrogallol group in these compounds provides multiple hydrogen bond interactions or chelates with Mg2+ in the RdRp active site. Pyridoxine derivative DMB220 (EC50 = 2.7 ± 0.6 μM) and one quinolone-like compound (EC50 = 3.3 ± 0.5 μM) with metal-chelating groups [30,31], are reported to inhibit DENV. Yet no metal chelators targeting virus RdRp have been approved for antivirus therapy.
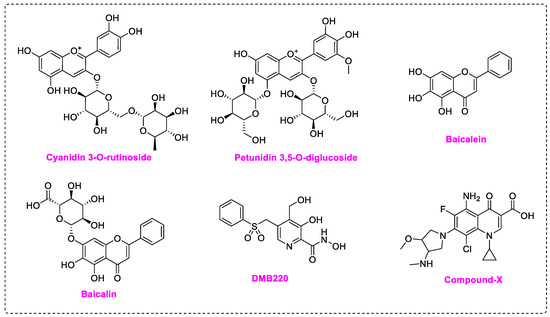
Figure 2.
Structures of non-nucleoside inhibitors targeting SARS-CoV-2/DENV RdRp.
In this study, in order to search for potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 and DENV RdRp, we screened metal ion chelators from an in-house compound library, based on our SARS-CoV-2 RdRp inhibition screening assay. Two compounds DF-47 and DF-51 were chosen, then re-evaluated for their IC50 values and cellular activities in vitro. Docking studies and molecular dynamic simulation studies identified them as active inhibitors towards both SARS-CoV-2 and DENV RdRp. Discovery of these novel inhibitors offers future choice of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor development, and reveals critical residues around RdRp catalytic site for target-based drug designing.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. In-House Library Screening For Potent Rdrp Inhibitors
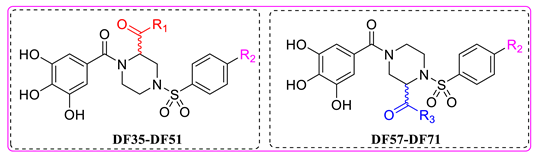
In this study, we evaluated RdRp binding activity of an in-house compound library containing metal ion chelators with piperazine scaffold (over 100 compounds of polyphenol, 1-hydroxy-1,8-naphthyridinone, 5-hydroxypyrido [2,3-b]pyrazinone, and 4-hydroxyquinazolinone analogues, originally designed and synthesized for anti-HIV-1, see Supplementary Material) [32,33,34,35,36] screened by established high-throughput enzyme assays of RdRp complex, as novel antiviral therapeutic candidates for COVID-19 through target activity verification and cell-based activity evaluation. A polymerase reaction system was built to evaluate the residual activity of RdRp in the presence of inhibitors [37,38]. Recombinant non-structural proteins were expressed, purified, and mixed in assay buffer to form the SARS-CoV-2 polymerase complex. The RNA template applied in the assay was specially designed to form a hairpin structure at 3’ end as the primer of polymerase reaction, and carries a 6-FAM label at 5’ end. After a reasonable time for polymerase reaction progress, the system was immediately quenched. The produced RNA chain was visualized and quantified on gel. The amount of full-length RNA product relates to RdRp activity. Preliminary screening involves all compounds under a single concentration of 50 μM. A total of 11 compounds with top inhibition rates were selected for RdRp inhibition tests under gradient concentrations (listed in Table 1). The visualized results from the gel experiments are displayed in Figure 3.

Table 1.
Compounds with top inhibition rates.
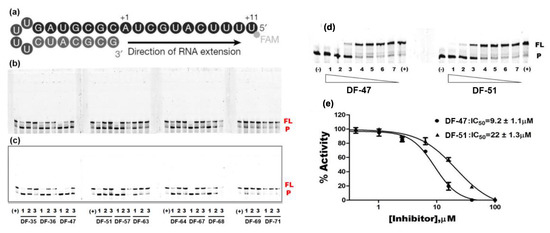
Figure 3.
Inhibition of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity of 11 compounds. (a) Graphic representation of the 5′-6 FAM-labeled hairpin RNA substrate as primer-template used to monitor the inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp activity. +1 and +11, the positions of the first and the last nucleotide incorporated, respectively. (b) Gel picture with auto-contrast. Compound concentration: 1. 20; 2. 10; 3. 5 µM; (-): reaction in the absence of rNTPs; (+): reaction in the absence of compound. P: FAM-labeled RNA primer; FL: full-length RNA product. The data shown are from one representative experiment. (c) Gel picture with adjusted contrast. (d) Gel pictures of DF-47 and DF-51. The concentrations of the compounds used are as follows: 1. 100; 2. 40; 3. 16; 4. 6.4; 5. 2.6; 6. 1; 7. 0.4 µM. (e) Dose–response curves of DF-47 and DF-51.
2.2. Evaluation of Virus Inhibition Activity
For the selected compounds listed above, we further evaluated their enzymatic inhibition potency under three concentration gradients (5, 10, and 20 μM), and the density of visualized stripes represent concentrations of RNA template and product in each well. At a concentration of 20 µM, most of the compounds still exhibited significant inhibition of RdRp activity. At 10 μM, DF-36, DF-47, DF-51, and Baicalein remained partially active, whereas at 5 µM, only limited activity was observed (Figure 3c). To obtain accurate IC50 values for DF-47 and DF-51, both compounds were again tested under seven concentrations ranging from 0.4 to 100 μM (Figure 3d) to depict full dose–response curves. DF-47 turned out to be the most potent SARS-CoV-2 RdRp inhibitor with an IC50 of 9.2 ± 1.1 μM. Unlike RDV-TP which causes delayed chain-termination during RNA synthesis via incorporation of the nucleotide analog by the RdRp [39,40], these polyphenols are most likely to act by chelating with the magnesium ions of active center, thus directly blocking SARS-CoV-2 RdRp function.
To further exploit pan-RNA virus inhibition of the compounds in Table 1, the compounds were evaluated as potential inhibitors of the RdRp domain of DENV NS5. We used a fluorescent-based assay to screen the compounds from Table 1 as potential DENV RdRp inhibitors. Only DF-47 and DF-51 were endowed with detectable inhibition towards DENV RdRp (Table 2). DF-51 displayed a low-micromolar IC50 value of 4.8 ± 0.7 µM towards DENV RdRp, whereas DF-47 had relatively weaker inhibition, in contrast to the results of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp.

Table 2.
Inhibition of dengue virus RdRp activity assessed in a cell-free fluorescent plate assay.a.
2.3. Antiviral Activity of DF-47 and DF-51
Subsequently, we measured the antiviral activity of DF-47 and DF-51 towards SARS-CoV-2 and DENV3 in the BSL-3 (biosafety level 3) laboratory, along with their cytotoxicity to corresponding cell lines. Remdesivir and Baicalein were employed as positive controls in cellular SARS-CoV-2 inhibition tests. The test results were depicted in Table 3. The activity of the positive control was consistent with that reported in the literature [29], which proved the validity of our method. Unfortunately, DF-47 and DF-51, despite their good inhibitory activity against RdRp, displayed no significant antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. However, both compounds showed moderate inhibition of DENV3 in A549 cells with measurable EC50 values, consistent to their IC50 values. In addition, DF-47 and DF-51 displayed no cytotoxicity for either Vero E6 or A549 cells (CC50 > 100 μM).

Table 3.
Antiviral activity and cytotoxicity of polyphenols and positive controls.
The absence of antiviral activity towards SARS-CoV-2 might be due to the poor membrane permeability resulted from multiple phenolic hydroxy groups. To verify this, we utilized the Membrane permeability prediction module [41,42] in Schrödinger suites to quantitate cell-entering property of DF-47 and its analogs, along with two proposed prodrugs DF-47-pro/DF-51-pro (tri-isobutyryl ester). The permeability was evaluated by the Membrane dG Insert, of which higher absolute value represents lower permeability. As shown in Table 4, all the DF series compounds possessed extraordinarily low predicted permeability, compared with their prodrugs. This explains why DF-47 lacked cellular activity and hints for further modifications. Therefore, we will further chemically modify the compound according to the design strategy of prodrug.

Table 4.
Permeability prediction value of selected compounds.
2.4. In Silico Study
As DF-47 and DF-51 are non-nucleoside inhibitors with polyphenol group, their possible mechanism of inhibition might be through binding to the RdRp by chelating with the Mg2+ at the active site. In order to explore their mechanism, we conducted in silico studies to determine the possible binding mode between DF-47 and SARS-CoV-2 RdRp.
First, docking results demonstrated that DF-47 could bind to SARS-CoV-2 RdRp with a binding energy of −7.916 kcal/mol, which displayed stronger binding energy than that of Remdesivir (−6.5 kcal/mol) [40]. Most importantly, DF-47 is likely to chelate with two Mg2+ of RdRp. Therefore, it is a reasonable assumption that DF-47 inhibits RdRp activity through chelating with Mg2+ and blocking its active site.
Figure 4a,b shows the 2D-interaction diagram and the 3D docking pose of DF-47. The two Mg2+ directly interacted with the phenolic hydroxyl groups, enabling DF-47 to anchor in the entry tunnel of NTPs. Meanwhile, Tyr619, Asp760, Asp761, and Glu811 bind to the ligand through metal coordination bonds. Other interactions with essential residues in conserved motifs or with amino acids responsible for NTP recognition are also observed [37]; for example, the hydrogen bond interaction between Cys799 and the amino group of DF-47, as well as between Lys551 and the amide oxygen in the ligand structure. The benzenesulfonamide and bisphenyl moieties have Pi-Pi stacking with His810 and His439, respectively, whereas Arg836 and phenyl generated Pi-cation interaction. These interactions with free RdRp may lead to a loss in its recognition and catalytic activity. For DF-51, it adopted a slightly different binding position, yet still maintained metal coordination with the two magnesium ions (Figure 4c,d), according to the docking results.
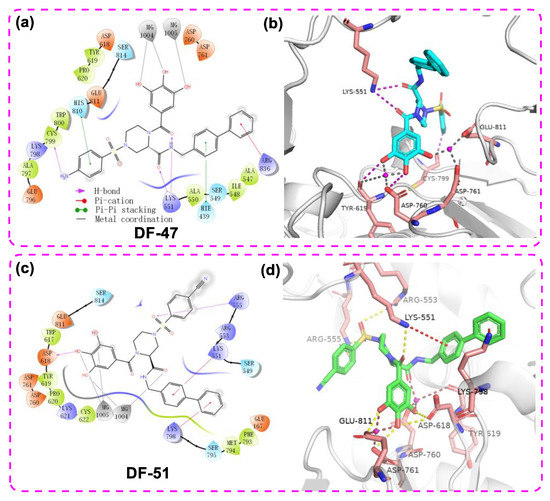
Figure 4.
The 2D ligand–protein interaction diagram (a)/3D docking pose (b) of DF-47 with DENV3 NS5 and the 2D ligand–protein interaction diagram (c)/3D docking pose (d) of DF-51 with SARS-CoV-2 RdRp (PDB ID: 7BV2). The pink spheres represent Mg2+. The purple arrows indicate the hydrogen bonds; the red line represents Pi–cation interaction; the gray line represents metal coordination; the green lines represent pi-pi stacking.
The docking study also revealed multiple interactions between DF-51 and RdRp domain of DENV3 NS5 (Figure 5 a,b). The binding energy reached −8.061 kcal/mol, while chelation of the single Mg2+ and several hydrogen bonds were hypothetically established. In addition to binding with metal ion, the polyphenol moiety formed cation-π stacking with protonated Lys689 by its electron-rich phenyl ring. Two amide oxygen atoms snugly contacted with Cys709 and Ser710, together with the cyano group reaching backbone NH of Gly536. These H-bonds are supposed to stabilize DF-51 at the hydrophilic pocket of RdRp catalytic center. At the far end, the biphenyl sidearm fitted into a shallow groove formed by Tyr606 and Ile797, which accounts for additional hydrophobic contacts. This bulky group is supposed to restrict the conformational changes of priming loop, which is an essential moiety in catalytic function [12,13]. Given that the Mg2+ of DENV3 RdRp may not mediate catalytic process [43], inhibition of DF-51 most likely resulted from blocking the NTP tunnel and disturbing priming loop conformation. In another docking study, DF-47 exhibited a similar binding mode with that of DF-57, but formed less interactions with nearby residues (Figure 5 c,d).
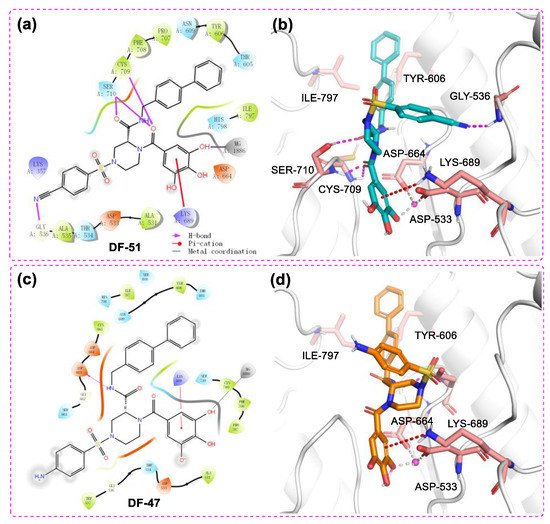
Figure 5.
The 2D ligand–protein interaction diagram (a)/3D docking pose (b) of DF-51 with DENV3 NS5 and the 2D ligand–protein interaction diagram (c)/3D docking pose (d) of DF-47 with DENV3 NS5 RdRp domain (PDB ID: 2J7U). The pink spheres represent Mg2+. The purple arrows represent the hydrogen bonds; the red line represents Pi–cation interaction; the gray line represents metal coordination.
To further evaluate the binding stability of DF-47 and DF-51 towards SARS-CoV-2/DENV3 RdRp, RMSD and total energy (MMGBSA) were predicted through MD simulation systems. The average position fluctuations of ligand and protein atoms, represented by RMSD value, were shown in Figure 6. For DF-47 complexed with SARS-CoV-2 RdRp, the ligand RMSD remained lower than that of protein RMSD, indicating its stable binding in active site. However, it is also observable that the RMSD value of DF-47 is slightly unstable (Figure 6a). In the case of DENV3 RdRp and DF-51, significant fluctuations of ligand RMSD ranges from 0 to 300 ns of simulation. However, the RMSD value of DF-51 remained stable around 2–2.5 angstroms during the last 200 ns of MD simulation, signifying its well-fitting into the active site (Figure 6b). The average ligand binding free energy of DF-47 and DF-51 were calculated by MMGBSA evaluation. DF-47 has a biding energy of −124.02 kcal/mol towards SARS-CoV-2 RdRp, while DF-51 has higher binding energy (−81.77 kcal/mol) with DENV3 RdRp, corresponding to its lower binding stability.
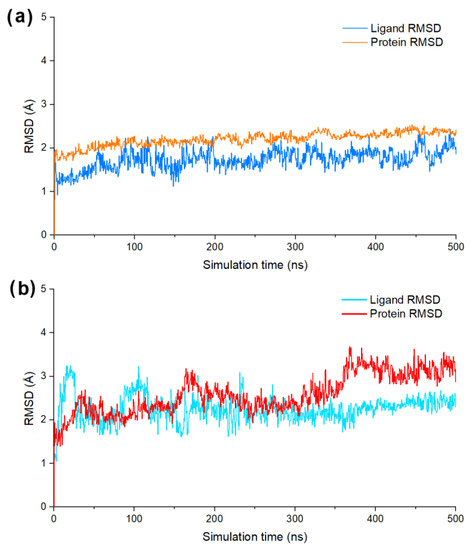
Figure 6.
(a) The ligand/protein RMSD value of DF-47 bind with SARS-CoV-2 RdRp; (b) the ligand/protein RMSD value of DF-51 bind with DENV3 RdRp.
To evaluate the stability of chelation interaction between pyrogallol group and Mg2+, the distance between 4-OH group and Mg2+ of SARS-CoV-2/DENV3 RdRp was calculated. Both models showed a stable and close contact of phenol-OH group and Mg2+ in protein model during the whole process of simulation, demonstrating that their tight binding are contributed by metal chelation (Figure 7a,b).
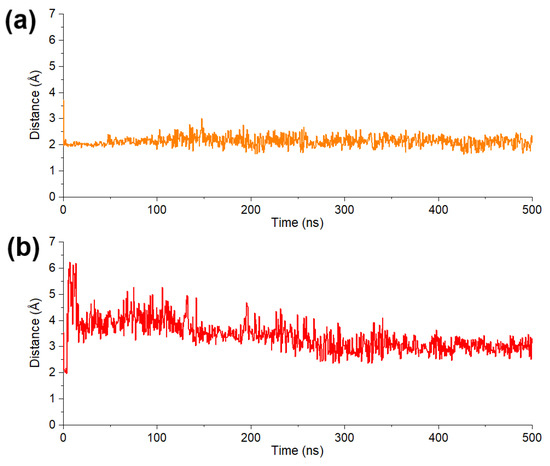
Figure 7.
(a) Average distance between 4-OH of pyrogallol moiety in DF-47 and two Mg2+. (b) Distance between 4-OH of pyrogallol moiety in DF-51 and Mg2+.
Accumulating studies are proving the inhibition activity of polyphenols towards different enveloped RNA viruses, such as influenza, dengue, HIV, SARS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 [44,45]. Here, we demonstrated the antiviral activity of DF-47 and DF-51 against SARS-CoV-2 and DENV3 through interacting with RdRp by metal chelation. Such inhibition across different RNA viruses is noteworthy. We presume this class of compounds obtain strong interaction with RdRp by anchoring into the metal-containing catalytic center via the pyrogallol moiety, and adapting to nearby tunnels with flexible piperazine scaffold joint with H-bond donor/acceptors. However, additional research on structural biology is still needed to depict a comprehensive mechanism and key pharmacophores.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Compounds and the Stock Solution
All the compounds were synthesized and published by our laboratory as racemic mixtures [32,33,34,35,36]. Each compound was prepared as a 10 mM stock solution with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, Sigma Aldrich, Belgium) and then stored at −20 °C. In the cellular antivirus experiment, MEM (Gibco, NY, USA), containing 2% fetal bovine serum (FBS) was used to dilute the stock solution into gradients.
3.2. Gel-based SARS-CoV-2 RdRp Assay
Enzyme assays were performed with purified recombinant SARS-CoV-2 RdRp complex nsp12/nsp8/nsp7. The RNA sequence used for the RdRp assay is/56-FAM/rUrUrU rUrCrA rUrGrC rUrArC rGrCrG rUrArG rUrUr UrUrC rUrArC rGrCrG with hairpin structure [37,38]. RNA was annealed in 50 mM NaCl and 10 mM Na-HEPES pH 7.5 by heating the solution to 75 °C and gradually cooling to 4 °C. Reactions were carried out at 30 °C with 500 nM nsp12, 1 μM nsp7, 1.5 μM nsp8, and 200 nM RNA in the reaction buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 15 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 2 mM MnCl2, 1 mM MgCl2). Test compounds of desired concentration were added, incubated for 5 min, and the reactions were initiated by adding rNTPs to 5 μM. RNA extension reactions were stopped at the desired times by adding 2× stop buffer (8 M urea, 20 mM EDTA, 1× Tris-borate-EDTA (TBE), 0.2% Orange G). Samples were heated for 5 min at 95 °C and separated by electrophoresis in denaturing 20% acrylamide (19:1) gels (8 M urea, 1 × TBE) using BioRad Mini-PROTEAN Tetra System. The RNA products were visualized and quantified using Typhoon FLA9500 (GE Healthcare) and ImageQuant software. Dose–response data were analyzed by nonlinear regression using GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 (Graphpad company) software. The mean of IC50 values and standard deviation (SD) were determined from the results of two independent experiments.
3.3. Fluorescent Plate DENV RdRp Assay
Expression and purification of recombinant Dengue virus NS5 has been described previously [46]. Florescent plate assay based on poly rC RNA and the fluorescent dye PicoGreen was well established for screening inhibitors against Dengue virus RdRp activity [47,48]. RdRp assays were performed in a 60 μL reaction mixture containing 1.5 μM DENV NS5, 1 µg poly rC, 100 μM GTP, various concentrations of compounds, 5% DMSO, 40 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.0), 2 mM MnCl2, and 5 mM DTT. The reaction was incubated at 30 °C for 60 min and terminated with 10 mM EDTA after which 100 μL of 200-fold diluted fluorescent dye PicoGreen in TE buffer was added to each well and incubated for 5 min at room temperature. Microplate reader was used to quantitate the amount of dsRNA Fluorescence, under excitation and emission wavelengths of 480 and 520 nm, respectively. Dose-response data were analyzed by nonlinear regression using GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 software. The mean of IC50 values and standard deviation (SD) were determined from the results of two independent experiments.
3.4. Cells and Viruses
The SARS-CoV-2 isolate used in this study was the Beta-Cov/Belgium/GHB-03021/2020 (EPI ISL407976|2020-02-03). The isolate was passaged 7 times on Vero E6 cells which introduced two series of amino acid deletions in the spike protein [49]. The infectious content of the virus stock was determined by titration on Vero E6 cells. SARS-CoV-2 was used at 0.001 TCID50/cell.
Vero E6 cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM; Gibco cat no 41965-039), supplemented with heat-inactivated 10% v/v fetal calf serum (FCS; HyClone) and 500 µg/mL Geneticin (Gibco cat no 10131-0275) and kept under 5% CO2 at 37 °C. All SARS-CoV-2-related experimental work was performed in the certified, high-containment biosafety level-3 facilities of the Rega Institute at the KU Leuven.
3.5. In Vitro Antiviral Assays
The SARS-CoV-2 antiviral assay is derived from the previously established SARS-CoV assay [50]. In this assay, fluorescence of VeroE6-eGFP cells (provided by Dr. K. Andries J&JPRD; Beerse, Belgium) declines after infection with SARS-CoV-2 due to the cytopathogenic effect of the virus. In the presence of an antiviral compound, the cytopathogenicity is inhibited and the fluorescent signal maintained. Stock solutions of the various compounds in DMSO (10 mM) were prepared. On day -1, the test compounds were serially diluted in assay medium (DMEM supplemented with 2% v/v FCS). The plates were incubated (37 °C, 5% CO2 and 95% relative humidity) overnight. On day 0, the diluted compounds were then mixed with SARS-CoV-2 at 20 TCID50/well and VeroE6-eGFP cells corresponding to a final density of 25,000 cells/well in 96-well blackview plates (Greiner Bio-One, Vilvoorde, Belgium; Catalog 655090). The plates were incubated in a humidified incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2. At 4 days p.i., the wells were examined for eGFP expression using an argon laser-scanning microscope. The microscope settings were excitation at 488 nm and emission at 510 nm and the fluorescence images of the wells were converted into signal values. The results were expressed as EC50 values defined as the concentration of compound achieving 50% inhibition of the virus-reduced eGFP signals as compared to the untreated virus-infected control cells. Toxicity of compounds in the absence of virus was evaluated in a standard MTS-assay as reported previously [51].
The virus DENV3 clinical strain and A549 cells were used in the cell-based qRT-PCR antiviral assays. Evaluation of antiviral activity was performed as described previously [52]. Briefly, cells infected by dengue virus in the presence of 5-fold serial dilutions of compounds were maintained for 72 h. Supernatant was collected and the virus yield was measured by Cells Direct One-step qRT-PCR kit (Thermo Fisher), according to manufacturer’s instructions. Dose-response data were analyzed by nonlinear regression using GraphPad Prism software. The toxicity of compounds was evaluated in standard MTS analysis without virus in A549 cell line [51]. Graphpad Prism 9.2.0 was used to calculate EC50 (half maximal effective concentration) and CC50 (half cytotoxic concentration) values.
3.6. In Silico Study
The protein structures for computational simulation were downloaded from the Protein Database Bank (PDB). SARS-CoV-2 RdRp/RNA complex (PDB ID: 7BV2) and Dengue Virus NS5 RNA Dependent RNA Polymerase Domain (PDB ID: 2J7U) was selected as docking receptors.
Docking simulation procedure: all the calculation processes were supported by the corresponding modules of Schrodinger 2021-4 suite (www.schrodinger.com accessed on 13 November 2022) and was performed on DELL Precision T5500 workstation. Firstly, compounds were optimized with the Ligprep model with default parameters, and a pair of chiral isomers are generated for each compound. The ionic state under the physiological condition of ligand (pH = 7.0) was added; OPLS4 force filed was selected to optimize and obtain the ligand molecules required for screening. The preparation of the protein was completed by the protein preparation wizard module. A series of processes such as hydrogenation, charging, elimination of conflicting amino acid residues and energy minimization of the protein crystal structure were carried out with default parameters, and then the Remdesivir molecule of the composite crystal structure is extracted to obtain the receptor protein. The binding position of Remdesivir was used to locate the receptor grid for ligands. Finally, the Glide module [53,54] was used to dock the optimized ligands with the receptor protein with extra precision (XP). At the same time, baicalein and baicalin were used as training set to adjust molecular docking method, optimize parameter settings, and obtain a strong predictive docking model. According to the established docking model, Schrodinger 2021-4 Glide XP module was used for molecular docking of the compounds. The docking poses were visualized by Pymol (Schrödinger, LLC. DeLano Scientific, San Francisco, CA, USA, https://pymol.org accessed on 13 November 2022).
MD simulations were performed to further investigate the dynamic interactions between RdRp and the polyphenols. All simulations were conducted by using Schrodinger version 2021-4, and employed OPLS-4 force field. The previously generated polyphenol docking complex was employed as the starting coordinates, which was then filled into a proper box and solvated with water (TIP3P). The whole system was then added corresponding Na+ or Cl- to neutralize all charges. Then 0.15 M NaCl was additionally added to simulate salt concentration under physiological condition. The whole system was relaxed with default set and the productive simulation was then performed for 500 ns under standard state (300 K, 1 bar). The result trajectories were then analyzed and the RMSD of the ligand was calculated.
4. Conclusions
Through an overall screening of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp inhibition of our in-house compound library, 11 hit compounds were preliminarily selected. The hit compounds were verified through SARS-CoV-2 and DENV RdRp inhibition experiment. DF-47 exhibited the IC50 = 9.2 ± 1.1 μM against SARS-CoV-2 RdRp, meanwhile DF-51 inhibited RdRp function of DENV with an IC50 value of 4.8 ± 0.7 μM. Subsequently, the binding mode of ligands and RdRp was predicted through molecular docking, then validated by molecular dynamics simulation and free energy calculation. The results confirmed our hypothesis that the polyphenols chelate with two Mg2+ at the active site of RdRp, thereby inhibiting its replication function unlike the reported nucleoside RdRp inhibitors which cause chain-termination or lethal mutation. Regretfully, the in vitro activity at the cellular level was unsatisfying, which was attributed to low membrane permeability. Computational prediction suggested that DF-47 and DF-51 could be modified to their prodrugs to improve the cell activity. Meanwhile, for this series of polyphenols, antivirus activity screening towards a broader panel of RNA viruses should be conducted in the future.
In summary, a series of polyphenols that inhibit the activity of SARS-CoV-2 and DENV RdRp were discovered through library screening, target activity verification, cell activity determination and biophysical property prediction. The uncommon inhibition towards both coronavirus and flavivirus hints for their future development to broad-spectrum non-nucleoside polymerase inhibitors of RNA viruses.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules28010160/s1, general experimental methods; synthetic routes; preparation of intermediates; general procedure for compounds except DF-51; spectral data for compounds except DF-51; synthetic procedure and spectral data of DF-51; NMR spectra of final compounds; MS spectra of final compounds; HPLC traces of representative compounds; Full list of in-house metal chelator library compounds.
Author Contributions
H.X., P.Z., and X.L. proposed conceptual design idea and supervised the project; S.G., L.S., D.K. and L.J. and designed and performed the experiments; H.X., A.F. and M.O. expressed enzymes and performed assays. F.Z. and L.S. carried out the molecular docking and RMSD; F.Z., Y.C. and D.K were responsible for data curation and processing; S.D.J., D.J., J.N. and L.V. completed the antiviral activity evaluation and cytotoxicity; S.G. and L.S. prepared the draft; P.Z., S.D.J., D.S. and H.X. revised the manuscript; P.H. and X.L. provided the founding. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Shandong Provincial Key research and development project (No.2019JZZY021011), Science Foundation for Outstanding Young Scholars of Shandong Province (ZR2020JQ31), Foreign cultural and educational experts Project (GXL20200015001), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2021A1515110740), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M702003), Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation for Youths (ZR2022QH036), Natural Science Foundation of China, (grant numbers 81773794 and 81974507).The SARS-CoV-2 screening was performed using the ‘Caps-It’ research infrastructure (project ZW13-02) that was financially supported by the Hercules Foundation (Research Foundation Flanders) and Rega Foundation, KU Leuven.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or supplementary material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
COVID-19: Coronavirus Disease 2019; SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2; RdRp, RNA-dependent-RNA-polymerase; DENV, Dengue virus; Multiplicity of Infection (MOI); nucleoside inhibitors (NIs); Protein Data Bank (PDB); RDV-TP; 1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-ol (HOBt); Biosafety Level 3 (BSL-3); 1-ethyl-3-dimethylpropanylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI); Thin layer chromatography (TLC).
References
- Li, H.; Liu, S.; Yu, X.; Tang, S.; Tang, C.K. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Current Status and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Feikin, D.R.; Higdon, M.M.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Andrews, N.; Araos, R.; Goldberg, Y.; Groome, M.J.; Huppert, A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Smith, P.; et al. Duration of Effectiveness of Vaccines Against SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Disease: Results of a Systematic Review and Meta-Regression. Lancet 2022, 399, 924–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavige, G.N.; Jeewandara, C.; Ogg, G.S. Dengue and COVID-19: Two sides of the same coin. J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 29, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prapty, C.N.B.S.; Rahmat, R.; Araf, Y.; Shounak, S.K.; Noor-A-Afrin; Rahaman, T.I.; Hosen, M.J.; Zheng, C.; Hossain, M.G. SARS-CoV-2 and dengue virus co-infection: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, e2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladipo, H.J.; Rabiu, I.; Tajudeen, Y.A. Dengue Virus and SARS-CoV-2 Co-infection Dynamics: An Emerging Threat Among African Countries. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 82, 104398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.T.; Dickens, B.S.L.; Chew, L.Z.X.; Choo, E.L.W.; Koo, J.R.; Aik, J.; Ng, L.C.; Cook, A.R. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Interventions on Dengue Transmission. PLoS Negl. Trop Dis. 2020, 14, e0008719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicenti, I.; Zazzi, M.; Saladini, F. SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase as a Therapeutic Target for COVID-19. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2021, 31, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yin, W.; Xu, H.E. RNA-Dependent RNA polymerase: Structure, Mechanism, and Drug Discovery for COVID-19. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 538, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picarazzi, F.; Vicenti, I.; Saladini, F.; Zazzi, M.; Mori, M. Targeting the RdRp of Emerging RNA Viruses: The Structure-Based Drug Design Challenge. Molecules 2020, 25, 5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Noble, C.; Shi, P. The Dengue Virus NS5 Protein as a Target for Drug Discovery. Antiviral. Res. 2015, 119, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, I.J.D.S.; Santos-Júnior, P.F.D.S.; Aquino, T.M.; Araújo-Júnior, J.X.; Silva-Júnior, E.F.D. Insights on Dengue and Zika NS5 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp) Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Qiang, T.; Liang, C.; Ren, X.; Jia, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Wan, M.; YuWen, X.; Li, H.; et al. RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp) Inhibitors: The Current Landscape and Repurposing for the COVID-19 Pandemic. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 213, 113201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Du, G.; Du, R.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Y.; Fu, S.; Gao, L.; Cheng, Z.; Lu, Q.; et al. Remdesivir in Adults with Severe COVID-19: A Randomised, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Multicentre Trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.D.; Lye, D.C.B.; Hui, D.S.; Marks, K.M.; Bruno, R.; Montejano, R.; Spinner, C.D.; Galli, M.; Ahn, M.Y.; Nahass, R.G.; et al. Remdesivir for 5 or 10 Days in Patients with Severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinner, C.D.; Gottlieb, R.L.; Criner, G.J.; Arribas López, J.R.; Cattelan, A.M.; Soriano Viladomiu, A.; Ogbuagu, O.; Malhotra, P.; Mullane, K.M.; Castagna, A.; et al. Effect of Remdesivir vs. Standard Care on Clinical Status at 11 Days in Patients with Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 324, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanni, S.E.; Silvinato, A.; Floriano, I.; Bacha, H.A.; Barbosa, A.N.; Bernardo, W.M. Use of Remdesivir in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2022, 48, e20210393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naydenova, K.; Muir, K.W.; Wu, L.F.; Zhang, Z.; Coscia, F.; Peet, M.J.; Castro-Hartmann, P.; Qian, P.; Sader, K.; Dent, K.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase in the Presence of Favipiravir-RTP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2021946118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FUJIFILM. Available online: https://www.fujifilm.com/jp/ja/news/list/8698 (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- FDA News Release. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-additional-oral-antiviral-treatment-covid-19-certain (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Good, S.S.; Westover, J.; Jung, K.H.; Zhou, X.J.; Moussa, A.; La Colla, P.; Collu, G.; Canard, B.; Sommadossi, J. AT-527, a Double Prodrug of a Guanosine Nucleotide Analog, Is a Potent Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro and a Promising Oral Antiviral for Treatment of COVID-19. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e02479-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Trials Arena. Atea’s AT-527 Fails to Meet Primary Goal of Phase II COVID-19 Trial. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrialsarena.com/news/atea-at-527-primary-goal/ (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Good, S.S.; Shannon, A.; Lin, K.; Moussa, A.; Julander, J.G.; La Colla, P.; Collu, G.; Canard, B.; Sommadossi, J.P. Evaluation of AT-752, a Double Prodrug of a Guanosine Nucleotide Analog with In Vitro and In Vivo Activity against Dengue and Other Flaviviruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0098821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcelli, M.; Rogolino, D.; Sechi, M.; Rispoli, G.; Fisicaro, E.; Compari, C.; Grandi, N.; Corona, A.; Tramontano, E.; Pannecouque, C.; et al. Antiretroviral activity of metal-chelating HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 83, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, U.; Attenni, B.; Malancona, S.; Colarusso, S.; Conte, I.; Di Filippo, M.; Harper, S.; Pacini, B.; Giomini, C.; Thomas, S.; et al. 2-(2-Thienyl)-5,6-dihydroxy-4-carboxypyrimidines as inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase: Discovery, SAR, modeling, and mutagenesis. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carcelli, M.; Rogolino, D.; Bacchi, A.; Rispoli, G.; Fisicaro, E.; Compari, C.; Sechi, M.; Stevaert, A.; Naesens, L. Metal-chelating 2-hydroxyphenyl amide pharmacophore for inhibition of influenza virus endonuclease. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Crich, D.; Pegan, S.; Lou, L.; Hansen, M.; Booth, C.; Desrochers, E.; Mullininx, L.; Starling, E.; Chang, K.; et al. Polyphenols as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp). Molecules 2021, 26, 7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandi, K.; Musall, K.; Oo, A.; Cao, D.; Liang, B.; Hassandarvish, P.; Lan, S.; Slack, R.; Kirby, K.; Bassit, L.; et al. Baicalein and Baicalin Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent-RNA Polymerase. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.T.; Colby-Germinario, S.P.; Hassounah, S.; Quashie, P.K.; Han, Y.; Oliveira, M.; Stranix, B.R.; Wainberg, M.A. Identification of a Pyridoxine-Derived Small-Molecule Inhibitor Targeting Dengue Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 60, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobori, H.; Uemura, K.; Toba, S.; Sanaki, T.; Shishido, T.; Hall, W.W.; Orba, Y.; Sawa, H.; Sato, A. Identification of quinolone derivatives as effective antiDengue virus agents. Antivir. Res. 2020, 184, 104969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Cheng, X.; Poongavanam, V.; Kongsted, J.; Álvarez, M.; Luczkowiak, J.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biologic evaluation of novel galloyl derivatives as HIV-1 RNase H inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, F.; Borrego, D.; Zhao, F.; Río, J.M.D.; Frutos-Beltrán, E.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; López-Carrobles, N.; Gao, S.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel double-winged galloyl derivatives as HIV-1 RNase H inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 240, 114563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Cheng, X.; Sun, L.; Song, S.; Álvarez, M.; Luczkowiak, J.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E.; Menéndez-Arias, L.; Zhan, P.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 3-Hydroxyquinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-diones as Dual Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase-associated RNase H and Integrase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3836–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Gao, P.; Dong, G.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Daelemans, D.; De Clercq, E.; Pannecouque, C.; et al. 5-Hydroxypyrido[2,3-b]pyrazin-6(5H)-one Derivatives As Novel Dual Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase-associated Ribonuclease H and Integrase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 155, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Huang, T.; Tan, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, T.; Menéndez-Arias, L.; Pannecouque, C.; et al. 1-Hydroxypyrido[2,3-d] Pyrimidin-2(1H)-ones As Novel Selective HIV Integrase Inhibitors Obtained Via Privileged Substructure-based Compound Libraries. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 5779–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillen, H.S.; Kokic, G.; Farnung, L.; Dienemann, C.; Tegunov, D.; Cramer, P. Structure of Replicating SARS-CoV-2 Polymerase. Nature 2020, 584, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Svetlov, V.; Wolf, Y.; Koonin, E.; Nudler, E.; Artsimovitch, I. Allosteric Activation of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase by Remdesivir Triphosphate and Other Phosphorylated Nucleotides. Mbio 2021, 12, e0142321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.; Thai, N.; Truong, D.; Li, M. Remdesivir Strongly Binds to Both RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase and Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2: Evidence from Molecular Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 11337–11348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.; Tchesnokov, E.; Woolner, E.; Perry, J.; Feng, J.; Porter, D.; Götte, M. Remdesivir is a Direct-acting Antiviral that Inhibits RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase from Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 with High Potency. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6785–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.S.; Mijalkovic, J.; Borrelli, K.; Jacobson, M.P. Testing Physical Models of Passive Membrane Permeation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1621–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.S.; Sindhikara, D.; Jacobson, M.P. Simple Predictive Models of Passive Membrane Permeability Incorporating Size-Dependent Membrane-Water Partition. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2016, 56, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malet, H.; Massé, N.; Selisko, B.; Romette, J.; Alvarez, K.; Guillemot, J.; Tolou, H.; Yap, T.; Vasudevan, S.; Lescar, J.; et al. The Flavivirus Polymerase as a Target for Drug Discovery. Antiviral. Res. 2008, 80, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, G.; Maisto, M.; Schisano, C.; Ciampaglia, R.; Narciso, V.; Tenore, G.C.; Novellino, E. Resveratrol as a Novel Anti-Herpes Simplex Virus Nutraceutical Agent: An Overview. Viruses 2018, 10, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Lin, H.; Chen, T.; Hsu, Y.; Liu, C.; Hwang, G.; Wan, L. Polygonum Cuspidatum and its Active Components Inhibit Replication of the Influenza Virus through Toll-like Receptor 9-induced Interferon Beta Expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117602. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.T.; Colby-Germinario, S.P.; Hassounah, S.A.; Fogarty, C.; Osman, N.; Palanisamy, N.; Han, Y.; Oliveira, M.; Quan, Y.; Wainberg, M.A. Evaluation of Sofosbuvir (β-D-2’-deoxy-2’-α-fluoro-2’-β-C-methyluridine) as an Inhibitor of Dengue Virus Replication. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, H.; Saito, A.; Mikuni, J.; Nakayama, E.; Koyama, H.; Honma, T.; Shirouzu, M.; Sekine, S.; Shioda, T. Discovery of a Small Molecule Inhibitor Targeting Dengue Virus NS5 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase. PLoS. Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, D.; Li, Q.; Pang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, Z.; Liang, C.; Cen, S. Identification of a Broad-Spectrum Viral Inhibitor Targeting a Novel Allosteric Site in the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerases of Dengue Virus and Norovirus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudewijns, R.; Thibaut, H.; Kaptein, S.; Li, R.; Vergote, V.; Seldeslachts, L.; Van Weyenbergh, J.; De Keyzer, C.; Bervoets, L.; Sharma, S.; et al. STAT2 Signaling Restricts Viral Dissemination but Drives Severe Pneumonia in SARS-CoV-2 infected hamsters. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivens, T.; Van den Eynde, C.; Van Acker, K.; Nijs, E.; Dams, G.; Bettens, E.; Ohagen, A.; Pauwels, R.; Hertogs, K. Development of a Homogeneous Screening Assay for Automated Detection of Antiviral Agents Active Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-associated Coronavirus. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 129, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochmans, D.; Leyssen, P.; Neyts, J. A Novel Method for High-Throughput Screening to Quantify Antiviral Activity Against Viruses that Induce Limited CPE. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 183, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikatas, A.; Vervaeke, P.; Meyen, E.; Llor, N.; Ordeix, S.; Boonen, I.; Bletsa, M.; Kafetzopoulou, L.; Lemey, P.; Amat, M.; et al. A Novel Series of Indole Alkaloid Derivatives Inhibit Dengue and Zika Virus Infection by Interference with the Viral Replication Complex. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0234920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 2. Enrichment Factors in Database Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).