Conversion of Polypropylene Waste into Value-Added Products: A Greener Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
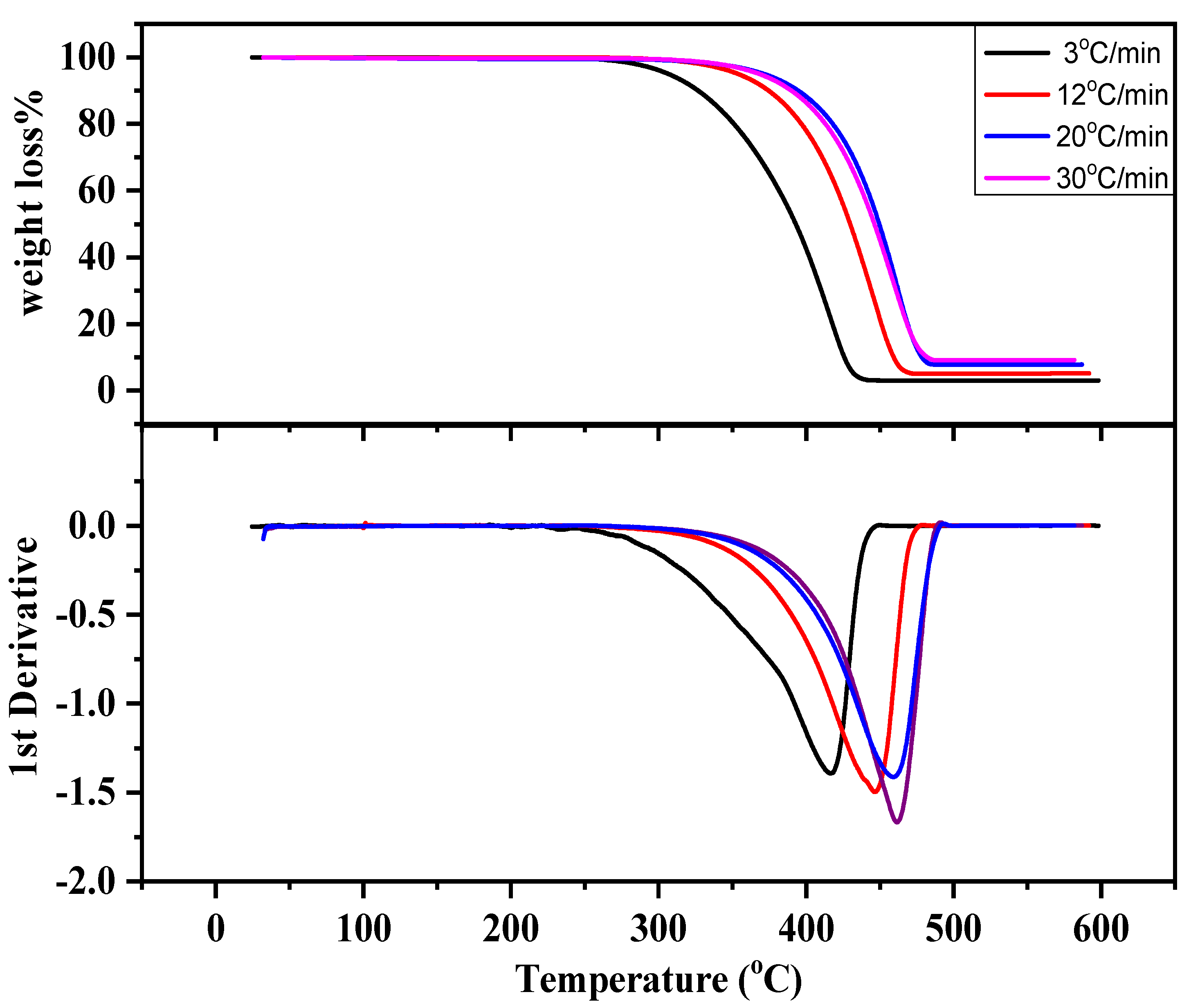
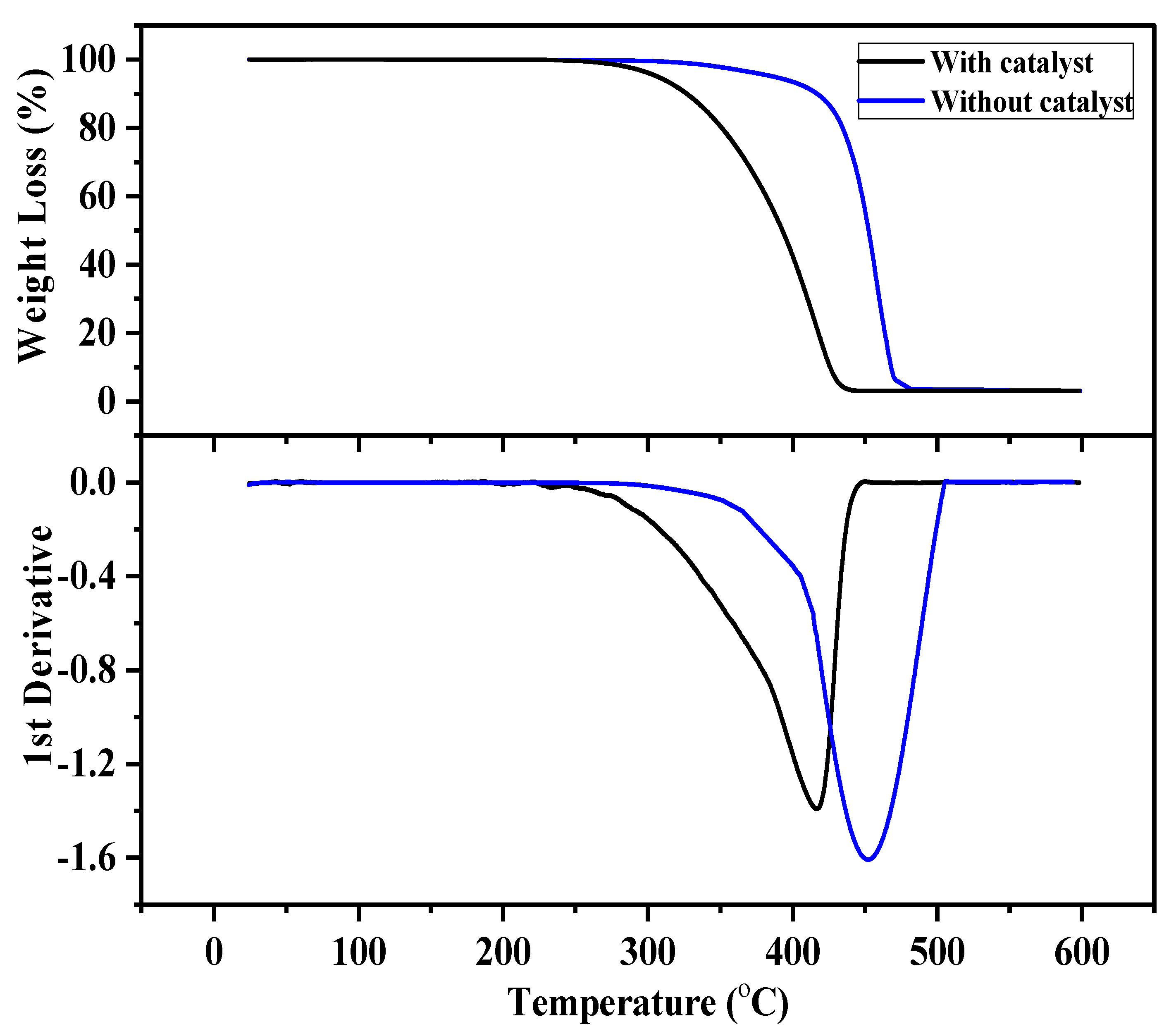
2.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis
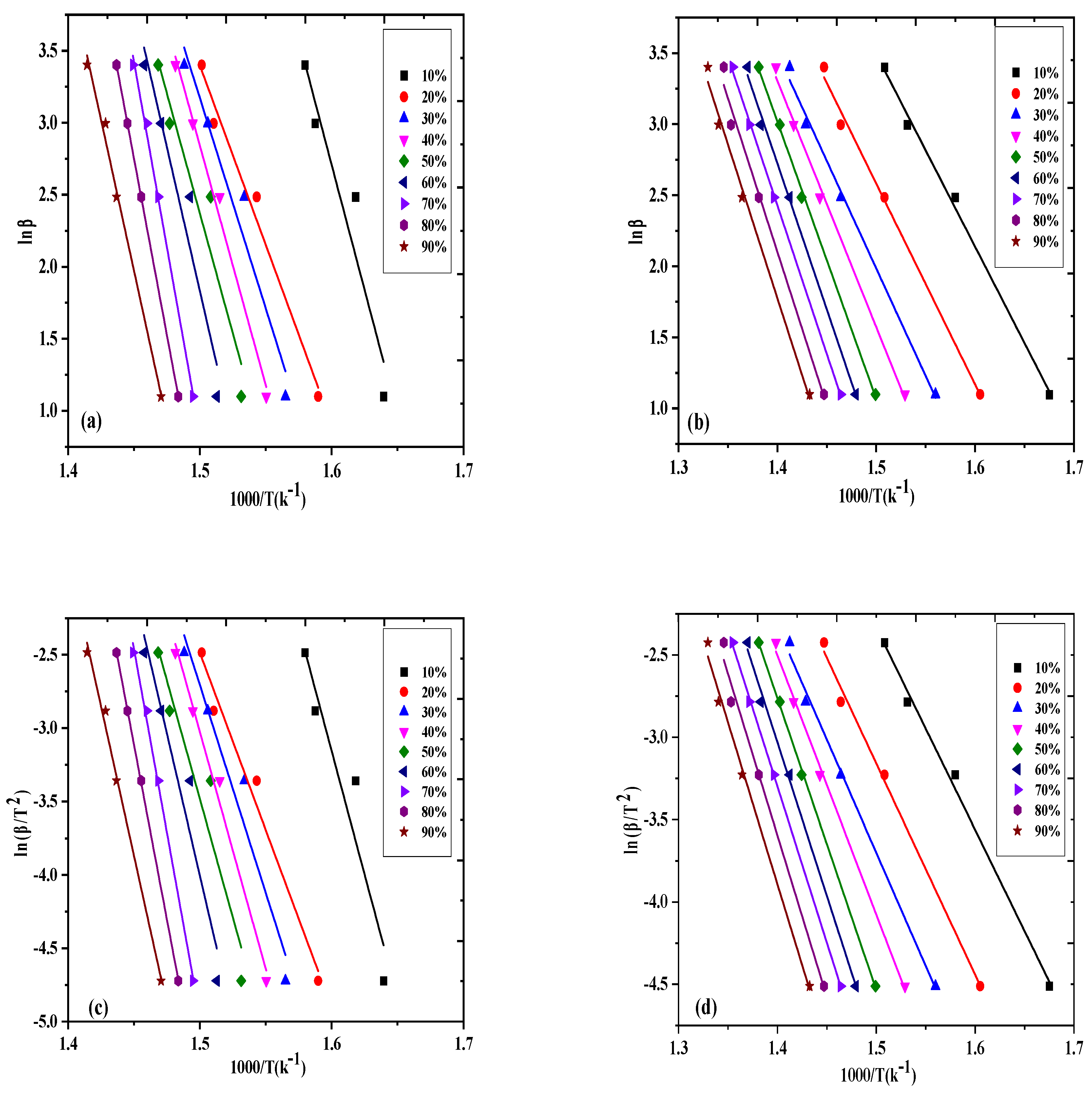
2.2. Kinetic Study
2.2.1. Ozawa–Flynn–Wall Equation
2.2.2. Kissinger–Akahira–Sunnose Equation
2.3. Pyrolysis of Polypropylene
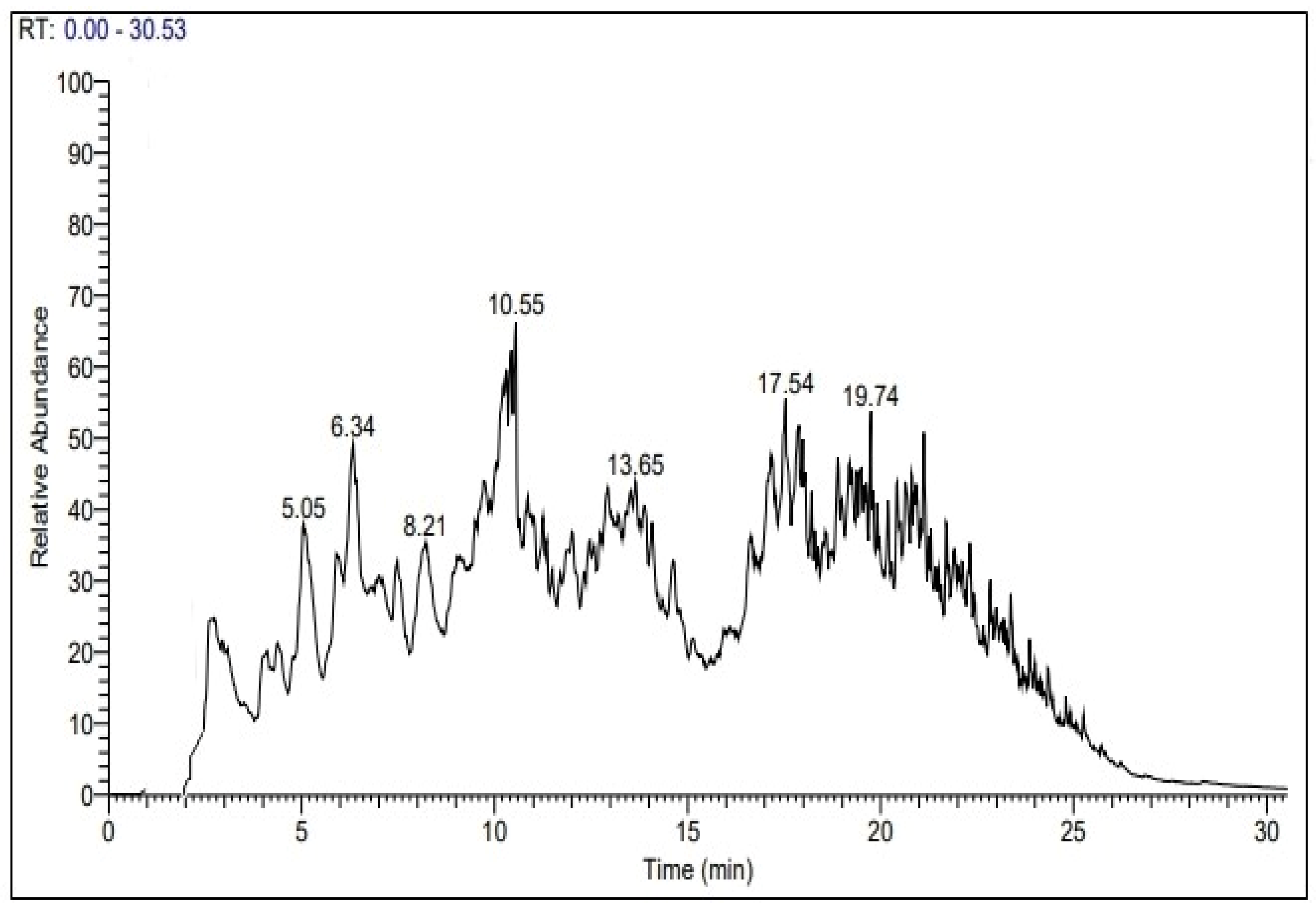
2.4. GC-MS
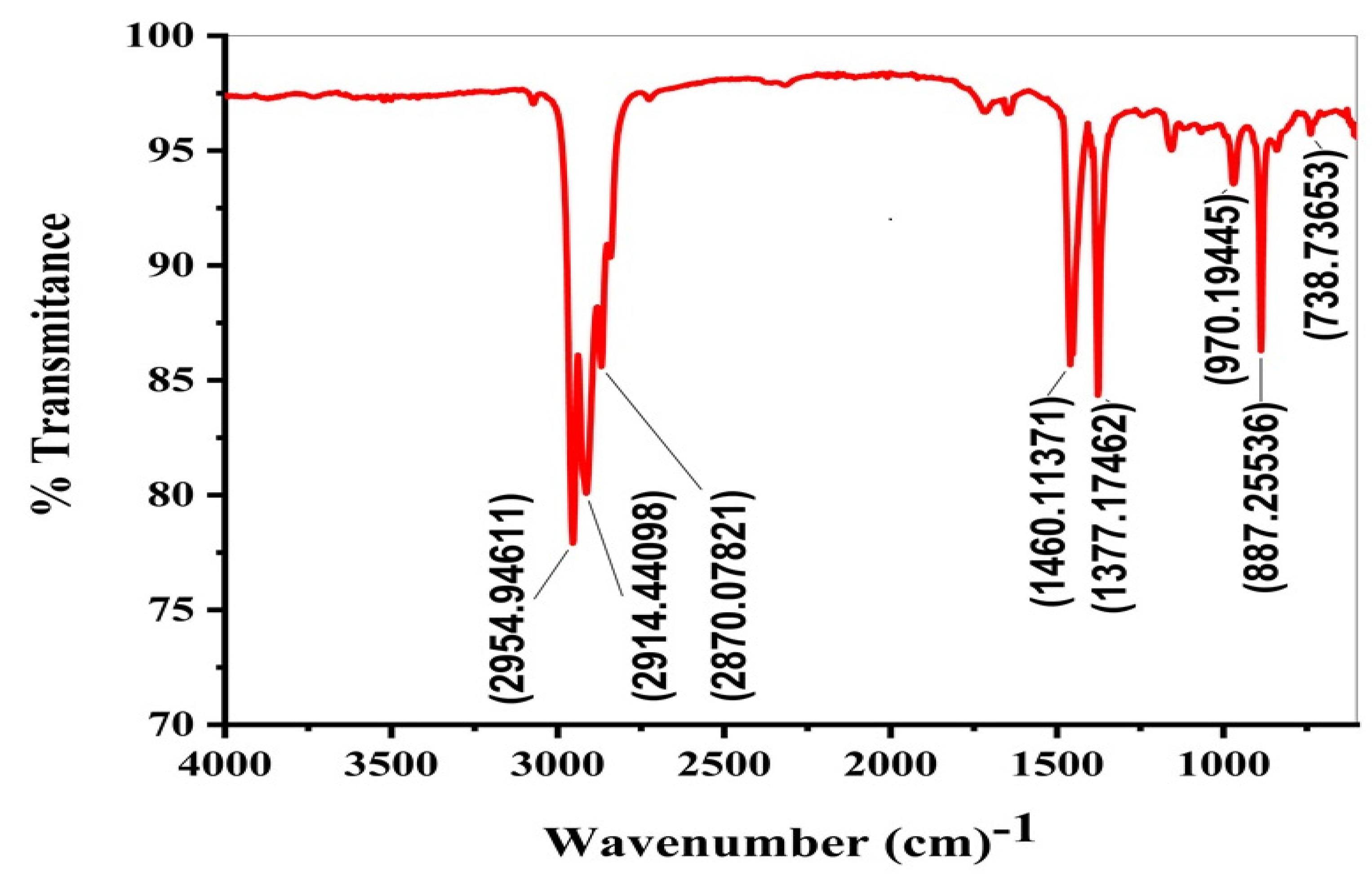
2.5. FTIR
2.6. Fuel Properties
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Material
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis and Kinetic Study
3.2.1. Ozawa–Flynn–Wall
3.2.2. Kissinger–Akahira–Sunnose
3.3. Pyrolysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamad, K.; Kaseem, M.; Deri, F. Recycling of waste from polymer materials: An overview of the recent works. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2801–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Song, B.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Wen, X.; Tang, W. Are biodegradable plastics a promising solution to solve the global plastic pollution? Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achilias, D.S.; Roupakias, C.; Megalokonomos, P.; Lappas, A.A.; Antonakou, V. Chemical recycling of plastic wastes made from polyethylene (LDPE and HDPE) and polypropylene (PP). J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koerner, G.R.; Koerner, R.M. Polymeric Geomembrane Components in Landfill Liners. In Solid Waste Landfilling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 313–341. [Google Scholar]
- Hundertmark, T.; Mayer, M.; Mcnally, C.; Simons, T.J.; Witte, C. How Plastics-Waste Recycling Could Transform the Chemical Industry; McKinsey & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wichai-utcha, N.; Chavalparit, O. 3Rs Policy and plastic waste management in Thailand. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 21, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salem, S.; Lettieri, P.; Baeyens, J. Recycling and recovery routes of plastic solid waste (PSW): A review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2625–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, M.; Tamilkolundu, S.; Murugesan, C. Conversion of plastic waste to fuel. In Plastic Waste and Recycling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 385–399. [Google Scholar]
- Nanda, S.; Berruti, F. Municipal solid waste management and landfilling technologies: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1433–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiopu, A.M.; Gavrilescu, M. Municipal solid waste landfilling and treatment of resulting liquid effluents. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2010, 9, 993–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Vasudeo, R.A.; Abitha, V.K.; Vinayak, K.; Jayaja, P.; Gaikwad, S. Sustainable Development Through Feedstock Recycling of Plastic Wastes. Macromol. Symp. 2016, 362, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Tiwari, P. Valorization of packaging plastic waste by slow pyrolysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 128, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.; De Fátima Marques, M. Thermal and catalytic pyrolysis of plastic waste. Polimeros 2016, 26, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskolczi, N.; Angyal, A.; Bartha, L.; Valkai, I. Fuels by pyrolysis of waste plastics from agricultural and packaging sectors in a pilot scale reactor. Fuel Processing Technol. 2009, 90, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcilla, A.; García-Quesada, J.C.; Sánchez, S.; Ruiz, R. Study of the catalytic pyrolysis behaviour of polyethylene–polypropylene mixtures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2005, 74, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Ghoshal, A. Model-free kinetics analysis of decomposition of polypropylene over Al-MCM-41. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 460, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Yen, H.Y. Fluidised bed pyrolysis of polypropylene over cracking catalysts for producing hhydrocarbons. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 89, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, J.; Khan, M.A.; Ali, G.; Iqbal, M.; Shah, A.; Shah, M.R.; Rehman, N.U. Pyrolysis of Polypropylene over Zeolite Mordenite Ammonium: Kinetics and Products distribution. J. Polym. Eng. 2019, 39, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, J.; Khan, M.A.; Iqbal, M.; Shah, A.; Khan, R.A.; Sayed, M.; Mahmood, T. Comparative Study of Kinetics of the Thermal Decomposition of Polypropylene Using Different Methods. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lee, S.W.; Yuan, G.; Lei, J.; Lin, S.; Weerachanchai, P.; Wang, J.-Y. Investigation into the Catalytic Activity of Microporous and Mesoporous Catalysts in the Pyrolysis of Waste Polyethylene and Polypropylene Mixture. Energies 2016, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tekin, K.; Akalın, M.K.; Kadı, Ç.; Karagöz, S. Catalytic degradation of waste polypropylene by pyrolysis. J. Energy Inst. 2021, 85, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obalı, Z.; Sezgi, N.; Doğu, T. Catalytic degradation of polypropylene over alumina loaded mesoporous catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 207–208, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briceno, J.; Lemos, M.A.; Lemos, F. Kinetic analysis of the degradation of HDPE+PP polymer mixtures. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2021, 53, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Chang, C.-Y.; Hor, J.-L.; Shih, S.-M.; Chen, L.-W.; Chang, F.-W. On the thermal treatment of plastic mixtures of MSW: Pyrolysis kinetics. Waste Manag. 1993, 13, 221–235. [Google Scholar]
- Das, P.; Tiwari, P. Thermal degradation kinetics of plastics and model selection. Thermochim. Acta 2017, 654, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, M.H. Chemical catalysed recycling of polypropylene over a spent FCC catalyst and various commercial cracking catalysts using TGA. Thermochim. Acta 2008, 470, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulkas, A.; El harfi, K.; El Bouadili, A. Thermal degradation behaviors of polyethylene and polypropylene. Part I: Pyrolysis kinetics and mechanisms. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Silvarrey, L.S.; Phan, A.N. Kinetic study of municipal plastic waste. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 16352–16364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esmizadeh, E.; Tzoganakis, C.; Mekonnen, T.H. Degradation Behavior of Polypropylene during Reprocessing and Its Biocomposites: Thermal and Oxidative Degradation Kinetics. Polymers 2020, 12, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audisio, G.; Silvani, A.; Beltrame, P.L.; Carniti, P. Catalytic thermal degradation of polymers. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1984, 7, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, A.; de Marco, I.; Caballero, B.M.; Laresgoiti, M.F.; Adrados, A. Influence of time and temperature on pyrolysis of plastic wastes in a semi-batch reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.S.; Czernik, S.R.; Piskorz, J.; St G Radlein, D.A. Fast Pyrolysis of Plastic Wastes. Energy Fuels 1990, 4, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inguanzo, M.; Domínguez, A.; Menéndez, J.; Blanco, C.; Pis, J. On the pyrolysis of sewage sludge: The influence of pyrolysis conditions on solid, liquid and gas fractions. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2002, 63, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.A.; Williams, P.T. Analysis of products derived from the fast pyrolysis of plastic waste. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1997, 40–41, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papuga, S.V.; Gvero, P.M.; Vukić, L.M. Temperature and time influence on the waste plastics pyrolysis in the fixed bed reactor. Therm. Sci. 2016, 20, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, B.P.S.; Almeida, D.; Maria de Fatima, V.M.; Henriques, C.A. Petrochemical feedstock from pyrolysis of waste polyethylene and polypropylene using different catalysts. Fuel 2018, 215, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Nisar, J.; Iqbal, M.; Shah, A.; Khan, R.A.; Sirajuddin; Bhatti, I.A.; Amin, R. Pyrolysis of polypropylene over a LZ-Y52 molecular sieve: Kinetics and the product distribution. Iran. Polym. J. 2019, 28, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindikar, M.; Khaladkar, M.; Yb, S.; Mr, S.; My, K. Use of Catalyst in Pyrolysis of Polypropylene Waste into Liquid Fuel. Int. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 4, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, A.; Singh, R.K. Experimental optimization of process for the thermo-catalytic degradation of waste polypropylene to liquid fuel. Adv. Energy Eng. 2013, 1, 74–84. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. Annual Book of ASTM Standard Part 23; American Society of Testing Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- IP. Standards for Petroleum and Its Products, Part I; Institute of Petroleum: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, I.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, H.; Ishaq, M.; Tariq, R.; Gul, K.; Ahmad, W. Pyrolysis study of polypropylene and polyethylene into premium oil products. Int. J. Green Energy 2015, 12, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| α | Ozawa–Flynn–Waal Model | Kissinger–Akahira–Sunnose Model | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Catalytic | Catalytic | Non-Catalytic | Catalytic | |||||||||
| Ea (kJ·mol−1) | A (min−1) | R2 | Ea (kJ·mol−1) | A (min−1) | R2 | Ea (kJ·mol−1) | A (min−1) | R2 | Ea (kJ·mol−1) | A (min−1) | R2 | |
| 0.1 | 109.95 | 9.1 × 108 | 0.992 | 102.74 | 7.1 × 108 | 0.994 | 108.76 | 4.0 × 108 | 0.983 | 99.77 | 1.0 × 108 | 0.992 |
| 0.2 | 119.43 | 6.3 × 109 | 0.991 | 110.64 | 1.2 × 109 | 0.99 | 113.08 | 7.3 × 108 | 0.983 | 108.08 | 1.9 × 108 | 0.992 |
| 0.3 | 127.46 | 9.3 × 109 | 0.990 | 118.55 | 1.3 × 109 | 0.992 | 121.91 | 9.1 × 108 | 0.993 | 113.90 | 3.3 × 108 | 0.993 |
| 0.4 | 141.52 | 9.9 × 1010 | 0.991 | 134.35 | 1.9 × 1010 | 0.993 | 129.70 | 9.9 × 109 | 0.996 | 124.71 | 9.9 × 108 | 0.996 |
| 0.5 | 151.58 | 7.9 × 1011 | 0.993 | 150.16 | 2.9 × 1011 | 0.997 | 139.38 | 3.0 × 1010 | 0.996 | 141.34 | 3.0 × 109 | 0.996 |
| 0.6 | 167.61 | 9.1 × 1011 | 0.991 | 158.06 | 6.1 × 1011 | 0.999 | 153.32 | 6.5 × 1011 | 0.993 | 149.65 | 6.5 × 1010 | 0.999 |
| 0.7 | 174.83 | 1.2 × 1012 | 0.991 | 164.38 | 1.2 × 1012 | 0.999 | 168.16 | 1.9 × 1012 | 0.995 | 157.97 | 1.9 × 1011 | 0.995 |
| 0.8 | 183.57 | 6.3 × 1012 | 0.984 | 170.71 | 1.3 × 1012 | 0.984 | 173.13 | 7.1 × 1012 | 0.997 | 162.12 | 3.1 × 1011 | 0.999 |
| 0.9 | 198.66 | 9.3 × 1012 | 0.989 | 173.08 | 9.3 × 1011 | 0.989 | 184.28 | 9.3 × 1012 | 0.991 | 166.28 | 5.3 × 1011 | 0.991 |
| S. No. | Parameters | This Work | ASTM Standard Values [40,41] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel | Kerosene | Gasoline | |||
| 1 | Density (g/mL) | 0.781 | 0.83–0.85 | 0.78–0.82 | 0.720–0.736 |
| 2 | Fluidity | 0.819 | 2.4–5.3 | 1.54–2.20 | 0.775–0.839 |
| 3 | Viscosity (cP) | 1.133 | 0.9–1.5 | 0.775–0.839 | 1.2–1.8 |
| 4 | Specific gravity | 0.743 | 0.83–0.85 | 0.72–0.73 | 0.78–0.82 |
| 5 | API gravity | 55.877 | 38.98–34.97 | 62.34–65.03 | 49.91–41.06 |
| 6 | Kinematic viscosity (nm2/s) | 1.591 | 1.3–5.3 | 1.076–1.140 | 1.54–2.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nisar, J.; Aziz, M.; Shah, A.; Shah, I.; Iqbal, M. Conversion of Polypropylene Waste into Value-Added Products: A Greener Approach. Molecules 2022, 27, 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27093015
Nisar J, Aziz M, Shah A, Shah I, Iqbal M. Conversion of Polypropylene Waste into Value-Added Products: A Greener Approach. Molecules. 2022; 27(9):3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27093015
Chicago/Turabian StyleNisar, Jan, Maria Aziz, Afzal Shah, Iltaf Shah, and Munawar Iqbal. 2022. "Conversion of Polypropylene Waste into Value-Added Products: A Greener Approach" Molecules 27, no. 9: 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27093015
APA StyleNisar, J., Aziz, M., Shah, A., Shah, I., & Iqbal, M. (2022). Conversion of Polypropylene Waste into Value-Added Products: A Greener Approach. Molecules, 27(9), 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27093015







