Preventive Effects of Anthocyanins from Lyciumruthenicum Murray in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Are Related to the Regulation of Intestinal Microbiota and Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
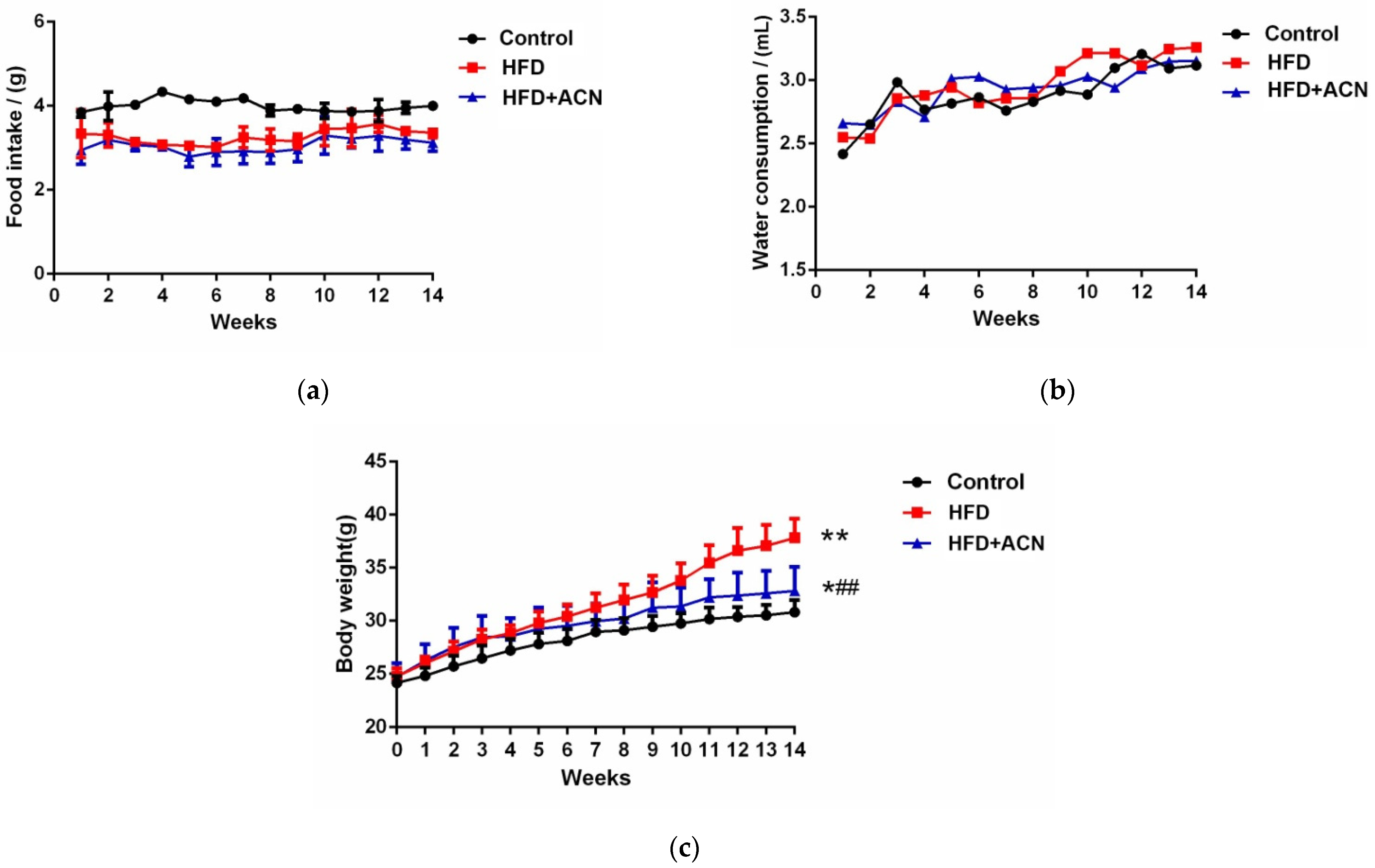
2.1. Anthocyanins Extract from the Fruits of L. ruthenicum Reduced the Body Weight of High-Fat-Fed Mice
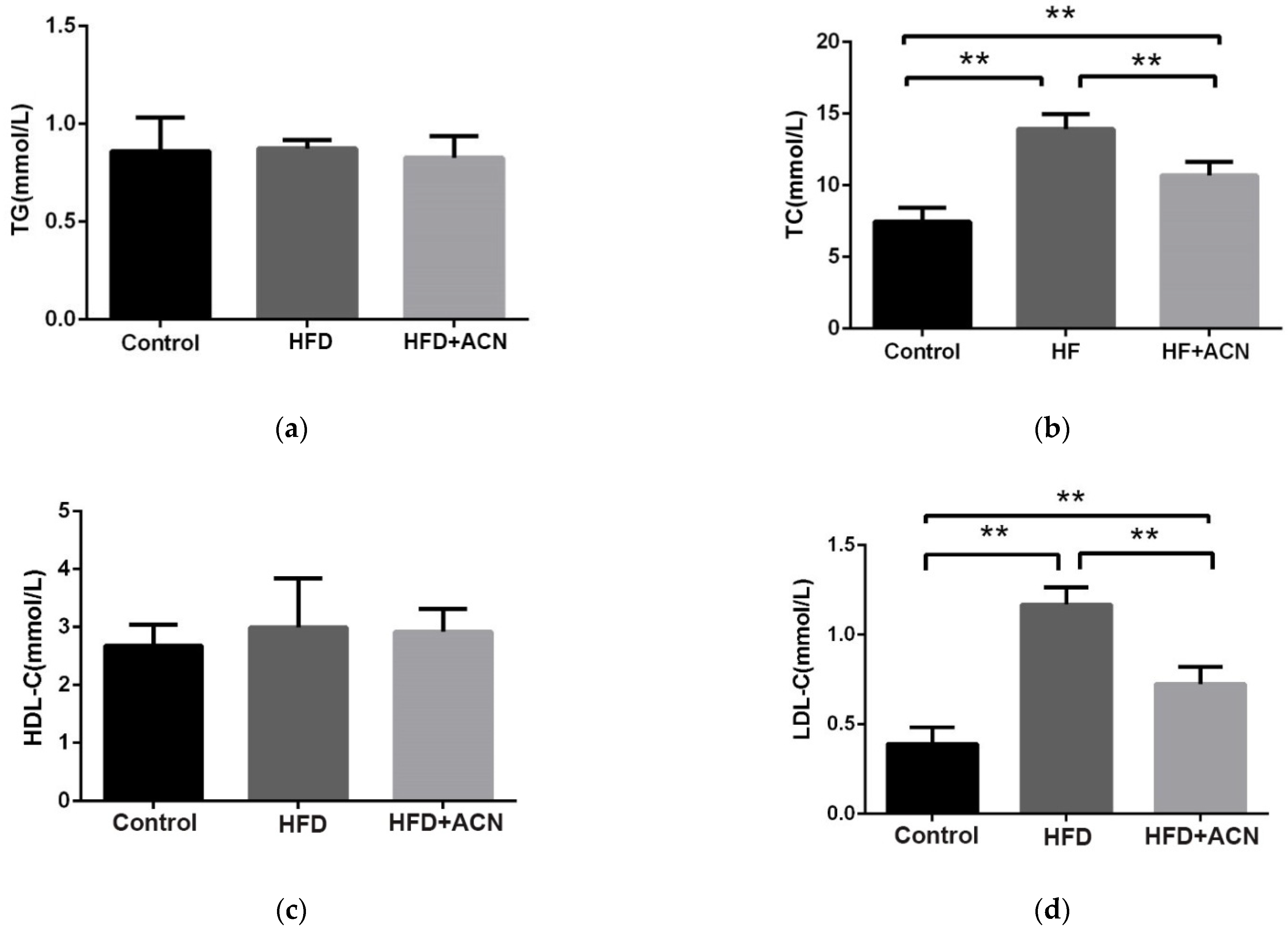
2.2. Effects of Anthocyanin Extract from the Fruits of L. ruthenicum on the Serum Lipid Levels in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice
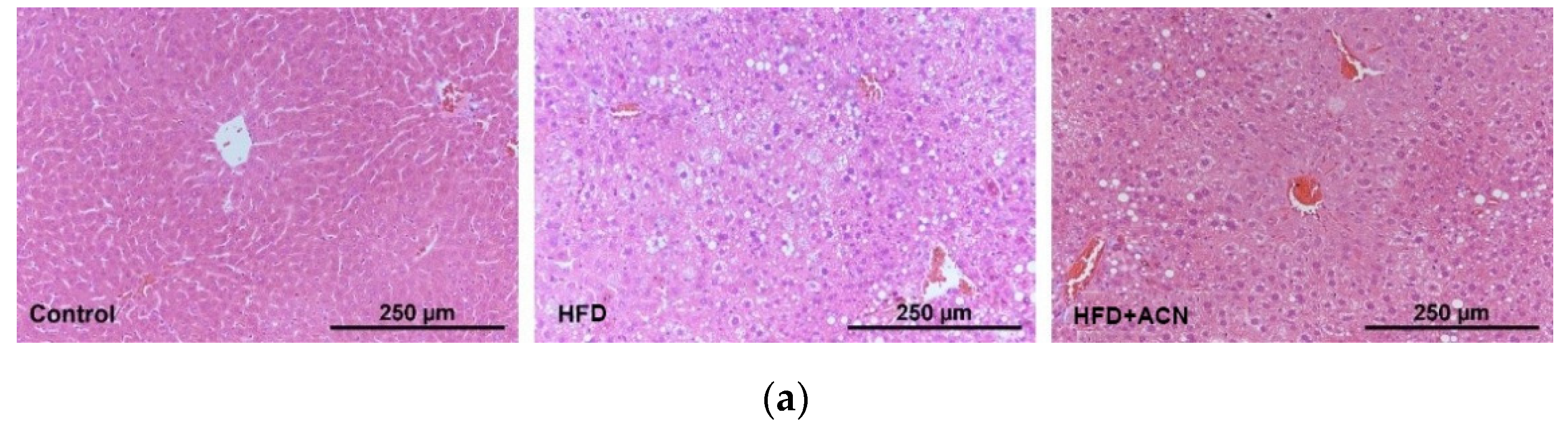
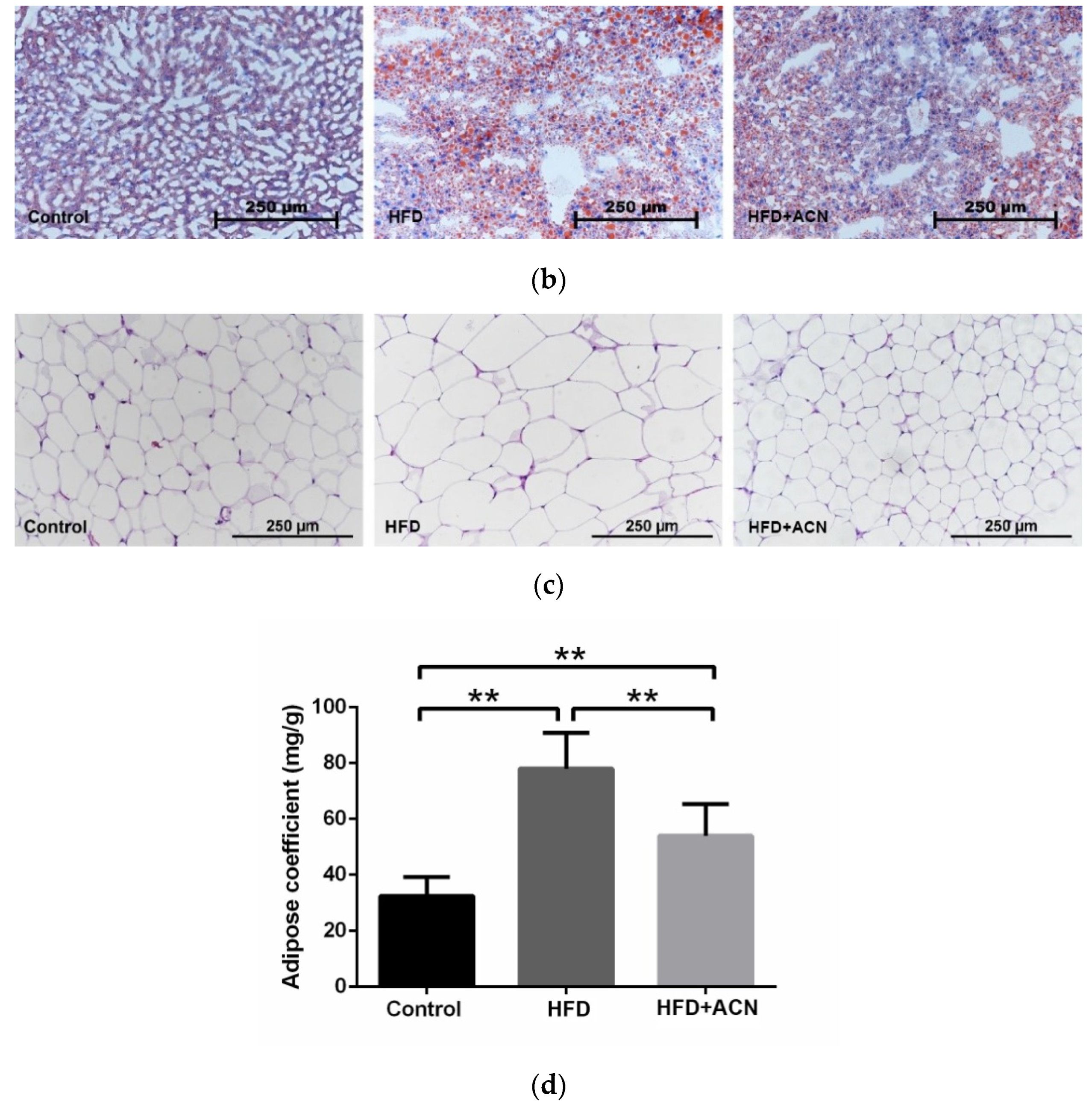
2.3. Anthocyanin Extract from the Fruits of L. ruthenicum Ameliorated High-Fat-Diet-Induced Lipid Accumulation in the Liver and Adipose Tissues in Mice
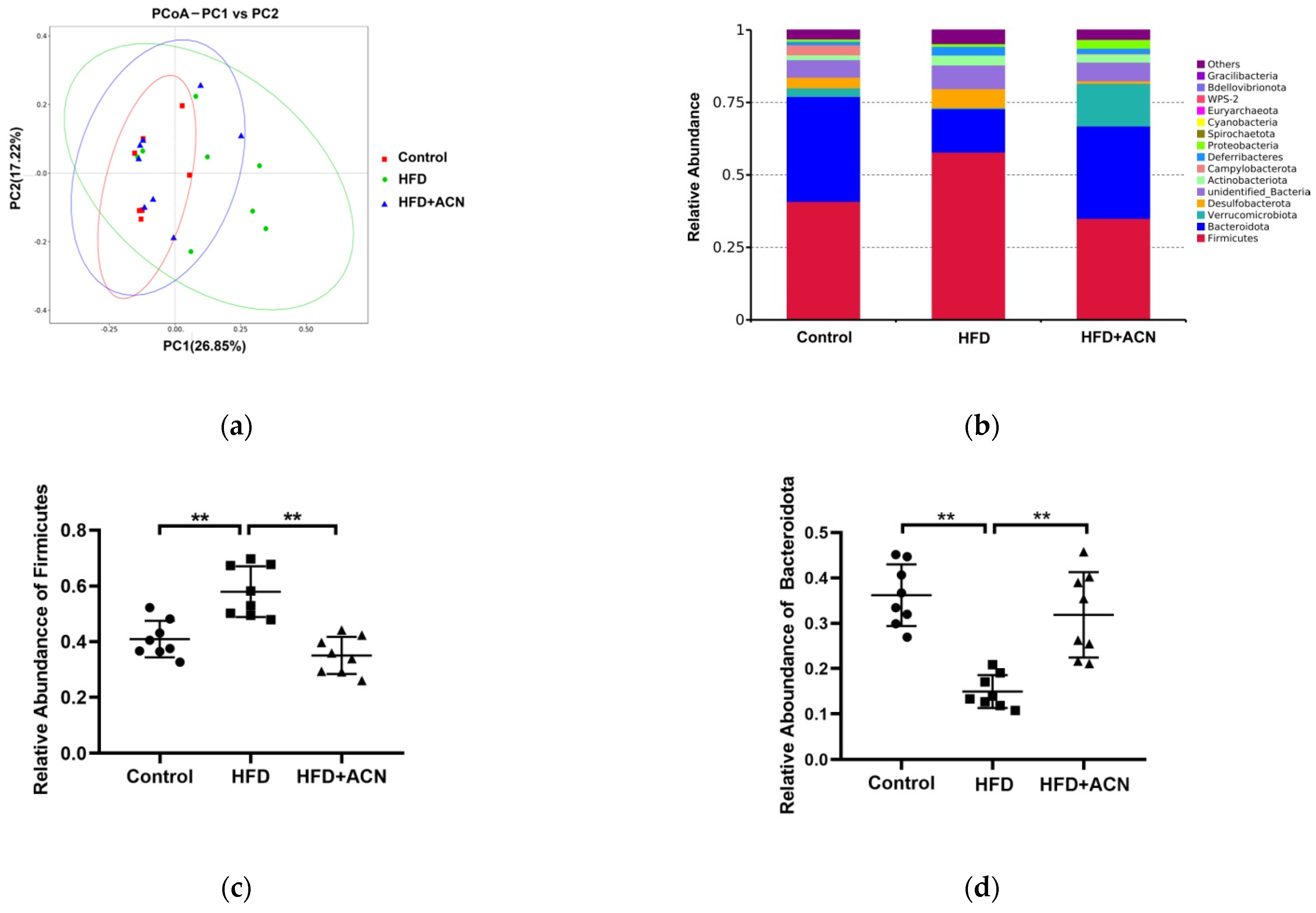
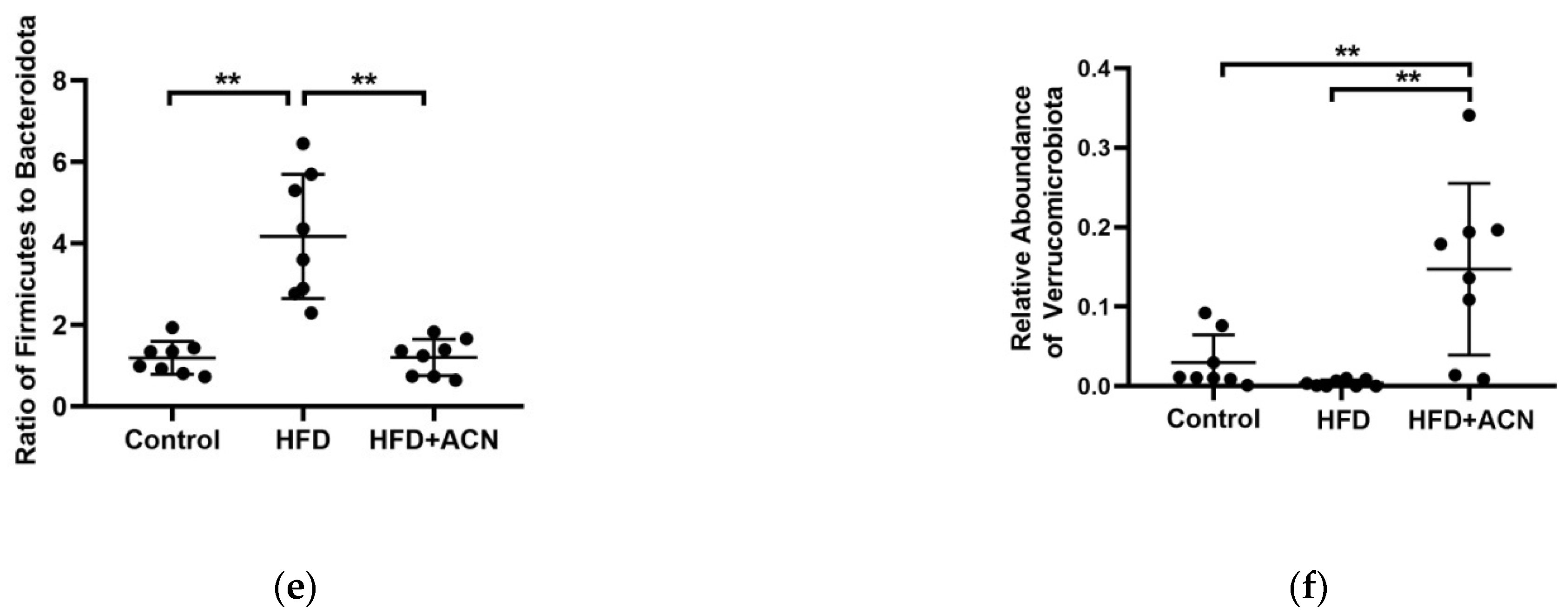
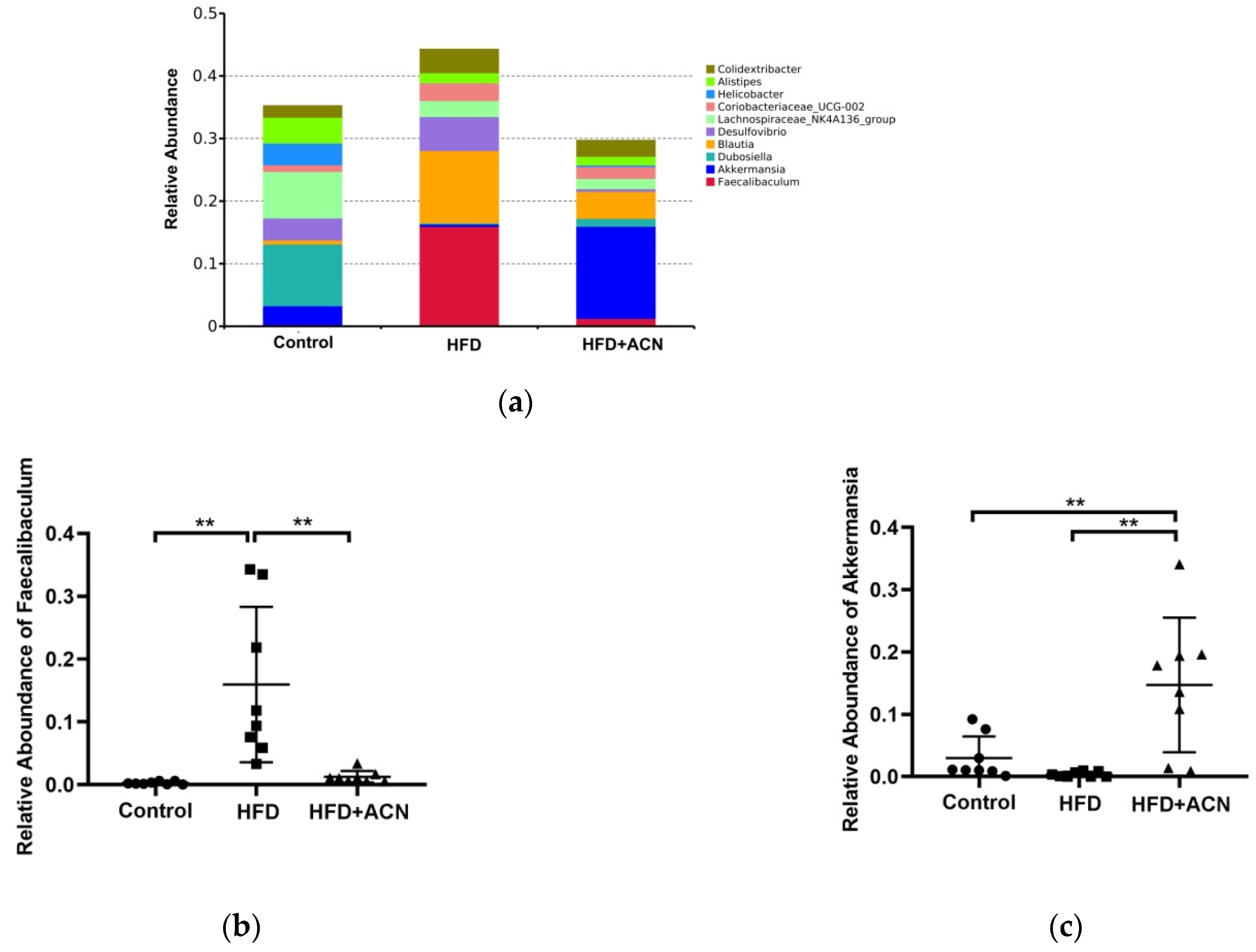
2.4. Anthocyanins Extract from the Fruits of L. ruthenicum Regulated the Intestinal Microbiota in High-Fat-Fed Mice
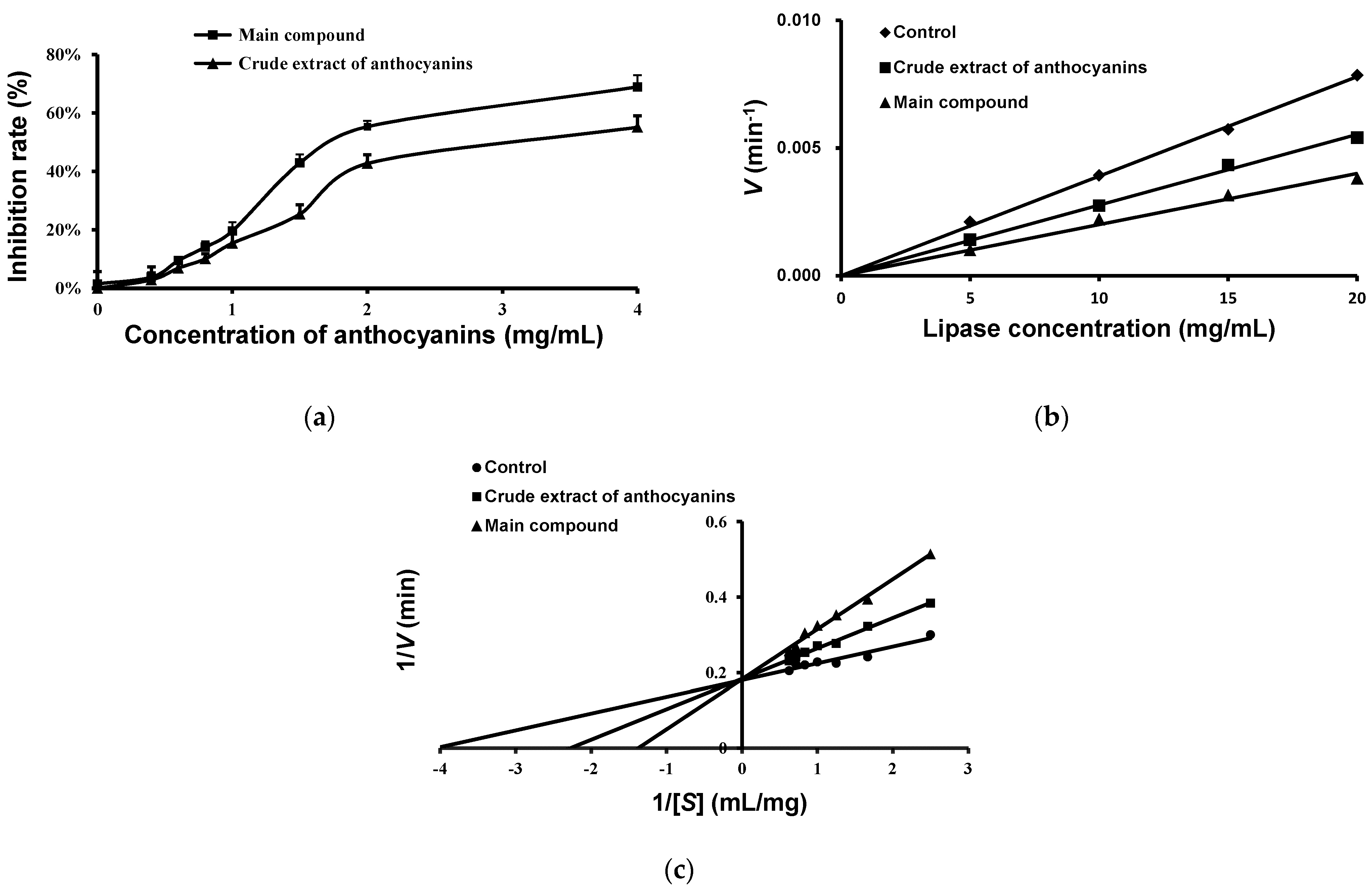
2.5. Effects of Anthocyanins from the Fruits of L. ruthenicum on Pancreatic Lipase Activity
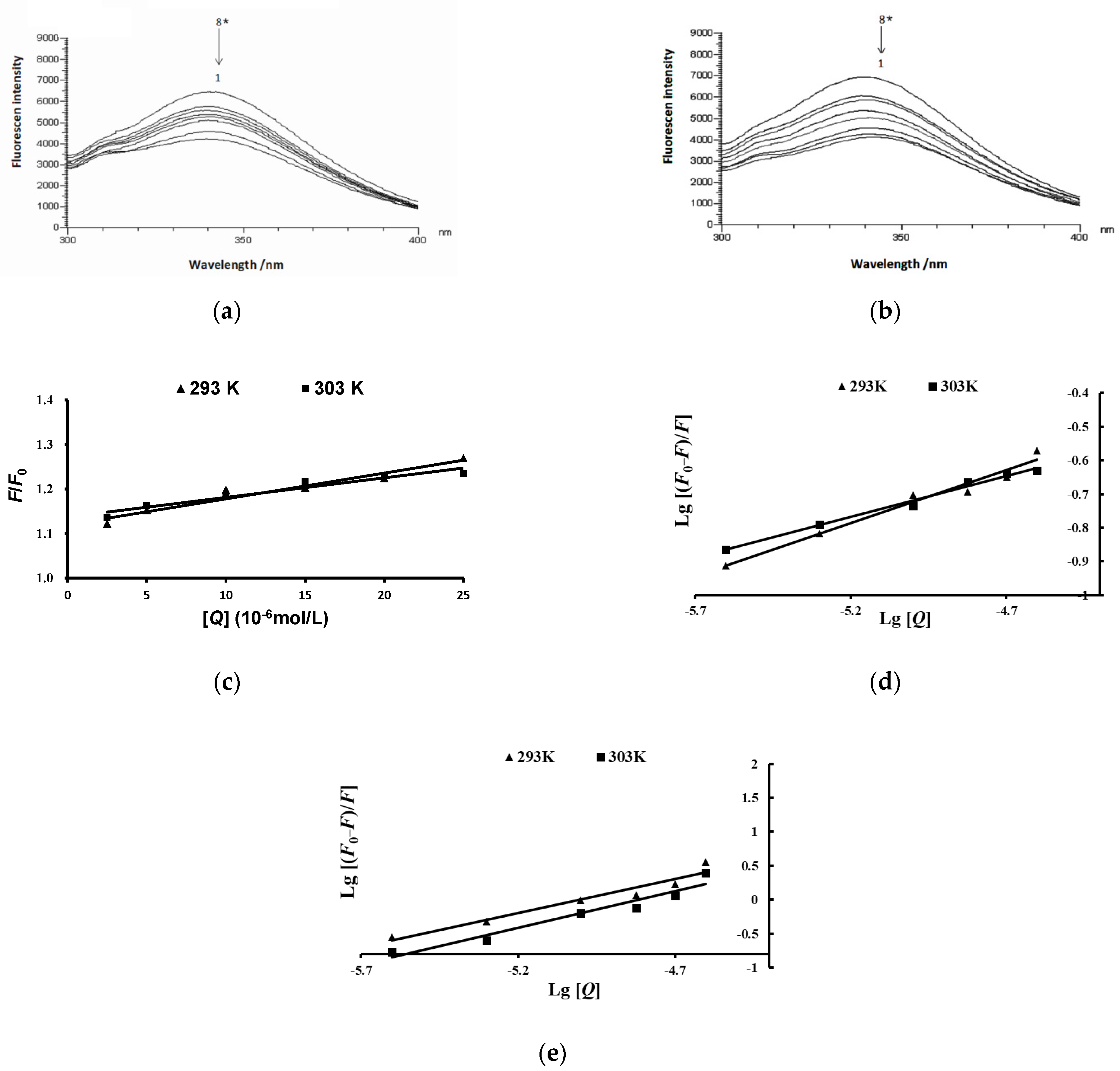
2.6. Effects of Anthocyanins from the Fruits of L. ruthenicum on the Fluorescence Spectra of Pancreatic Lipase
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of the Anthocyanins from L. ruthenicum
4.3. Animals and Samples
4.4. Determination of Serum Lipid Levels
4.5. Calculation of the Adipose Coefficient
4.6. Histological Observation of Liver and Adipose Tissue
4.7. Bacterial DNA Extraction, 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing, and Biological Information Analysis
4.8. Pancreatic Lipase Activity Assay
4.9. IC50, Inhibition Type, and Ki Values
4.10. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Measurement
4.11. Thermodynamic Parameters Assessment
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hu, L.; Huang, X.; You, C.; Li, J.; Hong, K.; Li, P.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Gao, R.; et al. Prevalence of overweight, obesity, abdominal obesity and obesity-related risk factors in southern China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183934. [Google Scholar]
- Carla, L.; Giuseppe, P.; Claudia Blasetti, F.; Massimo, F.; Stefano, M. Metabolically healthy versus metabolically unhealthy obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; An, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y. Alterations of bile acids and gut microbiota in obesity induced by high fat diet in rat model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3624–3632. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Inaba, N.; Mimaki, Y. Daisaikoto inhibits pancreatic lipase activity and decreases serum triglyceride levels in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 1485–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, B.; Ali Ashfaq, U.; Usman Mirza, M. Medicinal plant phytochemicals and their inhibitory activities against pancreatic lipase: Molecular docking combined with molecular dynamics simulation approach. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Graff, S.; Mario, F.; Ziegelmann, P.; Spritzer, P. Effects of orlistat vs. metformin on weight loss-related clinical variables in women with PCOS: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2016, 70, 450–461. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, L.; Palaniswamy, D.; Mohankumar, S.K. Targeting obesity with plant-derived pancreatic lipase inhibitors: A comprehensive review. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104681. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Guo, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, L.; Liu, R.; Yin, J. Anthocyanins in black rice, soybean and purple corn increase fecal butyric acid and prevent liver inflammation in high fat diet-induced obese mice. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3178–3186. [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski, M.; Weeks, T.L.; Hazen, S.L. Gut microbiota and cardiovascular disease. Circul. Res. 2020, 127, 553–570. [Google Scholar]
- Rufino, A.T.; Costa, V.M.; Carvalho, F.; Fernandes, E. Flavonoids as antiobesity agents: A review. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 556–585. [Google Scholar]
- Morais, C.A.; de Rosso, V.V.; Estadella, D.; Pisani, L.P. Anthocyanins as inflammatory modulators and the role of the gut microbiota. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Shen, X.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Zheng, X. Black current anthocyanins improve lipid metabolism and modulate gut microbiota in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2001090. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Yan, Y.; Ran, L.W.; Mi, J.; Sun, Y.; Lu, L.; Gao, Y.; Zeng, X.X.; Cao, Y.L. Isolation, antioxidant property and protective effect on PC12 cell of the main anthocyanin in fruit of Lycium ruthenicum Murray. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 30, 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.L.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Luo, Q.; Liu, X.; Yan, Y.M.; Jin, B.; Cao, Y.L.; Zeng, X.X.; Ran, L.W. The main anthocyanin monomer of Lycium ruthenicum Murray induces apoptosis through the ROS/PTEN/PI3K/Akt/caspase 3 signaling pathway in prostate cancer DU-145 cells. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1818–1828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Yan, Y.M.; Wan, P.; Dong, W.; Huang, K.; Ran, L.W.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Zeng, X.X.; Cao, Y.L. Effects of long-term intake of anthocyanins from Lycium ruthenicum Murray on the organism health and gut microbiota in vivo. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108952. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Zhou, W.; Xu, W.; Peng, Y.; Yan, Y.; Lu, L.; Mi, J.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y. The main anthocyanin monomer from Lycium ruthenicum Murray fruit mediates obesity via modulating the gut microbiota and improving the intestinal barrier. Foods 2021, 11, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, B.; Zhao, J.; Xie, X.; Chen, T.; Yin, Y.; Zhai, R.; Wang, X.; An, W.; Li, J. Anthocyanins from the fruits of Lycium ruthenicum Murray improve high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance by ameliorating inflammation and oxidative stress in mice. Food Func. 2021, 12, 3855–3871. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, F.J.; Vichitphan, S.; Han, J.; Vichitphan, K. Alternative approach for specific tyrosinase inhibitor screening: Uncompetitive inhibition of tyrosinase by Moringa oleifera. Molecules 2021, 26, 4576. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, K.; Pederick, W.; Santhakumar, A.B. Anthocyanins in obesity-associated thrombogenesis: A review of the potential mechanism of action. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy, A.; Bertoia, M.; Chiuve, S.; Flint, A.; Forman, J.; Rimm, E.B. Habitual intake of anthocyanins and flavanones and risk of cardiovascular disease in men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 587–594. [Google Scholar]
- Moruzzi, M.; Klöting, N.; Blüher, M.; Martinelli, I.; Tayebati, S.K.; Gabrielli, M.G.; Roy, P.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Cifani, C.; Lupidi, G.; et al. Tart cherry juice and seeds affect pro-inflammatory markers in visceral adipose tissue of high-fat diet obese rats. Molecules 2021, 26, 1403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Qi, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhu, R.; Chen, W.; Zheng, X.; Yu, T. Dietary supplementation with purified mulberry (Morus australis Poir) anthocyanins suppresses body weight gain in high-fat diet fed C57BL/6 mice. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Bjursell, M.K.; Himrod, J.; Deng, S.; Carmichael, L.K.; Chiang, H.C.; Hooper, L.V.; Gordon, J.I. A genomic view of the human-bacteroides thetaiotaomicron symbiosis. Science 2003, 299, 2074–2076. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.M.; Peng, Y.; Tang, J.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Li, X.; Ran, L.W.; Zeng, X.X.; Cao, Y.L. Effects of anthocyanins from the fruit of Lycium ruthenicum Murray on intestinal microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 533–541. [Google Scholar]
- Jamar, G.; Estadella, D.; Pisani, L.P. Contribution of anthocyanin-rich foods in obesity control through gut microbiota interactions. BioFactors 2017, 43, 507–516. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, K.; Deng, Y.; Chen, R.; Liang, S.; Xie, H.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Q. Effects of ShenlingBaizhu powder herbal formula on intestinal microbiota in high-fat diet-induced NAFLD rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Goulet, O. Potential role of the intestinal microbiota in programming health and disease. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Q.; Feng, S.; Arjan, N.; Chen, W. A next generation probiotic, Akkermansia muciniphila. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3227–3236. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, N.; Zhang, G.; Hu, X.; Pan, J.; Zhou, Z.; Gong, D. Inhibition mechanism of baicalein and baicalin on xanthine oxidase and their synergistic effect with allopurinol. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 50, 172–182. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, T.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L. Physicochemical stability-increasing effects of anthocyanin via a co-assembly approach with an amphiphilic peptide. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, Y. Mechanistic and conformational studies on the interaction of food dye amaranth with human serum albumin by multispectroscopic methods. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Gonzalez, A.I.; Alvarez-Parrilla, E.; Díaz-Sánchez, Á.G.; de la Rosa, L.A.; Núñez-Gastélum, J.A.; Vazquez-Flores, A.A.; Gonzalez-Aguilar, G.A. In vitro inhibition of pancreatic lipase by polyphenols: A kinetic, fluorescence spectroscopy and molecular docking study. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 55, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Li, J.; Song, Y.; Cong, S.; Wang, H.; Tan, M. Molecular interaction of fluorescent carbon dots from mature vinegar with human hemoglobin: Insights from spectroscopy, thermodynamics and AFM. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, R.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Peighambardoust, S.H.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Adsorption of crystal violet dye using activated carbon of lemon wood and activated carbon/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite from aqueous solutions: A kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Molecules 2021, 26, 2241. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.M.; Dai, Y.; Ran, L.W.; Cao, Y.; Luo, Q.; Li, X.Y.; Qin, K.; Dai, G.L.; Zeng, X.X. Composition and in vitro antioxidant activity of anthocyanins extracted from Lycium ruthenicum Murr. with different fruits and vegetables. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2014, 35, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Meeran, M.; Azimullah, S.; Al Ahbabi, M.M.; Jha, N.K.; Lakshmanan, V.K.; Goyal, S.N.; Ojha, S. Nootkatone, a dietary fragrant bioactive compound, attenuates dyslipidemia and intramyocardial lipid accumulation and favorably alters lipid metabolism in a rat model of myocardial injury: An in vivo and in vitro study. Molecules 2020, 25, 5656. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, S.; Thakur, S.; Mangal, M.; Mangal, A.K.; Gupta, R. DNA barcoding for specific and sensitive detection of Cuminum cyminum adulteration in Buniumpersicum. Phytomedicine 2018, 50, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar]
- McDougall, G.J.; Kulkarni, N.N.; Stewart, D. Berry polyphenols inhibit pancreatic lipase activity in vitro. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Yoshimura, N.; Matsumura, S.; Wada, H.; Hoshino, M.; Makino, S.; Morimoto, M. α-glucosidase and pancreatic lipase inhibitory activities of diterpenes from Indian Mango Ginger (Curcuma amada Roxb.) and its derivatives. Molecules 2019, 24, 4071. [Google Scholar]
- Goncalves, R.; Mateus, N.; De Freitas, V. Study of the interaction of pancreatic lipase with procyanidins by optical and enzymatic methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11901–11906. [Google Scholar]

| Groups | Raw PE | Effective Tags | AvgLen (nt) | Effective% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 102,275.0 ± 6293.5 | 63,610.9 ± 3458.7 | 416.6 ± 1.1 | 62.2 ± 1.7 |
| HFD | 103,448.4 ± 6110.5 | 63,364.3 ± 3605.0 | 415.4 ± 2.2 | 61.3 ± 1.4 |
| HFD + ACN | 99,454.8 ± 8725.6 | 61,244.4 ± 4140.6 | 415.4 ± 1.3 | 61.7 ± 1.7 |
| Groups | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | ACE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6.6 ± 0.4 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 661.0 ± 87.0 | 664.4 ± 90.1 |
| HFD | 5.9 ± 0.6 * | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 548.9 ± 114.2 * | 553.8 ± 116.7 |
| HFD + ACN | 6.1 ± 0.4 * | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 637.8 ± 98.6 | 646.3 ± 99.9 |
| Groups | IC50 (mg/mL) | Vmax/min−1 | Km (mg/mL) | K (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | --- | 5.46 | 0.25 | ---- |
| Crude extract of anthocyanins | 3.03 ± 0.43 | 5.46 | 0.44 | 3.80 |
| Main compound | 1.80 ± 0.20 | 5.46 | 0.73 | 0.88 |
| Groups | T (K) | Ksv (104 L/mol) | Kq (1012 L/(mol·s)) | Ka (L/mol) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude extract of anthocyanins | 293 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 7.14 | 0.34 |
| 303 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 3.15 | 0.24 | |
| Main compound | 293 | 6.03 | 6.03 | 15.53 × 104 | 1.08 |
| 303 | 4.19 | 4.19 | 9.69 × 104 | 0.99 |
| Groups | T (K) | ΔH (KJ/mol) | ΔS (J/mol/K) | ΔG (KJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude extract of anthocyanins | 293 | −32.57 | −12.03 | −29.04 |
| 303 | −32.57 | −12.03 | −28.92 | |
| Main compound | 293 | −60.37 | −189.70 | −4.79 |
| 303 | −60.37 | −190.01 | −2.80 |
| Composition | Proportion |
|---|---|
| Casein | 19.47% |
| Corn starch | 4.99% |
| Maltodextrin | 9.98% |
| Sucrose | 34.11% |
| Cellulose | 4.99% |
| Corn oil | 0.99% |
| Anhydrous milk fat | 19.97% |
| Cholesterol | 0.15% |
| Small material | 5.35% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, N.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Lang, Y.-Z.; Lu, L.; Mi, J.; Cao, Y.-L.; Yan, Y.-M.; Ran, L.-W. Preventive Effects of Anthocyanins from Lyciumruthenicum Murray in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Are Related to the Regulation of Intestinal Microbiota and Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase Activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072141
Li N, Liu X, Zhang J, Lang Y-Z, Lu L, Mi J, Cao Y-L, Yan Y-M, Ran L-W. Preventive Effects of Anthocyanins from Lyciumruthenicum Murray in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Are Related to the Regulation of Intestinal Microbiota and Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase Activity. Molecules. 2022; 27(7):2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072141
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Na, Xi Liu, Jing Zhang, Yan-Zhi Lang, Lu Lu, Jia Mi, You-Long Cao, Ya-Mei Yan, and Lin-Wu Ran. 2022. "Preventive Effects of Anthocyanins from Lyciumruthenicum Murray in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Are Related to the Regulation of Intestinal Microbiota and Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase Activity" Molecules 27, no. 7: 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072141
APA StyleLi, N., Liu, X., Zhang, J., Lang, Y.-Z., Lu, L., Mi, J., Cao, Y.-L., Yan, Y.-M., & Ran, L.-W. (2022). Preventive Effects of Anthocyanins from Lyciumruthenicum Murray in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Are Related to the Regulation of Intestinal Microbiota and Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase Activity. Molecules, 27(7), 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072141





