The Synthesis and Initial Evaluation of MerTK Targeted PET Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
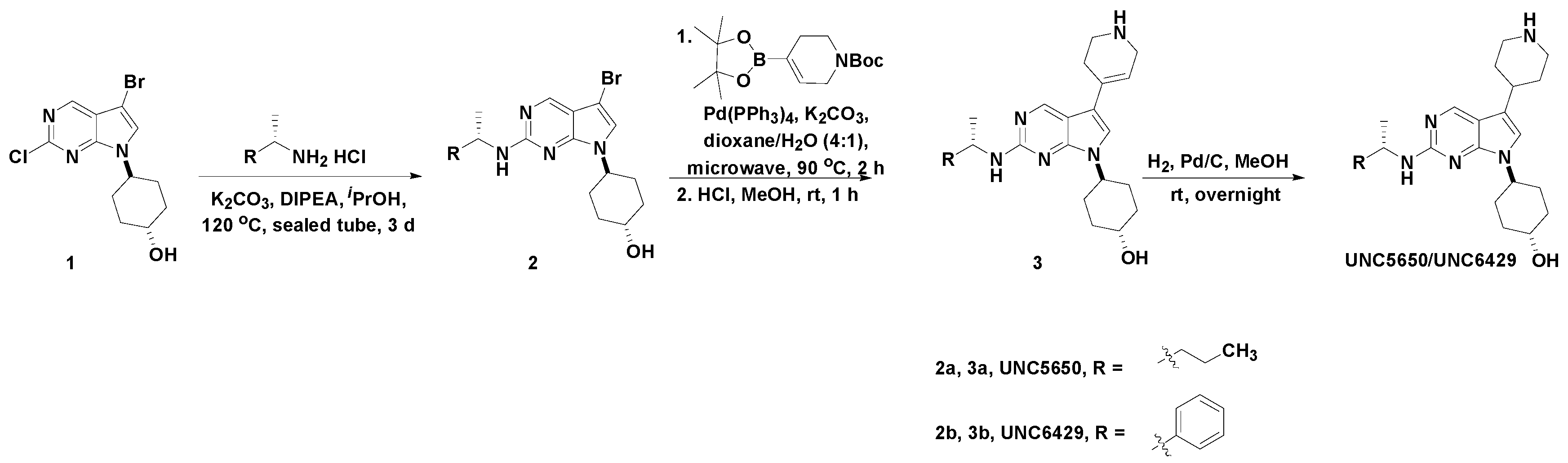
2.1. Chemistry
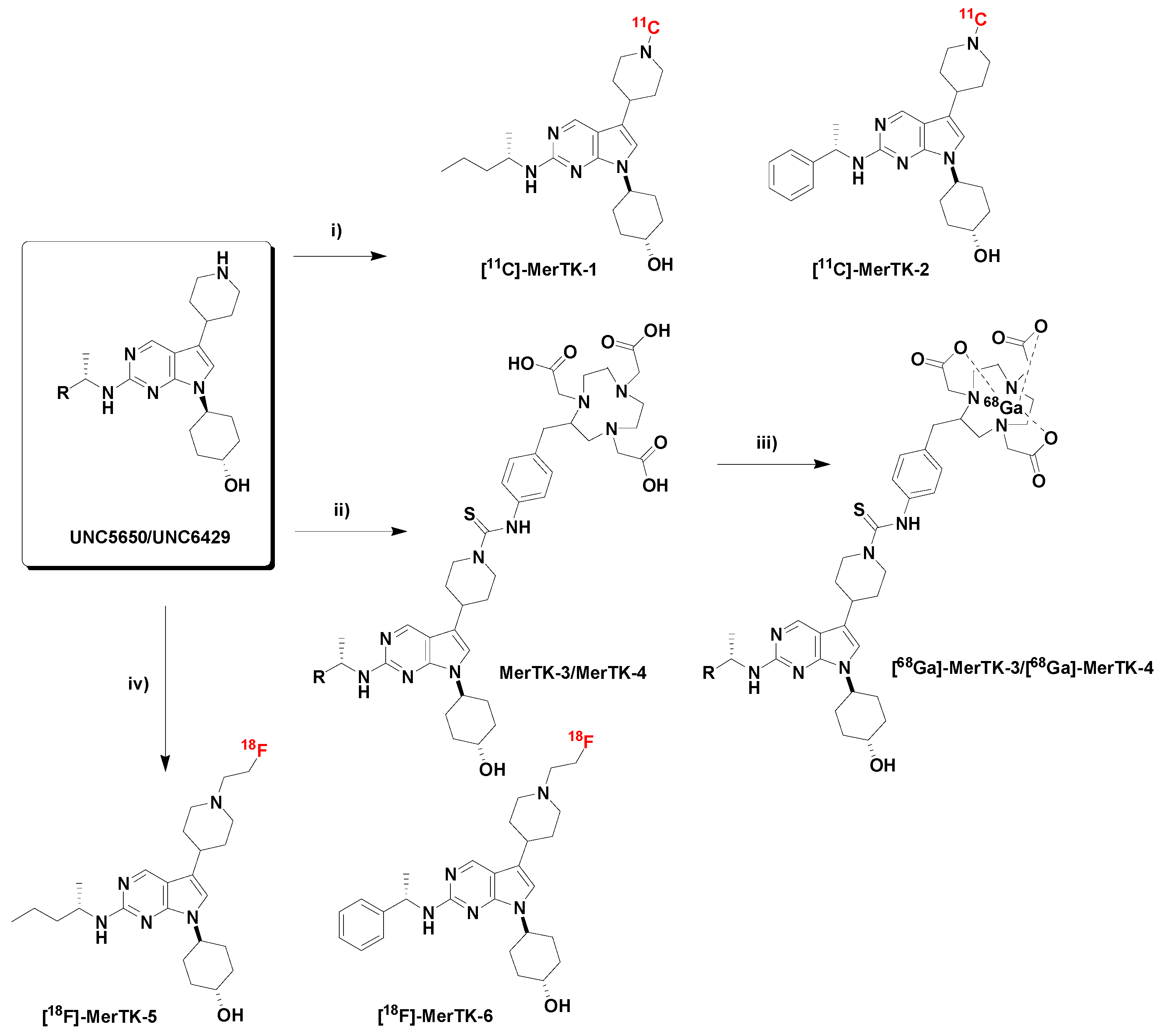
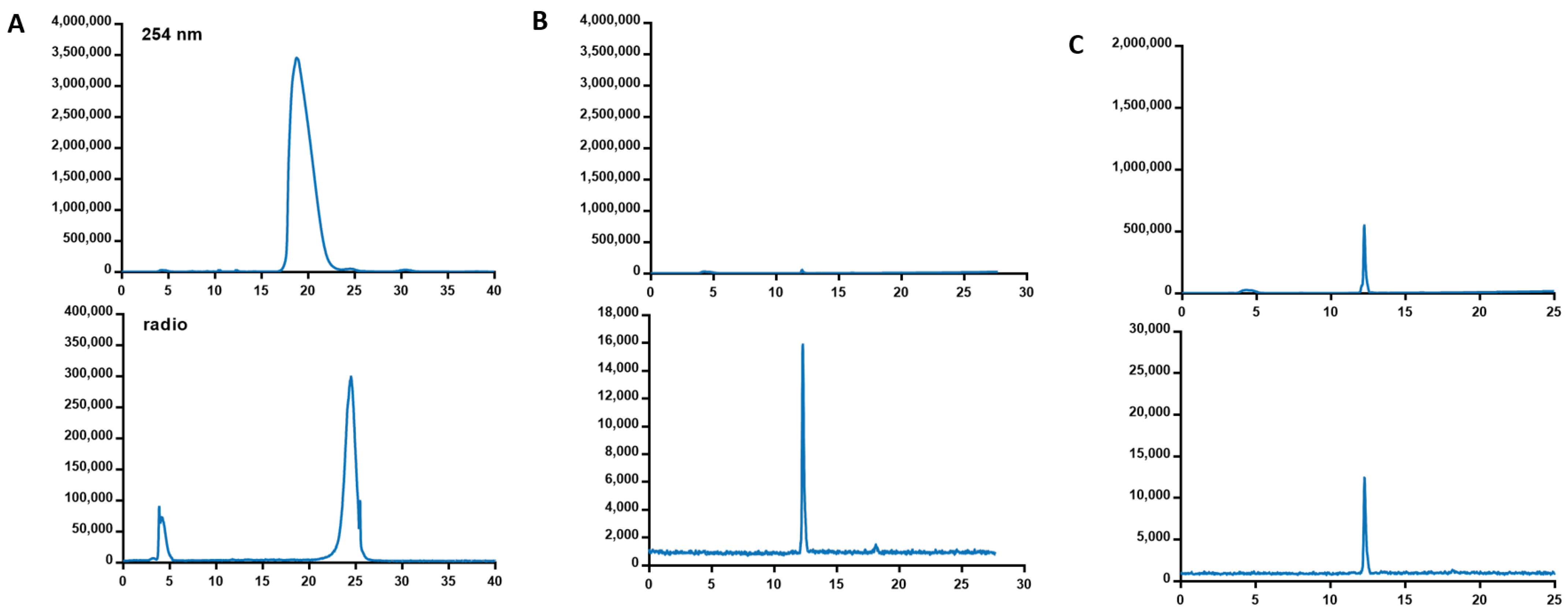
2.2. Radiochemistry
2.3. Evaluation of the LogP
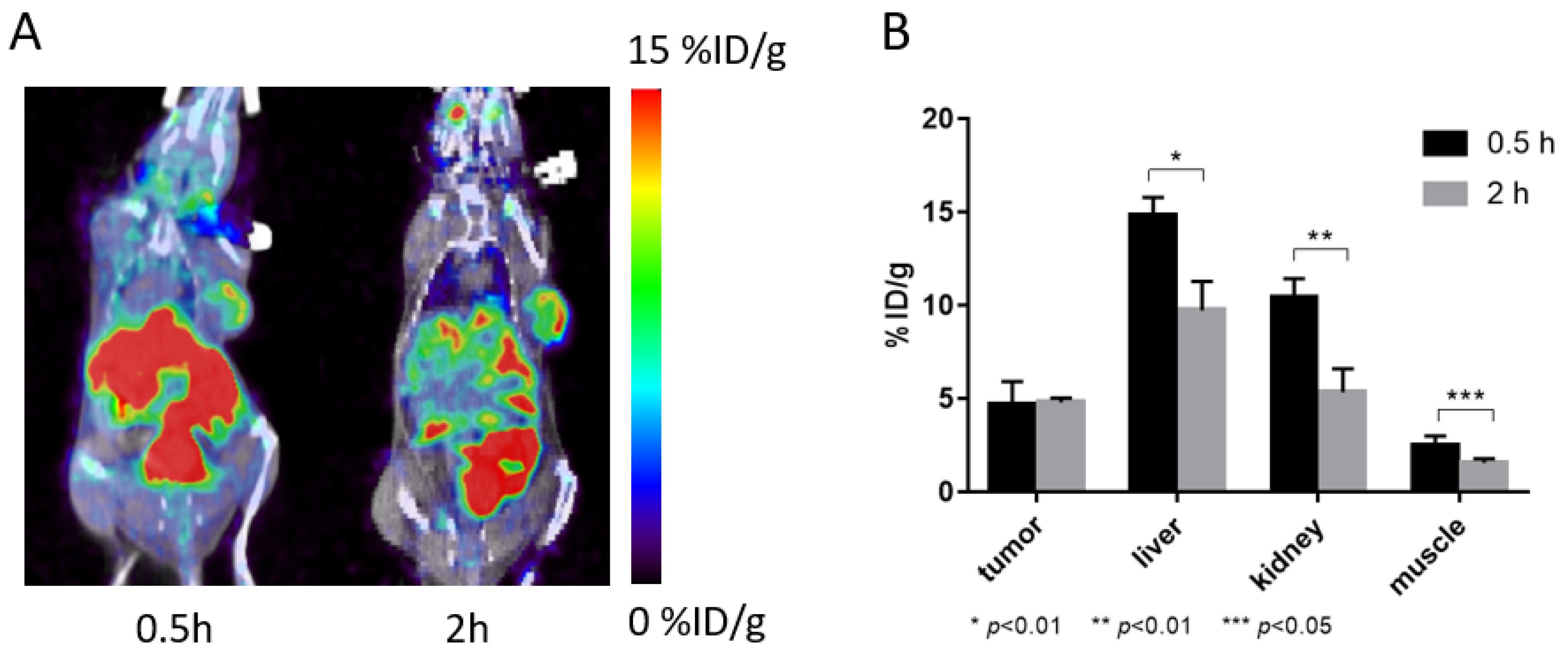
2.4. PET Imaging Study on Mice
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of UNC5650
3.1.2. Synthesis of UNC6429
3.1.3. Synthesis of MerTK-1
3.1.4. Synthesis of MerTK-2
3.1.5. Synthesis of MerTK-3/MerTK-4
3.1.6. Synthesis of MerTK-5
3.1.7. Synthesis of Compound MerTK-6
3.1.8. Microcapillary Electrophoresis (MCE) Assays
3.2. Radiochemistry
3.3. Evaluation of LogP
3.4. Mouse Model
3.5. PET Imaging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Linger, R.M.; Cohen, R.A.; Cummings, C.T.; Sather, S.; Migdall-Wilson, J.; Middleton, D.H.; Lu, X.; Baron, A.E.; Franklin, W.A.; Merrick, D.T.; et al. Mer or Axl receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition promotes apoptosis, blocks growth and enhances chemosensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3420–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Graham, D.K.; DeRyckere, D.; Davies, K.D.; Earp, H.S. The TAM family: Phosphatidylserine sensing receptor tyrosine kinases gone awry in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 769–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Jacobsen, K.M.; Henry, C.J.; Huey, M.G.; Parker, R.E.; Page, L.S.; Hill, A.A.; Wang, X.; Frye, S.V.; Earp, H.S.; et al. MERTK inhibition alters the PD-1 axis and promotes anti-leukemia immunity. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e97941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Liu, Y. MERTK Inhibition: Potential as a treatment strategy in EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, J.; Sambade, M.J.; Sather, S.; Moschos, S.J.; Tan, A.C.; Winges, A.; DeRyckere, D.; Carson, C.C.; Trembath, D.G.; Tentler, J.J.; et al. MERTK receptor tyrosine kinase is a therapeutic target in melanoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2257–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahajan, N.P.; Whang, Y.E.; Mohler, J.L.; Earp, H.S. Activated tyrosine kinase Ack1 promotes prostate tumorigenesis: Role of Ack1 in polyubiquitination of tumor suppressor Wwox. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10514–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Frady, L.N.; Bash, R.E.; Cohen, S.M.; Schorzman, A.N.; Su, Y.T.; Irvin, D.M.; Zamboni, W.C.; Wang, X.; Frye, S.V. MerTK as a therapeutic target in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Leung, J.Y.; Fan, C.; Popov, K.I.; Su, S.; Qian, J.; Wang, X.; Holtzhausen, A.; Ubil, E.; et al. MERTK mediated novel site Akt phosphorylation alleviates SAV1 suppression. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cummings, C.T.; Deryckere, D.; Earp, H.S.; Graham, D.K. Molecular pathways: MERTK signaling in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5275–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemke, G. Biology of the TAM receptors. CSH Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a009076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.S.; Jacobsen, K.M.; Wofford, A.M.; DeRyckere, D.; Stanford, J.; Prieto, A.L.; Redente, E.; Sandahl, M.; Hunter, D.M.; Strunk, K.E.; et al. MerTK inhibition in tumor leukocytes decreases tumor growth and metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3231–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huelse, J.M.; Fridlyand, D.M.; Earp, S.; DeRyckere, D.; Graham, D.K. MERTK in cancer therapy: Targeting the receptor tyrosine kinase in tumor cells and the immune system. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 213, 107577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, S.; Austin, L.; Cristofanilli, M. Cancer stem cells: Implications for cancer therapy. Oncology 2014, 28, 1101–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Mechanisms and implications of metabolic heterogeneity in cancer. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beccaria, M.; Cabooter, D. Current developments in LC-MS for pharmaceutical analysis. Analyst 2020, 145, 1129–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gridelli, C.; Rossi, A.; Carbone, D.P.; Guarize, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Mok, T.; Petrella, F.; Spaggiari, L.; Rosell, R. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2015, 1, 15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, H.; Tsujino, I.; Yoshinaga, K. 18F-Fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography in cardiac sarcoidosis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 1773–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Z. Imaging metabotropic glutamate receptor system: Application of positron emission tomography technology in drug development. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 1892–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieb, S.; Eleftheriou, A.; Warnock, G.; Guckenberger, M.; Riesterer, O. Longitudinal PET imaging of tumor hypoxia during the course of radiotherapy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 2201–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.W.; Vivash, L.; Mudududdl, R.; Nguyen, N.; Hermans, S.J.; Shackleford, D.M.; Field, J.; Xue, L.; Aprico, A.; Hancock, N.C.; et al. Development of [18F]MIPS15692, a radiotracer with in vitro proof-of concept for the imaging of MER tyrosine kinase (MERTK) in neuroinflflammatory disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 226, 113822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; DeRyckere, D.; Hunter, D.; Liu, J.; Stashko, M.A.; Minson, K.A.; Cummings, C.T.; Lee, M.; Glaros, T.G.; Newton, D.L.; et al. UNC2025, a potent and orally bioavailable MER/FLT3 dual inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7031–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeRyckere, D.; Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Huey, M.G.; Hill, A.A.; Tyner, J.W.; Jacobsen, K.M.; Page, L.S.; Kirkpatrick, G.G.; Eryildiz, F.; Montgomery, S.A.; et al. UNC2025, a MERTK small molecule inhibitor, is therapeutically effective alone and in combination with methotrexate in leukemia models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McIver, A.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Stashko, M.; Nichols, J.; Miley, M.; Norris-Drouin, J.; Machius, M.; DeRyckere, D. Discovery of macrocyclic pyrimidines as MerTK-specific inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Stashko, M.A.; DeRyckere, D.; Vasileiadi, E.; Parker, R.E.; Hunter, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Highly selective MERTK inhibitors achieved by a single methyl group. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10242–10254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Stashko, M.A.; Minson, K.A.; Huey, M.G.; Zhou, Y.; Earp, H.S.; Kireev, D.; et al. UNC5293, a potent, orally available and highly MERTK-selective inhibitor. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 220, 113534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Liu, Q.; Sui, H.; Guo, H.; Peng, L.; Li, F.; Lang, L.; Jacobson, O.; Zhu, Z.; Mao, F.; et al. Combined 68 Ga-NOTA-evans blue lymphoscintigraphy and 68 Ga-NOTA-RM26 PET/CT evaluation of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. Bioconjug. Chem. 2020, 31, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Shen, K.; Park, H.; Zhang, T.; Wu, X.; Hu, M.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; et al. Development of novel F-18-PET agents for tumor hypoxia imaging. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 5593–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palangka, C.R.A.P.; Hanaoka, H.; Yamaguchi, A.; Murakami, T.; Tsushima, Y. Al18F-labeled alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) peptide derivative for the early detection of melanoma. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2019, 33, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favata, M.; Lasky, K.; Lo, Y.; Feldman, P.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Stevens, C.; Ye, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, K.; et al. Abstract 3759: Characterization of INCB081776, a potent and selective dual AXL/MER kinase inhibitor. In Proceedings of the AACR Annual Meeting 2018, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 April 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Lew, E.D.; Seelige, R.; Tindall, E.A.; Walsh, C.; Fagan, P.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Nevarez, R.; Oh, J.; Tucker, K.D.; et al. Immuno-oncological efficacy of RXDX-106, a novel TAM (TYRO3, AXL, MER) family small-molecule kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1996–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Compound | Structure | MerTK IC50 (nM) a | Axl IC50 (nM) a | Tyro3 IC50 (nM) a | Flt3 IC50 (nM) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MerTK-1 | 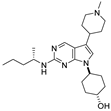 | 4.2 | 370 | 65 | 850 |
| MerTK-2 | 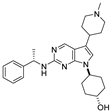 | 61 | 1700 | 180 | >30,000 |
| MerTK-4 | 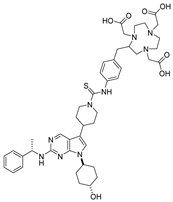 | 13 | 4100 | 180 | >30,000 |
| MerTK-5 | 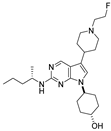 | 15 | 1100 | 190 | 1000 |
| MerTK-6 | 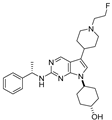 | 37 | 2100 | 120 | 5500 |
| Kinase | Peptide Substrate | Kinase (nM) | ATP (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mer | 5-FAM-EFPIYDFLPAKKK-CONH2 | 1.7 | 22.3 |
| Axl | 5-FAM-KKKKEEIYFFF-CONH2 | 16 | 200 |
| Tyro3 | 5-FAM-EFPIYDFLPAKKK-CONH2 | 5 | 40 |
| Flt3 | 5-FAM-KKKKEEIYFFF-CONH2 | 0.3 | 275 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, X.; Ma, X.; Li, B.; Ding, R.; Stashko, M.A.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. The Synthesis and Initial Evaluation of MerTK Targeted PET Agents. Molecules 2022, 27, 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051460
Wang L, Zhou Y, Wu X, Ma X, Li B, Ding R, Stashko MA, Wu Z, Wang X, Li Z. The Synthesis and Initial Evaluation of MerTK Targeted PET Agents. Molecules. 2022; 27(5):1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051460
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Li, Yubai Zhou, Xuedan Wu, Xinrui Ma, Bing Li, Ransheng Ding, Michael A. Stashko, Zhanhong Wu, Xiaodong Wang, and Zibo Li. 2022. "The Synthesis and Initial Evaluation of MerTK Targeted PET Agents" Molecules 27, no. 5: 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051460
APA StyleWang, L., Zhou, Y., Wu, X., Ma, X., Li, B., Ding, R., Stashko, M. A., Wu, Z., Wang, X., & Li, Z. (2022). The Synthesis and Initial Evaluation of MerTK Targeted PET Agents. Molecules, 27(5), 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051460







