Green Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Eucalyptus globulus Extract and Their Application in the Removal of Heavy Metals from Agricultural Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
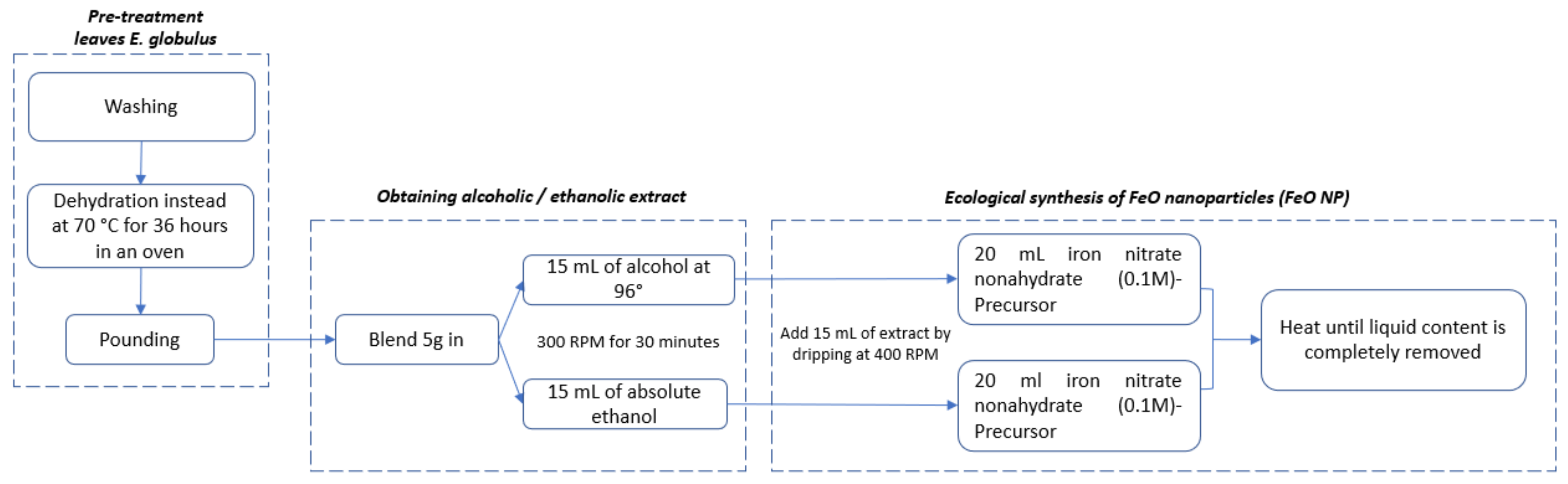
2.1. Preparation of the E. globulus Extract: Evaluation of the Type of Solvent
2.2. Sustainable Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (FeO NPs)
2.3. Characterization of FeO NPs
2.4. Evaluation of the Elimination of Heavy Metals Present in Agricultural Soil
3. Results
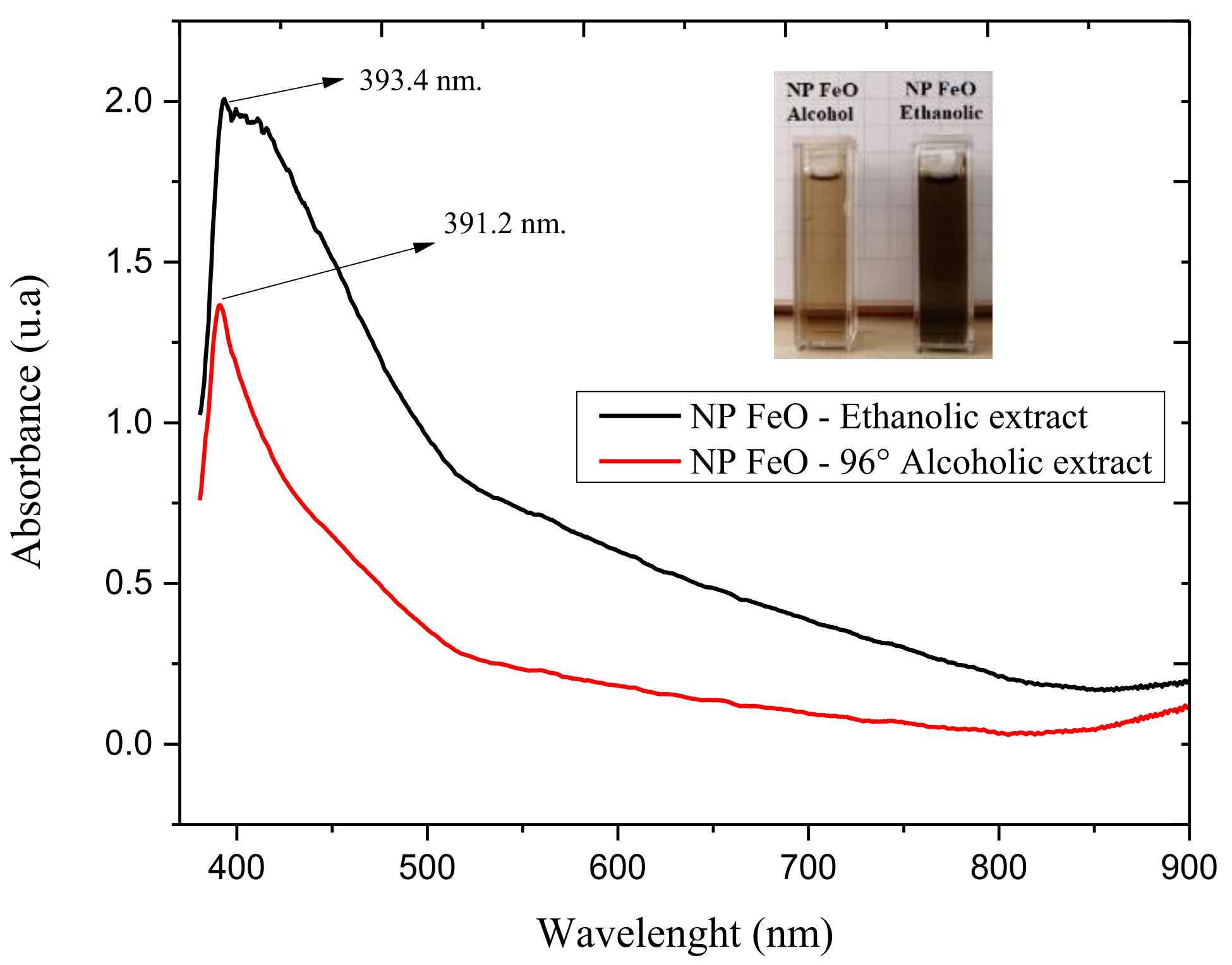
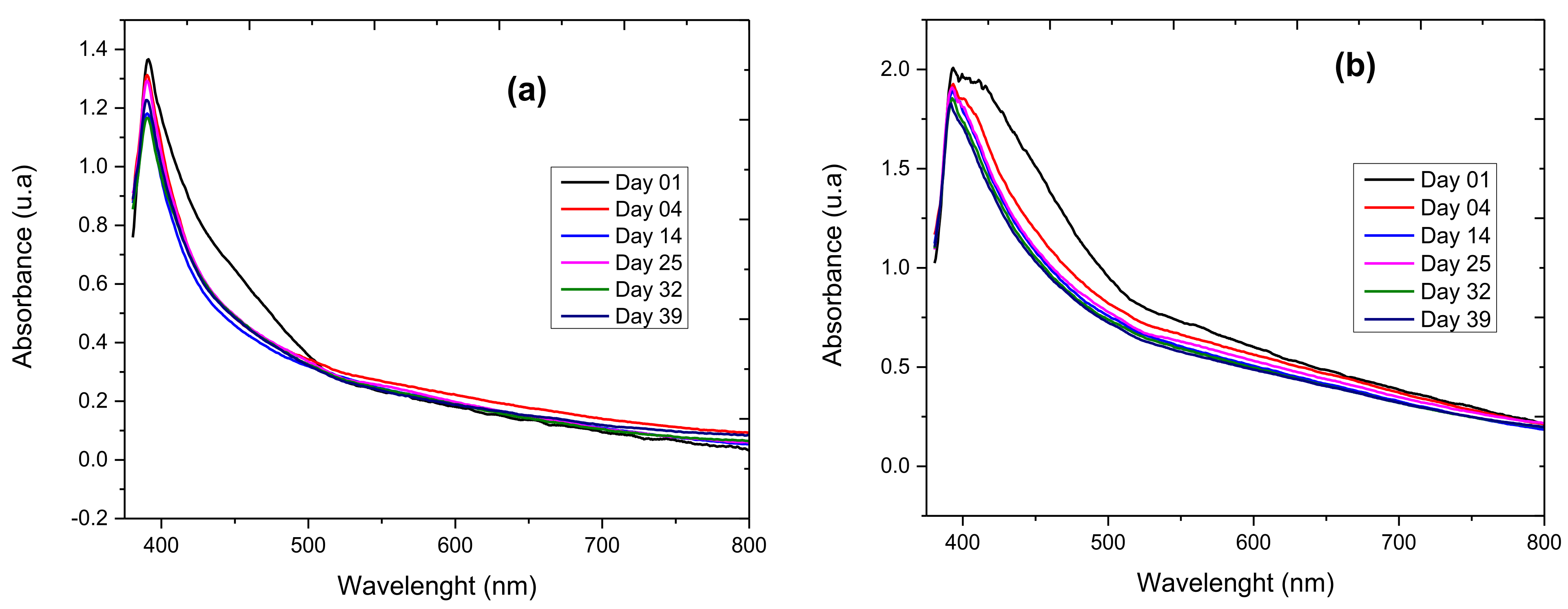
3.1. Characterization by UV-vis Spectrophotometry
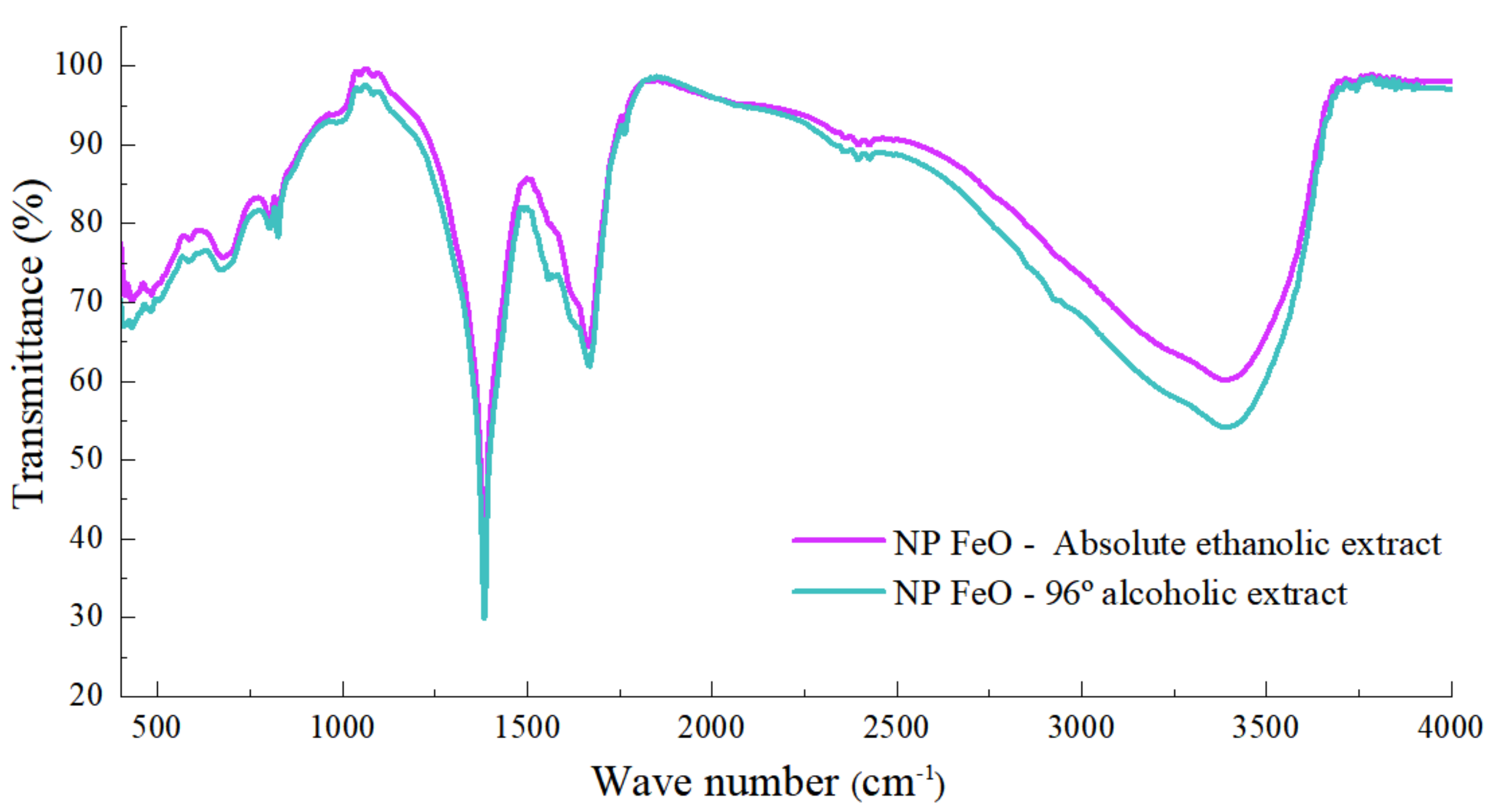
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
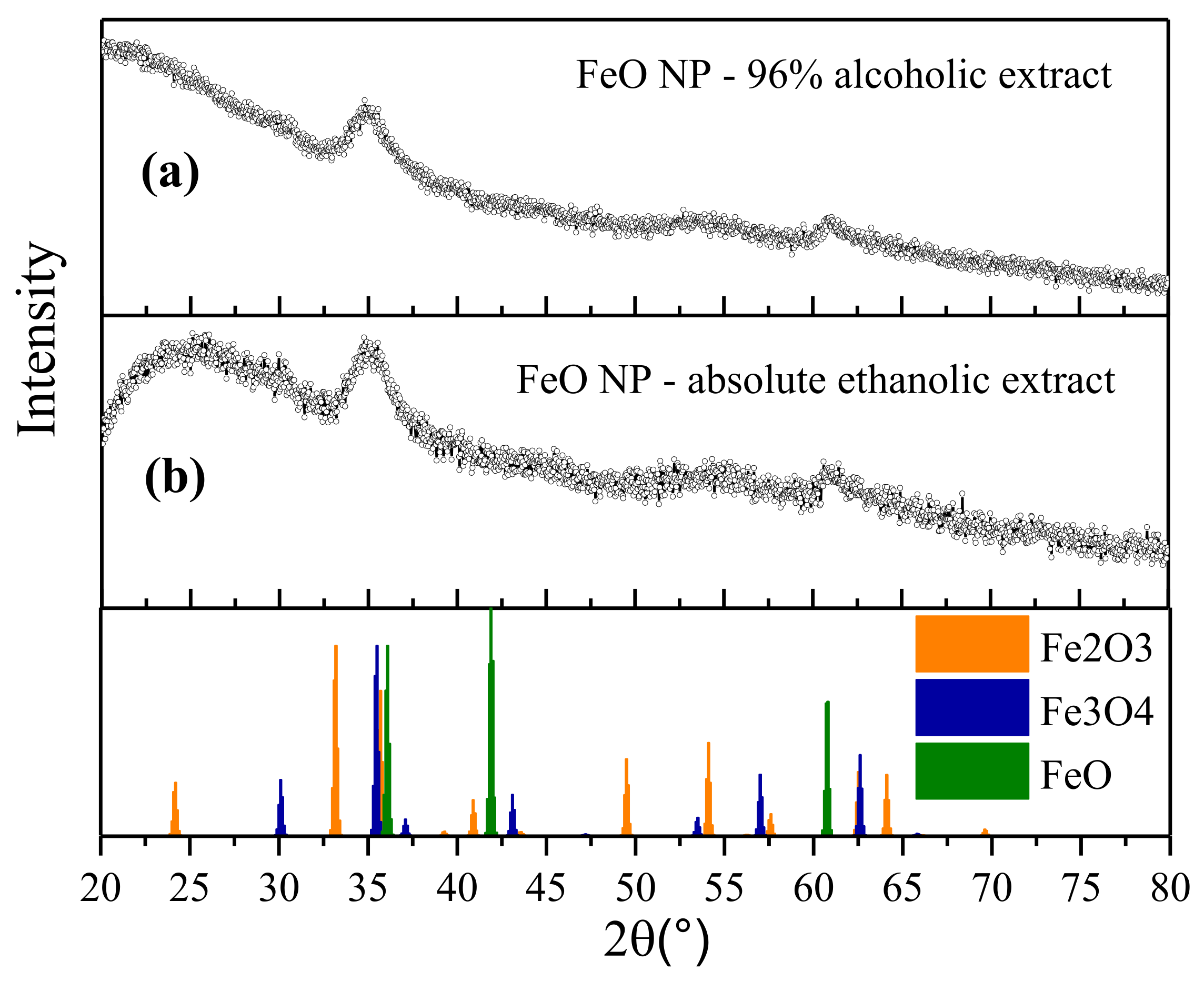
3.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
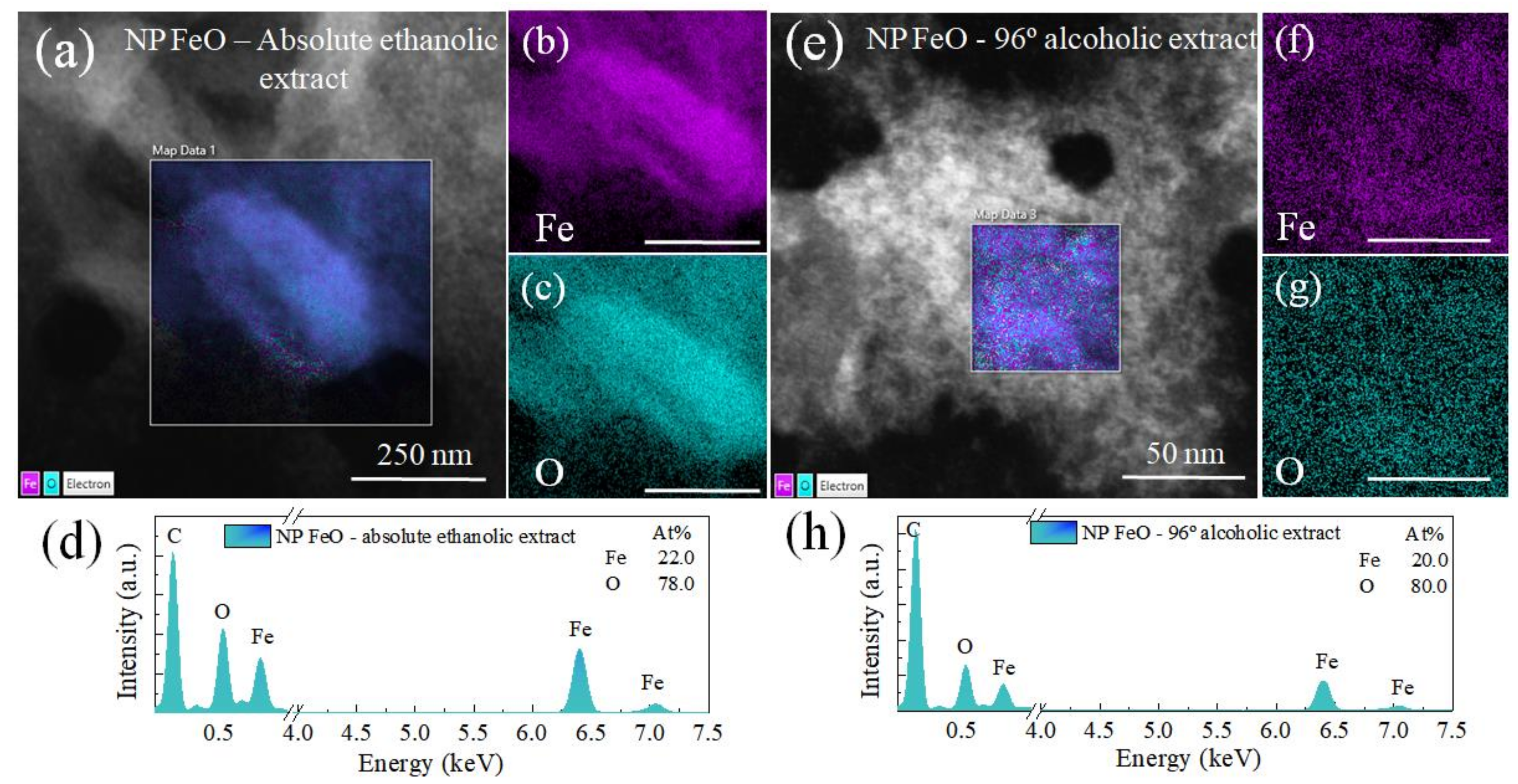
3.4. Elemental Composition—Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS)
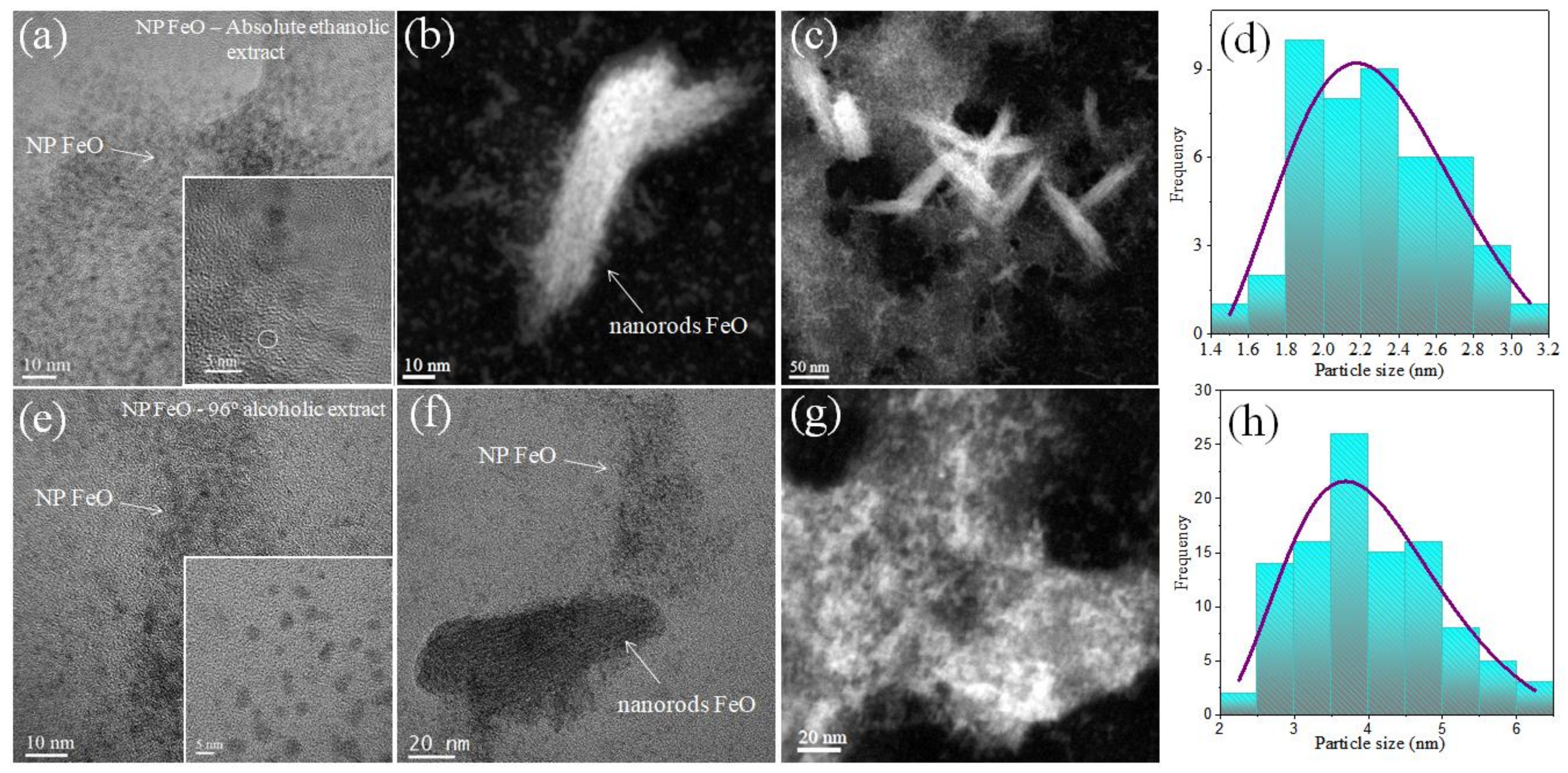
3.5. Characterization of FeO NPs by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM/STEM)
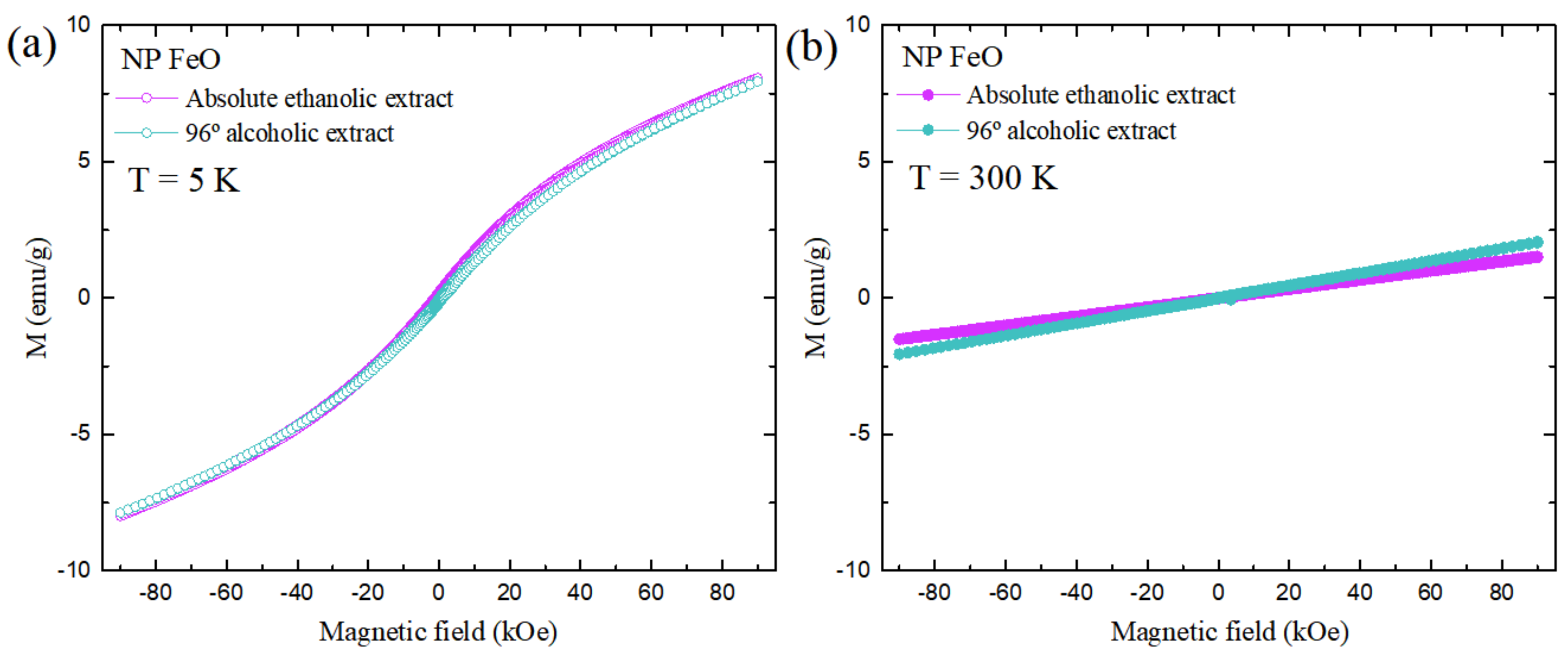
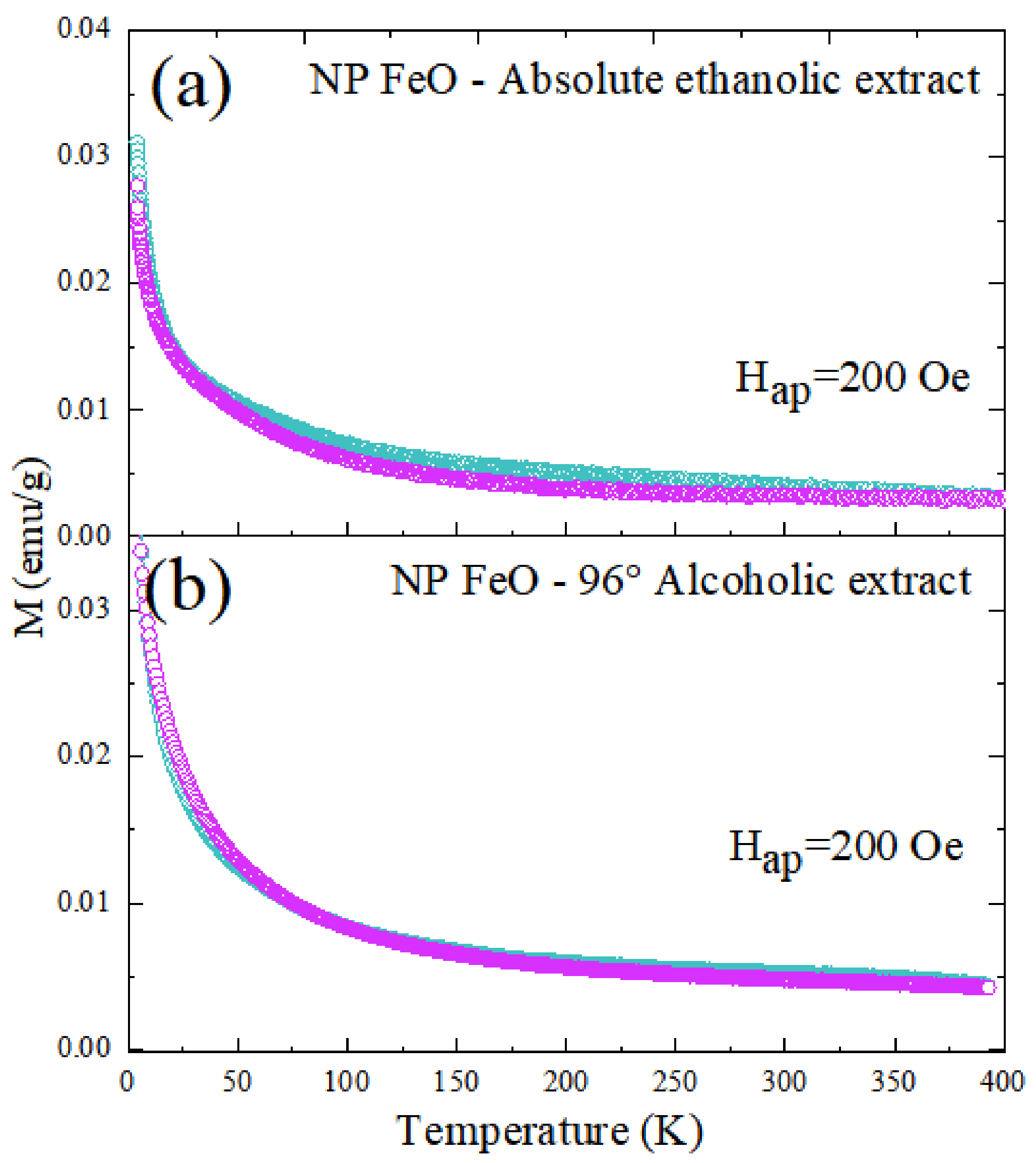
3.6. Characterization of Magnetic Properties of SPIONs
3.7. Zeta Potential
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ang, M.J.Y.; Chan, S.Y.; Goh, Y.-Y.; Luo, Z.; Lau, J.W.; Liu, X. Emerging strategies in developing multifunctional nanomaterials for cancer nanotheranostics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, W.; Zhu, D.; Mei, L. Symphony of nanomaterials and immunotherapy based on the cancer–Immunity cycle. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 12, 107–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, S.G.; Robert, B.; Salim, A.; Ananthan, P.; Sivaramakrishnan, M.; Subramaniam, S.; Natesan, S.; Suresh, R.; Rajeshkumar, G.; Maran, J.P.; et al. Nanotechnology based solutions to combat zoonotic viruses with special attention to SARS, MERS, and COVID 19: Detection, protection and medication. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 159, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Yang, X.; An, N.; Yang, F.; Sun, J.; Xing, Y.; Shang, H. Advances in the application of nanotechnology in reducing cardiotoxicity induced by cancer chemotherapy. In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Xu, H.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Fan, G.; Sun, W. Adsorption performance of boron nitride nanomaterials as effective drug delivery carriers for anticancer drugs based on density functional theory. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2021, 1203, 113360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Pandey, G.; Rawtani, D. Functionalized nanomaterials driven antimicrobial food packaging: A technological advancement in food science. Food Control 2022, 131, 108469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, C.; Lan, L.; Ping, J.; Ye, Z.; Ying, Y. Nanomaterial-based biosensors for agro-product safety. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishoge, O.K.; Zhang, L.; Suntu, S.L.; Jin, H.; Zewde, A.A.; Qi, Z. Remediation of water and wastewater by using engineered nanomaterials: A review. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2018, 53, 537–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Naushad, M.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Iqbal, J. Engineered nanoparticles for removal of pollutants from wastewater: Current status and future prospects of nanotechnology for remediation strategies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunhikrishnan, A.; Shon, H.K.; Bolan, N.S.; El Saliby, I.; Vigneswaran, S. Sources, Distribution, Environmental Fate, and Ecological Effects of Nanomaterials in Wastewater Streams. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 277–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Chen, G.; Liu, G.; Huang, X.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, M.; Xu, D.; et al. Enzyme inhibition methods based on Au nanomaterials for rapid detection of organophosphorus pesticides in agricultural and environmental samples: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuthameena, S.; Dhayalini, K.; Balraj, B.; Siva, C.; Senthilkumar, N. Two step synthesis and electrochemical behavior of SnO2 nanomaterials for electrical energy storage devices. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 131, 108803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Mahanty, A.; Gupta, S.K.; Choudhury, A.R.; Daware, A.; Bhattacharjee, S. Nanotechnology: A next-generation tool for sustainable aquaculture. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Quintero, A.; Palencia, M. A critical analysis of environmental sustainability metrics applied to green synthesis of nanomaterials and the assessment of environmental risks associated with the nanotechnology. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukweenadhi, J.; Setiawan, K.I.; Avanti, C.; Kartini, K.; Rupa, E.J.; Yang, D.C. Scale-up of green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using ethanol extract of Plantago major L. leaf and its antibacterial potential. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlawat, G.; Choudhury, A.R. A review on the biosynthesis of metal and metal salt nanoparticles by microbes. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12944–12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patiño-Ruiz, D.; Sánchez-Botero, L.; Tejeda-Benitez, L.; Hinestroza, J.; Herrera, A. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Cymbopogon citratus extract and sodium carbonate salt: Nanotoxicological considerations for potential environmental applications. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Yang, S.; Ding, B.; Yang, H. Synthesis of colloidal metal and metal alloy nanoparticles for electrochemical energy applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2880–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, D.; Banerjee, P. Green Nanotechnology—A New Hope for Medical Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 36, ISBN 9133943338457. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.M.; Yu, M.; Chen, H.; Yang, H.; Xu, Q. One-step synthesis of mixed valence FeOX nanoparticles supported on biomass activated carbon for degradation of bisphenol A by activating peroxydisulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano-Soria, A.; López-Sánchez, J.; Granados-Miralles, C.; Varela, M.; Navarro, E.; González, C.; Marín, P. Novel one-pot sol-gel synthesis route of Fe3C/few-layered graphene core/shell nanoparticles embedded in a carbon matrix. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 902, 163662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, A.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Synthesis and characterization of FeSe2 nanoparticles and FeSe2/FeO(OH) nanocomposites by hydrothermal method. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 625, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupracz, P.; Coy, E.; Grochowska, K.; Karczewski, J.; Rysz, J.; Siuzdak, K. The pulsed laser ablation synthesis of colloidal iron oxide nanoparticles for the enhancement of TiO2 nanotubes photo-activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 530, 147097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L. Direct thermal annealing synthesis of FeO nanodots anchored on N-doped carbon nanosheet for long-term electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 398, 139361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Gao, X.; Chen, P. Wan One-step synthesis of FeO(OH) nanoparticles by electric explosion of iron wire underwater. Def. Technol. 2022, 18, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi Kajani, A.; Bordbar, A.K. Biogenic magnetite nanoparticles: A potent and environmentally benign agent for efficient removal of azo dyes and phenolic contaminants from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Green chemistry for nanoparticle synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5778–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virkutyte, J.; Varma, R.S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles: Biodegradable polymers and enzymes in stabilization and surface functionalization. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Raouf, N.; Alharbi, R.M.; Al-Enazi, N.M.; Alkhulaifi, M.M.; Ibraheem, I.B.M. Rapid biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the marine red alga Laurencia catarinensis and their characterization. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Raouf, N.; Al-Enazi, N.M.; Ibraheem, I.B.M.; Alharbi, R.M.; Alkhulaifi, M.M. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by using of the marine brown alga Padina pavonia and their characterization. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, A.; Mishra, V.; Chundawat, T.S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from green algae (Botryococcus braunii) and its catalytic behavior for the synthesis of benzimidazoles. Chem. Data Collect. 2019, 20, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, R.; Ezhumalai, G.; Gnanadesigan, M. A green approach for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Chlorella vulgaris and its application in photocatalytic dye degradation activity. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefzadi, M.; Rahimi, Z.; Ghafori, V. The green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from green alga Enteromorpha flexuosa (wulfen) J. Agardh. Mater. Lett. 2014, 137, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aygün, A.; Özdemir, S.; Gülcan, M.; Cellat, K.; Şen, F. Synthesis and characterization of Reishi mushroom-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles for the biochemical applications. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 178, 112970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owaid, M.N. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Pleurotus (oyster mushroom) and their bioactivity: Review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 12, 100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, I.K.; Maity, K.; Islam, S.S. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using a glucan of an edible mushroom and study of catalytic activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, J.A.A.; Salah Eddine, L.; Abderrhmane, B.; Alonso-González, M.; Guerrero, A.; Romero, A. Green synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles by pheonix dactylifera leaf extract and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 17, 100280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.S.H.; Miah, M.Y.; Paul, S.C.; Aka, T.D.; Saha, O.; Rahaman, M.M.; Sharif, M.J.I.; Habiba, O.; Ashaduzzaman, M. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticle using Carica papaya leaf extract: Application for photocatalytic degradation of remazol yellow RR dye and antibacterial activity. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Chand Mali, S.; Trivedi, R. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Enicostemma axillare (Lam.) leaf extract. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2814–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamilarasi, P.; Meena, P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) using Gomphrena globosa (Globe amaranth) leaf extract and their characterization. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 33, 2209–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidovix, T.B.; Quesada, H.B.; Januário, E.F.D.; Bergamasco, R.; Vieira, A.M.S. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Punica granatum leaf extract applied to the removal of methylene blue. Mater. Lett. 2019, 257, 126685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, N.; Babu, P.J.; Mahanta, C.; Bora, U. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using alcoholic flower extract of Nyctanthes arbortristis and in vitro investigation of their antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 46, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutan, N.A.; Manolescu, D.S.; Fierascu, I.; Neblea, A.M.; Sutan, C.; Ducu, C.; Soare, L.C.; Negrea, D.; Avramescu, S.M.; Fierascu, R.C. Phytosynthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles enhance in vitro antioxidant and mitostimulatory activity of Aconitum toxicum Reichenb. rhizomes alcoholic extracts. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 93, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullón, B.; Gullón, P.; Lú-Chau, T.A.; Moreira, M.T.; Lema, J.M.; Eibes, G. Optimization of solvent extraction of antioxidants from Eucalyptus globulus leaves by response surface methodology: Characterization and assessment of their bioactive properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 108, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiva, D.M.; Araújo, S.; Gominho, J.; Carneiro, A.D.C.; Pereira, H. Potential of Eucalyptus globulus industrial bark as a biorefinery feedstock: Chemical and fuel characterization. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 123, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.K.; Kataria, N.; Garg, V.K. Green fabrication of ZnO nanoparticles using Eucalyptus spp. leaves extract and their application in wastewater remediation. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z. The formation of iron nanoparticles by Eucalyptus leaf extract and used to remove Cr(VI). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, J.; Zhang, H.; Luo, D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using eucalyptus leaf extract. Mater. Lett. 2015, 144, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeizi, Z.; Benbouzid, H.; Ouchenane, S.; Yılmaz, D.; Culha, M.; Bououdina, M. Biosynthesis of Zinc oxide nanoparticles from essential oil of Eucalyptus globulus with antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activities. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripireddy, B.; Mandal, B.K. Facile green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Eucalyptus globulus and their photocatalytic and antioxidant activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Green synthesis of Fe nanoparticles using eucalyptus leaf extracts for treatment of eutrophic wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z. Characterization of iron nanoparticles/reduced graphene oxide composites synthesized by one step eucalyptus leaf extract. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, X.; Guo, M.; Luo, F.; Chen, Z. One-step green synthesis of bimetallic Fe/Ni nanoparticles by eucalyptus leaf extract: Biomolecules identification, characterization and catalytic activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baragaño, D.; Alonso, J.; Gallego, J.R.; Lobo, M.C.; Gil-Díaz, M. Zero valent iron and goethite nanoparticles as new promising remediation techniques for As-polluted soils. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Sun, M.; Su, B.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Immobilization of cadmium in polluted soils by phytogenic iron oxide nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mystrioti, C.; Xanthopoulou, T.D.; Tsakiridis, P.; Papassiopi, N.; Xenidis, A. Comparative evaluation of five plant extracts and juices for nanoiron synthesis and application for hexavalent chromium reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeh, A.A.A. Green Silver Nanoparticles for Enhancing the Phytoremediation of Soil and Water Contaminated by Fipronil and Degradation Products. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeh, A.A.; Ibrahim Saber, R.A. Green nano-phytoremediation and solubility improving agents for the remediation of chlorfenapyr contaminated soil and water. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.; Stawiński, W.; Slonina, P.; Pinto, A.R.; Grosso, J.P.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Albergaria, J.T.; Delerue-Matos, C. Application of green zero-valent iron nanoparticles to the remediation of soils contaminated with ibuprofen. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prabhakar, R.; Samadder, S.R. Jyotsana Aquatic and terrestrial weed mediated synthesis of iron nanoparticles for possible application in wastewater remediation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arularasu, M.V.; Devakumar, J.; Rajendran, T.V. An innovative approach for green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles: Characterization and its photocatalytic activity. Polyhedron 2018, 156, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, M.; Bhatia, T.; Gupta, R. Green & sustainable synthetic route of obtaining iron oxide nanoparticles using Hylocereus undantus (pitaya or dragon fruit). Mater. Today Proc. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan Kumar, K.; Mandal, B.K.; Siva Kumar, K.; Sreedhara Reddy, P.; Sreedhar, B. Biobased green method to synthesise palladium and iron nanoparticles using Terminalia chebula aqueous extract. Spectrochim. Acta—Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 102, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, D.; Choo, S.G.; Yi, J.; Ding, J.; Xue, J.M. Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles via a solvent-free thermal decomposition route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharoen, K.; Sirivat, A. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2012, 177, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.; Singh, L.P.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Lead (Pb2+) and copper (Cu2+) remediation from water using superparamagnetic maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles synthesized by Flame Spray Pyrolysis (FSP). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 492, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karade, V.C.; Dongale, T.D.; Sahoo, S.C.; Kollu, P.; Chougale, A.D.; Patil, P.S.; Patil, P.B. Effect of reaction time on structural and magnetic properties of green-synthesized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 120, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, M.; Alijani, H.Q.; Fakheri, B.; Mobasseri, M.M.; Heydarpour, M.; Farahani, Z.K.; Khan, A.U. Super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): Greener synthesis using Stevia plant and evaluation of its antioxidant properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Fulekar, M.H. Biogenic synthesis of maghemite nanoparticles (γ-Fe2O3) using Tridax leaf extract and its application for removal of fly ash heavy metals (Pb, Cd). Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 20704–20710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periakaruppan, R.; Chen, X.; Thangaraj, K.; Jeyaraj, A.; Nguyen, H.H.; Yu, Y.; Hu, S.; Lu, L.; Li, X. Utilization of tea resources with the production of superparamagnetic biogenic iron oxide nanoparticles and an assessment of their antioxidant activities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, A.; Alsawalha, M.; Alomayri, T. Biogenic synthesis of husked rice-shaped iron oxide nanoparticles using coconut pulp (Cocos nucifera L.) extract for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B dye and their in vitro antibacterial and anticancer activity. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar, G.I.; Briceño, S.; Suarez, J.; Flores, S.; González, G. Biogenic synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera and chitosan and its evaluation on corn germination. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmat-Campos, D.; Abreu, A.C.; Romero-Cano, M.S.; Urquiaga-Zavaleta, J.; Contreras-Cáceres, R.; Delfín-Narciso, D.; Juárez-Cortijo, L.; Nazario-Naveda, R.; Rengifo-Penadillos, R.; Fernández, I. Unraveling the Active Biomolecules Responsible for the Sustainable Synthesis of Nanoscale Silver Particles through Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Metabolomics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 17816–17827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, T.B.; Ahmaruzzaman, M.; Begum, S. A rapid, facile and green synthesis of Ag@AgCl nanoparticles for the effective reduction of 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu Demirezen, D.; Yıldız, Y.Ş.; Yılmaz, Ş.; Demirezen Yılmaz, D. Green synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles using Ficus carica (common fig) dried fruit extract. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 127, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Habib, F.; Darwish, N.; Shanableh, A. Iron sulfide nanoparticles prepared using date seed extract: Green synthesis, characterization and potential application for removal of ciprofloxacin and chromium. Powder Technol. 2021, 380, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, M.P.; Aquino, M.G.; Calanchi, E.T. Síntesis Y Caracterización De Nanopartículas Superparamagnéticas Obtenidas Por Precipitación En Microemulsión Inversa Para Aplicaciones Biomédicas. Rev. Soc. Quím. Perú 2013, 79, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Gholami, L.; Kazemi Oskuee, R.; Tafaghodi, M.; Ramezani Farkhani, A.; Darroudi, M. Green facile synthesis of low-toxic superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) and their cytotoxicity effects toward Neuro2A and HUVEC cell lines. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 9263–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Gong, A.; Chen, B.; Zheng, J.; Chen, T.; Shen, Z.; Wu, A. Exploring a new SPION-based MRI contrast agent with excellent water-dispersibility, high specificity to cancer cells and strong MR imaging efficacy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 126, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; You, C.; Song, Z.; Yu, B.; Shen, Y. Influences of different synthesis conditions on properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, M.; Abhilash, P.C. Nanotechnology for Soil Remediation: Revitalizing the Tarnished Resource; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128185988. [Google Scholar]
- Mazarji, M.; Minkina, T.; Sushkova, S.; Mandzhieva, S.; Bidhendi, G.N.; Barakhov, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Effect of nanomaterials on remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons-contaminated soils: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 284, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliemanzadeh, A.; Fekri, M. The application of green tea extract to prepare bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron and its performance on removal of Cr(VI): Effect of relative parameters and soil experiments. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 239, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Ministerio Ambiente, P. Estándares de Calidad Ambiental (ECA) para Suelo; Poder Ejecutivo: Lima, Peru, 2013; pp. 491497–491499. [Google Scholar]
- Gheju, M. Hexavalent Chromium Reduction with Zero-Valent Iron (ZVI) in Aquatic Systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 222, 103–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; He, F.; Su, B.; Sun, M.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. The stabilizing mechanism of cadmium in contaminated soil using green synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles under long-term incubation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 379, 120832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Su, B.; Sun, M.; Chen, B.; Chen, Z. Biosynthesized iron oxide nanoparticles used for optimized removal of cadmium with response surface methodology. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, S.; Serkan Yalçın, M.; Kılınç, E. Preconcentrations of Ni(II) and Pb(II) from water and food samples by solid-phase extraction using Pleurotus ostreatus immobilized iron oxide nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosain, A.N.A.; El Nemr, A.; El Sikaily, A.; Mahmoud, M.E.; Amira, M.F. Surface modifications of nanochitosan coated magnetic nanoparticles and their applications in Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Chrome | Cadmium | Lead | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Abs | Initial ppm | Final ppm | % Removal | Abs | Initial ppm | Final ppm | % Removal | Abs | Initial ppm | Final ppm | % Removal |
| M3 | −0.079 | 204.43 | −34.01 | 100% | 0 | 0.251 | 0 | 100% | 0.15 | 497.26 | 438.54 | 11.8% |
| M2 | −0.269 | −114.28 | 0.005 | −0.10 | 0.17 | 497.26 | 0% | |||||
| M1 | −0.294 | −124.85 | 0.003 | −0.20 | 0.27 | 790.86 | 0% | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrade-Zavaleta, K.; Chacon-Laiza, Y.; Asmat-Campos, D.; Raquel-Checca, N. Green Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Eucalyptus globulus Extract and Their Application in the Removal of Heavy Metals from Agricultural Soil. Molecules 2022, 27, 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041367
Andrade-Zavaleta K, Chacon-Laiza Y, Asmat-Campos D, Raquel-Checca N. Green Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Eucalyptus globulus Extract and Their Application in the Removal of Heavy Metals from Agricultural Soil. Molecules. 2022; 27(4):1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041367
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrade-Zavaleta, Karin, Yessica Chacon-Laiza, David Asmat-Campos, and Noemi Raquel-Checca. 2022. "Green Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Eucalyptus globulus Extract and Their Application in the Removal of Heavy Metals from Agricultural Soil" Molecules 27, no. 4: 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041367
APA StyleAndrade-Zavaleta, K., Chacon-Laiza, Y., Asmat-Campos, D., & Raquel-Checca, N. (2022). Green Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Eucalyptus globulus Extract and Their Application in the Removal of Heavy Metals from Agricultural Soil. Molecules, 27(4), 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041367







