Advances in Management of Bladder Cancer—The Role of Photodynamic Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
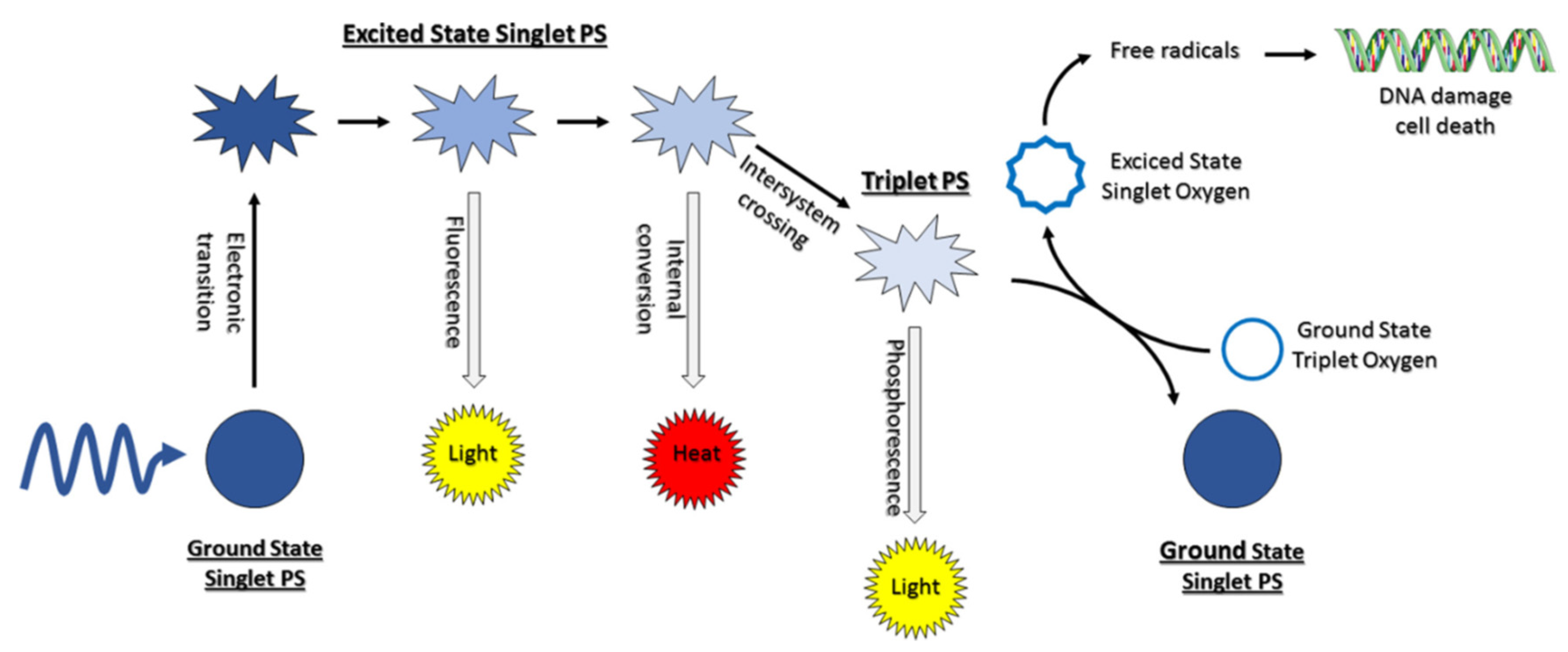
2. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) in General
3. Photodynamic Therapy in Bladder Cancer
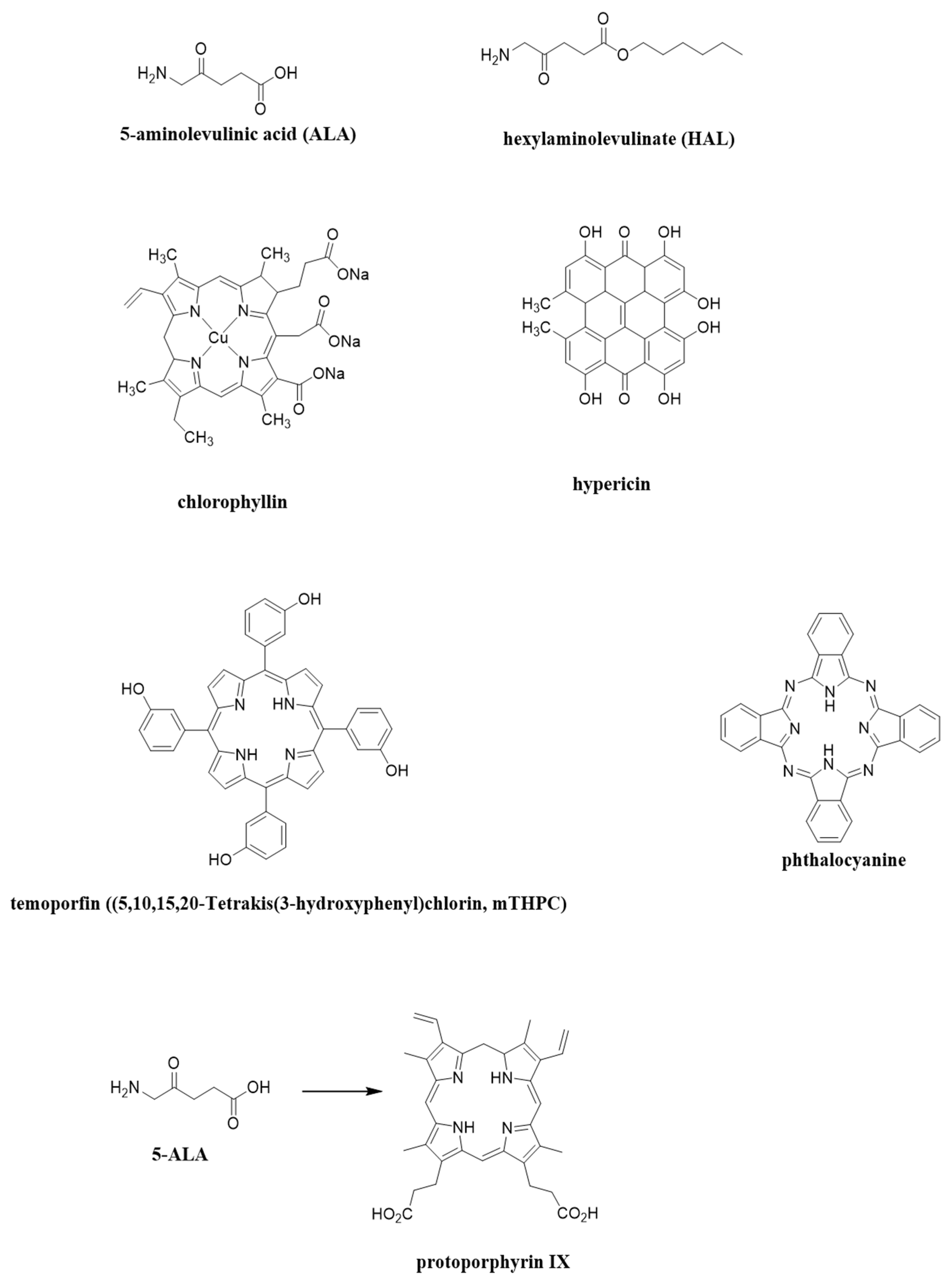
3.1. Using Different Synthetic Photosensitizers
3.1.1. 5-Aminolevulinic Acid (ALA or Levlan)
3.1.2. Hexaminolevulinic Acid (HAL)
3.2. Herbal Photosensitizers
3.2.1. Hypericin
3.2.2. Chlorophyllin
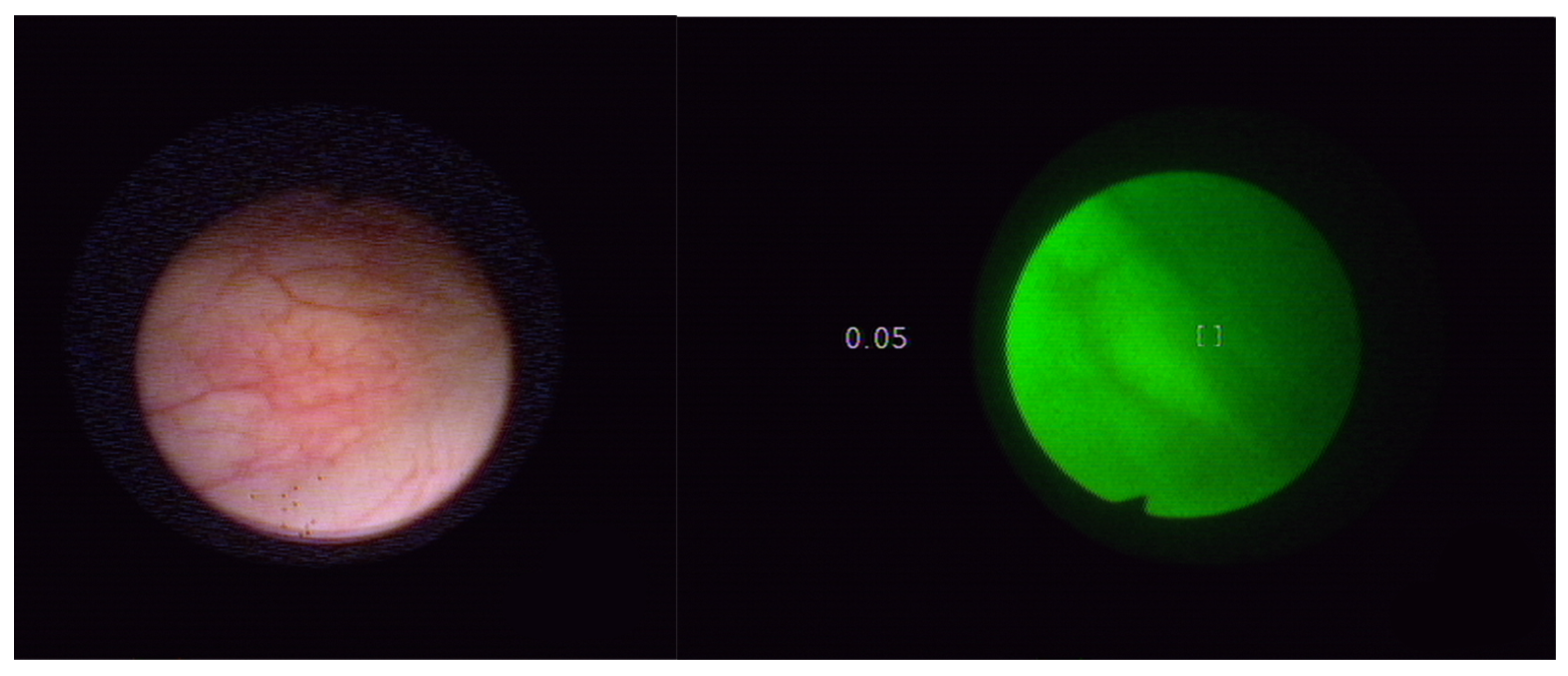
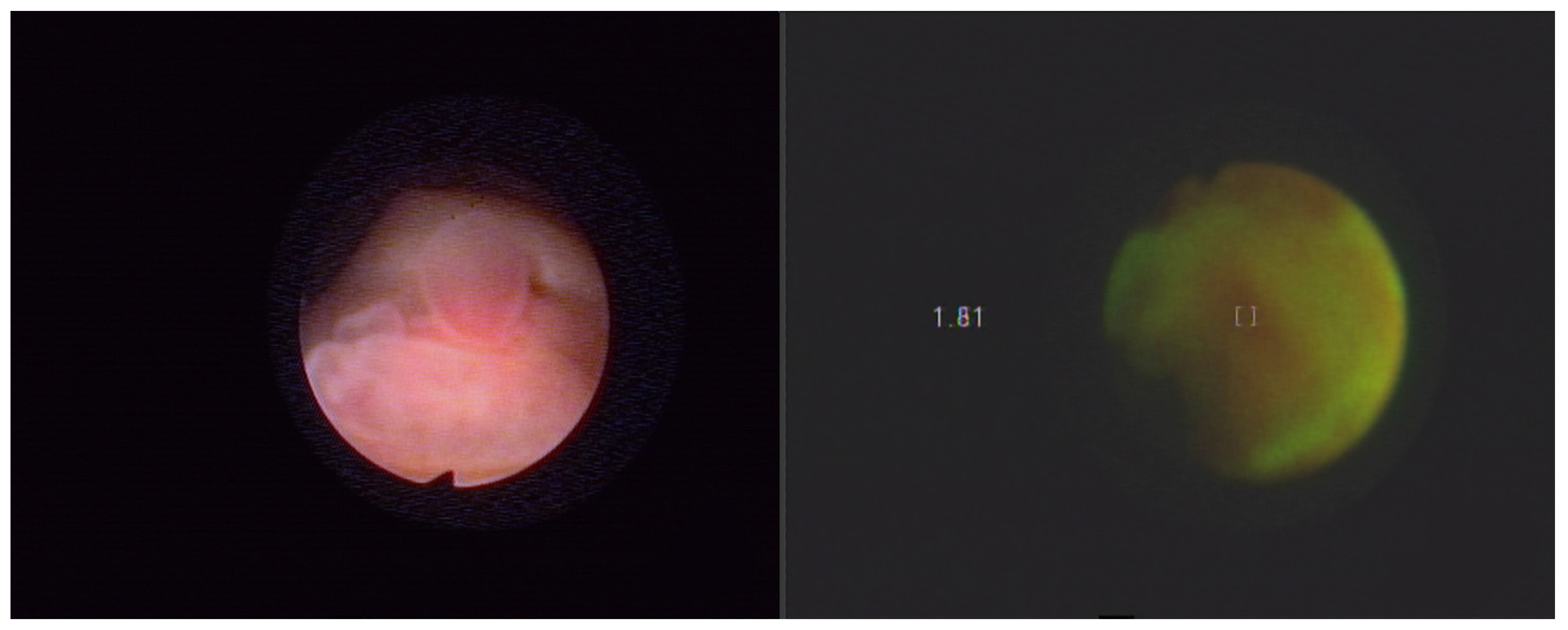
4. Autofluorescence Cystoscopy
- ALA [(1.5 g or 180 mM) in 50 mL of sodium carbonate buffer solution], which must be instilled and retained in the bladder for 2–3 h prior to cystoscopy,
- HAL [(8 mM) in 50 mL of phosphate buffer solution], instilled and retained in the bladder for 1 h before [73].
5. Light Sources in Applications for PDD and PDT of Bladder Cancer
6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farling, K.B. Bladder cancer: Risk factors, diagnosis, and management. Nurse Pract. 2017, 42, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoni, S.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Znaor, A.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Bladder Cancer Incidence and Mortality: A Global Overview and Recent Trends. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botteman, M.F.; Pashos, C.L.; Redaelli, A.; Laskin, B.; Hauser, R. The health economics of bladder cancer: A comprehensive review of the published literature. Pharmacoeconomics 2003, 21, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochenek, K.; Aebisher, A.; Międzybrodzka, A.; Cieślar, G.; Kawczyk-Krupka, A. Methods for bladder cancer diagnosis—The role of autofluorescence and photodynamic diagnosis. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 27, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supit, W.; Mochtar, C.A.; Santoso, R.B.; Umbas, R. Outcomes of radical cystectomy and bladder preservation treatment for muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Asian J. Surg. 2014, 37, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, M.A.; Hurst, C.D. Molecular biology of bladder cancer: New insights into pathogenesis and clinical diversity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Lin, Y.C. Anti-EGFR Indocyanine Green-Mitomycin C-Loaded Perfluorocarbon Double Nanoemulsion: A Novel Nanostructure for Targeted Photochemotherapy of Bladder Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkali, Z.; Chan, T.; Manoharna, M.; Algaba, T.; Busch, C.; Cheng, L.; Kiemeney, L.; Kriegmair, M.; Montironi, R.; Murphy, W.M.; et al. Bladder cancer: Epidemiology, staging and grading, and diagnosis. Urology 2005, 66 (Suppl. 1), 4–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiński, M. Fluorescence diagnosis of bladder neoplasms. Przegląd Urologiczny 2013, 2, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.S.; Bochner, B.H.; Chou, R.; Dreicer, R.; Kamat, A.M.; Lerner, S.P.; Lotan, Y.; Meeks, J.J.; Michalski, J.M.; Morgan, T.M.; et al. Treatment of Non-Metastatic Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: AUA/ASCO/ASTRO/SUO Guideline. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svedsen, C.; James, A.; Matulewicz, R.S.; Moreton, E.; Sosnowski, R.; Sherman, S.; Jaspers, I.; Gordon, T.; Bjurlin, M.A. Carcinogenic biomarkers of exposure in the urine of heated tobacco product users associated with bladder cancer: A systematic review. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, T.; Nabi, G. Potential of urinary biomarkers in early bladder cancer diagnosis. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2007, 7, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.; Stenzl, A.; Sharma, A.; Vasdev, N. Urinary biomarkers in bladder cancer: A review of the current landscape and future directions. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chueng, G.; Sahai, A.; Billia, M.; Dasgupta, P.; Khan, M.S. Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Xiao, D.; Bu, Y.; Long, J.; Yang, X.; Lv, S.; Yang, X. Novel Combination Therapies for the Treatment of Bladder Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 27, 539527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Karashima, T.; Inoue, K. Photodynamic diagnosis and therapy for urothelial carcinoma and prostate cancer: New imaging technology and therapy. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 26, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prout, G.R., Jr.; Lin, C.W.; Benson, R., Jr.; Nseyo, U.O.; Daly, J.J.; Griffin, P.P.; Kinsey, J.; Tian, M.E.; Lao, Y.H.; Mian, Y.Z.; et al. Photodynamic therapy with hematoporphyrin derivative in the treatment of superficial transitional-cell carcinoma of the bladder. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 12, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Fan, J.; Chao, H.; Peng, X. Recent progress in photosensitizers for overcoming the challenges of photodynamic therapy: From molecular design to application. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 4185–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algorri, J.F.; Ochoa, M.; Roldán-Varona, P.; Rodríguez-Cobo, L.; López-Higuera, J.M. Photodynamic Therapy: A Compendium of Latest Reviews. Cancers 2021, 13, 4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, M.S.; Cadet, J.; di Mascio, P.; Ghogare, A.A.; Greer, A.; Hamblin, M.R.; Lorente, C.; Nunez, S.C.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Thomas, A.H.; et al. Type I and Type II Photosensitized Oxidation Reactions: Guidelines and Mechanistic Pathways. Photochem. Photobiol. 2017, 93, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, C.A.; Evans, D.H.; Abrahamse, H. Photodynamic therapy (PDT): A short review on cellular mechanisms and cancer research applications for PDT. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2009, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowski, S.; Knap, B.; Przystupski, D.; Saczko, J.; Kędzierska, E.; Knap-Czop, K.; Kotlińska, J.; Michel, O.; Kotowski, K.; Kulbacka, J. Photodynamic therapy—Mechanisms, photosensitizers and combinations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dima, V.F.; Ionescu, M.D.; Balotescu, C.; Dima, S.F. Photodynamic therapy and some clinical applications in oncology. Roum. Arch. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 61, 159–205. [Google Scholar]
- Vrouenraets, M.B.; Visser, G.W.; Snow, G.B.; van Dongen, G.A. Basic principles, applications in oncology and improved selectivity of photodynamic therapy. Anticancer Res. 2003, 23, 505–522. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 1986, 232, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatidis, L.; Masquelier, M.; Vitols, S. Elevated uptake of low density lipoprotein by drug resistant human leukemic cell lines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 2169–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llaverias, G.; Danilo, C.; Mercier, I.; Daumer, K.; Capozza, F.; Williams, T.M.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P.; Frank, P.G. Role of cholesterol in the development and progression of breast cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorin, A.; Gabitova, L.; Astsaturov, I. Regulation of cholesterol biosynthesis and cancer signaling. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, P.M.R.; Mo, H.; McConathy, W.J.; Sabnis, N.; Lacko, A.G. The role of cholesterol metabolism and cholesterol transport in carcinogenesis: A review of scientific findings, relevant to future cancer therapeutics. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.R.; Newman, E.L. Photosensitizer targeting in photodynamic therapy. II. Conjugates of haematoporphyrin with serum lipoproteins. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 1994, 26, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano, A.P.; Demidova, T.N.; Hamblin, M.R. Mechanisms in photodynamic therapy: Part three—Photosensitizer pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, tumor localization and modes of tumor destruction. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2005, 2, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, H.; Meyers, A.D.; Musani, A.I.; Wang, L.; Tagg, R.; Barqawi, A.B.; Chen, Y.K. Photodynamic therapy for treatment of solid tumors—Potential and technical challenges. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 7, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krammer, B. Vascular effects of photodynamic therapy. Anticancer Res. 2001, 21, 4271–4277. [Google Scholar]
- Dobson, J.; de Queiroz, G.F.; Golding, J.P. Photodynamic therapy and diagnosis: Principles and comparative aspects. Vet. J. 2018, 233, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzini, G.; Colin, P.; Betrouni, N.; Nevoux, P.; Ouzzane, A.; Puech, P.; Villers, A.; Mordon, S. Photodynamic therapy in urology: What can we do now and where are we heading? Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2012, 9, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monro, S.; Colón, K.L.; Yin, H.; Roque, J., 3rd; Konda, P.; Gujar, S.; Thummel, R.P.; Lilge, L.; Cameron, C.G.; McFarland, S.A. Transition Metal Complexes and Photodynamic Therapy from a Tumor-Centered Approach: Challenges, Opportunities, and Highlights from the Development of TLD1433. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 797–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, A.G.; Clichici, S.; Daicoviciu, D.; Olteanu, D.; Mureşan, A.; Dreve, S. Photodynamic therapy—Indications and limits in malignant tumors treatment. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 46, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Nseyo, U.O.; Lamm, D.L. Immunotherapy of bladder cancer. Semin. Surg. Oncol. 1997, 13, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simelane, N.W.N.; Kruger, C.A.; Abrahamse, H. Photodynamic diagnosis and photodynamic therapy of colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41560–41576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, N.; Andersson-Engels, S.; Segersten, U.; Malmstrom, P.U. An overview on preclinical and clinical experiences with photodynamic therapy for bladder cancer. Can. J. Urol. 2011, 18, 5778–5786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aboumarzouk, O.; Valentine, R.; Buist, R.; Ahmad, S.; Nabi, G.; Eljamel, S.; Moseley, H.; Kata, S.G. Laser-induced autofluorescence spectroscopy: Can it be of importance in detection of bladder lesions? Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2015, 12, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenkman, E.; Lamm, D.L. Superficial bladder cancer therapy. Sci. World J. 2004, 28, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamek, M.; Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Mostowy, A.; Czuba, Z.; Krol, W.; Kasperczyk, S.; Jakobisiak, M.; Golab, J.; Sieroń, A. Topical ALA—PDT modifies neutrophils’ chemiluminescence, lymphocytes’ interleukin-1beta secretion and serum level of transforming growth factor beta1 in patients with nonmelanoma skin malignancies—A clinical study. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2005, 2, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Ledwon, A.; Malyszek, J.; Sieron, A. Balanoposthitis with epithelial dysplasia treated by photodynamic therapy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2007, 4, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieroń, A.; Sieroń-Stołtny, K.; Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Latos, W.; Kwiatek, S.; Straszak, D.; Bugaj, A.M. The role of fluorescence diagnosis in clinical practice. OncoTargets Ther. 2013, 6, 977–982. [Google Scholar]
- Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Waśkowska, J.; Raczkowska-Siostrzonek, A.; Kościarz-Grzesiok, A.; Kwiatek, S.; Straszak, D.; Latos, W.; Koszowski, R.; Sieroń, A. Comparison of cryotherapy and photodynamic therapy in treatment of oral leukoplakia. Potodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2012, 9, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachor, R.; Shea, C.R.; Gillies, R.; Hasan, T. Photosensitized destruction of human bladder carcinoma cells treated with chlorin e6-conjugated microspheres. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 1580–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachor, R.; Reich, E.; Rück, A.; Hautmann, R. Aminolevulinic acid for photodynamic therapy of bladder carcinoma cells. Urol. Res. 1996, 24, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waidelich, R.; Beyer, W.; Knüchel, R.; Stepp, H.; Baumgartner, R.; Schröder, J.; Hofstetter, A.; Kriegmair, M. Whole bladder photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid using a white light source. Urology 2003, 61, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonenko, E.V.; Kaprin, A.D.; Alekseev, B.Y.; Apolikhin, O.I.; Slovokhodov, E.K.; Ivanova-Radkevich, V.I.; Urlova, A.N. 5-Aminolevulinic acid in intraoperative photodynamic therapy of bladder cancer (results of multicenter trial). Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2016, 16, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K. 5-Aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy for bladder cancer. Int. J. Urol. 2017, 24, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, J.A.; Douglass, J. The role of hexaminolevulinate fluorescence cystoscopy in bladder cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Urol. 2007, 4, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaucher, L.; Jichlinski, P.; Lange, N.; Ritter-Schenk, C.; van den Bergh, H.; Kucera, P. Hexyl-aminolevulinate-mediated photodynamic therapy: How to spare normal urothelium. An in vitro approach. Lasers Surg. Med. 2007, 39, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bader, M.J.; Stepp, H.; Beyer, W.; Pongratz, T.; Sroka, R.; Kriegmair, M.; Zaak, D.; Welschof, M.; Tilki, D.; Stief, C.G.; et al. Photodynamic therapy of bladder cancer—A phase I study using hexaminolevulinate (HAL). Urol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamuhabwa, A.R.; Agostinis, P.; D’Hallewin, M.A.; Kasran, A.; de Witte, P.A. Photodynamic activity of hypericin in human urinary bladder carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2000, 20, 2579–2584. [Google Scholar]
- Saw, C.L.; Olivo, M.; Soo, K.C.; Heng, P.W. Delivery of hypericin for photodynamic applications. Cancer Lett. 2006, 8, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühleisen, L.; Alev, M.; Unterweger, H.; Subatzus, D.; Pöttler, M.; Friedrich, R.P.; Alexiou, C.; Janko, C. Analysis of Hypericin-Mediated Effects and Implications for Targeted Photodynamic Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Jiang, N.; Wang, G.; Chu, Y.; Lin, W.; Qian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Chen, G. Autophagy inhibition sensitizes bladder cancer cells to the photodynamic effects of the novel photosensitizer chlorophyllin e4. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2014, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wu, Z.; Li, W.; Jia, G.; Lu, J.; Fang, J.; Chen, G. Chlorophyllin e4 is a novel photosensitizer against human bladder cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Gomaa, I.; Ali, S.E.; El-Tayeb, T.A.; Abdel-Kader, M.H. Chlorophyll derivative mediated PDT versus methotrexate: An in vitro study using MCF-7 cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2012, 9, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.P.; Steiner, H.; Stenzl, A.; Akkad, T.; Bartsch, G.; Holtl, L. Photodynamic therapy with intravesical instillation of 5-aminolevulinic acid for patients with recurrent superficial bladder cancer: A single-center study. Urology 2003, 61, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaneshar, S.; Patil, K.; Bulbule, M.; Kinjawadekar, V.; Joshi, D.; Joshi, V. Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2014, 27, 125–141. [Google Scholar]
- Szliszka, E.; Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Czuba, Z.P.; Sieron, A.; Krol, W. Effect of ALA-mediated photodynamic therapy in combination with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRA IL) on bladder cancer cells. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2011, 64, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szygula, M.; Wojciechowski, B.; Adamek, M.; Pietrusa, A.; Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Cebula, W.; Zieleznik, W.; Biniszkiewicz, T.; Duda, W.; Sieroń, A. Fluorescent diagnosis of urinary bladder cancer-a comparison of two diagnostic modalities. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2004, 1, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Bugaj, A.M.; Latos, W.; Wawrzyniec, K.; Oleś, P.; Mertas, A.; Czuba, Z.; Król, W.; Sieroń-Stołtny, K.; Sieroń, A. ALA-mediated photodynamic effect onapoptosis induction and secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor(MIF) and of monocyte chemotactic protein(MCP-1) by colon cancer cells in normoxia and in hypoxia-like conditions in vitro. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2015, 12, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, S.; Ida, M.; Wang, X.; Naito, Y.; Kawaguchi, M. Oral 5-aminolevulinic acid administration prior to transurethral resection of bladder tumor causes intraoperative hypotension: Propensity score analysis. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 34, 102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytlewski, J.D.; Scalora, N.; Garcia, K.; Tanas, M.; Toor, F.; Miller, B.; Allen, B.; Milhem, M.; Monga, V. Photodynamic Therapy Using Hippo Pathway Inhibitor Verteporfin: A Potential Dual Mechanistic Approach in Treatment of Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesslich, T.; Berlanda, J.; Plaetzer, K.; Krammer, B.; Berr, F. Comparative characterization of the efficiency and cellular pharmacokinetics of Foscan- and Foslip-based photodynamic treatment in human biliary tract cancer cell lines. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2007, 6, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josefsen, L.B.; Boyle, R.W. Photodynamic Therapy and the Development of Metal-Based Photosensitisers. Metal Based Drugs 2008, 2008, 276109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Diaz, R.R.; Cho, K.S.; Lim, M.S.; Chung, J.S.; Kim, W.T.; Ham, W.S.; Choi, Y.D. Efficacy and safety of photodynamic therapy for recurrent, high grade nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer refractory or intolerant to bacille Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gándara, L.; Sandes, E.; di Venosa, G.; Prack Mc Cormick, B.; Rodriguez, L.; Mamone, L.; Batlle, A.; Eiján, A.M.; Casas, A. The natural flavonoid silybin improves the response to Photodynamic Therapy of bladder cancer cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2014, 133, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegmair, M.; Baumgartner, R.; Knüchel, R.; Stepp, H.; Hofstädter, F.; Hofstetter, A. Detection of early bladder cancer by 5-aminolevulinic acid induced porphyrin fluorescence. J. Urol. 1996, 155, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waidelich, R.; Stepp, H.; Baumgartner, R.; Weninger, E.; Hofstetter, A.; Kriegmair, M. Clinical experience with 5-aminolevulinic acid and photodynamic therapy for refractory superficial bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2001, 165, 1904–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drăgoescu, O.; Tomescu, P.; Pănuş, A.; Enache, M.; Maria, C.; Stoica, L.; Pleşea, I.E. Photodynamic diagnosis of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer using hexaminolevulinic acid. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2011, 52, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Burgués, J.P.; Conde, G.; Oliva, J.; Abascal, J.M.; Iborra, I.; Puertas, M.; Ordoño, F.; Grupo BLUE (Blue Light Urologic Endoscopy). Diagnóstico fotodinámico con hexaminolevulinato en el cáncer vesical no músculo invasivo: Experiencia del grupo BLUE [Hexaminolevulinate photodynamic diagnosis in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: Experience of the BLUE group]. Actas Urol. Esp. 2011, 35, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jichlinski, P.; Leisinger, H.J. Fluorescence cystoscopy in the management of bladder cancer: A help for the urologist! Urol. Int. 2005, 74, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colapaoli, L.; Thorsen, J.; Nopp, A.; Guttormsen, A.B. A case of anaphylactic shock possibly caused by intravesical Hexvix. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2006, 50, 1165–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, E.D.; Dolphin, D. Second Generation Photodynamic Agents: A Review. J. Clin. Laser Med. Surg. 1993, 11, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Nishie, H.; Hayashi, N.; Tanaka, M.; Nomoto, A.; Yano, S.; Joh, T. New Photodynamic Therapy with next-Generation Photosensitizers. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormond, A.B.; Freeman, H.S. Dye Sensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy. Materials 2013, 6, 817–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankenberg-Dinkel, N. Bacterial heme oxygenases. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2004, 6, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, L.-M.; Belin, D.; Carson, M.J.; Beckwith, J. Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose pBAD promoter. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 4121–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Nikaido, H. Efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria. Drugs 2004, 64, 159–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.R.; Viveiros, J.; Yang, C.; Ahmadi, A.; Ganz, R.A.; Tolkoff, M.J. Helicobacter pylori accumulates photoactive porphyrins and is killed by visible light. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2822–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schempp, C.M.; Winghofer, B.; Langheinrich, M.; Schöpf, E.; Simon, J.C. Hypericin levels in human serum and interstitial skin blister fluid after oral single-dose and steady-state administration of Hypericum perforatum extract (St. John’s wort). Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 1999, 12, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantieghem, A.; Xu, Y.; Declercq, W.; Vandenabeele, P.; Denecker, G.; Vandenheede, J.R.; Merlevede, W.; de Witte, P.A.; Agostinis, P. Different pathways mediate cytochrome c release after photodynamic therapy with hypericin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2001, 74, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantieghem, A.; Assefa, Z.; Vandenabeele, P.; Declercq, W.; Courtois, S.; Vandenheede, J.R.; Merlevede, W.; de Witte, P.; Agostinis, P. Hypericin-induced photosensitization of HeLa cells leads to apoptosis or necrosis. Involvement of cytochrome c and procaspase-3 activation in the mechanism of apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 1998, 27, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Trepel, M.; Grimmel, C.; Schabet, M.; Bremen, D.; Krajewski, S.; Reed, J.C. Hypericin-induced apoptosis of human malignant glioma cells is light-dependent, independent of bcl-2 expression, and does not require wild-type p53. Neurol. Res. 1997, 19, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupkó, I.; Kamuhabwa, A.R.; D’Hallewin, M.A.; Baert, L.; de Witte, P.A. In vivo photodynamic activity of hypericin in transitional cell carcinoma bladder tumors. Int. J. Oncol. 2001, 18, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couldwell, W.T.; Hinton, D.R.; He, S.; Chen, T.C.; Sebat, I.; Weiss, M.H.; Law, R.E. Protein kinase C inhibitors induce apoptosis in human malignant glioma cell lines. FEBS Lett. 1994, 23, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, B.; Verwanger, T. Molecular response to hypericin-induced photodamage. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, L.M.; Kleemann, B.; Cooper, S.; Kidson, S.H. Melanomas display increased cytoprotection to hypericin-mediated cytotoxicity through the induction of autophagy. Cell Biol. Int. 2009, 33, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinis, P.; Vantieghem, A.; Merlevede, W.; de Witte, P.A. Hypericin in cancer treatment: More light on the way. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 34, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, H.G.; Lau, W.K.; Olivo, M.; Tan, P.H.; Cheng, C.W. Is photodynamic diagnosis using hypericin better than white-light cystoscopy for detecting superficial bladder carcinoma? BJU Int. 2005, 95, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubin, A.; Meissner, P.; Wierrani, F.; Burner, U.; Bodenteich, A.; Pytel, A.; Schmeller, N. Fluorescence diagnosis of bladder cancer with new water soluble hypericin bound to polyvinylpyrrolidone: PVP-hypericin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, N.E.; Kim, A.; Nseyo, U.U.; Tsimaris, I.; Chung, T.D.; Miller, T.A.; Redlak, M.; Nseyo, U.O.; Skalkos, D. Hypericum perforatum L. extract—Novel photosensitizer against human bladder cancer cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2006, 84, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuvaneswari, R.; Gan, Y.Y.; Soo, K.C.; Olivo, M. Targeting EGFR with photodynamic therapy in combination with Erbitux enhances in vivo bladder tumor response. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lihuan, D.; Jingcun, Z.; Ning, J.; Guozeng, W.; Yiwei, C.; Wei, L.; Jing, Q.; Yuanfang, Z.; Gang, C. Photodynamic therapy with the novel photosensitizer chlorophyllin f induces apoptosis and autophagy in human bladder cancer cells. Lasers Surg. Med. 2014, 46, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Z.; Song, Z.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Chen, G. Chlorophyllin e6-mediated photodynamic therapy inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 2181–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.M.; Darafsheh, A. Light sources and dosimetry techniques for photodynamic therapy. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 96, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beigzadeh, A.M.; Rashidian Vaziri, M.R.; Ziaie, F.; Sharif, S. A new optical method for online monitoring of the light dose and dose profile in Photodynamic Therapy. Lasers Surg. Med. 2020, 52, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamuhabwa, A.; Agostinis, P.; Ahmed, B.; Landuyt, W.; van Cleynenbreugel, B.; van Poppel, H.; de Witte, P. Hypericin as a potential phototherapeutic agent in superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2004, 3, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamuhabwa, A.A.; Roskams, T.; D’Hallewin, M.A.; Baert, L.; van Poppel, H.; de Witte, P.A. Whole bladder wall photodynamic therapy of transitional cell carcinoma rat bladder tumors using intravesically administered hypericin. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 107, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamuhabwa, A.A.; Cosserat-Gerardin, I.; Didelon, J.; Notter, D.; Guillemin, F.; Roskams, T.; D’Hallewin, M.A.; Baert, L.; de Witte, P.A. Biodistribution of hypericin in orthotopic transitional cell carcinoma bladder tumors: Implication for whole bladder wall photodynamic therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 97, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Staveren, H.J.; Keijzer, M.; Keesmaat, T.; Jansen, H.; Kirkel, W.J.; Beek, J.F.; Star, W.M. Integrating sphere effect in whole-bladder wall photodynamic therapy: III. Fluence multiplication, optical penetration and light distribution with an eccentric source for human bladder optical properties. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, F.A.; Oussoren, Y.; te Poele, J.A.; Horenblas, S.; Mooi, W.J. Functional and histological damage in the mouse bladder after photodynamic therapy. Br. J. Cancer 1992, 65, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marynissen, J.P.; Jansen, H.; Star, W.M. Treatment system for whole bladder wall photodynamic therapy with in vivo monitoring and control of light dose rate and dose. J. Urol. 1989, 142, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaki, T.; Hisazumi, H.; Hirata, A.; Kunimi, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Amano, T.; Kumaki, O.; Koshida, K.; Nishino, A.; Nakazima, K. Photodynamic therapy of superficial bladder tumors. Hinyokika Kiyo 1986, 32, 1941–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Hisazumi, H.; Naito, K.; Uchibayashi, T.; Hirata, A.; Komatsu, K. Integral photodynamic therapy of superficial bladder tumors with special reference to carcinoma in situ. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. Suppl. 1991, 138, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubrak, T.; Karakuła, M.; Czop, M.; Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Aebisher, D. Advances in Management of Bladder Cancer—The Role of Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030731
Kubrak T, Karakuła M, Czop M, Kawczyk-Krupka A, Aebisher D. Advances in Management of Bladder Cancer—The Role of Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030731
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubrak, Tomasz, Michał Karakuła, Marcin Czop, Aleksandra Kawczyk-Krupka, and David Aebisher. 2022. "Advances in Management of Bladder Cancer—The Role of Photodynamic Therapy" Molecules 27, no. 3: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030731
APA StyleKubrak, T., Karakuła, M., Czop, M., Kawczyk-Krupka, A., & Aebisher, D. (2022). Advances in Management of Bladder Cancer—The Role of Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules, 27(3), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030731










