Compritol-Based Alprazolam Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Sustained Release of Alprazolam: Preparation by Hot Melt Encapsulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Compritol 888 ATO Based ALP-Loaded SLNs Synthesis
2.1.1. Lipid Screening Study
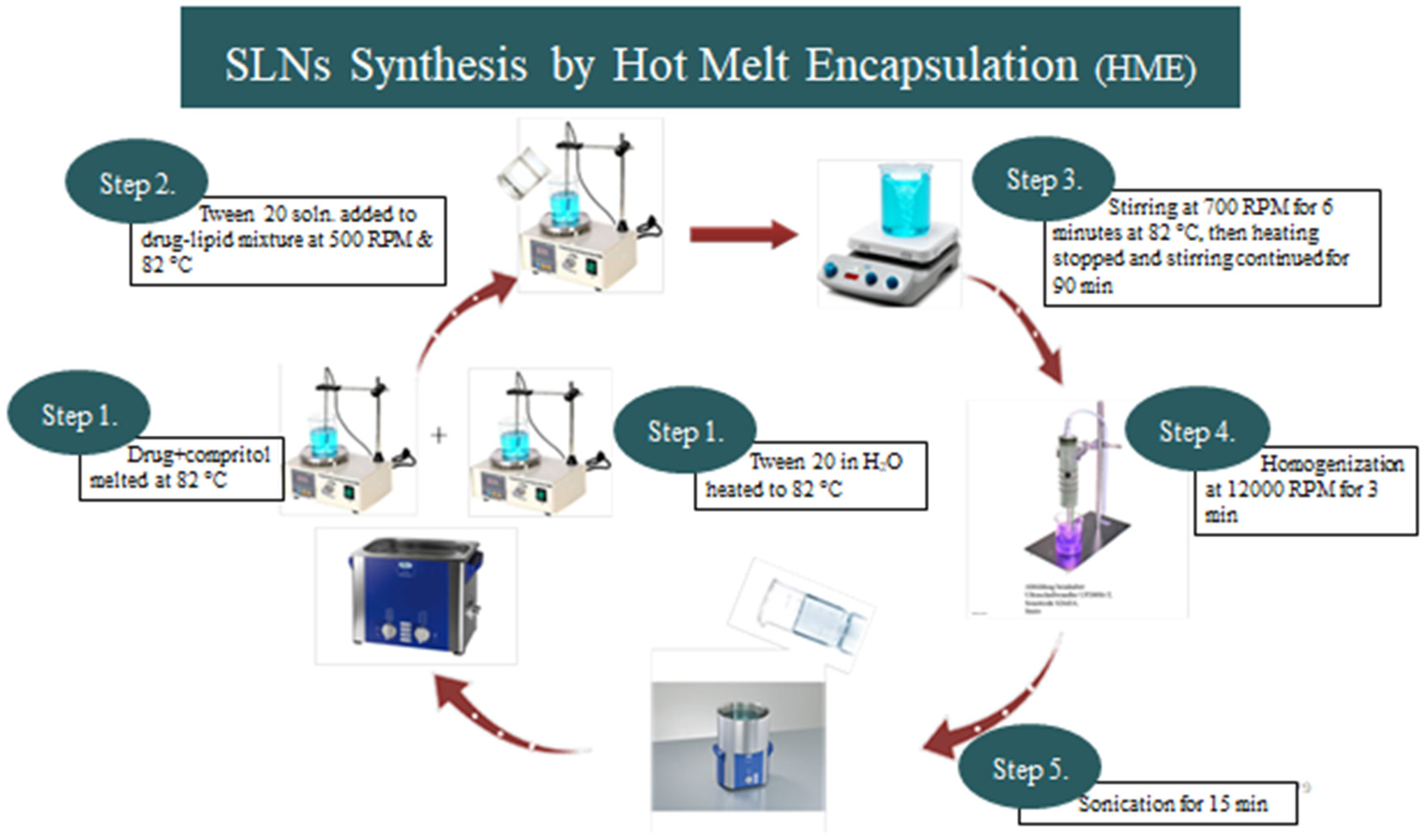
2.1.2. ALP-SLNs
2.2. Entrapment Efficiency (EE) and Drug Loading (DL)
2.3. Characterization of ALP-SLNs
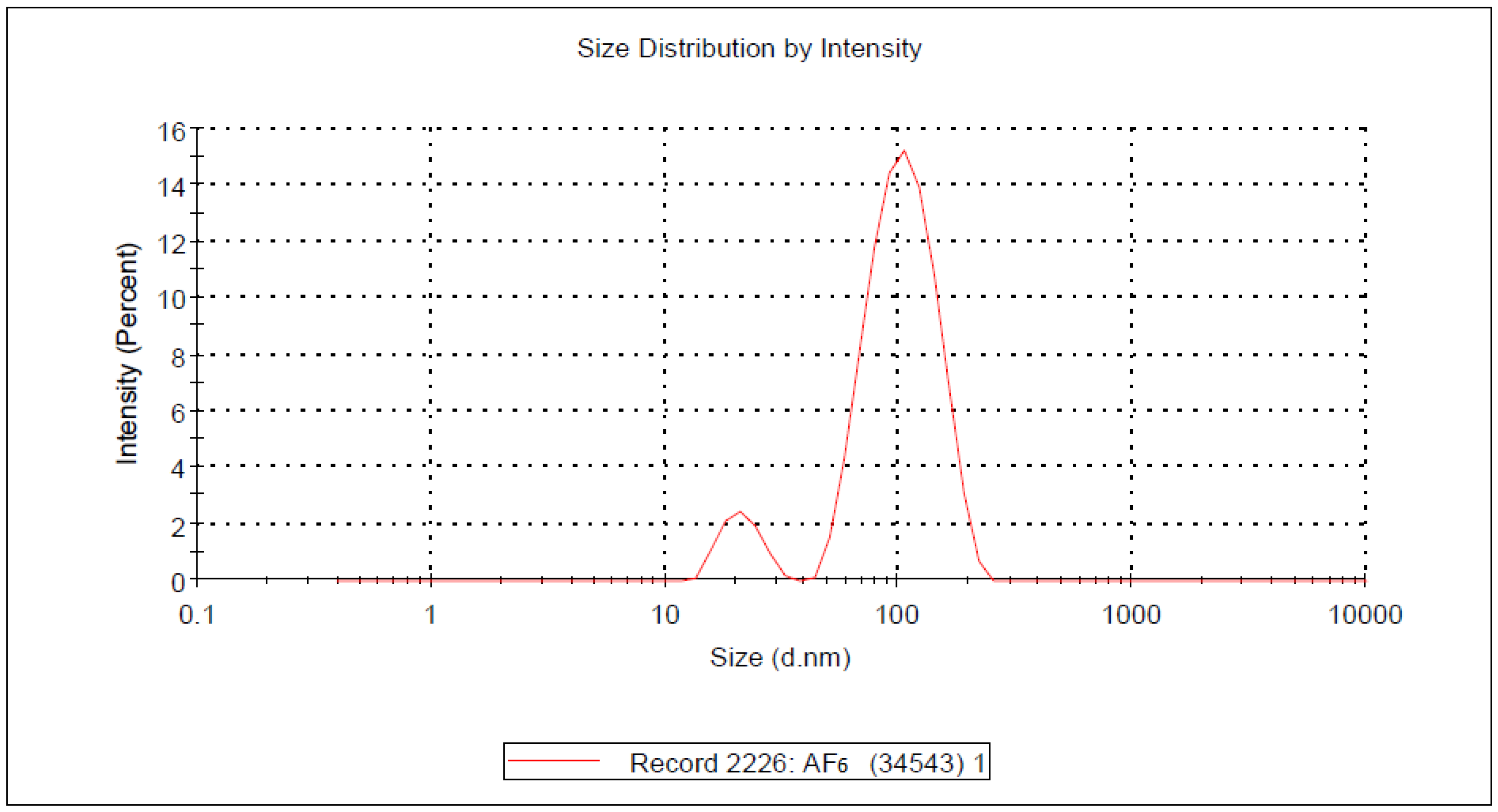
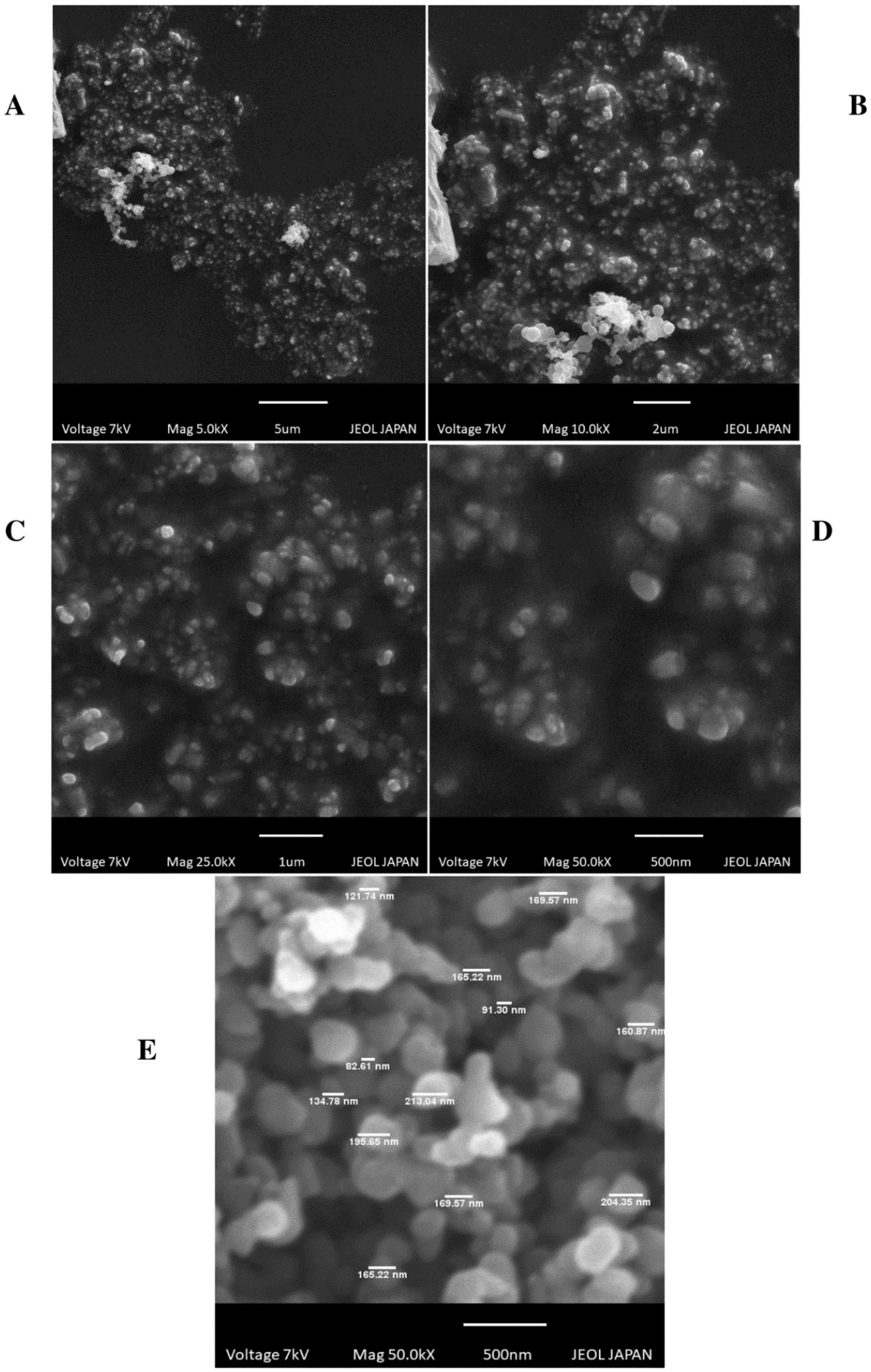
2.3.1. Particle Size and Morphological Study
- Dynamic light scattering (DLS)
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.2. Polydispersity Index
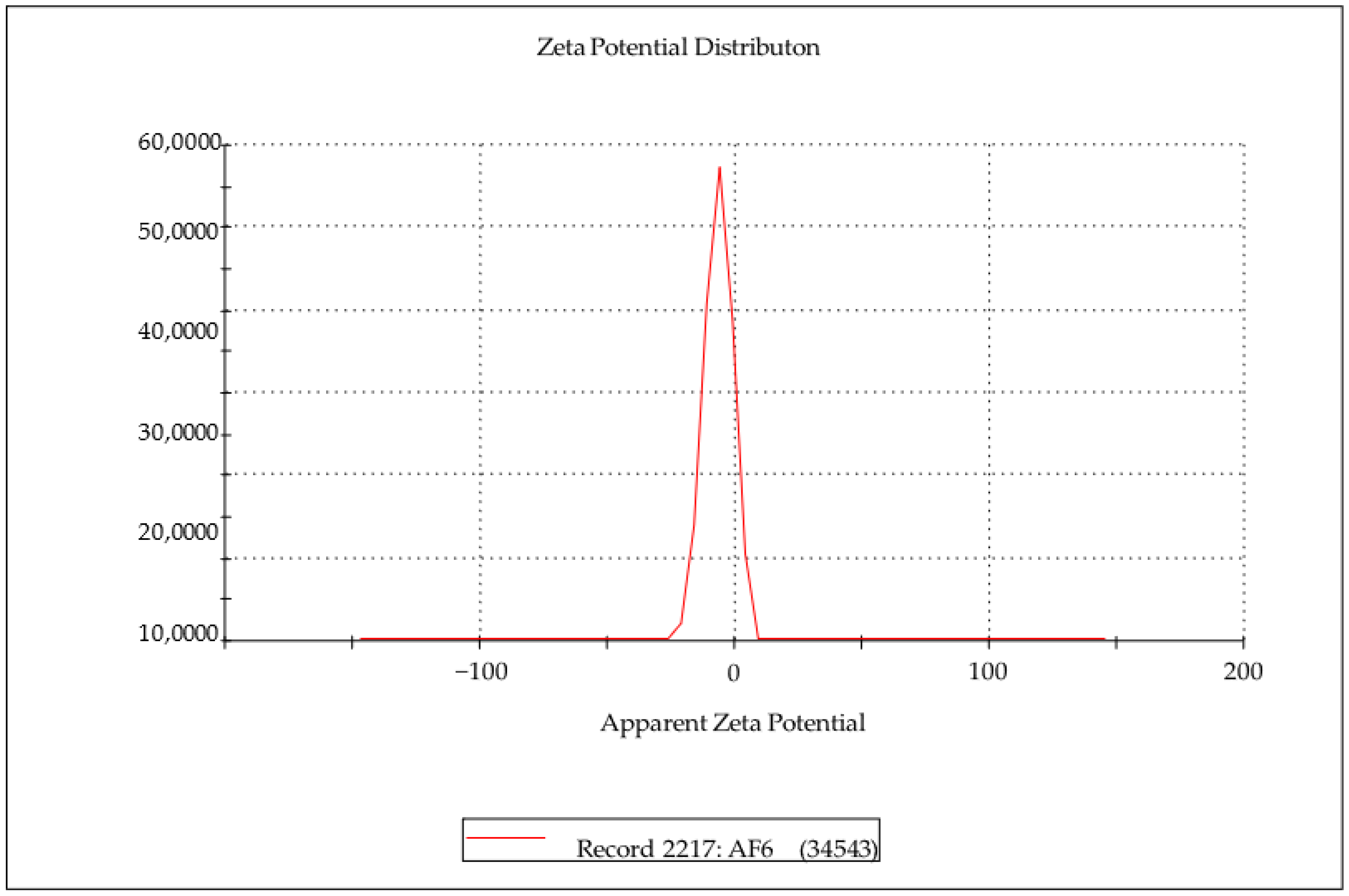
2.4. Characterization of Surface Chemistry of ALP-SLNs
Zeta Potential
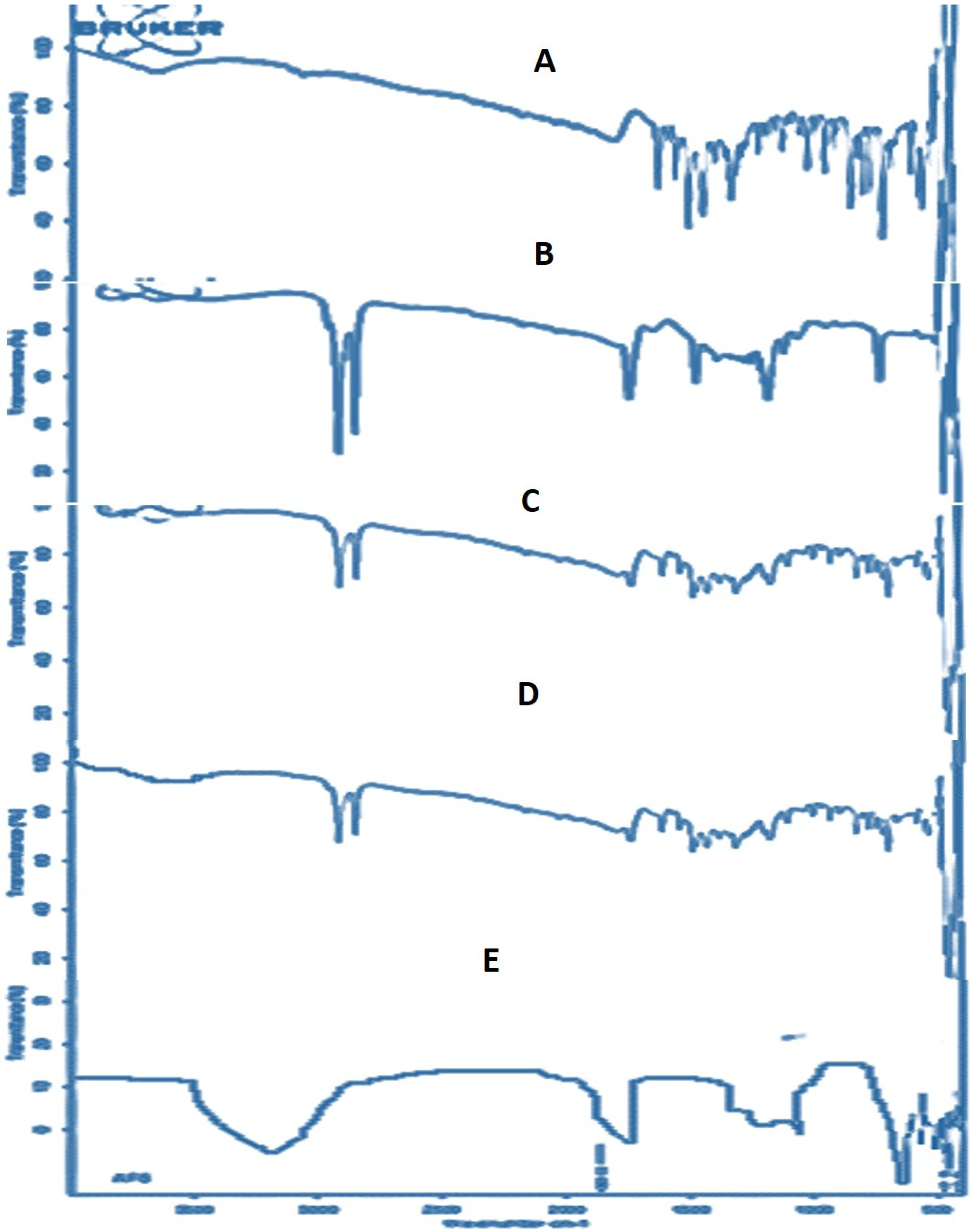
2.5. FTIR Analysis
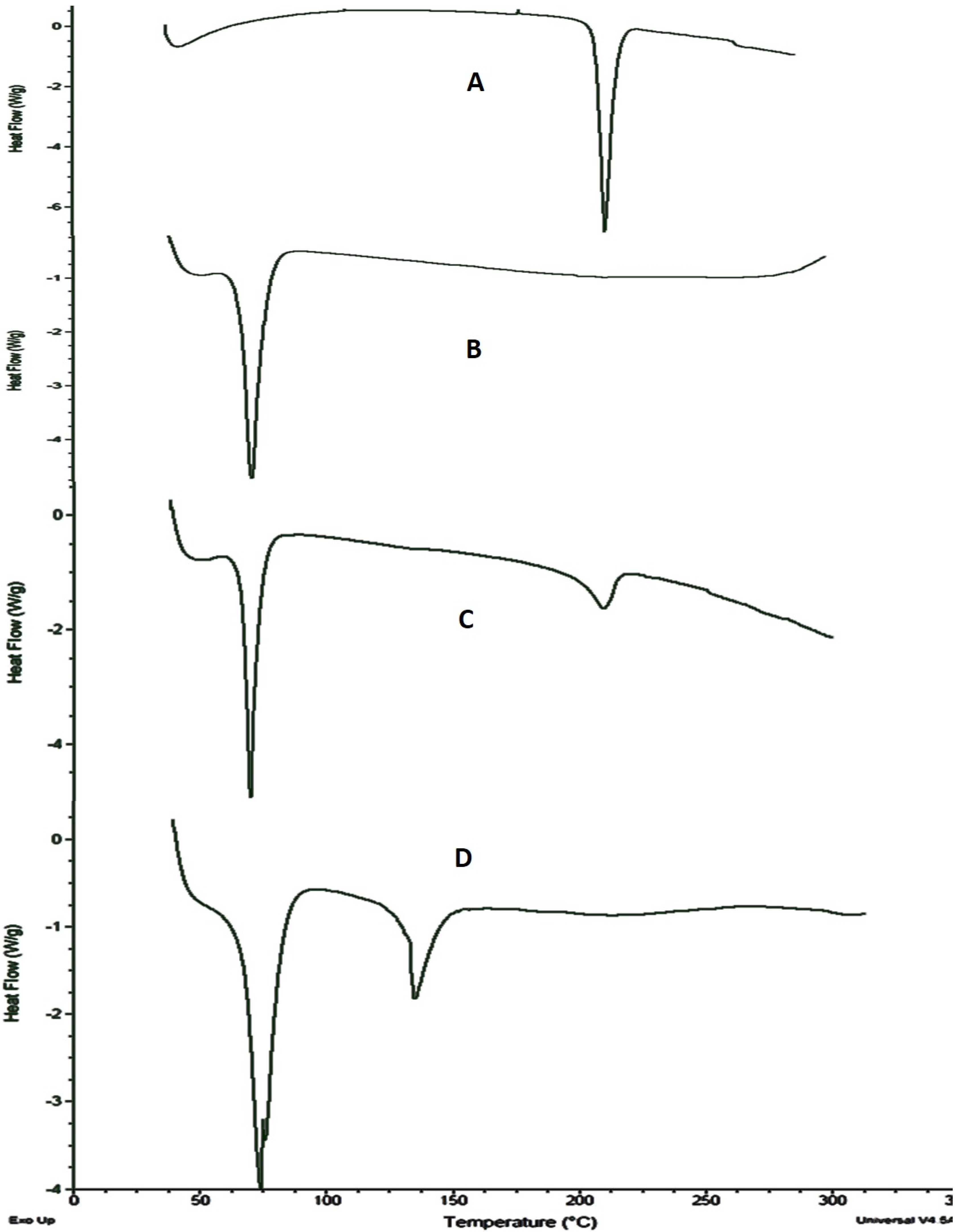
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetric (DSC) Analysis
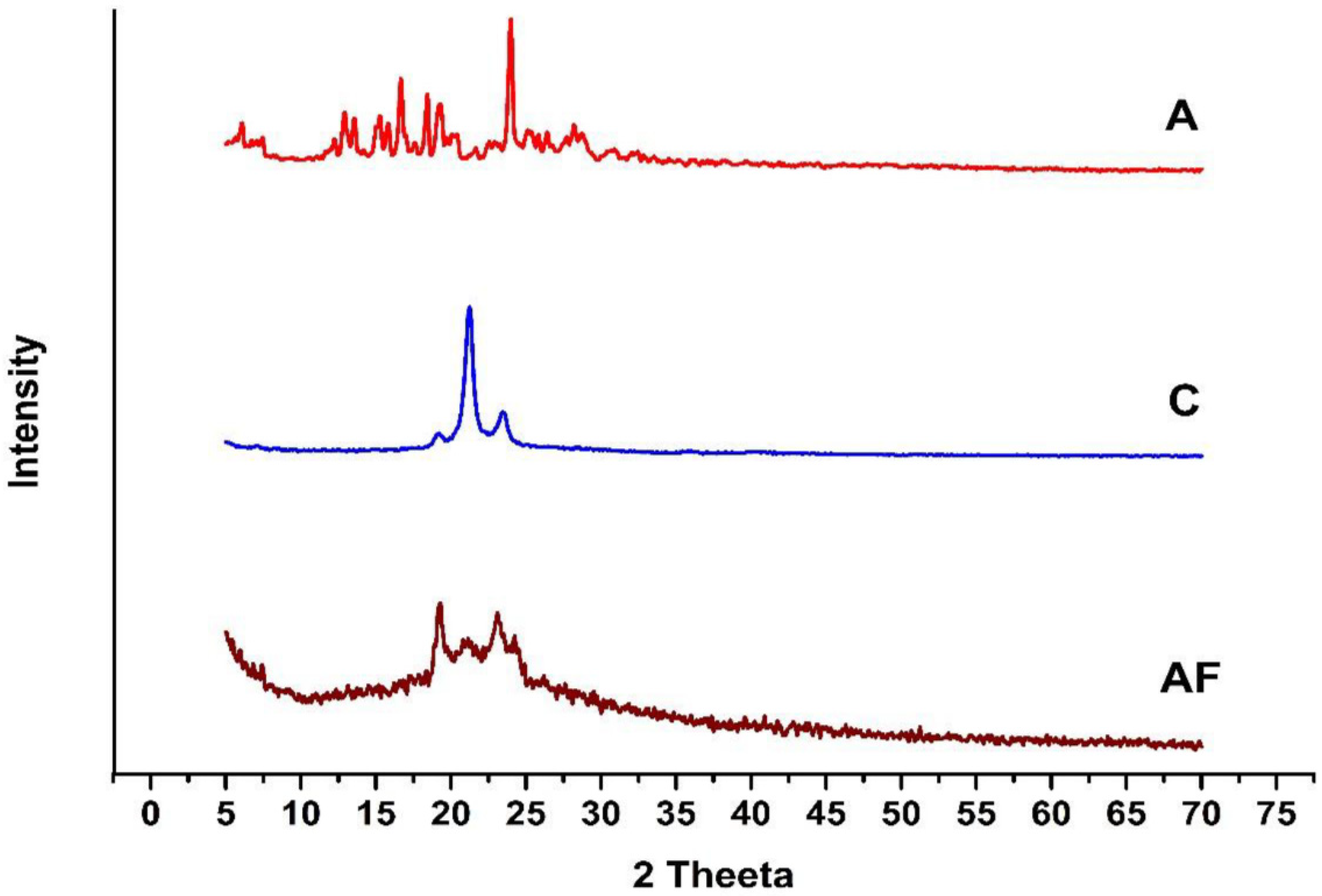
2.7. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
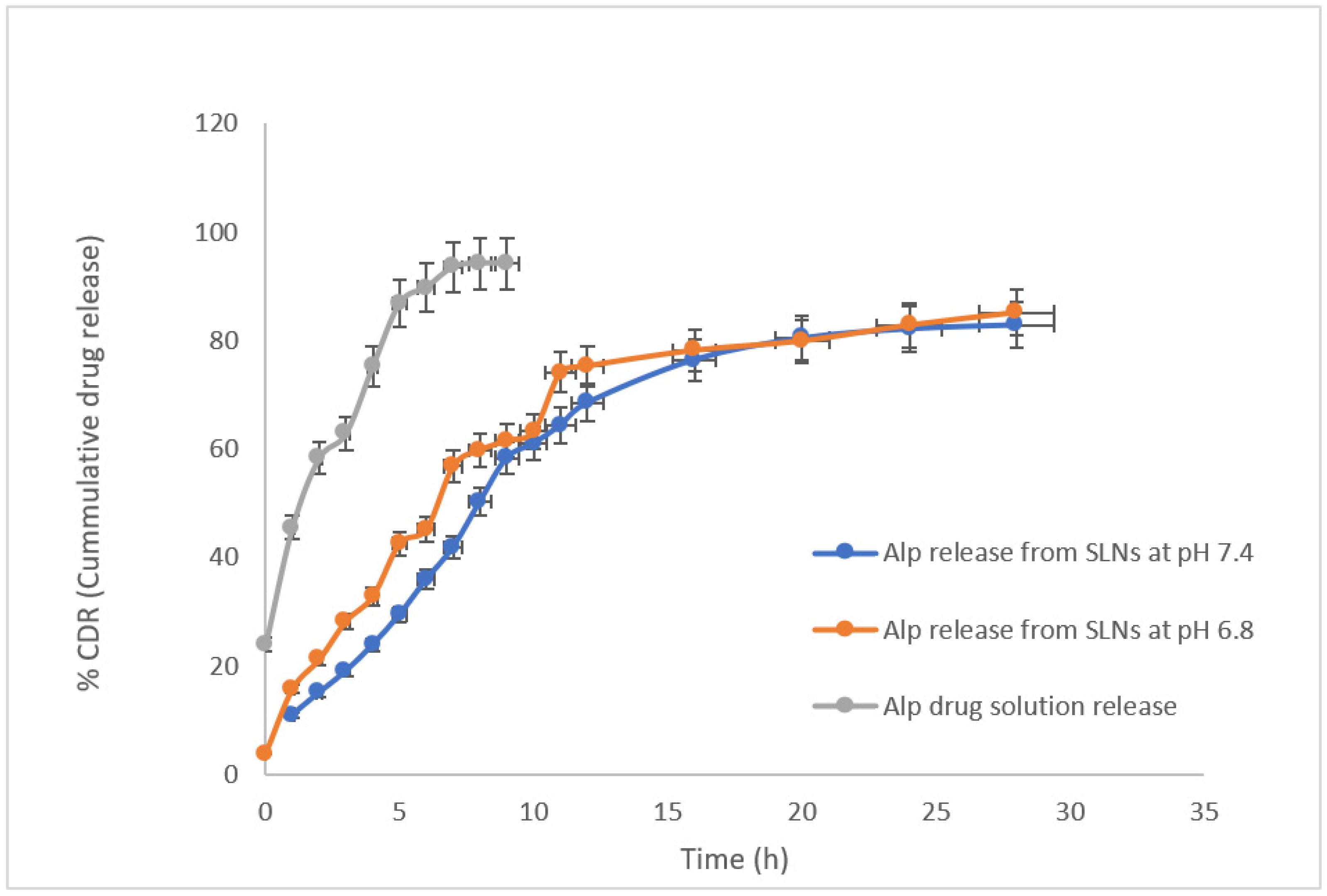
2.8. In Vitro Drug Release Study
2.9. Calculation of Release Kinetics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Lipid Screening Study
4.3. Preparation of Alprazolam-SLNs
4.4. Particle Size and Morphological Study
4.4.1. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
4.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.5. Surface Chemistry of Alprazolam SLNs
Zeta Potential
4.6. Entrapment Efficiency (EE) and Drug Loading (DL)
4.7. HPLC Analysis of Drug
4.8. Fourier Transform-Infrared (FTIR) Spectrophotometric Analysis
4.9. DSC Analysis
4.10. XRD Analysis
4.11. In-Vitro Release Study
4.12. In-Vitro Drug Release Kinetics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Das, S.; Chaudhury, A. Recent advances in lipid nanoparticle formulations with solid matrix for oral drug delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, R.; Paliwal, S.R.; Kenwat, R.; Kurmi, B.D.; Sahu, M.K. Solid lipid nanoparticles: A review on recent perspectives and patents. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2020, 30, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, P.; Narayanasamy, D. Lipid nanoparticles: Different preparation techniques, characterization, hurdles, and strategies for the production of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for oral drug delivery. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2017, 6, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Sharma, J.; Singh, M.; Saini, V. Solid lipid nanoparticles: A promising technology for delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs. ACTA Pharm. Sci. 2018, 56, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jaiswal, P.; Gidwani, B.; Vyas, A. Nanostructured lipid carriers and their current application in targeted drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B.; Silva, A.M. Hansen solubility parameters (HSP) for prescreening formulation of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN): In vitro testing of curcumin-loaded SLN in MCF-7 and BT-474 cell lines. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qushawy, M.; Nasr, A. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) as nano drug delivery carriers: Preparation, characterization and application. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2020, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kesarla, R.; Chotai, N.; Misra, A.; Omri, A. Systematic approach for the formulation and optimization of solid lipid nanoparticles of efavirenz by high pressure homogenization using design of experiments for brain targeting and enhanced bioavailability. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 5984014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithani, K.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Slipper, I.; Mostafa, S.; Miolane, C.; Cuppok, Y.; Marchaud, D.; Douroumis, D. Sustained release solid lipid matrices processed by hot-melt extrusion (HME). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 110, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastruzzi, C. Lipospheres in Drug Targets and Delivery: Approaches, Methods, and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Khairnar, S.V.; Pagare, P.; Thakre, A.; Nambiar, A.R.; Junnuthula, V.; Abraham, M.C.; Kolimi, P.; Nyavanandi, D.; Dyawanapelly, S. Review on the scale-up methods for the preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Ahmad, S.; Madni, A.; Ahmad, I.; Shahzad, M.N. Single-step extraction for simultaneous quantification of desvenlafaxine and alprazolam in human spiked plasma by RP-HPLC. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jores, K.; Mehnert, W.; Bunjes, H.; Drechsler, M.; Mäder, K. From solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) to nanospoons. Visions and reality of colloidal lipid dispersions. In Proceedings of 30th Controlled Release Society Annual Meeting, Glasgow, UK, 19–23 July 2003; p. 181. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, M.R.; San Martin-Gonzalez, M.F. Characterization of ergocalciferol loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, N8–N13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, V.L.; Choudhari, P.B.; Bhatia, N.M.; Bhatia, M.S. Characterization of pharmaceutical nanocarriers: In vitro and in vivo studies. In Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery and Therapy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 33–58. [Google Scholar]
- Jores, K.; Mehnert, W.; Drechsler, M.; Bunjes, H.; Johann, C.; Mäder, K. Investigations on the structure of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and oil-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles by photon correlation spectroscopy, field-flow fractionation and transmission electron microscopy. J. Control. Release 2004, 95, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Sara, U.V.S.; Chauhan, I.; Gaur, P.K.; Singh, A.P.; Puri, D.; Ameeduzzafar. Solid lipid nanoparticles for nose to brain delivery of donepezil: Formulation, optimization by Box–Behnken design, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1838–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, V.; Saraf, S.A. Glyceryl behenate and its suitability for production of aceclofenac solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Yang, Q.; Bagby, T.R.; Forrest, M.L. Lymphatic drug delivery using engineered liposomes and solid lipid nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunath, K.; Reddy, J.S.; Venkateswarlu, V. Solid lipid nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharm. 2005, 27, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, C.; Ruick, R.; Müller, R. The smartLipids®–3rd Generation of Lipid Nanoparticles after SLN® and NLC®. In Proceedings of the Controlled Release Society Annual Meeting, Edinburgh, UK, 26–29 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jaspart, S.; Piel, G.; Delattre, L.; Evrard, B. Solid lipid microparticles: Formulation, preparation, characterisation, drug release and applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.; Almeida, A.; Müller, R. Lipid nanoparticles (SLN®, NLC®) for cutaneous drug delivery: Structure, protection and skin effects. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2007, 3, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbary, G.; Fahmy, R.H. Diazepam-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Design and characterization. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Tamayo-Esquivel, D.; Ganem-Quintanar, A.; Allémann, E.; Doelker, E. Adaptation and optimization of the emulsification-diffusion technique to prepare lipidic nanospheres. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 26, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.P.; Saraf, S.K.; Saraf, S.A. SLN approach for nose-to-brain delivery of alprazolam. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2012, 2, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, S.H.; Montazer, M.; Naghdi, N.; Toliyat, T. Formulation and characterization of alprazolam-loaded nanoliposomes: Screening of process variables and optimizing characteristics using RSM. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, S.; Maji, N.; Nayak, A.K.; Sen, K.K.; Basu, S.K. Development of chitosan-based nanoparticles through inter-polymeric complexation for oral drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S. Nanoparticles types, classification, characterization, fabrication methods and drug delivery applications. In Natural Polymer Drug Delivery Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 33–93. [Google Scholar]
- Jannin, V.; Cuppok, Y. Hot-melt coating with lipid excipients. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, W.; Elnoby, A.; El-Gowelli, H.M.; Elgindy, N. Hybrid polymeric matrices for oral modified release of Desvenlafaxine succinate tablets. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathe, N.; Henriksen, B.; Chauhan, H. Physicochemical characterization techniques for solid lipid nanoparticles: Principles and limitations. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, J.; Yousefian, H.; Sadeghi, H. Targeted nanostructured lipid carrier for brain delivery of artemisinin: Design, preparation, characterization, optimization and cell toxicity. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 21, 225s–241s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
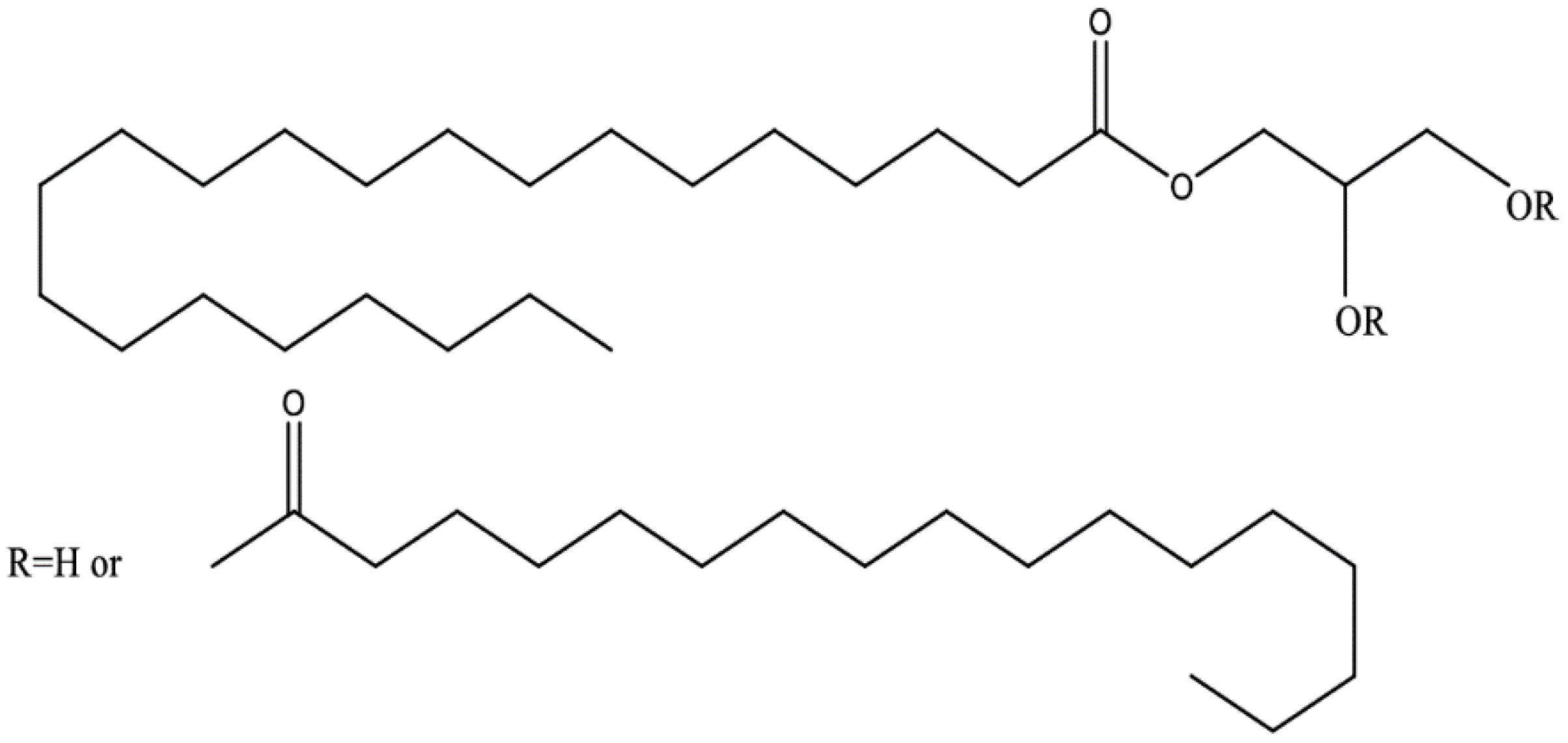
| Lipids | Time (Minutes) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 30 | 45 | 60 | |
| Waxes | ||||
| Beeswax | − | − | − | − |
| Monoglycerides | ||||
| Glyceryl caprylate (Imwitor® 308) | − | − | − | − |
| Glyceryl laurate (Imwitor® 312) | − | − | − | − |
| Glyceryl stearate (Imwitor® 900 P) | − | − | − | + |
| Triglycerides | ||||
| Trimyristin (Dynasan® 114) | − | − | − | − |
| Tripalmitin (Dynasan® 116) | − | − | − | − |
| Tristearin (Dynasan® 118) | − | − | − | − |
| Diglycerides | ||||
| Glyceryl palmitostearate (Precirol® ATO) | − | − | + | + |
| Glyceryl behenate (Compritol® 888 ATO) | + | + | + | + |
| Fatty acids | ||||
| Oleic acid | − | − | + | + |
| Stearic acid | − | − | − | + |
| ALP-SLNs | Lipid: ALP | Lipid: Surfactant | Entrapment Efficiency (%) | Drug Loading | Drug Loading (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF1 | 5:1 | 1:3 | 42.35 | 1.031 | 51.6 |
| AF2 | 10:1 | 1:3 | 54.68 | 1.333 | 66.65 |
| AF3 | 15:1 | 1:3 | 57.75 | 1.408 | 70.4 |
| AF4 | 20:1 | 1:3 | 74.75 | 1.823 | 71.15 |
| AF5 | 25:1 | 1:3 | 78.65 | 1.868 | 73.4 |
| AF6 | 30:1 | 1:3 | 89.4 | 1.958 | 77.9 |
| AF7 | 35:1 | 1:3 | 63.45 | 1.547 | 72.35 |
| AF8 | 40:1 | 1:3 | 67.8 | 1.653 | 62.65 |
| AF9 | 45:1 | 1:3 | 63.55 | 1.793 | 59.65 |
| AF10 | 50:1 | 1:3 | 64.35 | 1.663 | 53.15 |
| Formulation Code | Particle Size (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) | PI |
|---|---|---|---|
| AF1 | 100.72 ± 036 | −6.87 ± 0.25 | 0.362 ± 0.12 |
| AF2 | 117.39 ± 0.0 | −8.17 ± 0.15 | 0.443 ± 0.23 |
| AF3 | 127.39 ± 0.49 | −9.37 ± 0.15 | 0.415 ± 0.26 |
| AF4 | 104.35 ± 0.52 | −7.36 ± 0.125 | 0.175 ± 0.14 |
| AF5 | 126.09 ± 0.58 | −8.98 ± 0.25 | 0.359 ± 0.31 |
| AF6 | 140.34 ± 1.13 | −6.71 ± 0.126 | 0.067 ± 0.08 |
| AF7 | 180.36 ± 1.18 | −13.81 ± 0.35 | 0.312 ± 0.05 |
| AF8 | 147.83 ± 1.0 | −11.6 ± 0.05 | 0.135 ± 0.31 |
| AF9 | 155.65 ± 1.0 | −13.5 ± 0.1 | 0.247 ± 0.41 |
| AF10 | 130.43 ± 1.5 | −8.39 ± 0.10 | 0.429 ± 0.06 |
| Optimized ALP-SLNs | Correlation Coefficient (R2) | Release Exponent (n) of Korsmeyer-Peppas | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-Order | First Order | Higuchi | Korsmeyer-Peppas | Weibull Model | ||
| AF6 | 0.8542 | 0.9197 | 0.9880 | 0.9687 | 0.9590 | 0.644 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, H.; Ahmad, S.; Madni, A.; Rao, I.; Ghazwani, M.; Hani, U.; Umair, M.; Ahmad, I.; Rai, N.; Ahmed, M.; et al. Compritol-Based Alprazolam Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Sustained Release of Alprazolam: Preparation by Hot Melt Encapsulation. Molecules 2022, 27, 8894. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248894
Rao H, Ahmad S, Madni A, Rao I, Ghazwani M, Hani U, Umair M, Ahmad I, Rai N, Ahmed M, et al. Compritol-Based Alprazolam Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Sustained Release of Alprazolam: Preparation by Hot Melt Encapsulation. Molecules. 2022; 27(24):8894. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248894
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Huma, Saeed Ahmad, Asadullah Madni, Iqra Rao, Mohammed Ghazwani, Umme Hani, Muhammad Umair, Imtiaz Ahmad, Nadia Rai, Maqsood Ahmed, and et al. 2022. "Compritol-Based Alprazolam Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Sustained Release of Alprazolam: Preparation by Hot Melt Encapsulation" Molecules 27, no. 24: 8894. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248894
APA StyleRao, H., Ahmad, S., Madni, A., Rao, I., Ghazwani, M., Hani, U., Umair, M., Ahmad, I., Rai, N., Ahmed, M., & Khan, K. u. R. (2022). Compritol-Based Alprazolam Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Sustained Release of Alprazolam: Preparation by Hot Melt Encapsulation. Molecules, 27(24), 8894. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248894







