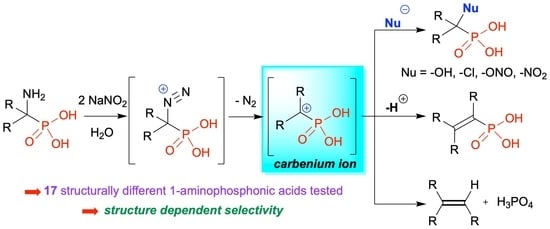
Deamination of 1-Aminoalkylphosphonic Acids: Reaction Intermediates and Selectivity
Abstract
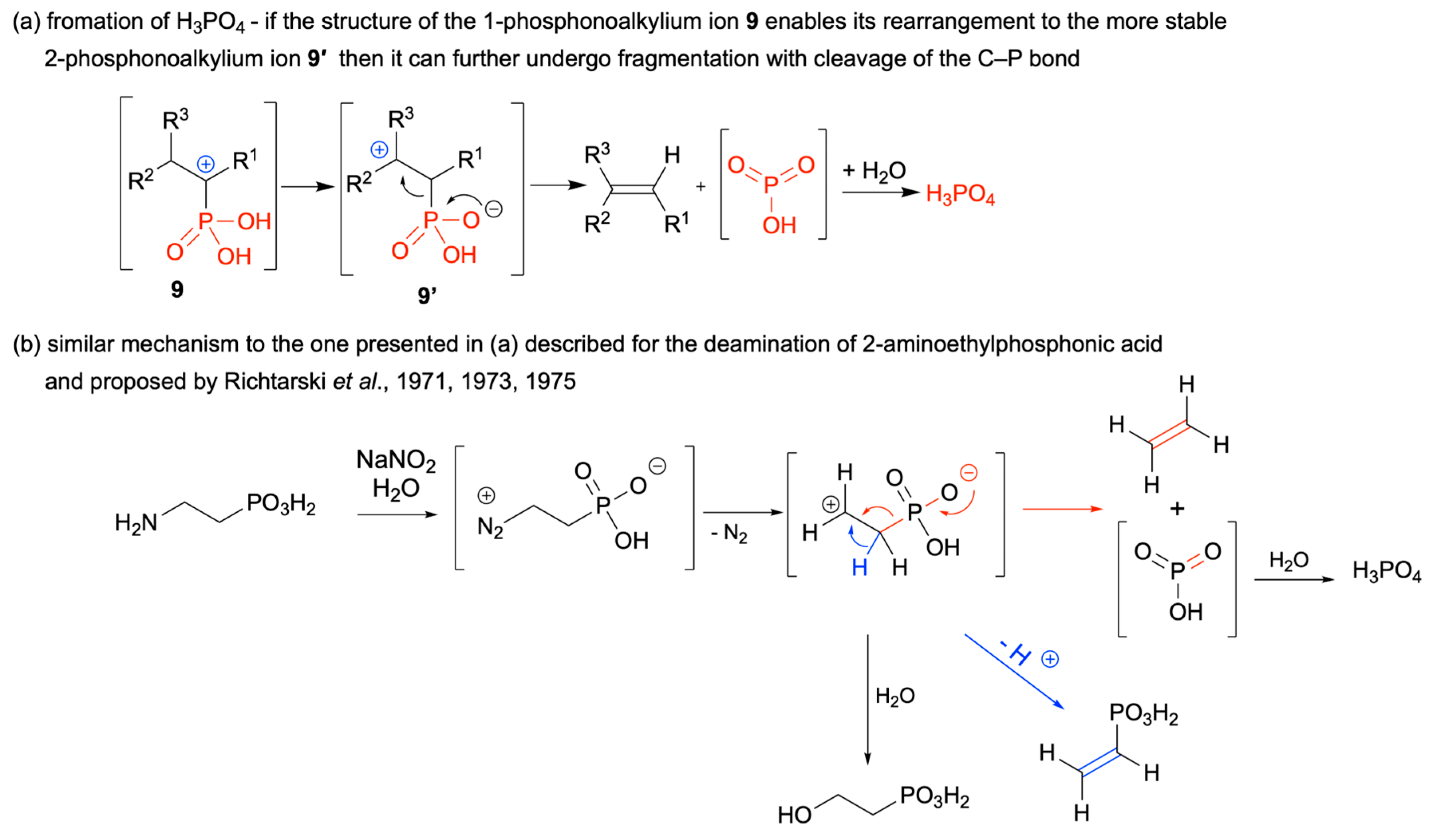
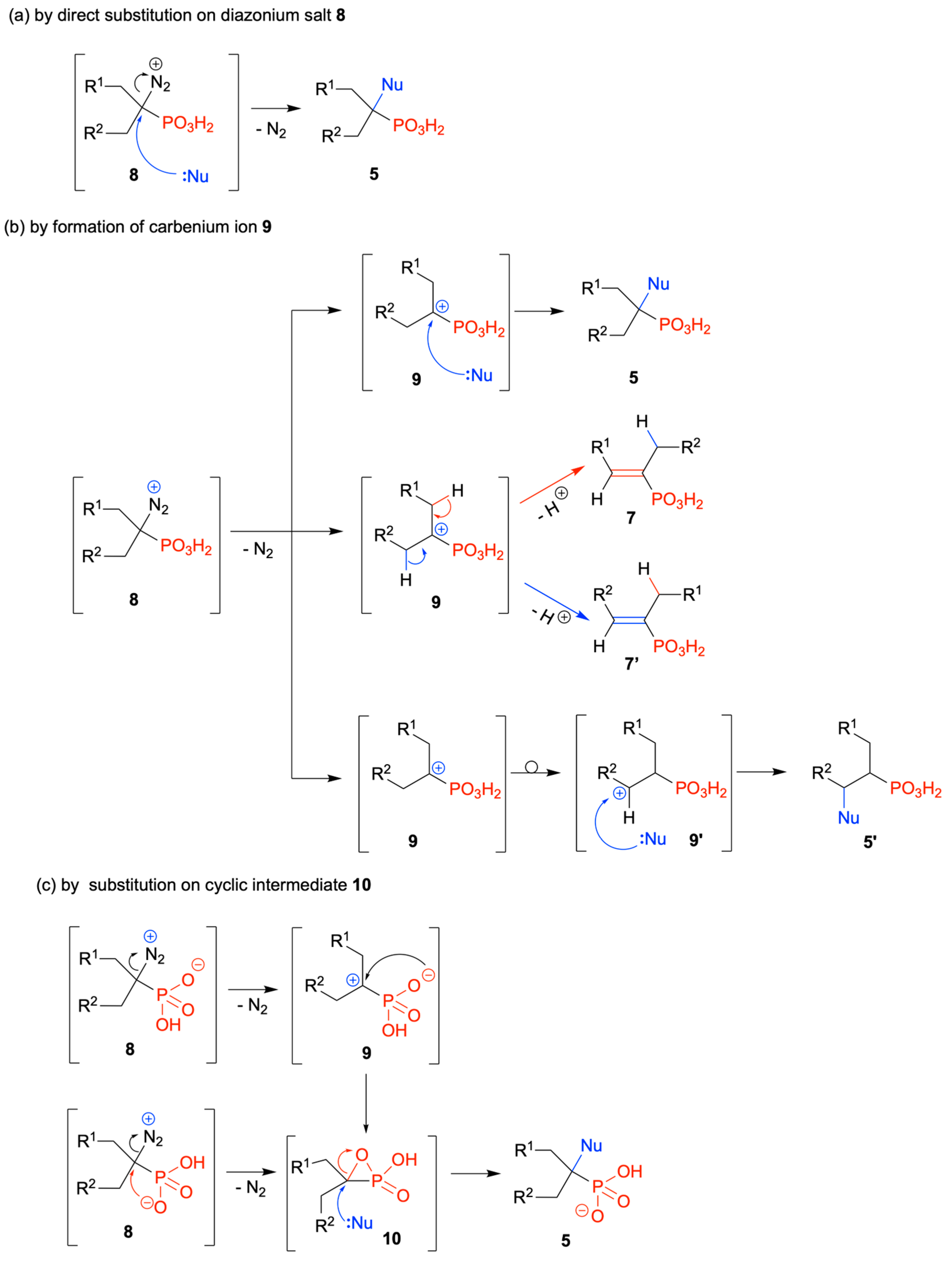
1. Introduction
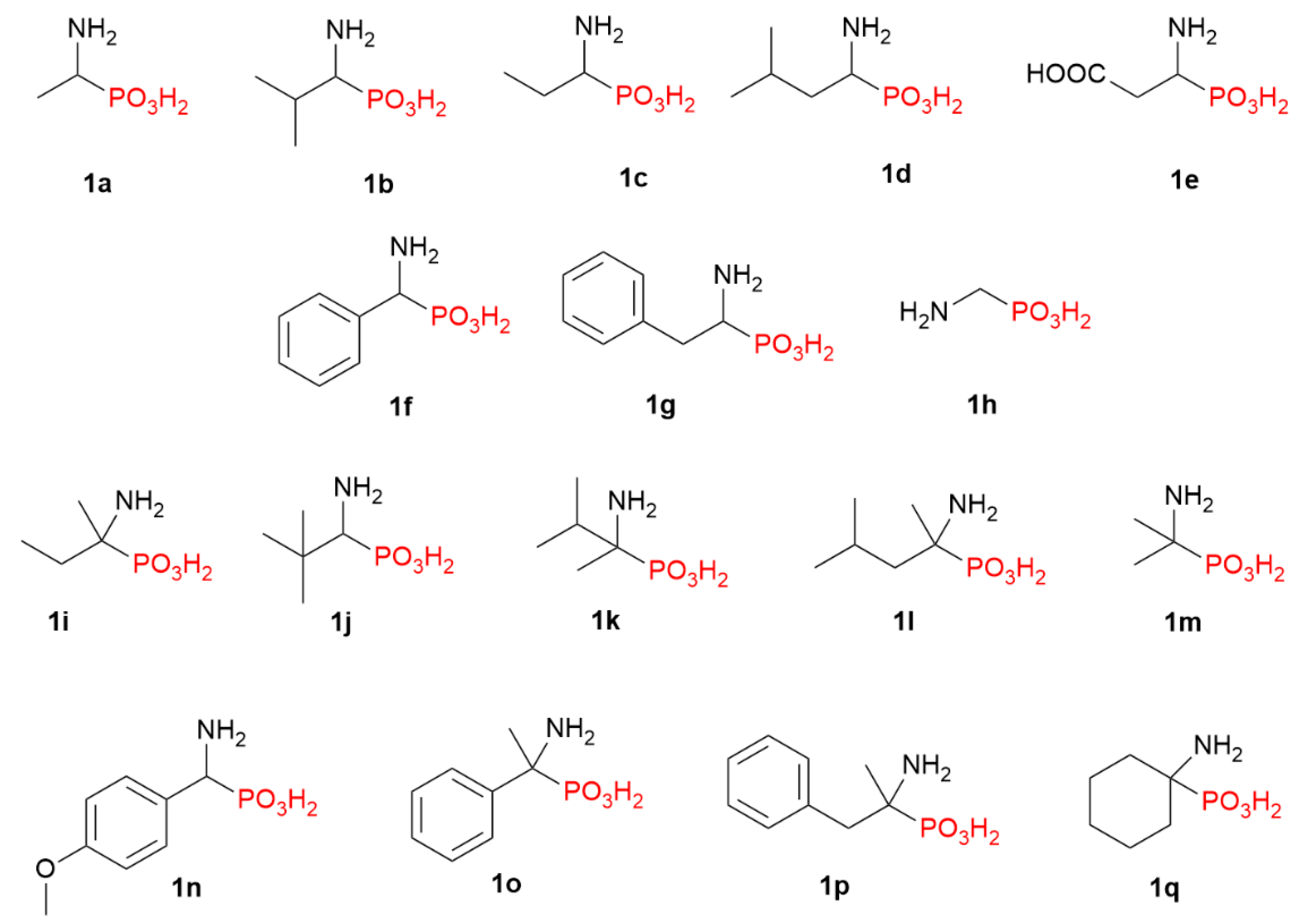
2. Results
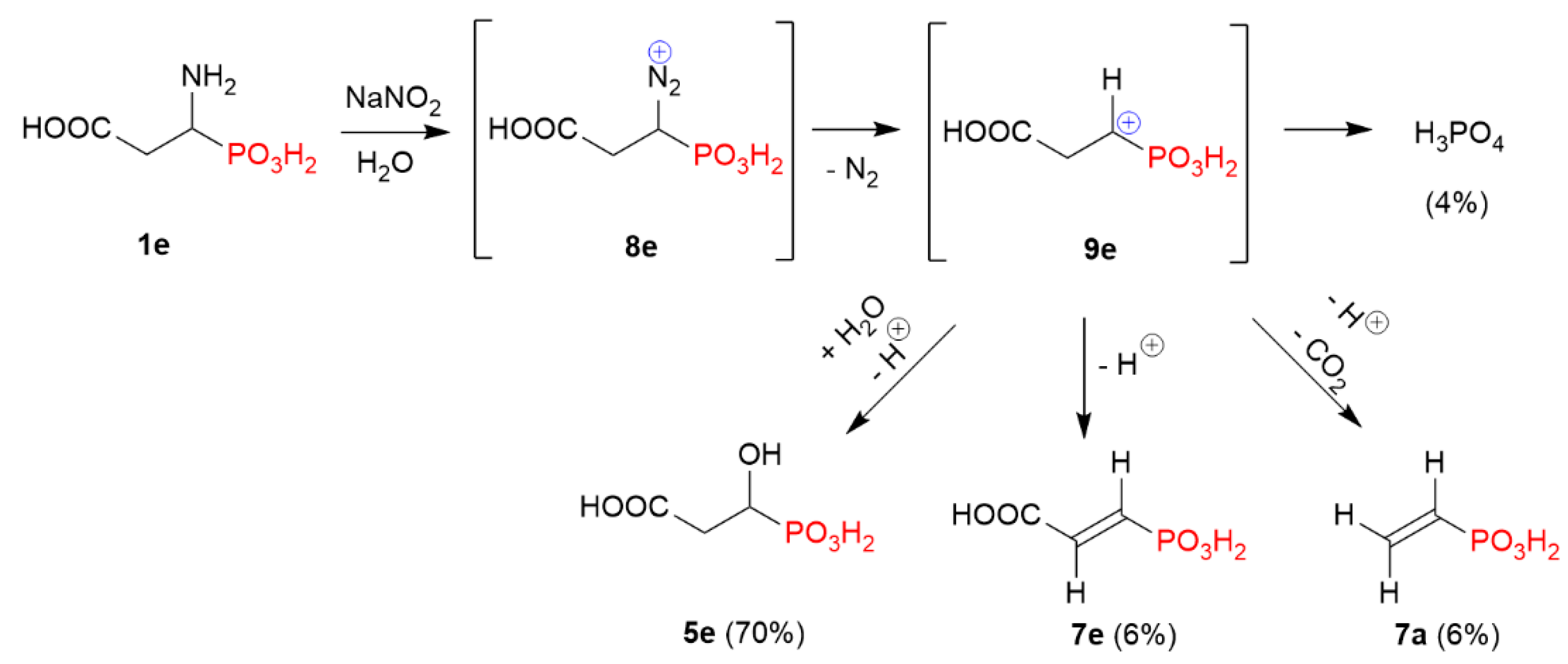
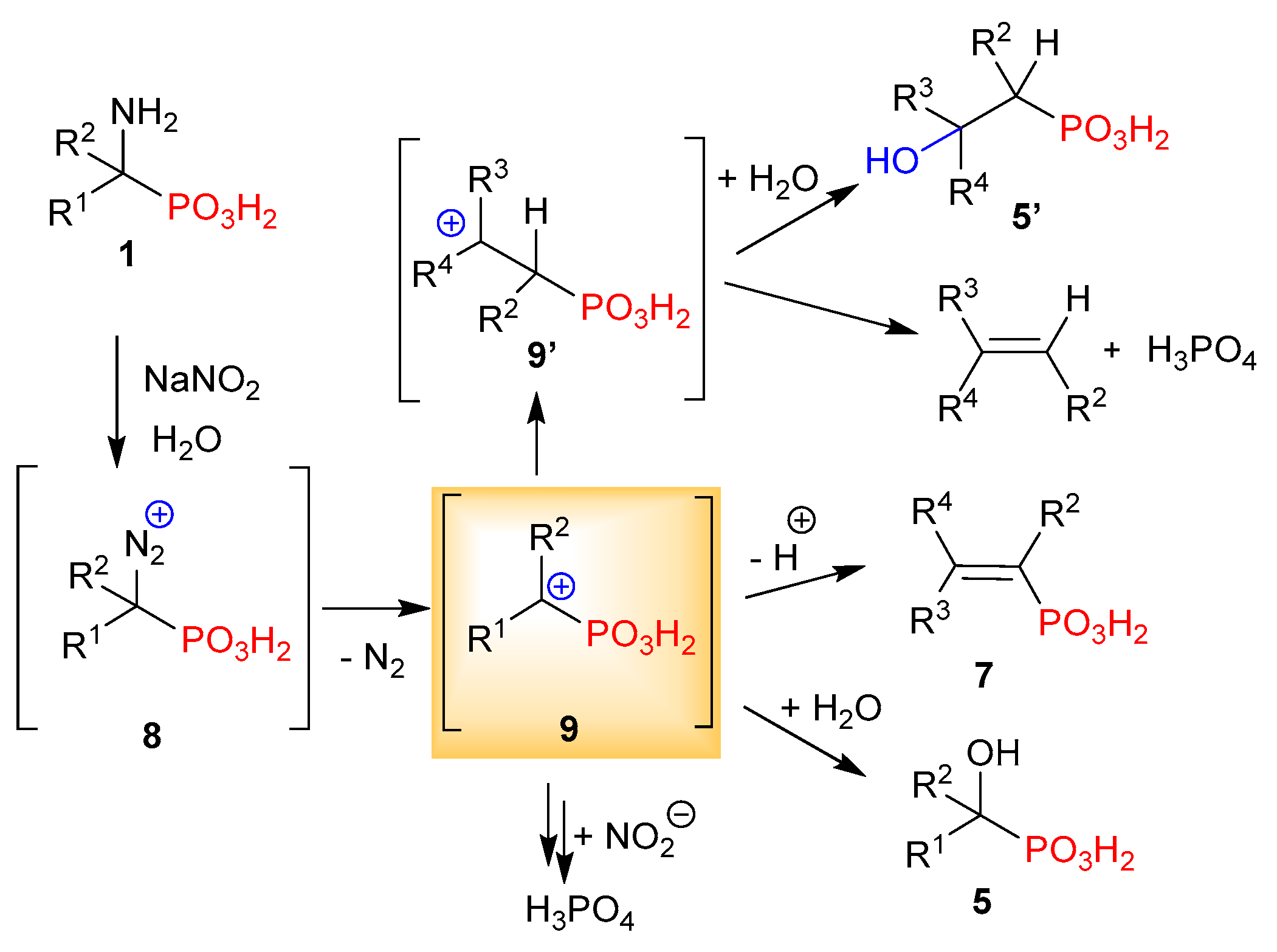
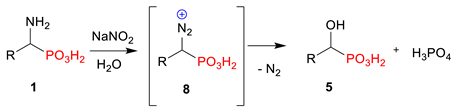
2.1. Diazotization of 2-Aminoalkanoic Acids vs. 1-Aminoalkylphosphonic Acids—Preliminary Experiments
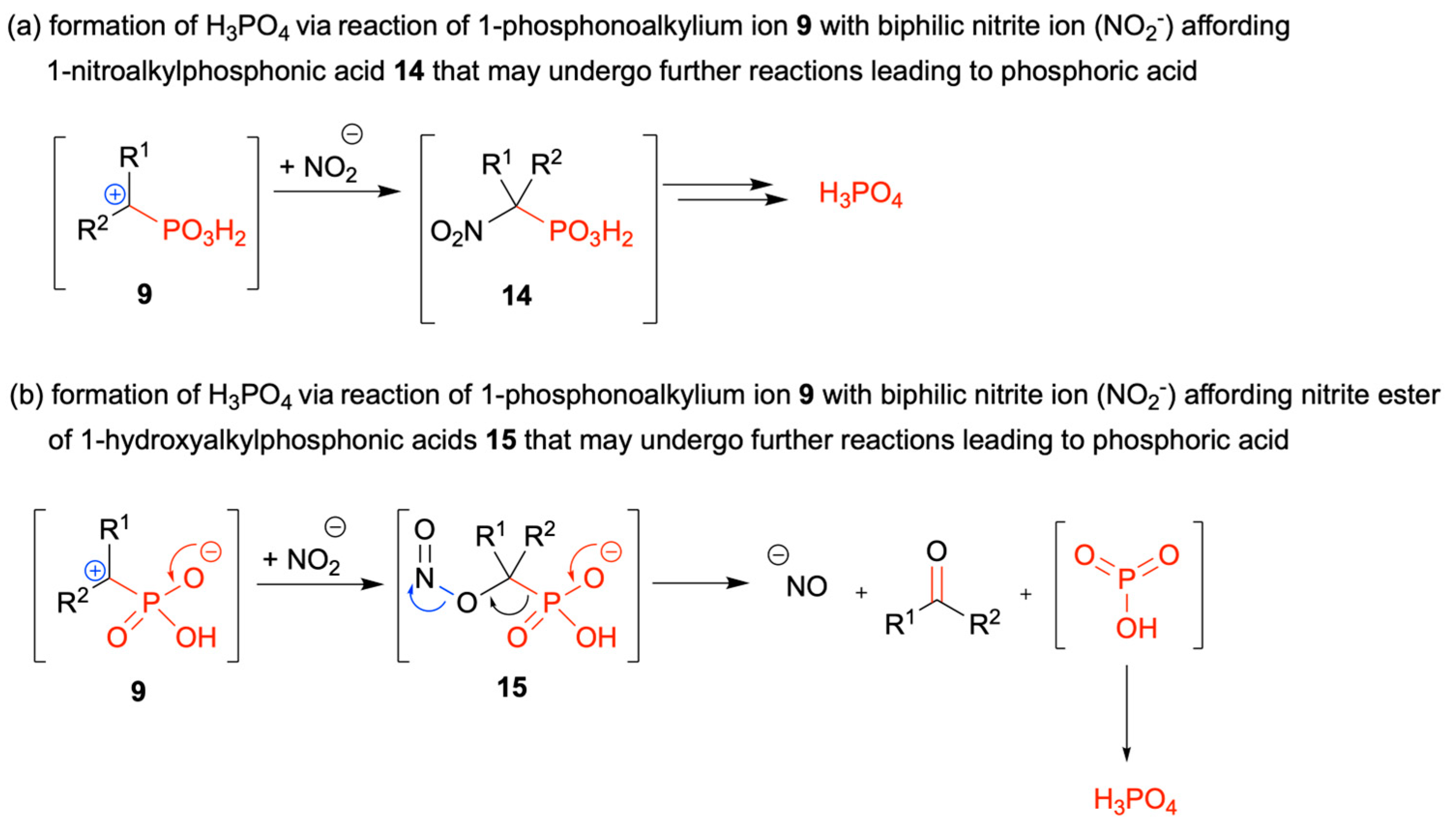
2.2. Diazotization of 1-Aminoalkylphosphonic Acids—Optimized Reaction Conditions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Reagents
3.3. Deamination of 1-Aminoalkylphosphonic Acids 1 and 2-Aminoalkanoic Acids 2 in 5M HCl
3.4. Deamination of 1-Aminoalkylphosphonic Acids 1 in Water
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, C.; Luo, X.; Chen, N.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J. C–P natural products as next-generation herbicides: Chemistry and biology of glufosinate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3344–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demmer, C.S.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, N.; Bunch, L. Review on modern advances of chemical methods for the introduction of a phosphonic acid group. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 7981–8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Fan, Y.C.; Sun, Z.; Wu, Y.; Kwon, O. Phosphine organocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 10049–10293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehbi, M.; Mehdi, A.; Negrell, C.; David, G.; Alaaeddine, A.; Ameduri, B. Phosphorus-containing fluoropolymers: State of the art and applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendels, S.; Chavez, T.; Bonnet, M.; Salmeia, K.A.; Gaan, S. Recent developments in organophosphorus flame retardants containing P-C bond and their applications. Materials 2017, 10, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabre, A.; Riera, A.; Verdaguer, X. P-Stereogenic amino-phosphines as chiral ligands: From privileged intermediates to asymmetric catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, M.M. Synopsis of recent synthetic methods and biological applications of phosphinic acid derivatives. Tetrahedron 2020, 76, 131251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.B.; Gallo-Rodriguez, C. The role of the phosphorus atom in drug design. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 190–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevrain, C.M.; Berchel, M.; Couthon, H.; Jaffres, P.-A. Phosphonic acid: Preparation and applications. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 2186–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, A.P. Recent advances in the discovery of competitive protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors for the treatment of diabetes, obesity, and cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2333–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.; Kasibhatla, S.R.; Xiao, W.; Liu, Y.; DaRe, J.; Taplin, F.; Reddy, K.R.; Scarlato, G.R.; Gibson, T.; van Poelje, P.D.; et al. Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase inhibitors. 2. Design, synthesis, and structure—Activity relationship of a series of phosphonic acid containing benzimidazoles that function as 5′-adenosinemonophosphate (AMP) mimics. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maryanoff, B.E. Inhibitors of serine proteases as potential therapeutic agents: The road from thrombin to tryptase to cathepsin G. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 769–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassaux, P.; Hamel, M.; Gulea, M.; Delbruck, H.; Mercuri, P.S.; Horsfall, L.; Dehareng, D.; Kupper, M.; Frere, J.-M.; Hoffmann, K.; et al. Mercaptophosphonate Compounds as Broad-Spectrum Inhibitors of the Metallo-β-lactamases. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4862–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, T.S.; Zhou, S.-Y.; Joshi, B.V.; Balasubramanian, R.; Yang, T.; Liang, B.T.; Jacobson, K.A. Structure−activity relationship of (N)-methanocarba phosphonate analogues of 5′-AMP as cardioprotective agents acting through a cardiac P2X receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2562–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-U.; Shi, Z.-D.; Worthy, K.M.; Bindu, L.K.; Dharmawardana, P.G.; Choyke, S.J.; Bottaro, D.P.; Fisher, R.J.; Burke, T.R., Jr. Examination of Phosphoryl-Mimicking Functionalities within a Macrocyclic Grb2 SH2 Domain-Binding Platform. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3945–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Haemers, T.; Wiesner, J.; Van Poecke, S.; Goeman, J.; Henschker, D.; Beck, E.; Jomaa, H.; Van Calenbergh, S. Synthesis of α-substituted fosmidomycin analogues as highly potent Plasmodium falciparum growth inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 1888–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, B.L.; Srinivas, R.V.; Kim, C.; Bischofberger, N.; Fridland, A. Anti-human immunodeficiency virus activity and cellular metabolism of a potential prodrug of the acyclic nucleoside phosphonate 9-R-(2-phosphonomethoxypropyl)adenine (PMPA), bis(isopropyloxymethylcarbonyl)PMPA. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestro, A.; del Corte, X.; López-Francés, A.; Martínez de Marigorta, E.; Palacios, F.; Vicario, J. Asymmetric Synthesis of Tetrasubstituted α-Aminophosphonic Acid Derivatives. Molecules 2021, 26, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, P.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis of α-Aminophosphonates and Related Derivatives; The Last Decade of the Kabachnik–Fields Reaction. Molecules 2021, 26, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keglevich, G. Microwaves as “Co-Catalysts” or as Substitute for Catalysts in Organophosphorus Chemistry. Molecules 2021, 26, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rádai, Z.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis and Reactions of α-Hydroxyphosphonates. Molecules 2018, 23, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keglevich, G.; Bálint, E. The Kabachnik–Fields Reaction: Mechanism and Synthetic Use. Molecules 2012, 17, 12821–12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, X.-Y.; Zou, Y.-X. Recent Advances in the Construction of Phosphorus-Substituted Heterocycles, 2009–2019. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 1724–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestro, A.; Martinez de Marigorta, E.; Palacios, F.; Vicario, J. α-Iminophosphonates: Useful Intermediates for Enantioselective Synthesis of α-Aminophosphonates. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2020, 9, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. Recent Advances in the Catalytic Asymmetric Construction of Phosphorus-Substituted Quaternary Carbon Stereocenters. Synthesis 2018, 50, 440–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez, M.; Viveros-Ceballos, J.L.; Cativiela, C.; Sayago, F.J. An update on the stereoselective synthesis of α-aminophosphonic acids and derivatives. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 1745–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brol, A.; Olszewski, T.K. Synthesis and stability of 1-aminoalkylphosphonic acid quaternary ammonium salts. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 6422–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acha, A.; Zineb, A.; Hacene, K.; Yasmine, C.; Racha, G.; Rachida, Z.; Nour-Eddine, A. Recent advances in the synthesis of α-aminophosphonates: A review. Chem. Select 2021, 6, 6137–6149. [Google Scholar]
- Kudzin, M.H.; Drabowicz, J.; Jordan, F.; Kudzin, Z.H.; Urbaniak, P. Reactivity of aminophosphonic acids. 2. Stability in solutions of acids and bases. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2019, 194, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudzin, M.H.; Drabowicz, J.; Jordan, F.; Kudzin, Z.H.; Urbaniak, P. Reactivity of aminophosphonic acids. 3. Reaction with hydrogen peroxide. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2019, 194, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypryk, M.; Drabowicz, J.; Gostynski, B.; Kudzin, M.H.; Kudzin, Z.H.; Urbaniak, P. 1-(Acylamino)alkylphosphonic acids-alkaline deacylation. Molecules 2018, 23, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drabowicz, J.; Jordan, F.; Kudzin, M.H.; Kudzin, Z.H.; Stevens, C.V.; Urbaniak, P. Reactivity of aminophosphonic acids. Oxidative dephosphonylation of 1-aminoalkylphosphonic acids by aqueous halogens. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 2308–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudzin, Z.H.; Kudzin, M.H.; Drabowicz, J.; Stevens, C.V. Aminophosphonic acids—phosphorus analogues of natural amino acids. Part 1: Syntheses of α-aminophosphonic acids. Curr. Org. Chem. 2011, 15, 2015–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mear, S.J.; Jamison, T.F. Diazotization of S-sulfonyl-cysteines. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 15001–15007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.X.; O’Brien, M.; Ley, S.V. Continuous multiple liquid-liquid separation: Diazotization of amino acids in flow. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4246–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuhr-Hansen, N.; Padrah, S.; Strømgaard, K. Facile synthesis of α-hydroxy carboxylic acids from the corresponding α-amino acids. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 4149–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deechongkit, S.; You, S.-L.; Kelly, J.W. Synthesis of all nineteen appropriately protected chiral α-hydroxy acid equivalents of the α-amino acids for Boc-Solid-Phase Depsi-peptide Synthesis. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humber, D.C.; Jones, M.F.; Payne, J.J.; Ramsay, M.V.J.; Zacharie, B.; Jin, H.; Siddiqui, A.; Evans, C.A.; Tse, H.L.A.; Mansour, T.S. Expeditious preparation of (−)-2′-deoxy-3′-thiacytidine. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 4625–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biel, M.; Deck, P.; Giannis, A.; Waldmann, H. Synthesis and evaluation of acyl protein thioesterase 1 (APTI) inhibitors. Chem.-Eur. J. 2006, 12, 4121–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.R.; Saddiqa, A.; Çakmak, O. Chiral pool-based synthesis of naptho-fused isocoumarins. Chirality 2015, 27, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.X.; Bielitza, M.; Koos, P.; Ley, S.V.A. Total synthesis of the ammonium ionophore, (−)-enniatin B. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 4077–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lücke, D.; Dalton, T.; Ley, S.V.; Wilson, Z.E. Synthesis of natural and unnatural cyclooligomeric depsipeptides enabled by flow chemistry. Chem. -Eur. J. 2016, 22, 4206–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthes, D.; Richter, L.; Müller, J.; Denisiuk, A.; Feifel, S.C.; Xu, Y.; Espinosa-Artiles, P.; Sussmuth, R.D.; Molnar, I. In vitro chemoenzymatic and in vivo biocatalytic synthesis of new beauvericin analogues. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5674–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolsky-Papkov, M.; Agashi, K.; Olaye, A.; Shakesheff, K.; Domb, A.J. Polymer carriers for drug delivery in tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasal, R.M.; Janorkar, A.V.; Hirt, D.E. Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Tong, R.; Cheng, J. Synthesis of water-soluble poly(α-hydroxy acids) from living ring opening polymerization of O-benzyl-L-serine carboxyanhydrides. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupido, T.; Spengler, J.; Burger, K.; Albericio, F. NO as temporary guanidino-protecting group provides efficient access to Pbf-protected argininic acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 6733–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, I.; Lee, M.-T.; Lee, J.; Jung, M.; Lee, W.; Yoon, J. Synthesis of optically active phthaloyl D-aminooxy acids from L-amino acids or l-hydroxy acids as building blocks for the preparation of aminooxy peptides. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 7667–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabachnik, M.I.; Medved, T.Y. Organophosphorus compounds. XIV. Synthesis of aminophosphonic acids. Izv. Akad. Nauk. SSSR Seriya Khimicheskaya 1950, 635–640. [Google Scholar]
- Medved, T.Y.; Kabachnik, M.I. New method of synthesis of aminophosphonic acids. II. Reaction of ketones with dialkyl phosphites and ammonia. Izv. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1954, 314–322. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, H.; Worms, K.H. (1-Hydroxyalkylidene)diphosphonic Acids. Patent DE 2165833, 4 September 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, H.; Worms, K.H. Arylchloromethanediphosphonic Acids. Patent DE 2601644, 5 January 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Worms, K.H.; Blum, H. Reactions of 1-aminoalkane-1,1-diphosphonic acids with nitrous acid. Z. Fuer Anorg. Und Allg. Chem. 1979, 457, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasto, D.J. A theoretical analysis of the interaction of the phosphonate and sulfonyl groups with a carbocationic center. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creary, X. Electronegatively substituted carbocations. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 1625–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creary, X. Carbocationic and related processes in reactions of α-keto mesylates and triflates. Acc. Chem. Res. 1985, 18, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creary, X.; Geiger, C.C.; Hilton, K. Mesylate derivatives of α-hydroxy phosphonates. Formation of carbocations adjacent to the diethyl phosphonate group. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creary, X.; Underiner, T.L. Underiner Stabilization demands of diethyl phosphonate substituted carbocations as revealed by substituent effects. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 2165–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppenhoefer, B.; Schuring, V. (S)-2-Chloroalkanoic acids of high enantiomeric purity from (S)-2-amino acids: (S)-2-Chloropropanoic acid. Org. Synth. 1988, 66, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Pilar Garcıa-Santos, M.; Gonzalez-Mancebo, S.; Hernandez-Benito, J.; Calle, E.; Casado, J. Reactivity of amino acids in nitrosation reactions and its relation to the alkylating potential of their products. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, T.; Taylor, J. The action of nitrous acid on amino-compounds. Part II. Aliphatic amino-acids. J. Chem. Soc. 1928, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlenmeyer, E.; Lipp, A. Synthesis of tyrosine. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1883, 219, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalik, J.; Zygmunt, J.; Mastalerz, P. Determination of absolute configuration of optically active 1-aminoalkanephosphonic acids by chemical correlations. Phosphorus Sulfur Relat. Elem. 1983, 18, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastalerz, P.; Richtarski, G. Ethylene formation by fragmentation of 2-aminoethylphosphonic and 2- aminoethylphenylphosphinic acid. Rocz. Chem. 1971, 45, 763–768. [Google Scholar]
- Richtarski, G.; Mastalerz, P. Deamination and rearrangement of (1-phenyl-1-hydroxy-2- aminoethyl)phosphonic acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 1973, 5, 4069–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richtarski, G.; Soroka, M.; Mastalerz, P.; Starzemska, H. Deamination and rearrangement of 1-hydroxy-1- phenyl-2-aminoethylphosphonic acid. Rocz. Chem. 1975, 49, 2001–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, A.T. Deamination of amino acids by nitrous acid with particular reference to glycine. The chemistry underlying the Van Slyke determination of α-amino acids. J. Chem. Soc. 1950, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroka, M. Comments on the synthesis of aminomethylphosphonic acid. Synthesis 1989, 7, 547–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroka, M.; Mastalerz, P. The synthesis of phosphonic and phosphinic analogs of aspartic acid and asparagine. Rocz. Chem. 1976, 50, 661–666. [Google Scholar]
- Soroka, M. The synthesis of 1-aminoalkylphosphonic acids. A revised mechanism of the reaction of phosphorus trichloride, amides and aldehydes or ketones in acetic acid (Oleksyszyn reaction). Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1990, 1990, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldeman, W.; Soroka, M. The preparation of dialkyl 1-hydroxyalkylphosphonates in the reaction of trialkyl phosphites with oxonium salts derived from aldehydes or ketones. Synthesis 2006, 2006, 3019–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltser, A.E.; Zaitsev, D.A.; Ivanova, T.V.; Babenko, T.G.; Barskova, E.N. Addition of morpholine and pyrrolidine to isopropenylphosphonic acid in situ. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 49, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazis, V.J.; Koeller, K.J.; Spilling, C.D. Reactions of Chiral Phosphorous Acid Diamides: The Asymmetric Synthesis of Chiral α-Hydroxy Phosphonamides, Phosphonates, and Phosphonic Acids. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Pan, J.; Davis, K.M.; Schaperdoth, I.; Wang, B.; Boal, A.K.; Krebs, C.; Bollinger, J.M. Steric enforcement of cis-epoxide formation in the radical C–O-coupling reaction by which (S)-2-hydroxypropyl-phosphonate epoxidase (HppE) produces Fosfomycin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 20397–20406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, H.R.; Ismail, F.; Pianka, M.; Wan, C.-W. The formation of α-amino- and α-hydroxyalkanephosphonic acids in the reactions of phosphite esters with aldehydes and alkyl carbamates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2000, 164, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehler, E.; Kanzler, S. Synthesis of phosphonic acids related to the antibiotic fosmidomycin from allylic α- and γ-hydroxyphosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1996, 112, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, H.; Heuschmann, M. Three-membered heterocycles. 12. Synthesis of a phosphirane oxide. Liebigs Ann. Der Chem. 1981, 5, 977–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, G.L.; Westheimer, F.H. Stereochemistry of unsaturated phosphonic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 3557–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prishchenko, A.A.; Livantsov, M.V.; Novikova, O.P.; Livantsova, L.I.; Petrosyan, V.S. Synthesis of new functionalized aryl-substituted methylphosphonic and methylenediphosphonic acids and their derivatives. Heteroat. Chem. 2016, 27, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueppel, M.L.; Marvel, J.T. Proton and phosphorus-31P NMR spectra of substituted methylphosphonic acids with indirect determination of phosphorus-31P shifts. Org. Magn. Reson. 1976, 8, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Moon, S.-J.; Liu, P.; Zhao, Z.; Lipscomb, J.D.; Liu, A.; Liu, H.-W. Determination of the Substrate Binding Mode to the Active Site Iron of (S)-2-Hydroxypropylphosphonic Acid Epoxidase Using 17O-Enriched Substrates and Substrate Analogues. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 12628–12638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Breuer, E. Direct Approach to α-Hydroxyphosphonic and α,ω-Dihydroxyalkane-α,ω-bisphosphonic Acids by the Reduction of (Bis)acylphosphonic Acids. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 5107–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, U.; Helvig, C.F.; Petkovich, P.M. Phosphate Management with Small Molecules. U.S. Patent US 9198923; (Granted 2015-12.01),
- De Macedo Puyau, P.; Perie, J.J. Synthesis Of Substrate Analogues And Inhibitors For The Phosphoglycerate Mutase Enzyme. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1997, 129, 13–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz-Diaz, C.I.; Galvez-Ruano, E.; Hernandez-Laguna, A.; Bellanato, J. Synthesis, Molecular Structure, and Spectroscopical Properties of Alkenylphosphonic Derivatives. 1. Vinyl-, Propenyl-, (Bromoalkenyl)-, and (Cyanoalkenyl)phosphonic Compounds. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, S.J.; Moedritzer, K. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of the P-C(OH)-P to P-CO-P rearrangement: Tetraethyl-1-hydroxyalkylidenediphosphonates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1962, 84, 1876–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-C.; Mansoorabadi, S.O.; Liu, H.-W. Reaction of HppE with Substrate Analogues: Evidence for Carbon-Phosphorus Bond Cleavage by a Carbocation Rearrangement. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8153–8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Murakami, K.; Seki, T.; He, X.; Yeung, S.M.; Kuzuyama, T.; Seto, H.; Liu, H.W. Protein Purification and Function Assignment of the Epoxidase Catalyzing the Formation of Fosfomycin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 4619–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Substrate | R1 | R1 | Conversion of 1 to 5 b | Conversion of 1 to 7 b | Conversion of 1 to H3PO4 b |
| 1 | 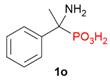 | H | Ph | 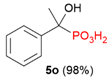 | - | 2% |
| 2 | 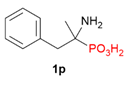 | Ph | Me |  | 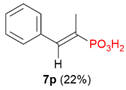 | 3% |
| 3 |  | H | Me | 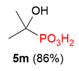 |  | 2% |
| 4 |  | H | H | 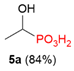 | 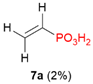 | 10% |
| 5 |  | Me | H | 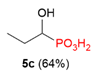 |  | 26% |
| 6 | 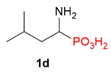 | iPr | H | 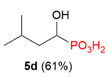 | 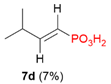 | 27% |
| 7 | 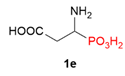 | COOH | H | 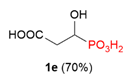 | 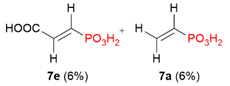 | 4% |
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Substrate | R | Conversion of 1 to 5 b | Conversion of 1 to H3PO4 b |
| 1 | 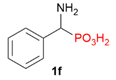 | Ph |  | 3% |
| 2 | 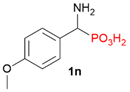 | 4-MeOPh | 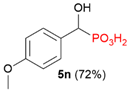 | 25% |
| 3 |  | H | 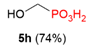 | 9% |
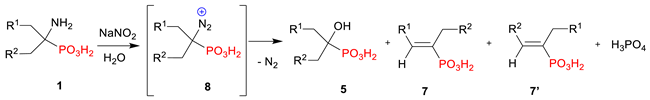 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Substrate | R1 | R1 | Conversion of 1 to 5 b | Conversion of 1 to 7 b | Conversion of 1 to H3PO4 b | |
| 1 |  | C3H6 | 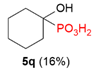 | 7% | |||
| 2 |  | iPr | H | 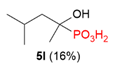 | 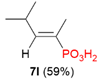 |  | 7% |
| 3 | 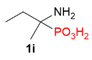 | Me | H | 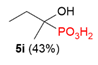 | 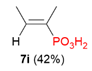 | 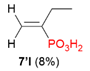 | 8% |
 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Substrate | R1 | R1 | Conversion of 1 to 5 b | Conversion of 1 to 7 b | Conversion of 1 to 5′ b | Conversion of 1 to H3PO4 b |
| 1 | 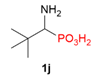 | Me | H |  | - | 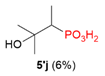 | 86% |
| 2 | 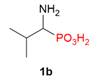 | H | H | 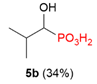 | - | 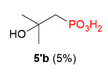 | 59% |
| 3 |  | H | Me | 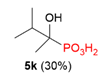 | 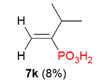 | 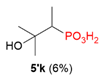 | 40% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brol, A.; Olszewski, T.K. Deamination of 1-Aminoalkylphosphonic Acids: Reaction Intermediates and Selectivity. Molecules 2022, 27, 8849. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248849
Brol A, Olszewski TK. Deamination of 1-Aminoalkylphosphonic Acids: Reaction Intermediates and Selectivity. Molecules. 2022; 27(24):8849. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248849
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrol, Anna, and Tomasz K. Olszewski. 2022. "Deamination of 1-Aminoalkylphosphonic Acids: Reaction Intermediates and Selectivity" Molecules 27, no. 24: 8849. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248849
APA StyleBrol, A., & Olszewski, T. K. (2022). Deamination of 1-Aminoalkylphosphonic Acids: Reaction Intermediates and Selectivity. Molecules, 27(24), 8849. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248849