Dissipation Kinetics and Safety Evaluation of Flonicamid in Four Various Types of Crops
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Sample Extraction and Purification
2.3. UHPLC-MS/MS Parameters
2.4. Preparation of Stock Solutions and Generation of Standard Curves
2.5. The Addition and Reclamation Test
2.6. Method Validation
2.7. Field Trials
2.8. Dietary Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of UHPLC-MS/MS Conditions
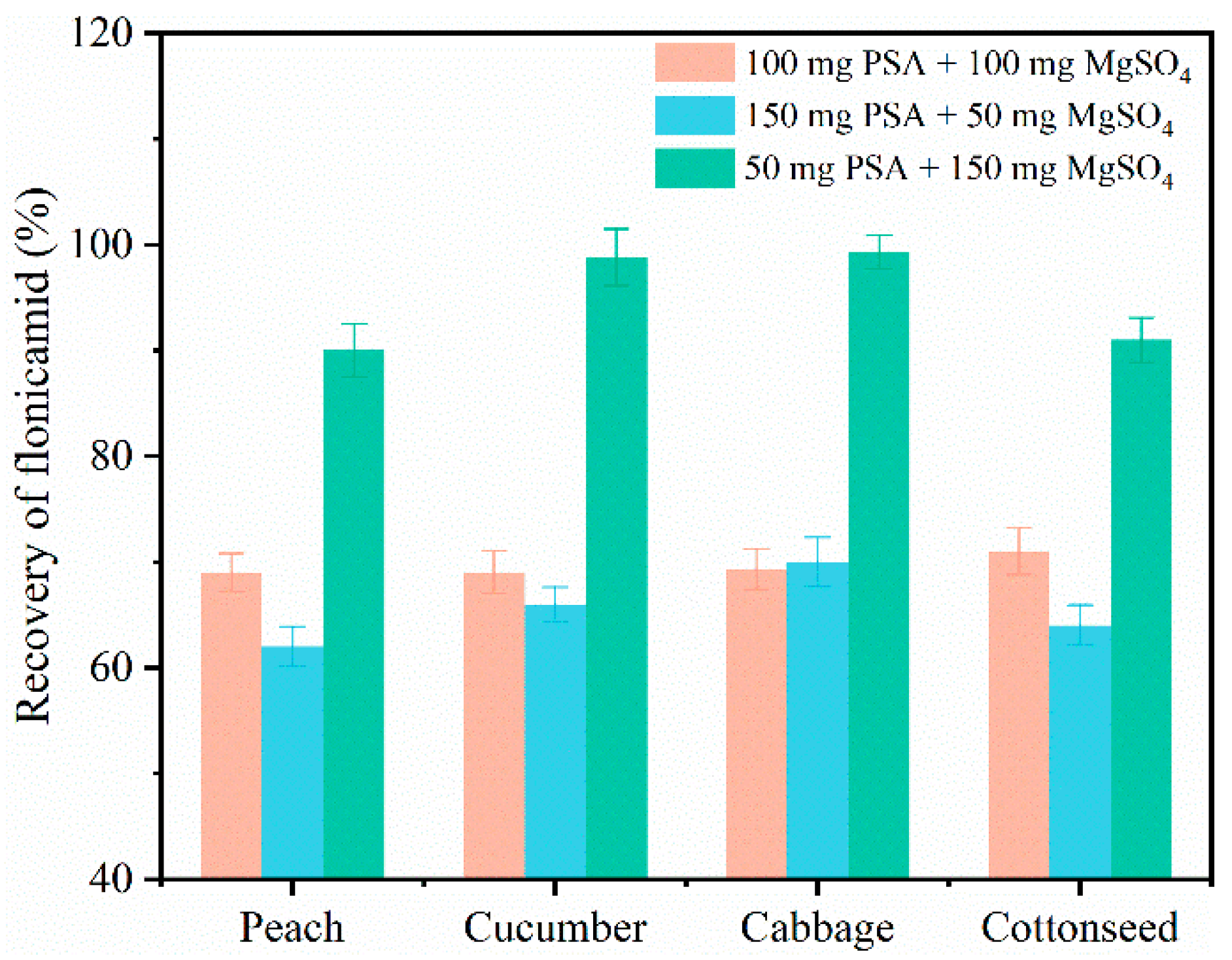
3.2. Optimization of Sample Pretreatment
3.3. Method Validation
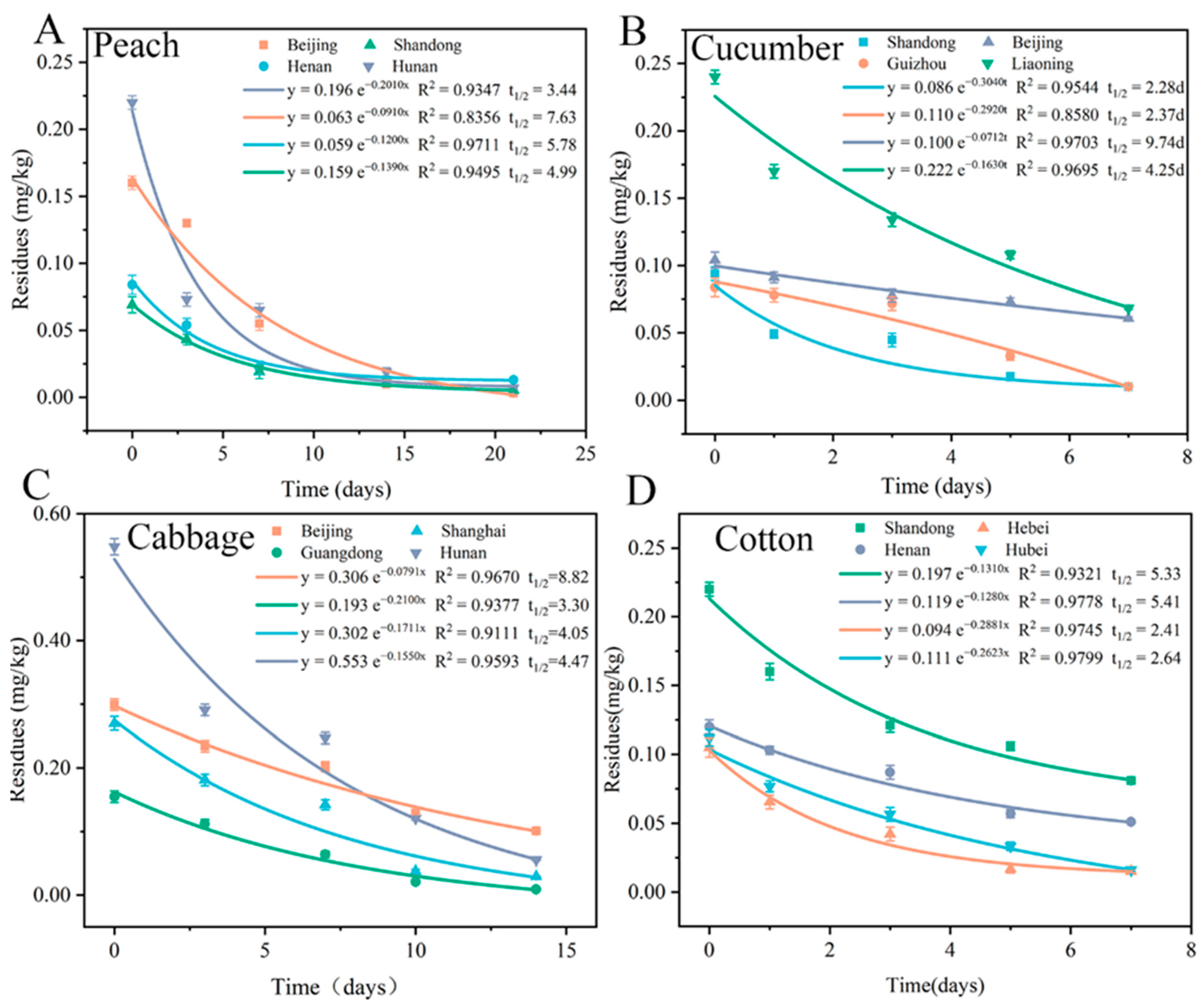
3.4. Dissipation and Terminal Residues of Flonicamid in Four Crops
3.5. Dietary Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amaro, A.C.E.; Ramos, A.R.P.; Macedo, A.C.; Ono, E.O.; Rodrigues, J.D. Effects of the fungicides azoxystrobin, pyraclostrobin and boscalid on the physiology of Japanese cucumber. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 228, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Uddin, M.R.; Park, W.T.; Kim, Y.B.; Seo, J.M.; Kim, S.J.; Nou, I.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.R.; Park, S.U. Accumulation of anthocyanin and related genes expression during the development of cabbage seedlings. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.J.; Ma, R.J.; Cai, Z.X.; Yu, M.L.; Zhang, Z. Diversity, population structure, and evolution of local peach cultivars in China identified by simple sequence repeats. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Li, X.F.; Xiong, S.W.; An, J.; Han, Y.C.; Wang, L.F.; Lei, Y.P.; Yang, B.F.; Xing, F.F.; Xin, M.H.; et al. Orychophragmus violaceus as a winter cover crop ismore conducive to agricultural sustainability than Vicia villosa in cotton-fallow systems. Arch. Agron. Soil. Sci. 2021, 68, 1905800. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Collins, E.M.; Tao, L.; Lu, C.S. Simultaneous determination of residues in pollen and high-fructose corn syrup from eight neonicotinoid insecticides by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 2013, 405, 9251–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Yoneda, T.; Akiyoshi, N. Research and development of a novel insecticide, flonicamid. J. Pestic. Sci. 2014, 39, 179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Wang, Y.J.; Xue, J.; Wang, P.S.; Shi, S.M. Dietary Exposure Risk Assessment of Flonicamid and Its Effect on Constituents after Application in Lonicerae Japonicae Flos. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 66, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Du, G.M.; Xu, D.; Chen, L.Y.; Zha, X.X.; Guo, Z.Y. Residual behavior and dietary intake risk assessment of flonicamid, dinotefuran and its metabolites on peach trees. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5842–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.G.; Zhu, Y.L.; Dong, F.S.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Y.Q. Dissipation and residue of flonicamid in cucumber, apple and soil under field conditions. Anal. Chem. 2014, 94, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.E.I.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Khattab, M.M. Residues and dissipation kinetic of abamectin, chlorfenapyr and pyridabenacaricides in green beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) under field conditions using QuEChERS method and HPLC. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2020, 55, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.; Du, H.; Zhu, Q.; Dong, Z.; Li, H. Risk assessment of pesticide residues in dietary intake of celery in China. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 73, 578–586. [Google Scholar]
- Hengel, M.J.; Miller, M. Analysis of Flonicamid and Its Metabolites in Dried Hops by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8033–8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Sun, Y.M.; Yang, T.; Wu, Y.L. Determination of flonicamid and its metabolites residues in cucumber and apple by LC-MS/MS. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2012, 30, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.K.; Kwon, H.Y.; Hong, S.M.; Kim, T.K. Simultaneous determination of flonicamid, imidacloprid, and its metabolites in paprika by QuEChERS and tandem mass spectrometry. J. Korean. Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2015, 58, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ruiz, R.; Romero-González, R.; Martínez Vidal, J.L.; Garrido Frenich, A. Determination of flonicamid and its metabolites in bell pepper using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry (Orbitrap). Food Addit. Contam. B 2016, 33, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Ghany, M.F.; Hussein, L.A.; El Azab, N.F. Multiresidue Analysis of Five Neonicotinoid Insecticides and Their Primary Metabolite in Cucumbers and Soil Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode-Array Detection. J. Aoac. Int. 2017, 100, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Jin, F.; Cao, X.L.; Shao, Y.; Wang, J.; She, Y.X. Residue behaviors and risk assessment of flonicamid and its metabolites in the cabbage field ecosystem. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Xue, J.; Jin, H.Y.; Ma, S.C. Dissipation of flonicamid in honeysuckle and its transfer during brewing process. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 65, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehotay, S.J. Quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe (QuEChERS) approach for determining pesticide residues. In Pesticide Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 19, pp. 239–261. [Google Scholar]
- SANTE. Guidance Document on Method Validation and Quality Control Procedures for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed; SANTE: Austin, TX, USA, 2019; p. 12682. [Google Scholar]
- Hoff, R.B.; Rübensam Jank, G.L.F.; Barreto, M.C.R.; Peralba, T.M.; Pizzolato, M.S.; Barceló Díaz-Cruz, D. Analytical quality assurance in veterinary drug residue analysis methods: Matrix effects determination and monitoring for sulfonamides analysis. Talanta 2015, 132, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, P.; Cao, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, G. Residual behavior and risk assessment of the mixed formulation of benzene kresoxim-methyl and fluazinam in cucumber field application. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 2016, 188, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wang, M. Dissipation, occurrence and risk assessment of a phenylurea herbicide tebuthiuron in sugarcane and aquatic ecosystems in South China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Nutrition Society. The Chinese Dietary Guidelines; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.J.; Bian, Y.L.; Feng, Y.Z. Degradation of chlorfenapyr and thiamethoxam residues in asparagus and risk assessment of dietary intake. Agrochemicals 2021, 60, 654–658. [Google Scholar]
- Oliva, J.; Cermeno, S.; Camara, M.A.; Martinez, G.; Barba, A. Disappearance of six pesticides in fresh and processed zucchini, bioavailability and health risk assessment. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, K. Determination of the dissipation dynamics and residue behaviors of chlorantraniliprole in sugarcane and soil by LC-MS/MS. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 2017, 189, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Jiao, B. Residue level, persistence and safety of spirodiclofen-pyridaben mixture in citrus fruits. Food Chem. 2015, 194, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subirats, X.; Reinstadler, S.; Porras, S.; Raggi, M.; Kenndler, E. Comparison of methanol and acetonitrile as solvents for the separation of sertindole and its major metabolites by capillary zone electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 3315–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiga, P.; Delerue-Matos, C. A throughput method using the quick easy cheap effective rugged safe method for the quantification of ibuprofen and its main metabolites in soils. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 3436–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Yang, S.; Li, X.X.; He, L.F.; Zhu, J.M.; Mu, W.; Liu, F. Residue determination of pyraclostrobin, picoxystrobin and its metabolite in pepper fruit via UPLC-MS/MS under open field conditions. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2019, 182, 109445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.P.; Caldas, S.S.; Primel, E.G. Comparison of QuEChERS sample preparation methods for the analysis of pesticide residues in canned and fresh peach. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.Y.; Zhao, Z.X.; Lu, W.; Dong, X.; Hu, J.Y.; Liu, X.L. Evaluation of Dissipation Behavior, Residues, and Dietary Risk Assessment of Fludioxonil in Cherry via QuEChERS Using HPLC-MS/MS Technique. Molecules 2021, 26, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walorczyk, S.; Drozdzy’ nski, D.; Kierzek, R. Determination of pesticide residues in samples of green minor crops by gas chromatography and ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry. Talanta 2015, 132, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, J.; Liu, X. Dissipation behavior, residues distribution and dietary risk assessment of tembotrione and its metabolite in maize via QuEChERS using HPLC-MS/MS technique. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Mu, P.; Jia, Y.; Qian, Y.; Qiu, J. Simultaneous determination of 58 pesticides and relevant metabolites in eggs with a multi-functional filter by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1593, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valese, A.C.; Molognoni, L.; De Souza, N.C.; de Sá, P.; Antunes, L.; Costa, A.C.O.; Barreto, F.; Daguer, H. Development, validation and different approaches for the measurement uncertainty of a multiclass veterinary drugs residues LC-MS method for feeds. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1053, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLCMS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pesticide | Retention Time (min) | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Daughter Ion (m/z) | RF (V) | CE (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flonicamid | 1.8 | 230.1 | 203.0 174.1 | 116 | 16.37 17.17 |
| Analyte | Matrix | Me | Linear Regression Equation | R2 | LOQ (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flonicamid | Solvent | 1.07 | y = 2,057,469.1x − 2725.1 | 0.999 | 0.01 |
| Peach | y = 2,198,889.5x − 983.8 | 1.000 | |||
| Solvent | 0.98 | y = 6,267,384.0x − 5559.5 | 1.000 | 0.01 | |
| Cucumber | y = 6,159,848.6x − 397.5 | 1.000 | |||
| Solvent | 0.98 | y = 11,194,433.4x − 26,234.8 | 0.999 | 0.01 | |
| Cabbage | y = 10,975,030.1x − 17,906.0 | 0.999 | |||
| Solvent | 0.98 | y = 9,414,632.4x − 8540.8 | 0.999 | 0.01 | |
| Cottonseed | y = 9,262,984.6x − 7830.6 | 0.999 |
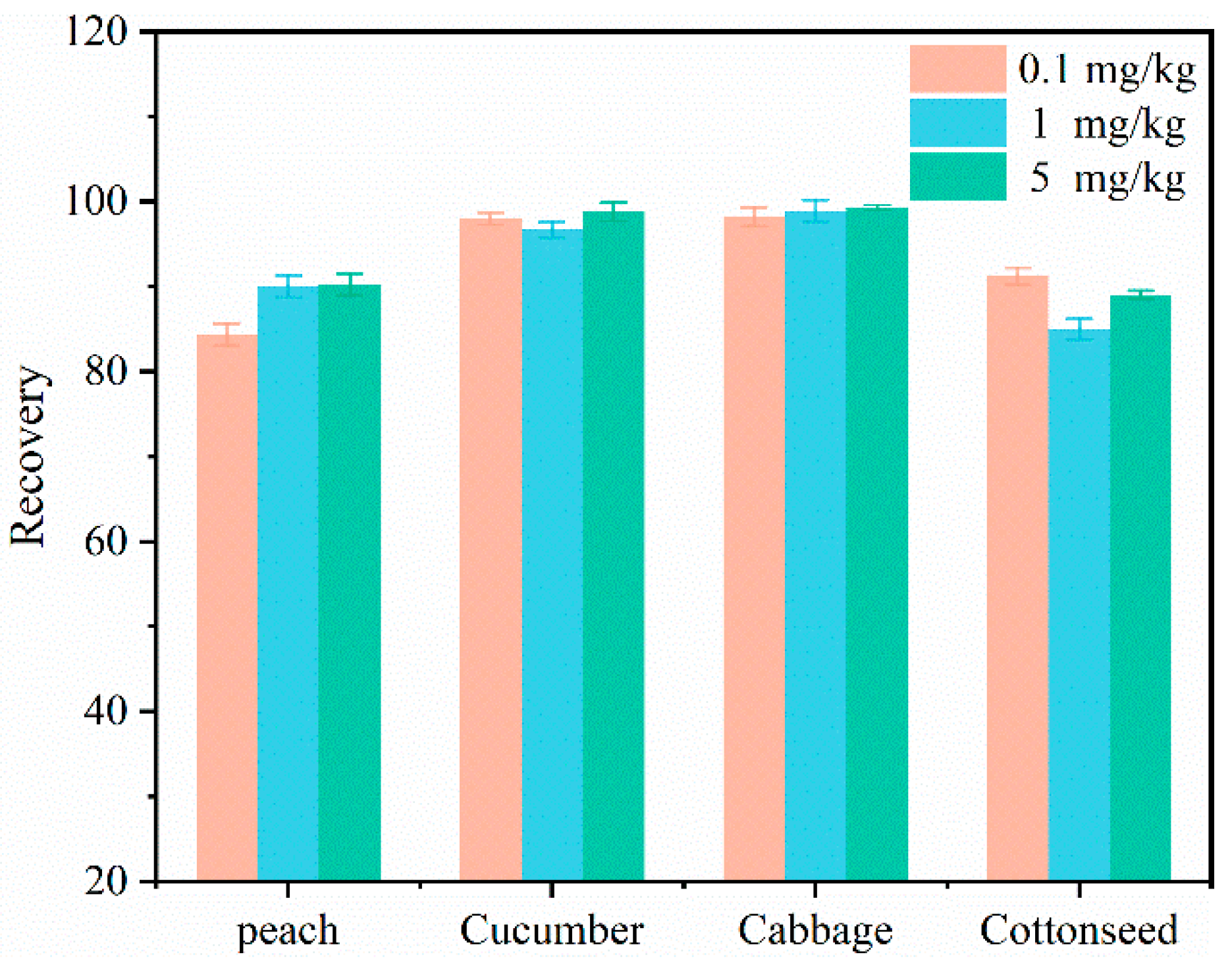
| Pesticide | Crop | Spiked Level/(mg/kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 1 | 5 (3 *) | |||||
| Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Flonicamid | Peach | 84.3 | 2.6 | 90.0 | 1.6 | 90.2 | 2.3 |
| Cucumber | 98.0 | 5.95 | 96.7 | 0.41 | 98.8 | 4.31 | |
| Cabbage | 98.2 | 4.12 | 98.9 | 3.48 | 99.3 | 1.07 | |
| Cottonseed | 91.2 | 3.1 | 85.0 | 4.6 | 89.0 | 1.6 | |
| Test Site | Application Dose | Application Times (Freq) | Harvest Interval (Days) | Residual Quantity (mg/kg) | STMR (mg/kg) | HR (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peach | Inner Mongolia, Shanxi, Beijing, Shandong, Henan, Jiangsu, Hunan, Guizhou | 37.5 (mg/kg) | 1 | 14 | <0.01, 0.01, 0.013, 0.015, 0.019, 0.049, 0.063, 0.13 | 0.017 | 0.130 |
| 21 | <0.01 (4), 0.013, 0.014, 0.015, 0.022 | 0.012 | 0.022 | ||||
| Cucumber | Liaoning, Inner Mongolia, Shanxi, Beijing, Shandong Tai’an, Henan, Shandong Qingdao, Anhui, Shanghai, Hunan, Hubei, Guizhou | 75 (g/ha) | 1 | 3 | 0.0158, 0.0192, 0.0202, 0.0218, 0.0427, 0.0447, 0.0520, 0.0571, 0.0717, 0.0764, 0.0777, 0.134 | 0.0484 | 0.134 |
| 5 | <0.01 (2), 0.0155, 0.0160, 0.0175, 0.0257, 0.0301, 0.0327, 0.0331, 0.0708, 0.0730, 0.108 | 0.0279 | 0.108 | ||||
| Cabbage | Shanxi, Beijing, Shandong, Henan, Anhui, Shanghai, Hunan, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Hubei, Guizhou, Guangdong | 67.5 (g/ha) | 1 | 7 | <0.01 (2), 0.0121, 0.0155, 0.0170, 0.0879, 0.111, 0.112, 0.142, 0.202, 0.247, 0.286 | 0.0994 | 0.286 |
| 10 | <0.01 (5), 0.0135, 0.0263, 0.0291, 0.0556, 0.101, 0.121, 0.129 | 0.0199 | 0.129 | ||||
| Cotton | Hebei, Shandong, Henan, Anhui, Hunan, Jiangxi, Beijing, Hubei | 60 (g/ha) | 1 | 7 | <0.01, 0.0119, 0.0175, 0.0889, 0.124, 0.142, 0.227, 0.246 | 0.0532 | 0.246 |
| 10 | <0.01 (2), 0.0135, 0.0151, 0.0163, 0.0572, 0.0930, 0.129 | 0.0157 | 0.129 |
| Food Classification | Fi(kg) | Reference Residue Limits | Sources | NEDI (mg) | ADI (mg) | Risk Quotient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice and its products | 0.2399 | 0.5 | China | 0.11995 | ADI × 63 | |
| Tubers | 0.0495 | 0.2 | China | 0.00990 | ||
| Light vegetable | 0.1837 | 0.0994 | STMR | 0.01826 | ||
| Fruits | 0.0457 | 1 | China | 0.04570 | ||
| Vegetable oil | 0.0327 | 0.2 | China | 0.00654 | ||
| Total | 0.5515 | 0.20035 | 4.41 | 4.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liang, X.; Bai, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhang, W.; Wang, N.; Pang, X.; Li, Y. Dissipation Kinetics and Safety Evaluation of Flonicamid in Four Various Types of Crops. Molecules 2022, 27, 8615. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238615
Zhang T, Xu Y, Zhou X, Liang X, Bai Y, Sun F, Zhang W, Wang N, Pang X, Li Y. Dissipation Kinetics and Safety Evaluation of Flonicamid in Four Various Types of Crops. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8615. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238615
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tao, Yue Xu, Xuan Zhou, Xiaojie Liang, Yang Bai, Fengshou Sun, Wenwen Zhang, Ning Wang, Xiuyu Pang, and Yuekun Li. 2022. "Dissipation Kinetics and Safety Evaluation of Flonicamid in Four Various Types of Crops" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8615. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238615
APA StyleZhang, T., Xu, Y., Zhou, X., Liang, X., Bai, Y., Sun, F., Zhang, W., Wang, N., Pang, X., & Li, Y. (2022). Dissipation Kinetics and Safety Evaluation of Flonicamid in Four Various Types of Crops. Molecules, 27(23), 8615. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238615






