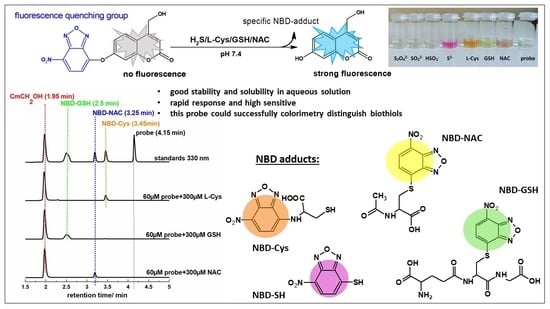
HPLC Study of Product Formed in the Reaction of NBD-Derived Fluorescent Probe with Hydrogen Sulfide, Cysteine, N-acetylcysteine, and Glutathione
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
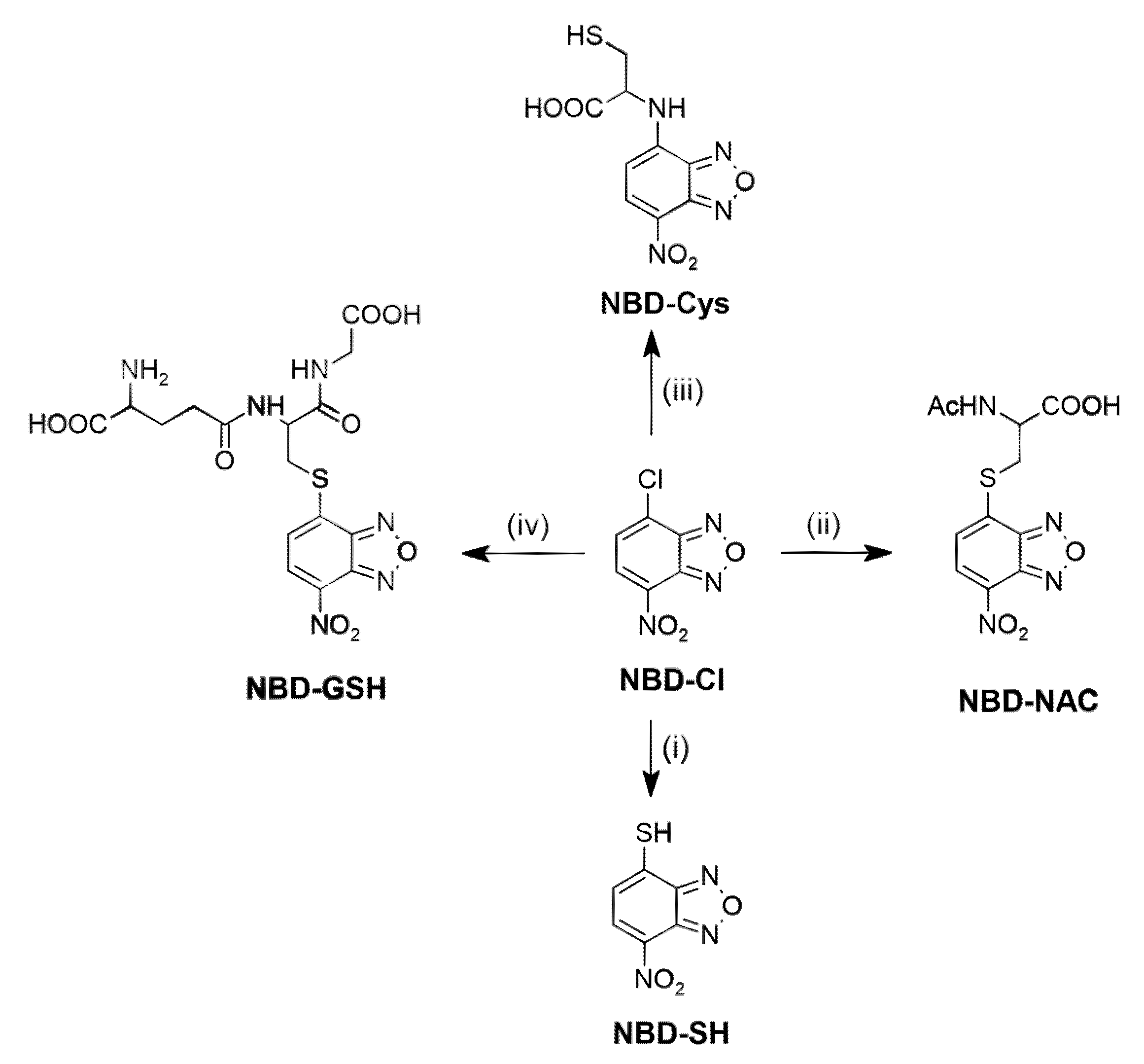
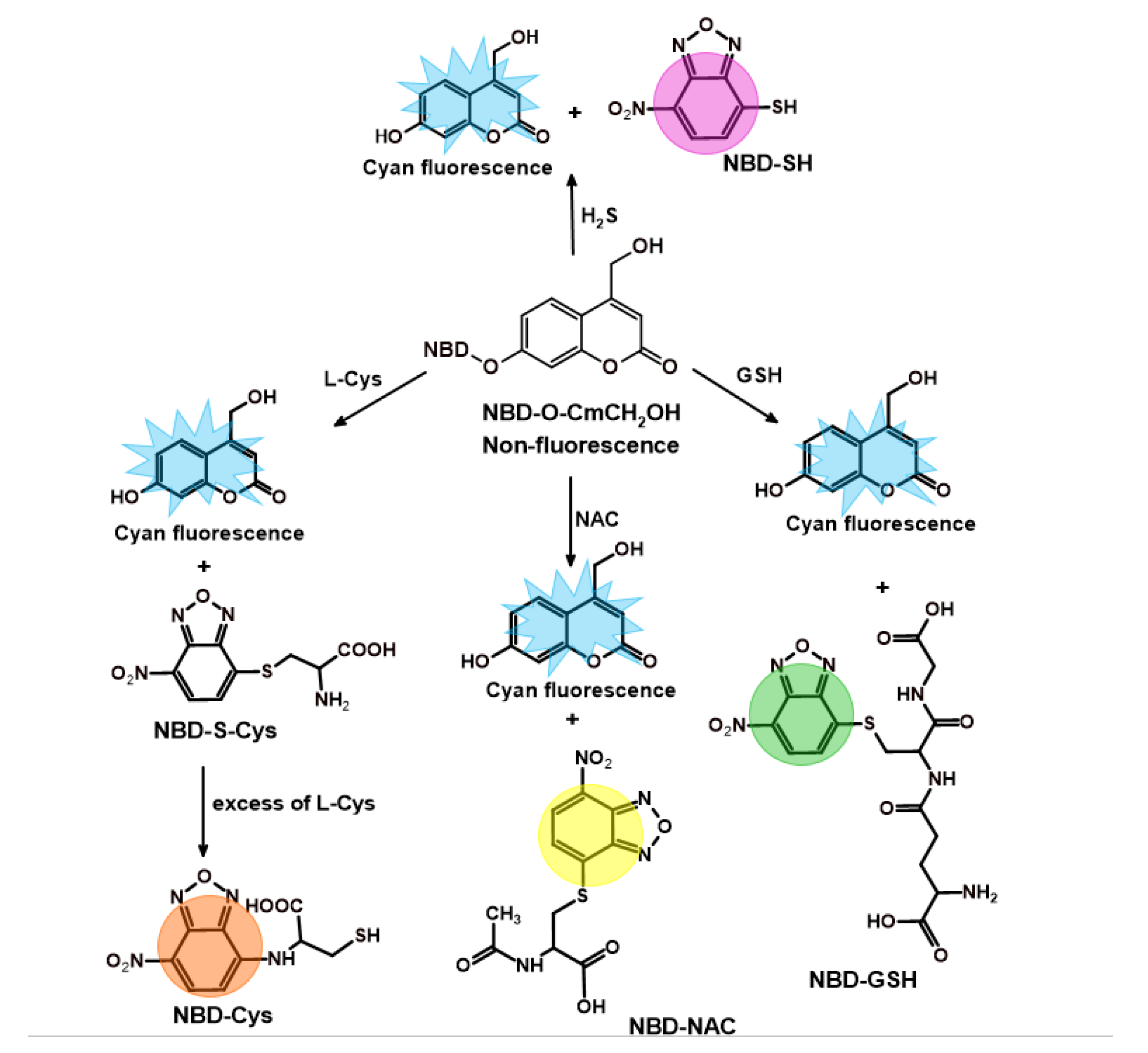
2.1. Synthesis of the Probe and H2S/Biothiols-Specific Product
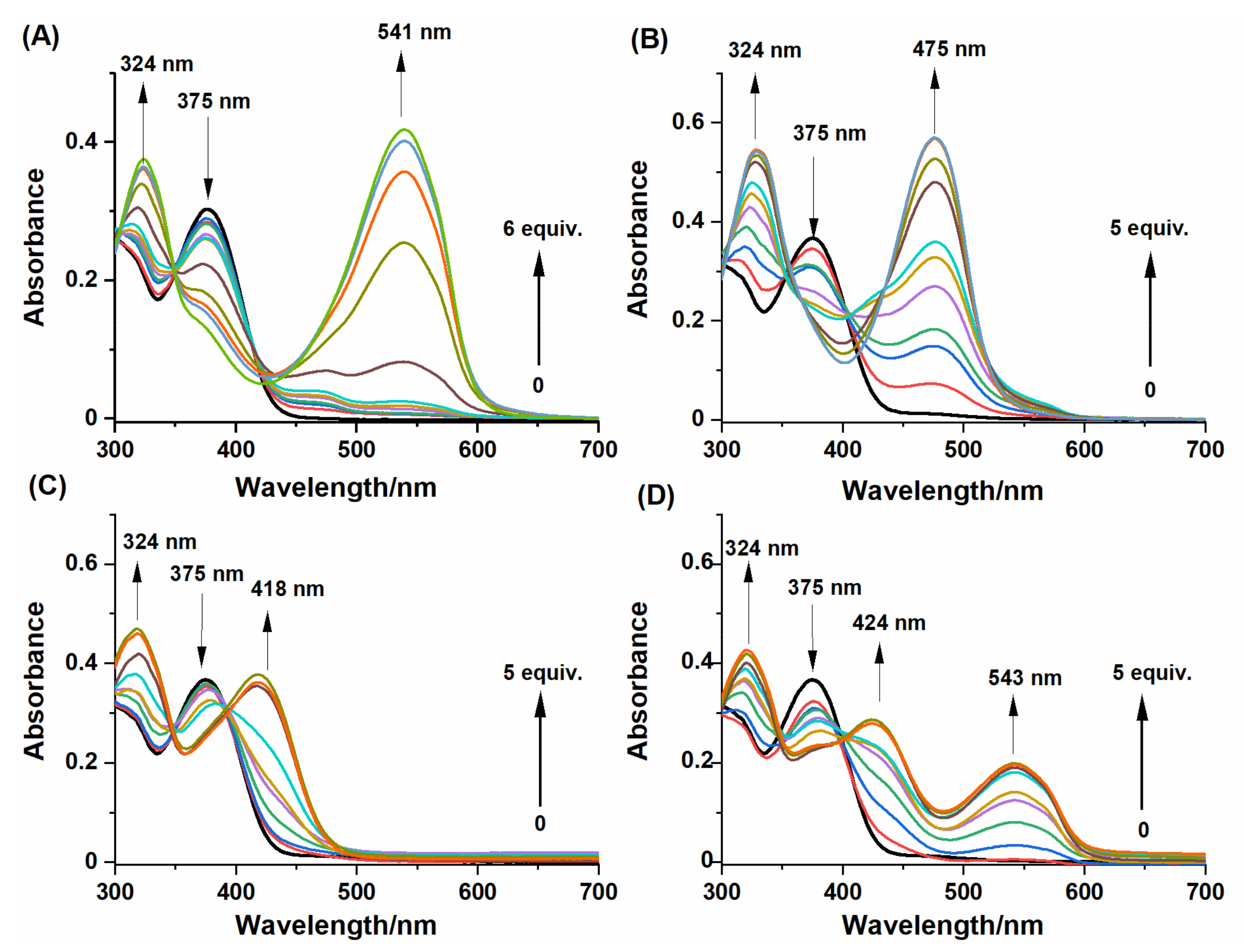
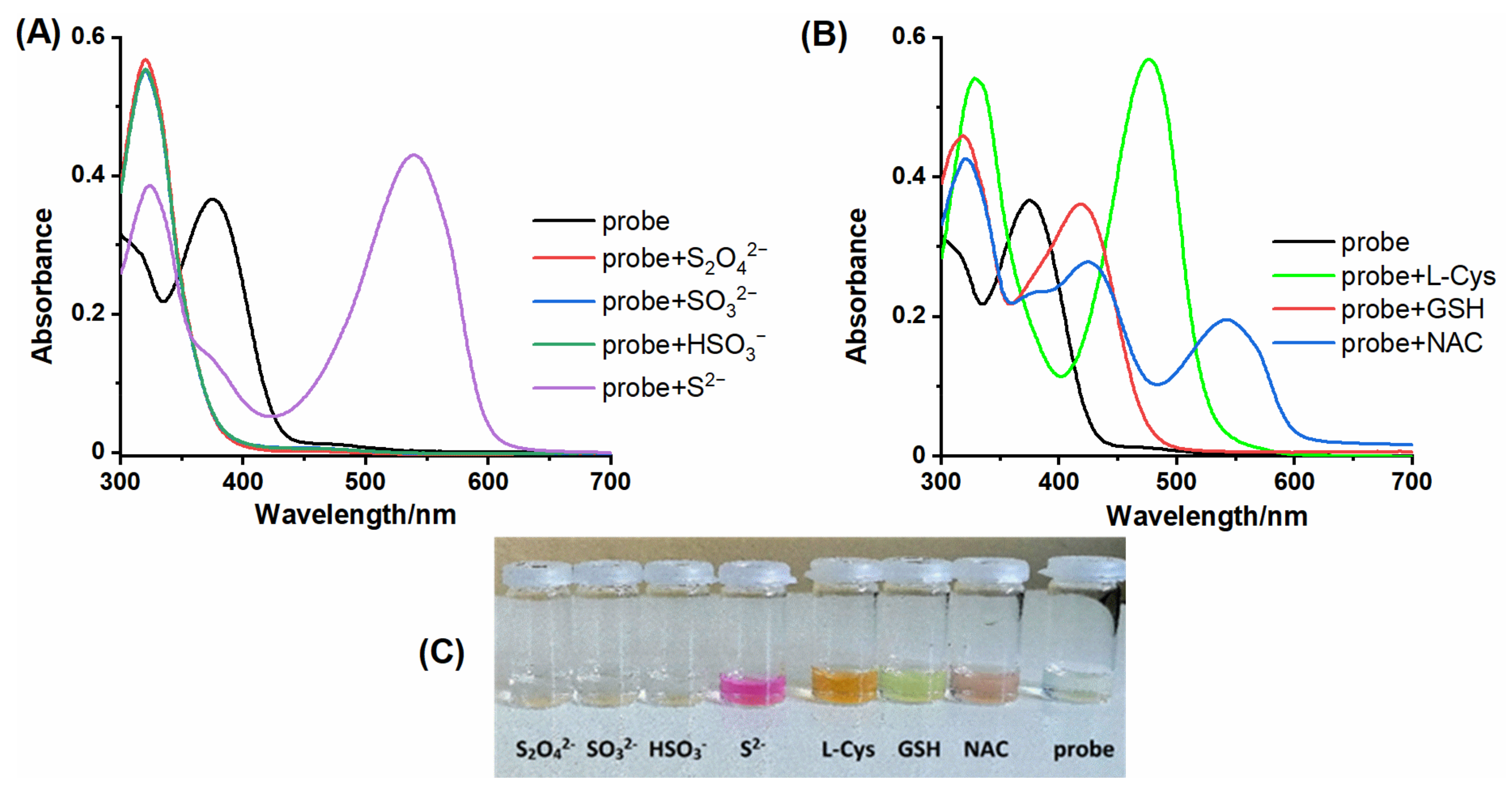
2.2. Spectral Response of NBD-O-CmCH2OH toward Na2S and Biothiols
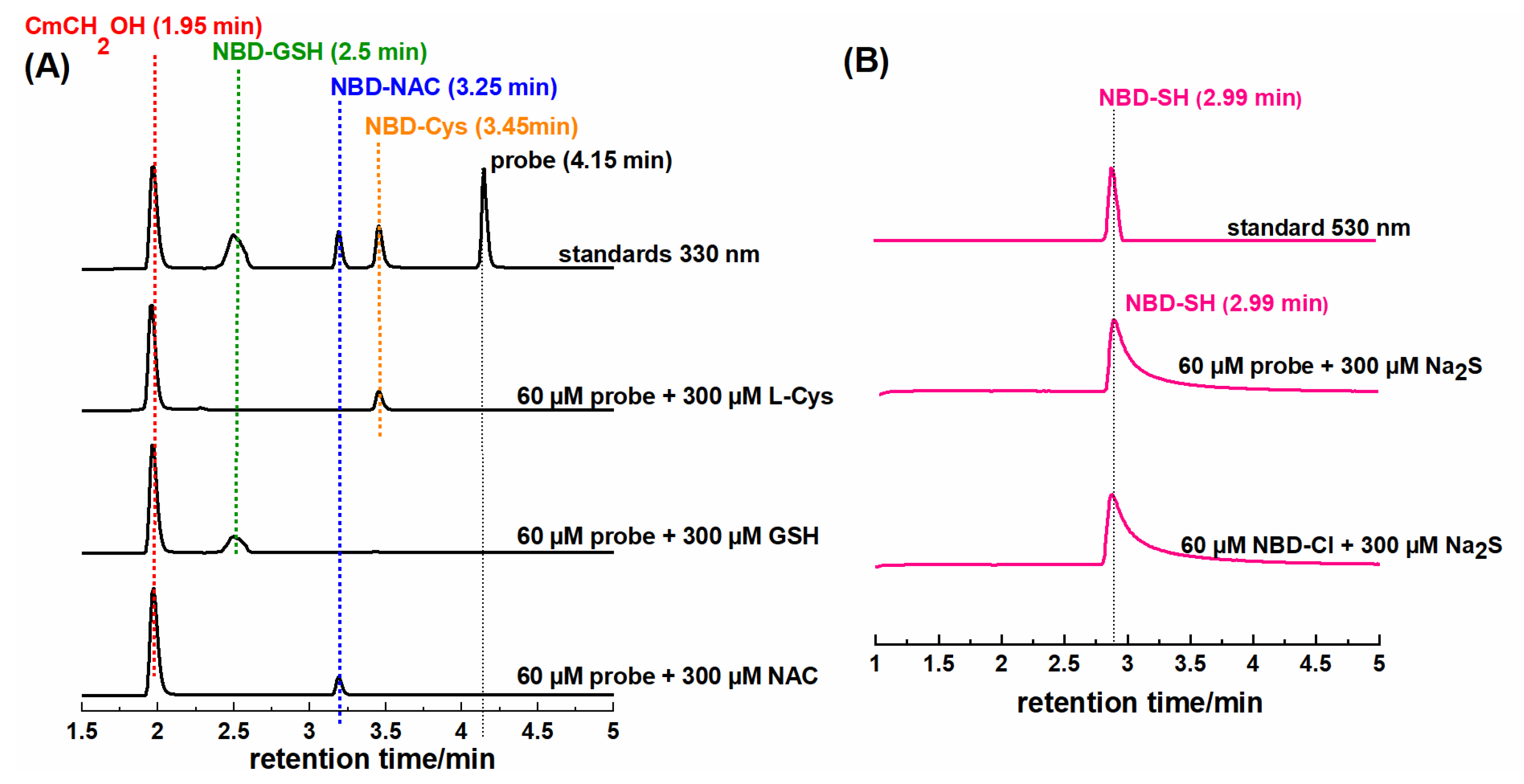
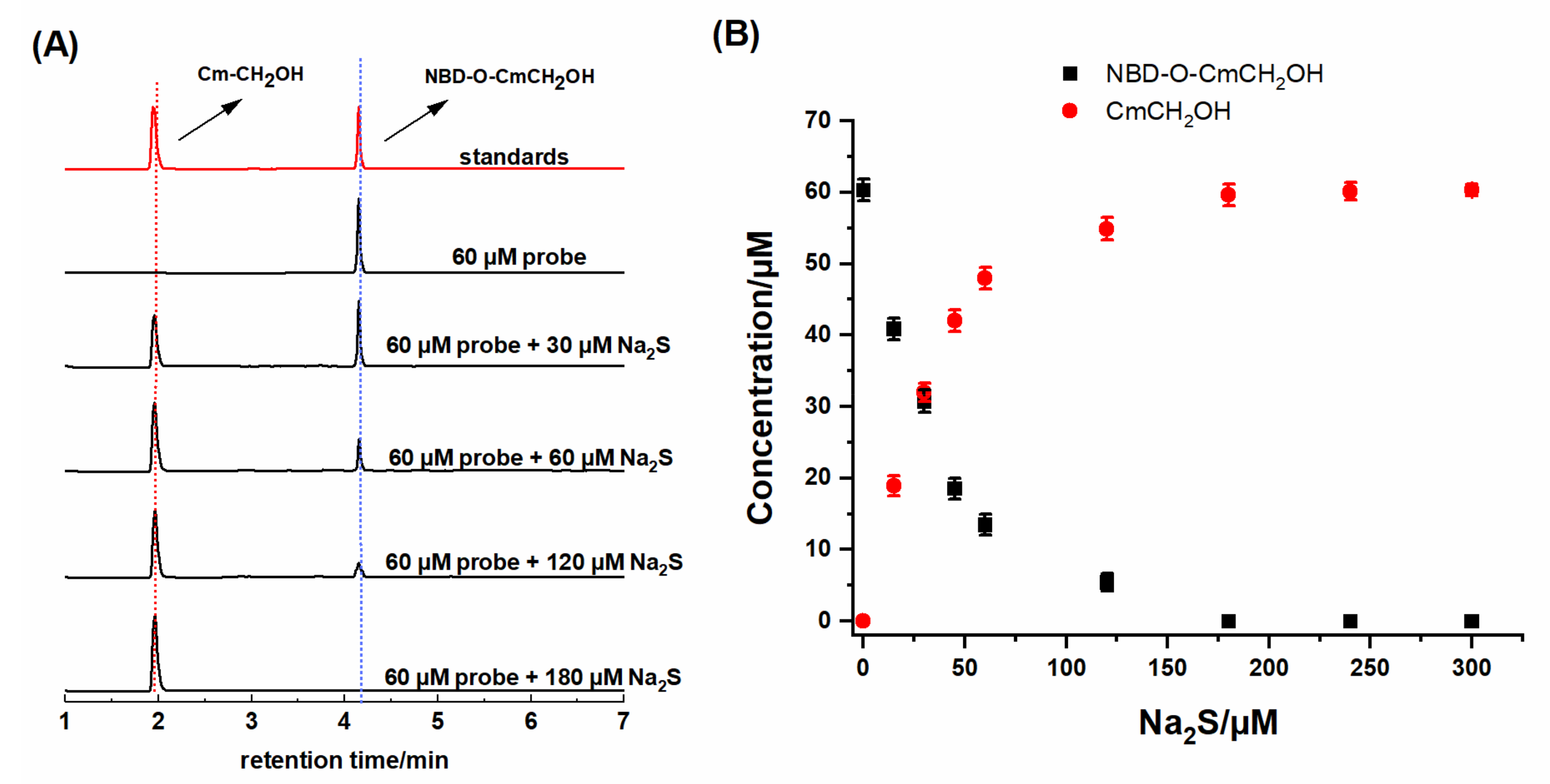
2.3. HPLC and Fluorescence Measurements
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Instruments
3.2. Synthesis
3.2.1. Synthesis of 4-Chloromethyl-7-Hydroxycoumarin (CmCH2Cl)
3.2.2. Synthesis of 7-Hydroxy-4-(Hydroxylmethyl)-2H-Chromen-2-One (CmCH2OH)
3.2.3. Synthesis of 7-Nitrobenzofurazan Ether-4-Hydroxylmethylcoumarin (NBD-O-CmCH2OH)
3.2.4. Synthesis of 7-Nitrobenzo[c][1,2,5]Oxadiazole-4-Thiol (NBD-SH)
3.2.5. Synthesis of 4-Nitrobenz-2-Oxa-1,3-Diazole (NBD) Derived Compounds: NBD-Cys, NBD-GSH, NBD-NAC
3.3. UV-Vis, Fluorescent, and HPLC Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| H2S | hydrogen sulfide |
| NAC | N-acetylcysteine |
| GSH | glutathione |
| Cys | L-Cysteine |
| NBD-Cl | 4-Chloro-7-nitrobenzo[c][1,2,5]oxadiazole |
| NBD-GSH | 7-nitrobenzo[c][1,2,5]oxadiazole-4-glutathione |
| NBD-NAC | N-acetyl-S-(7-nitrobenzo[c][1,2,5]oxadiazol-4-yl)cysteine |
| NBD-Cys | 7-nitrobenzo[c][1,2,5]oxadiazole-4-cysteine |
| CmCH2Cl | 4-chloromethyl-7-hydroxycoumarin |
| CmCH2OH | 7-hydroxy-4-(hydroxylmethyl)-2H-chromen-2-one |
| NBD-O-CmCH2OH | 7-nitrobenzofurazan ether-4-hydroxylmethylcoumarin |
| MeCN | acetonitrile |
| PB buffer | phosphate buffer |
| Na2S | sodium sulfide |
References
- Zhu, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Jia, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Sheng, W.; Zhu, B. A Simple Long-wavelength Fluorescent Probe for Simultaneous Discrimination of Cysteine/Homocysteine and Glutathione/Hydrogen Sulfide with Two Separated Fluorescence Emission Channels by Single Wavelength Excitation. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Shang, L.; Liang, S.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Xin, C.; Zhao, J.; Deng, M.; Wang, Q.; He, Q.; et al. Development and applications of a coumarin-based “turn-on” fluorescent probe for effectively discriminating reduced glutathione from homocysteine and cysteine in living cells and organisms. Dyes Pigments 2021, 194, 109625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, H.; Zhu, H. A fluorescence turn-on probe for hydrogen sulfide and biothiols based on PET & TICT and its imaging in HeLa cells. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 244, 118839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Luo, W.; Diao, Q. A novel ratiometric fluorescent probe for selective detection and imaging of H2S. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 246, 118959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wen, G.; Wang, W.; Cheng, K.; Guo, Q.; Tian, S.; Liu, C.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Controllable Cleavage of C–N Bond-Based Fluorescent and Photoacoustic Dual-Modal Probes for the Detection of H2S in Living Mice. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 2020–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, C.; Papapetropoulos, A. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CII: Pharmacological Modulation of H2S Levels: H2S Donors and H2S Biosynthesis Inhibitors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 497–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Shang, Q.; Yao, J.; Ji, Y. Hydrogen sulfide: A gaseous signaling molecule modulates tissue homeostasis: Implications in ophthalmic diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, H.; Fang, L.; Bian, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, C. H2S Donor and Bone Metabolism. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 661601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, H.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, F.; Luo, X.; Wang, D. A highly sensitive and selective fluorescence turn-on probe for the sensing of H2S in vitro and in vivo. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 254, 119620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivanovic, J.; Filipovic, M. Hydrogen sulfide: Stench from the past as a mediator of the future. Biochemist 2016, 38, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. Physiological Implications of Hydrogen Sulfide: A Whiff Exploration That Blossomed. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 791–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coletta, C.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Erdelyi, K.; Olah, G.; Módis, K.; Panopoulos, P.; Asimakopoulou, A.; Gerö, D.; Sharina, I.; Martin, E. Hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide are mutually dependent in the regulation of angiogenesis and endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9161–9166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Peng, L.; Yuan, G.; Ding, H.; Tan, L.; Zhou, Y. A smart mitochondria-targeting TP-NIR fluorescent probe for the selective and sensitive sensing of H2S in living cells and mice. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 7315–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, Q.; Fan, J.; Jiang, N.; Wang, J.; Xia, J.; Peng, X. A fluorescent probe for H2S in vivo with fast response and high sensitivity. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 16225–16228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Yu, F. A semi-naphthorhodafluor-based red-emitting fluorescent probe for tracking of hydrogen polysulfide in living cells and zebrafish. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 247, 119105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvert, J.; Jha, S.; Gundewar, S.; Elrod, J.; Ramachandran, A.; Pattillo, C.; Kevil, C.; Lefer, D. Hydrogen Sulfide Mediates Cardioprotection Through Nrf2 Signaling. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, Y.; Shimamoto, K.; Hanaoka, K. Chemical tools for the study of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and sulfane sulfur and their applications to biological studies. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2016, 58, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H. Hydrogen sulfide as a neuromodulator. Mol. Neurobiol. 2002, 26, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Ying, J.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, C. The biologic effect of hydrogen sulfide and its function in various diseases. Medicine 2018, 97, e13065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, S.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, B. A dual-site fluorescent probe for separate detection of hydrogen sulfide and bisulfite. Dyes Pigments 2019, 160, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Xia, Q.; Feng, G. Iminocoumarin-based red to near-infrared fluorescent turn-on probe with a large Stokes shift for imaging H2S in living cells and animals. Dyes Pigments 2019, 163, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Zhou, E.; Gong, S.; Feng, G. A red to near-infrared fluorescent probe featuring a super large Stokes shift for light-up detection of endogenous H2S. Dyes Pigments 2019, 160, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H. Protective effect of hydrogen sulfide on monocrotaline induced pulmonary arterial hypertension via inhibition of the endothelial mesenchymal transition. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zhao, C.; Shen, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G. The role of hydrogen sulfide in gastric mucosal damage. Med. Gas. Res. 2019, 9, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Huo, F.; Yin, C. A ‘naked-eye’ ratiometric and NIR fluorescent detection for hydrogen sulphide with quick response and high selectivity for and its bioimaging. Dyes Pigments 2019, 165, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, D.; Xue, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H. Ultrafast response fluorescent probe with red-emission for monitoring hydrogen sulfide in vivo and in vitro. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2019, 382, 111974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Han, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wu, W.; Xu, Z. A ratiometric fluorescent probe for hydrogen sulfide in neat aqueous solution and its application in lysosome-targetable cell imaging. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 270, 120835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mei, Y.; Li, H.; Song, Q. Rapid and sensitive detection of H2S by a 4-phenylselenium coumarin as a dual-active-site fluorescent probe. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 354, 131202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuiling, S.; Huayu, W.; Tianjun, N.; Kaiwen, C.; Chunpo, G. A dicyanoisophorone-based near-infrared fluorescent probe with fast detection for H2S in living cells and zebrafish. J. Lumin. 2022, 243, 118669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothi, D.; Iyer, S. A highly sensitive naphthalimide based fluorescent “turn-on” sensor for H2S and its bio-imaging applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2022, 427, 113802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubuka, T.; Abe, T.; Kajikawa, R.; Morino, K. Determination of hydrogen sulfide and acid-labile sulfur in animal tissues by gas chromatography and ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2001, 757, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.; Serag, A.; Farag, M. Emerging analytical tools for the detection of the third gasotransmitter H2S, a comprehensive review. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 27, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, T.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Guo, W. A Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Biological Signaling Molecule H2S: Fast Response and High Selectivity. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 4717–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Tian, B.; Tong, T.; Zhang, J. A colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent probe with a large stokes shift for detection of hydrogen sulfide. Dyes Pigments 2015, 123, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, K.; Hou, J.; Wu, M.; Huang, Z.; Yu, X. BINOL-Based Fluorescent Sensor for Recognition of Cu(II) and Sulfide Anion in Water. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 8350–8354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Wu, M.; Wang, S.; Qin, J.; Li, P. Synthesis and preliminary exploration of a NIR fluorescent probe for the evaluation of androgen dependence of prostate cancer. Talanta 2022, 239, 123058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Meng, J.; Bao, W.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Tian, Z. Mitochondrion-targeting near-infrared fluorescent probe for detecting intracellular nanomolar level hydrogen sulfide with high recognition rate. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, W.; Qing, Z.; Weiwei, L.; Wenbin, C.; Zhen, X.; Long, Y. NBD-based colorimetric and fluorescent turn-on probes for hydrogen sulfide. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słowiński, D.; Świerczyńska, M.; Grzelakowska, A.; Szala, M.; Kolińska, J.; Romański, J.; Podsiadły, R. Hymecromone naphthoquinone ethers as probes for hydrogen sulfide detection. Dyes Pigments 2021, 196, 109765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, V.; Chen, W.; Xian, M.; Chang, C. Chemical Probes for Molecular Imaging and Detection of Hydrogen Sulfide and Reactive Sulfur Species in Biological Systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4596–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świerczyńska, M.; Słowiński, D.; Grzelakowska, A.; Szala, M.; Romański, J.; Pierzchała, K.; Siarkiewicz, P.; Michalski, R.; Podsiadły, R. Selective, stoichiometric and fast-response fluorescent probe based on 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole fluorophore for hypochlorous acid detection. Dyes Pigments 2021, 193, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Feng, G. Smart probe for rapid and simultaneous detection and discrimination of hydrogen sulfide, cysteine/homocysteine, and glutathione. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Choi, J.; Park, T.; Chang, S. Reaction-based colorimetric and fluorogenic signaling of hydrogen sulfide using a 7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole–coumarin conjugate. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Shi, Z.; Tu, Y.; Pu, S. A dual emission fluorescent probe enables simultaneous detection and discrimination of Cys/Hcy and GSH and its application in cell imaging. Dyes Pigments 2019, 165, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Luo, H.; Liu, X.; Foley, J.W.; Song, X. Broadly applicable Strategy for the fluorescence based detection and differentiation of glutathione and cysteine/homocysteine: Demonstration in vitro and in vivo. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3638–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tong, Z.; Xi, Z.; Qiu, X.; Yi, L. Rational design and synthesis of fast-response NBD-based fluorescent probes for biothiols. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 5781–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammers, M.; Pluth, M. Ratiometric Measurement of Hydrogen Sulfide and Cysteine/Homocysteine Ratios Using a Dual-Fluorophore Fragmentation Strategy. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7135–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, N.; Makani, V.; Pranay, J.; Alvala, R.; Qureshi, I.; Kumar, P.; Bharath, R.; Nagaraj, C.; Yerramsetty, S.; Pal-Bhadra, M.; et al. Synthesis, 18F-radiolabeling and apoptosis inducing studies of novel 4, 7-disubstituted coumarins. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 97, 103663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Liu, G.; Wang, F.; Zhub, Z.; Feng, C. Galactose-decorated light-responsive hydrogelator precursors for selectively killing cancer cells. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballal, S.; Trujillo, M.; Cuevasanta, E.; Bartesaghi, S.; Möller, M.; Folkes, L.; García-Bereguiaín, M.; Gutiérrez-Merino, C.; Wardman, P.; Denicola, A.; et al. Reactivity of hydrogen sulfide with peroxynitrite and other oxidants of biological interest. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummanapelli, A.; Vasudevan, S. Initio MD Simulations of the Brønsted Acidity of Glutathione in Aqueous Solutions: Predicting pKa Shifts of the Cysteine Residue. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 15353–15358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazary, A.; Awwad, N.; Ibrahium, H.; Shati, A.; Alfaifi, M.; Ju, Y. Protonation Equilibria of N-Acetylcysteine. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 19598–19605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yue, J.; Chao, J.; Huo, F.; Yin, C. A new strategy for the fluorescence discrimination of Cys/Hcy and GSH/H2S simultaneously colorimetric detection for H2S. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. 2020, 227, 117537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, C.; Yuan, R.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Jia, P.; Zhu, B.; Sheng, W. A simple highly specific fluorescent probe for simultaneous discrimination of cysteine/ homocysteine and glutathione/hydrogen sulfide in living cells and zebrafish using two separated fluorescence channels under single wavelength excitation. Analyst 2019, 144, 4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Sun, X.; Xing, Z.; Wu, R. A facile probe for fluorescence turn-on and simultaneous naked-eyes discrimination of H2S and biothiols (Cys and GSH) and its application. J. Fluoresc. 2022, 32, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Luo, L.; Chen, L.; Tang, Z.; Zeng, R.; Xu, M.; Chen, S. Dual-emission fluorescent probe for discriminative sensing of biothiols. Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 50, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Han, L.; Fan, Y.; Qing, M.; Li, N.; Luo, H. A simple fluorescent probe with two different fluorescence signals for rapid sequence distinguishing of Cys/Hcy/GSH and intracellular imaging. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 184, 108722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, J.; Dong, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, Q. Fluorescent probe for sensitive discrimination of Hcy and Cys/GSH in living cells via dual-emission. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1074, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, H.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, X.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Qin, F.; Zhai, Y.; Ye, Y.; et al. A bifunctional fluorescent probe based on PET & ICT for simultaneously recognizing Cys and H2S in living cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2022, 230, 112441. [Google Scholar]


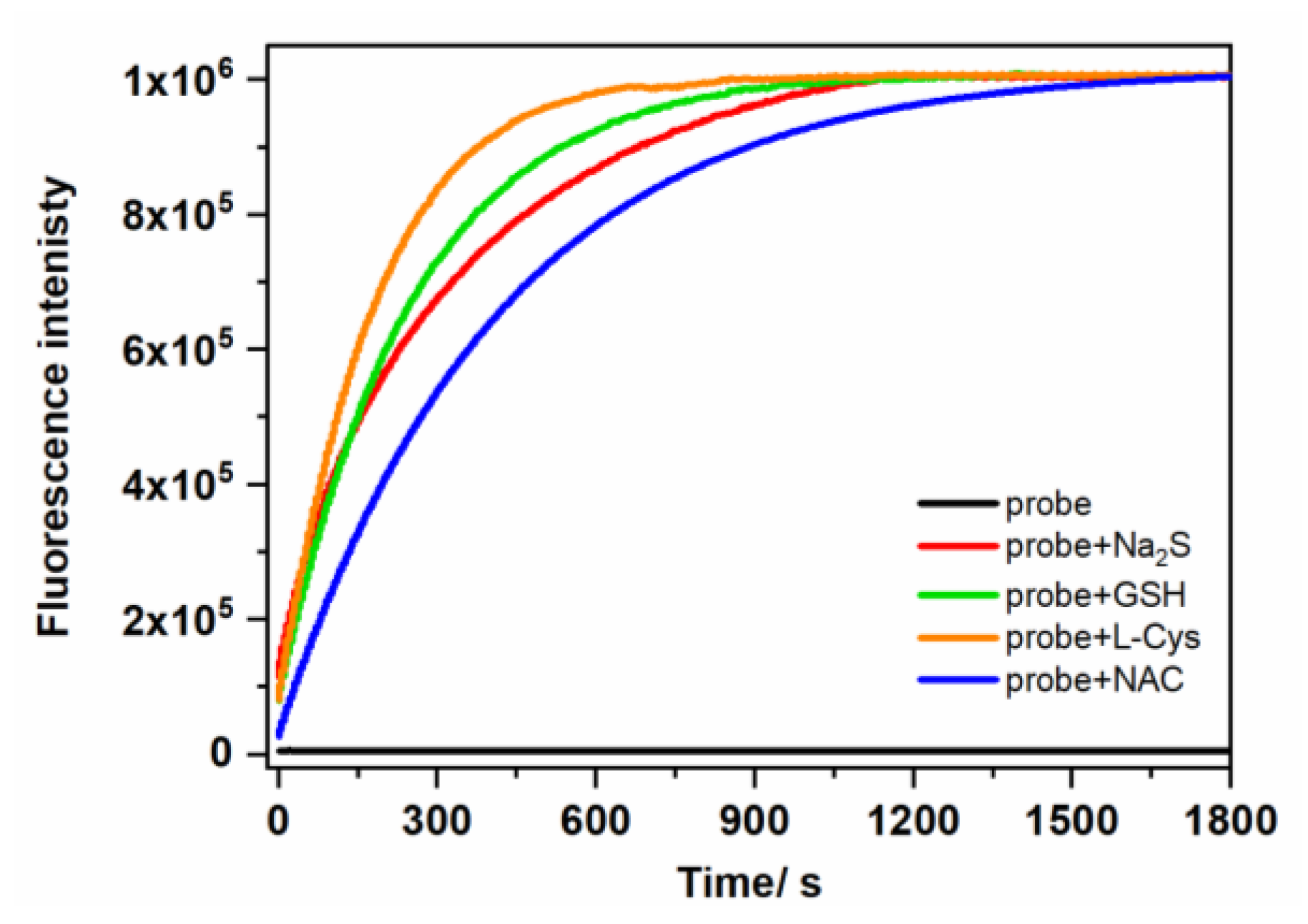
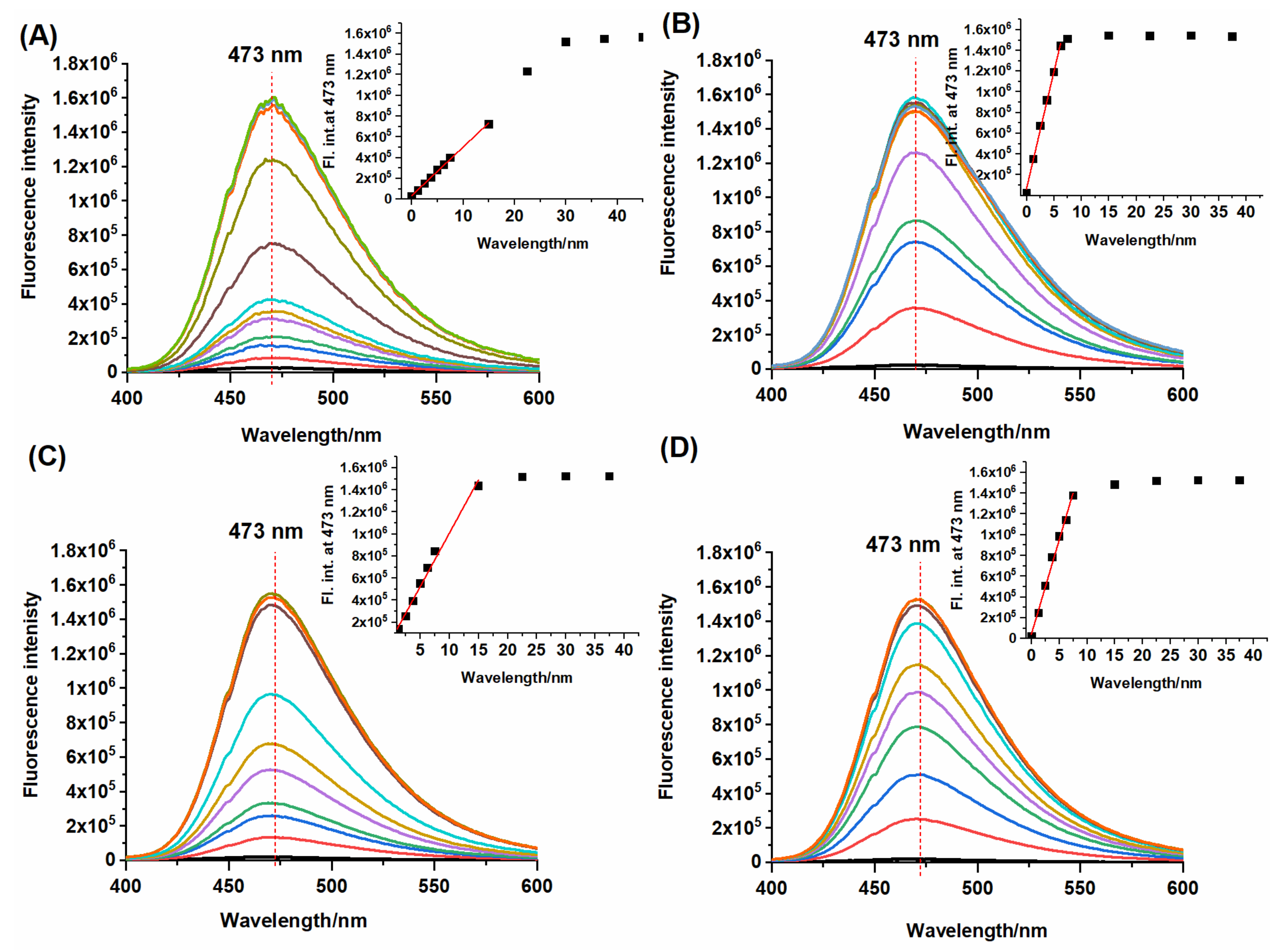
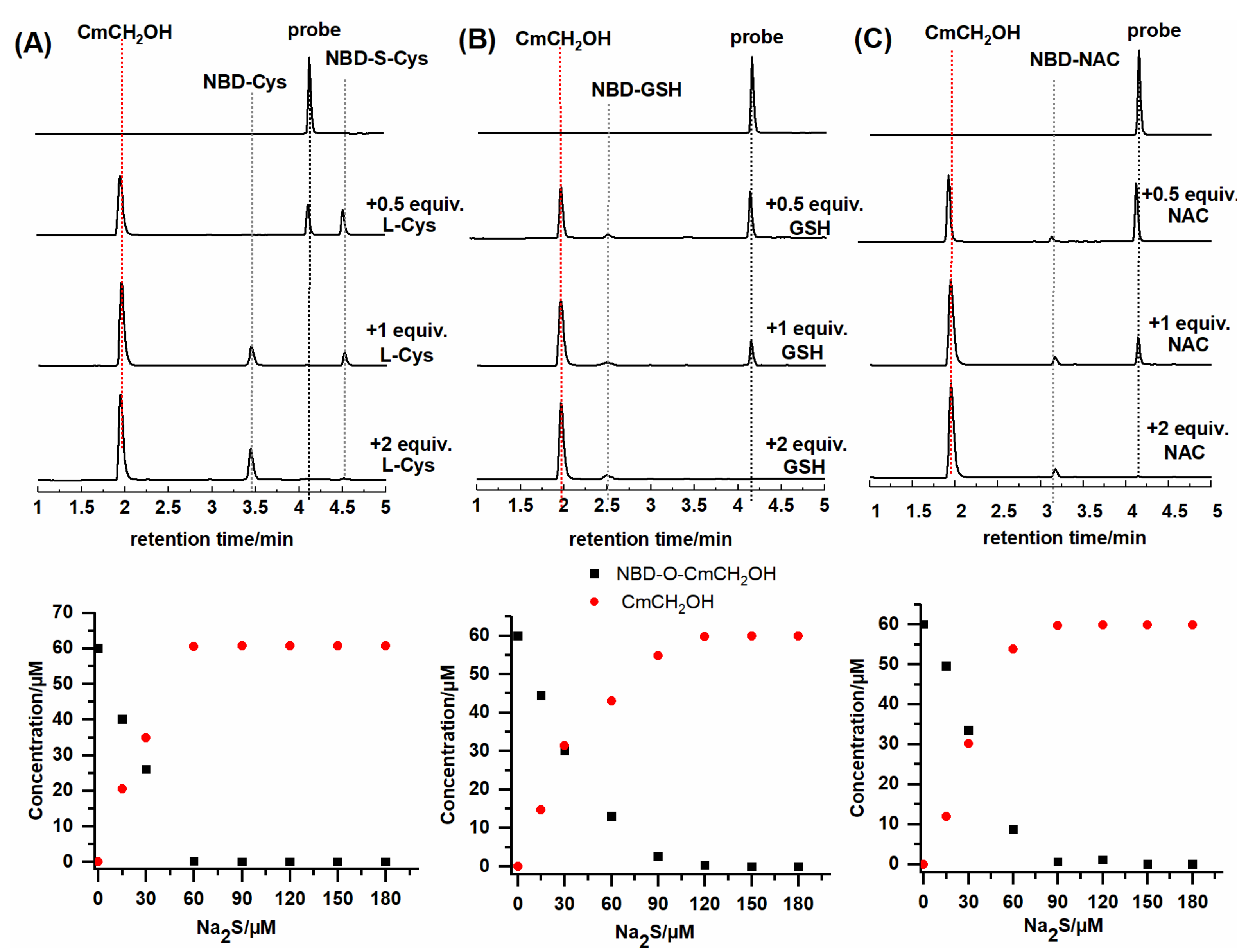
| kobs (103 s−1) | LOD (nM) | |
|---|---|---|
| H2S (pKa 7.0 a) | 3.02 | 140 |
| GSH (pKa 8.66 b) | 4.00 | 60 |
| L-Cys (pKa 8.33 b) | 5.64 | 26 |
| NAC (pKa 9.43 c) | 2.5 | 32 |
| Thiol-Specific Product | λmax (nm) | Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| NBD-SH | 541 | 2.99 |
| NBD-GSH | 418 | 2.50 |
| NBD-Cys | 475 | 3.45 |
| NBD-NAC | 543, 424 | 3.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Słowiński, D.; Świerczyńska, M.; Romański, J.; Podsiadły, R. HPLC Study of Product Formed in the Reaction of NBD-Derived Fluorescent Probe with Hydrogen Sulfide, Cysteine, N-acetylcysteine, and Glutathione. Molecules 2022, 27, 8305. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238305
Słowiński D, Świerczyńska M, Romański J, Podsiadły R. HPLC Study of Product Formed in the Reaction of NBD-Derived Fluorescent Probe with Hydrogen Sulfide, Cysteine, N-acetylcysteine, and Glutathione. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8305. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238305
Chicago/Turabian StyleSłowiński, Daniel, Małgorzata Świerczyńska, Jarosław Romański, and Radosław Podsiadły. 2022. "HPLC Study of Product Formed in the Reaction of NBD-Derived Fluorescent Probe with Hydrogen Sulfide, Cysteine, N-acetylcysteine, and Glutathione" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8305. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238305
APA StyleSłowiński, D., Świerczyńska, M., Romański, J., & Podsiadły, R. (2022). HPLC Study of Product Formed in the Reaction of NBD-Derived Fluorescent Probe with Hydrogen Sulfide, Cysteine, N-acetylcysteine, and Glutathione. Molecules, 27(23), 8305. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238305