Characterization of Polyhydroxybutyrate, PHB, Synthesized by Newly Isolated Haloarchaea Halolamina spp.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation, Screening, and Identification of Haloarchaeal Strains Showing PHA-Producing Capacities
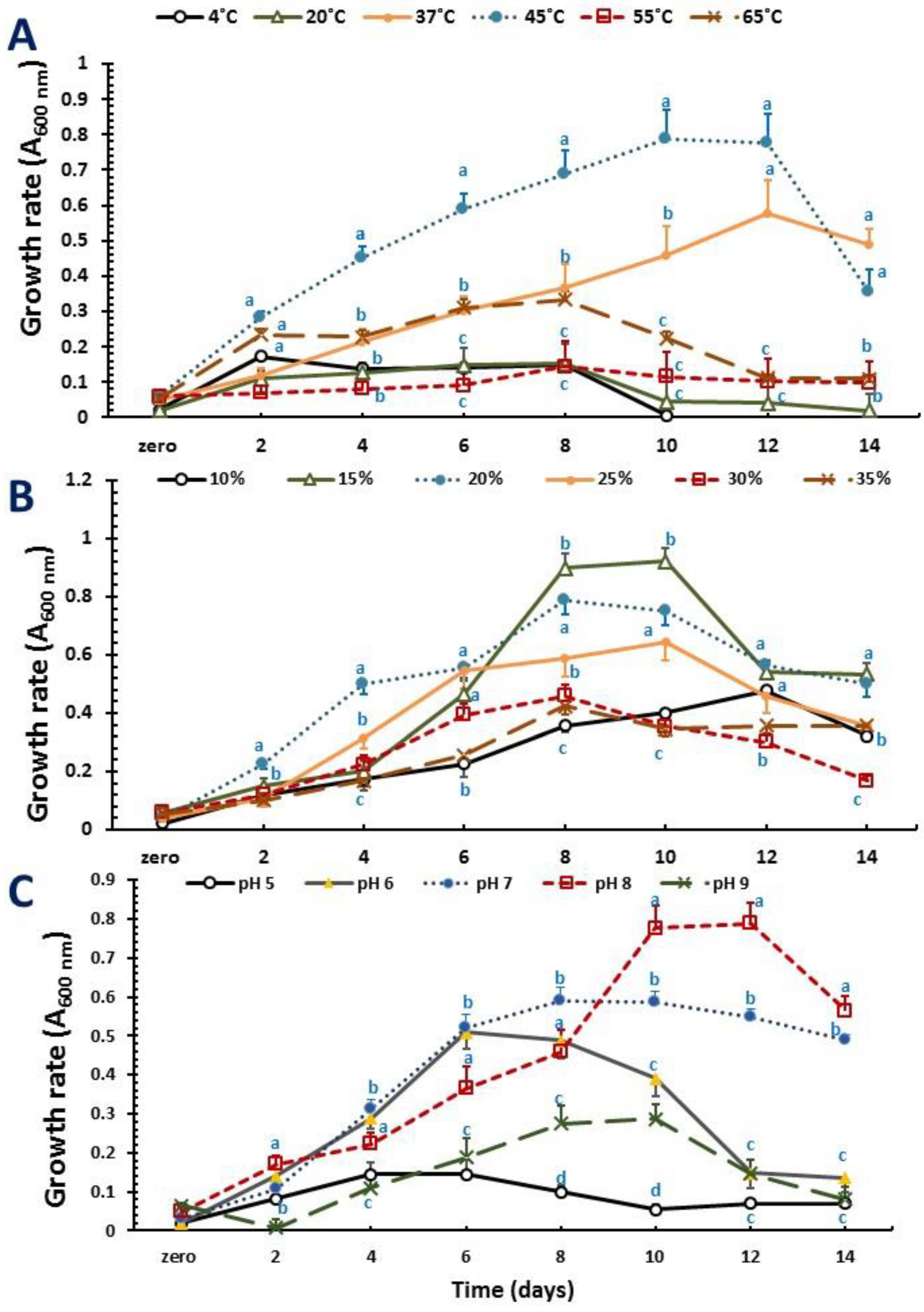
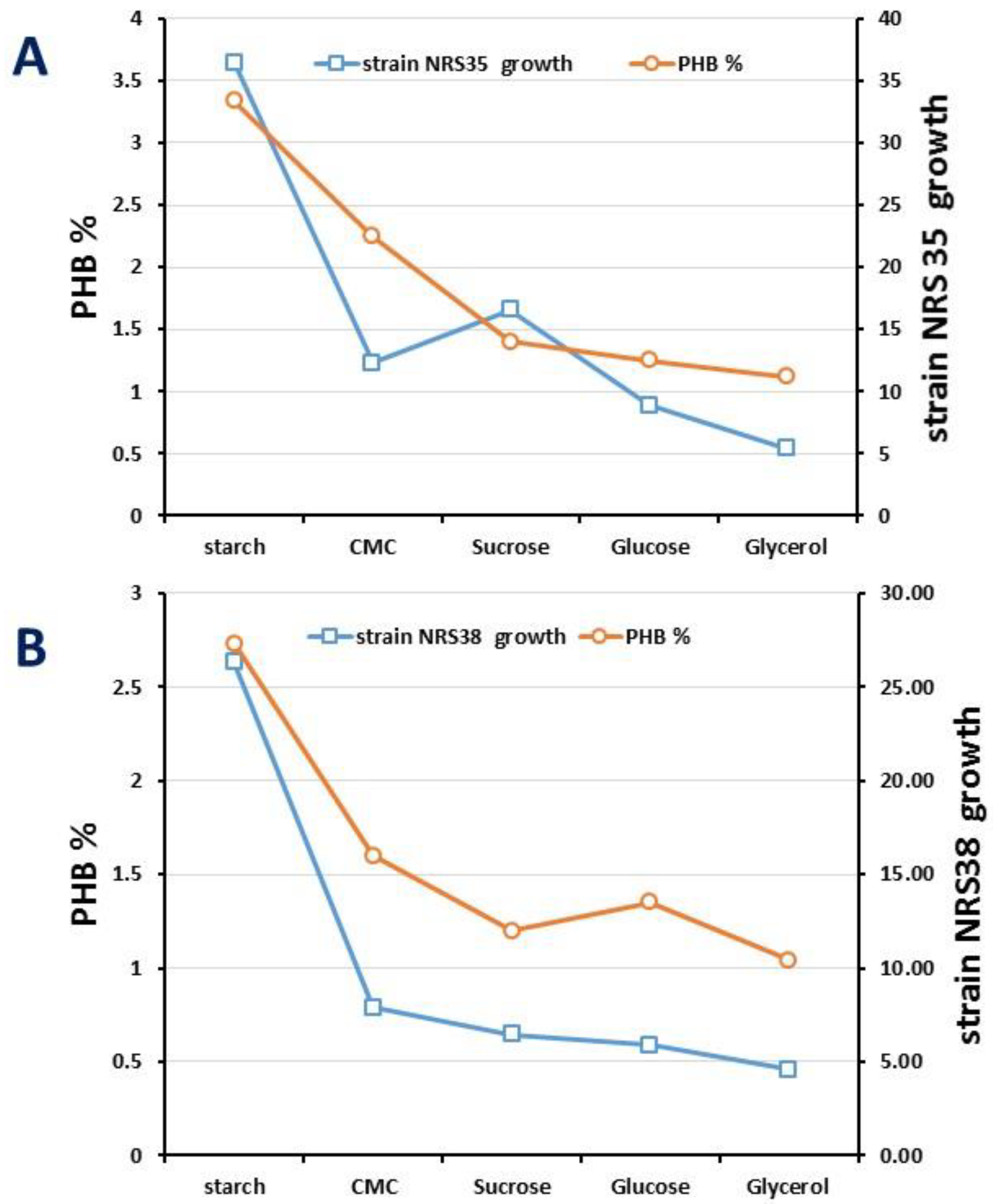
2.2. Optimization of Growth Conditions and PHA Production
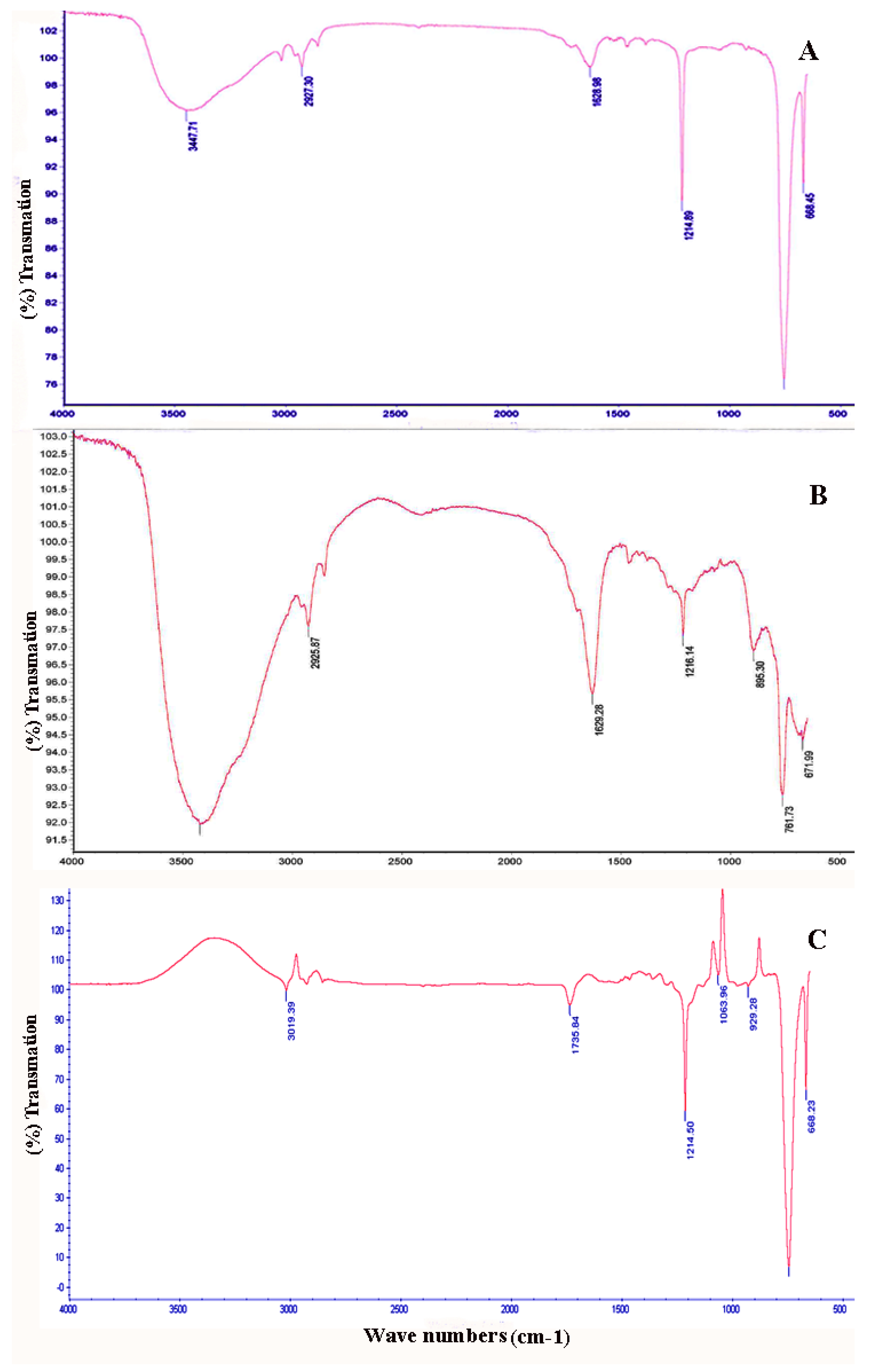
2.3. FTIR Analysis
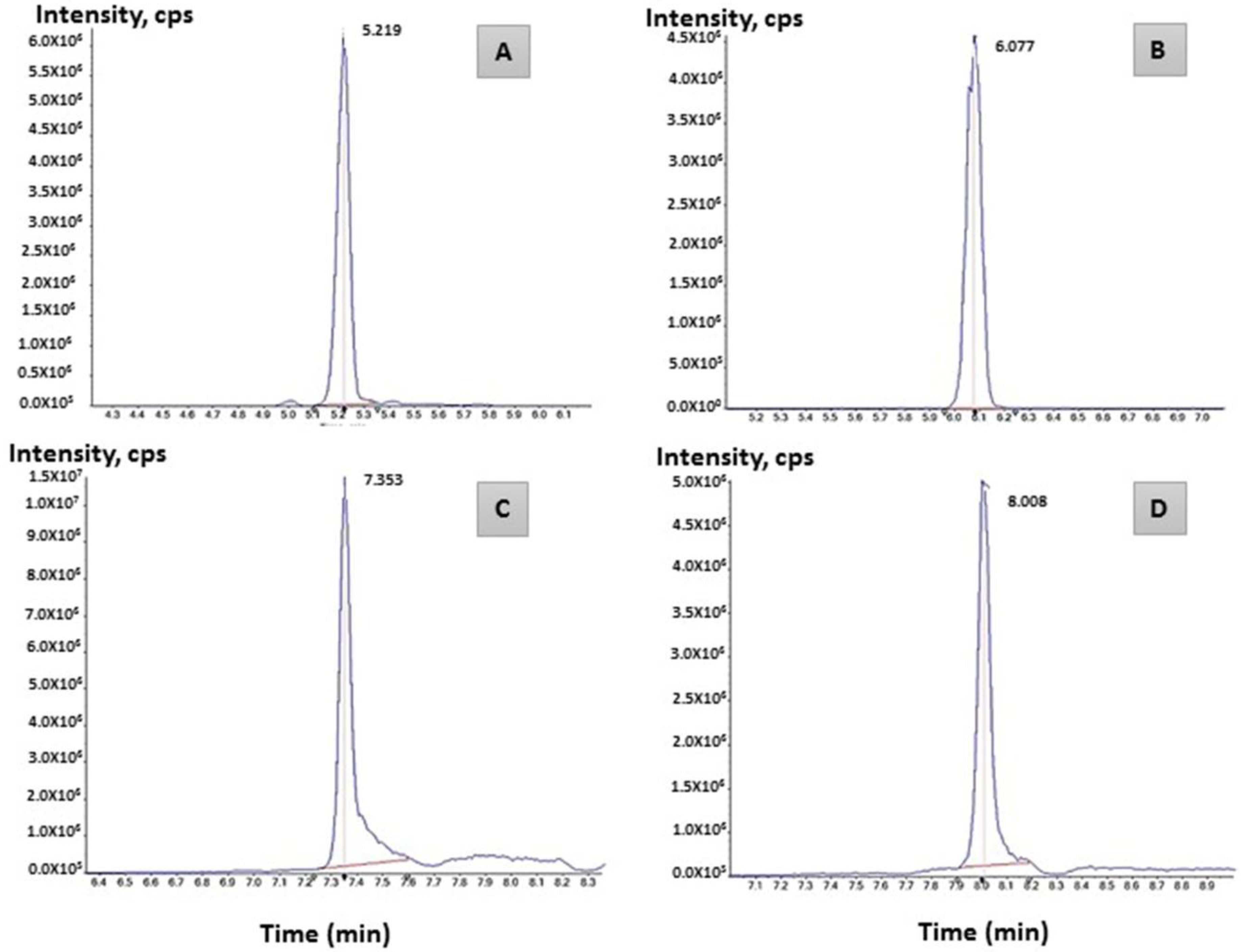
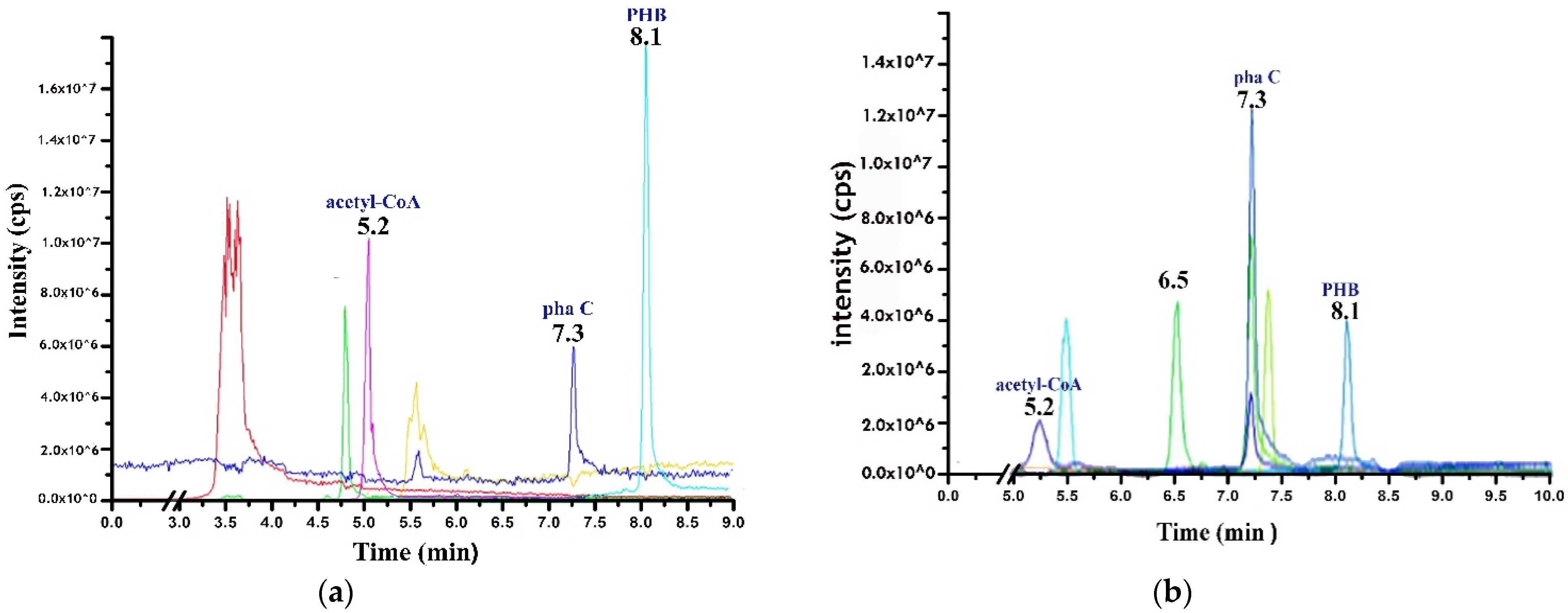
2.4. LC–MS/MS Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling and Site Description
4.2. Enrichment, Isolation, and Growth Conditions
4.3. Screening for PHA-Producing Haloarchaeal Isolates
4.4. Identification of the Potential Strains
4.5. Optimization of Growth Conditions of the Potential PHA-Producing Haloarchaeal Strains
4.6. Extraction of the Polymer
4.7. Characterization of the Biopolymer by FTIR
4.8. Characterization of Biopolymer by LC–MS/MS
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nikolaivits, E.; Pantelic, B.; Azeem, M.; Taxeidis, G.; Babu, R.; Topakas, E.; Fournet, M.B.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Progressing Plastics Circularity: A Review of Mechano-Biocatalytic Approaches for Waste Plastic (Re)valorization. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 696040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napathorn, S.C.; Visetkoop, S.; Pinyakong, O.; Okano, K.; Honda, K. Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) Production Using an Arabinose-Inducible Expression System in Comparison with Cold Shock Inducible Expression System in Escherichia coli. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.K.; Anjum, I.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H.; Anjum, S. An overview on feasible production of bioplastic polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) in transgenic plants. In Bioplastics for Sustainable Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 555–579. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, S.; Kailashiya, C.; Singh, M.; Tiwari, A. An Initiative to Reduce Polymer Pollution by Introducing Biopolymer Synthesized by Microorganisms with the Use of Various Organic Waste with Economically Effective and Biodegradability. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2021, 6, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Yaqoob, M.; Aggarwal, P. An overview of biodegradable packaging in food industry. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekhi, P.; Goswami, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Debnath, M. Polyhydroxyalkanoates biopolymers toward decarbonizing economy and sustainable future. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 42, 668–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourmentza, C.; Plácido, J.; Venetsaneas, N.; Burniol-Figols, A.; Varrone, C.; Gavala, H.N.; Reis, M.A.M. Recent Advances and Challenges towards Sustainable Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Production. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simó-Cabrera, L.; García-Chumillas, S.; Hagagy, N.; Saddiq, A.; Tag, H.; Selim, S.; AbdElgawad, H.; Agüero, A.A.; Sánchez, F.M.; Cánovas, V.; et al. Haloarchaea as Cell Factories to Produce Bioplastics. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, M. Polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis at the edge of water activitiy-haloarchaea as biopolyester factories. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karray, F.; Ben Abdallah, M.; Baccar, N.; Zaghden, H.; Sayadi, S. Production of poly (3-Hydroxybutyrate) by Haloarcula, Halorubrum, and Natrinema haloarchaeal genera using starch as a carbon source. Archaea 2021, 2021, 8888712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugappriya, M.; Sudarsanam, D.; Joseph, J.; Mir, M.A.; Selvaraj, C. Applications of polyhydroxyalkanoates based nanovehicles as drug carriers. In Biotechnological Applications of Polyhydroxyalkanoates; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 125–169. [Google Scholar]
- Altekar, W.; Rajagopalan, R. Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity in halophilic Archaebacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 1990, 153, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaus, B.; Lama, L.; Esposito, E.; Manca, M.C.; Improta, R.; Bellitti, M.R.; Duckworth, A.W.; Grant, W.D.; Gambacorta, A. Haloarcula spp able to biosynthesize exo- and endopolymers. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 23, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezayen, F.F.; Gutiérrez, M.C.; Steinbüchel, A.; Tindall, B.J.; Rehm, B.H. Halopiger aswanensis sp. nov., a polymer-producing and extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from hypersaline soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hezayen, F.F.; Rehm, B.H.; Eberhardt, R.; Steinbüchel, A. Polymer production by two newly isolated extremely halophilic archaea: Application of a novel corrosion-resistant bioreactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 54, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hezayen, F.F.; Tindall, B.J.; Steinbüchel, A.; Rehm, B.H. Characterization of a novel halophilic archaeon, Halobiforma haloterrestris gen. nov., sp. nov., and transfer of Natronobacterium nitratireducens to Halobiforma nitratireducens comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, D.G.; Janssen, P.; Itoh, T.; Kamekura, M.; Li, Z.; Jensen, G.; Rodriguez-Valera, F.; Bolhuis, H.; Dyall-Smith, M.L. Haloquadratum walsbyi gen. nov., sp. nov., the square haloarchaeon of Walsby, isolated from saltern crystallizers in Australia and Spain. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, I.; Poli, A.; Finore, I.; Huertas, F.J.; Gambacorta, A.; Pelliccione, S.; Nicolaus, G.; Lama, L.; Nicolaus, B. Haloterrigena hispanica sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from Fuente de Piedra, southern Spain. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Li, M.; Hou, J.; Wu, L.; Zhou, J.; Xiang, H. Comparison of four phaC genes from Haloferax mediterranei and their function in different PHBV copolymer biosynthesis in Haloarcula hispanica. Saline Syst. 2010, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legat, A.; Gruber, C.; Zangger, K.; Wanner, G.; Stan-Lotter, H. Identification of polyhydroxyalkanoates in Halococcus and other haloarchaeal species. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.J.; Liao, Y.; Ye, J.; Kuchel, R.P.; Poljak, A.; Raftery, M.J.; Cavicchioli, R. Cold adaptation of the Antarctic haloarchaea Halohasta litchfeldiae and Halorubrum lacusprofundi. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2210–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohme, S.; Hacıosmanoğlu, G.G.; Eroğlu, M.S.; Kasavi, C.; Genç, S.; Can, Z.S.; Oner, E.T. Halomonas smyrnensis as a cell factory for co-production of PHB and levan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amulya, K.; Katakojwala, R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Mohan, S.V. Low carbon biodegradable polymer matrices for sustainable future. Compos. Part C Open Access 2021, 4, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, S.; Keshavarz, T.; Roy, I. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Biodegradable polymers with a range of applications. Journal of chemical technology & biotechnology: International research in process. Environ. Clean Technol. 2007, 82, 233–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, S.; Fatma, T. Cyanobacterial polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB): Screening, optimization and characterization. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, C.; Shakya, P.; Shrestha, R.; Pal, S.; Manandhar, P. Isolation of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) producing bacteria, optimization of culture conditions for PHB production, extraction and characterization of PHB. Nepal J. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzmann, P.D.; Stackebrandt, E.; Sanderson, K.; Volkman, J.K.; Cameron, D.E.; Stevenson, P.L.; Burton, H.R. Halobacterium lacusprofundi sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium isolated from Deep Lake, Antarctica. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1988, 11, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allers, T. Overexpression and purification of halophilic proteins in Haloferax volcanii. Bioeng. Bugs 2010, 1, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran-Reyna, A.; Coker, J.A. The effects of extremes of pH on the growth and transcriptomic profiles of three haloarchaea. F1000Research 2014, 3, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, T. Yield of poly-D (-)-3-hydroxybutyrate from various carbon sources: A theoretical study. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1993, 41, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.-Y.A.; Chen, C.-L.; Li, L.; Ge, L.; Wang, L.; Razaad, I.M.N.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Mo, Y.; Wang, J.-Y. Start research on biopolymer polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): A review. Polymers 2014, 6, 706–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wise, M.J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Hu, J.; Wang, C. Bioinformatics analysis of metabolism pathways of archaeal energy reserves. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, A.; Mitra, A.; Arumugam, M.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Sadhukhan, S.; Ray, A.; Mukherjee, J. Utilization of vinasse for the production of polyhydroxybutyrate by Haloarcula marismortui. Folia Microbiol. 2012, 57, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagagy, N.; Saddiq, A.A.; Tag, H.M.; Abdelgawad, H.; Selim, S. Characterization of bioplastics produced by haloarchaeon Haloarcula sp. strain NRS20 using cost-effective carbon sources. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 105404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, W.N.; Jamil, N.; Ali, I.; Ayaz, M.H.; Hasnain, S. Screening for polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)-producing bacterial strains and comparison of PHA production from various inexpensive carbon sources. Ann. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Greca, L.G.; Xiang, W.; Lehtonen, J.; Huan, S.; Nugroho, R.W.N.; Tardy, B.L.; Rojas, O.J. Adsorption and assembly of cellulosic and lignin colloids at oil/water interfaces. Langmuir 2018, 35, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasirajan, L.; Maupin-Furlow, J.A. Halophilic archaea and their potential to generate renewable fuels and chemicals. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 1066–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pomares, F.; Bautista, V.; Ferrer, J.; Pire, C.; Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Bonete, M.-J.; Marhuenda-Egea, F. α-Amylase activity from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei. Extremophiles 2003, 7, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann-Krauss, C.; Koller, M.; Muhr, A.; Fasl, H.; Stelzer, F.; Braunegg, G. Archaeal Production of Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Co- and Terpolyesters from Biodiesel Industry-Derived By-Products. Archaea 2013, 2013, 129268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, T.M.; Chen, C.W.; Chan, T.H. Preparation and characterization of poly (hydroxyalkanoate) from the fermentation of Haloferax mediterranei. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2006, 17, 1425–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, M.; Hesse, P.; Bona, R.; Kutschera, C.; Atli´c, A.; Braunegg, G. Biosynthesis of high quality polyhydroxyalkanoate Co- And terpolyesters for potential medical application by the archaeon Haloferax mediterranei. Macromol. Symp. 2007, 253, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Han, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, J.; Xiang, H. Genetic and biochemical characterization of the poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) synthase in Haloferax mediterranei. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 4173–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wu, L.P.; Hou, J.; Zhao, D.; Xiang, H. Biosynthesis, characterization, and hemostasis potential of tailor-made poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co3-hydroxyvalerate) produced by Haloferax mediterranei. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Z.; Xue, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, D.H.; Han, J.; Xiang, H. Engineering Haloferax mediterranei as an efficient platform for high level production of lycopene. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgaonkar, B.B.; Bragança, J.M. Biosynthesis of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) by Halogeometricum borinquense strain E3. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 78, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferre-Guell, A.; Winterburn, J. Biosynthesis and characterization of polyhydroxyalkanoates with controlled composition and microstructure. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenjian, A. (Ed.) Fundamentals of Fermentation Media. In Essentials in Fermentation Technology; Springer International Publishing (Learning Materials in Biosciences): New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 41–84. [Google Scholar]
- Taran, M. Utilization of petrochemical wastewater for the production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) by Haloarcula sp. IRU1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wei, X.; Cai, P.; Huang, Q.; Rong, X.; Liang, W. Preferential adsorption of extracellular polymeric substances from bacteria on clay minerals and iron oxide. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 83, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouchane, H.; Najjari, A.; Neifar, M.; Cherif, H.; Askri, R.; Naili, F.; Ouzari, H.I.; Cherif, A. Unravelling the characteristics of a heteropolysaccharide–protein from an Haloarchaeal strain with flocculation effectiveness in heavy metals and dyes removal. Environ. Technol. 2018, 41, 2180–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ortega, M.A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, A.I.; Camacho-Ruíz, R.M.; Córdova, J.; del Rocío López-Cuellar, M.; Chavarría-Hernández, N.; González-García, Y. Physicochemical characterization and emulsifying properties of a novel exopolysaccharide produced by haloarchaeon Haloferax mucosum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Deng, X.; Sun, W.; Hu, L.; Zhong, H.; He, Z.; Xiong, D. Extracellular polymeric substances of acidophilic microorganisms play a crucial role in heavy metal ions adsorption. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 19, 4857–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Zhong, H.; He, Z. Heavy metal ions removed from imitating acid mine drainages with a thermoacidophilic archaea: Acidianus manzaensis YN25. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouchane, H.; Najjari, A.; Cherif, H.; Neifar, M.; Sghaier, H.; Ouzari, H.I.; Cherif, A. Carboxymethylated sulfated heteroexopolysaccharide from a haloarchaeal strain as potential biomolecule for harmless adjuvant therapy in cancer treatment. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 8907958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, L.M. Chemical structural and chain conformational characterization of some bioactive polysaccharides isolated from natural sources. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahnia, M.; Makhdoumi, A.; Mashreghi, M.; Eshghi, H. Exploring the potentials of halophilic prokaryotes from a solar saltern for synthesizing nanoparticles: The case of silver and selenium. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Lv, L.; Chen, J.C.; Chen, G.Q. Controlling microbial PHB synthesis via CRISPRi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 5861–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.Q.; Driscoll, B.T.; Charles, T.C. Requirement for the enzymes acetoacetyl coenzyme A synthetase and poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) synthase for growth of Sinorhizobium meliloti on PHB cycle intermediates. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Santos, M.; Koskimäki, J.J.; Alves, L.P.S.; de Souza, E.M.; Jendrossek, D.; Pirttilä, A.M. The protective role of PHB and its degradation products against stress situations in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 45, fuaa058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaeminck, E.; Quataert, K.; Uitterhaegen, E.; De Winter, K.; Soetaert, W.K. Advanced PHB fermentation strategies with CO2-derived organic acids. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 343, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.M.L.; Lemos, P.C.; Serafim, L.S.; Oliveira, C.; Eiroa, M.; Albuquerque, M.G.E.; Ramos, A.M.; Oliveira, R.; Reis, M.A.M. Recent Advances in Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production by Mixed Aerobic Cultures: From the Substrate to the Final Product. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 885–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdam, B.; Brennan Fournet, M.; McDonald, P.; Mojicevic, M. Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and Factors Impacting Its Chemical and Mechanical Characteristics. Polymers 2020, 12, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvigneau, S.; Dürr, R.; Behrens, J.; Kienle, A. Advanced kinetic modeling of bio-co-polymer poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) production using fructose and propionate as carbon sources. Processes 2021, 9, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.G.E.; Doetsch, R.N.; Robinow, C.F. Determinative and cytological light microscopy. In Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology; Gerhardt, P., Murray, R.G.E., Wood, W.A., Krieg., N.R., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 21–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ventosa, A.; Gutierrez, M.C.; Kamekura, M.; Zvyagintseva, I.S.; Oren, A. Taxonomic study of Halorubrum distributum and proposal of Halorubrum terrestre sp. Int. J. Syst. Evolution Microbiol. 2004, 54, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.M. Wood waste—Carbon source for polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) production Int. J. For. Wood Sci. 2017, 4, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sathiyanarayanan, G.; Bhatia, S.K.; Song, H.S.; Jeon, J.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, Y.; Gand Yang, Y.H. Production and characterization of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer from Arctic psychrotrophic bacterium Pseudomonas sp. PAMC28620. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, S.; Iqbal, S.; Jamil, N. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) production using paper mill wastewater as carbon source in comparison with glucose. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 9, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, S.; Sarkar, B.; Samantaray, D.P.; Daware, A.; Maity, S.; Pattnaik, S.; Bhattacharjee, S. Bioconversion of fish solid waste into PHB using Bacillus subtilis based submerged fermentation process. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Shi, M.; Wang, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J. A parallel-column LC–MS/MS method for high-throughput analysis of eight antiepileptic drugs in clinical therapeutic drug monitoring. Chromatographia 2017, 80, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggers, J.; Steinbüchel, A. Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) degradation in Ralstonia eutropha H16 is mediated stereoselectively to (S)-3-hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A (CoA) via crotonyl-CoA. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 3213–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Strains | |
|---|---|---|
| NRS_35 | NRS_38 | |
| Pigmentation | Red | Orange-red |
| Cell morphology | Pleomorphic | Pleomorphic |
| Motility | + | - |
| NaCl range (%) | 10–35 | 10–35 |
| Temp. range (°C) | 30–65 | 25–45 |
| pH range | 6.0–9.0 | 7.0–9.0 |
| H2S production | - | - |
| Hydrolysis of: | ||
| Gelatin | - | - |
| Casein | - | + |
| Starch | + | + |
| Tween 80 | - | - |
| Carbon sources for growth: | ||
| D-Galactose | - | + |
| DL-Lactate | + | - |
| D-Mannose | + | + |
| Pyruvate | - | + |
| Acetate | + | + |
| Glycine | + | - |
| DNA G+C content (mol%) | 59.0 | 57.0 |
| Carbon Source | Strain NRS_35 (mg/L) | Strain NRS_38 (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Starch | 41.67 ± 2.10 a | 36.63 ± 3.20 a |
| CMC | 11.25 ± 1.08 b | 14.789 ± 1.55 b |
| Sucrose | 10.65 ± 1.03 b | 10.647 ± 1.40 c |
| Glucose | 8.99 ± 0.98 b | 12.587 ± 2.14 b |
| Glycerol | 14.33 ± 1.42 c | 11.458 ± 1.08 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hagagy, N.; Saddiq, A.A.; Tag, H.M.; Selim, S.; AbdElgawad, H.; Martínez-Espinosa, R.M. Characterization of Polyhydroxybutyrate, PHB, Synthesized by Newly Isolated Haloarchaea Halolamina spp. Molecules 2022, 27, 7366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217366
Hagagy N, Saddiq AA, Tag HM, Selim S, AbdElgawad H, Martínez-Espinosa RM. Characterization of Polyhydroxybutyrate, PHB, Synthesized by Newly Isolated Haloarchaea Halolamina spp. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217366
Chicago/Turabian StyleHagagy, Nashwa, Amna A. Saddiq, Hend M. Tag, Samy Selim, Hamada AbdElgawad, and Rosa María Martínez-Espinosa. 2022. "Characterization of Polyhydroxybutyrate, PHB, Synthesized by Newly Isolated Haloarchaea Halolamina spp." Molecules 27, no. 21: 7366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217366
APA StyleHagagy, N., Saddiq, A. A., Tag, H. M., Selim, S., AbdElgawad, H., & Martínez-Espinosa, R. M. (2022). Characterization of Polyhydroxybutyrate, PHB, Synthesized by Newly Isolated Haloarchaea Halolamina spp. Molecules, 27(21), 7366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217366









