Isolation and Identification of Secondary Metabolites Produced by Phytopathogenic Fungus Corynespora cassiicola from Hevea brasiliensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Phytopathogenic Fungal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Spectral and Physical Data of Compounds 1 and 2
3.5. Electronic Circular Dichroism Calculation
3.6. Phytotoxic Assay
3.7. Antimicrobial Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Qi, D.L.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Huang, Y.Q. Current situation of Chinese natural rubber industry and development suggestions. Chin. J. Trop. Agric. 2013, 33, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, T.; Li, B.X.; Feng, Y.L.; Liu, X.B.; Zheng, X.L.; Huang, G.X. Safety assessment of Corynespora leaf fall disease on natural rubber and related industries in China. Chin. J. Trop. Agric. 2019, 39, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.B.; Cai, J.M.; Pan, X.X.; Gao, H.H.; Peng, J.H.; Huang, G.X. Rapid molecular identification and detection of Corynespora cassiicola of Hevea brasiliensis. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2008, 29, 489–493. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.H.; Gou, J.Y.; Zhao, D.L.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Ma, G.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, C.S. Phytotoxicity and anti-phytopathogenic activities of marine-derived fungi and their secondary metabolites. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 37573–37580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Xue, M.Y.; Shen, Z.; Jia, X.W.; Hou, X.W.; Lai, D.W.; Zhou, L.G. Phytotoxic secondary metabolites from fungi. Toxins 2021, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, M.; Aloi, F.; Nocera, P.; Cacciola, S.O.; Surico, G.; Evidente, A. Phytotoxic metabolites isolated from Neufusicoccum batangarum, the causal agent of the scabby canker of cactus pear (Opuntia ficus-indica L.). Toxins 2020, 12, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkkan, M.; Andolfi, A.; Zonno, M.C.; Erper, I.; Perrone, C.; Cimmino, A.; Vurro, M.; Evidente, A. Phytotoxins produced by Pestalotiopsis guepinii, the causal agent of hazelnut twig blight. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2011, 50, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Pedras, M.S.C.; Biesenthal, C.J. Isolation, structure determination, and phytotoxicity of unusual dioxopiperazines from the phytopathogenic fungus Phoma lingam. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 905–909. [Google Scholar]
- Paranagama, P.A.; Wijeratne, E.M.K.; Burns, A.M.; Marron, M.T.; Gunatilaka, M.K.; Arnold, A.E.; Gunatilaka, A.A.L. Heptaketides from Corynespora sp. inhabiting the cavern beard lichen, Usnea cavernosa: First report of metabolites of an endolichenic fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1700–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.L.; Shao, C.L.; Gan, L.S.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.Y. Chromone derivatives from a sponge-derived strain of the fungus Corynespora cassiicola. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, W.; Aly, A.H.; Wray, V.; Proksch, P.; Debbab, A. Unusual octalactones from Corynespora cassiicola, an endophyte of Laguncularia racemose. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 6611–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.X.; Feng, Y.L.; Liu, X.B.; Cai, J.M.; Lu, C.M.; Zheng, X.L.; Huang, G.X. Genetic diversity and pathogenic variability among isolates of Corynespora cassiicola from tropical crops in China. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2019, 40, 2456–2465. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.X.; Yang, Y.; Cai, J.M.; Liu, X.B.; Shi, T.; Li, C.P.; Chen, Y.P.; Xu, P.; Huang, G.X. Genomic characteristics and comparative genomics analysis of two Chinese Corynespora cassiicola strains causing Corynespora leaf fall (CLF) disease. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paguigan, N.D.; Raja, H.A.; Day, C.S.; Oberlies, N.H. Acetophenone derivatives from a freshwater fungal isolate of recently described Lindgomyces madisonensis (G416). Phytochemistry 2016, 126, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.Y.; Song, H.C.; Li, J.H.; Tang, Y.S.; Sun, R.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.P.; Wang, L.M.; Shen, K.Z.; Wang, C.R.; et al. Ymf 1029A-E, Preussomerin analogues from the fresh-water-derived fungus YMF 1.01029. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Gao, J.M.; Chen, H.; Zhang, A.L.; Tang, M. Toxins from a symbiotic fungus, Leptographium qinlingensis associated with Dendroctonus armandi and their in vitro toxicities to Pinus armandi seedlings. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 134, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankawa, U.; Shimada, H.; Sato, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Yamasaki, K. Biosynthesis of scytalone. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 3536–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhang, D.W.; Guo, S.X.; Wang, C.L. Chemical constituents of an endophytic fungus Chaetosphaeronema sp. from Phlomis younghusbandii Mukerjee. Chin. Med. Biotechnol. 2014, 9, 453–456. [Google Scholar]
- Coombe, R.G.; Jacobs, J.J.; Watson, T.R. Constituents of some Curvularia species. Aust. J. Chem. 1968, 21, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Fang, G.Q.; Zheng, J.H.; Guo, D.A.; Kou, J.P.; Duan, Y.P.; Qin, C. Non-anthraquinone constituents from Rheum sublanceolatum C. Y. Cheng et Kao. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2001, 26, 551–553. [Google Scholar]
- Que, D.M.; Dai, H.F.; Huang, G.X.; Dai, W.J.; Mei, W.L. Chemical constituents from the endophytic fungus Rhizoctonia sp. J5 of Antiaris toxicaria. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2009, 21, 424–427. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.C.; Shi, J.G.; He, L. Mono-, bi-, and triphenanthrenes from the tubers of Cremastra appendiculata. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Lee, D.G.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, S.H.; Nam, K.W.; Lee, S. Isolation and identification of phytochemical constituents from the fruits of Acanthopanax senticosus. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 7, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.T.; Wu, W.C.; Zhou, D.D.; Deng, X.L.; Zhang, S.Q.; Yuan, J.Z.; Xu, J.; Guo, Z.K. Bioactive components of two endophytic fungi from Hainan mangrove plants. J. Shenzhen Univ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 39, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.F.; Li, X. Detection method of inoculation on Citrus leaves in vitro with Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2000, 19, 421–423. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.W.; Xu, B.G.; Wang, J.Y.; Su, Z.Z.; Lin, F.C.; Zhang, C.L.; Kubicek, C.P. Bioactive metabolites from Phoma species, an endophytic fungus from the Chinese medicinal plant Arisaema erubescens. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2012, 93, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwada, Y.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Studies on Rhubarb (Rhei Rhizoma). VI. Isolation and characterization of stilbenes. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1984, 32, 3501–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.Y.; Sun, C.E.; Hua, W.S. The synthesis of p-hydroxyphenylethyl alcohol. Chin. J. Syn. Chem. 2002, 10, 481–484. [Google Scholar]
- Cafieri, F.; Fattorusso, E.; Gavagnin, M.; Santacroce, C. 3β,5α,6β-Trihydroxysterols from the Mediterranean bryozoan Myriapora truncata. J. Nat. Prod. 1985, 48, 944–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
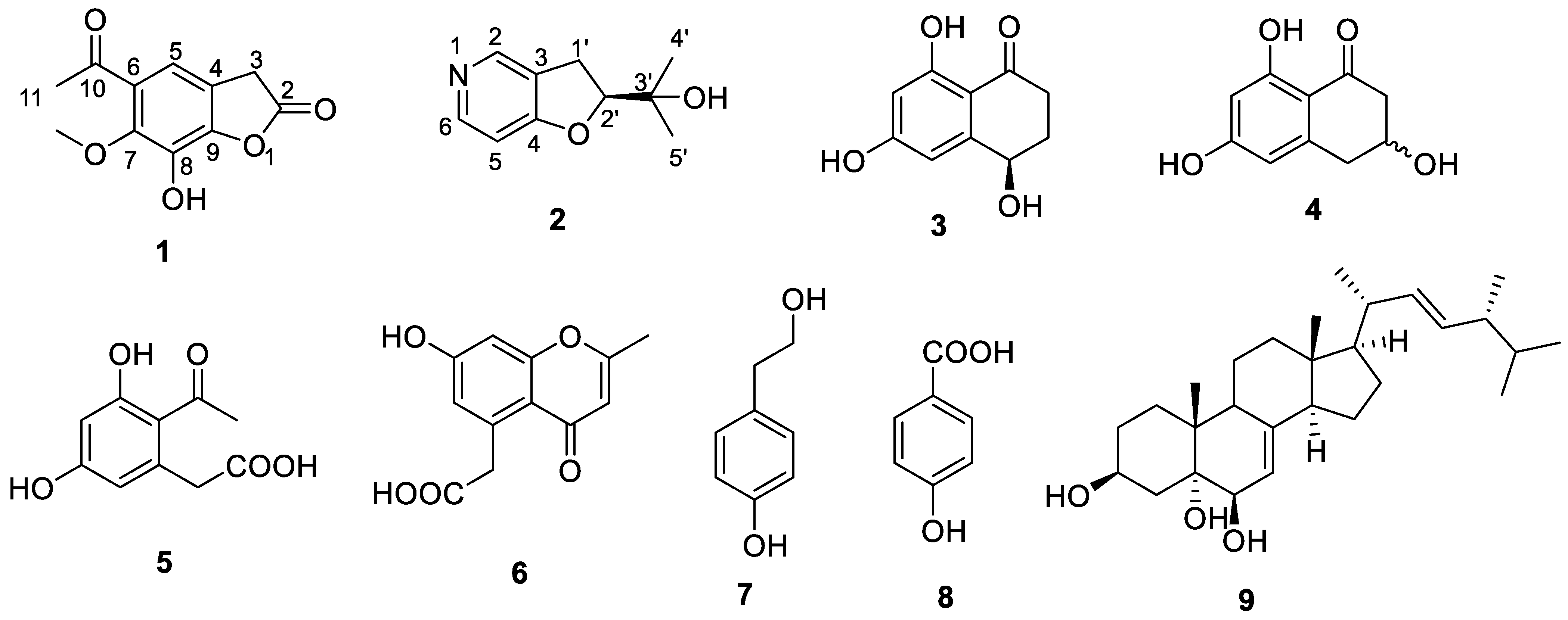

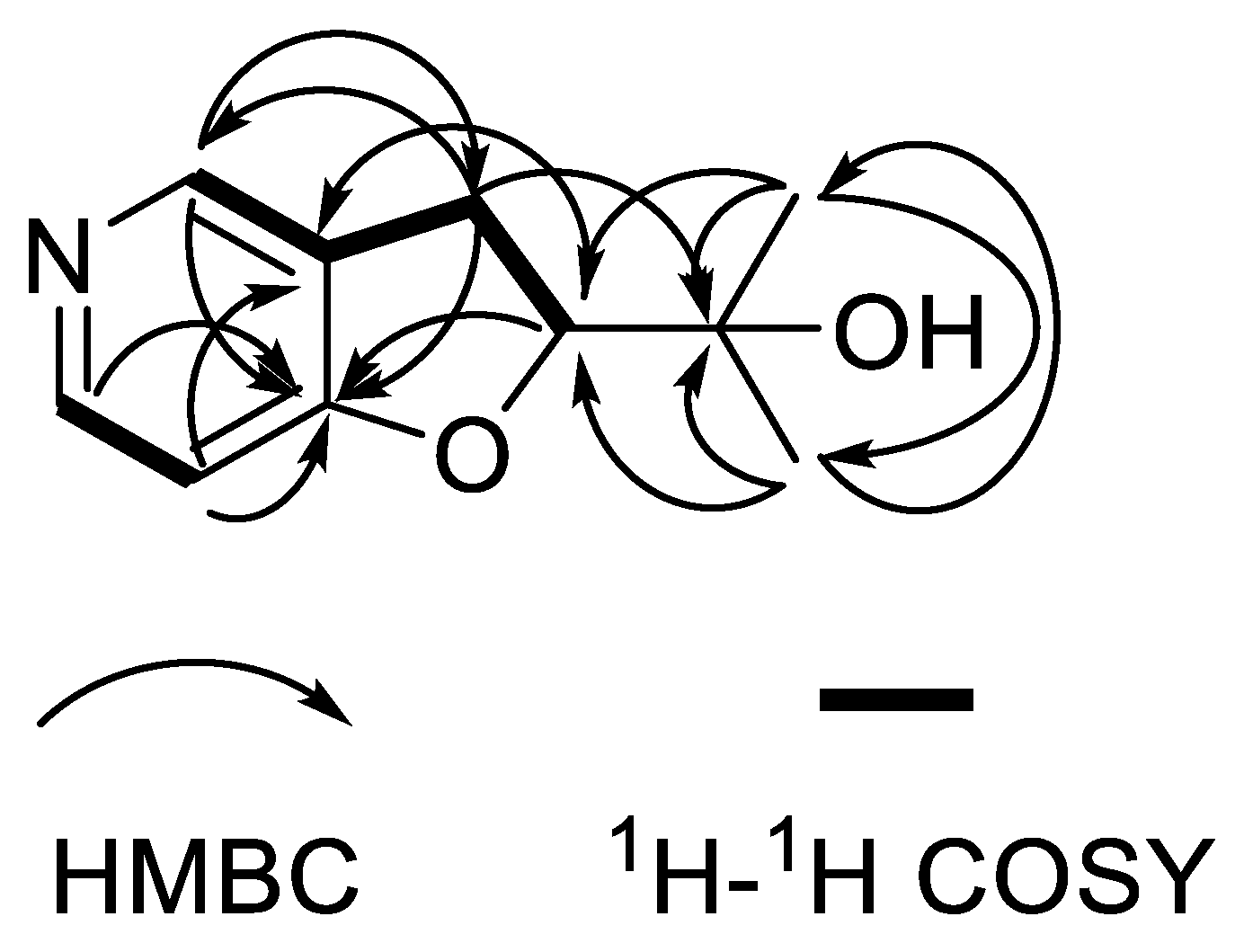
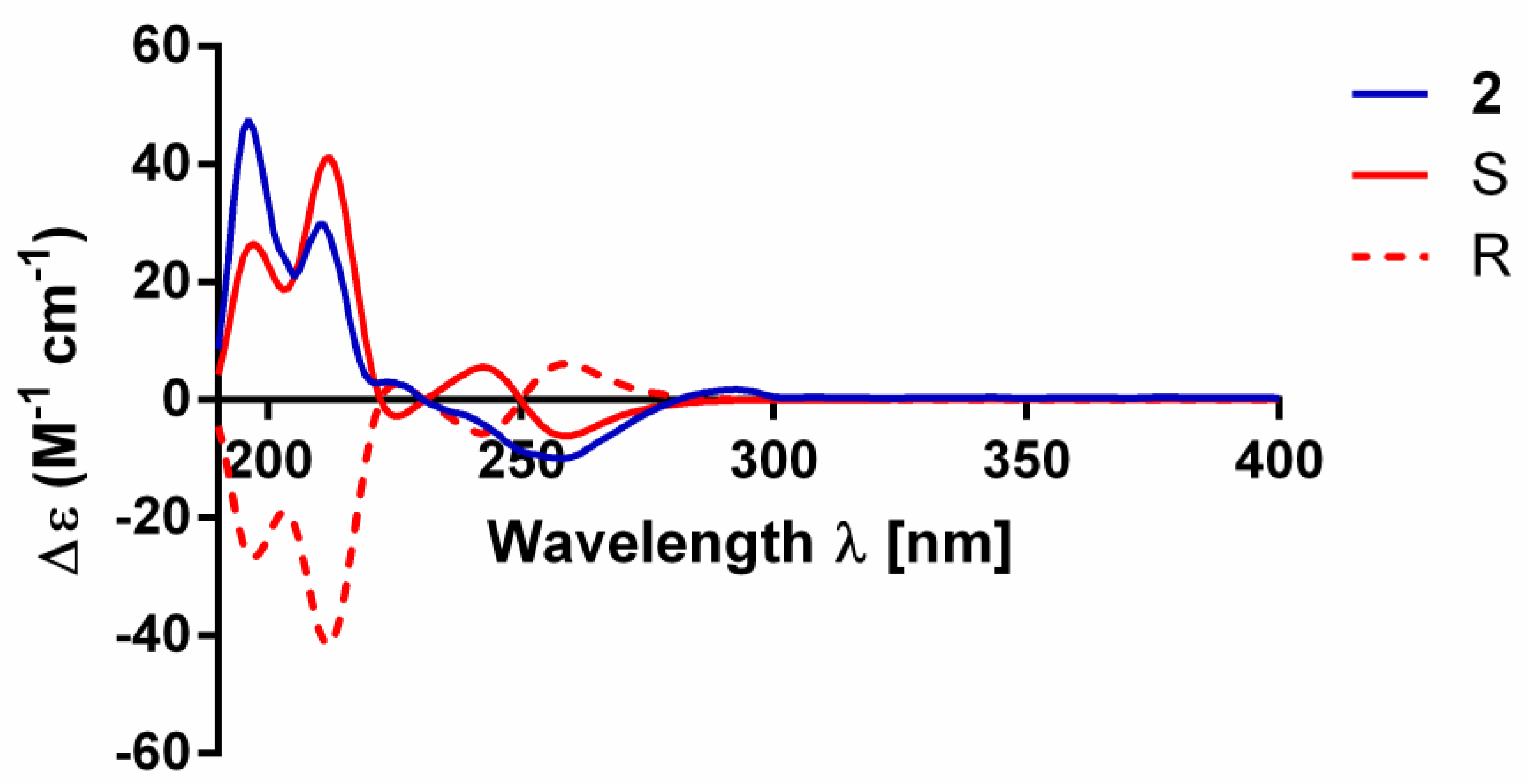
| Position | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Type |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 172.5, C | |
| 3 | 3.45, s | 38.7, CH2 |
| 4 | 129.4, C | |
| 5 | 6.24, s | 111.0, CH |
| 6 | 120.5, C | |
| 7 | 134.1, C | |
| 8 | 150.2, C | |
| 8-OH | 9.51, br s | |
| 9 | 151.8, C | |
| 10 | 202.2, C | |
| 11 | 2.39, s | 31.9, CH3 |
| 7-OCH3 | 3.69, s | 60.0, CH3 |
| Position | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Type |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 7.79, s | 127.5, CH |
| 3 | 128.2, C | |
| 4 | 163.8, C | |
| 5 | 6.69, d (8.2) | 108.9, CH |
| 6 | 7.77, d (7.7) | 131.4, CH |
| 1′ | 3.17, dd (8.9, 4.5) | 31.1, CH2 |
| 2′ | 4.63, t (8.8) | 91.1, CH |
| 3′ | 72.5, C | |
| 4′ | 1.25, s | 25.1, CH3 |
| 5′ | 1.22, s | 25.3, CH3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Abulaizi, A.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Huang, G. Isolation and Identification of Secondary Metabolites Produced by Phytopathogenic Fungus Corynespora cassiicola from Hevea brasiliensis. Molecules 2022, 27, 7360. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217360
Yang X, Guo Z, Yang Y, Abulaizi A, Xiong Z, Zhang S, Li B, Huang G. Isolation and Identification of Secondary Metabolites Produced by Phytopathogenic Fungus Corynespora cassiicola from Hevea brasiliensis. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7360. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217360
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaoyan, Zhikai Guo, Yang Yang, Ailiman Abulaizi, Zijun Xiong, Shiqing Zhang, Boxun Li, and Guixiu Huang. 2022. "Isolation and Identification of Secondary Metabolites Produced by Phytopathogenic Fungus Corynespora cassiicola from Hevea brasiliensis" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7360. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217360
APA StyleYang, X., Guo, Z., Yang, Y., Abulaizi, A., Xiong, Z., Zhang, S., Li, B., & Huang, G. (2022). Isolation and Identification of Secondary Metabolites Produced by Phytopathogenic Fungus Corynespora cassiicola from Hevea brasiliensis. Molecules, 27(21), 7360. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217360






