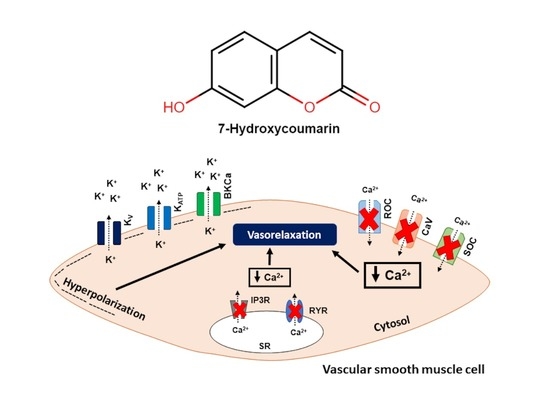
7-Hydroxycoumarin Induces Vasorelaxation in Animals with Essential Hypertension: Focus on Potassium Channels and Intracellular Ca2+ Mobilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
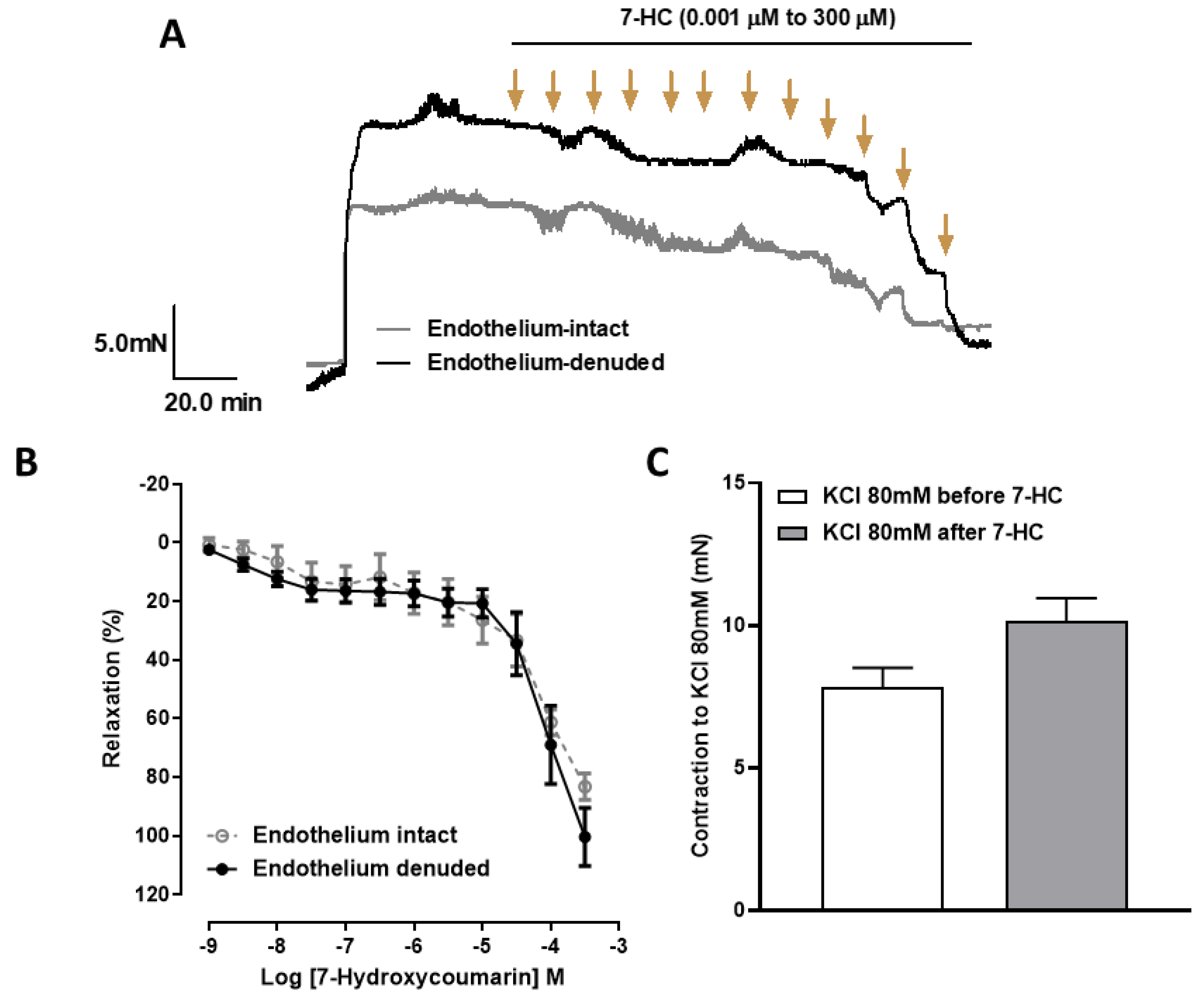
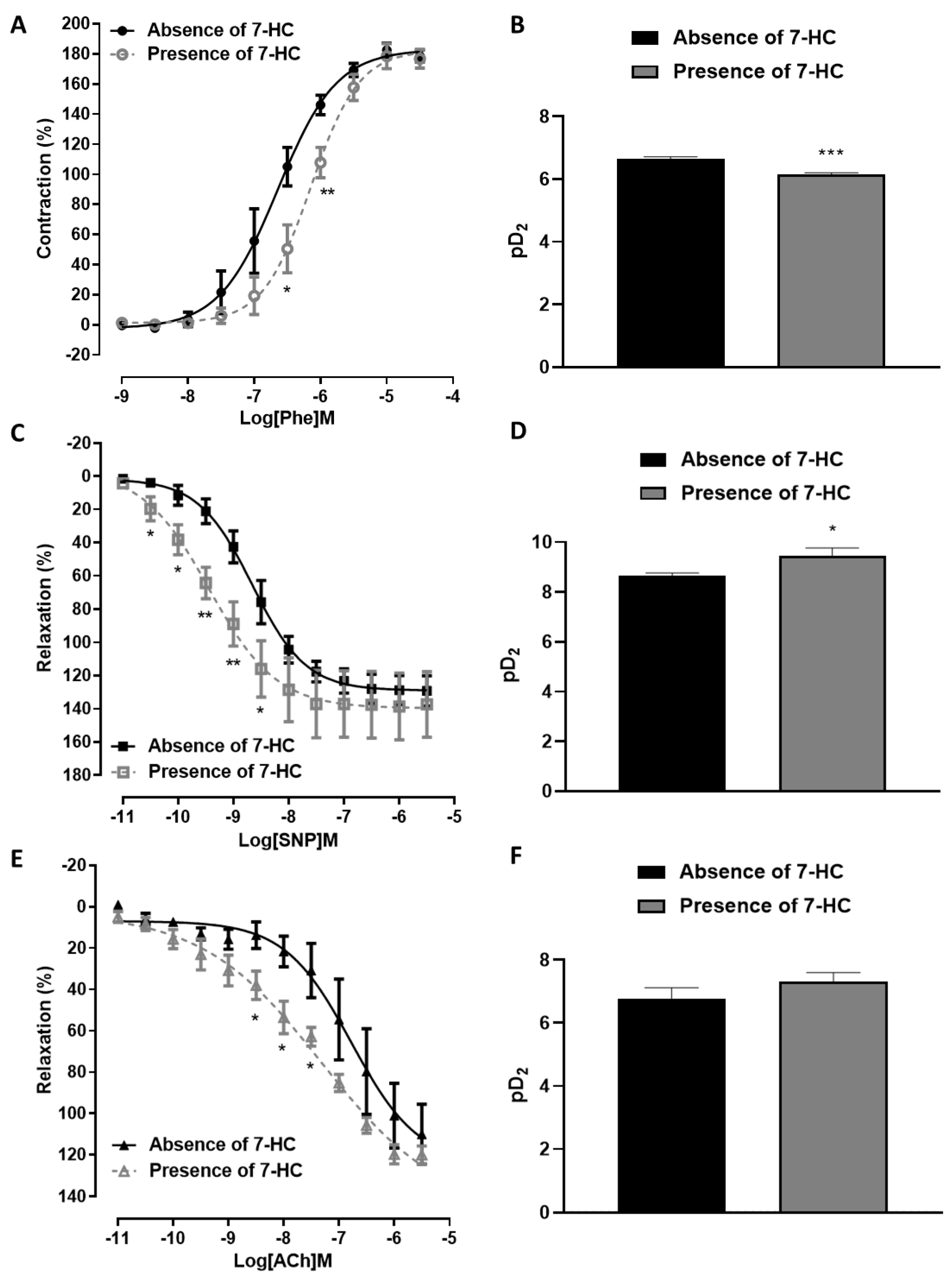
2.1. 7-HC Induces Endothelium-Independent-Relaxation in the Mesenteric Artery in Hypertensive Rats
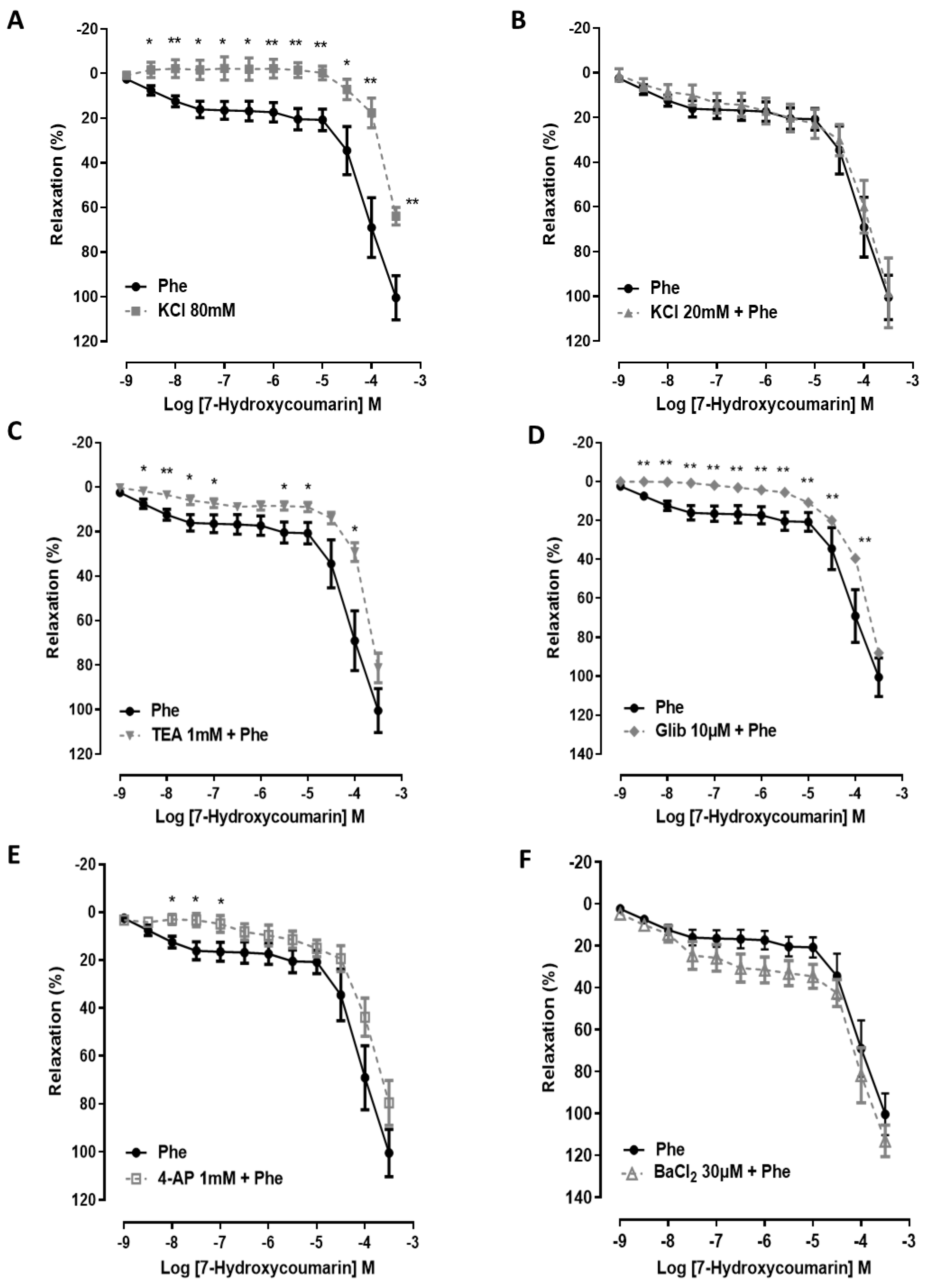
2.2. The Vasorelaxation Induced by 7-HC Involves K+ Channel Activation in Hypertensive Rats
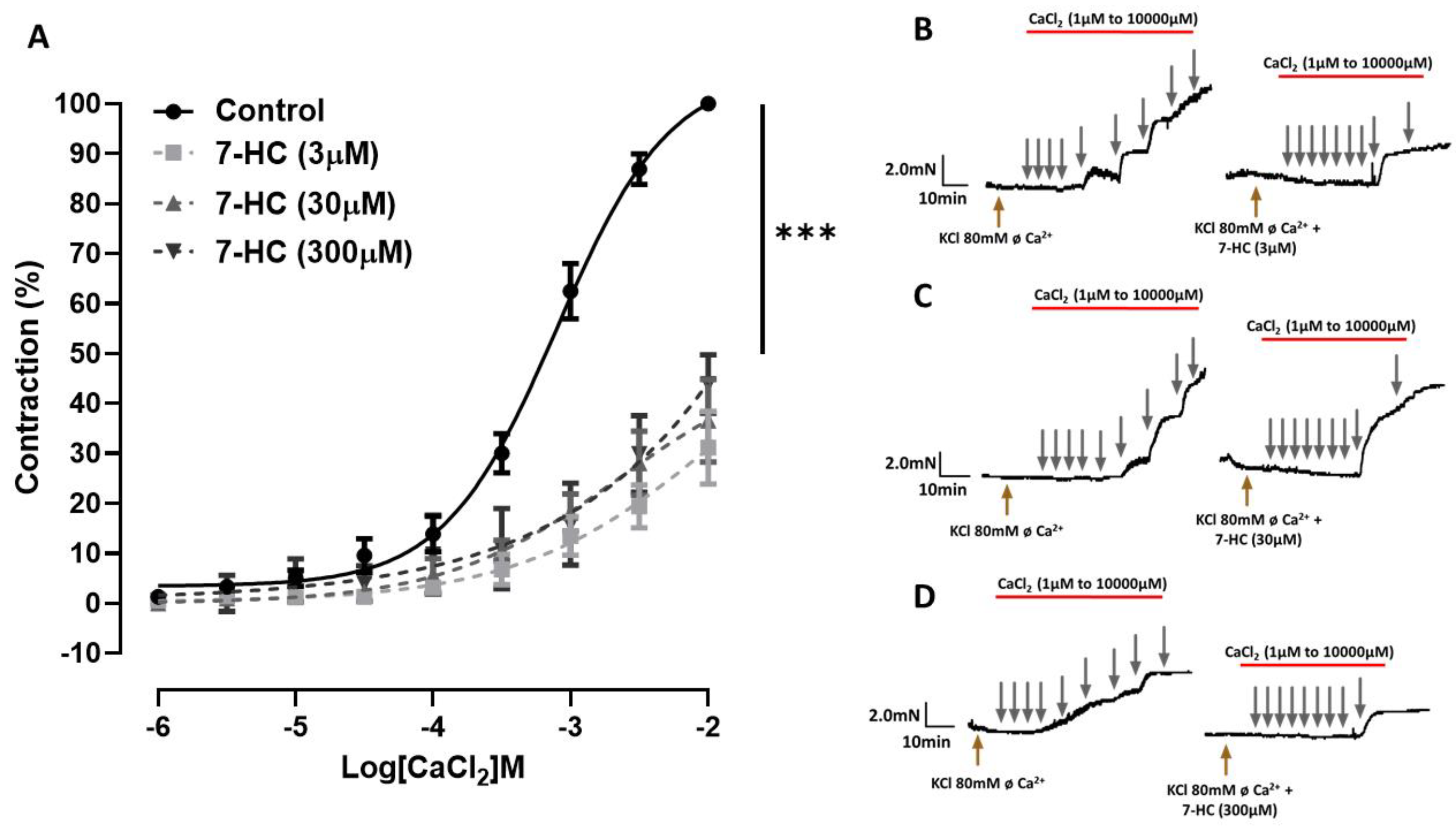
2.3. Effect of 7-HC on the CaCl2-Induced Concentration–Response Curves
2.4. Effect of Store-Operated Calcium Entry (SOCE) Inhibition on the Relaxation Induced by 7-HC in Hypertensive Rats
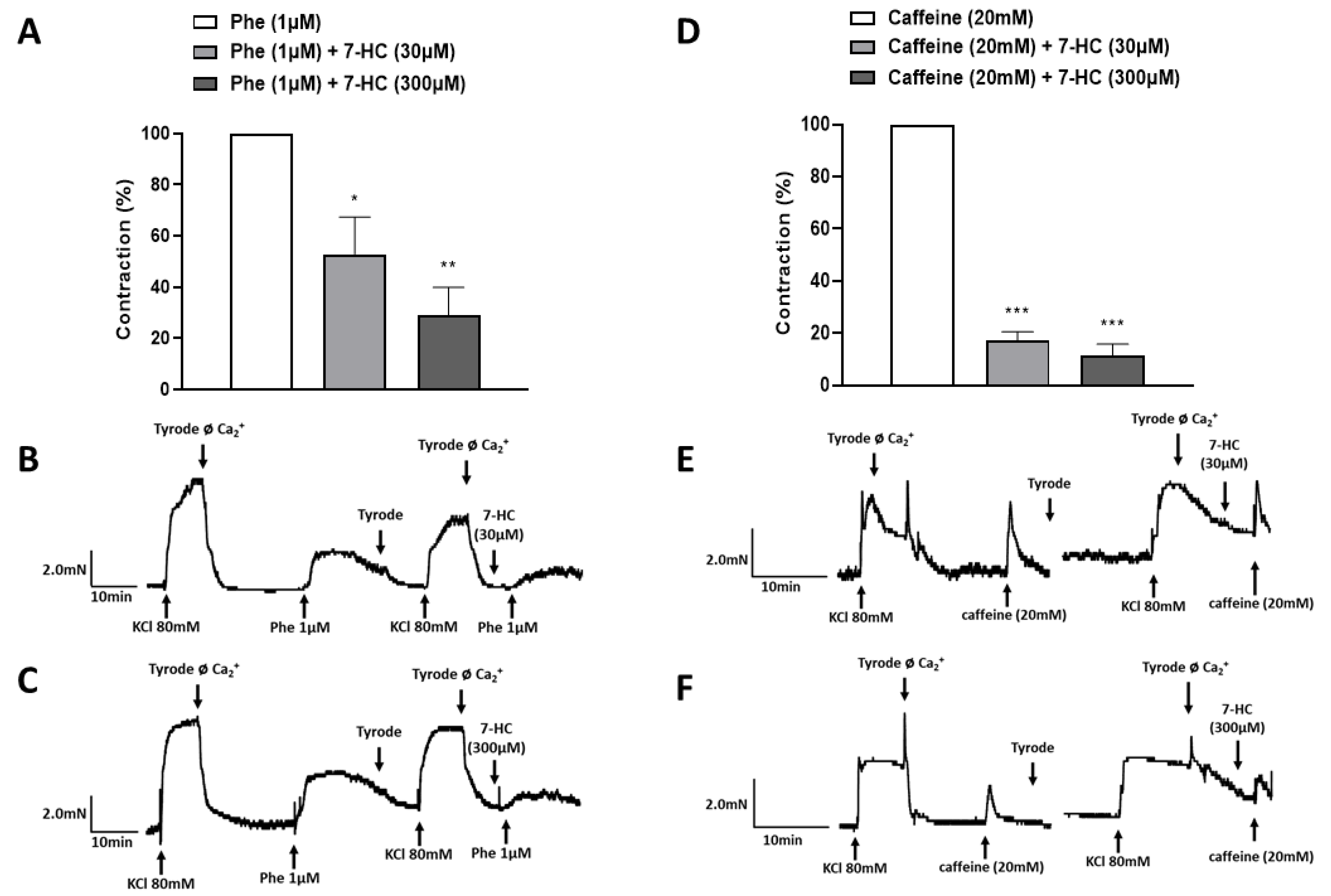
2.5. Effect of 7-HC on the Mobilization of Calcium from Intracellular Stores
2.6. Influence of 7-HC Pre-Incubation on Vascular Reactivity in Hypertensive Rats
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs and Solutions
4.3. Isolation of the Superior Mesenteric Arteries
4.4. Effect of 7-HC on the Vasculature
4.5. Evaluation of K+ Channel Activity in the 7-HC-Induced Vasorelaxation Response
4.6. Investigation of the Effects Induced by 7-HC in Ca2+ Influx
4.7. Investigation of 7-HC-Induced Mobilization of Calcium from Intracellular Stores
4.8. Influence of 7-HC on the Vascular Reactivity in Hypertensive Rats
4.9. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2017 Risk Factor Collaborators. Global, Regional, and National Comparative Risk Assessment of 84 Behavioural, Environmental and Occupational, and Metabolic Risks or Clusters of Risks for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Stu. Lancet 2018, 392, 1923–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, T.; Borghi, C.; Charchar, F.; Khan, N.A.; Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Ramirez, A.; Schlaich, M.; Stergiou, G.S.; Tomaszewski, M.; et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1334–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Ghorani, H.; Götzinger, F.; Böhm, M.; Mahfoud, F. Arterial Hypertension—Clinical Trials Update 2021. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acelajado, M.C.; Hughes, Z.H.; Oparil, S.; Calhoun, D.A. Treatment of Resistant and Refractory Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, R.M.; Calhoun, D.A.; Bakris, G.L.; Brook, R.D.; Daugherty, S.L.; Dennison-Himmelfarb, C.R.; Egan, B.M.; Flack, J.M.; Gidding, S.S.; Judd, E.; et al. Resistant Hypertension: Detection, Evaluation, and Management: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2018, 72, E53–E90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamirault, G.; Artifoni, M.; Daniel, M.; Barber-Chamoux, N. Nantes University Hospital Working Group On Hypertension Resistant Hypertension: Novel Insights. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2020, 16, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikrishna, D.; Godugu, C.; Dubey, P.K. A Review on Pharmacological Properties of Coumarins. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 113–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-Y.; Zhang, W.; He, L.-C.; Cao, Y.-X. Imperatorin Induces Vasodilatation Possibly via Inhibiting Voltage Dependent Calcium Channel and Receptor-Mediated Ca2+ Influx and Release. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 573, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najmanová, I.; Doseděl, M.; Hrdina, R.; Anzenbacher, P.; Filipský, T.; Říha, M.; Mladěnka, P. Cardiovascular Effects of Coumarins besides Their Antioxidant Activity. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 830–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.J.; Romero, M.A.; Silva, M.S.; Silva, B.A.; Medeiros, I.A. Intracellular Calcium Mobilization as a Target for the Spasmolytic Action of Scopoletin. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida Barros, T.A.; de Freitas, L.A.R.; Filho, J.M.B.; Nunes, X.P.; Giulietti, A.M.; de Souza, G.E.; dos Santos, R.R.; Soares, M.B.P.; Villarreal, C.F. Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of 7-Hydroxycoumarin in Experimental Animal Models: Potential Therapeutic for the Control of Inflammatory Chronic Pain. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Araújo, R.S.A.; Guerra, F.Q.S.; de Lima, E.O.; de Simone, C.A.; Tavares, J.F.; Scotti, L.; Scotti, M.T.; de Aquino, T.M.; de Moura, R.O.; Mendonça, F.J.B.; et al. Synthesis, Structure-Activity Relationships (SAR) and in Silico Studies of Coumarin Derivatives with Antifungal Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1293–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, N.; Zhang, J.; Ma, S.; Zhao, Z.; Ellis, E.M. Hepatoprotective Effect of 7-Hydroxycoumarin against Methyl Glyoxal Toxicity via Activation of Nrf2. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 276, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, F.O.; Nonato, F.R.; Couto, R.D.; Barbosa Filho, J.M.; Nunes, X.P.; Ribeiro dos Santos, R.; Soares, M.B.P.; Villarreal, C.F. Mechanisms Involved in the Antinociceptive Effects of 7-Hydroxycoumarin. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccard, N.; Mechiche, H.; Nazeyrollas, P.; Manot, L.; Lamiable, D.; Devillier, P.; Millart, H. Effects of 7-Hydroxycoumarin (Umbelliferone) on Isolated Perfused and Ischemic-Reperfused Rat Heart. Arzneimittelforschung 2000, 50, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesh, G.S.; Nagoor Meeran, M.F.; Selvaraj, P. Protective Effects of 7-Hydroxycoumarin on Dyslipidemia and Cardiac Hypertrophy in Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarction in Rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2016, 30, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, Q.L.; dos Anjos Moraes, R.; Froes, T.Q.; Castilho, M.S.; de Araújo, R.S.A.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Meira, C.S.; Pereira Soares, M.B.; Silva, D.F. Inhibition of Intracellular Ca2+ Mobilization and Potassium Channels Activation Are Involved in the Vasorelaxation Induced by 7-Hydroxycoumarin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 887, 173525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayet, J.; Hughes, A. Cardiac and Vascular Pathophysiology in Hypertension. Heart 2003, 89, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhoutte, P.M.; Shimokawa, H.; Feletou, M.; Tang, E.H.C. Endothelial Dysfunction and Vascular Disease—A 30th Anniversary Update. Acta Physiol. 2017, 219, 22–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Qu, J.; He, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Y. Calcium in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Elasticity and Adhesion: Novel Insights Into the Mechanism of Action. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.S.; Jesus, R.L.C.; Simões, L.O.; Vasconcelos, W.P.; Medeiros, I.A.; Veras, R.C.; Casais-E-Silva, L.L.; Silva, D.F. NO Production and Potassium Channels Activation Induced by Crotalus Durissus Cascavella Underlie Mesenteric Artery Relaxation. Toxicon 2017, 133, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, R.D.A.; Alves, Q.L.; Camargo, S.B.; de Azevedo Medeiros, C.F.; de Melo Jesus, A.; da Hora, V.R.S.; Stiz, D.S.; Corrêa, R.; Cechinel-Filho, V.; Silva, D.F. Itaconimides Derivatives Induce Relaxation in Mesenteric Artery and Negative Inotropism by Inhibition of CA2+ Influx. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 72, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.F.; de Figueiredo, G.F.; Pedro, L.P.; Amorin, Y.M.; Andrade, J.T.; Passos, T.F.; Rodrigues, F.F.; Souza, I.L.A.; Gonçalves, T.P.R.; Dos Santos Lima, L.A.R.; et al. Umbelliferone (7-Hydroxycoumarin): A Non-Toxic Antidiarrheal and Antiulcerogenic Coumarin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.T.; Quayle, J.M. Physiological Roles and Properties of Potassium Channels in Arterial Smooth Muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 268, C799–C822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondéjar-Parreño, G.; Cogolludo, A.; Perez-Vizcaino, F. Potassium (K+) Channels in the Pulmonary Vasculature: Implications in Pulmonary Hypertension Physiological, Pathophysiological and Pharmacological Regulation. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 225, 107835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Horst, J.; Manville, R.W.; Hayes, K.; Thomsen, M.B.; Abbott, G.W.; Jepps, T.A. Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) Metabolites Induce Vasodilation and Hypotension by Activating Kv7 Potassium Channels Directly and Indirectly. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, R.H. Changes in the Expression and Function of Arterial Potassium Channels during Hypertension. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2002, 38, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratz, I.N.; Swafford, A.N.; Kanagy, N.L.; Dick, G.M. Reduced Functional Expression of K+ Channels in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells from Rats Made Hypertensive with N{omega}-Nitro-L-Arginine. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H1284–H1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.H.; Lozinskaya, I.; Dietz, N.J. Differences in K+ Current Components in Mesenteric Artery Myocytes from WKY and SHR. Am. J. Hypertens. 2001, 14, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieves-Cintrón, M.; Syed, A.U.; Nystoriak, M.A.; Navedo, M.F. Regulation of Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels in Vascular Smooth Muscle during Hypertension and Metabolic Disorders. Microcirculation 2018, 25, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Igarashi, T.; Kaneko, H.; Yamaki, F.; Mochizuki, Y.; Aida, M.; Taniguchi, H.; Tanaka, H.; Shigenobu, K. NO-Mediated MaxiK(Ca) Channel Activation Produces Relaxation of Guinea Pig Aorta Independently of Voltage-Dependent L-Type Ca2+ Channels. Gen. Pharmacol. 2000, 34, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellman, G.C. Ion Channels and Calcium Signaling in Cerebral Arteries Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurol. Res. 2006, 28, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisheri, K.D.; Cipkus, L.A.; Taylor, C.J. Mechanism of Action of Minoxidil Sulfate-Induced Vasodilation: A Role for Increased K+ Permeability. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1988, 245, 751–760. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E.; Boesgaard, S.; Aldershvile, J. K+ Channel Opening: A New Drug Principle in Cardiovascular Medicine. Heart 1996, 76, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.-J.; Zuo, J.; Lee, R.M.K.W.; Janssen, L.J. Alteration of Arterial Smooth Muscle Potassium Channel Composition and BKCa Current Modulation in Hypertension. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 514, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajada, S.; Cidad, P.; Moreno-Domínguez, A.; Pérez-García, M.T.; López-López, J.R. High Blood Pressure Associates with the Remodelling of Inward Rectifier K+ Channels in Mice Mesenteric Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 6075–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.A.; Yang, Y.; Ella, S.R.; Davis, M.J.; Braun, A.P. Large Conductance, Ca2+-Activated K+ Channels (BKCa) and Arteriolar Myogenic Signaling. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hajj, H.; Chandrasekhar, B.; Kadavil, E.A.; Oriowo, M.A. Interaction of BKCa Channel Modulators with Adrenergic Agonists in the Rat Aorta Is Influenced by Receptor Reserve. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2004, 41, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, K.; Rummery, N.M.; Grayson, T.H.; Hill, C.E. Attenuation of Conducted Vasodilatation in Rat Mesenteric Arteries during Hypertension: Role of Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels. J. Physiol. 2004, 561, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.G. Hypertension and Vascular Aging. Korean Circ. J. 2006, 36, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajada, S.; Cidad, P.; Colinas, O.; Santana, L.F.; López-López, J.R.; Pérez-García, M.T. Down-Regulation of CaV1.2 Channels during Hypertension: How Fewer CaV1.2 Channels Allow More Ca2+ into Hypertensive Arterial Smooth Muscle. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 6175–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.H.; Rusch, N.J. New Expression Profiles of Voltage-Gated Ion Channels in Arteries Exposed to High Blood Pressure. Microcirculation 2002, 9, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, P.-Y.; Cheng, J.; Mao, L.; Wen, J.; Tan, X.-Q.; Liu, Z.-F.; Zeng, X.-R. Function of BKCa Channels Is Reduced in Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells from Han Chinese Patients with Hypertension. Hypertension 2013, 61, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Shi, L. BKCa Channel Activity and Vascular Contractility Alterations with Hypertension and Aging via Β1 Subunit Promoter Methylation in Mesenteric Arteries. Hypertens. Res. 2018, 41, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühler, F.R.; Bolli, P.; Erne, P.; Kiowski, W.; Müller, F.B.; Hulthén, U.L.; Ji, B.H. Position of Calcium Antagonists in Antihypertensive Therapy. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1985, 7, S21-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, C. Joint National Committee JNC8 Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension in Adults. Am. Fam. Physician 2014, 90, 503–504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iversen, B.M.; Arendshorst, W.J. Exaggerated Ca2+ Signaling in Preglomerular Arteriolar Smooth Muscle Cells of Genetically Hypertensive Rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, F260–F270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabet, F.; Savoia, C.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Touyz, R.M. Differential Calcium Regulation by Hydrogen Peroxide and Superoxide in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells from Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2004, 44, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, P.F.; Bonnet, S.; Ludwig, L.M.; Bonnet, P.; Rusch, N.J. Upregulation of L-Type Ca2+ Channels in Mesenteric and Skeletal Arteries of SHR. Hypertension 2002, 40, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potje, S.R.; Isbatan, A.; Tostes, R.C.; Bendhack, L.M.; Dull, R.O.; Carvalho-de-Souza, J.L.; Chignalia, A.Z. Glypican 1 and Syndecan 1 Differently Regulate Noradrenergic Hypertension Development: Focus on IP3R and Calcium. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 172, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.-J.; Zhang, L.-F.; Ma, J.; Cheng, H.-W. Functional Alterations in Cerebrovascular K+ and Ca2+ Channels Are Comparable between Simulated Microgravity Rat and SHR. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H1265–H1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohya, Y.; Tsuchihashi, T.; Kagiyama, S.; Abe, I.; Fujishima, M. Single L-Type Calcium Channels in Smooth Muscle Cells from Resistance Arteries of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Hypertension 1998, 31, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, F.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, F.; Shi, L. Epigenetic Regulation of L-Type Voltage-Gated Ca2+ Channels in Mesenteric Arteries of Aging Hypertensive Rats. Hypertens. Res. 2017, 40, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozinskaya, I.M.; Cox, R.H. Effects of Age on Ca2+ Currents in Small Mesenteric Artery Myocytes from Wistar-Kyoto and Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Hypertension 1997, 29, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, F.P.; Yung, L.M.; Yao, X.; Laher, I.; Huang, Y. Store-Operated Calcium Entry in Vascular Smooth Muscle. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellner, S.K.; Arendshorst, W.J. Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry Is Exaggerated in Fresh Preglomerular Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells of SHR. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 2132–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leijten, P.A.; van Breemen, C. The Effects of Caffeine on the Noradrenaline-Sensitive Calcium Store in Rabbit Aorta. J. Physiol. 1984, 357, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.M.; Taylor, C.W. IP3 Receptors—Lessons from Analyses Ex Cellula. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 132, 222463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziolkowski, N.; Grover, A.K. Functional Linkage as a Direction for Studies in Oxidative Stress: Alpha-Adrenergic Receptors. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 88, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konukoglu, D.; Uzun, H. Endothelial Dysfunction and Hypertension. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 956, 511–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, G.J.; Ding, H.; Lovren, F.; Kubes, P.; Triggle, C.R. Acetylcholine-Induced Relaxation of Peripheral Arteries Isolated from Mice Lacking Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 128, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comerma-Steffensen, S.; Risso, A.; Ascanio-Evanoff, E.; Zerpa, H. Endothelium-Dependent Relaxation Mechanisms Involve Nitric Oxide and Prostanoids in the Isolated Bovine Digital Vein. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 42, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Jiang, J.; Xia, J.; Jiang, R. Icariin Improves SHR Erectile Function via Inhibiting ENOS Uncoupling. Andrologia 2018, 50, e13084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Youn, J.-Y.; Cai, H. Mechanisms and Consequences of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Dysfunction in Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.I.; Andrews, K.L.; Jefferis, A.; Jennings, G.L.; Sampson, A.K.; Chin-Dusting, J.P.F. Vascular Dysfunction in the Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat Is Dependent on Constrictor Prostanoid Activity and Y Chromosome Lineage. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potje, S.R.; Grando, M.D.; Chignalia, A.Z.; Antoniali, C.; Bendhack, L.M. Reduced Caveolae Density in Arteries of SHR Contributes to Endothelial Dysfunction and ROS Production. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, J.A. Endothelial Function. Circulation 2011, 124, e108–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielis, J.F.; Quirynen, L.; Briedé, J.J.; Roelant, E.; Cos, P.; Van Schil, P.E.Y. Pathogenetic Role of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Uncoupling during Lung Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 52, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touyz, R.M.; Schiffrin, E.L. Role of Calcium Influx and Intracellular Calcium Stores in Angiotensin II-Mediated Calcium Hyper-Responsiveness in Smooth Muscle from Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. J. Hypertens. 1997, 15, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.C.; Reckelhoff, J.F. State-of-the-Art Lecture. Role of Angiotensin and Oxidative Stress in Essential Hypertension. Hypertension 1999, 34, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernanz, R.; Martínez-Revelles, S.; Palacios, R.; Martín, A.; Cachofeiro, V.; Aguado, A.; García-Redondo, L.; Barrús, M.T.; de Batista, P.R.; Briones, A.M.; et al. Toll-like Receptor 4 Contributes to Vascular Remodelling and Endothelial Dysfunction in Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3159–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoutte, P.M.; Feletou, M.; Taddei, S. Endothelium-Dependent Contractions in Hypertension. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 144, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Leung, S.W.S.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Man, R.Y.K. Wy14643 Improves Vascular Function in the Aorta of the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat Mainly by Activating Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors Alpha. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 696, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.F.; Araújo, I.G.A.; Albuquerque, J.G.F.; Porto, D.L.; Dias, K.L.G.; Cavalcante, K.V.M.; Veras, R.C.; Nunes, X.P.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Araújo, D.A.M.; et al. Rotundifolone-Induced Relaxation Is Mediated by BK(Ca) Channel Activation and Ca(v) Channel Inactivation. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 109, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langton, P.D.; Nelson, M.T.; Huang, Y.; Standen, N.B. Block of Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels in Mammalian Arterial Myocytes by Tetraethylammonium Ions. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 260, H927–H934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-P.; Zang, W.-J.; Kong, S.-S.; Yu, X.-J.; Sun, L.; Zhao, X.-F.; Wang, S.-X.; Zheng, X.-H. Vasorelaxant Effect of Isopropyl 3-(3, 4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-Hydroxypropanoate, a Novel Metabolite from Salvia Miltiorrhiza, on Isolated Rat Mesenteric Artery. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 579, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, A.; Kubo, S.; Nakaya, Y.; Ishiki, T.; Kuroda, R.; Sekiguchi, F.; Kawao, N.; Nishikawa, H. Distinct Roles for Protease-Activated Receptors 1 and 2 in Vasomotor Modulation in Rat Superior Mesenteric Artery. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 61, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insuk, S.O.; Chae, M.R.; Choi, J.W.; Yang, D.K.; Sim, J.H.; Lee, S.W. Molecular Basis and Characteristics of KATP Channel in Human Corporal Smooth Muscle Cells. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2003, 15, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sakata, K.; Karaki, H. Effects of a Novel Smooth Muscle Relaxant, KT-362, on Contraction and Cytosolic Ca2+ Level in the Rat Aorta. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1991, 102, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jesus, R.L.C.; Silva, I.L.P.; Araújo, F.A.; Moraes, R.A.; Silva, L.B.; Brito, D.S.; Lima, G.B.C.; Alves, Q.L.; Silva, D.F. 7-Hydroxycoumarin Induces Vasorelaxation in Animals with Essential Hypertension: Focus on Potassium Channels and Intracellular Ca2+ Mobilization. Molecules 2022, 27, 7324. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217324
Jesus RLC, Silva ILP, Araújo FA, Moraes RA, Silva LB, Brito DS, Lima GBC, Alves QL, Silva DF. 7-Hydroxycoumarin Induces Vasorelaxation in Animals with Essential Hypertension: Focus on Potassium Channels and Intracellular Ca2+ Mobilization. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7324. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217324
Chicago/Turabian StyleJesus, Rafael L. C., Isnar L. P. Silva, Fênix A. Araújo, Raiana A. Moraes, Liliane B. Silva, Daniele S. Brito, Gabriela B. C. Lima, Quiara L. Alves, and Darizy F. Silva. 2022. "7-Hydroxycoumarin Induces Vasorelaxation in Animals with Essential Hypertension: Focus on Potassium Channels and Intracellular Ca2+ Mobilization" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7324. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217324
APA StyleJesus, R. L. C., Silva, I. L. P., Araújo, F. A., Moraes, R. A., Silva, L. B., Brito, D. S., Lima, G. B. C., Alves, Q. L., & Silva, D. F. (2022). 7-Hydroxycoumarin Induces Vasorelaxation in Animals with Essential Hypertension: Focus on Potassium Channels and Intracellular Ca2+ Mobilization. Molecules, 27(21), 7324. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217324