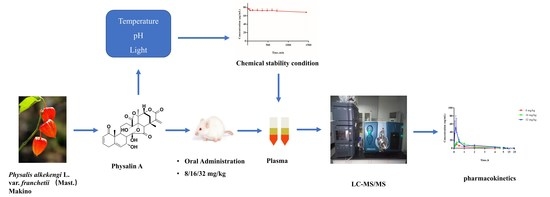
A Rapid and Sensitive LC−MS/MS Method for the Quantitation of Physalin A with Special Consideration to Chemical Stability in Rat Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Investigation of the Chemical Stability of Physalin A
2.2. Method Development
2.3. Method Validation
2.3.1. Selectivity
2.3.2. Linearity of Calibration Curve and LLOQ
2.3.3. Precision and Accuracy
2.3.4. Extraction Recovery and Matrix Effect
2.3.5. Stability
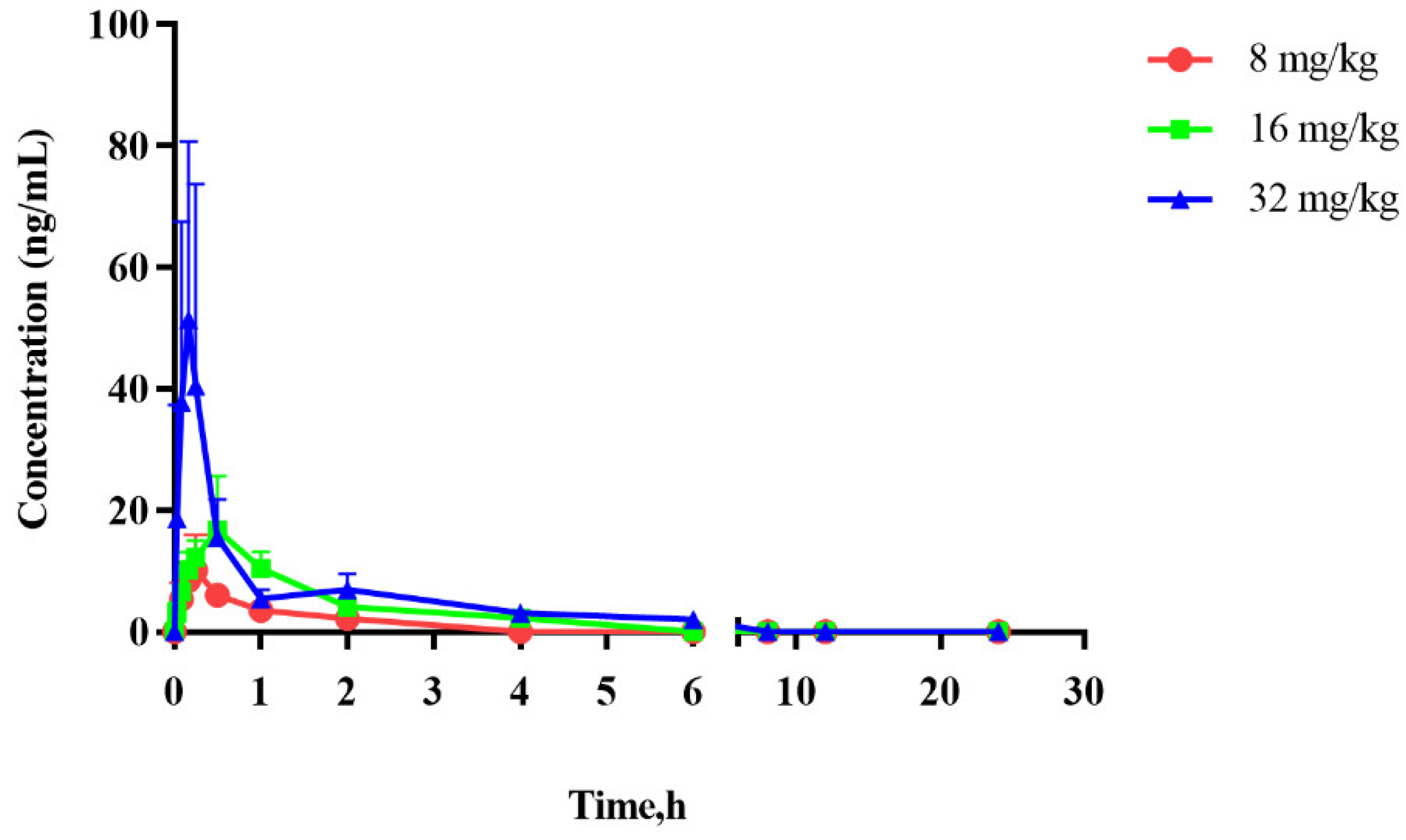
2.4. Pharmacokinetic Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Investigation of the Chemical Stability of Physalin A
3.3. Animals
3.4. Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Conditions
3.5. Preparation of Standard and Quality Control Samples
3.6. Sample Preparation
3.7. Method Validation
3.8. Pharmacokinetic Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Qiu, L.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, Z.H.; Chen, L.X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, H.X.; Yao, X.S.; Qiu, F. Steroids and flavonoids from Physalis alkekengi var. franchetii and their inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.K.; Xie, S.D.; Xu, W.X.; Nian, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Peng, X.R.; Ding, Z.T.; Qiu, M.H. Six new physalins from Physalis alkekengi var. franchetii and their cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity. Fitoterapia 2016, 112, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Qiu, L.; Wang, X.; Qiu, F.; Wong, Y.; Yao, X. Physalins A and B inhibit androgen-independent prostate cancer cell growth through activation of cell apoptosis and downregulation of androgen receptor expression. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1584–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, M.; Makino, B.; Taga, T.; Miwa, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Furuta, T.; Yamamura, H.; Butsugan, Y.; Ogawa, K. Crystal structures of 5α,6α-epoxy and 2,3-dihydro derivatives of physalin B, a 13,14-seco-16,24-cyclosteroid, and their 1H NMR spectral analysis. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1994, 67, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y. The research of nuclear magnetic resonance spectral characteristics on physalin. J. Math. Med. 2014, 27, 583–585. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Chinese Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 360–361. [Google Scholar]
- Sabourian, R.; Karimpour-Razkenari, E.; Saeedi, M.; Bagheri, M.S.; Khanavi, M.; Sadati, N.; Akbarzadeh, T.; Ardekani, M.R. Physalis alkekengi: A review of its therapeutic effects. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 9, 1472–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Helvaci, S.; Kökdil, G.; Kawai, M.; Duran, N.; Duran, G.; Güvenç, A. Antimicrobial activity of the extracts and physalin D from Physalis alkekengi and evaluation of antioxidant potential of physalin D. Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.M.; Liu, J.J.; Shen, X.F.; Du, G.Y. Study on artificial cultivation technology and utilization of Physalis. Liaoning Agric. Sci. 1996, 2, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.L.; Wang, X.Z. Study on chemical constituents of Chinese Lantern injection. J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1986, 3, 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.Z.; Cui, W.C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Yang, X.L.; Li, W.L. Clinical study on the treatment of infant tonsillitis with Ru’e Detoxicate Mixture. J. Shandong Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1997, 16, 344–345. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.L.; Ju, C.G.; Guan, H.J.; Xu, L.; Xu, N.; Wang, B. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) determination of five active ingredients in the calyces of Physalis alkekengi L. var. franchetii (mast.) Mskino. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 2438–2442. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, L.; Yuan, Y.; Luo, L.; Chen, Z.; Ma, X.; Ma, Z.; Cheng, L. Physalins with anti-inflammatory activity are present in Physalis alkekengi var. franchetii and can function as Michael reaction acceptors. Steroids 2012, 77, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Zang, L.H.; Feng, Y.S.; Chen, L.X.; Kang, N.; Tashiro, S.; Onodera, S.; Qiu, F.; Ikejima, T. Physalin A induces apoptosis via p53-Noxa-mediated ROS generation, and autophagy plays a protective role against apoptosis through p38-NF-kappaB survival pathway in A375-S2 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Zang, L.H.; Feng, Y.S.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.W.; Chen, L.X.; Kang, N.; Tashiro, S.; Onodera, S.; Qiu, F.; et al. Physalin A induces apoptotic cell death and protective autophagy in HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Feng, Y.S.; Zang, L.H.; Liu, W.W.; Ding, L.Q.; Chen, L.X.; Kang, N.; Hayashi, T.; Tashiro, S.; Onodera, S.; et al. Nitric oxide induces apoptosis and autophagy; autophagy down-regulates NO synthesis in physalin A-treated A375-S2 human melanoma cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 71, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Dai, C.; Fu, Y.; Loo, J.F.; Xia, D.; Gao, S.P.; Ma, Z.; Chen, Z. Physalin exerts anti-tumor activity in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by suppressing JAK/STAT3 signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9462–9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Jian, J.F.; Cao, S.J.; Zhang, Q.; Mao, Y.W.; Huang, Y.Y.; Peng, Y.F.; Qiu, F.; Gao, X.M. Physalin A induces G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in human non-small cell lung cancer cells: Involvement of the p38 MAPK/ROS pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 415, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lin, M.; Hu, X.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lou, Y.; ShenTu, J.; Wu, L. Simultaneous pharmacokinetics and stability studies of physalins in rat plasma and intestinal bacteria culture media using liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Ding, L.; Oppong, M.; Pan, G.; Qiu, F. LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of flavonoids and physalins in rat plasma: Application to pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Physalis alkekengi var. franchetii (Chinese lantern) extract. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, e3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ouyang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jia, X.; You, S.; He, X.; Di, X. Development of a sensitive LC-MS/MS method for the determination of bilobalide in rat plasma with special consideration of ex vivo bilobalide stability: Application to a preclinical pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 95, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, B.; Kawai, M.; Yamamura, H.; Araki, S.; Butsugan, Y. Tautomerism between exomethylene type physalins and oxymethylenebridged physalins. Pharmazie 2002, 57, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.P.; Li, L.Y.; Li, J.R.; Yu, M.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Q.M.; Gu, Y.C.; Zhang, T.; Zou, Z.M. Silencing Tautomerization to Isolate Unstable Physalins from Physalis minima. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 1522–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation. 2001. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/guidanceComplianceregulatoryInformation/guidances/UCM070107.pdf (accessed on 17 October 2022).



| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Found Concentration (ng/mL) | Intraday RSD (%) | Interday RSD (%) | Accuracy RE (%) | Matrix Effect (%) | Recovery (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physalin A | 6.00 | 6.32 ± 0.23 | 3.7 | 8.1 | 2.2 | 92.9 ± 9.43 | 61.8 ± 4.78 |
| 40.0 | 40.6 ± 0.69 | 1.7 | 3.2 | 0.9 | 83.0 ± 3.10 | 53.9 ± 2.71 | |
| 300 | 321 ± 6.49 | 2.0 | 6.3 | 5.1 | 85.7 ± 2.30 | 61.4 ± 1.65 | |
| IS | 30.0 | - | - | - | - | 99.5 ± 2.99 | 88.7 ± 2.33 |
| Nominal Concentration | Auto-Sampler 0 h | Auto-Sampler 2 h | Auto-Sampler 4 h | Auto-Sampler 8 h | Auto-Sampler 12 h | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) |
| 6.00 | 2.7 | −0.3 | 4.4 | −0.3 | 3.9 | −5.2 | 9.7 | −3.9 | 8.6 | −4.3 |
| 300 | 4.5 | 3.6 | 4.0 | 5.2 | 4.3 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 0.1 |
| Parameters | 8 mg/kg | 16 mg/kg | 32 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUC0–t (mg/L·h) | 7.07 ± 2.85 | 24.53 ± 9.90 | 35.41 ± 10.99 |
| AUC0–∞ (mg/L·h) | 9.39 ± 3.39 | 28.76 ± 7.72 | 41.65 ± 13.44 |
| Cmax (mg/L) | 10.94 ± 5.32 | 17.82 ± 8.19 | 72.08 ± 18.15 |
| Tmax (h) | 0.19 ± 0.07 | 0.50 ± 0.27 | 0.15 ± 0.06 |
| t1/2z (h) | 0.67 ± 0.33 | 1.15 ± 0.34 | 1.60 ± 1.03 |
| Vz/F (L/kg) | 841 ± 350 | 964 ± 358 | 1706 ± 884 |
| CLz/F (L/h/kg) | 939 ± 299 | 581 ± 111 | 867 ± 375 |
| MRT0–t (h) | 0.54 ± 0.18 | 1.18 ± 0.27 | 1.03 ± 0.42 |
| MRT0–∞ (h) | 1.00 ± 0.44 | 1.76 ± 0.37 | 1.85 ± 1.04 |
| Compound | Q1 | Q3 | DP (V) | EP (V) | CE (V) | CXP (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physalin A | 525.1 | 148.9 | −30 | −10 | −40 | −17 |
| Tolbutamide (IS) | 269.8 | 169.9 | −100 | −10 | −30 | −17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, T.; Feng, X. A Rapid and Sensitive LC−MS/MS Method for the Quantitation of Physalin A with Special Consideration to Chemical Stability in Rat Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 7272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217272
Li Y, Zhao N, Zhang T, Feng X. A Rapid and Sensitive LC−MS/MS Method for the Quantitation of Physalin A with Special Consideration to Chemical Stability in Rat Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217272
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yang, Na Zhao, Tingting Zhang, and Xinchi Feng. 2022. "A Rapid and Sensitive LC−MS/MS Method for the Quantitation of Physalin A with Special Consideration to Chemical Stability in Rat Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217272
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhao, N., Zhang, T., & Feng, X. (2022). A Rapid and Sensitive LC−MS/MS Method for the Quantitation of Physalin A with Special Consideration to Chemical Stability in Rat Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study. Molecules, 27(21), 7272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217272