Synthesis and Application of New Salan Titanium Complexes in the Catalytic Reduction of Aldehydes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
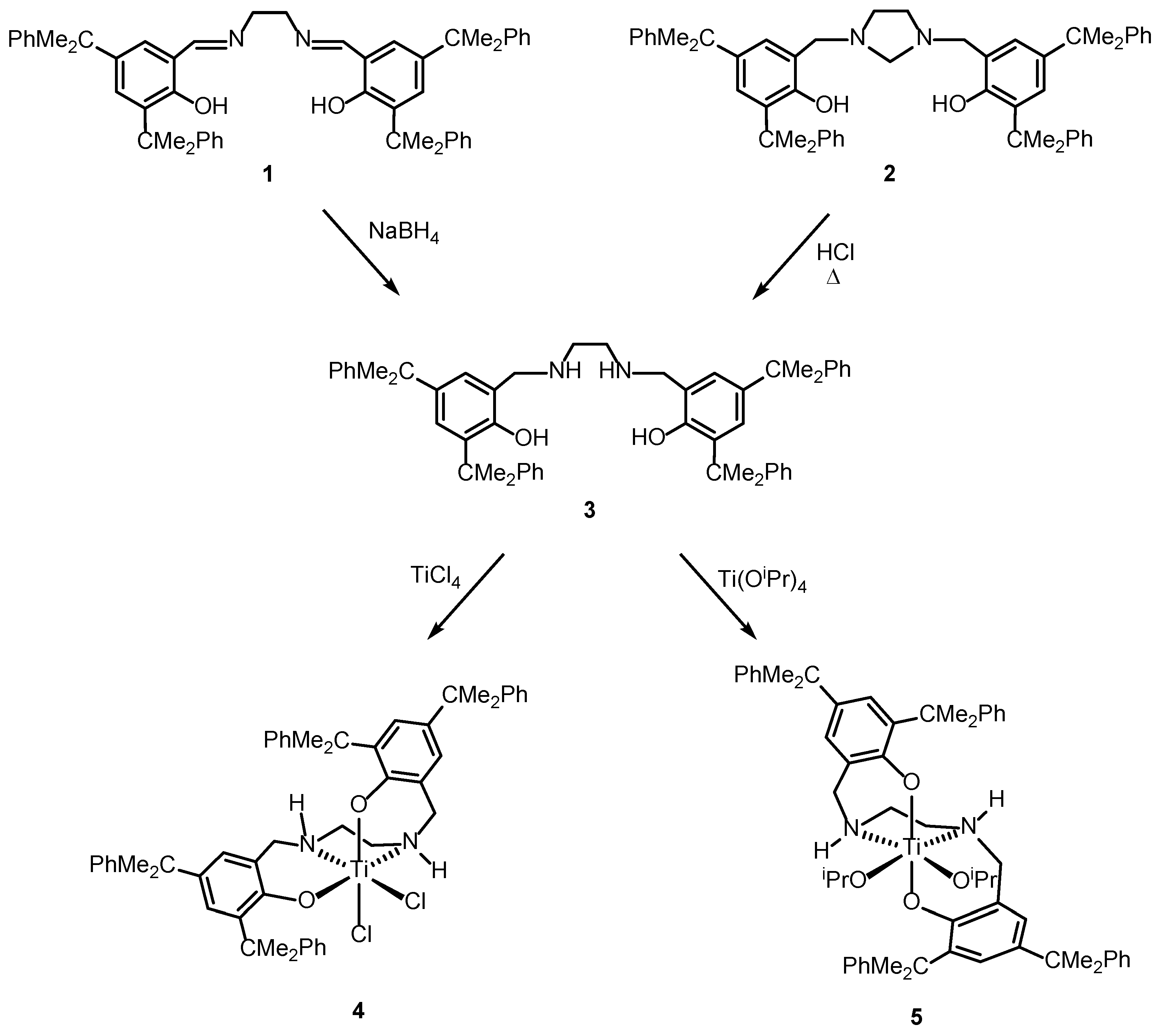
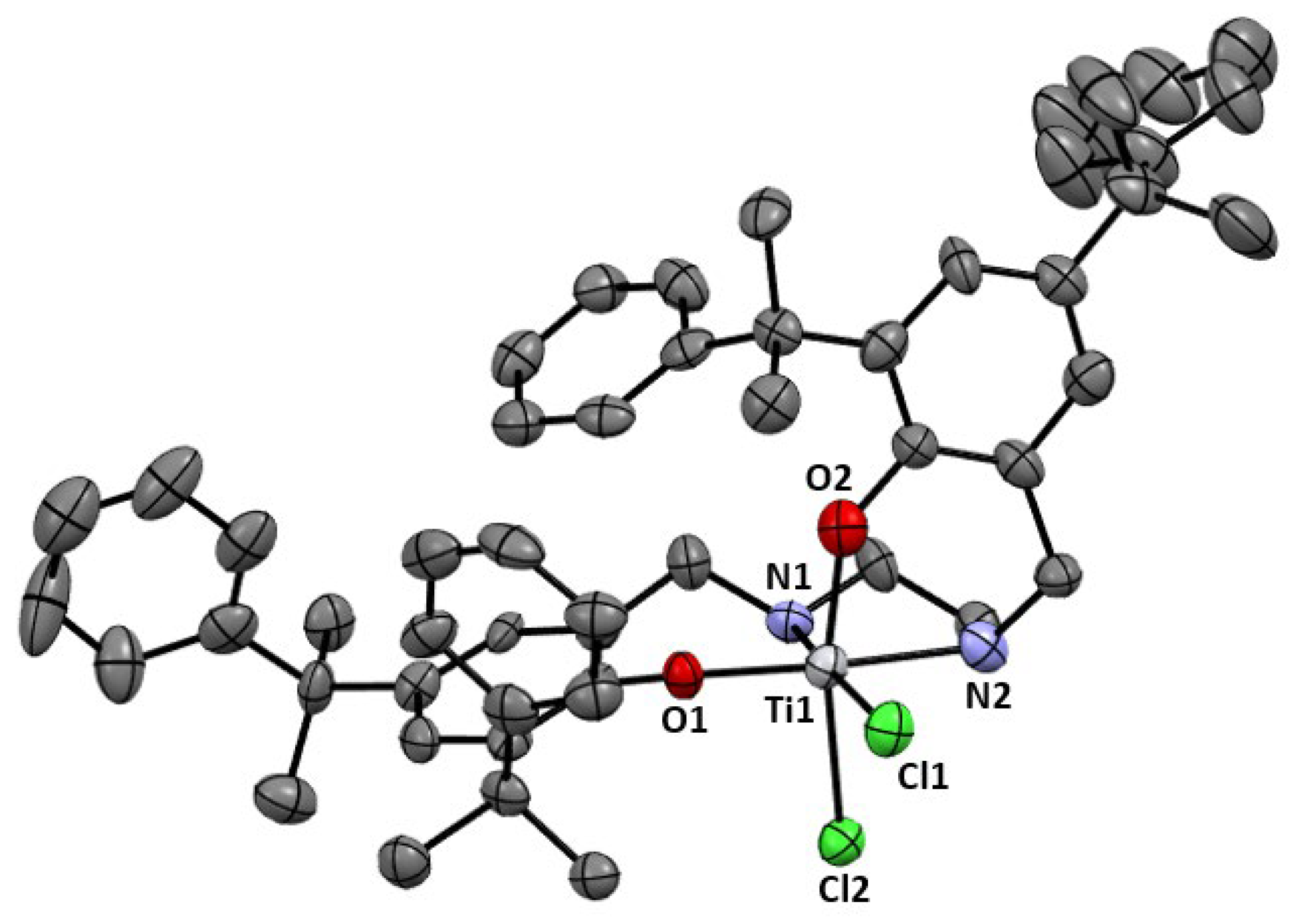
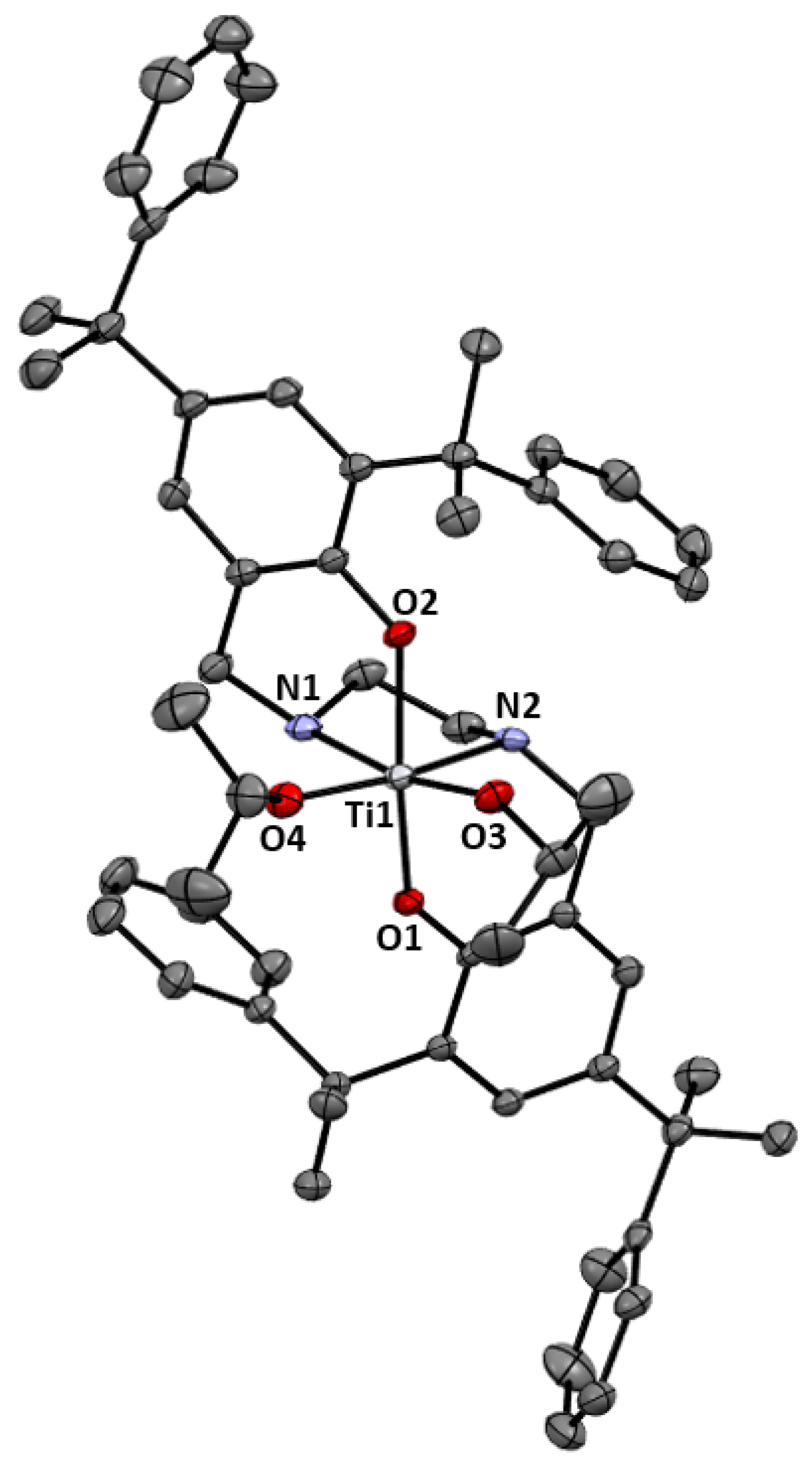
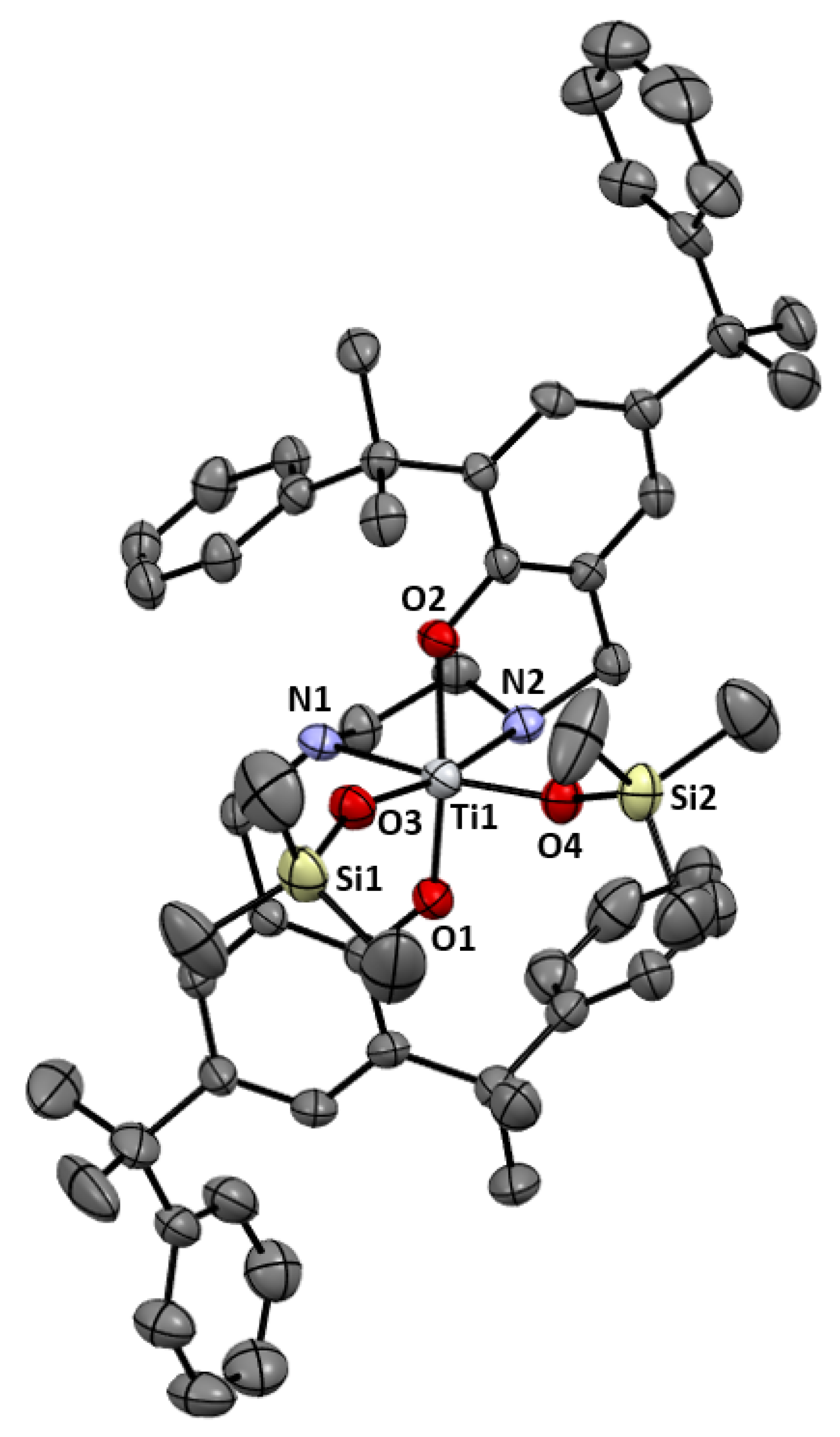
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
2.2. Catalytic Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Considerations
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of the Compounds
3.2.1. 2-Hydroxy-3,5-Bis(2-Phenylpropan-2-yl)Benzaldehyde
3.2.2. 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(Ethane-1,2-Diylbis(Azaneylylidene))Bis(methaneylylidene))Bis(2,4-Bis(2-Phenylpropan-2-yl)Phenol), 1
3.2.3. 6,6′-(Imidazolidine-1,3-Diylbis(Methylene))Bis(2,4-Bis(2-Phenylpropan-2-yl)Phenol), 2
3.2.4. 6,6′-((Ethane-1,2-Diylbis(Azanediyl))Bis(Methylene))Bis(2,4-Bis(2-Phenylpropan-2-yl)phenol), H2N2O2H2, 3
3.2.5. [(H2N2O2)TiCl2], 4
3.2.6. [(H2N2O2)Ti(OiPr)2], 5
3.2.7. H2N2O2Na2, 6
3.3. General Procedure for the Catalytic Reduction of Aldehydes
3.4. General Procedure for Single Crystal X-ray Crystallography
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Xiong, H.; Li, L.; Liu, E.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, G. A chiral multidentate salan-supported heterobimetallic catalyst for asymmetric Friedel-Crafts reaction. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2017, 84, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, J.; Mu, Y. Synthesis of chiral salan ligands with bulky substituents and their application in Cu-catalyzed asymmetric Henry reaction. J. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 928, 121546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gu, H.; Zhu, X.; Nam, W.; Wang, B. Zirconium-Salan Catalyzed Enantioselective α-Hydroxylation of β-Keto Esters. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 2976–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunda, S.; Udvardy, A.; Voronova, K.; Joó, F. Organic Solvent-Free, Pd(II)-Salan Complex-Catalyzed Synthesis of Biaryls via Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling in Water and Air. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 15486–15492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.; Kopilov, J.; Lamberti, M.; Venditto, V.; Kol, M. Same Ligand, Different Metals: Diiodo-Salan Complexes of the Group 4 Triad in Isospecific Polymerization of 1-Hexene and Propylene. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 1689–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białek, M.; Pochwała, M.; Spaleniak, G. Olefin polymerization and copolymerization by complexes bearing [ONNO]-Type salan ligands: Effect of ligand structure and metal type (titanium, zirconium, and vanadium). J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2014, 52, 2111–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meppelder, G.-J.M.; Fan, H.-T.; Spaniol, T.P.; Okuda, J. Group 4 Metal Complexes Supported by [ONNO]-Type Bis(o-aminophenolato) Ligands: Synthesis, Structure, and α-Olefin Polymerization Activity. Organometallics 2009, 28, 5159–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H.; Yuan, D.; Nie, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Cui, D. Synthesis and Characterization of Dinuclear Salan Rare-Earth Metal Complexes and Their Application in the Homo- and Copolymerization of Cyclic Esters. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 9028–9038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmura, A.J.; Davidson, M.G.; Jones, M.D.; Lunn, M.D.; Mahon, M.F.; Johnson, A.F.; Khunkamchoo, P.; Roberts, S.L.; Wong, S.S.F. Group 4 Complexes with Aminebisphenolate Ligands and Their Application for the Ring Opening Polymerization of Cyclic Esters. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 7250–7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumrit, P.; Hormnirun, P. Aluminum Initiators Supported by Asymmetric [ONNO’]-Type Salan Ligands for the Ring-Opening Polymerization of rac-Lactide. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Sawada, Y.; Katsuki, T. Asymmetric epoxidation of olefins catalyzed by Ti(salan) complexes using aqueous hydrogen peroxide as the oxidant. Pure Appl. Chem. 2008, 80, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat, J.L.; De, S.R.; Kumar, G.; Adebesin, A.M.; Gandham, S.K.; Falck, J.R. Regio- and Enantioselective Catalytic Monoepoxidation of Conjugated Dienes: Synthesis of Chiral Allylic cis-Epoxides. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1058–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsi, E.P.; Samsonenko, D.G.; Bryliakov, K.P. Titanium Salan Catalysts for the Asymmetric Epoxidation of Alkenes: Steric and Electronic Factors Governing the Activity and Enantioselectivity. Chem.-Eur. J. 2014, 20, 14329–14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adão, P.; Avecilla, F.; Bonchio, M.; Carraro, M.; Pessoa, J.C.; Correia, I. Titanium(IV)-Salan Catalysts for Asymmetric Sulfoxidation with Hydrogen Peroxide. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2010, 5568–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsi, E.P.; Bryliakov, K.P. Titanium-salan-catalyzed asymmetric sulfoxidations with H2O2: Design of more versatile catalysts. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 27, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsi, E.P.; Bryliakov, K.P. Ti-Salan catalyzed asymmetric sulfoxidation of pyridylmethylthiobenzimidazoles to optically pure proton pump inhibitors. Cat. Today 2017, 279, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maru, M.S.; Barroso, S.; Adão, P.; Alves, L.G.; Martins, A.M. New salan and salen vanadium complexes: Synthesis and application in sulfoxidation catalysis. J. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 870, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhu, C. Enantioselective Pinacol Coupling of Aryl Aldehydes Catalyzed by Chiral Salan-Mo(IV) Complexes. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 10029–10034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Dai, Z.; Li, C.; Zhu, C. Enantioselective pinacol coupling reaction of aromatic aldehydes catalyzed by chiral vanadium complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2009, 694, 3219–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, M.M.V.; Singh, B.K.D.; Parihar, J.A. Microwave-assisted coupling of carbonyl compound: An efficient synthesis of olefin. J. Chem. Res. 2004, 2004, 760–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Vila, J.L. Obtaining of alkenes by reductive coupling of carbonylic compounds; Synthesis of Z,E-6-dodecene, synthesis of flexibilene and isocaryophylene, mechanistic views. Boliv. J. Chem. 2018, 35, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J. Wolff-Kishner Reaction. In Name Reactions, 6th ed.; Li, J.J., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 583–585. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J. Clemmensen Reduction. In Name Reactions, 6th ed.; Li, J.J., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 109–111. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfrom, M.L.; Karabinos, J.V. Carbonyl Reduction by Thioacetal Hydrogenolysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1944, 66, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.C.A.; Fernandes, T.A.; Fernandes, A.C. Highly Efficient Deoxygenation of Aryl Ketones to Arylalkanes Catalyzed by Dioxidomolybdenum Complexes. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 2016, 3109–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argouarch, G. Mild and efficient rhodium-catalyzed deoxygenation of ketones to alkanes. New. J. Chem. 2019, 43, 11041–11044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalutharage, N.; Yi, C.S. Scope and Mechanistic Analysis for Chemoselective Hydrogenolysis of Carbonyl Compounds Catalyzed by a Cationic Ruthenium Hydride Complex with a Tunable Phenol Ligand. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2015, 137, 11105–11114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, S.L.; Mahon, M.F.; Jones, M.D. Monomeric Ti(IV) homopiperazine complexes and their exploitation for the ring opening polymerization of rac-lactide. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miller, M.; Tshuva, E.Y. Synthesis of Pure Enantiomers of Titanium(IV) Complexes with Chiral Diaminobis(Phenolato) Ligands and Their Biological Reactivity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeori, A.; Groysman, S.; Goldberg, I.; Kol, M. Diastereoisomerically Selective Enantiomerically Pure Titanium Complexes of Salan Ligands: Synthesis, Structure, and Preliminary Activity Studies. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 4466–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.D.; Davidson, M.G.; Kociok-Kohn, G. New titanium and zirconium initiatores for the production of polylactide. Polyhedron 2010, 29, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, S.N.; Jung, C.F.; Shalumova, T.; Tanski, J.M. Chiral-at-metal tetrahydrosalen complexes of resolved titanium(IV) sec-butoxides: Ligand wrapping and multiple asymmetric catalytic induction. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2009, 362, 3134–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, C.M.; Tshuva, E.Y. Markedly different cytotoxicity of the two enantiomers of C2-symmetrical Ti(IV) penolato complexes; mechanistic implications. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 1182–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meker, S.; Manna, C.M.; Peri, D.; Tshuva, E.Y. Major impact of N-methylation on cytotoxic and hydrolysis of salan Ti(IV) complexes: Sterics and electronics are intertwined. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 9802–9809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SAINT, Version 7.03A; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1997–2003.
- Sheldrick, G.M.; SADABS. Software for Empirical Absorption Corrections; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Altomare, A.; Burla, M.C.; Camalli, M.; Cascarano, G.L.; Giacovazzo, C.; Guagliardi, A.; Moliterni, A.G.G.; Polidori, G.; Spagna, R. SIR97: A new tool for crystal structure determination and refinement. J. Appl. Cryst. 1999, 32, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burla, M.C.; Caliandro, R.; Camalli, M.; Carrozzini, B.; Cascarano, G.L.; De Caro, L.; Giacovazzo, C.; Polidori, G.; Spagna, R. SIR2004: An improved tool for crystal structure determination and refinement. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2005, 38, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure and refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Farrugia, L.J. WinGX suite for small-molecule single-crystal crystallography. J. Appl. Cryst. 1999, 32, 837–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A.L. PLATON SQUEEZE: A tool for the calculation of the disordered solvent contribution to the calculated structure factors. Acta Cryst. C Struct. Chem. 2015, C71, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
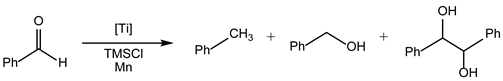
| Entry | Catalyst | Solvent | T (°C) | t (h) | Conv. (%) | Alkane (%) | Alcohol (%) | Diol (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | THF | 30 | 24 | 93 | 75 | 9 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 | THF | 55 | 4 | 82 | 78 | 0 | 2 |
| 3 c | 4 | THF | 55 | 4 | 55 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 4 | THF | 55 | 7 | 91 | 89 | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | 4 | THF | 55 | 24 | 94 | 92 | 0 | 1 |
| 6 | 4 | EtOH | 55 | 4 | 47 | 46 | 1 | 0 |
| 7 | 4 | n-Bu2O/H2O | 55 | 24 | 44 | 40 | 4 | 0 |
| 8 | 5 | THF | 30 | 24 | 75 | 69 | 5 | 0 |
| 9 | - | THF | 55 | 4 | 29 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| 10 | - | EtOH | 55 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
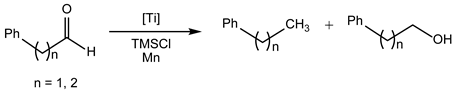
| Entry | Substrate | t (h) | Conv. (%) | Alkane (%) | Alcohol (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PhCH2C(O)H | 24 | 99 | 87 | 0 |
| 2 | PhCH2CH2C(O)H | 24 | 99 | 84 | 0 |
| Compound | 42.(C4H10O)3 | 5 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C116 H146 Cl4 N4 O7 Ti2 | C58 H72 N2 O4 Ti | C58 H76 N2 O4 Si2 Ti |
| Formula weight | 1945.91 | 909.05 | 969.26 |
| Temperature (K) | 150 (2) | 150 (2) | 294 (2) |
| Crystal system, space group | Tetragonal, I41/a | Triclinic, P-1 | Triclinic, P-1 |
| a (Å) | 25.4100 (1) | 11.664 (3) | 10.315 (2) |
| b (Å) | 25.4100 (1) | 15.050 (6) | 14.434 (4) |
| c (Å) | 33.3570 (2) | 16.062 (5) | 19.035 (5) |
| α(º) | 90 | 73.87 (2) | 79.30 (1) |
| β(º) | 90 | 86.84 (1) | 86.65 (1) |
| γ(º) | 90 | 67.29 (1) | 88.76 (2) |
| Volume (Å3) | 21537.6 (2) | 2494.3 (15) | 2779.9 (12) |
| Z | 8 | 2 | 2 |
| Calculated density (g m−3) | 1.200 | 1.210 | 1.158 |
| Absorption coefficient (mm−1) | 0.303 | 0.220 | 0.242 |
| F (000) | 8304 | 976 | 1040 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.20 × 0.26 × 0.34 | 0.10 × 0.16 × 0.22 | 0.08 × 0.08 × 0.14 |
| θ range for data collection (°) | 1.007–25.576 | 3.163–27.046 | 1.978–26.558 |
| Limiting indices | −30 ≤ h ≤ 30, −30 ≤ k ≤ 30, −37 ≤ l ≤ 40 | −14 ≤ h ≤ 11, −18 ≤ k ≤ 14, −20 ≤ l ≤ 20 | −12 ≤ h ≤ 12, −18 ≤ k ≤ 18, −23 ≤ l ≤ 23 |
| Reflections collected/unique | 117534/10101 [Rint = 0.2329] | 26502/10473 [Rint = 0.0730] | 62151/10227 [Rint = 0.3149] |
| Completeness to θ = 25.242 | 99.9 | 99.5 | 88.8 |
| Data/restraints/parameters | 10029/0/612 | 10473/0/606 | 10227/0/626 |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.519 | 0.961 | 0.842 |
| Final R indices [I > 2σ(I)] a | R1 = 0.1579, wR2 = 0.4442 | R1 = 0.0558, wR2 = 0.1186 | R1 = 0.0897, wR2 = 0.2013 |
| R indices (all data) a | R1 = 0.2840, wR2 = 0.4777 | R1 = 0.1105, wR2 = 0.1365 | R1 = 0.2545, wR2 = 0.2425 |
| Largest diff. peak/hole (e Å−3) | 1.176 and −0.592 | 0.379 and −0.720 | 0.748 and −0.469 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hipólito, J.; Martins, A.M.; Alves, L.G. Synthesis and Application of New Salan Titanium Complexes in the Catalytic Reduction of Aldehydes. Molecules 2022, 27, 6821. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206821
Hipólito J, Martins AM, Alves LG. Synthesis and Application of New Salan Titanium Complexes in the Catalytic Reduction of Aldehydes. Molecules. 2022; 27(20):6821. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206821
Chicago/Turabian StyleHipólito, Joana, Ana M. Martins, and Luis G. Alves. 2022. "Synthesis and Application of New Salan Titanium Complexes in the Catalytic Reduction of Aldehydes" Molecules 27, no. 20: 6821. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206821
APA StyleHipólito, J., Martins, A. M., & Alves, L. G. (2022). Synthesis and Application of New Salan Titanium Complexes in the Catalytic Reduction of Aldehydes. Molecules, 27(20), 6821. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206821






