In Vivo Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Takifugu obscurus Based on Solid-Phase Microextraction Coupled with Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of SPME Fibers
2.2. In Vitro Evaluation of SPME Fibers
2.3. Method Optimization
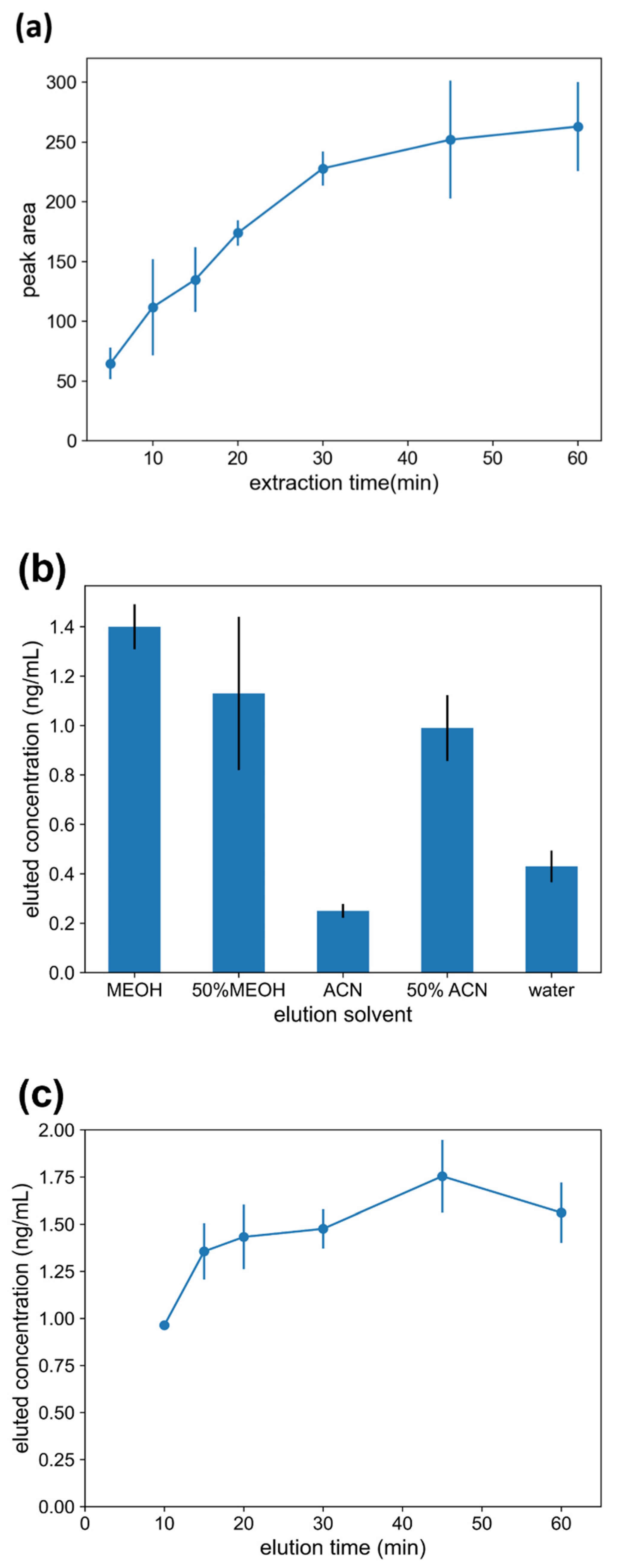
2.3.1. Extraction Time
2.3.2. Elution Solvent
2.3.3. Elution Time
2.4. Method Evaluation
2.5. In Vivo SPME Extraction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Preparation of SPME Fibers
3.2.1. Preparation of Coating Solution
3.2.2. Dipping Process of Fibers
3.2.3. Addition of PNE Bionic Sheath
3.3. Characterization of SPME Fibers
3.4. Extraction Performance Evaluation
3.5. Exposure Experiment
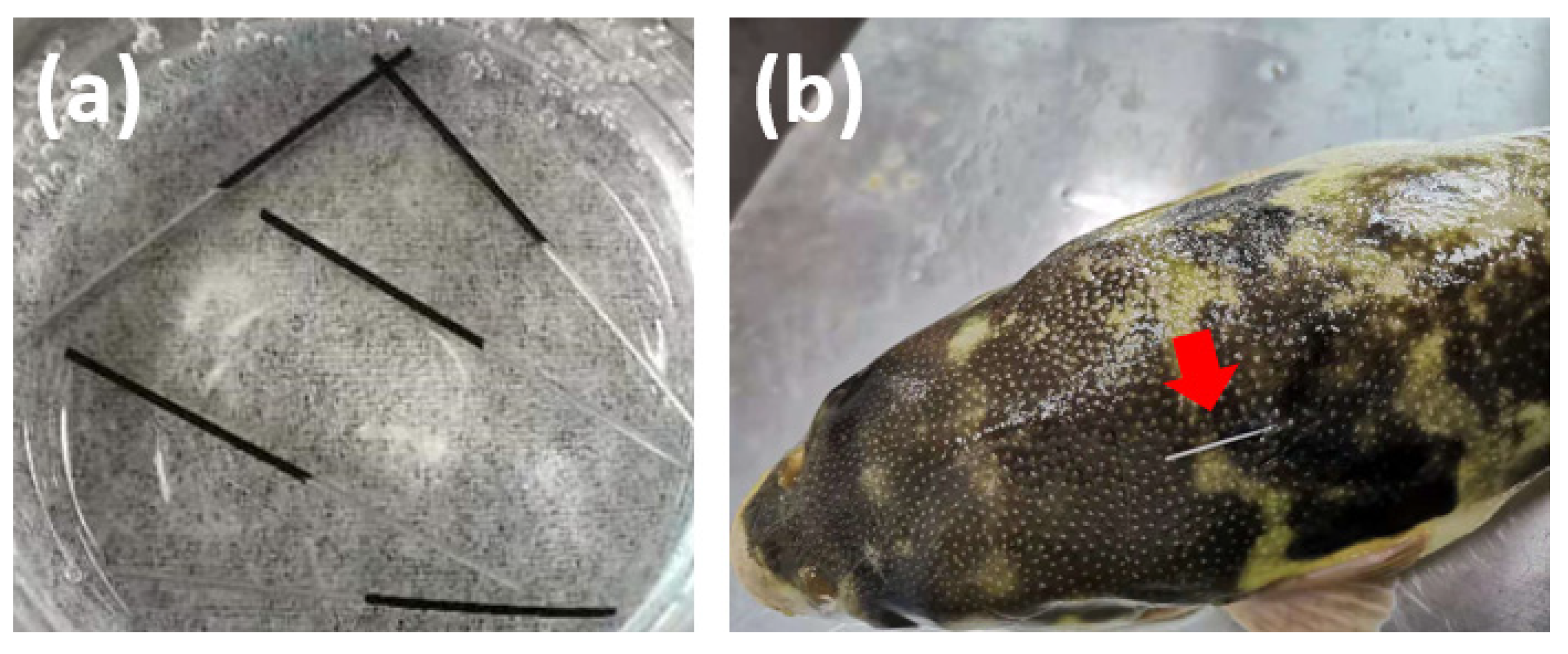
3.6. In Vivo SPME Extraction
3.7. Instrumentation (UPLC-MS/MS)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhang, N.L.; Ayed, C.; Wang, W.L.; Liu, Y. Sensory-Guided Analysis of Key Taste-Active Compounds in Pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13809–13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, J.; Rodríguez, L.; Blanco, L.; Vieites, J.; Cabado, A. Tetrodotoxin, an Extremely Potent Marine Neurotoxin: Distribution, Toxicity, Origin and Therapeutical Uses. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6384–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O. Tetrodotoxin—Distribution and accumulation in aquatic organisms, and cases of human intoxication. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 220–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T. TTX accumulation in pufferfish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2006, 1, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z. Study on Processing of Tetrodotoxin Mechanism of Poisoning and Preparation. Food Sci. 2003, 24, 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi, T.; Ebesu, J.S.M. Puffer Poisoning: Epidemiology and Treatment. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2001, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H. Differences in susceptibility of mouse strains to tetrodotoxin. Toxicon 2016, 119, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Lijun, Y.; Zhaojie, L.I.; Meng, Z.; Xiaohua, S.; Yumin, L.I.U. Quantitative Detection of Tetrodotoxin Using Kunming Strain Mice. Food Sci. 2011, 32, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, S.; Chen, Q.A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Jin, N.; Pang, J.; Wang, S. Development of ELISA and colloidal gold immunoassay for tetrodotoxin detetcion based on monoclonal antibody. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.W.; Liu, H.X.; Jin, Y.B.; Li, S.F.; Bi, X.; Chung, S.; Zhang, S.S.; Jiang, Y.Y. Separation, identification and quantification of tetrodotoxin and its analogs by LC-MS without calibration of individual analogs. Toxicon 2011, 57, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzoughet, J.K.; Campbell, K.; Barnes, P.; Cooper, K.M.; Chevallier, O.P.; Elliott, C.T. Comparison of sample preparation methods, validation of an UPLC-MS/MS procedure for the quantification of tetrodotoxin present in marine gastropods and analysis of pufferfish. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid phase microextraction with thermal elution using fused silica optical fibers. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, J.; Harris, C.M. Great Ideas of a Decade. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, G.F.; Vuckovic, D.; Pawliszyn, J. Nondestructive Sampling of Living Systems Using in Vivo Solid-Phase Microextraction. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2784–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.A.; Chen, G.S.; Qiu, J.L.; Xu, J.Q.; Wang, J.H.; Zhu, F.; Ouyang, G.F. Determination of four salicylic acids in aloe by in vivo solid phase microextraction coupling with liquid chromatography-photodiode array detection. Talanta 2018, 184, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.L.; Chen, G.S.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhang, T.L.; Wu, J.Y.; Wang, F.X.; Xu, J.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, F.; Ouyang, G.F. Bioinspired Polyelectrolyte-Assembled Graphene-Oxide-Coated C18 Composite Solid-Phase Microextraction Fibers for In Vivo Monitoring of Acidic Pharmaceuticals in Fish. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5841–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Huang, S.; Xu, J.; Ouyang, G.; Liu, Y. PLGA-based nanofibers with biomimetic polynoradrenaline sheath for rapid in vivo sampling of tetrodotoxin and sulfonamides in pufferfish. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3655–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodstein, J.; McElfresh, J.S.; Barbour, J.D.; Ray, A.M.; Hanks, L.M.; Millar, J.G. Identification and Synthesis of a Female-Produced Sex Pheromone for the Cerambycid Beetle Prionus Californicus. J. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 35, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, D.; Goldoni, M.; Corradi, M.; Acampa, O.; Carbognani, P.; Internullo, E.; Casalini, A.; Mutti, A. Determination of aldehydes in exhaled breath of patients with lung cancer by means of on-fiber-derivatisation SPME-GC/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 878, 2643–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Huang, J.; Yang, Q.; Ni, C.; Xie, X.; Shi, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhu, F.; Ouyang, G. Fabrications of novel solid phase microextraction fiber coatings based on new materials for high enrichment capability. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajek, H.; Jonik, J.; Witkiewicz, Z.; Wawer, T.; Purchala, M. Applications of Graphene and Its Derivatives in Chemical Analysis. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 50, 445–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhou, H.; Cheng, J. Fabrication of graphene oxide incorporated polymer monolithic fiber as solid phase microextraction device for determination of organophosphate esters in soil samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1588, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashakkori, P.; Erdem, P.; Merdivan, M.; Bozkurt, S.S. Determination of Phthalate Esters in Water and Coffee by Solid-Phase Microextraction Using Vinyl Terminated Imidazolium Based Ionic Liquid Grafted on Graphene Oxide Coatings. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 2307–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Suk, J.W.; Potts, J.R.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene and graphene oxide: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3906–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskin, M.B.; Xu, R.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Dong, M.; Besenbacher, F.; Chen, M. Poly(norepinephrine) as a functional bio-interface for neuronal differentiation on electrospun fibers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 9446–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.; Xu, D.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L. Interfacial reactions in graphene oxide/polyacrylonitrile composite films. Compos. Interfaces 2020, 28, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Y.; Huang, J.T.; Xue, Z.H.; Wang, X.M. Electrospun graphene oxide/carbon composite nanofibers with well-developed mesoporous structure and their adsorption performance for benzene and butanone. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.; Yun, J.; Seo, Y.; Byun, H.; Hou, J.; Kim, J.H. Mixed Dye Removal Efficiency of Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile-Graphene Oxide Composite Membranes. Polymers 2020, 12, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.R.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.H.; Luo, W.H. Fabrication of GO/PAN Nanofiber Membrane Grafted with Chitosan as Efficient Adsorbent for Dye Removal. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 2943–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, X.W.; Liu, Y.G.; Cheng, B.H.; Huang, Z.H.; Fang, M.H.; Min, X. Processing, microstructure and electrochemical properties of reduced graphene oxide reinforced carbon nanofiber formed by gyration. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 767, 138393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qiu, J.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ouyang, G. Rapid in vivo determination of tetrodotoxin in pufferfish (Fugu) muscle by solid-phase microextraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2017, 171, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Samples | LOD | LOQ | Linear Range | R2 | Reproducibility (RSD, %, n = 6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-Fiber | Inter-Fiber | |||||
| TTX aqueous | 11.8 ng·mL−1 | 81.3 ng·mL−1 | 100–1000 ng·mL−1 | 0.9955 | 13.0 | 4.63 |
| TTX spiked fish | 32 ng·g−1 | 150 ng·g−1 | 150–1000 ng·g−1 | 0.9895 | 36.1 | 8.82 |
| Pufferfish Number | Exposure Days | Calculated TTX Content (ng·g−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 2 | 141 |
| 3 | 6 | 480 |
| 4 | 7 | 91 |
| 5 | 7 | 25 |
| 6 | 7 | 53 |
| Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Declustering Potential (V) | Collision Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 320 | 302 | 80 | 40 |
| 162 | 80 | 35 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, H.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y. In Vivo Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Takifugu obscurus Based on Solid-Phase Microextraction Coupled with Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2022, 27, 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186122
Meng H, Jiang S, Zhang Y, Hu Y, Liu Y. In Vivo Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Takifugu obscurus Based on Solid-Phase Microextraction Coupled with Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2022; 27(18):6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186122
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Hengli, Shui Jiang, Yin Zhang, Yun Hu, and Yuan Liu. 2022. "In Vivo Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Takifugu obscurus Based on Solid-Phase Microextraction Coupled with Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 27, no. 18: 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186122
APA StyleMeng, H., Jiang, S., Zhang, Y., Hu, Y., & Liu, Y. (2022). In Vivo Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Takifugu obscurus Based on Solid-Phase Microextraction Coupled with Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 27(18), 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186122








