Identification of Estradiol Benzoate as an Inhibitor of HBx Using Inducible Stably Transfected HepG2 Cells Expressing HiBiT Tagged HBx
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
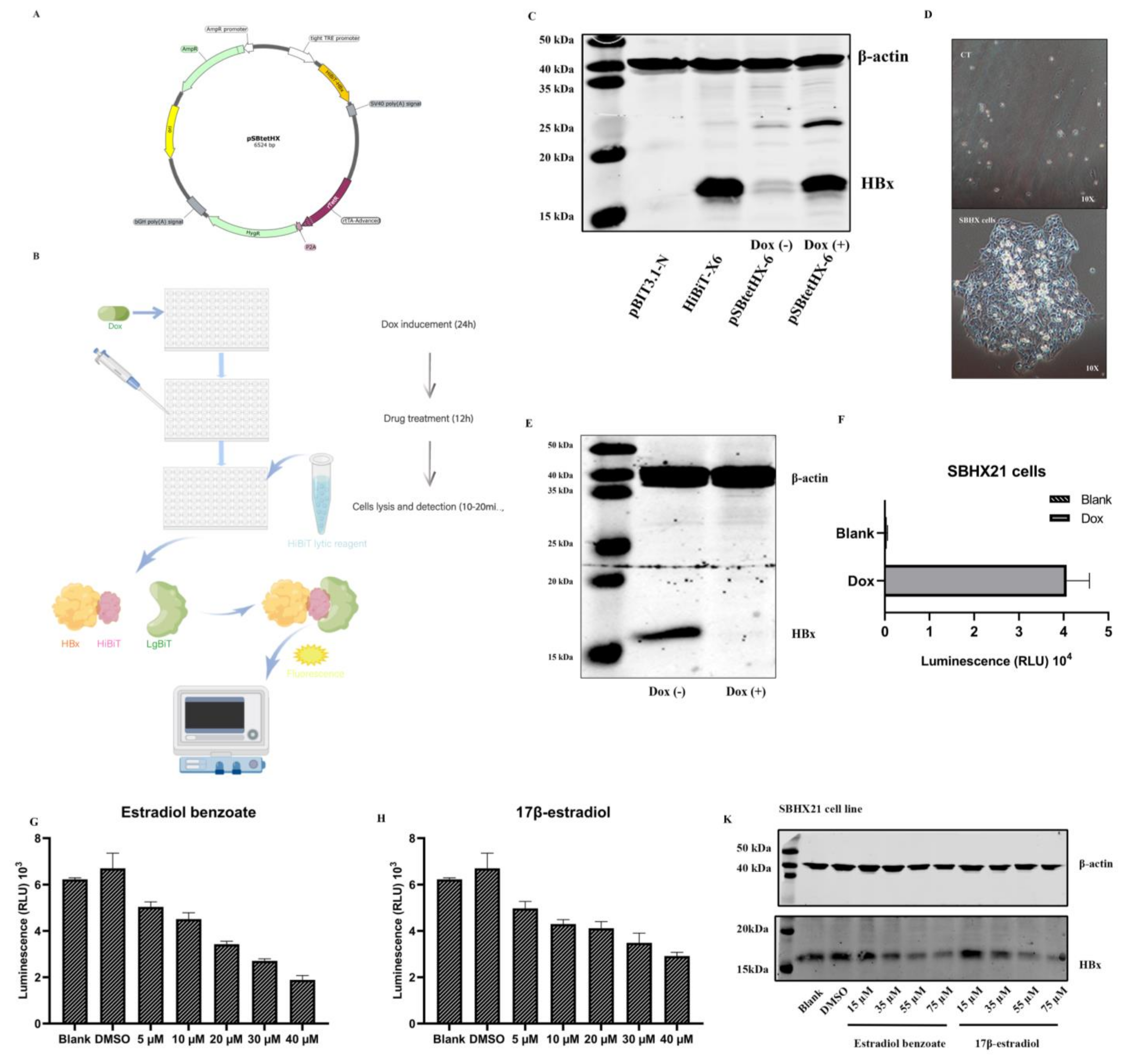
2.1. Establishment of the SNHX21 Cell Line
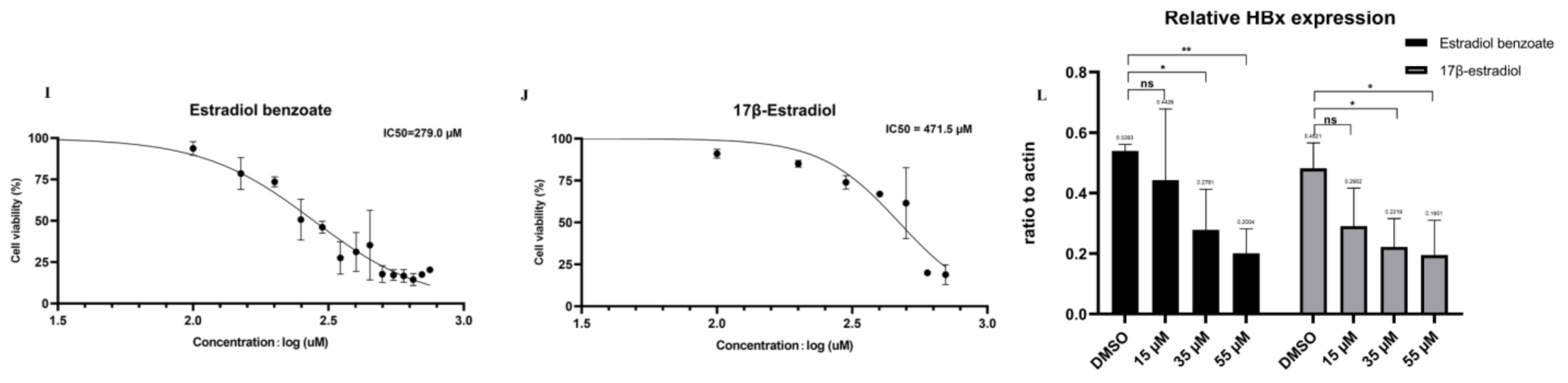
2.2. Drug Screening Results Identify Estradiol Benzoate as an Inhibitor of HBx
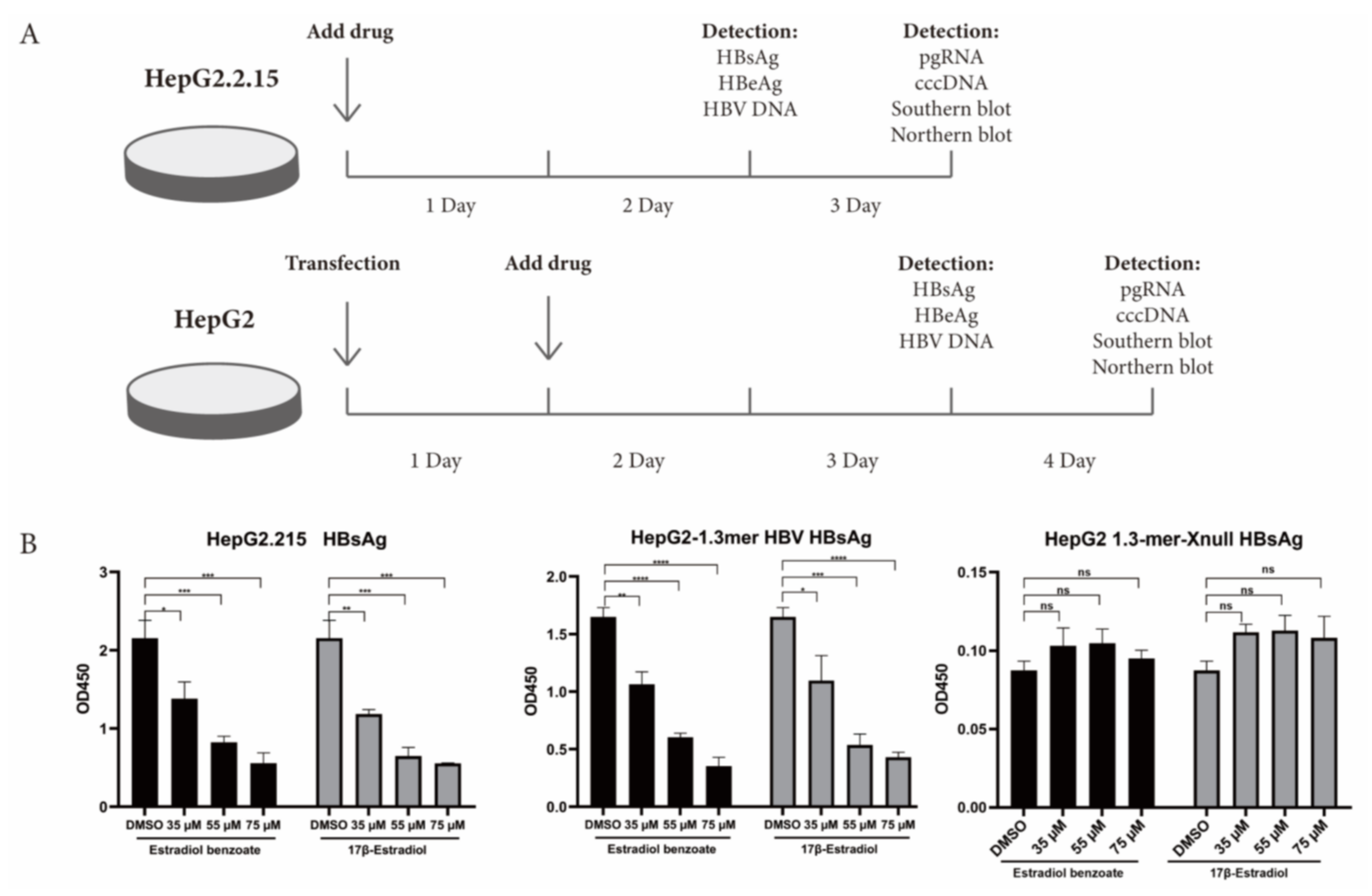
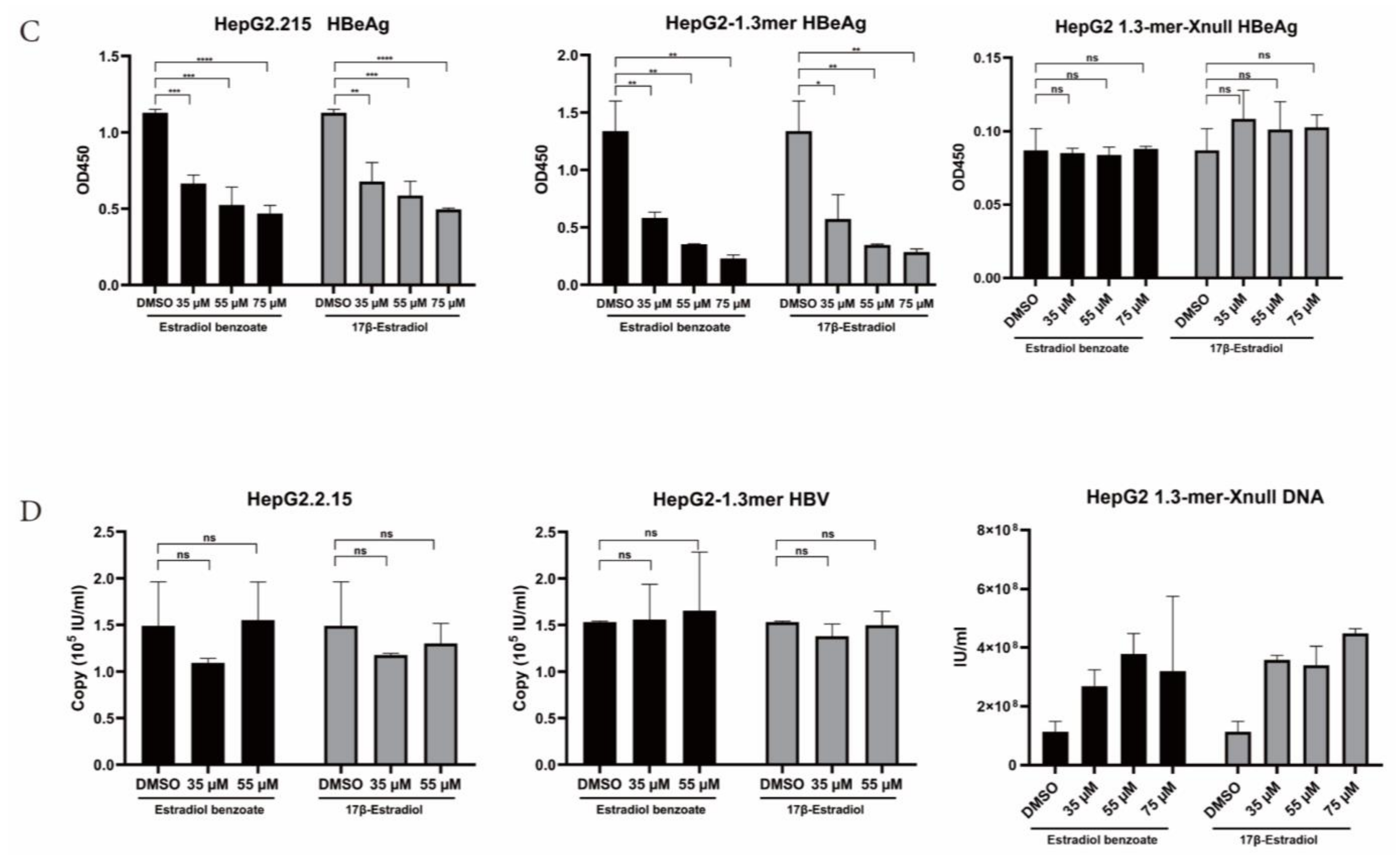
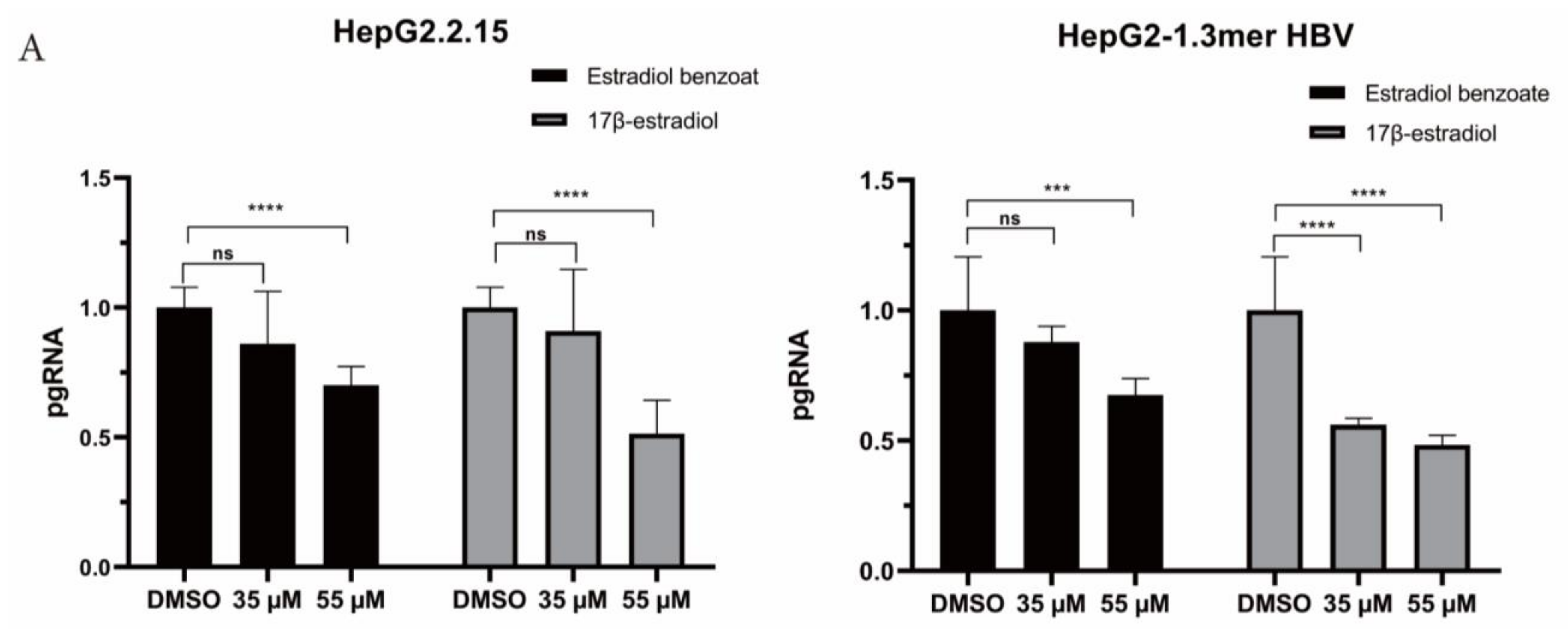
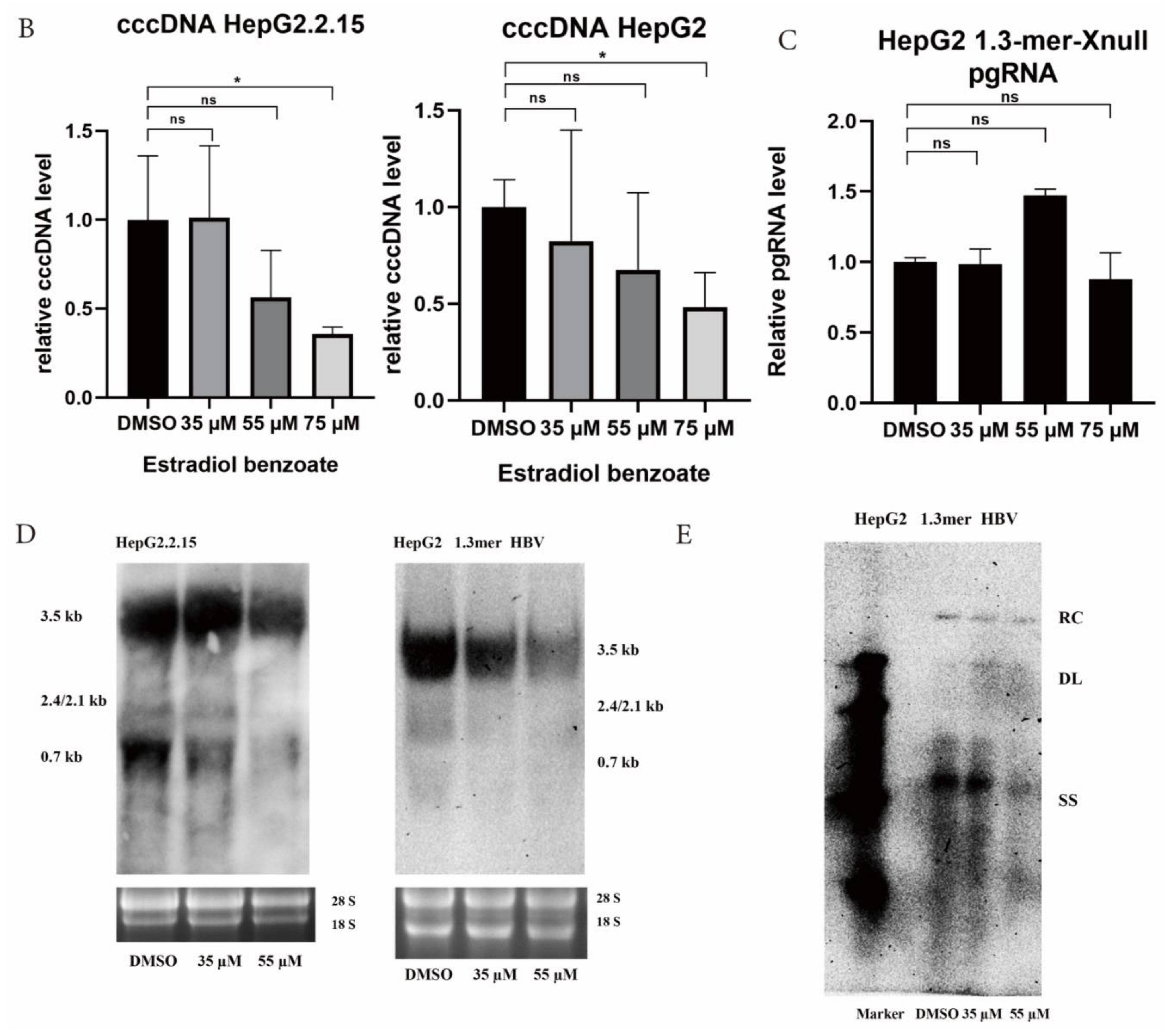
2.3. Estradiol Benzoate Inhibits HBV Activity
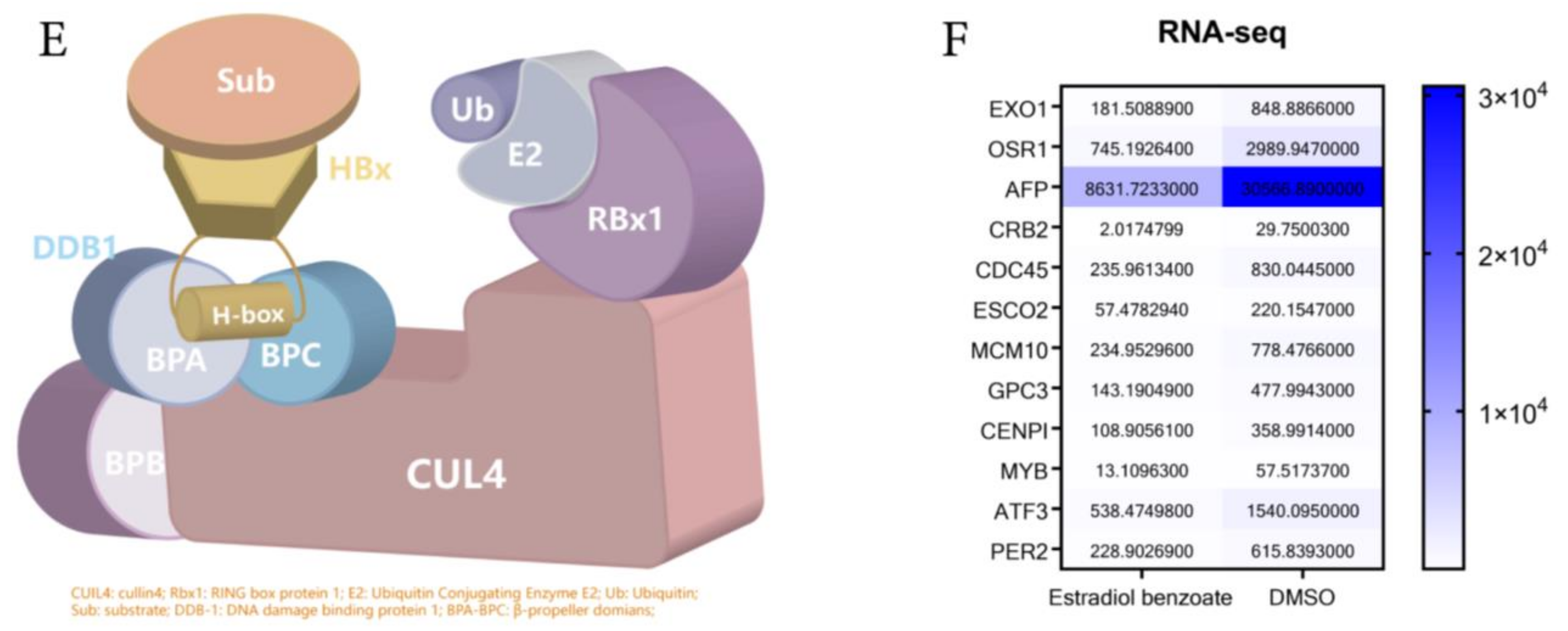
2.4. Estradiol Benzoate and HBx-Binding Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.2. Plasmids
4.3. Cell Line Establishment
4.4. Drug Library Screening
4.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.6. Western Blot
4.7. Quantitative Assay of Supernatant HBsAg, HBeAg, and HBV DNA
4.8. Viral RNA Analysis
4.9. Analysis of Viral DNA
4.10. HBx–Estradiol Benzoate Modeling
4.11. RNA-Seq
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis B. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Easl 2017 clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fung, S.; Choi, H.S.J.; Gehring, A.; Janssen, H.L.A. Getting to hbv cure: The promising paths forward. Hepatology 2022, 76, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Hildt, E. Intracellular trafficking of HBV particles. Cells 2020, 9, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Guo, S.; Schrodi, S.J. Mechanisms of DNA methylation in virus-host interaction in hepatitis b infection: Pathogenesis and oncogenetic properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.Y.; Sohn, B.H.; Yu, E.; Suh, D.J.; Chung, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Surzycki, S.J.; Lee, Y.I. Aberrant epigenetic modifications in hepatocarcinogenesis induced by hepatitis B virus X protein. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1476–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Robert, E.I.; van Breugel, P.C.; Strubin, M.; Zheng, N. A promiscuous alpha-helical motif anchors viral hijackers and substrate receptors to the CUL4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase machinery. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Teng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, P.; Song, X.; Lu, J.; et al. LINC01431 promotes histone H4R3 methylation to impede HBV covalently closed circular DNA transcription by stabilizing PRMT1. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, Y.; Yun, H.; Zheng, W.; Geng, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X. HBX represses WDR77 to enhance HBV replication by DDB1-mediated WDR77 degradation in the liver. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8362–8378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, T.; Faure-Dupuy, S.; Rolland, M.; Schuehle, S.; Hizir, Z.; Calderazzo, S.; Zhuang, X.; Wettengel, J.; Lopez, M.A.; Barnault, R.; et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Alpha-Mediated RelB/APOBEC3B Down-Regulation Allows Hepatitis B Virus Persistence. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1766–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.-J.; Kong, K.-Y.E.; Gao, W.-W.; Tang, H.-M.V.; Chaudhary, V.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chan, C.P.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Yuen, M.-F.; et al. Interplay between SIRT1 and hepatitis B virus X protein in the activation of viral transcription. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1860, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, D.L.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, N.; Xu, X.; Deng, Q.; Teng, X.-M.; Wang, K.-S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Han, Z.-G. Epigenetic modification induced by hepatitis b virus x protein via interaction with de novo DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivasudhan, E.; Blake, N.; Lu, Z.; Meng, J.; Rong, R. Hepatitis B viral protein HBX and the molecular mechanisms modulating the hallmarks of hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive review. Cells 2022, 11, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.-G.; Yuan, S.-X.; Tao, Q.-F.; Yu, J.; Cai, J.; Yang, Y.; Guo, X.-G.; Lin, K.-Y.; Ma, J.-Z.; Dai, D.-S.; et al. A novel HBX genotype serves as a preoperative predictor and fails to activate the JAK1/STATS pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kekulé, A.S.; Lauer, U.; Weiss, L.; Luber, B.; Hofschneider, P.H. Hepatitis B virus transactivator HBX uses a tumour promoter signalling pathway. Nature 1993, 361, 742–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, R.; Liu, W.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Hou, X.; Cai, S.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Yang, F.; Tan, X.; et al. The effects and underlying mechanisms of hepatitis B virus X gene mutants on the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 836517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.-T.; Hu, J.-L.; Ren, J.-H.; Yu, H.-B.; Zhong, S.; Wong, V.K.W.; Law, B.Y.K.; Chen, W.-X.; Xu, H.-M.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; et al. Dicoumarol, an NQO1 inhibitor, blocks cccDNA transcription by promoting degradation of HBX. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wei, L.; Xu, W. E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21 restricts hepatitis B virus replication by targeting HBX for proteasomal degradation. Antivir. Res. 2021, 192, 105107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawono, R.G.; Abe, T.; Qu, M.; Kuroki, D.; Deng, L.; Matsui, C.; Ryo, A.; Suzuki, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Sugiyama, M.; et al. HERC5 E3 ligase mediates isgylation of hepatitis B virus X protein to promote viral replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Song, H.; Xiao, Q.; Wei, Q.; Pang, X.; Gao, Y.; Tan, G. Type-III interferon stimulated gene TRIM31 mutation in an HBV patient blocks its ability in promoting HBX degradation. Virus Res. 2022, 308, 198650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, S.; Ely, A.; Crowther, C.; Moolla, N.; Salazar, F.H.; Marion, P.L.; Ferry, N.; Weinberg, M.S.; Arbuthnot, P. Effective inhibition of HBV replication in vivo by anti-HBX short hairpin RNAs. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szotek, E.L.; Narasipura, S.D.; Al-Harthi, L. 17β-estradiol inhibits HIV-1 by inducing a complex formation between β-catenin and estrogen receptor α on the HIV promoter to suppress HIV transcription. Virology 2013, 443, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khode, V.; Patil, S.; Kaveeshwar, V.; Ruikar, K.; Bargale, A.; Sarathkumar, E.; Patil, S. Ubiquitin mediated degradation of EGFR by 17 β-estradiol in triple negative MDA-MB-231 (TNBC) breast cancer cells line. Curr. Mol. Med. 2021, 22, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Rao, Z.; Qin, H.; Wei, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhou, L.; Wu, X. Effect of Yin-Zhi-Huang on up-regulation of Oatp2, Ntcp, and Mrp2 proteins in estrogen-induced rat cholestasis. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montalto, G.; Cervello, M.; Giannitrapani, L.; Dantona, F.; Terranova, A.; Castagnetta, L.A.M. Epidemiology, risk factors, and natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 963, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.; Zhou, G.; Zhai, Y.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yao, Z.; Shen, Y.; Qiang, B.; et al. Association of estrogen receptor alpha polymorphisms with susceptibility to chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2004, 40, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.-T.; Ye, J.; Xia, S.-L.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Su, Q.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Li, X. Polymorphism of estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) is associated with virological response to entecavir (ETV) in nucleoside-naïve adult patients with chronic hepatitis B. Infection 2013, 41, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almog, Y.; Klein, A.; Adler, R.; Laub, O.; Tur-Kaspa, R. Estrogen suppresses hepatitis b virus expression in male athymic mice transplanted with HBV transfected Hep G-2 cells. Antiviral Res. 1992, 19, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muain, M.F.A.; Cheo, K.H.; Omar, M.N.; Hamzah, A.S.A.; Lim, H.N.; Salleh, A.B.; Tan, W.S.; Tajudin, A.A. Gold nanoparticle-decorated reduced-graphene oxide targeting anti hepatitis B virus core antigen. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 122, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ding, L.; Yuan, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Huang, C.; Ye, Q. Hepatitis B virus X protein and the estrogen receptor variant lacking exon 5 inhibit estrogen receptor signaling in hepatoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 3095–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Yeh, S.; Lin, W.; Yeh, K.-H.; Yuan, Q.; Xia, N.; Chen, D.-S.; Chen, P.-J. Estrogen receptor α represses transcription of HBV genes via interaction with hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 989–998.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magri, A.; Barbaglia, M.N.; Foglia, C.Z.; Boccato, E.; Burlone, M.E.; Cole, S.; Giarda, P.; Grossini, E.; Patel, A.H.; Minisini, R.; et al. 17,β-estradiol inhibits hepatitis C virus mainly by interference with the release phase of its life cycle. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashida, K.; Shoji, I.; Deng, L.; Jiang, D.-P.; Ide, Y.-H.; Hotta, H. 17β-estradiol inhibits the production of infectious particles of hepatitis C virus. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 54, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sells, M.A.; Chen, M.L.; Acs, G. Production of hepatitis b virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forgues, M.; Marrogi, A.J.; Spillare, E.A.; Wu, C.-G.; Yang, Q.; Yoshida, M.; Wang, X.W. Interaction of the hepatitis B virus X protein with the CRM1-dependent nuclear export pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22797–22803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowarz, E.; Löscher, D.; Marschalek, R. Optimized sleeping beauty transposons rapidly generate stable transgenic cell lines. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mátés, L.; Chuah, M.K.L.; Belay, E.; Jerchow, B.; Manoj, N.; Acosta-Sanchez, A.; Grzela, D.; Schmitt, A.; Becker, K.; Matrai, J.; et al. Molecular evolution of a novel hyperactive sleeping beauty transposase enables robust stable gene transfer in vertebrates. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, Z.; Jung, H.-S.; Ryu, D.-K.; Ryu, W.-S. Genetic dissection of naturally occurring basal core promoter mutations of hepatitis B virus reveals a silent phenotype in the overlapping X gene. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2272–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirt, B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J. Mol. Biol. 1967, 26, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, M.; Wu, J.; Shi, Y. Structural and biochemical analysis of BCL-2 interaction with the hepatitis b virus protein HBX. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2074–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Identification of Estradiol Benzoate as an Inhibitor of HBx Using Inducible Stably Transfected HepG2 Cells Expressing HiBiT Tagged HBx. Molecules 2022, 27, 5000. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27155000
He J, Wu J, Chen J, Zhang S, Guo Y, Zhang X, Han J, Zhang Y, Guo Y, Lin Y, et al. Identification of Estradiol Benzoate as an Inhibitor of HBx Using Inducible Stably Transfected HepG2 Cells Expressing HiBiT Tagged HBx. Molecules. 2022; 27(15):5000. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27155000
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jingjing, Jingwen Wu, Jingwen Chen, Shenyan Zhang, Yifei Guo, Xueyun Zhang, Jiajia Han, Yao Zhang, Yue Guo, Yanxue Lin, and et al. 2022. "Identification of Estradiol Benzoate as an Inhibitor of HBx Using Inducible Stably Transfected HepG2 Cells Expressing HiBiT Tagged HBx" Molecules 27, no. 15: 5000. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27155000
APA StyleHe, J., Wu, J., Chen, J., Zhang, S., Guo, Y., Zhang, X., Han, J., Zhang, Y., Guo, Y., Lin, Y., Yu, W., Kong, Y., Shen, Z., Mao, R., & Zhang, J. (2022). Identification of Estradiol Benzoate as an Inhibitor of HBx Using Inducible Stably Transfected HepG2 Cells Expressing HiBiT Tagged HBx. Molecules, 27(15), 5000. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27155000






