Anti-Colon Cancer Activity of Dietary Phytochemical Soyasaponin I and the Induction of Metabolic Shifts in HCT116
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
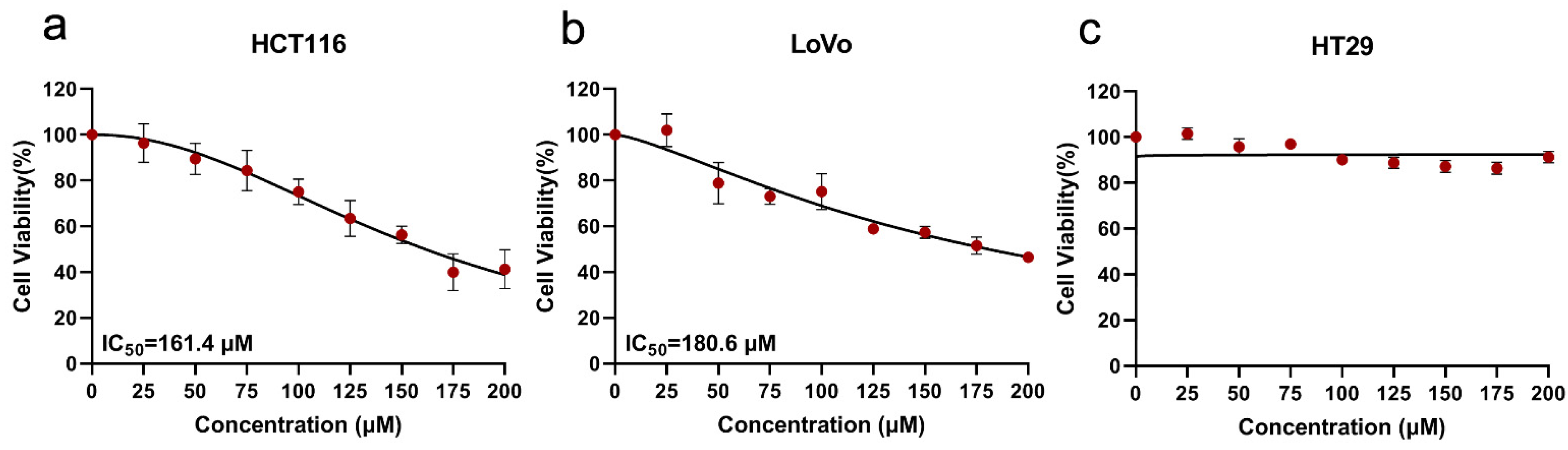
2.1. Effect of SsI on the Proliferation of Three Colon Cancer Cell Lines
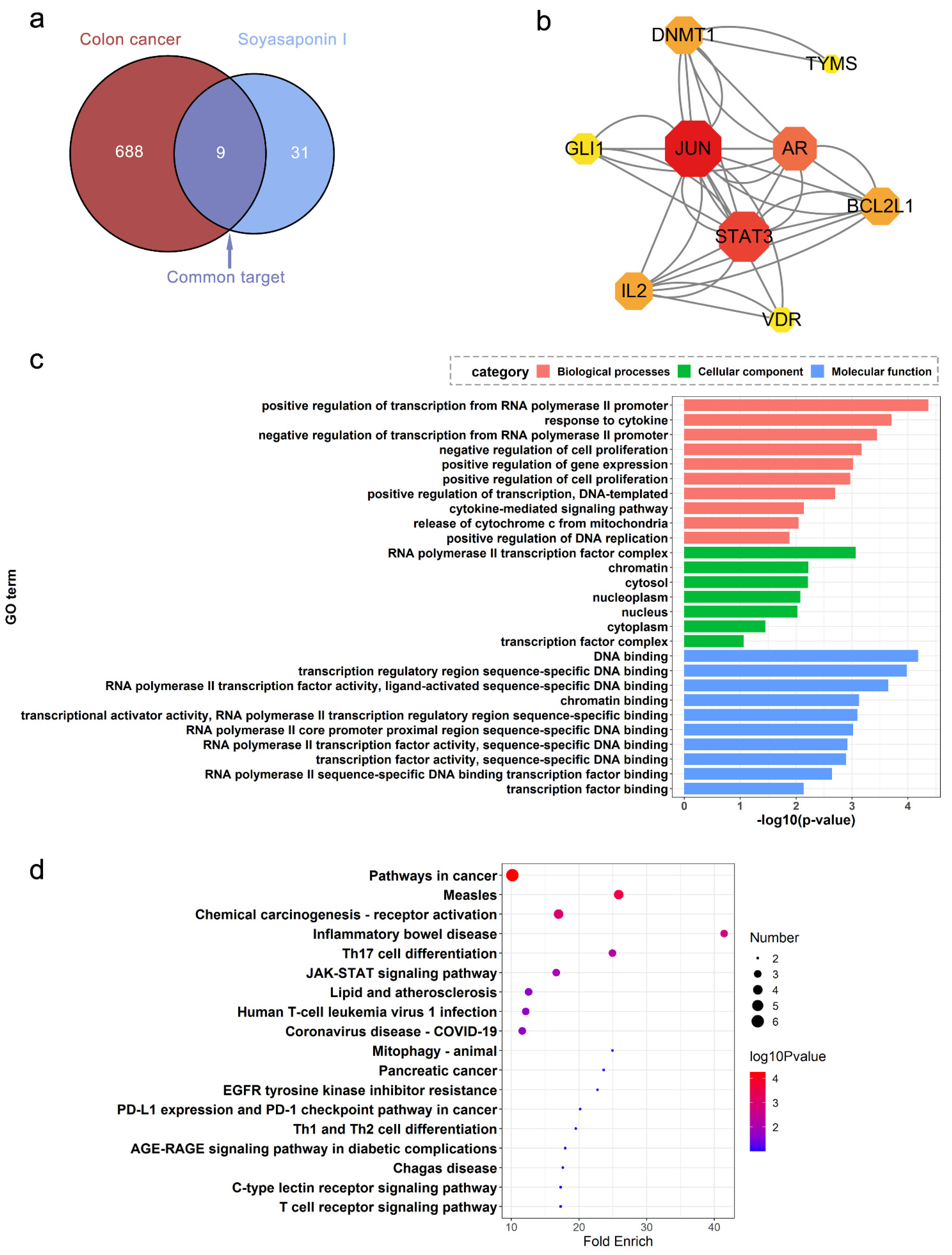
2.2. Potential Targets and Pathways for SsI against Colon Cancer
2.3. Metabolomic Analysis for SsI against HCT116
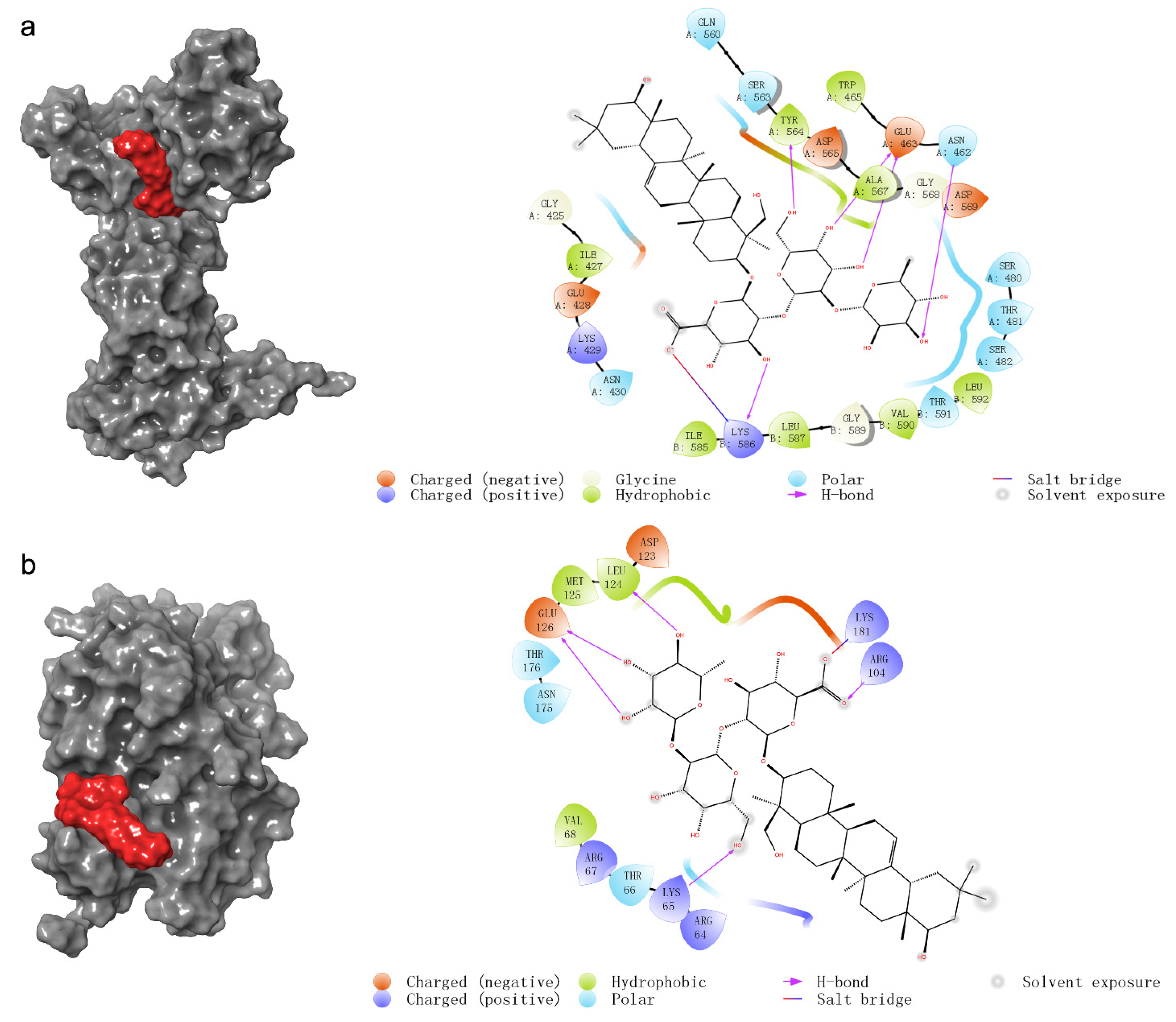
2.4. The Prediction of Molecular Docking
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Stock Solution of SsI
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Evaluation of Cell Proliferation
4.4. Network Pharmacologic Analysis
4.4.1. Screen of Interaction Targets
4.4.2. Enrichment Analysis and Construction of the Compound-Target-Pathway Network
4.5. Metabolomic Analysis
4.6. Molecular Docking
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladabaum, U.; Dominitz, J.A.; Kahi, C.; Schoen, R.E. Strategies for Colorectal Cancer Screening. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Garrett, W.S.; Chan, A.T. Nutrients, foods, and colorectal cancer prevention. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1244–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Afrin, S.; Giampieri, F.; Gasparrini, M.; Forbes-Hernandez, T.Y.; Cianciosi, D.; Reboredo-Rodriguez, P.; Zhang, J.; Manna, P.P.; Daglia, M.; Atanasov, A.G.; et al. Dietary phytochemicals in colorectal cancer prevention and treatment: A focus on the molecular mechanisms involved. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 38, 107322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, K.; Quiles, J.L.; Daglia, M.; Xiao, J.; Xu, B. Dietary phytochemicals modulate intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction and autoimmune diseases. Food Front. 2021, 2, 357–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Popovich, D.G. Group B oleanane triterpenoid extract containing soyasaponins I and III from soy flour induces apoptosis in Hep-G2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5315–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.P.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A. Saponins in pulses and their health promoting activities: A review. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Donat, P.; Fernandez-Blanco, C.; Sagratini, G.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M. Effects of soyasaponin I and soyasaponins-rich extract on the Alternariol-induced cytotoxicity on Caco-2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 77, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Lin, T.W.; Chang, W.W.; Wu, C.Y.; Lo, W.H.; Wang, P.H.; Tsai, Y.C. Soyasaponin-I-modified invasive behavior of cancer by changing cell surface sialic acids. Gynecol. Oncol. 2005, 96, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.W.; Yu, C.Y.; Lin, T.W.; Wang, P.H.; Tsai, Y.C. Soyasaponin I decreases the expression of alpha 2,3-linked sialic acid on the cell surface and suppresses the metastatic potential of B16F10 melanoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 341, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, P.; Wen, K.; Horng, H.; Chang, C.; Chen, Y.; Lee, W.; Wang, P. The role of alpha 2,3-linked sialylation on clear cell type epithelial ovarian cancer. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 57, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Park, Y.; Yeo, H.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D. Soyasaponin I attenuates TNBS-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting NF-kappa B pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10929–10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, L.; Chen, J.; Sun, S.; Mao, L.; Chu, X.; Deng, H.; Cai, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Cao, W. Soyasaponins can blunt inflammation by inhibiting the reactive oxygen species-mediated activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-kB pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Sun, S.; Zha, D.; Wu, J.; Mao, L.; Deng, H.; Chu, X.; Luo, H.; Zha, L. Soyasaponins prevent H2O2-induced inhibition of gap junctional intercellular communication by scavenging reactive oxygen species in rat liver cells. Nutr. Cancer 2014, 66, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Heo, H.; Yang, J.; Han, M.; Kim, D.; Kwon, Y.K. Soyasaponin I improved neuroprotection and regeneration in memory deficient model rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berhow, M.A.; Cantrell, C.L.; Duval, S.M.; Dobbins, T.A.; Maynes, J.; Vaughn, S.F. Analysis and quantitative determination of group B saponins in processed soybean products. Phytochem. Anal. 2002, 13, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.A.; Berhow, M.; Singletary, K.W. Induction of macroautophagy in human colon cancer cells by soybean B-group triterpenoid saponins. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurfinkel, D.M.; Rao, A.V. Soyasaponins: The relationship between chemical structure and colon anticarcinogenic activity. Nutr. Cancer 2003, 47, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, S.; Martini, G.; Rinaldi, B.; Martinelli, E.; Donniacuo, M.; Berrino, L.; Vitagliano, D.; Morgillo, F.; Barra, G.; De Palma, R.; et al. Primary and acquired resistance of colorectal cancer to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody can be overcome by combined treatment of regorafenib with cetuximab. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2975–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boutaghane, N.; Voutquenne-Nazabadioko, L.; Harakat, D.; Simon, A.; Kabouche, Z. Triterpene saponins of Genista ulicina Spach. Phytochemistry 2013, 93, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrovsky, V.S.; Chepikova, O.E.; Davydov, D.Z.; Zamyatnin, A.J.; Lukashev, A.N.; Lukasheva, E.V. Amino acid degrading enzymes and their application in cancer therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 446–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukasheva, E.V.; Babayeva, G.; Karshieva, S.S.; Zhdanov, D.D.; Pokrovsky, V.S. L-Lysine alpha-oxidase: Enzyme with anticancer properties. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokrovsky, V.S.; Treshalina, H.M.; Lukasheva, E.V.; Sedakova, L.A.; Medentzev, A.G.; Arinbasarova, A.Y.; Berezov, T.T. Enzymatic properties and anticancer activity of L-lysine alpha-oxidase from Trichoderma cf. aureoviride Rifai BKMF-4268D. Anticancer Drugs 2013, 24, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Han, M.; Han, S.; Kim, D. Metabolism of soyasaponin I by human intestinal microflora and its estrogenic and cytotoxic effects. Biomol. Ther. 2009, 17, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Iverson, D. Estrogen in obesity-associated colon cancer: Friend or foe? Protecting postmenopausal women but promoting late-stage colon cancer. Cancer Causes Control 2012, 23, 1767–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.A.; Lee, M.K.; Nam, K.H.; Chung, W.Y.; Park, C.S.; Lee, J.H.; Noh, T.; Yang, W.I.; Rhee, Y.; Lim, S.K.; et al. Expression and role of estrogen receptor alpha and beta in medullary thyroid carcinoma: Different roles in cancer growth and apoptosis. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 195, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzo, P.; Caiazza, F.; Moreno, S.; Marino, M. Role of ERbeta palmitoylation in the inhibition of human colon cancer cell proliferation. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2007, 14, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Leo, A.; Barone, M.; Maiorano, E.; Tanzi, S.; Piscitelli, D.; Marangi, S.; Lofano, K.; Ierardi, E.; Principi, M.; Francavilla, A. ER-beta expression in large bowel adenomas: Implications in colon carcinogenesis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2008, 40, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Kominea, A.; Vandoros, G.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Andricopoulos, P.; Varakis, I.; Sotiropoulou-Bonikou, G.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Oestrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) is abundantly expressed in normal colonic mucosa, but declines in colon adenocarcinoma paralleling the tumour’s dedifferentiation. Eur. J. Cancer 2003, 39, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Waters, C.E.; Lewis, A.E.; Langman, M.J.; Eggo, M.C. Oestrogen-induced apoptosis in colonocytes expressing oestrogen receptor beta. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 174, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorelli, G.; Picariello, L.; Martineti, V.; Tonelli, F.; Brandi, M.L. Functional estrogen receptor beta in colon cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 261, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowlands, J.C.; Berhow, M.A.; Badger, T.M. Estrogenic and antiproliferative properties of soy sapogenols in human breast cancer cells in vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Yoshida, I.; Nakae, S.; Okita, K.; Gouda, M.; Matsubara, M.; Yokota, K.; Ishiguro, H.; Tada, T. Crystal structure of human mono-phosphorylated ERK1 at Tyr204. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, R.J.; Likis, F.E. Estrogen: Physiology, pharmacology, and formulations for replacement therapy. J. Midwifery Womens Health 2002, 47, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, R.W.; Fang, M.; Park, S.M.; Hutchinson, L.; Green, M.R. A KRAS-directed transcriptional silencing pathway that mediates the CpG island methylator phenotype. Elife 2014, 3, e2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Mo, Y.Y.; Echeveste, C.E.; Oshima, K.; Zhang, J.; Yearsley, M.; Lin, C.W.; Yu, J.; Liu, P.; Du, M.; et al. Black raspberries attenuate colonic adenoma development in Apc (Min) mice: Relationship to hypomethylation of promoters and gene bodies. Food Front. 2020, 1, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zheng, Y.L.; Hyde, W.; Hendrich, S.; Murphy, P.A. Human fecal metabolism of soyasaponin I. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2689–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Reddy, M.B.; Hendrich, S.; Murphy, P.A. Soyasaponin I and sapongenol B have limited absorption by Caco-2 intestinal cells and limited bioavailability in women. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1867–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neacsu, M.; Raikos, V.; Benavides-Paz, Y.; Duncan, S.H.; Duncan, G.J.; Christie, J.S.; Johnstone, A.M.; Russell, W.R. Sapogenol is a major microbial metabolite in human plasma associated with high protein soy-based diets: The relevance for functional food formulations. Foods 2020, 9, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagratini, G.; Caprioli, G.; Maggi, F.; Font, G.; Giardina, D.; Manes, J.; Meca, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Sirocchi, V.; Torregiani, E.; et al. Determination of soyasaponins I and betag in raw and cooked legumes by solid phase extraction (SPE) coupled to liquid chromatography (LC)-mass spectrometry (MS) and assessment of their bioaccessibility by an in vitro digestion model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery v6.8. Available online: https://david-d.ncifcrf.gov/ (accessed on 21 February 2022).
- STRING v11.5. Available online: https://string-db.org/ (accessed on 21 February 2022).
- Jang, W.; Choi, B.; Song, S.; Lee, N.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Jeong, C. Multi-omics analysis reveals that ornithine decarboxylase contributes to erlotinib resistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 92727–92742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zelena, E.; Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Carroll, K.M.; Begley, P.; O’Hagan, S.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Wilson, I.D.; et al. Development of a robust and repeatable UPLC-MS method for the long-term metabolomic study of human serum. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Want, E.J.; Masson, P.; Michopoulos, F.; Wilson, I.D.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Loftus, N.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global metabolic profiling of animal and human tissues via UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MetaboAnalyst v5.0. Available online: https://www.metaboanalyst.ca/ (accessed on 17 March 2022).
- Cui, Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ma, Y.H.; Yu, H.Y.; Zhao, X.Z.; Zhang, L.H.; Ge, S.Q.; Zhang, G.W.; Qin, X.D. A network pharmacology approach to investigate the mechanism of Shuxuening injection in the treatment of ischemic stroke. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 257, 112891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
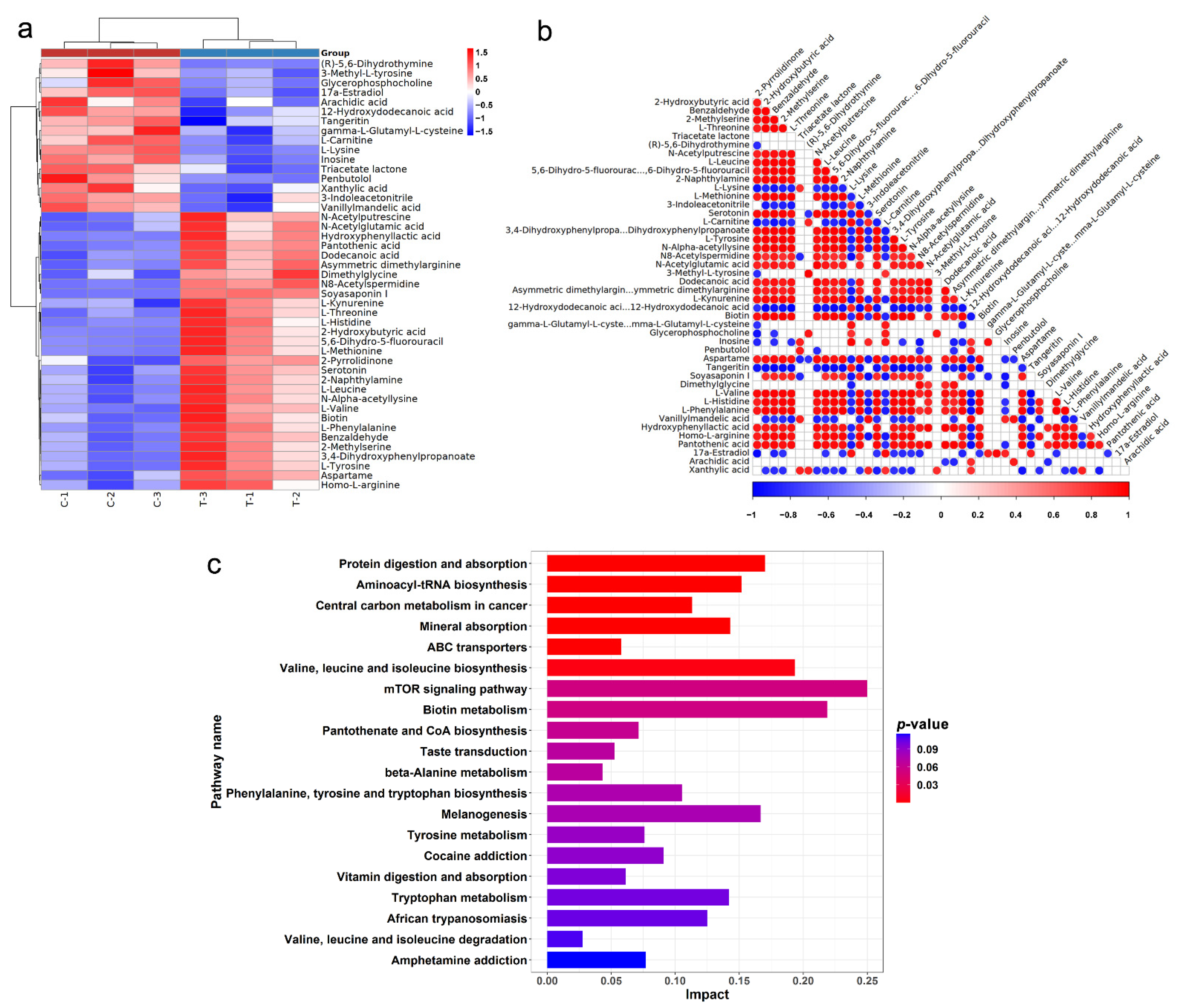
| Name | KEGG Entry | log2(FC) | p-Value | VIP | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soyasaponin I | C08983 | 15.52 | 0 | 1.82 | up |
| Dodecanoic acid | C02679 | 2.24 | 0.0036 | 1.74 | up |
| N8-Acetylspermidine | C01029 | 1.21 | 0.0001 | 1.80 | up |
| 2-Hydroxybutyric acid | C05984 | 0.99 | 0.0433 | 1.68 | up |
| L-Methionine | C00073 | 0.99 | 0.0402 | 1.69 | up |
| 5,6-Dihydro-5-fluorouracil | C16630 | 0.98 | 0.0408 | 1.68 | up |
| Pantothenic acid | C00864 | 0.97 | 0.0013 | 1.83 | up |
| 2-Pyrrolidinone | C11118 | 0.92 | 0.0132 | 1.65 | up |
| Hydroxyphenyllactic acid | C03672 | 0.86 | 0.0349 | 1.76 | up |
| Biotin | C00120 | 0.83 | 0.0205 | 1.62 | up |
| 2-Naphthylamine | C02227 | 0.79 | 0.0165 | 1.64 | up |
| Xanthylic acid | C00655 | −0.8 | 0.0383 | 1.60 | down |
| Triacetate lactone | C02752 | −0.84 | 0.0189 | 1.60 | down |
| 3-Methyl-L-tyrosine | C20800 | −0.86 | 0.0395 | 1.52 | down |
| Vanillylmandelic acid | C05584 | −1.31 | 0.0259 | 1.64 | down |
| Penbutolol | C07416 | −1.41 | 0.0121 | 1.65 | down |
| L-Lysine | C00047 | −1.54 | 0.0003 | 1.79 | down |
| Arachidic acid | C06425 | −1.69 | 0.0465 | 1.53 | down |
| (R)-5,6-Dihydrothymine | C21028 | −3.00 | 0.0283 | 1.72 | down |
| 17a-Estradiol | C02537 | −3.13 | 0.0047 | 1.78 | down |
| Category | Protein | PDB ID | Docking Score * | Amino Acid Residues |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| common target proteins of network pharmacology | DNMT1 | 3epz | −5.314 | ASN462, GLU463, TYR564, LYS586 |
| STAT3 | 6njs | −3.863 | ARG609, SER611, GLU612, SER613 | |
| VDR | 1db1 | −3.706 | SER265, GLU395, ARG402 | |
| BCL2L1 | 1bxl | −3.396 | ARG34, GLU36, GLU44 | |
| IL2 | 1irl | −3.192 | THR3, GLN13, GLU95 | |
| GLI1 | 2gli | - | - | |
| AR | 1t65 | - | - | |
| JUN | 1s9k | - | - | |
| TYMS | 1hvy | - | - | |
| key proteins of the estrogen signaling pathway | ERK1 | 2zoq | −4.313 | Lys65, Arg104, Glu126, Leu124, Lys181 |
| ERK2 | 4qp6 | −3.917 | ILE86, ASP106 | |
| ESR1(ER-α) | 1a52 | - | - | |
| ESR2(ER-β) | 1qkm | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, X.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, N.; Zeng, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, R. Anti-Colon Cancer Activity of Dietary Phytochemical Soyasaponin I and the Induction of Metabolic Shifts in HCT116. Molecules 2022, 27, 4382. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144382
Xia X, Lin Q, Zhao N, Zeng J, Yang J, Liu Z, Huang R. Anti-Colon Cancer Activity of Dietary Phytochemical Soyasaponin I and the Induction of Metabolic Shifts in HCT116. Molecules. 2022; 27(14):4382. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144382
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Xuewei, Qianmin Lin, Ning Zhao, Jinzi Zeng, Jiajia Yang, Zhiyuan Liu, and Riming Huang. 2022. "Anti-Colon Cancer Activity of Dietary Phytochemical Soyasaponin I and the Induction of Metabolic Shifts in HCT116" Molecules 27, no. 14: 4382. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144382
APA StyleXia, X., Lin, Q., Zhao, N., Zeng, J., Yang, J., Liu, Z., & Huang, R. (2022). Anti-Colon Cancer Activity of Dietary Phytochemical Soyasaponin I and the Induction of Metabolic Shifts in HCT116. Molecules, 27(14), 4382. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144382







