Curcumin Derivative C66 Suppresses Pancreatic Cancer Progression through the Inhibition of JNK-Mediated Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
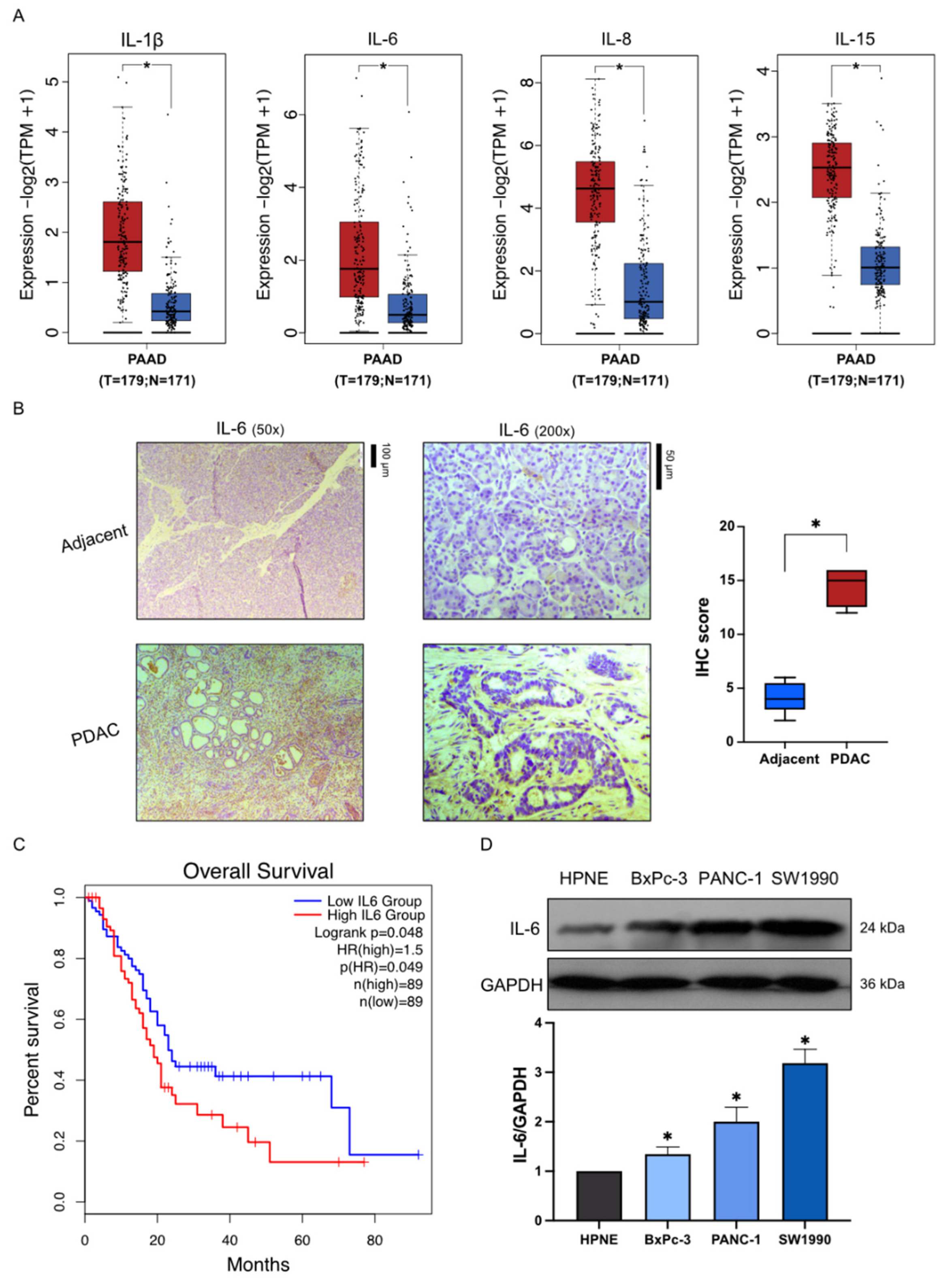
2.1. High Expression of Inflammatory Factors in Pancreatic Cancer
2.2. Inhibition of Inflammatory Factors by C66
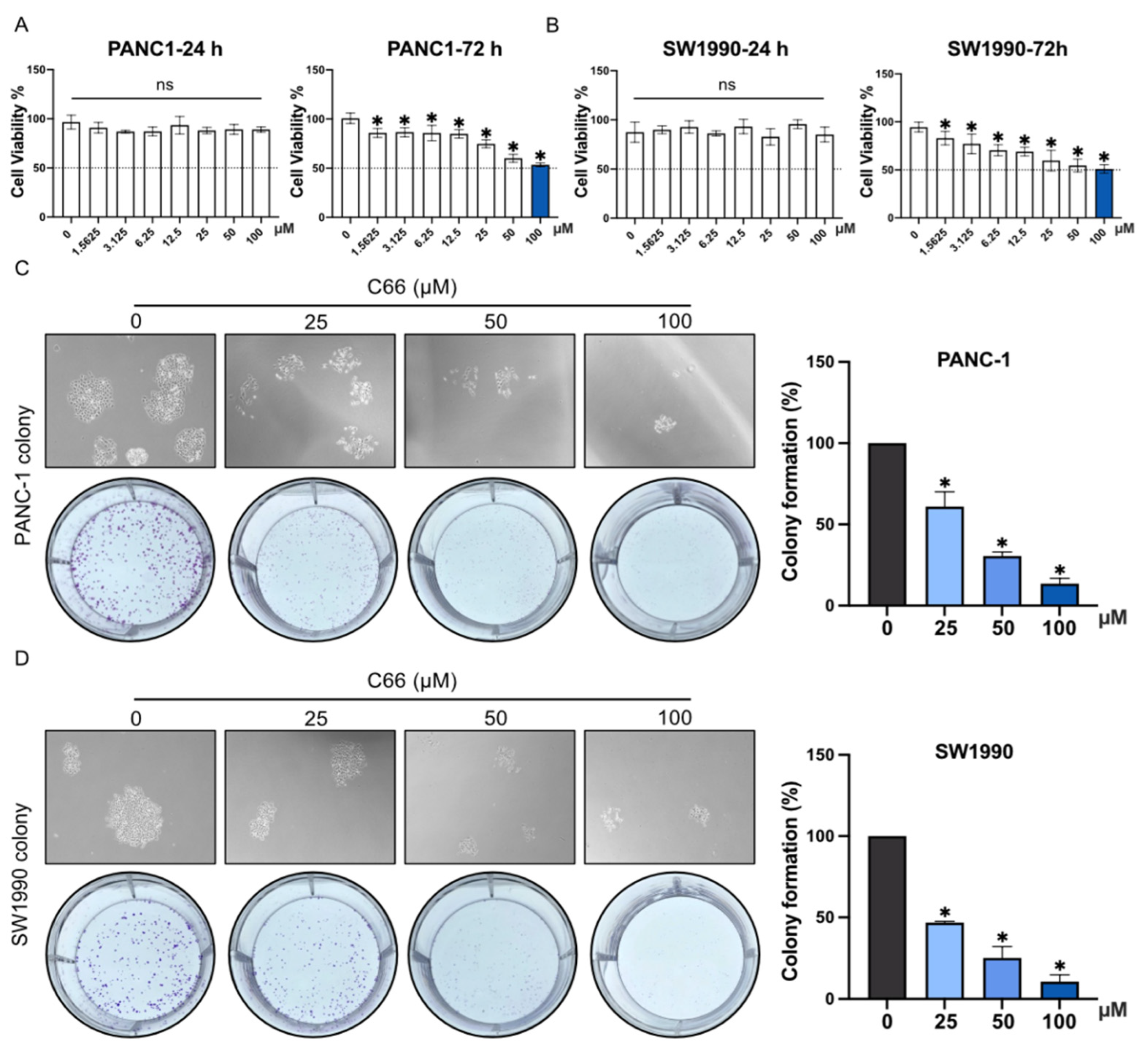
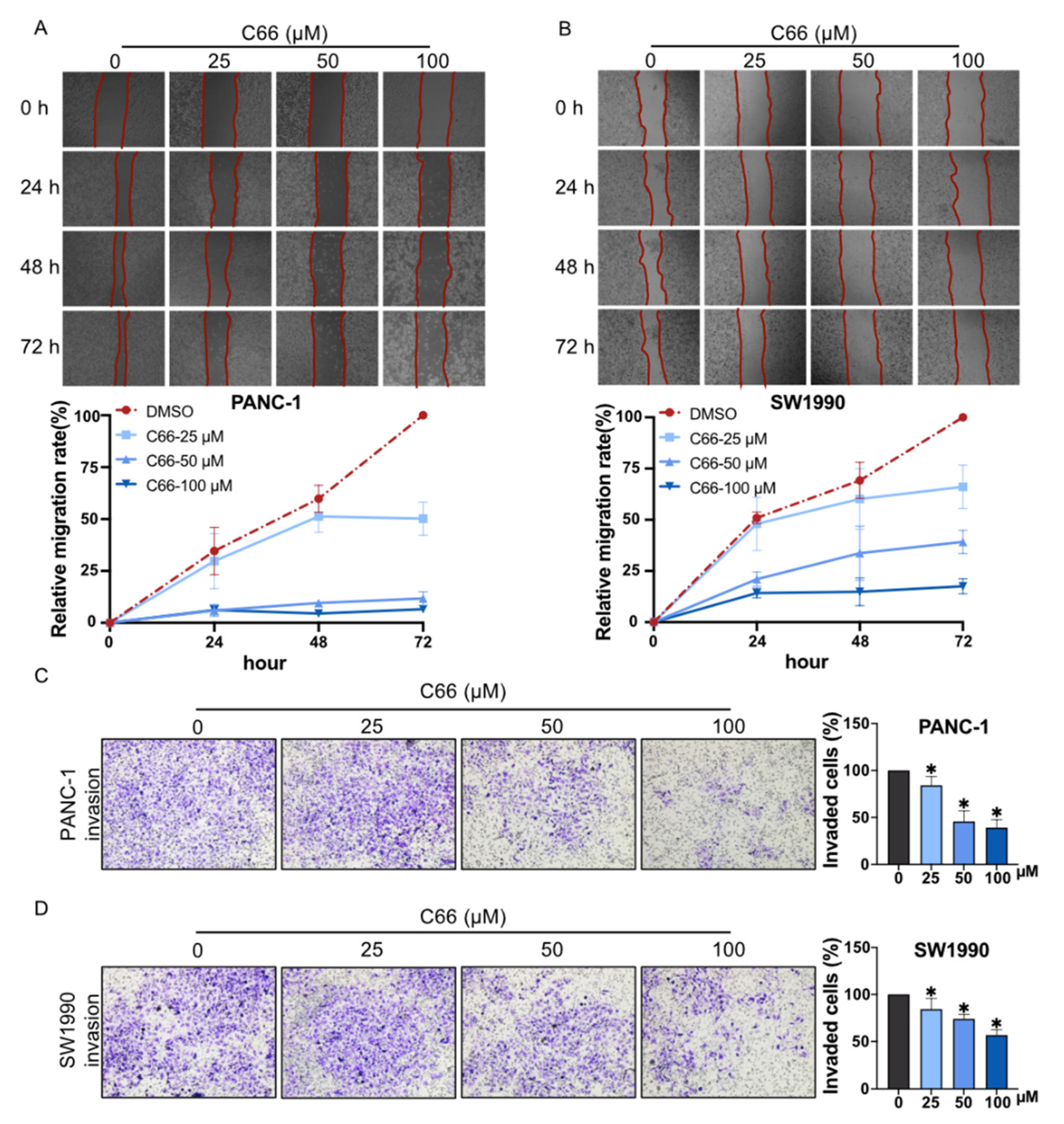
2.3. Inhibition of the Proliferation and Migration of Pancreatic Cancer Cells by C66
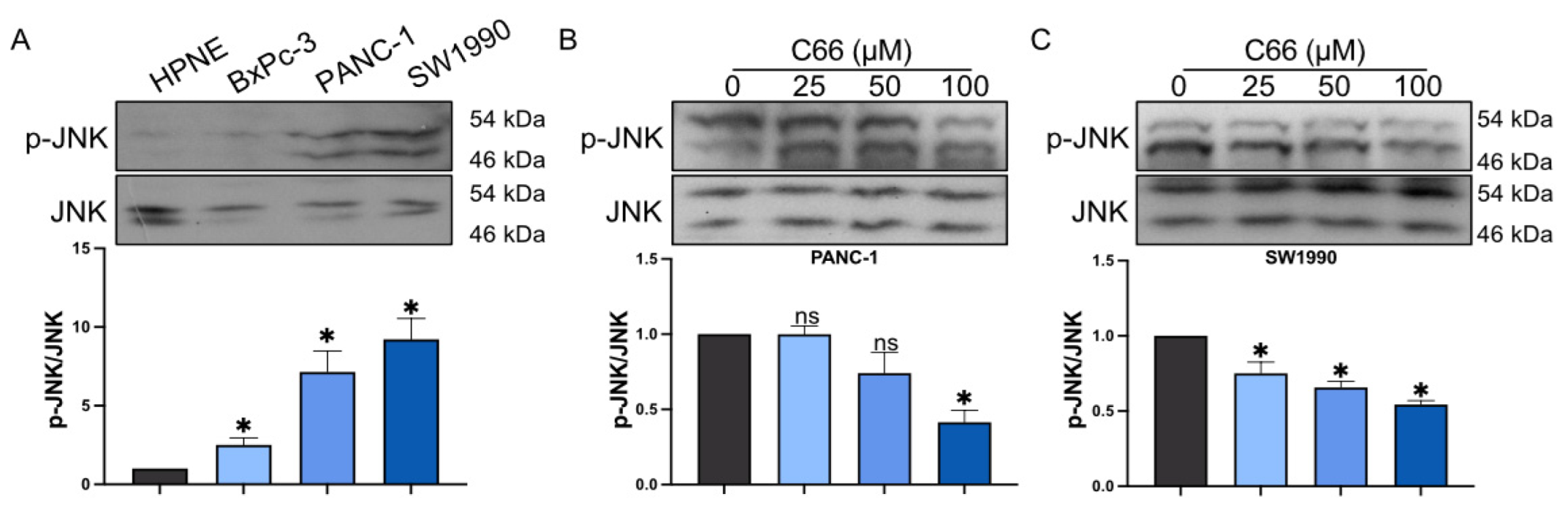
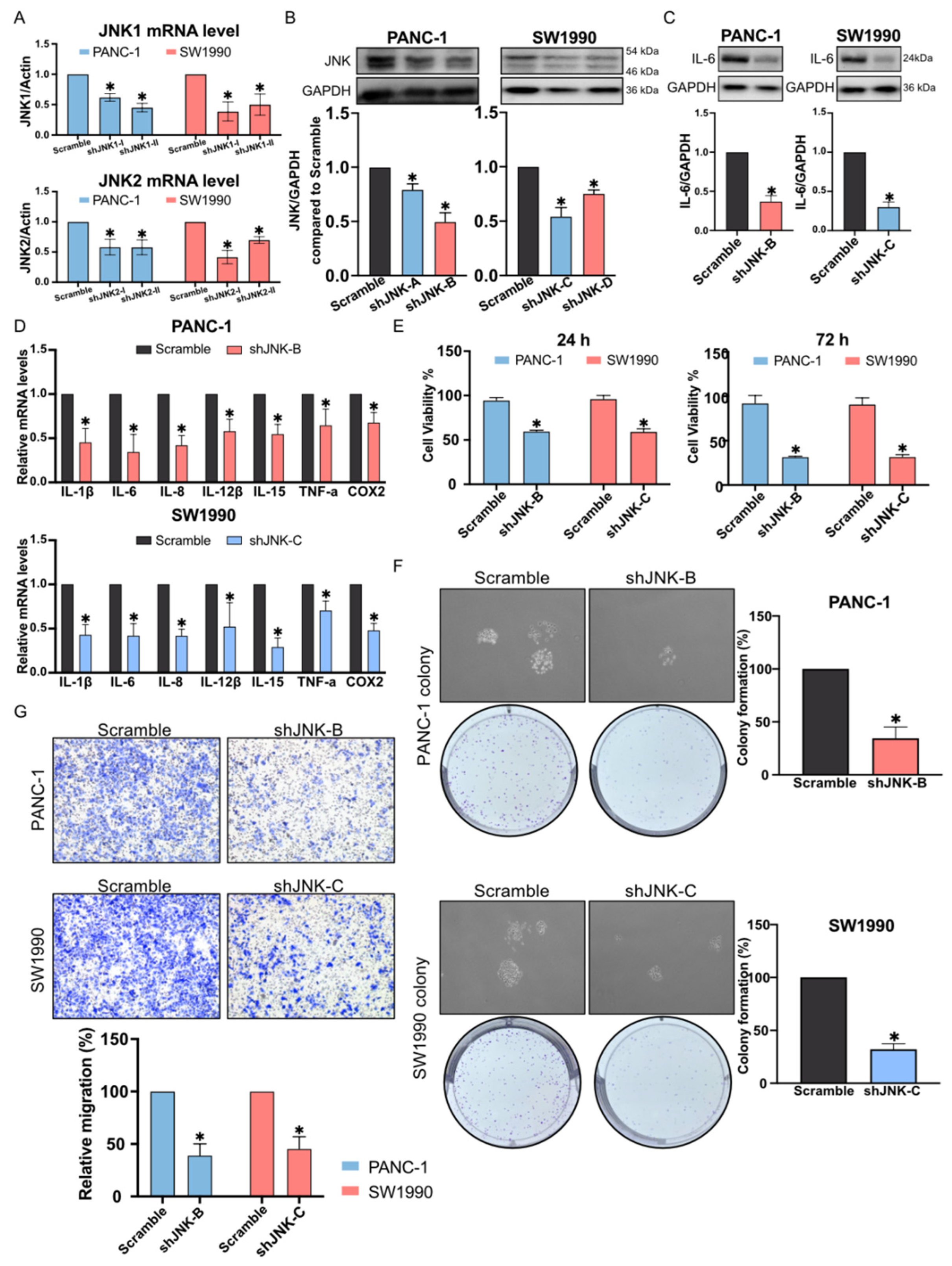
2.4. Reduction in Pancreatic Cancer Cell Inflammation by C66 Targeting JNK
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Chemicals
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. JNK Knockdown
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Western Blot Assay
4.6. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.7. Cell Proliferation
4.7.1. CCK-8 Assay
4.7.2. Colony Formation Assay
4.8. Migration Assay
4.8.1. Scratch Wound Assay
4.8.2. Transwell Assay
4.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Macchini, M.; Centonze, F.; Peretti, U.; Orsi, G.; Militello, A.M.; Valente, M.M.; Cascinu, S.; Reni, M. Treatment opportunities and future perspectives for pancreatic cancer patients with germline BRCA1-2 pathogenic variants. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 100, 102262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, F.; Mo, X.; Hu, C.; Wang, M.; Xu, H.; Yao, C.; Xia, H.; Lan, L. Centromere protein F is identified as a novel therapeutic target by genomics profile and contributing to the progression of pancreatic cancer. Genomics 2021, 113, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-J.; Hu, M.-H.; Xu, F.-G.; Xu, H.-J.; She, J.-J.; Xia, H.-P. Understanding the inflammation-cancer transformation in the development of primary liver cancer. Hepatoma Res. 2018, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Tarique, M.; Muhammad, N.; Naz, H.; Hafeez, A.; Zughaibi, T.A.; Kamal, M.A.; Rehan, M. A Critical Transcription Factor NF-κB as a Cancer Therapeutic Target and its Inhibitors as Cancer Treatment Options. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 4117–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundy, J.; Gearing, L.J.; Gao, H.; West, A.C.; McLeod, L.; Deswaerte, V.; Yu, L.; Porazinski, S.; Pajic, M.; Hertzog, P.J.; et al. TLR2 activation promotes tumour growth and associates with patient survival and chemotherapy response in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2021, 40, 6007–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lin, H.; Ouyang, R.; Yang, Y.; Peng, J. Prognostic significance of the systemic immune-inflammation index in pancreatic carcinoma patients: A meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20204401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wu, W.; Jacevic, V.; Franca, T.C.C.; Wang, X.; Kuca, K. Selective inhibitors for JNK signalling: A potential targeted therapy in cancer. J. Enzyme. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipner, M.B.; Peng, X.L.; Jin, C.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; East, M.P.; Rashid, N.U.; Moffitt, R.A.; Herrera Loeza, S.G.; Morrison, A.B.; et al. Irreversible JNK1-JUN inhibition by JNK-IN-8 sensitizes pancreatic cancer to 5-FU/FOLFOX chemotherapy. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, K.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; et al. Inhibition of JNK phosphorylation by a novel curcumin analog prevents high glucose-induced inflammation and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes and the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3497–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalli, M.; Li, R.; Mills, G.B.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Zervantonakis, I.K. Mechanical Stress Signaling in Pancreatic Cancer Cells Triggers p38 MAPK- and JNK-Dependent Cytoskeleton Remodeling and Promotes Cell Migration via Rac1/cdc42/Myosin II. Mol. Cancer Res. 2022, 20, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, J.G.; Sung, G.H.; Yang, S.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.H.; Ha, V.T.; Kim, H.G.; Yi, Y.S.; et al. Kaempferol, a dietary flavonoid, ameliorates acute inflammatory and nociceptive symptoms in gastritis, pancreatitis, and abdominal pain. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, F.; Liu, B.; Shen, C. Kaempferol potentiates the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to erlotinib via inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and epidermal growth factor receptor. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 1587–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Ye, T.; Xiang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lou, B.; Zhang, F.; Chen, B.; Zhou, M. Quercetin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, decreases invasiveness and metastasis, and reverses IL-6 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition, expression of MMP by inhibiting STAT3 signaling in pancreatic cancer cells. Onco. Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 4719–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Sun, L.; Lei, J.; Wu, Z.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Z. Curcumin inhibits pancreatic cancer cell invasion and EMT by interfering with tumor-stromal crosstalk under hypoxic conditions via the IL-6/ERK/NF-κB axis. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Xu, F.; Zhu, X.; Bai, B.; Guo, L.; Liang, G.; Shan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B. Inhibition Of JNK Phosphorylation By Curcumin Analog C66 Protects LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 4161–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, L.; Hu, X.; Hu, X.; Yin, S.; Chen, J.; He, H.; Hong, S.; Yang, B.; Singh, K.K.; Feng, J.; et al. Curcumin analogue C66 attenuates obesity-induced renal injury by inhibiting chronic inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, L.; Zou, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fang, Q.; Jiang, L.; Chen, G.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of allylated and prenylated mono-carbonyl analogs of curcumin as anti-inflammatory agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 74, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Species | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| JNK1 | Human | ACACCACAGAAATCCCTAGAAG CACAGCATCTGATAGAGAAGGT |
| JNK2 | Human | ATCAGAATCTGAGCGAGACAAA CAAACAGTGATGTATGGGTGAC |
| IL-1β | Human | GCCAGTGAAATGATGGCTTATT AGGAGCACTTCATCTGTTTAGG |
| IL-6 | Human | CACTGGTCTTTTGGAGTTTGAG GGACTTTTGTACTCATCTGCAC |
| IL-8 | Human | AACTGAGAGTGATTGAGAGTGG ATGAATTCTCAGCCCTCTTCAA |
| IL-12β | Human | TAAGATGCGAGGCCAAGAATTA TACTCATACTCCTTGTTGTCCC |
| TNF-a | Human | TGCACTTTGGAGTGATCGGC ACTCGGGGTTCGAGAAGATG |
| COX2 | Human | TGTCAAAACCGAGGTGTATGTA AACGTTCCAAAATCCCTTGAAG |
| β-actin | Human | GATTCCTATGTGGGCGACGA AGGTCTCAAACATGATCTGGGT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, R.; Deng, J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, L.; Liang, G.; Chen, X.; Xu, Z. Curcumin Derivative C66 Suppresses Pancreatic Cancer Progression through the Inhibition of JNK-Mediated Inflammation. Molecules 2022, 27, 3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103076
Chen H, Jiang Y, Liu R, Deng J, Chen Q, Chen L, Liang G, Chen X, Xu Z. Curcumin Derivative C66 Suppresses Pancreatic Cancer Progression through the Inhibition of JNK-Mediated Inflammation. Molecules. 2022; 27(10):3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103076
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hongjin, Yuchen Jiang, Rongdiao Liu, Jie Deng, Qinbo Chen, Lingfeng Chen, Guang Liang, Xiong Chen, and Zheng Xu. 2022. "Curcumin Derivative C66 Suppresses Pancreatic Cancer Progression through the Inhibition of JNK-Mediated Inflammation" Molecules 27, no. 10: 3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103076
APA StyleChen, H., Jiang, Y., Liu, R., Deng, J., Chen, Q., Chen, L., Liang, G., Chen, X., & Xu, Z. (2022). Curcumin Derivative C66 Suppresses Pancreatic Cancer Progression through the Inhibition of JNK-Mediated Inflammation. Molecules, 27(10), 3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103076






