Folding and Unfolding of Exogenous G-Rich Oligonucleotides in Live Cells by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy of o-BMVC Fluorescent Probe
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. FLIM Images of o-BMVC for Monitoring the Exogenous G4s in CL1-0 Live Cells
2.2. FLIM Images of o-BMVC for Monitoring the Exogenous Single-Stranded HT23 in CL1-0 Live Cells
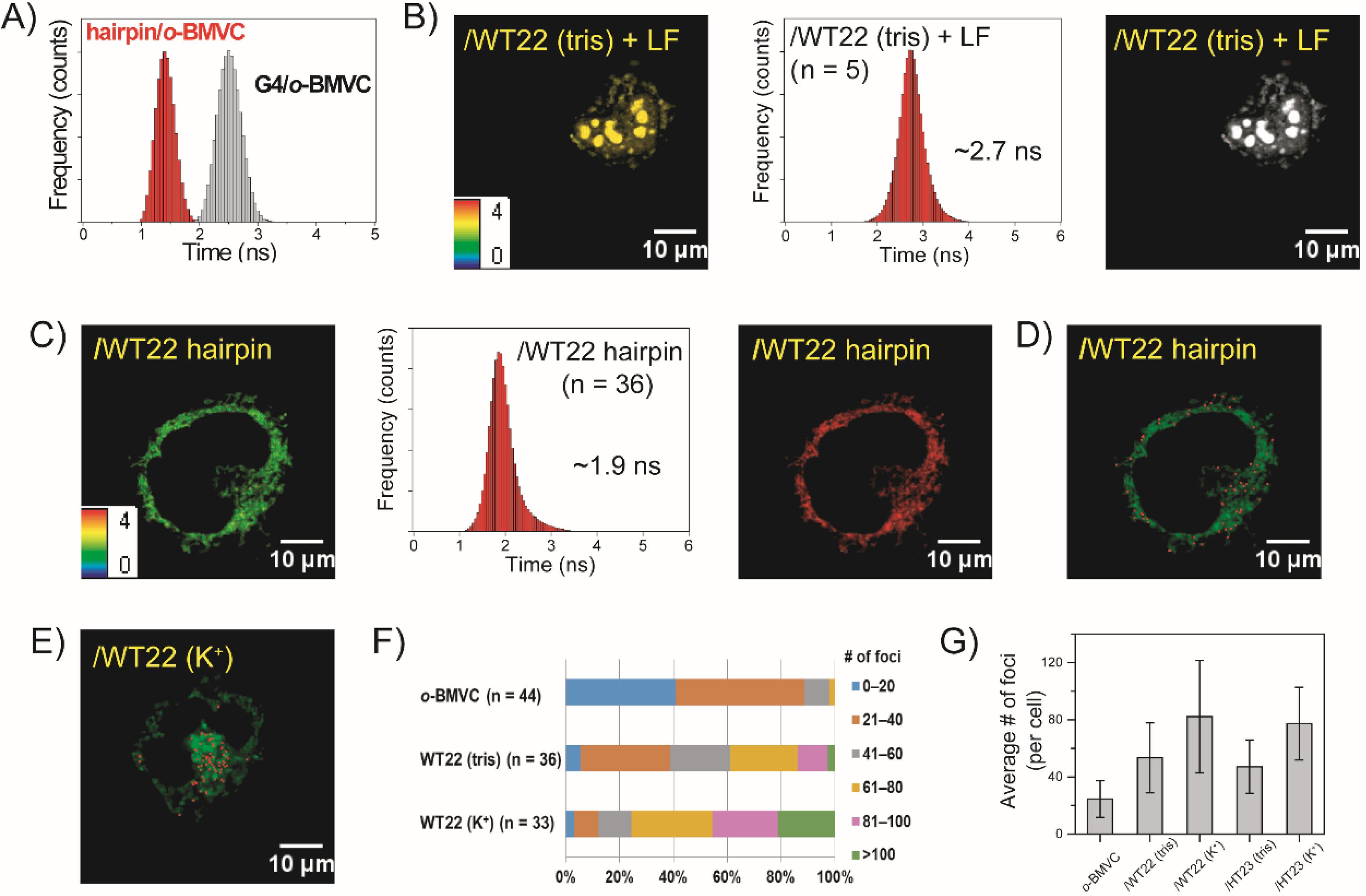
2.3. FLIM Images of o-BMVC for Monitoring the Exogenous WT22 in CL1-0 Live Cells
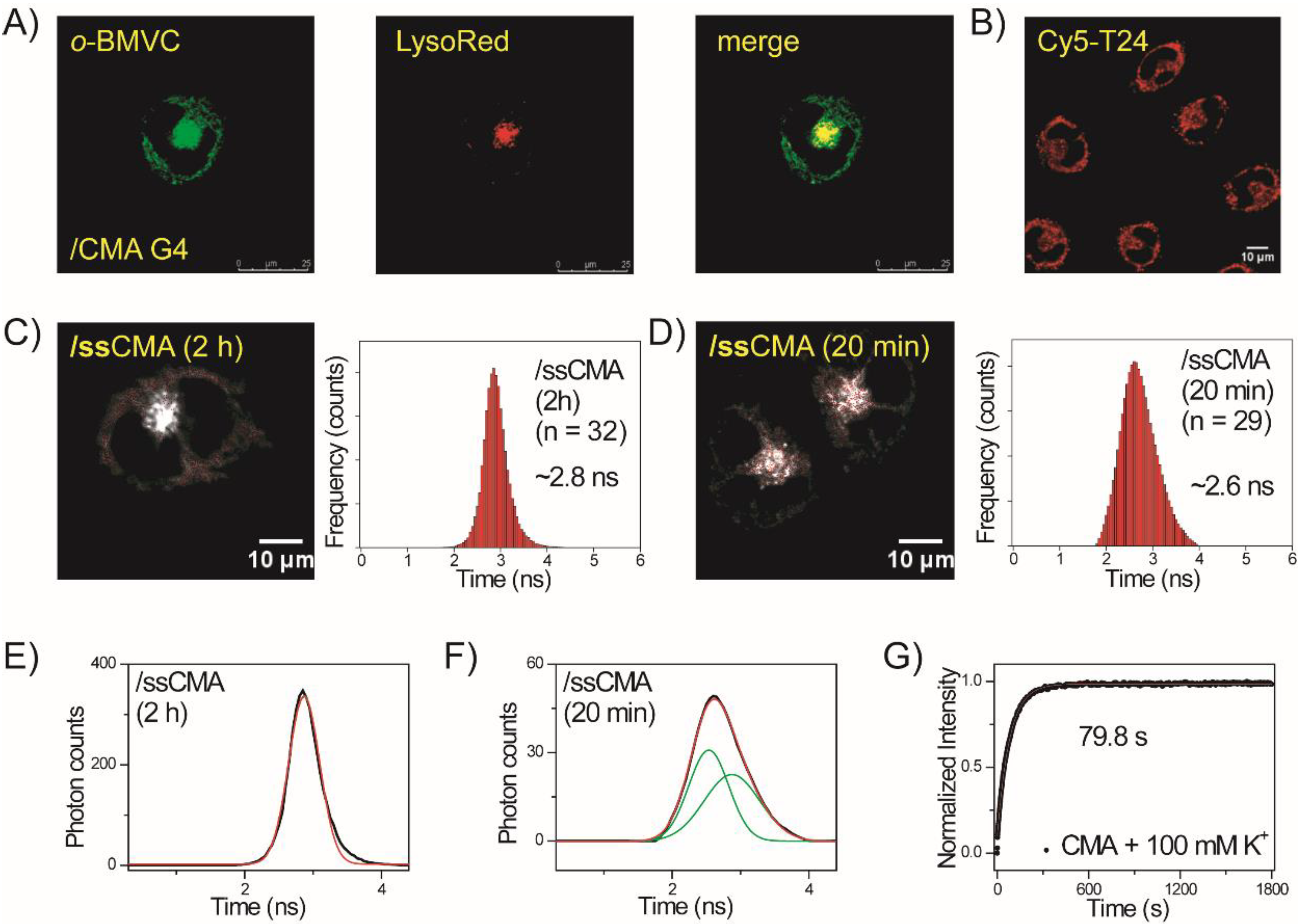
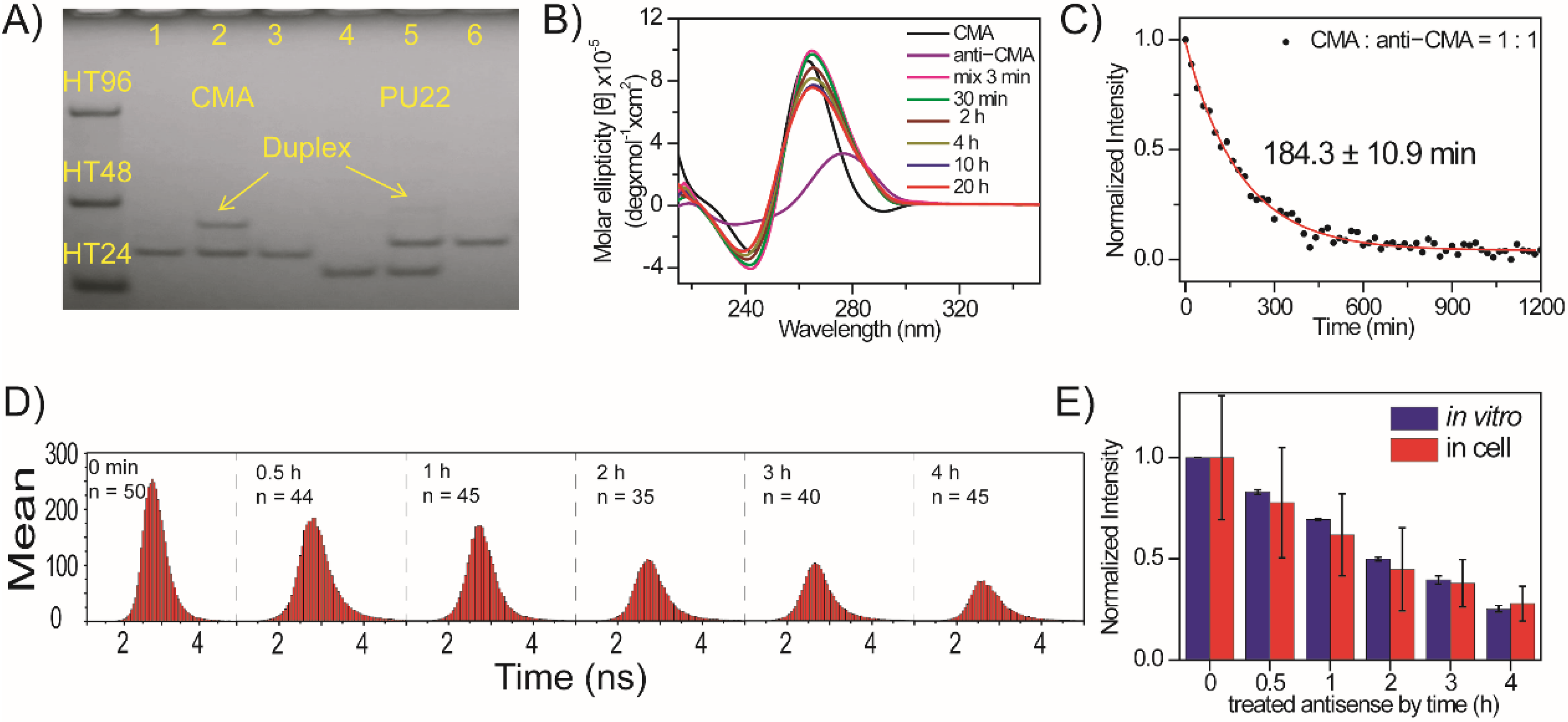
2.4. Folding of Exogenous Single-Stranded CMA into G4 Structures in CL1-0 Live Cells
2.5. Unfolding of Exogenous CMA G4 Structure by Its Anti-CMA in CL1-0 Live Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Properties of o-BMVC Molecule
4.2. Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM)
4.3. Confocal Microscopy
4.4. Circular Dichroism (CD)
4.5. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE)
4.6. Cell Cultures
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. Prevalence of quadruplexes in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2908–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, A.K.; Johnston, M.; Neidle, S. Highly prevalent putative quadruplex sequence motifs in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2901–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, V.S.; Marsico, G.; Boutell, J.M.; di Antonio, M.; Smith, G.P.; Balasubramanian, S. High-resolution sequencing of DNA G-quadruplex secondary structures in the human genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, D.; Gilbert, W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature 1988, 334, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundquist, W.I.; Klug, A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature 1989, 342, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.R.; Raghuraman, M.K.; Cech, T.R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: The G-quartet model. Cell 1989, 59, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D.; Lipps, H.J. G-quadruplexes and their regulatory roles in biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 8627–8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biffi, G.; Tannahill, D.; McCafferty, J.; Balasubramanian, S. Quantitative visualization of DNA G-quadruplex structures in human cells. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.Y.; Chien, C.H.; Chu, J.F.; Huang, W.C.; Lin, M.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Chang, T.C. Fluorescent probe for visualizing guanine-quadruplex DNA by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 101309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Chavez, E.A.; Platt, J.; Johnson, F.B.; Brosh, R.M., Jr.; Sen, D.; Lansdorp, P.M. Detection of G-quadruplex DNA in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krafcikova, M.; Dzatko, S.; Caron, C.; Granzhan, A.; Fiala, R.; Loja, T.; Teulade-Fichou, M.-P.; Fessl, T.; Haensel-Hertsch, R.; Mergny, J.-L.; et al. Monitoring DNA ligand interactions in living human cells using NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 13281–13285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.-Y.; Chen, W.-W.; Chu, I.-T.; Wang, C.-L.; Chang, C.-C.; Lin, M.-C.; Lou, P.-J.; Chang, T.-C. The G-quadruplex fluorescent probe 3,6-bis(1-methyl-2-vinyl-pyridinium) carbazole diiodide as a biosensor for human cancers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, K.N.; Zhu, B.C.; Xia, X.Y.; Ji, L.N.; Mao, Z.W. Quantitative detection of G-quadruplex DNA in live cells based on photon counts and complex structure discrimination. Angew. Chem. 2020, 59, 9719–9726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, P.A.; Lewis, B.W.; Gonzalez-Garcia, J.; Porreca, R.M.; Lim, A.H.M.; Cadinu, P.; Martin-Pintado, N.; Mann, D.J.; Edel, J.B.; Vannier, J.B.; et al. Visualising G-quadruplex DNA dynamics in live cells by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.-Y.; Shih, S.-R.; Wang, C.-P.; Lin, S.-J.; Jan, I.-S.; Wang, C.-L.; Liu, S.-Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Lou, P.-J.; Chang, T.-C. Pilot imaging study of o-BMVC foci for discrimination of indeterminate cytology in diagnosing fine-needle aspiration of thyroid nodules. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedoris, K.C.; Thomas, S.D.; Clarkson, C.R.; Muench, D.; Islam, A.; Singh, R.; Miller, D.M. Genomic c-Myc quadruplex DNA selectively kills leukemia. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 1, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, P.J.; Kahlon, J.B.; Thomas, S.D.; Trent, J.O.; Miller, D.M. Antiproliferative activity of G-rich oligonucleotides correlates with protein binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 26369–26377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Lin, C.-P.; Fu, X.; Wood, L.M.; Liu, A.A.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.; Barbieri, C.M.; Pilch, D.; Liu, L. G-quadruplexes induces apoptosis in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11808–11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Chien, C.H.; Chang, T.C. In-cell optical imaging of exogenous G-quadruplex DNA by fluorogenic ligands. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 10605–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, A.T. Human telomeric G-quadruplex: Structures of DNA and RNA sequences. FEBS 2010, 277, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heddi, B.; Phan, A.T. Structure of Human Telomeric DNA in Crowded Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 9824–9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, S.; Michor, F. DNA secondary structures and epigenetic determinants of cancer genome evolution. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Beraldi, D.; Lensing, S.V.; Marsico, G.; Zyner, K.; Parry, A.; di Antonio, M.; Pike, J.; Kimura, H.; Narita, M.; et al. G-quadruplex structures mark human regulatory chromatin. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.H.; Wang, Z.F.; Tseng, T.Y.; Li, M.H.; Hsu, S.T.; Lin, J.J.; Chang, T.C. Conformational transition of a hairpin structure to G-quadruplex within the WNT1 gene promoter. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from Gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathad, R.I.; Hatzakis, E.; Dai, J.; Yang, D. c-MYC promoter G-quadruplex formed at the 5′-end of NHE III1 element: Insights into biological relevance and parallel-stranded G-quadruplex stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 9023–9033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wu, P.; Ohmichi, T.; Sugimoto, N. Characterization and thermodynamic properties of quadruplex/duplex competition. FEBS Lett. 2002, 526, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kan, Z.Y.; Zeng, Z.X.; Hao, Y.H.; Chen, H.; Tan, Z. Determining the folding and unfolding rate constants of nucleic acids by biosensor. Application to telomere G-quadruplex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13255–13264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, C.L.; Chang, T.C. Antisense oligonucleotides used to identify telomeric G-quadruplexes in metaphase chromosomes and fixed cells by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy of o-BMVC foci. Molecules 2020, 25, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Di Antonio, M.; Balasubramanian, S. DNA G-quadruplexes in the human genome: Detection, functions and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, D.; Spiegel, J.; Zyner, K.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. The regulation and functions of DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chu, I.T.; Yeh, T.A.; Chen, D.Y.; Wang, C.L.; Chang, T.C. Effects of length and loop composition on structural diversity and similarity of (G3TG3NmG3TG3) G-quadruplexes. Molecules 2020, 25, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, R.E.; Zoncu, R. The lysosome as a cellular centre for signalling, metabolism and quality control. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabio, A.; Bonifacino, J.S. Lysosomes as dynamic regulators of cell and organismal homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Patel, D.J. Solution structure of the human telomeric repeat d[AG3(T2AG3)3] G-tetraplex. Structure 1993, 1, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, G.N.; Lee, M.P.; Neidle, S. Crystal structure of parallel quadruplexes from human telomeric DNA. Nature 2002, 417, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrus, A.; Chen, D.; Dai, J.; Bialis, T.; Jones, R.A.; Yang, D. Human telomeric sequence forms a hybrid-type intramolecular G-quadruplex structure with mixed parallel/antiparallel strands in potassium solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 2723–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu, K.N.; Phan, A.T.; Kuryavyi, V.; Lacroix, L.; Patel, D.J. Structure of the human telomere in K+ solution: An intramolecular (3+1) G-quadruplex scaffold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9963–9970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.W.; Amrane, S.; Bouaziz, S.; Xu, W.; Mu, Y.; Patel, D.J.; Luu, K.N.; Phan, A.T. Structure of the human telomere in K+ solution: A stable basket-type G-quadruplex with only two G-tetrad layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4301–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, D.; Sugimoto, N. Molecular crowding effects on structure and stability of DNA. Biochimie 2008, 90, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Chang, T.C. Molecular engineering of G-quadruplex ligands based on solvent effect of polyethylene glycol. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 8711–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yang, P.C.; Luh, K.T.; Wu, R.; Wu, C.W. Characterization of the mucin differentiation in human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1992, 7, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Name | Sequence | Fluorescent Decay Times | |
|---|---|---|---|
| In Vitro | In Live Cells | ||
| PU22 | TGAG3TG4AG3TG4AA | 3.0 | 2.9 |
| AS1411 | (GGT)4TG(TGG)4 | 3.1 | 3.2 |
| CMA | TAG3AG3TAG3AG3T | 3.1 | 2.8 |
| HT23 | TAG3(T2AG3)3 | 2.8 | - |
| WT22 | G3CCACCG3CAG5CG3 | 2.5 | 2.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tseng, T.-Y.; Wang, C.-L.; Huang, W.-C.; Chang, T.-C. Folding and Unfolding of Exogenous G-Rich Oligonucleotides in Live Cells by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy of o-BMVC Fluorescent Probe. Molecules 2022, 27, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010140
Tseng T-Y, Wang C-L, Huang W-C, Chang T-C. Folding and Unfolding of Exogenous G-Rich Oligonucleotides in Live Cells by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy of o-BMVC Fluorescent Probe. Molecules. 2022; 27(1):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010140
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseng, Ting-Yuan, Chiung-Lin Wang, Wei-Chun Huang, and Ta-Chau Chang. 2022. "Folding and Unfolding of Exogenous G-Rich Oligonucleotides in Live Cells by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy of o-BMVC Fluorescent Probe" Molecules 27, no. 1: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010140
APA StyleTseng, T.-Y., Wang, C.-L., Huang, W.-C., & Chang, T.-C. (2022). Folding and Unfolding of Exogenous G-Rich Oligonucleotides in Live Cells by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy of o-BMVC Fluorescent Probe. Molecules, 27(1), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010140





