An RP-LC-UV-TWIMS-HRMS and Chemometric Approach to Differentiate between Momordicabalsamina Chemotypes from Three Different Geographical Locations in Limpopo Province of South Africa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Compounds
2.2. Statistical Analysis for Identification of Chemotype Markers
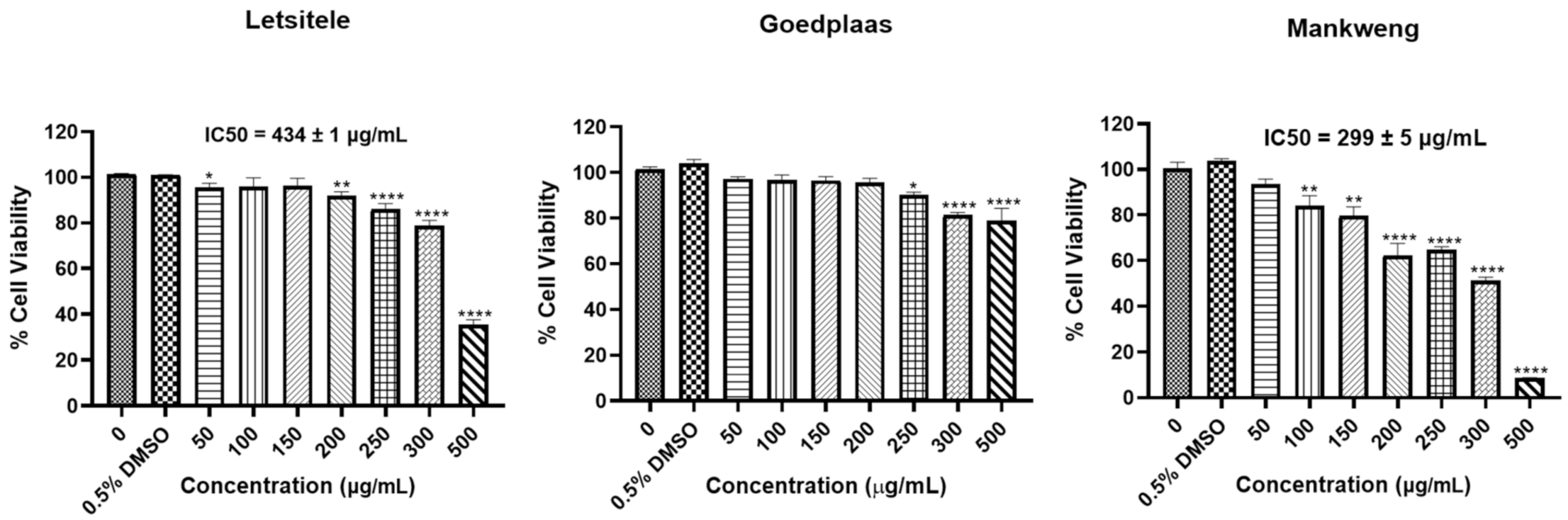
Cytotoxicity Study
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Material and Reagents
3.2. Sample Extraction
3.3. RP-LC-TWIMS-HRMS Conditions
3.4. Collisional Cross-Section Determination
3.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
4. Toxicity Study
4.1. Cell Culture and Maintenance and Treatment
4.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramalhete, C.; Mulhovo, S.; Molnar, J.; Ferreira, M.J.U. Triterpenoids from Momordica balsamina: Reversal of ABCB1-mediated multidrug resistance. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 5061–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalhete, C.; Lopes, D.; Mulhovo, S.; Molnár, J.; Rosário, V.E.; Ferreira, M.U. New antimalarials with a triterpenic scaffold from Momordica balsamina. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5254–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rocha, E.; Silva, L.F.; Ramalhete, C.; Nogueira, K.L.; Mulhovo, S.; Ferreira, M.J.U.; Pohlit, A.M. In vivo evaluation of isolated triterpenes and semi-synthetic derivatives as antimalarial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramalhete, C.; Filipa, P.; Lopes, D.; Mulhovo, S.; Rosário, V.E.; Prudêncio, M.; Ferreira, M.U. Triterpenoids as inhibitors of erythrocytic and liver stages of Plasmodium infections. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 7474–7481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramalhete, C.; Lopes, D.; Molnár, J.; Mulhovo, S.; Rosário, V.E.; Ferreira, M.U. Karavilagenin C derivatives as antimalarials. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarkson, C.; Maharaj, V.J.; Crouch, N.R.; Grace, O.M.; Pillay, P.; Matsabisa, M.G.; Bhagwandin, N.; Smith, P.J.; Folb, P.I. In vitro antiplasmodial activity of medicinal plants native to or naturalised in South Africa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 92, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalhete, C.; Mulhovo, S.; Lage, H.; Ferreira, M.-J.U. Triterpenoids from Momordica balsamina with a Collateral Sensitivity Effect for Tackling Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Cells. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramalhete, C.; Molnár, J.; Mulhovo, S.; Rosário, V.E.; Ferreira, M.U. New potent P-glycoprotein modulators with the cucurbitane scaffold and their synergistic interaction with doxorubicin on resistant cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6942–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramalhete, C.; Spengler, G.; Martins, A.; Martins, M.; Viveiros, M.; Mulhovo, S.; Ferreira, M.U.; Amaral, L. Inhibition of efflux pumps in meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis resistant strains by triterpenoids from Momordica balsamina. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 37, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalhete, C.; Magalhães, L.G.; Rodrigues, V.; Mulhovo, S.; Da Silva Filho, A.A.; Ferreira, M.-J.U. In Vitro Schistosomicidal Activity of Balsaminol F and Karavilagenin, C. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van De Venter, M.; Roux, S.; Bungu, L.C.; Louw, J.; Crouch, N.R.; Grace, O.M.; Maharaj, V.; Pillay, P.; Sewnarian, P.; Bhagwandin, N.; et al. Antidiabetic screening and scoring of 11 plants traditionally used in South Africa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 119, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalhete, C.; Mansoor, T.A.; Mulhovo, S.; Molnar, J.; Ferreira, M.-J. Cucurbitane-Type Triterpenoids from the African Plant Momordica balsamina. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2009–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.C.; Chiu, M.H.; Nie, R.L.; Cordell, G.A.; Qiu, S.X. Cucurbitacins and cucurbitane glycosides: Structures and biological activities†. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madala, N.E.; Tugizimana, F.; Steenkamp, P.A. Development and optimization of an UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS method based on an in-source collision induced dissociation approach for comprehensive discrimination of chlorogenic acids isomers from momordica plant species. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madala, N.E.; Piater, L.; Dubery, I.; Steenkamp, P. Distribution patterns of flavonoids from three Momordica species by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry: A metabolomic profiling approach. Braz. J. Pharmacogn. 2016, 26, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venter, P.; Causon, T.; Pasch, H.; de Villiers, A. Comprehensive analysis of chestnut tannins by reversed phase and hydrophilic interaction chromatography coupled to ion mobility and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1088, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veuthey, J.; Causon, T.; Cianferani, S.; Guillarme, D.; Mutabazi, A. Adding a new separation dimension to MS and LC–MS: What is the utility of ion mobility spectrometry? J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 20–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortmayr, K.; Causon, T.J.; Hann, S.; Koellensperger, G. Trends in Analytical Chemistry Increasing selectivity and coverage in LC-MS based metabolome analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmer, D.E.; Jarrold, M.F. Ion Mobility Measurement and their Applications to Cluster and Biomolecules. J. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 32, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, K.; Pringle, S.D.; Worthington, K.R.; Little, D.; Wildgoose, J.L.; Bateman, R.H. Applications of a travelling wave-based radio-frequency-only stacked ring ion guide. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 2401–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, S.D.; Giles, K.; Wildgoose, J.L.; Williams, J.P.; Slade, S.E.; Thalassinos, K.; Bateman, R.H.; Bowers, M.T.; Scrivens, J.H. An investigation of the mobility separation of some peptide and protein ions using a new hybrid quadrupole/travelling wave IMS/oa-ToF instrument. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 261, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, K.M.; May, J.C.; McLean, J.A.; Xu, L. Evaluation of Collision Cross Section Calibrants for Structural Analysis of Lipids by Traveling Wave Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7329–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merken, H.M.; Beecher, G.R. Measurement of Food Flavonoids by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 577–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, W.; Yong, Z.; Bai, N. High-performance liquid chromatographic fingerprint analysis for different origins of sea buckthorn berries. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1154, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, G.B.; Smagghe, G.; Coelus, S.; Adriaenssens, D.; De Winter, K.; Desmet, T.; Raes, K.; Van Camp, J. Collision cross section prediction of deprotonated phenolics in a travelling-wave ion mobility spectrometer using molecular descriptors and chemometrics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 924, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stander, M.A.; Van Wyk, B.; Taylor, M.J.C.; Long, H.S. Analysis of Phenolic Compounds in Rooibos Tea (Aspalathus linearis) with a Comparison of Flavonoid-Based Compounds in Natural Populations of Plants from Different Regions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10270–10281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuyckens, F.; Rozenberg, R.; De Hoffmann, E.; Claeys, M. Structure characterization of flavonoid O-diglycosides by positive and negative nano-electrospray ionization ion trap mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 36, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukics, V.; Guttman, A. Structural characterization of flavonoid glycosides by multi-stage mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2010, 29, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-L.; Vedernikova, I.; Van den Heuvel, H.; Claeys, M. Internal glucose residue loss in protonated O-diglycosyl flavonoids upon low-energy collision-induced dissociation. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 11, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu-Liang, M.; Cuyckens, F.; Van Den Heuvel, H.; Claeys, M. Mass spectrometric methods for the characterisation and differentiation of isomeric O-diglycosyl flavonoids. Phytochem. Anal. 2001, 12, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, Y.; Okabe, H.; Ymauchi, T. Studies on the Constituents of Momordica Charantia, L Studies on the Constituents of Momordica Charantia L. II. Isolation and Characterization of Minor Seed Glycosides, Momordicosides C, D and E. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrimpe-Rutledge, A.C.; Codreanu, S.G.; Sherrod, S.D.; Mclean, J.A. Untargeted Metabolomics Strategies—Challenges and Emerging Directions. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 27, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying small molecules via high resolution mass spectrometry: Communicating confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masike, K.; De Villiers, A.; Hoffman, E.W.; Brand, D.J.; Causon, T.; Stander, M.A. Detailed Phenolic Characterization of Protea Pure and Hybrid Cultivars by Liquid Chromatography-Ion Mobility-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-IM-HR-MS). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Aly, N.A.; Zhou, Y.; Dupuis, K.T.; Bilbao, A.; Paurus, V.L.; Orton, D.J.; Wilson, R.; Payne, S.H.; Smith, R.D.; et al. A structural examination and collision cross section database for over 500 metabolites and xenobiotics using drift tube ion mobility spectrometry. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 7724–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffiths, W.J. Tandem Mass Spectrometry in the study of Fatty Acids, Bile acids, and steroids. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2003, 22, 81–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, M.; Shimada, M.; Iida, T.; Goto, J.; Mano, N. Tandem mass spectrometric characterization of bile acids and steroid conjugates based on low-energy collision-induced dissociation. Steroids 2014, 80, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.; Ni, Z.; Vetter, D.; Hoffmann, R.; Fedorova, M. Electrochemical oxidation of cholesterol: An easy way to generate numerous oxysterols in short reaction times. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Low, C.E.; Smith, L.L. Sterol metabolism-XLV. Differentiation among monohydroxylated cholesterol derivatives by chromatography and mass spectrometry. J. Steroid Biochem. 1981, 14, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzazi-Fazeli, E.; Kleineisen, S.; Luf, W. Determination of cholesterol oxides in processed food using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry with atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 896, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrida, F.; Destaillats, F.; Robert, F.; Skibsted, L.H.; Dionisi, F. Formation and hydrolysis of triacylglycerol and sterols epoxides: Role of unsaturated triacylglycerol peroxyl radicals. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 37, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.G.; Li, G.Y.; Liang, J.; Ortori, C.A.; Yang, B.Y.; Kuang, H.X.; Barrett, D.A. A strategy for characterization of triterpene saponins in Caulophyllum robustum hairy roots by liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.Y.; Zhang, M.X.; Li, Y.L.; Ling, B.; Wang, G.C. Cucurbitane-type triterpenoids from the leaves of Momordica charantia. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 16, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Peng, X.; Yu, M.; Wan, L.; Zhu, G. Phytochemistry Letters Cucurbitane-type triterpenoids from the aerial parts of Momordica. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 16, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domon, B.; Costello, C.E. A systematic nomenclature for carbohydrate fragmentations in FAB-MS/MS spectra of glycoconjugates. Glycoconj. J. 1988, 5, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, J.G.; Petrov, A.S.; Walker, C.A.; Allen, S.J.; Pellissier, J.S.; Bush, M.F.; Hud, N.V.; Fernández, F.M. Collision cross section calibrants for negative ion mode traveling wave ion mobility-mass spectrometry. Analyst 2015, 140, 6853–6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanucara, F.; Holman, S.W.; Gray, C.J.; Eyers, C.E. The power of ion mobility-mass spectrometry for structural characterization and the study of conformational dynamics. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautenhahn, R.; Patti, G.J.; Rinehart, D.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS online: A web-based platform to process untargeted metabolomic data. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5035–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tautenhahn, R.; Bottcher, C.; Neumann, S. Highly sensitive feature detection for high resolution LC/MS. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruotolo, B.T.; Benesch, J.L.; Sandercock, A.M.; Hyung, S.; Robinson, C.V. Ion mobility-mass spectrometry analysis of large protein complexes. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chambers, M.C.; MacLean, B.; Burke, R.; Amodei, D.; Ruderman, D.L.; Neumann, S.; Gatto, L.; Fischer, B.; Pratt, B.; Egertson, J.; et al. A cross-platform toolkit for mass spectrometry and proteomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarani, G.; Abirami, A.; Siddhuraju, P. Food prospects and nutraceutical attributes of Momordica species: A potential tropical bioresources—A review. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2014, 3, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
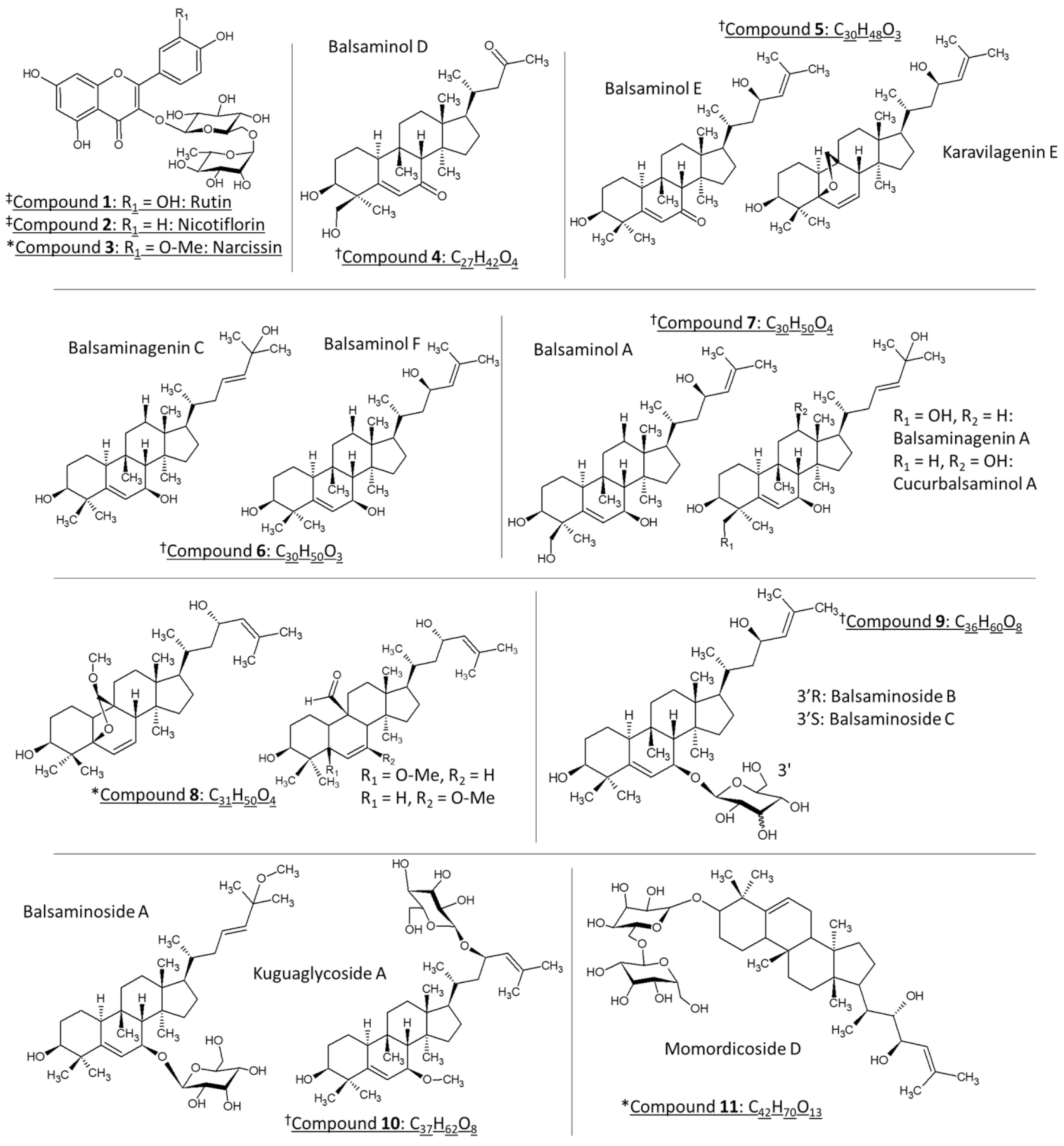



| Compound Name (No) | Molecular Formula | 12C Mass | Retention Time (min) | Exp. [M + H]+ | Mass Error (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin 3-O-rutinoside (Rutin) (1) | C27H30O16 | 610.1534 | 3.76 L,G,M | 611.1604 | −0.4 |
| Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside (Nicotiflorin) (2) | C27H31O15 | 594.1585 | 4.17 L,G,M | 595.1671 | 1.3 |
| Isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside (3) | C28H33O16 | 624.1690 | 4.29 L,G,M | 625.1782 | 2.1 |
| Compound No. (Name) | Molecular Formula | 12C Mass | Retention Time (min) | Exp. [M + H − H2O]+ | Mass Error (ppm) | Exp. [M + Na]+ | Mass Error (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound 4 (Balsaminol D) | C27H42O4 | 430.3083 | 10.69M | 413.3010 | −4.1 | ||
| Compound 5 (Balsaminol E, Karavilagenin E) | C30H48O3 | 456.3603 | (11.20, 11.55, 14.79) L, (8.01, 10.25) G, (8.55, 9.33, 9.74, 11.21) M | 439.3555 | −3.5 | ||
| Compound 6 (Balsaminagenin C, Balsaminol F) | C30H50O3 | 458.3760 | (9.18, 10.37, 10.60, 10.68, 10.95, 11.17, 11.29, 11.96, 12.46, 13.51, 13.71, 14.29) L, (9.18, 11.60, 11.96, 12.75, 13.71) G, (9.18, 11.29, 11.50, 11.96, 12.44, 13.71, 14.29) M | 441.3719 * | −1.8 | ||
| Compound 7 (Balsaminagenin A, Cucurbalsaminol A, Balsaminol A) | C30H50O4 | 474.3709 | (9.44, 9.83, 11.00, 11.35, 12.26) L, (9.44, 11.35) G, (8.56, 9.44, 11.00, 11.35) M | 457.3670 | −1.3 | ||
| Compound 8 | C31H50O4 | 486.3709 | (7.89, 7.97, 8.69, 8.77, 9.59, 10.37, 10.49, 12.23, 13.56) L, (7.89, 7.97, 8.77, 9.59, 9.83, 9.93, 10.37, 10.49, 12.21, 13.54) G, (7.89, 7.98, 8.69, 8.77, 9.57, 10.33, 10.46, 12.20, 13.53) M | 509.3618 | 3.3 |
| Compound No. (Name) | Molecular Formula | 12C Mass | Retention Time (min) | Exp. [M + NH4]+ | Mass Error (ppm) | Exp. [M + Na]+ | ppm | Exp. [M + K]+ | Mass Error (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound 9 (Balsaminoside B and C) | C36H60O8 | 620.4288 | (9.29, 9.41, 10.07, 10.19, 10.43, 10.60) L, (9.28, 9.40, 10.06, 10.18, 10.42, 10.59) G, (9.28, 9.39, 10.02, 10.18, 10.38, 10.55) M | 638.4632 | 0.0 | 643.4183 | 0.4 | 659.3943 | 3.5 |
| Compound 10 (Balsaminoside A and Kuguaglycoside A) | C37H62O8 | 634.4445 | (10.96, 11.17) L, (10.97, 11.16) G, (10.93, 11.16) M | 652.4774 | −2.1 | 657.4243 | −14.3 | 673.4089 | 3.9 |
| Compound 11 (Momordicoside D) | C42H70O13 | 782.4816 | (7.53, 7.59, 8.35, 8.44) L, (7.54, 7.59, 8.35, 8.46) G, (7.53, 7.59, 8.35, 8.43) M | 800.5133 | −2.7 | 805.4694 | −1.8 | 821.4448 | 0.0 |
Sample Availability: Samples are available from the authors. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venter, P.; Malemela, K.; Mbazima, V.; Mampuru, L.J.; Muller, C.J.F.; Riedel, S. An RP-LC-UV-TWIMS-HRMS and Chemometric Approach to Differentiate between Momordicabalsamina Chemotypes from Three Different Geographical Locations in Limpopo Province of South Africa. Molecules 2021, 26, 1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071896
Venter P, Malemela K, Mbazima V, Mampuru LJ, Muller CJF, Riedel S. An RP-LC-UV-TWIMS-HRMS and Chemometric Approach to Differentiate between Momordicabalsamina Chemotypes from Three Different Geographical Locations in Limpopo Province of South Africa. Molecules. 2021; 26(7):1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071896
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenter, Pieter, Kholofelo Malemela, Vusi Mbazima, Leseilane J. Mampuru, Christo J. F. Muller, and Sylvia Riedel. 2021. "An RP-LC-UV-TWIMS-HRMS and Chemometric Approach to Differentiate between Momordicabalsamina Chemotypes from Three Different Geographical Locations in Limpopo Province of South Africa" Molecules 26, no. 7: 1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071896
APA StyleVenter, P., Malemela, K., Mbazima, V., Mampuru, L. J., Muller, C. J. F., & Riedel, S. (2021). An RP-LC-UV-TWIMS-HRMS and Chemometric Approach to Differentiate between Momordicabalsamina Chemotypes from Three Different Geographical Locations in Limpopo Province of South Africa. Molecules, 26(7), 1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071896







