QSAR and Pharmacophore Modeling of Nitrogen Heterocycles as Potent Human N-Myristoyltransferase (Hs-NMT) Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
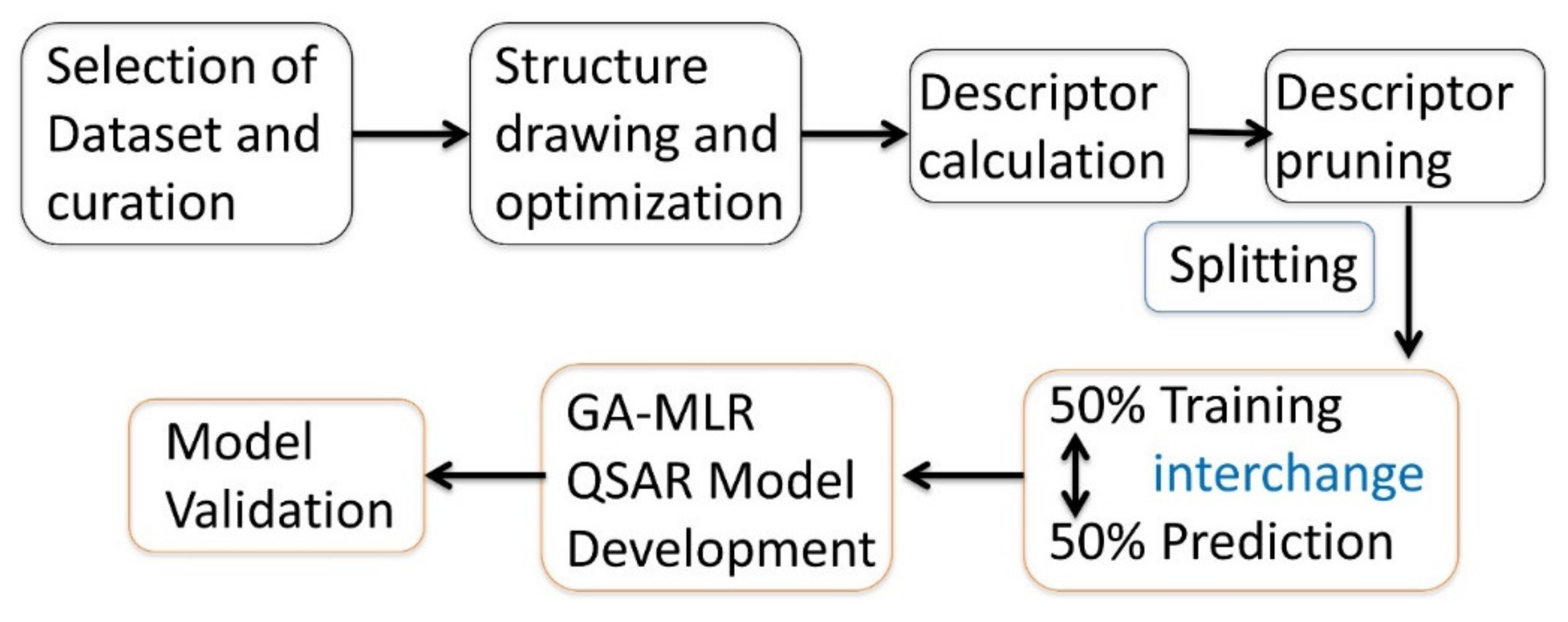
2. Experimental Methodology
2.1. Selection of Dataset
2.2. Calculation and Pruning of Molecular Descriptors
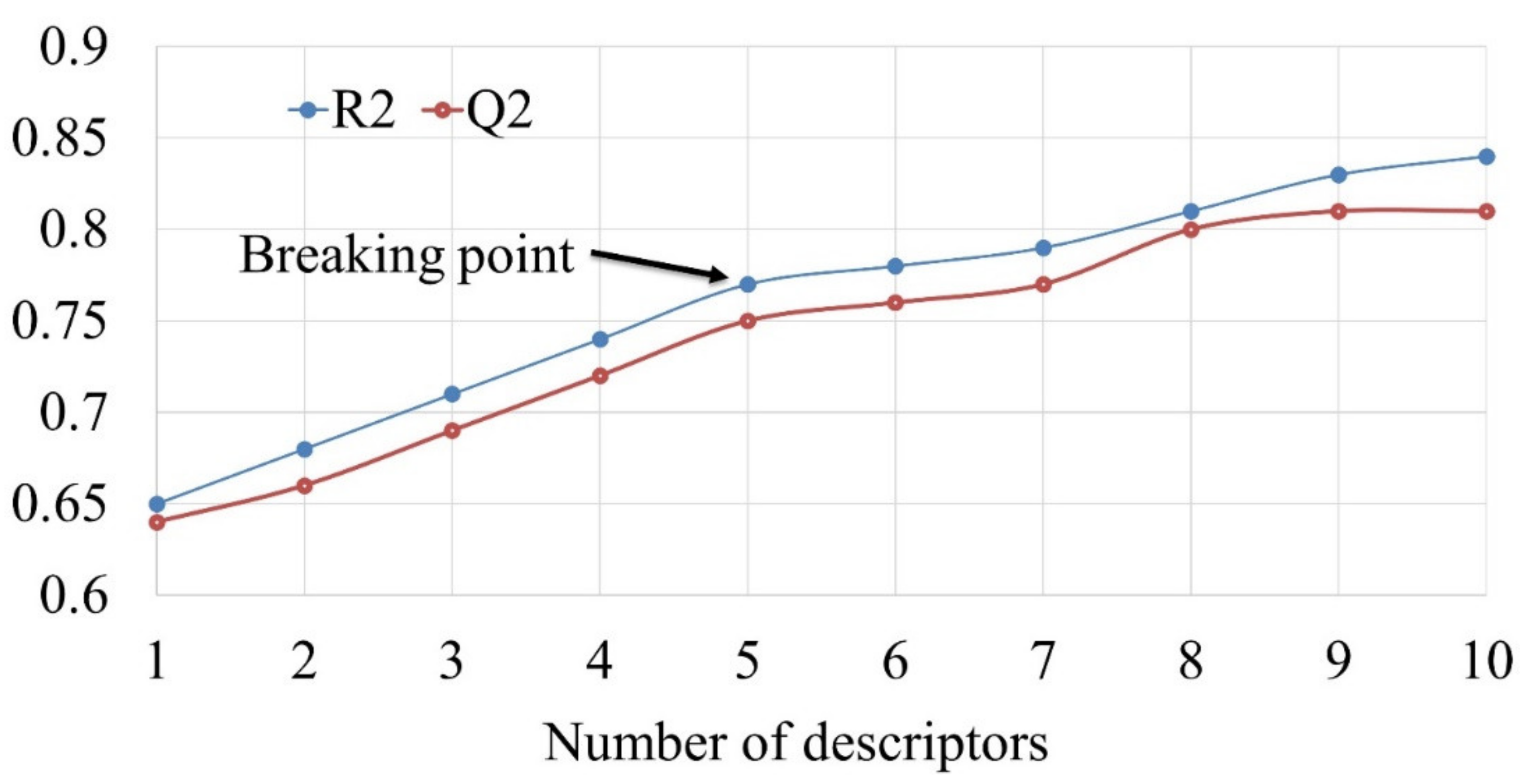
2.3. Subjective Feature Selection (Model Building)
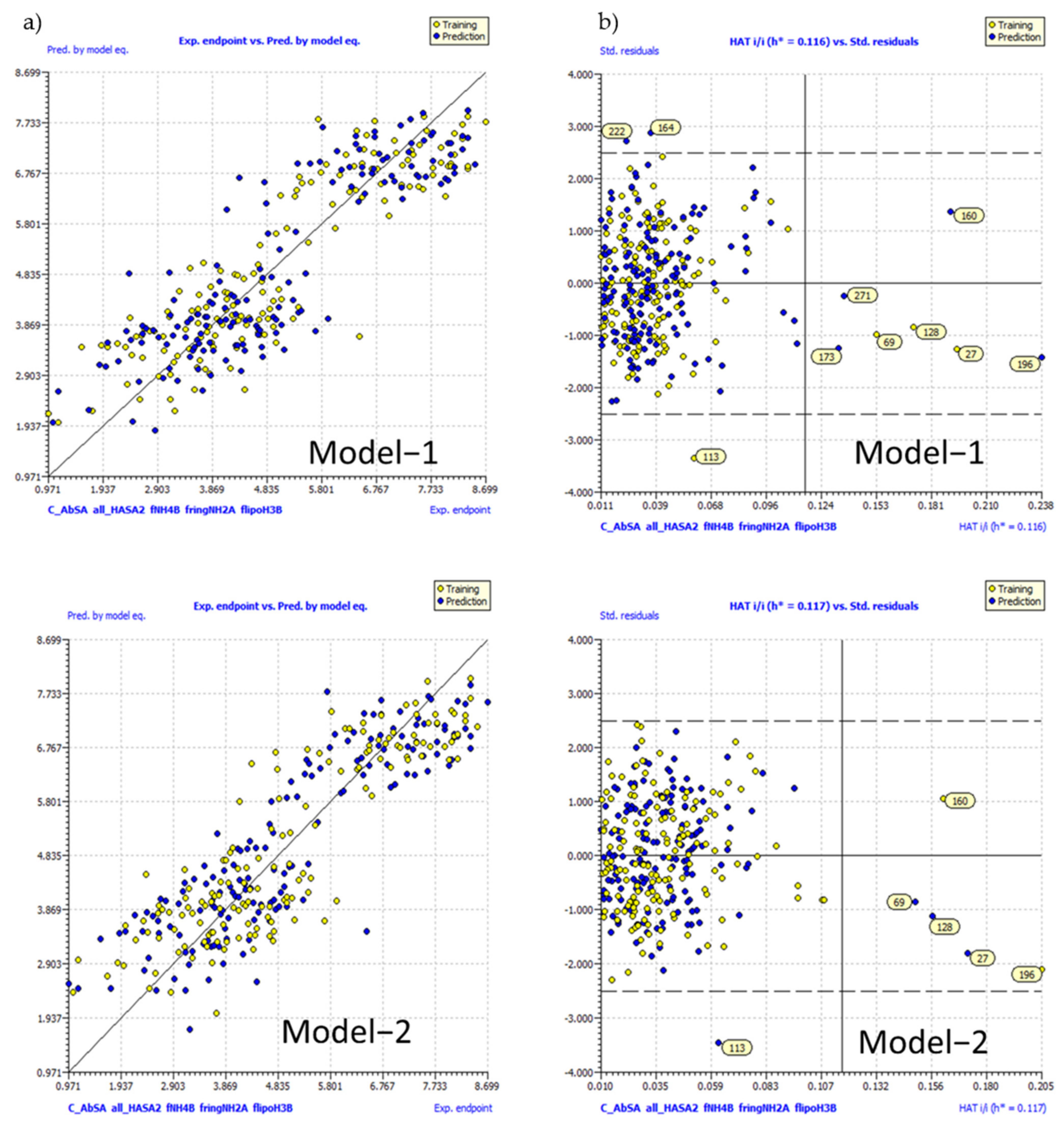
2.4. Validation of QSAR Models
2.5. Pharmacophore Modeling
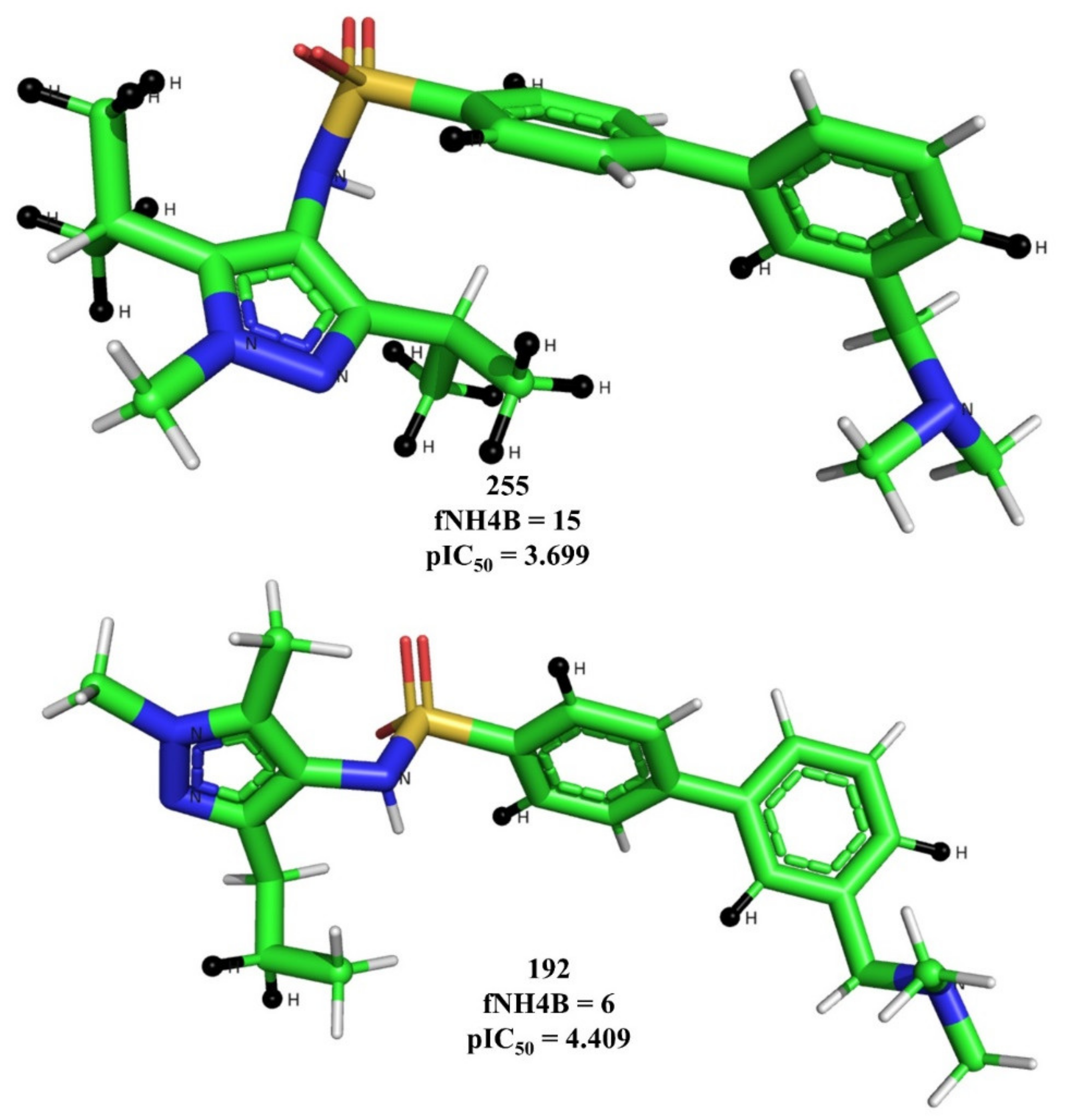
3. Results and Discussions
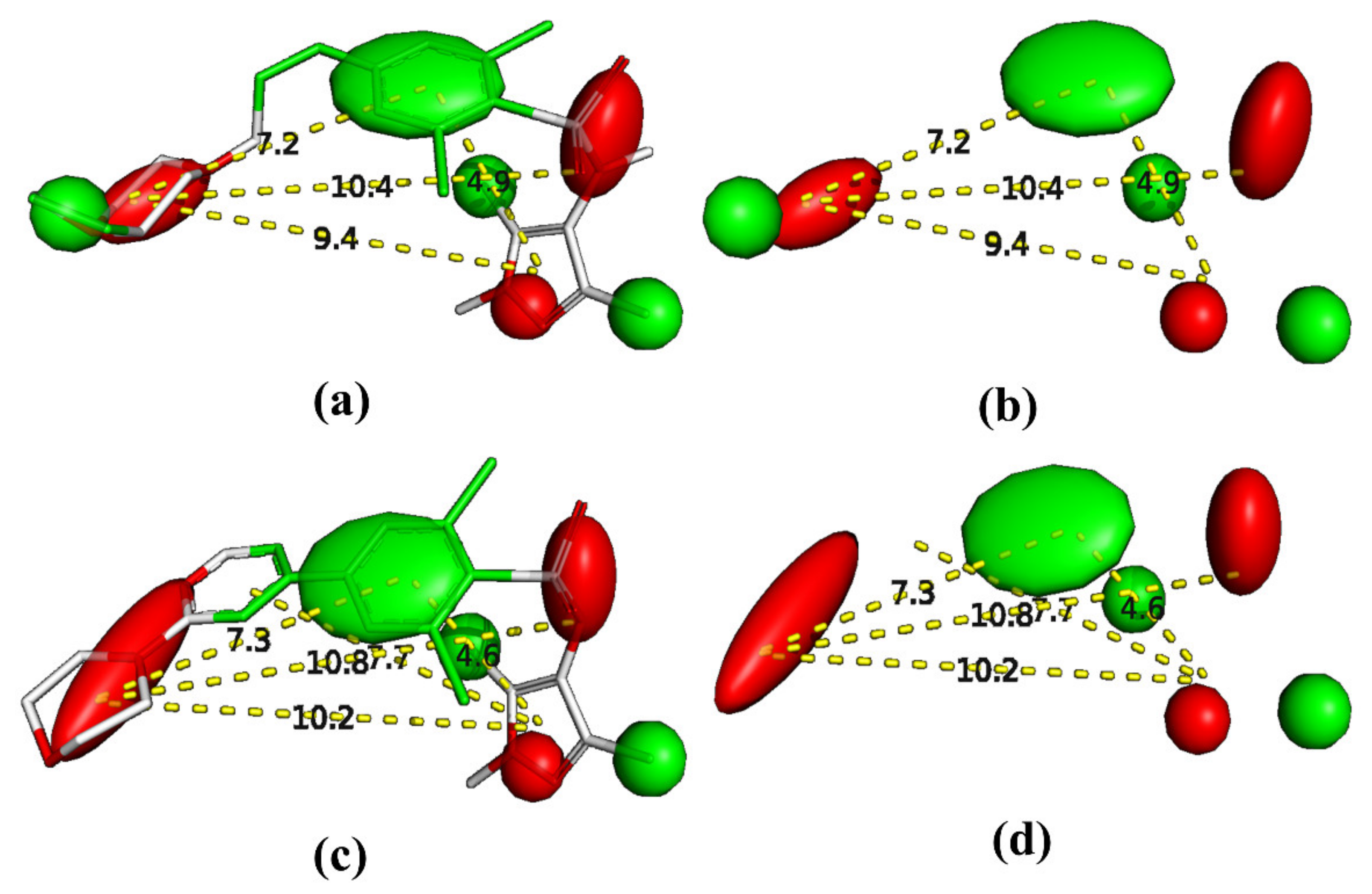
4. Pharmacophore Modeling
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
References
- Dian, C.; Pérez-Dorado, I.; Rivière, F.; Asensio, T.; Legrand, P.; Ritzefeld, M.; Shen, M.; Cota, E.; Meinnel, T.; Tate, E.W.; et al. High-resolution snapshots of human N-myristoyltransferase in action illuminate a mechanism promoting N-terminal Lys and Gly myristoylation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.; Ashraf, S.; Khalid, A.; Ul-Haq, Z. Exploring Novel N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Approach. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 13658–13670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frearson, J.A.; Brand, S.; McElroy, S.P.; Cleghorn, L.A.T.; Smid, O.; Stojanovski, L.; Price, H.P.; Guther, M.L.S.; Torrie, L.S.; Robinson, D.A.; et al. N-myristoyltransferase inhibitors as new leads to treat sleeping sickness. Nature 2010, 464, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ma, S. Recent Advances in The Discovery of N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.; Kumar, S.; Dimmock, J.R.; Sharma, K.R. Inhibition of Protein N-Myristoylation: A Therapeutic Protocol in Developing Anticancer Agents. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2012, 12, 667–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.R.; Brand, S.; Smith, V.; Robinson, D.A.; Thompson, S.; Smith, A.; Davies, K.; Mok, N.; Torrie, L.S.; Collie, I.; et al. A Molecular Hybridization Approach for the Design of Potent, Highly Selective, and Brain-Penetrant N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 8374–8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayliss, T.; Robinson, D.A.; Smith, V.C.; Brand, S.; McElroy, S.P.; Torrie, L.S.; Mpamhanga, C.; Norval, S.; Stojanovski, L.; Brenk, R.; et al. Design and Synthesis of Brain Penetrant Trypanocidal N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 9790–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, S.; Norcross, N.R.; Thompson, S.; Harrison, J.R.; Smith, V.C.; Robinson, D.A.; Torrie, L.S.; McElroy, S.P.; Hallyburton, I.; Norval, S.; et al. Lead Optimization of a Pyrazole Sulfonamide Series of Trypanosoma brucei N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors: Identification and Evaluation of CNS Penetrant Compounds as Potential Treatments for Stage 2 Human African Trypanosomiasis. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 9855–9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, S.; Wyatt, P.; Thompson, S.; Smith, V.; Bayliss, T.; Harrison, J.; Norcross, N.; Cleghorn, L.; Gilbert, I.; Brenk, R. N-MYRISTOYL TRANSFERASE INHIBITORS. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 60, 9790–9806. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, S.; Cleghorn, L.A.T.; McElroy, S.P.; Robinson, D.A.; Smith, V.C.; Hallyburton, I.; Harrison, J.R.; Norcross, N.R.; Spinks, D.; Bayliss, T.; et al. Discovery of a Novel Class of Orally Active Trypanocidal N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 55, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masand, V.H.; El-Sayed, N.N.E.; Bambole, M.U.; Patil, V.R.; Thakur, S.D. Multiple quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSARs) analysis for orally active trypanocidal N-myristoyltransferase inhibitors. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1175, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masand, V.H.; Mahajan, D.T.; Nazeruddin, G.M.; Hadda, T.B.; Rastija, V.; Alfeefy, A.M. Effect of information leakage and method of splitting (rational and random) on external predictive ability and behavior of different statistical parameters of QSAR model. Med. Chem. Res. 2015, 24, 1241–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramatica, P. Principles of QSAR Modeling. IJQSPR 2020, 5, 61–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Winkler, D.A. Understanding the Roles of the “Two QSARs”. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherkasov, A.; Muratov, E.N.; Fourches, D.; Varnek, A.; Baskin, I.I.; Cronin, M.; Dearden, J.; Gramatica, P.; Martin, Y.C.; Todeschini, R.; et al. QSAR modeling: Where have you been? Where are you going to? J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4977–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, J.C.; Cronin, M.T.; Kaiser, K.L. How not to develop a quantitative structure-activity or structure-property relationship (QSAR/QSPR). SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2009, 20, 241–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masand, V.H.; El-Sayed, N.N.E.; Mahajan, D.T.; Mercader, A.G.; Alafeefy, A.M.; Shibi, I.G. QSAR modeling for anti-human African trypanosomiasis activity of substituted 2-Phenylimidazopyridines. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1130, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramatica, P. External Evaluation of QSAR Models, in Addition to Cross-Validation Verification of Predictive Capability on Totally New Chemicals. Mol. Inform. 2014, 33, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramatica, P. On the development and validation of QSAR models. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 930, 499–526. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Fan, X. Why QSAR fails: An empirical evaluation using conventional computational approach. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masand, V.H.; Rastija, V.; Patil, M.K.; Gandhi, A.; Chapolikar, A. Extending the identification of structural features responsible for anti-SARS-CoV activity of peptide-type compounds using QSAR modelling. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2020, 31, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masand, V.H.; Elsayed, N.N.; Thakur, S.D.; Gawhale, N.; Rathore, M.M. Quinoxalinones Based Aldose Reductase Inhibitors: 2D and 3D-QSAR Analysis. Mol. Inform. 2019, 38, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masand, V.H.; El-Sayed, N.N.E.; Bambole, M.U.; Quazi, S.A. Multiple QSAR models, pharmacophore pattern and molecular docking analysis for anticancer activity of α, β-unsaturated carbonyl-based compounds, oxime and oxime ether analogues. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1157, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masand, V.H.; El-Sayed, N.N.E.; Mahajan, D.T.; Rastija, V. QSAR analysis for 6-arylpyrazine-2-carboxamides as Trypanosoma brucei inhibitors. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2017, 28, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masand, V.H.; Mahajan, D.T.; Maldhure, A.K.; Rastija, V. Quantitative structure–activity relationships (QSARs) and pharmacophore modeling for human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) activity of pyridyl benzamides and 3-(oxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-2-yl)anilides. Med. Chem. Res. 2016, 25, 2324–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masand, V.H.; Rastija, V. PyDescriptor: A new PyMOL plugin for calculating thousands of easily understandable molecular descriptors. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2017, 169, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.W. PaDEL-descriptor: An open source software to calculate molecular descriptors and fingerprints. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramatica, P.; Cassani, S.; Chirico, N. QSARINS-chem: Insubria datasets and new QSAR/QSPR models for environmental pollutants in QSARINS. J. Comput. Chem. 2014, 35, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramatica, P.; Chirico, N.; Papa, E.; Cassani, S.; Kovarich, S. QSARINS: A new software for the development, analysis, and validation of QSAR MLR models. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2121–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masand, V.H.; Mahajan, D.T.; Alafeefy, A.M.; Bukhari, S.N.A.; Elsayed, N.N. Optimization of antiproliferative activity of substituted phenyl 4-(2-oxoimidazolidin-1-yl) benzenesulfonates: QSAR and CoMFA analyses. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 77, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, V.; Todeschini, R.; Ballabio, D.; Grisoni, F. On the Misleading Use of Q2F3 for QSAR Model Comparison. Mol. Inform. 2019, 38, e1800029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirico, N.; Gramatica, P. Real external predictivity of QSAR models. Part 2. New intercomparable thresholds for different validation criteria and the need for scatter plot inspection. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 2044–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.P.; Kovarich, S.; Gramatica, P. QSAR model reproducibility and applicability A case study of rate constants of hydroxyl radical reaction models applied to polybrominated diphenyl ethers and (benzo-)triazoles. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, N.; Gramatica, P. Real external predictivity of QSAR models: How to evaluate it? Comparison of different validation criteria and proposal of using the concordance correlation coefficient. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2320–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramatica, P. Principles of QSAR models validation internal and external, QSAR & Combinatorial Science. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2007, 26, 694–701. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Chan, H.C.S.; Hu, Z. Using PyMOL as a platform for computational drug design. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2017, 7, e1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, C.; Fleischer, E.; Kehrein, J.; Borek, C.; Jaenicke, E.; Sotriffer, C.; Brenk, R. How To Design Selective Ligands for Highly Conserved Binding Sites: A Case Study UsingN-Myristoyltransferases as a Model System. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 63, 2095–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramatica, P.; Cassani, S.; Roy, P.P.; Kovarich, S.; Yap, C.W.; Papa, E. QSAR Modeling is not Push a Button and Find a Correlation: A Case Study of Toxicity of (Benzo-)triazoles on Algae. Mol. Inform. 2012, 31, 817–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, V.; Ballabio, D.; Todeschini, R. Comments on the definition of the Q2 parameter for QSAR validation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.R. The Trouble with QSAR (or How I Learned To Stop Worrying and Embrace Fallacy). J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2008, 48, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
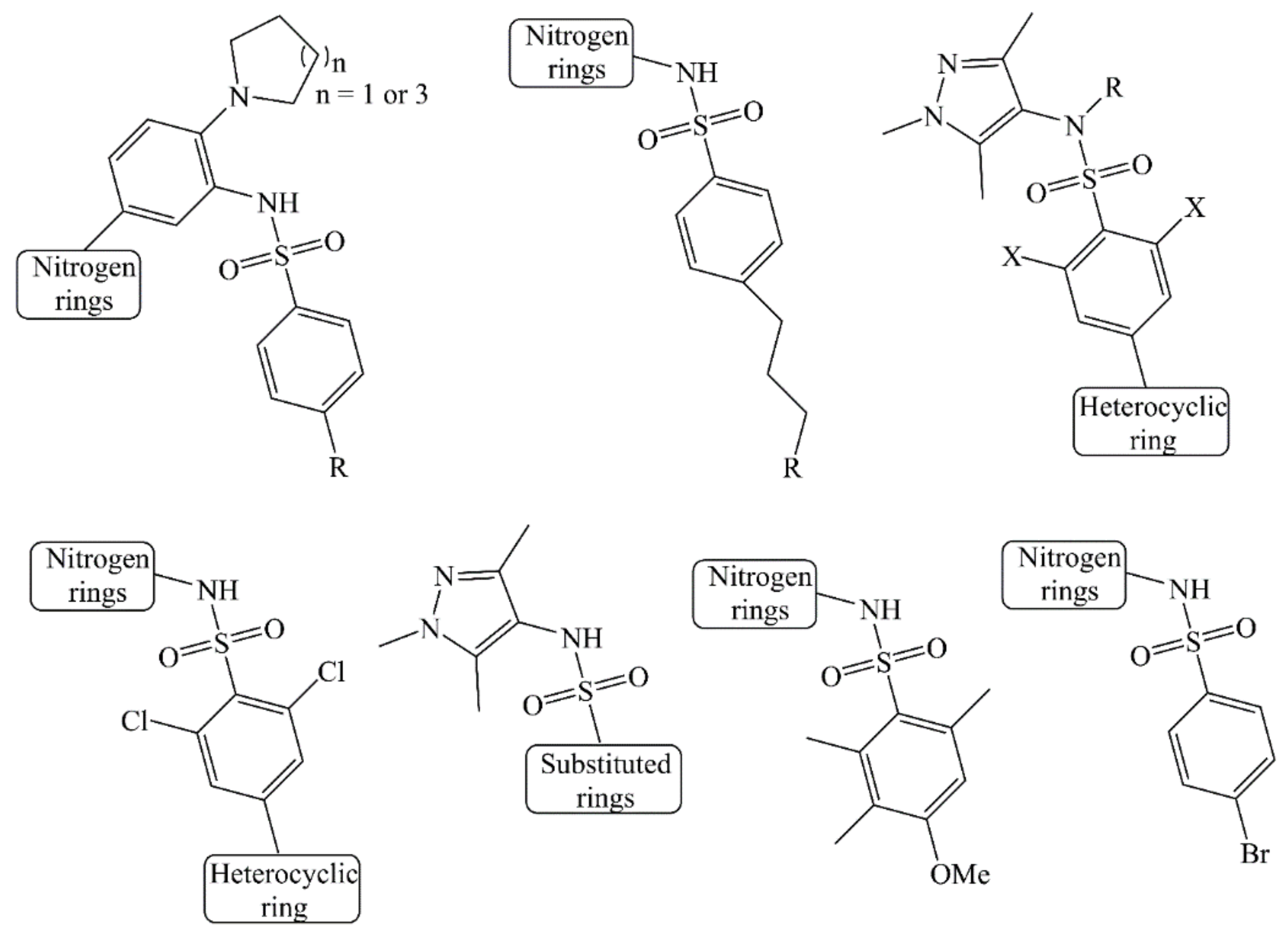



| S.N. | SMILES | IC50 (µM) | pIC50 (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | Cn(n1)c(C)c(c1C)N(C(F)F)S(=O)(=O)c(c(Cl)c2)c(Cl)cc2CCCO[C@H](C3)C[C@@H](N4C)CC[C@H]34 | 0.002 | 8.699 |
| 73 | Cn(n1)c(C)c(c1C)NS(=O)(=O)c(c(Cl)c2)c(Cl)cc2-c3cc(ncc3)N4CCNCC4 | 0.003 | 8.523 |
| 2 | Cn(n1)c(C)c(c1C)NS(=O)(=O)c(cc2)c(Cl)cc2-c3cc(ncc3)N4CCNCC4 | 0.004 | 8.398 |
| 78 | CC(C)Cc1c(c(C)n(n1)C)NS(=O)(=O)c(c(Cl)c2)c(Cl)cc2-c3cc(ncc3)N4CCNCC4 | 0.004 | 8.398 |
| 95 | C1CN(C)CCC1CCCCc2cc(Cl)c(c(Cl)c2)S(=O)(=O)Nc(c3C)c(C)n(n3)C | 0.004 | 8.398 |
| 293 | CC(C)Cc1ccc2ncccc2c1NS(=O)(=O)c1ccc(CCCO[C@H]2C[C@@H]3CC[C@H](C2)N3C)cc1 | 27000 | 1.569 |
| 82 | Cc1c(C)c(OC)cc(C)c1S(=O)(=O)Nc(c2C)cccn2 | 70000 | 1.155 |
| 83 | Cn1ncc(c1C)NS(=O)(=O)c2c(Cl)cc(Br)cc2Cl | 70800 | 1.15 |
| 84 | Cn(n1)c(C)c(c1C)NS(=O)(=O)c(c2F)ccc(Br)c2 | 87000 | 1.06 |
| 111 | Cn(n1)c(C)c(c1C)NS(=O)(=O)c(c2C)ccc(Br)c2 | 107000 | 0.971 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaki, M.E.A.; Al-Hussain, S.A.; Masand, V.H.; Akasapu, S.; Lewaa, I. QSAR and Pharmacophore Modeling of Nitrogen Heterocycles as Potent Human N-Myristoyltransferase (Hs-NMT) Inhibitors. Molecules 2021, 26, 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071834
Zaki MEA, Al-Hussain SA, Masand VH, Akasapu S, Lewaa I. QSAR and Pharmacophore Modeling of Nitrogen Heterocycles as Potent Human N-Myristoyltransferase (Hs-NMT) Inhibitors. Molecules. 2021; 26(7):1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071834
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaki, Magdi E. A., Sami A. Al-Hussain, Vijay H. Masand, Siddhartha Akasapu, and Israa Lewaa. 2021. "QSAR and Pharmacophore Modeling of Nitrogen Heterocycles as Potent Human N-Myristoyltransferase (Hs-NMT) Inhibitors" Molecules 26, no. 7: 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071834
APA StyleZaki, M. E. A., Al-Hussain, S. A., Masand, V. H., Akasapu, S., & Lewaa, I. (2021). QSAR and Pharmacophore Modeling of Nitrogen Heterocycles as Potent Human N-Myristoyltransferase (Hs-NMT) Inhibitors. Molecules, 26(7), 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071834






